Intensive Care Unit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
220px, Intensive care unit
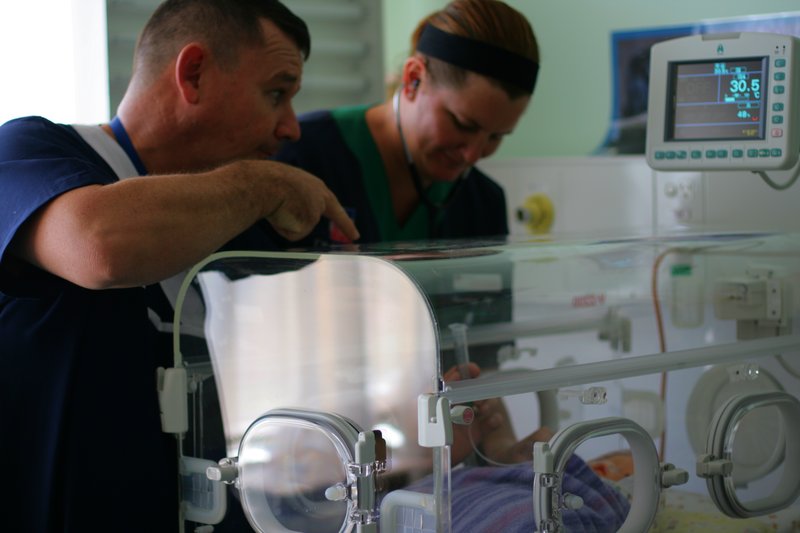
 An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.
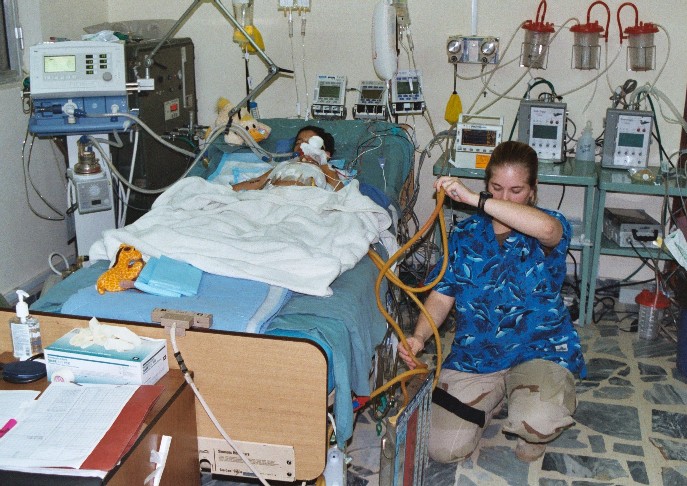
Intensive care units cater to patients with severe or life-threatening illnesses and injuries, which require constant care, close supervision from life support equipment and medication in order to ensure normal bodily functions. They are staffed by highly trained physicians, nurses and respiratory therapists who specialize in caring for critically ill patients. ICUs are also distinguished from general hospital wards by a higher staff-to-patient ratio and access to advanced medical resources and equipment that is not routinely available elsewhere. Common conditions that are treated within ICUs include acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, and other life-threatening conditions.
Patients may be referred directly from an emergency department or from a ward if they rapidly deteriorate, or immediately after surgery if the surgery is very invasive and the patient is at high risk of complications.
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.
Intensive care units cater to patients with severe or life-threatening illnesses and injuries, which require constant care, close supervision from life support equipment and medication in order to ensure normal bodily functions. They are staffed by highly trained physicians, nurses and respiratory therapists who specialize in caring for critically ill patients. ICUs are also distinguished from general hospital wards by a higher staff-to-patient ratio and access to advanced medical resources and equipment that is not routinely available elsewhere. Common conditions that are treated within ICUs include acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, and other life-threatening conditions.
Patients may be referred directly from an emergency department or from a ward if they rapidly deteriorate, or immediately after surgery if the surgery is very invasive and the patient is at high risk of complications.


Society of Critical Care Medicine
ICUsteps – Intensive care patient support charity
Organisation for Critical Care Transportation
* * {{Authority control Intensive care medicine Hospital departments
 An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.
Intensive care units cater to patients with severe or life-threatening illnesses and injuries, which require constant care, close supervision from life support equipment and medication in order to ensure normal bodily functions. They are staffed by highly trained physicians, nurses and respiratory therapists who specialize in caring for critically ill patients. ICUs are also distinguished from general hospital wards by a higher staff-to-patient ratio and access to advanced medical resources and equipment that is not routinely available elsewhere. Common conditions that are treated within ICUs include acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, and other life-threatening conditions.
Patients may be referred directly from an emergency department or from a ward if they rapidly deteriorate, or immediately after surgery if the surgery is very invasive and the patient is at high risk of complications.
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.
Intensive care units cater to patients with severe or life-threatening illnesses and injuries, which require constant care, close supervision from life support equipment and medication in order to ensure normal bodily functions. They are staffed by highly trained physicians, nurses and respiratory therapists who specialize in caring for critically ill patients. ICUs are also distinguished from general hospital wards by a higher staff-to-patient ratio and access to advanced medical resources and equipment that is not routinely available elsewhere. Common conditions that are treated within ICUs include acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, and other life-threatening conditions.
Patients may be referred directly from an emergency department or from a ward if they rapidly deteriorate, or immediately after surgery if the surgery is very invasive and the patient is at high risk of complications.
History
In 1854,Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale (; 12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the Crimean War ...
left for the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
, where triage was used to separate seriously wounded soldiers from those with non-life-threatening conditions.
Until recently, it was reported that Nightingale’s method reduced mortality from 40% to 2% on the battlefield. Although this was not the case, her experiences during the war formed the foundation for her later discovery of the importance of sanitary conditions in hospitals, a critical component of intensive care.
In 1950, anesthesiologist
Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology, or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicin ...
Peter Safar established the concept of advanced life support, keeping patient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other heal ...
s sedated and ventilated in an intensive care environment. Safar is considered to be the first practitioner of intensive care medicine as a speciality.
In response to a polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe sy ...
epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
(where many patients required constant ventilation and surveillance), Bjørn Aage Ibsen
Bjørn Aage Ibsen (August 30, 1915 – August 7, 2007) was a Danish anesthetist and founder of intensive-care medicine. He graduated in 1940 from medical school at the University of Copenhagen and trained in anesthesiology from 1949 to 1950 a ...
established the first intensive care unit in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
in 1953.
The first application of this idea in the United States was in 1955 by William Mosenthal, a surgeon at the Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center. In the 1960s, the importance of cardiac arrhythmias as a source of morbidity and mortality in myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
s (heart attacks) was recognized. This led to the routine use of cardiac monitoring in ICUs, especially after heart attacks.
Types
Hospitals may have various specialised ICUs that cater to a specific medical requirement or patient:


Equipment and systems
Common equipment in an ICU includes mechanical ventilators to assist breathing through anendotracheal tube
A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent airway and to ensure the adequate exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Many different types of tracheal tubes ar ...
or a tracheostomy tube
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The re ...
; cardiac monitors for monitoring Cardiac condition; equipment for the constant monitoring
Monitoring may refer to:
Science and technology Biology and healthcare
* Monitoring (medicine), the observation of a disease, condition or one or several medical parameters over time
* Baby monitoring
* Biomonitoring, of toxic chemical compounds, ...
of bodily functions; a web of intravenous lines
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
, feeding tubes, nasogastric tubes, suction pumps, drains, and catheters, syringe pumps; and a wide array of drugs to treat the primary condition(s) of hospitalization. Medically induced comas, analgesics, and induced sedation are common ICU tools needed and used to reduce pain and prevent secondary infections.
Quality of care
The available data suggests a relation between ICU volume and quality of care for mechanically ventilated patients. After adjustment for severity of illnesses, demographic variables, and characteristics of different ICUs (including staffing by intensivists), higher ICU staffing was significantly associated with lower ICU and hospitalmortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
s. A ratio of 2 patients to 1 nurse is recommended for a medical ICU, which contrasts to the ratio of 4:1 or 5:1 typically seen on medical floors. This varies from country to country, though; e.g., in Australia and the United Kingdom, most ICUs are staffed on a 2:1 basis (for high-dependency patients who require closer monitoring or more intensive treatment than a hospital ward can offer) or on a 1:1 basis for patients requiring extreme intensive support and monitoring; for example, a patient on a mechanical ventilator with associated anaesthetics or sedation such as propofol, midazolam and use of strong analgesics such as morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
, fentanyl
Fentanyl, also spelled fentanil, is a very potent synthetic opioid used as a pain medication. Together with other drugs, fentanyl is used for anesthesia. It is also used illicitly as a recreational drug, sometimes mixed with heroin, cocain ...
and/or remifentanil
Remifentanil is a potent, short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic drug. It is given to patients during surgery to relieve pain and as an adjunct to an anaesthetic. Remifentanil is used for sedation as well as combined with other medications fo ...
.
International guidelines recommend that every patient gets checked for delirium every day (usually twice or as much required) using a validated clinical tool. The two most widely used are the Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU) and the Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist (ICDSC). There are translations of these tools in over 20 languages and they are used globally in many ICU's.
Operational logistics
In the United States, up to 20% of hospital beds can be labelled as intensive-care beds; in the United Kingdom, intensive care usually will comprise only up to 2% of total beds. This high disparity is attributed to admission of patients in the UK only when considered the most severely ill. Intensive care is an expensive healthcare service. A recent study conducted in the United States found that hospital stays involving ICU services were 2.5 times more costly than other hospital stays. In the United Kingdom in 2003–04, the average cost of funding an intensive care unit was: * £838 per bed per day for a neonatal intensive care unit * £1,702 per bed per day for a pediatric intensive care unit * £1,328 per bed per day for an adult intensive care unitRemote collaboration systems
Some hospitals have installed teleconferencing systems that allow doctors and nurses at a central facility (either in the same building, at a central location serving several local hospitals, or in rural locations another more urban facility) to collaborate with on-site staff and speak with patients (a form of telemedicine). This is variously called an ''eICU'', ''virtual ICU'', or ''tele-ICU''. Remote staff typically have access to vital signs from live monitoring systems, and telectronic health records so they may have access to a broader view of a patient's medical history. Often bedside and remote staff have met in person and may rotate responsibilities. Such systems are beneficial to intensive care units in order to ensure correct procedures are being followed for patients vulnerable to deterioration, to access vital signs remotely in order to keep patients that would have to be transferred to a larger facility if need be he/she may have demonstrated a significant decrease in stability.See also
*ICU quality and management tools
The intensive care unit (ICU) is one of the major components of the current health care system. The advances in supportive care and monitoring resulted in significant improvements in the care of surgical and clinical patients. Nowadays aggressive ...
* Intensive Care Foundation, a charity in Australia and New Zealand
* ''Intensive Care Medicine'' (journal)
* Open-source ventilator
References
Further reading
*External links
* *Society of Critical Care Medicine
ICUsteps – Intensive care patient support charity
Organisation for Critical Care Transportation
* * {{Authority control Intensive care medicine Hospital departments