jade carving on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hardstone carving is a general term in
Hardstone carving is a general term in
 Hardstone carving falls under the general category of glyptic art, which covers small carvings and
Hardstone carving falls under the general category of glyptic art, which covers small carvings and
 The Chinese and other cultures often attributed specific properties for detecting and neutralizing
The Chinese and other cultures often attributed specific properties for detecting and neutralizing
File:Jade ornament.JPG, Chinese
 From the early civilizations of the near East descended the carving of vessels and small statues in
From the early civilizations of the near East descended the carving of vessels and small statues in
File:Augustus kameo.jpg, Ancient Roman cameo
 Beyond the Old World, hardstone carving was important in various
Beyond the Old World, hardstone carving was important in various
 Most hardstones, including jade and quartz varieties, have a
Most hardstones, including jade and quartz varieties, have a
agate glass
An inventory of the treasures of
File:Scarab satyr BM Gem 465.jpg,
Google books
* *Howard, Angela Falco, ''Chinese sculpture'', Yale University Press, 2006, ,
Google books
*Jones, Dalu & Michell, George, eds.; ''The Arts of Islam'',
Google books
*Luchs, Alison, ''Western decorative arts, Volume 1'', The Collections of the National Gallery of Art Systematic Catalogue, Oxford University Press US, 1995, ,
Google books
*Markel, Stephe
article: "Mughal Jades, A Technical and Sculptural Perspective. *"MMA": Department of Arts of Africa, Oceania, and the Americas. "Jade in Mesoamerica". In Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2000–
(October 2001) *Pope-Hennessy, Una, ''Early Chinese Jades'', reprint edn. READ BOOKS, 2008, ,
Google books
*Thoresen, Lisbet. "On Gemstones: Gemological and Analytical Studies of Ancient Intaglios and Cameos." In Ancient Glyptic Art- Gem Engraving and Gem Carving. https://web.archive.org/web/20081226040154/http://ancient-gems.lthoresen.com/ (February 2009) *Watson, William, & Ho, Chuimei. ''The arts of China after 1620'', Yale University Press Pelican history of art, Yale University Press, 2007, ,
''The Treasury of San Marco Venice''
1984, Metropolitan Museum of Art, (fully available online or as PDF from the MMA)
''Art of the Royal Court: Treasures in Pietre Dure from the Palaces of Europe''
Exhibition at the
Fabergé in the British
 Hardstone carving is a general term in
Hardstone carving is a general term in art history
Art history is the study of aesthetic objects and visual expression in historical and stylistic context. Traditionally, the discipline of art history emphasized painting, drawing, sculpture, architecture, ceramics and decorative arts; yet today, ...
and archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landsc ...
for the artistic carving of predominantly semi-precious
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semiprecious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opa ...
stones (but also of gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semiprecious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, ...
s), such as jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group ...
, rock crystal (clear quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical f ...
), agate
Agate () is a common rock formation, consisting of chalcedony and quartz as its primary components, with a wide variety of colors. Agates are primarily formed within volcanic and metamorphic rocks. The ornamental use of agate was common in Anci ...
, onyx
Onyx primarily refers to the parallel banded variety of chalcedony, a silicate mineral. Agate and onyx are both varieties of layered chalcedony that differ only in the form of the bands: agate has curved bands and onyx has parallel bands. The ...
, jasper
Jasper, an aggregate of microgranular quartz and/or cryptocrystalline chalcedony and other mineral phases,Kostov, R. I. 2010. Review on the mineralogical systematics of jasper and related rocks. – Archaeometry Workshop, 7, 3, 209-213PDF/ref ...
, serpentinite
Serpentinite is a rock composed predominantly of one or more serpentine group minerals, the name originating from the similarity of the texture of the rock to that of the skin of a snake. Serpentinite has been called ''serpentine'' or ''s ...
, or carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semi-precious gemstone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker (the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used ...
, and for an object made in this way. Normally the objects are small, and the category overlaps with both jewellery
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry ( U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a w ...
and sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable ...
. Hardstone carving is sometimes referred to by the Italian term ''pietre dure''; however, '' pietra dura'' (with an "a") is the common term used for stone inlay work, which causes some confusion.
From the Neolithic period
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
until about the 19th century such objects were among the most highly prized in a wide variety of cultures, often attributed special powers or religious significance, but today coverage in non-specialist art history tends to be relegated to a catch-all decorative arts
]
The decorative arts are arts or crafts whose object is the design and manufacture of objects that are both beautiful and functional. It includes most of the arts making objects for the interiors of buildings, and interior design, but not usua ...
or "minor arts" category. The types of objects carved have included those with ritual or religious purposes, engraved gems
An engraved gem, frequently referred to as an intaglio, is a small and usually semi-precious gemstone that has been carved, in the Western tradition normally with images or inscriptions only on one face. The engraving of gemstones was a major lux ...
as signet ring
A seal is a device for making an impression in wax, clay, paper, or some other medium, including an embossment on paper, and is also the impression thus made. The original purpose was to authenticate a document, or to prevent interference with a ...
s and other kinds of seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to imp ...
, handles, belt hook
The belt hook is a device for fastening that predates the belt buckle.
History
East Asia
The earliest archaeological evidence of belt hooks date to the 7th century BCE, in East Asia. Belt hooks were made with bronze, iron, gold, and jade. ...
s and similar items, vessels and purely decorative objects.
Scope of the term
 Hardstone carving falls under the general category of glyptic art, which covers small carvings and
Hardstone carving falls under the general category of glyptic art, which covers small carvings and sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable ...
in all categories of stone. The definition in this context of " hardstone" is unscientific and not very rigid, but excludes "soft" stones such as soapstone
Soapstone (also known as steatite or soaprock) is a talc-schist, which is a type of metamorphic rock. It is composed largely of the magnesium rich mineral talc. It is produced by dynamothermal metamorphism and metasomatism, which occur in the ...
(steatite) and mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s such as alabaster
Alabaster is a mineral or rock that is soft, often used for carving, and is processed for plaster powder. Archaeologists and the stone processing industry use the word differently from geologists. The former use it in a wider sense that include ...
, both widely used for carving, as well as typical stones for building and monumental sculpture
The term monumental sculpture is often used in art history and criticism, but not always consistently. It combines two concepts, one of function, and one of size, and may include an element of a third more subjective concept. It is often used for ...
, such as marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphose ...
and other types of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
, and sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
. These are typically not capable of a fine finish in very small carvings, and would wear in prolonged use. In other contexts, such as architecture, "hard stone" and "soft stone" have different meanings, referring to actual measured hardness using the Mohs scale of mineral hardness
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by t ...
and other measures. Some rocks used in architecture and monumental sculpture, such as granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
, are at least as hard as the gemstones, and others such as malachite
Malachite is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, with the formula Cu2CO3(OH)2. This opaque, green-banded mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, and most often forms botryoidal, fibrous, or stalagmitic masses, in fracture ...
are relatively soft but counted as hardstones because of their rarity and fine colour.
Essentially, any stone that is often used in jewellery is likely to count as a hardstone. Hard organic minerals such as amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In M ...
and jet are included, as well as the mineraloid
A mineraloid is a naturally occurring mineral-like substance that does not demonstrate crystallinity. Mineraloids possess chemical compositions that vary beyond the generally accepted ranges for specific minerals. For example, obsidian is an a ...
obsidian
Obsidian () is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock.
Obsidian is produced from felsic lava, rich in the lighter elements such as silicon ...
. Hardstones normally have to be drilled rather than worked with edged tools to achieve a fine finish. Geologically
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other E ...
speaking, most of the gemstones traditionally carved in the West are varieties of quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical f ...
, including: chalcedony
Chalcedony ( , or ) is a cryptocrystalline form of silica, composed of very fine intergrowths of quartz and moganite. These are both silica minerals, but they differ in that quartz has a trigonal crystal structure, while moganite is monocli ...
, agate
Agate () is a common rock formation, consisting of chalcedony and quartz as its primary components, with a wide variety of colors. Agates are primarily formed within volcanic and metamorphic rocks. The ornamental use of agate was common in Anci ...
, amethyst
Amethyst is a violet variety of quartz. The name comes from the Koine Greek αμέθυστος ''amethystos'' from α- ''a-'', "not" and μεθύσκω (Ancient Greek) / μεθώ (Modern Greek), "intoxicate", a reference to the belief that ...
, sard, onyx
Onyx primarily refers to the parallel banded variety of chalcedony, a silicate mineral. Agate and onyx are both varieties of layered chalcedony that differ only in the form of the bands: agate has curved bands and onyx has parallel bands. The ...
, carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semi-precious gemstone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker (the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used ...
, heliotrope, jasper
Jasper, an aggregate of microgranular quartz and/or cryptocrystalline chalcedony and other mineral phases,Kostov, R. I. 2010. Review on the mineralogical systematics of jasper and related rocks. – Archaeometry Workshop, 7, 3, 209-213PDF/ref ...
, and quartz in its uncoloured and transparent form, known as rock crystal. The various materials called jade have been dominant in East Asian and Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
n carving. Stones typically used for buildings and large sculpture are not often used for small objects such as vessels, although this does occur. For example, in the Uruk period
The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BC; also known as Protoliterate period) existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named af ...
of Sumerian culture (4th millennium BCE) heavy vases, cups and ewers of sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
and limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
have been found, but were not for common use, as the people of Uruk
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates east of modern Samawah, Muthanna Governorate, Al ...
had well-developed pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
.
History
Asia and the Islamic world
The art is very ancient, going back to theIndus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900& ...
and beyond, and major traditions include cylinder seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in length, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally ...
s and other small carvings in the Ancient Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
, which were also made in softer stones. Inlays of semi-precious stones were often used for decoration or highlights in sculptures of other materials, for example statues often had eyes inlaid with white shell and blue lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mine ...
or another stone.
Chinese jade
Chinese jade refers to the jade mined or carved in China from the Neolithic onward. It is the primary hardstone of Chinese sculpture. Although deep and bright green jadeite is better known in Europe, for most of China's history, jade has com ...
carving begins with the carving of ritual objects, including blades for '' ji'' and dagger-axe
The dagger-axe () is a type of pole weapon that was in use from the Erlitou culture until the Han dynasty in China. It consists of a dagger-shaped blade, mounted by its tang to a perpendicular wooden shaft. The earliest dagger-axe blades were ...
s clearly never intended for use, and the "Six Ritual Jades" including the '' bi'' and '' cong'', which according to much later literature represented heaven and earth respectively. These are found from the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
Liangzhu culture
The Liangzhu culture (; 3300–2300 BC) was the last Neolithic jade culture in the Yangtze River Delta of China. The culture was highly stratified, as jade, silk, ivory and lacquer artifacts were found exclusively in elite burials, while pottery ...
(3400-2250 BCE) onwards, and blades from the 2nd millennium BCE Shang Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty a ...
on. Traditional Chinese culture attaches strong powers to jade; the jade burial suit
A jade burial suit () is a ceremonial suit made of pieces of jade in which royal members in Han dynasty China were buried.
Structure
Of the jade suits that have been found, the pieces of jade are mostly square or rectangular in shape, thoug ...
s in which aristocrats of the Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
(206 BCE–220 CE) were buried were intended to preserve the body from decay.
 The Chinese and other cultures often attributed specific properties for detecting and neutralizing
The Chinese and other cultures often attributed specific properties for detecting and neutralizing poison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broa ...
to gemstones, a belief still alive in the European Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
, as shown by the works of Georgius Agricola
Georgius Agricola (; born Georg Pawer or Georg Bauer; 24 March 1494 – 21 November 1555) was a German Humanist scholar, mineralogist and metallurgist. Born in the small town of Glauchau, in the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire ...
, the "father of mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the proce ...
". The English word "jade" derives (via the Spanish ''piedra de ijada'') from the Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
belief that the mineral cured ailments of the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s and sides. The Han period also saw the beginning of the tradition of fine decorative jade carving which has lasted until modern times, though the fine carving of other hardstones did not develop until the 17th century, and then appears to have been produced in different workshops and styles from those for jade. In general whiteish nephrite jade was the most highly regarded in China until about 1800, when the deeper and brighter green of the best jadeite
Jadeite is a pyroxene mineral with composition Na Al Si2 O6. It is hard (Mohs hardness of about 6.5 to 7.0), very tough, and dense, with a specific gravity of about 3.4. It is found in a wide range of colors, but is most often found in shades ...
became more highly favoured. There are related Asian traditions of Korean jade carving, in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
and, to a much lesser extent, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
.
Smallish Sassanian
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
carvings are known, mostly for seals or jewellery; the central medallion of the "Cup of Chosroes" (gallery) is one of the largest. Egyptian carving of rock crystal into vessels appears in the late 10th century, and virtually disappears after about 1040. In 1062 the Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metr ...
palace of the Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a ...
was looted by his mercenaries, and the examples found in European treasuries, like the one illustrated, may have been acquired as the booty was dispersed. The rock crystal used in Egypt was apparently traded from East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
.
Until recently it was thought that jade carving was introduced to the central Asian Islamic world in the Timurid period, but it is becoming clearer that archers' thumb ring
A thumb ring is a piece of equipment designed to protect the thumb during archery. This is a ring of leather, stone, horn, wood, bone, antler, ivory, metal, ceramics, plastic, or glass which fits over the end of the thumb, coming to rest at ...
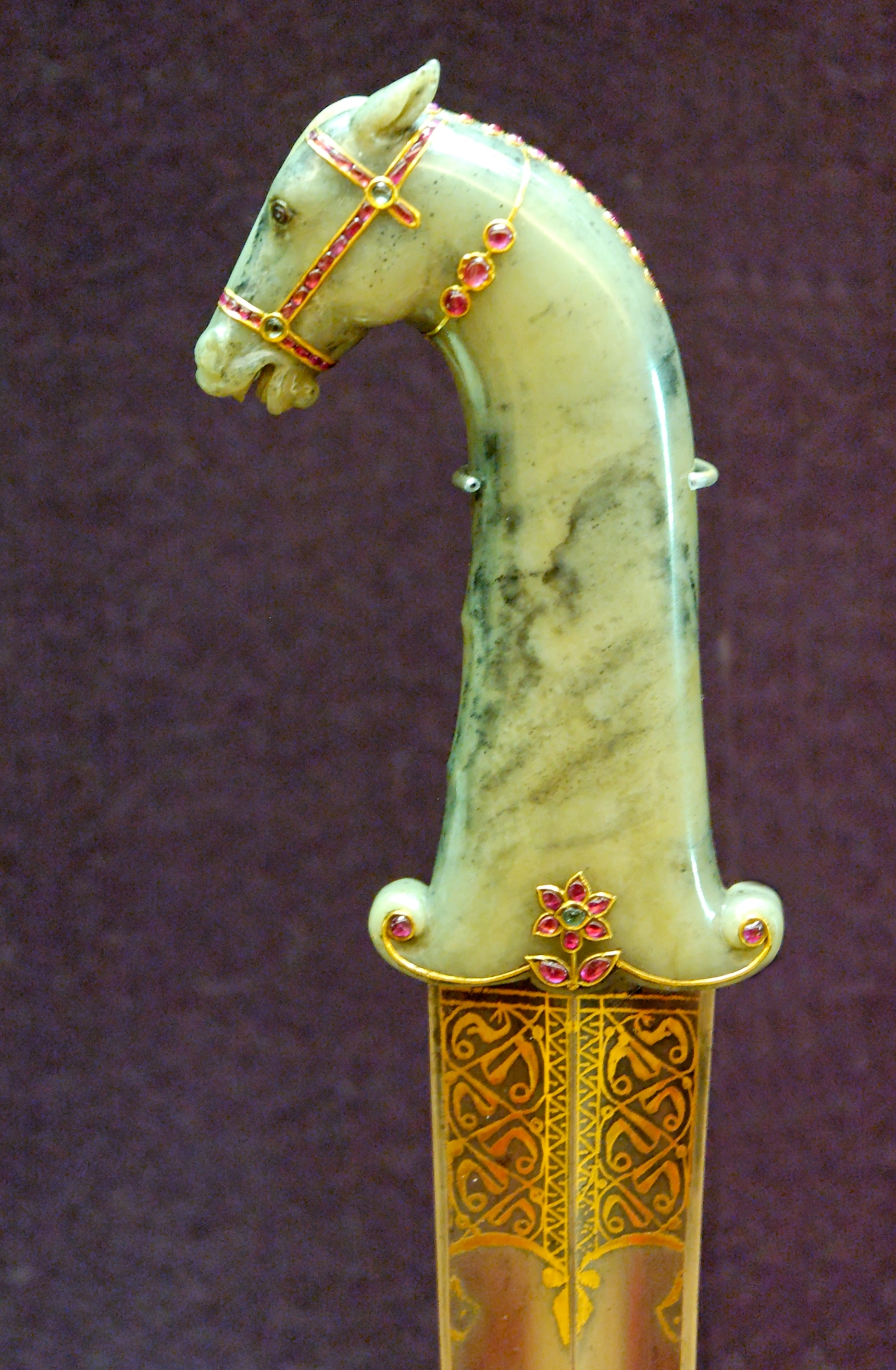
s, knife hilts, and various other objects had been carved for centuries, even millennia before, though in limited numbers. Islamic jades and other carvings reached a particular peak in the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, where apart from portable carvings inlaid panels of carved stones were included in buildings such as the Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal (; ) is an Islamic ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in the Indian city of Agra. It was commissioned in 1631 by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his favourite wife, ...
. The great wealth of the Mughal court allowed precious stones like rubies and emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr. and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991) ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p ...
s to be inset freely in objects. The court workshops of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
also produced lavish and elaborate objects, in similar styles but without reaching the artistic peaks of Mughal carving.
jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group ...
ornament, Western Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a war ...
File:Jade ornament with grape design.jpg, Chinese jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group ...
hair ornament, 1115–1234
File:Coupe de Chosroès.JPG, "Cup of Chosroes", from Sassanian
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. Rock crystal, glass, and other stones
File:Coupe Inde Musée Guimet 2497.jpg, Mughal cup of jade, emeralds, rubies and gold
Western traditions
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cu ...
, Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom ...
and subsequent Western art, and also Sassanian
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
; however it is not very significant in the art of ancient Egypt
Ancient Egyptian art refers to art produced in ancient Egypt between the 6th millennium BC and the 4th century AD, spanning from Prehistoric Egypt until the Christianization of Roman Egypt. It includes paintings, sculptu ...
, outside jewellery, as alabaster
Alabaster is a mineral or rock that is soft, often used for carving, and is processed for plaster powder. Archaeologists and the stone processing industry use the word differently from geologists. The former use it in a wider sense that include ...
was a more common material. The jade signet ring of Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun (, egy, twt-ꜥnḫ-jmn), Egyptological pronunciation Tutankhamen () (), sometimes referred to as King Tut, was an Egyptian pharaoh who was the last of his royal family to rule during the end of the Eighteenth Dynasty (ruled ...
has been called a "unique specimen" of Egyptian jade. Among the seals of the Minoan civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450 ...
during the Aegean Bronze Age
Aegean civilization is a general term for the Bronze Age civilizations of Greece around the Aegean Sea. There are three distinct but communicating and interacting geographic regions covered by this term: Crete, the Cyclades and the Greek mainlan ...
, the Pylos Combat Agate dated circa 1450 BC is considered one of the finest works of that era, depicting naturalistic details of the human body comparable to works of the much later Classical period.
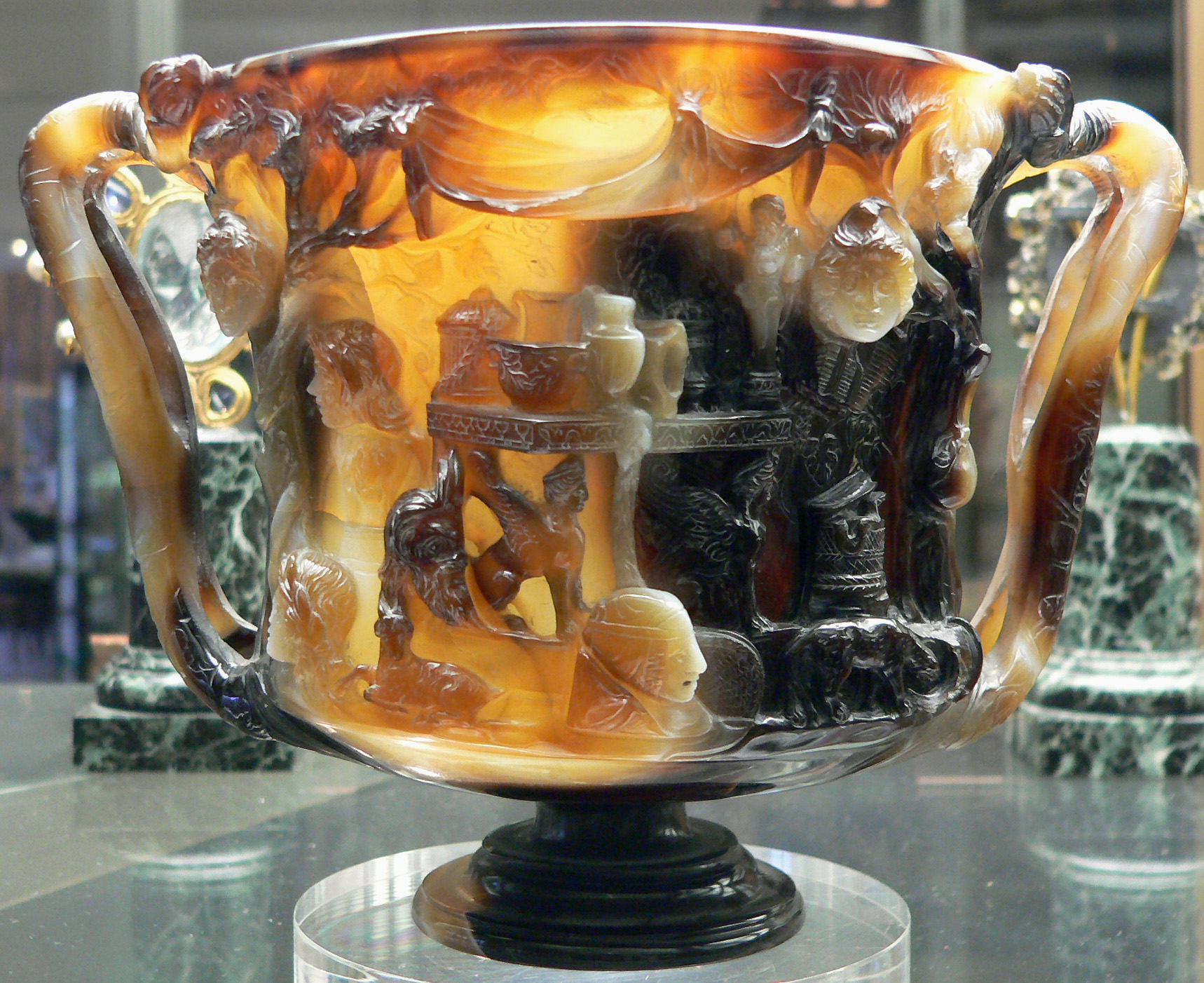
Hardstone carving more often refers to vessels and figures than smaller engraved gem
An engraved gem, frequently referred to as an intaglio, is a small and usually semi-precious gemstone that has been carved, in the Western tradition normally with images or inscriptions only on one face. The engraving of gemstones was a major lux ...
s for seal ring
A seal is a device for making an impression in wax, clay, paper, or some other medium, including an embossment on paper, and is also the impression thus made. The original purpose was to authenticate a document, or to prevent interference with ...
s or made as objéts d'art, which were the main artistic expression of hardstone carving in the Greek Classical and Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
periods, and are regarded separately. From the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
elaborate vessels in semi-precious stone begin to appear, mostly carved, some in cameo. The Cup of the Ptolemies
The Cup of the Ptolemies (French: ''Coupe des Ptolémées''), also known as the Cup of Saint Denis, is an onyx cameo two-handled cup, or ''kantharos''. The cup, decorated with Dionysiac vignettes and emblems, was carved at some point in Class ...
and Farnese Cup
The Farnese Cup or Tazza Farnese is a 2nd-century BC cameo hardstone carving bowl or cup made in Hellenistic Egypt in four-layered sardonyx agate, now in the Naples National Archaeological MuseumInv. MANN 27611. It is a 20 cm wide and si ...
both appear to have been made in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
in Ptolemaic Egypt, as does a simpler fluted sardonyx
Onyx primarily refers to the parallel banded variety of chalcedony, a silicate mineral. Agate and onyx are both varieties of layered chalcedony that differ only in the form of the bands: agate has curved bands and onyx has parallel bands. The c ...
cup in Washington which, like the Cup of the Ptolemies, was adapted to be a Christian chalice
A chalice (from Latin 'mug', borrowed from Ancient Greek () 'cup') or goblet is a footed cup intended to hold a drink. In religious practice, a chalice is often used for drinking during a ceremony or may carry a certain symbolic meaning.
R ...
, and given elaborate gold and jewelled mounts by Abbot Suger
Suger (; la, Sugerius; 1081 – 13 January 1151) was a French abbot, statesman, and historian. He once lived at the court of Pope Calixtus II in Maguelonne, France. He later became abbot of St-Denis, and became a close confidant to King Lou ...
for his Abbey of St Denis about 1140. The elaborately carved Rubens Vase
The Rubens vase is a Late Antique or early Byzantine hardstone carving of a single piece of agate in the form of a vase, named after a later owner, Peter Paul Rubens, (from 1619 to 1626), who in Flanders made a pedrawingof it, which is now held ...
, now in Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
, is thought to date from the 4th century.
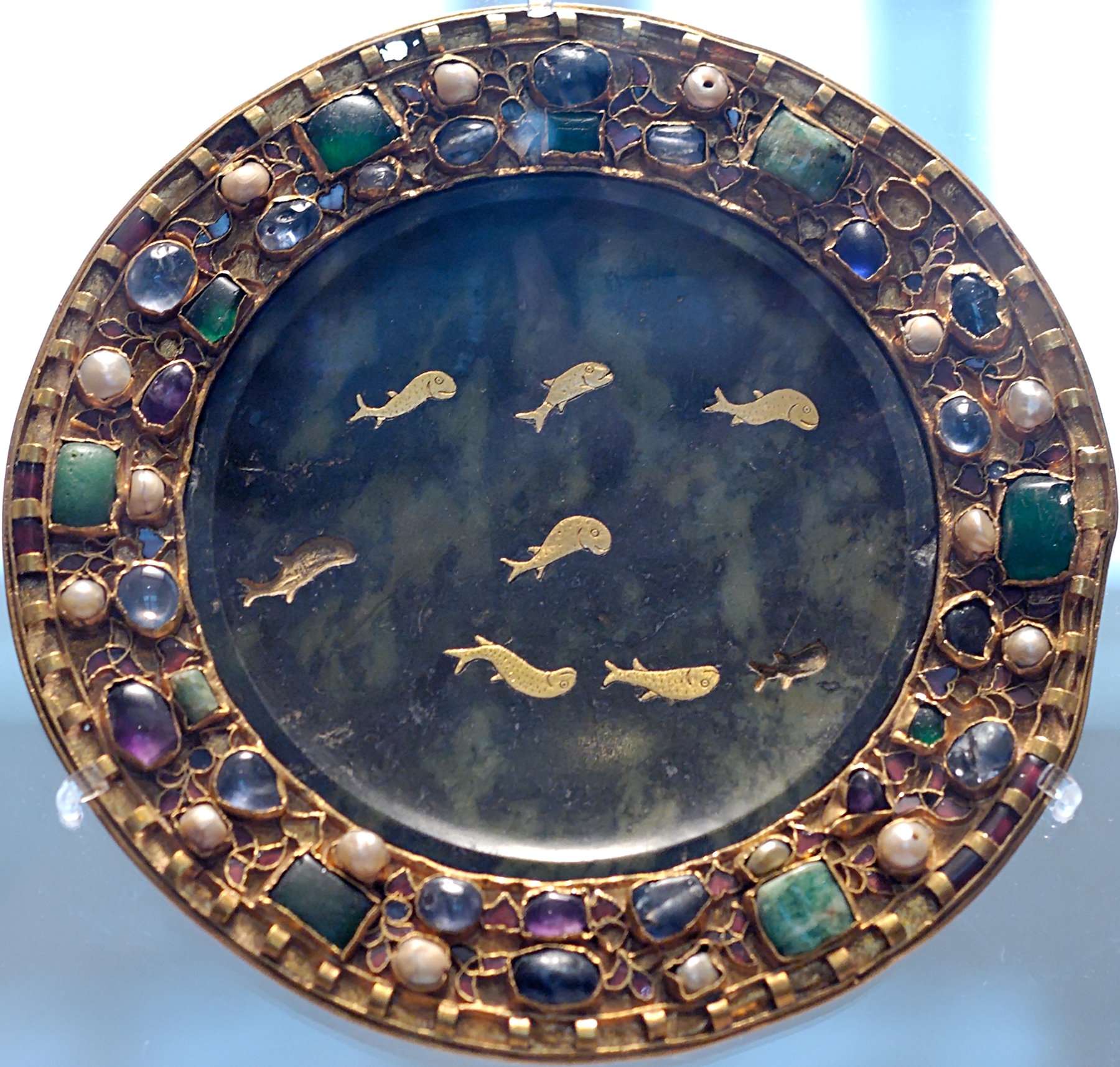
From the Late Antique plainer shapes for vessels appear, concentrating on showing the natural patterns of figured stones - survivals of these are hard to date, and mostly have survived in church treasuries with medieval mounts in goldsmith work. The best collection of Byzantine liturgical vessels is in the Treasury of San Marco, Venice
The Patriarchal Cathedral Basilica of Saint Mark ( it, Basilica Cattedrale Patriarcale di San Marco), commonly known as St Mark's Basilica ( it, Basilica di San Marco; vec, Baxéłega de San Marco), is the cathedral church of the Catholic Pat ...
, some of them booty from the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
. Byzantine art
Byzantine art comprises the body of Christian Greek artistic products of the Eastern Roman Empire, as well as the nations and states that inherited culturally from the empire. Though the empire itself emerged from the decline of Rome and lasted u ...
ists maintained a tradition throughout the Middle Ages, often working in clear rock crystal. There are a few large pieces from Carolingian art
Carolingian art comes from the Frankish Empire in the period of roughly 120 years from about 780 to 900—during the reign of Charlemagne and his immediate heirs—popularly known as the Carolingian Renaissance. The art was produced by and for th ...
, including the Lothair Crystal
The Lothair Crystal (also known as the Lothar Crystal or the Susanna Crystal) is an engraved gem from Lotharingia in northwest Europe, showing scenes of the biblical story of Susanna, dating from 855–869. The Lothair Crystal is an object in th ...
, and then a continuing tradition of rock crystal work, often used undecorated in reliquaries and other pieces in the same way as modern glass, for which they are often mistaken by modern viewers. By the end of the Middle Ages a wider variety of stones and objects are seen, used for both religious objects and secular ones.
The Opificio delle pietre dure The Opificio delle pietre dure, literally meaning ''Workshop of semi-precious stones'', is a public institute of the Italian Ministry for Cultural Heritage based in Florence. It is a global leader in the field of art restoration and provides teac ...
("Hardstone workshop") founded by the Medici in Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
in 1588 soon became the leading workshop in Europe, and developed the pietra dura style of multi-coloured inlay
Inlay covers a range of techniques in sculpture and the decorative arts for inserting pieces of contrasting, often colored materials into depressions in a base object to form Ornament (art), ornament or pictures that normally are flush with th ...
s, which use coloured marbles as well as gemstones. They also produced vessels and small sculptures from a single piece of stone, often mounted with gold, which was also a speciality of Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
ese workshops. Other rulers followed their example, including Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
, whose Peterhof Lapidary Works, founded in 1721, began the passion among Russian royalty and aristocrats for hardstones. Engraved gem production had already revived, centred on Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
but with artists in many countries, and gems of very high quality continued to be produced until the mid-19th century. The Mannerist
Mannerism, which may also be known as Late Renaissance, is a style in European art that emerged in the later years of the Italian High Renaissance around 1520, spreading by about 1530 and lasting until about the end of the 16th century in Ita ...
court taste of the 16th century delighted in extravagant vessels for serving fruit or sweetmeats, or display as table centrepieces or on sideboards, with hardstones augmented with mounts and bases in precious metal, enamel and jewels. One collection that has remained mostly together is the "Dauphin's Treasure" of Louis, Dauphin of France (1661–1711)
Louis, Dauphin of France (1 November 1661 – 14 April 1711), commonly known as Grand Dauphin, was the eldest son and heir apparent of King Louis XIV and his spouse, Maria Theresa of Spain. He became known as the Grand Dauphin after the birth of ...
, which passed to his son Philip V of Spain
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was King of Spain from 1 November 1700 to 14 January 1724, and again from 6 September 1724 to his death in 1746. His total reign of 45 years is the longest in the history of the Spanish mo ...
; over 120 objects are now displayed together in the Museo del Prado
The Prado Museum ( ; ), officially known as Museo Nacional del Prado, is the main Spanish national art museum, located in central Madrid. It is widely considered to house one of the world's finest collections of European art, dating from th ...
, many of which were already over a century old in the Dauphin's lifetime.
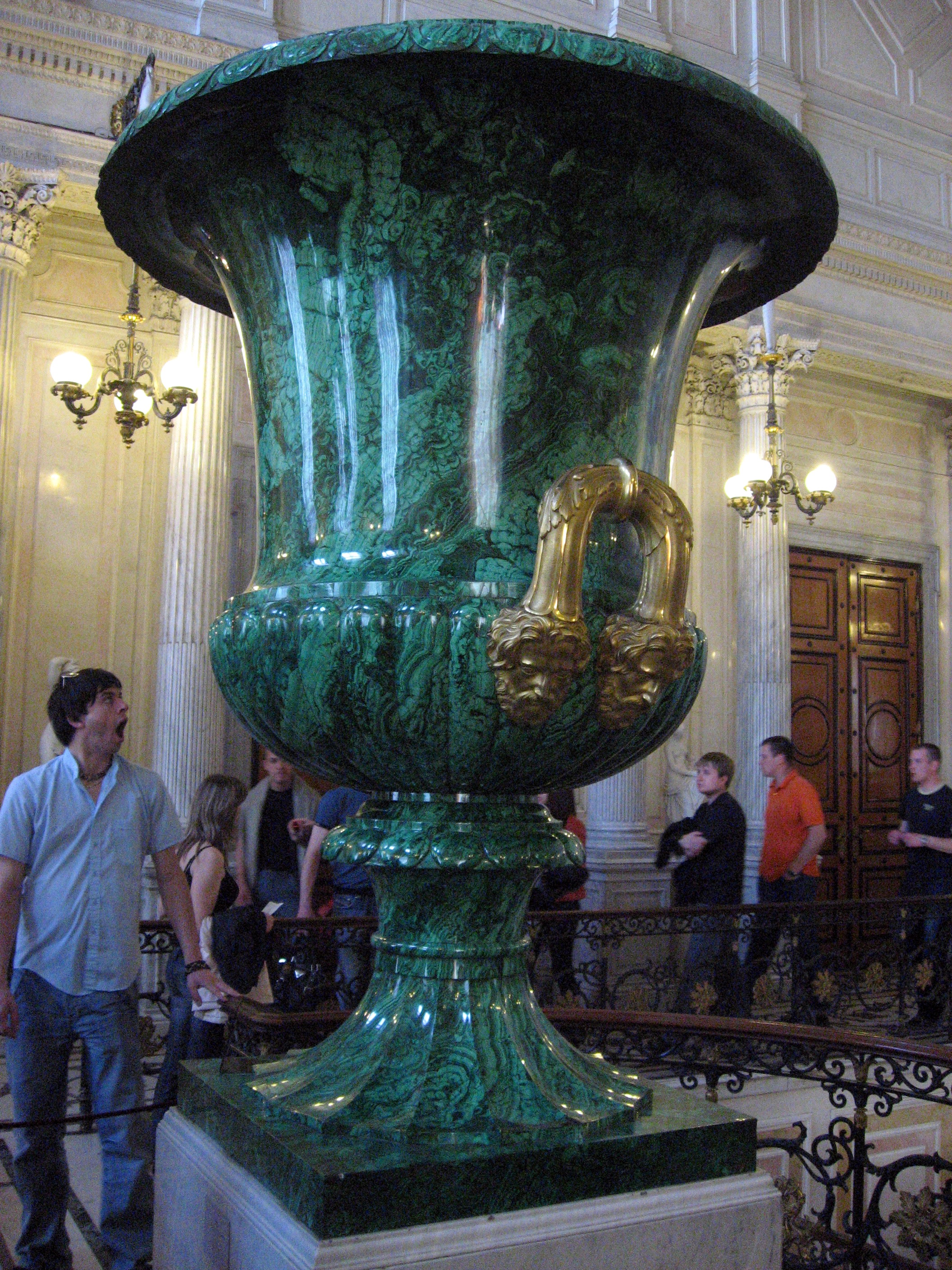
In contrast to the vast malachite
Malachite is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, with the formula Cu2CO3(OH)2. This opaque, green-banded mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, and most often forms botryoidal, fibrous, or stalagmitic masses, in fracture ...
vases that rather typify Russian carving (picture below), the last notable modern producer was Fabergé in pre-Revolutionary Russia. Before he produced the famous Imperial Easter Eggs he made his reputation with small hardstone figures of animals and people, typically only 25–75mm long or wide, and small vases with a few flowers—the vase and "water" in rock crystal and the flowers in various hardstones and enamel.
engraved gem
An engraved gem, frequently referred to as an intaglio, is a small and usually semi-precious gemstone that has been carved, in the Western tradition normally with images or inscriptions only on one face. The engraving of gemstones was a major lux ...
of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
File:Paten pietre dure Louvre OA11878.jpg, Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
paten
A paten or diskos is a small plate, used during the Mass. It is generally used during the liturgy itself, while the reserved sacrament are stored in the tabernacle in a ciborium.
Western usage
In many Western liturgical denominations, the ...
of sard, 6–7th century(?), with later mounts
File:Salero de ónice con sirena de oro (Prado O-1) 01b.jpg, Florentine(?) Mannerist
Mannerism, which may also be known as Late Renaissance, is a style in European art that emerged in the later years of the Italian High Renaissance around 1520, spreading by about 1530 and lasting until about the end of the 16th century in Ita ...
salt cellar, 16th century. Onyx
Onyx primarily refers to the parallel banded variety of chalcedony, a silicate mineral. Agate and onyx are both varieties of layered chalcedony that differ only in the form of the bands: agate has curved bands and onyx has parallel bands. The ...
bowl, gold mermaid, with gold and jewelled mounts.
File:The Punishment of Tityus, a rock crystal intaglio by Giovanni Bernardi, the British Museum.jpg, ''The Punishment of Tityos
Tityos or Tityus ( Ancient Greek: Τιτυός) was a giant from Greek mythology.
Family
Tityos was the son of Elara; his father was Zeus. He had a daughter named Europa who coupled with Poseidon and gave birth to Euphemus, one of the Argo ...
'', a rock crystal intaglio engraved gem by Giovanni Bernardi
Pre-Columbian and other traditions
 Beyond the Old World, hardstone carving was important in various
Beyond the Old World, hardstone carving was important in various Pre-Columbian cultures
This list of pre-Columbian cultures includes those civilizations and cultures of the Americas which flourished prior to the European colonization of the Americas.
Cultural characteristics
Many pre-Columbian civilizations established permanent o ...
, including jade in Mesoamerica and obsidian in Mesoamerica. Because its colour had associations with water and vegetation, jade was also a symbol of life to many cultures; the Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popul ...
placed jade beads in the mouths of the dead. Lacking iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
, jade was the hardest material the Pre-Columbians were able to work with, apart from emery.
A particular type of object running through the long history of Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
n cultures from the Olmec
The Olmecs () were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that ...
to the Maya and Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
is the face "mask" in semi-precious stone (they do not seem to have been for actually wearing), either carved from a single piece or of pieces inlaid on a backing of another material. Curators refer to "Olmec-style" face masks as despite being Olmec in style, to date no example has been recovered in a controlled archaeological Olmec context. However they have been recovered from sites of other cultures, including one deliberately deposited in the ceremonial precinct of Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was ...
(Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
), which would presumably have been about 2,000 years old when the Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
s buried it, suggesting these were valued and collected as Roman antiquities were in Europe. The Aztecs' own masks are more typically of turquoise
Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrated phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula . It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gemstone and ornamental stone for thousands of year ...
inlay, the Mayans' of jade inlay (see gallery).
Another supposed type of Pre-Columbian hardstone carving is the rock crystal skull
Crystal skulls are human skull hardstone carvings made of clear or milky white quartz (also called "rock crystal"), claimed to be pre-Columbian Mesoamerican artifacts by their alleged finders; however, these claims have been refuted for all of th ...
; however experts are now satisfied that all known large (life-size) examples are 19th-century forgeries, though some miniature ones may be genuinely Pre-Columbian.
The Māori people
The Māori (, ) are the indigenous Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand (). Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over severa ...
of New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
, developed the carving of ''pounamu
Pounamu is a term for several types of hard and durable stone found in southern New Zealand. They are highly valued in New Zealand, and carvings made from pounamu play an important role in Māori culture.
Name
The Māori word , also used ...
'' (jade) for weapons, tools and ornaments to a high standard.
Techniques
 Most hardstones, including jade and quartz varieties, have a
Most hardstones, including jade and quartz varieties, have a crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
structure that does not allow detailed carving by edged tools without great wastage and a poor finish. Working them has always been very time-consuming, which together with the cost of rare materials often traded from very far away, has accounted for the great expense of these objects. After sawing and perhaps chiselling to reach the approximate shape, stones were mostly cut by using abrasive powder from harder stones in conjunction with a hand-drill, probably often set in a lathe
A lathe () is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, and turning, with tools that are applied to the workpiece ...
, and by grinding-wheels. Emery has been mined for abrasive powder on Naxos
Naxos (; el, Νάξος, ) is a Greek island and the largest of the Cyclades. It was the centre of archaic Cycladic culture. The island is famous as a source of emery, a rock rich in corundum, which until modern times was one of the best ab ...
since antiquity, and was known in Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica. Some early types of seal were cut by hand, rather than a drill, which does not allow fine detail. There is no evidence that magnifying lenses were used by cutters in antiquity. The Chinese sometimes tipped their straight drills with less-valued diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, b ...
s.
A medieval guide to gem-carving techniques survives from Theophilus Presbyter
Theophilus Presbyter (fl. c. 1070–1125) is the pseudonymous author or compiler of a Latin text containing detailed descriptions of various medieval arts, a text commonly known as the ''Schedula diversarum artium'' ("List of various arts") or ''De ...
. Byzantine cutters used a flat-edged wheel on a drill for intaglio work, while Carolingian ones used round-tipped drills; it is unclear how they learned this technique. Mughal carvers also used drills. Inlay sections could be sawed by bow saws. In intaglio gems at least, the recessed cut surface is usually very well preserved, and microscopic examination is revealing of the technique used. The colour of several gemstones can be enhanced by a number of artificial methods, using heat, sugar and dyes. Many of these can be shown to have been used since antiquity - since the 7th millennium BC in the case of heating.
Imitations
As a highly prestigious artform using expensive materials, many different techniques for imitating hardstone carvings have been developed, some of which have themselves created significant artistic traditions. Celadon ware, with a jade coloured glaze, was important in China and Korea, and in early periods used for shapes typical of jade objects. Romancameo glass
Cameo glass is a luxury form of glass art produced by cameo glass engraving or etching and carving through fused layers of differently colored glass to produce designs, usually with white opaque glass figures and motifs on a dark-colored backgroun ...
was invented to imitate cameo gems, with the advantage that consistent layers were possible even in objects in the round. The small group of 11th(?)-century Hedwig glass
Hedwig glasses or Hedwig beakers are a type of glass beaker originating in the Middle East or Norman Sicily and dating from the 10th-12th centuries AD. They are named after the Silesian princess Saint Hedwig (1174–1245), to whom three of them ...
es are inspired by Fatimid rock-crystal vessels, and from the 18th century chandelier
A chandelier (; also known as girandole, candelabra lamp, or least commonly suspended lights) is a branched ornamental light fixture designed to be mounted on ceilings or walls. Chandeliers are often ornate, and normally use incandescent ...
s in cut glass
Cut glass or cut-glass is a technique and a style of decorating glass. For some time the style has often been produced by other techniques such as the use of moulding, but the original technique of cutting glass on an abrasive wheel is still u ...
drew from fantastically expensive rock crystal ones made for the court of Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
. In the Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( it, Rinascimento ) was a period in Italian history covering the 15th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Europe and marked the trans ...
agate glass
Moss Agate glass is a rare type of art glass
Art glass is a subset of glass art, this latter covering the whole range of art made from glass. Art glass normally refers only to pieces made since the mid-19th century, and typically to those pure ...
was perfected to imitate agate vessels with multicoloured figuration.An inventory of the treasures of
John, Duke of Berry
John of Berry or John the Magnificent (French: ''Jean de Berry'', ; 30 November 1340 – 15 June 1416) was Duke of Berry and Auvergne and Count of Poitiers and Montpensier. He was Regent of France during the minority of his nephew 1380-1388 ...
already records such a vase in 1416, but no example from this early seems to have survived.
Ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
have often been decorated to imitate gemstones, and wood, plaster and other materials painted to imitate stones. Scagliola
Scagliola (from the Italian ''scaglia'', meaning "chips") is a type of fine plaster used in architecture and sculpture. The same term identifies the technique for producing columns, sculptures, and other architectural elements that resemble inla ...
developed in Italy to imitate pietra dura inlays on plaster; less elaborate forms are called marbleizing. Medieval illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is often supplemented with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers, liturgical services and psalms, th ...
s often imitated both inlaid stone and engraved gems, and after printing took over paper marbling
Paper marbling is a method of aqueous surface design, which can produce patterns similar to smooth marble or other kinds of stone. The patterns are the result of color floated on either plain water or a viscous solution known as size, and then ca ...
continued as a manual craft for decorating end-papers and covers.
Gallery
Engraved gem
An engraved gem, frequently referred to as an intaglio, is a small and usually semi-precious gemstone that has been carved, in the Western tradition normally with images or inscriptions only on one face. The engraving of gemstones was a major lux ...
of a reclining satyr
In Greek mythology, a satyr ( grc-gre, σάτυρος, sátyros, ), also known as a silenus or ''silenos'' ( grc-gre, σειληνός ), is a male nature spirit with ears and a tail resembling those of a horse, as well as a permanent, ex ...
, Etruscan c. 550 BC, 2.2 cm wide. Note the vase shown "sideways"; it is characteristic of early gems that not all elements in the design are read from the same direction of view.
File:Mayan Jade.jpg, Jadeite
Jadeite is a pyroxene mineral with composition Na Al Si2 O6. It is hard (Mohs hardness of about 6.5 to 7.0), very tough, and dense, with a specific gravity of about 3.4. It is found in a wide range of colors, but is most often found in shades ...
pectoral
Pectoral may refer to:
* The chest region and anything relating to it.
* Pectoral cross, a cross worn on the chest
* a decorative, usually jeweled version of a gorget
* Pectoral (Ancient Egypt), a type of jewelry worn in ancient Egypt
* Pectorali ...
from the Maya Classic Period. (195mm high)
File:Flemish - Rock Crystal Reliquary - Walters 57695 - Back View A.jpg, Burgundian reliquary
A reliquary (also referred to as a ''shrine'', by the French term ''châsse'', and historically including '' phylacteries'') is a container for relics. A portable reliquary may be called a ''fereter'', and a chapel in which it is housed a ''fer ...
in rock crystal, partially enamelled, late 15th century
Notes
References
*Angold, Michael, ''The Fourth Crusade: Event and Context'', Pearson Education, 2003. , *Campbell, Gordon, ''The Grove Encyclopedia of Decorative Arts, Volume 1'', Oxford University Press US, 2006, , (links in notes) *Clark, Grahame, ''Symbols of excellence: precious materials as expressions of status'', Cambridge University Press, 1986, ,Google books
* *Howard, Angela Falco, ''Chinese sculpture'', Yale University Press, 2006, ,
Google books
*Jones, Dalu & Michell, George, eds.; ''The Arts of Islam'',
Arts Council of Great Britain
The Arts Council of Great Britain was a non-departmental public body dedicated to the promotion of the fine arts in Great Britain. It was divided in 1994 to form the Arts Council of England (now Arts Council England), the Scottish Arts Council ( ...
, 1976,
*Keene, Manuel, ''Old World Jades outside China, From Ancient Times to the Fifteenth Century'', in: Gülru Necipoğlu, Doris Behrens-Abouseif, Anna Contadini (eds), Muqarnas Series 21: ''Essays In Honor Of J.M. Rogers'' BRILL, 2005, ,
*Kornbluth, Genevra Alisoun. ''Engraved gems of the Carolingian empire'', Penn State Press, 1995, Google books
*Luchs, Alison, ''Western decorative arts, Volume 1'', The Collections of the National Gallery of Art Systematic Catalogue, Oxford University Press US, 1995, ,
Google books
*Markel, Stephe
article: "Mughal Jades, A Technical and Sculptural Perspective. *"MMA": Department of Arts of Africa, Oceania, and the Americas. "Jade in Mesoamerica". In Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2000–
(October 2001) *Pope-Hennessy, Una, ''Early Chinese Jades'', reprint edn. READ BOOKS, 2008, ,
Google books
*Thoresen, Lisbet. "On Gemstones: Gemological and Analytical Studies of Ancient Intaglios and Cameos." In Ancient Glyptic Art- Gem Engraving and Gem Carving. https://web.archive.org/web/20081226040154/http://ancient-gems.lthoresen.com/ (February 2009) *Watson, William, & Ho, Chuimei. ''The arts of China after 1620'', Yale University Press Pelican history of art, Yale University Press, 2007, ,
External links
*Buckton, David, et al.''The Treasury of San Marco Venice''
1984, Metropolitan Museum of Art, (fully available online or as PDF from the MMA)
''Art of the Royal Court: Treasures in Pietre Dure from the Palaces of Europe''
Exhibition at the
Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
Fabergé in the British
Royal Collection
The Royal Collection of the British royal family is the largest private art collection in the world.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King Charles III and overseen by the ...
- 277 pieces; see in particular pages 3–7
{{Authority control
Ancient art
Jewellery
Sculpture
Ancient Greek sculpture
Ancient Roman sculpture
Visual arts genres
Decorative arts
Lithics
de:Pietra dura
hi:पर्चिनकारी
it:Pietre dure
ml:പിയത്ര ദുരെ
pl:Pietra dura