Ice Rink on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An ice rink (or ice skating rink) is a frozen body of water and/or an artificial sheet of ice created using hardened chemicals where people can ice skate or play winter sports. Ice rinks are also used for exhibitions, contests and ice shows. The growth and increasing popularity of ice skating during the 1800s marked a rise in the deliberate construction of ice rinks in numerous areas of the world.
The word "rink" is a word of Scottish origin meaning, "course" used to describe the ice surface used in the sport of
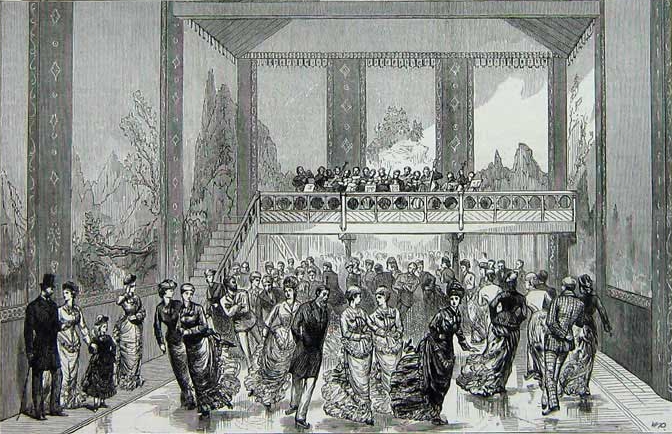 Early attempts in the construction of artificial ice rinks were first made in the 'rink mania' of 1841–44. The technology for the maintenance of natural ice did not exist, therefore these early rinks used a substitute consisting of a mixture of hog's lard and various salts. An item in the May 8, 1844 issue of Eliakim Littell's ''Living Age'' headed "The Glaciarium" reported that "This establishment, which has been removed to Grafton street East' Tottenham Court Road, was opened on Monday afternoon. The area of artificial ice is extremely convenient for such as may be desirous of engaging in the graceful and manly pastime of skating".Littell's Living Age, Volume 1, No. 4, p. 201
By 1844, these venues fell out of fashion as customers grew tired of the 'smelly' ice substitute. It wasn't until thirty years later that refrigeration technology developed to the point where natural ice could finally be feasibly used in the rink. The world's first mechanically frozen ice rink was the '' Glaciarium'', opened by John Gamgee, a British veterinarian and inventor, in a tent in a small building just off the
Early attempts in the construction of artificial ice rinks were first made in the 'rink mania' of 1841–44. The technology for the maintenance of natural ice did not exist, therefore these early rinks used a substitute consisting of a mixture of hog's lard and various salts. An item in the May 8, 1844 issue of Eliakim Littell's ''Living Age'' headed "The Glaciarium" reported that "This establishment, which has been removed to Grafton street East' Tottenham Court Road, was opened on Monday afternoon. The area of artificial ice is extremely convenient for such as may be desirous of engaging in the graceful and manly pastime of skating".Littell's Living Age, Volume 1, No. 4, p. 201
By 1844, these venues fell out of fashion as customers grew tired of the 'smelly' ice substitute. It wasn't until thirty years later that refrigeration technology developed to the point where natural ice could finally be feasibly used in the rink. The world's first mechanically frozen ice rink was the '' Glaciarium'', opened by John Gamgee, a British veterinarian and inventor, in a tent in a small building just off the

 Ice skating quickly became a favorite pastime and craze in several American cities around the mid 1800s spawning a construction period of several ice rinks.
Two early indoor ice rinks made of mechanically frozen ice in the United States opened in 1894, the
Ice skating quickly became a favorite pastime and craze in several American cities around the mid 1800s spawning a construction period of several ice rinks.
Two early indoor ice rinks made of mechanically frozen ice in the United States opened in 1894, the
 The oldest indoor artificial ice rink still in use in the United States is Boston, Massachusetts's,
The oldest indoor artificial ice rink still in use in the United States is Boston, Massachusetts's,
 The first building in
The first building in
 Many ice rinks consist of, or are found on, open bodies of water such as lakes, ponds, canals, and sometimes rivers; these can be used only in the
Many ice rinks consist of, or are found on, open bodies of water such as lakes, ponds, canals, and sometimes rivers; these can be used only in the

 In any climate, an arena ice surface can be installed in a properly built space. This consists of a bed of sand or occasionally a slab of
In any climate, an arena ice surface can be installed in a properly built space. This consists of a bed of sand or occasionally a slab of
 Modern rinks have a specific procedure for preparing the surface. With the pipes cold, a thin layer of water is sprayed on the sand or concrete to seal and level it (or in the case of concrete, to keep it from being marked). This thin layer is painted white or pale blue for better contrast; markings necessary for hockey or curling are also placed, along with logos or other decorations. Another thin layer of water is sprayed on top of this. The ice is built up to a thickness of .
Modern rinks have a specific procedure for preparing the surface. With the pipes cold, a thin layer of water is sprayed on the sand or concrete to seal and level it (or in the case of concrete, to keep it from being marked). This thin layer is painted white or pale blue for better contrast; markings necessary for hockey or curling are also placed, along with logos or other decorations. Another thin layer of water is sprayed on top of this. The ice is built up to a thickness of .
 The size of figure skating rinks can be quite variable, but the
The size of figure skating rinks can be quite variable, but the
 Although there is a great deal of variation in the dimensions of actual ice rinks, there are basically two rink sizes in use at the highest levels of
Although there is a great deal of variation in the dimensions of actual ice rinks, there are basically two rink sizes in use at the highest levels of
 Sledge hockey ( "Para ice hockey", or "sled hockey"), uses the same rink dimensions used by ice hockey rinks.
Sledge hockey ( "Para ice hockey", or "sled hockey"), uses the same rink dimensions used by ice hockey rinks.
 Ringette utilizes most of the standard ice hockey markings used by Hockey Canada, but the ringette rink uses additional free-pass dots in each of the attacking zones and centre zone areas as well as a larger goal crease area. Two additional free-play lines (1 in each attacking zone) are also required.
A ringette rink is an ice rink designed for ice hockey which has been modified to enable ringette to be played. Though some ice surfaces are designed strictly for ringette, these ice rinks with exclusive lines and markings for ringette are usually created only at venues hosting major ringette competitions and events. Most ringette rinks are found in
Ringette utilizes most of the standard ice hockey markings used by Hockey Canada, but the ringette rink uses additional free-pass dots in each of the attacking zones and centre zone areas as well as a larger goal crease area. Two additional free-play lines (1 in each attacking zone) are also required.
A ringette rink is an ice rink designed for ice hockey which has been modified to enable ringette to be played. Though some ice surfaces are designed strictly for ringette, these ice rinks with exclusive lines and markings for ringette are usually created only at venues hosting major ringette competitions and events. Most ringette rinks are found in
 The organized format of broomball uses the rink dimensions defined by a standard Canadian ice hockey rink.
The organized format of broomball uses the rink dimensions defined by a standard Canadian ice hockey rink.
 Speed skating tracks or "rinks" can either be created naturally or artificially and are made either outdoors or inside indoor facilities. Tracks may be created by having the lanes surround the exterior of an ice rink.
The sport requires the use of a special type of racing skate, the speed skating ice skate.
Speed skating tracks or "rinks" can either be created naturally or artificially and are made either outdoors or inside indoor facilities. Tracks may be created by having the lanes surround the exterior of an ice rink.
The sport requires the use of a special type of racing skate, the speed skating ice skate.
 In
In
 The Netherlands is home of Elfstedentocht, a 200 km distance skating race of which the tracks leads through the 11 different cities in
The Netherlands is home of Elfstedentocht, a 200 km distance skating race of which the tracks leads through the 11 different cities in
 Ice cross downhill, (formerly known as "Red Bull Crashed Ice" or " Crashed Ice"), is a
Ice cross downhill, (formerly known as "Red Bull Crashed Ice" or " Crashed Ice"), is a
 An example of an ice skating trail, or "rink", is the Rideau Canal Skateway in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, estimated at and long, which is equivalent to 90 Olympic-size skating rinks.
The rink is prepared by lowering the canal's water level and letting the canal water freeze. The rink is then resurfaced nightly by cleaning the ice of snow and flooding it with water from below the ice. The rink is recognized as the "world's largest naturally frozen ice rink" by the Guinness Book of World Records because "its entire length receives daily maintenance such as sweeping, ice thickness checks and there are toilet and recreational facilities along its entire length".
An example of an ice skating trail, or "rink", is the Rideau Canal Skateway in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, estimated at and long, which is equivalent to 90 Olympic-size skating rinks.
The rink is prepared by lowering the canal's water level and letting the canal water freeze. The rink is then resurfaced nightly by cleaning the ice of snow and flooding it with water from below the ice. The rink is recognized as the "world's largest naturally frozen ice rink" by the Guinness Book of World Records because "its entire length receives daily maintenance such as sweeping, ice thickness checks and there are toilet and recreational facilities along its entire length".

 The sport of
The sport of
 Crokicurl is a Canadian winter sport and is a large scale hybrid of
Crokicurl is a Canadian winter sport and is a large scale hybrid of
 Outdoor ice rinks and frozen ponds, rivers, and canals, serve several purposes, allowing for physical activities during the winter season such as recreational ice skating and
Outdoor ice rinks and frozen ponds, rivers, and canals, serve several purposes, allowing for physical activities during the winter season such as recreational ice skating and
is a citizen science program in
The Ice Rink – A Brief History
* RinkWatch'
is a citizen science research initiative that asks people to help environmental scientists monitor winter weather conditions and study the long-term impacts of climate change.
Comprehensive list of ice skating rinks
in the U.S. and Canada
Backyard Ice Rink Builder Community
{{Authority control Ice rinks, Playing field surfaces Sports venues Figure skating Bandy Ice hockey Sledge hockey Ringette Speed skating Broomball Sports rules and regulations
curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
, but was kept in use once the winter team sport of ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
became established.
There are two types of ice rinks in prevalent use today: natural ice rinks, where freezing
Freezing is a phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. In accordance with the internationally established definition, freezing means the solidification phase change of a liquid ...
occurs from cold ambient temperatures, and artificial ice rinks (or mechanically frozen), where a coolant produces cold temperatures in the surface below the water, causing the water to freeze. There are also synthetic ice rinks where skating surfaces are made out of plastics.
Besides recreational ice skating, some of its uses include: ice hockey, sledge hockey ( "Para ice hockey", or "sled hockey"), spongee ( sponge hockey), bandy, rink bandy, rinkball, ringette, broomball (both indoor and outdoor versions), Moscow broomball, speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
, figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, when contested at the 1908 Olympics in London. The Olympic disciplines are me ...
, ice stock sport, curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
, and crokicurl. However, Moscow broomball is typically played on a tarmac tennis court that has been flooded with water and allowed to freeze. The sports of broomball, curling, ice stock sport, spongee, Moscow broomball, and the game of crokicurl, do not use ice skates of any kind.
While technically not an ice rink, ice tracks and trails, such as those used in the sport of speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
and recreational or pleasure skating are sometimes referred to as "ice rinks".
Etymology
''Rink'', a Scottish word meaning 'course', was used as the name of a place wherecurling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
was played. As curling is played on ice, the name has been retained for the construction of ice areas for other sports and uses.
History
Great Britain
London, England
 Early attempts in the construction of artificial ice rinks were first made in the 'rink mania' of 1841–44. The technology for the maintenance of natural ice did not exist, therefore these early rinks used a substitute consisting of a mixture of hog's lard and various salts. An item in the May 8, 1844 issue of Eliakim Littell's ''Living Age'' headed "The Glaciarium" reported that "This establishment, which has been removed to Grafton street East' Tottenham Court Road, was opened on Monday afternoon. The area of artificial ice is extremely convenient for such as may be desirous of engaging in the graceful and manly pastime of skating".Littell's Living Age, Volume 1, No. 4, p. 201
By 1844, these venues fell out of fashion as customers grew tired of the 'smelly' ice substitute. It wasn't until thirty years later that refrigeration technology developed to the point where natural ice could finally be feasibly used in the rink. The world's first mechanically frozen ice rink was the '' Glaciarium'', opened by John Gamgee, a British veterinarian and inventor, in a tent in a small building just off the
Early attempts in the construction of artificial ice rinks were first made in the 'rink mania' of 1841–44. The technology for the maintenance of natural ice did not exist, therefore these early rinks used a substitute consisting of a mixture of hog's lard and various salts. An item in the May 8, 1844 issue of Eliakim Littell's ''Living Age'' headed "The Glaciarium" reported that "This establishment, which has been removed to Grafton street East' Tottenham Court Road, was opened on Monday afternoon. The area of artificial ice is extremely convenient for such as may be desirous of engaging in the graceful and manly pastime of skating".Littell's Living Age, Volume 1, No. 4, p. 201
By 1844, these venues fell out of fashion as customers grew tired of the 'smelly' ice substitute. It wasn't until thirty years later that refrigeration technology developed to the point where natural ice could finally be feasibly used in the rink. The world's first mechanically frozen ice rink was the '' Glaciarium'', opened by John Gamgee, a British veterinarian and inventor, in a tent in a small building just off the Kings Road
King's Road or Kings Road (or sometimes the King's Road, especially when it was the king's private road until 1830, or as a colloquialism by middle/upper class London residents), is a major street stretching through Chelsea and Fulham, both ...
in Chelsea, London
Chelsea is an affluent area in west London, England, due south-west of Charing Cross by approximately 2.5 miles. It lies on the north bank of the River Thames and for postal purposes is part of the south-western postal area.
Chelsea histori ...
, on 7 January 1876. Gamgee had become fascinated by the refrigeration technology he encountered during a study trip to America to look at Texas fever
Babesiosis or piroplasmosis is a malaria-like parasitic disease caused by infection with a eukaryotic parasite in the order Piroplasmida, typically a ''Babesia'' or ''Theileria'', in the phylum Apicomplexa. Human babesiosis transmission via tic ...
in cattle. In March of that same year it moved to a permanent venue at 379 Kings Road, where a rink measuring was established.
The rink was based on a concrete surface, with layers of earth, cow hair and timber planks. Atop these were laid oval copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
pipes carrying a solution of glycerine
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids know ...
with ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again ...
, nitrogen peroxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide (NTO), and occasionally (usually among ex-USSR/Russia rocket engineers) as amyl, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an equilibrium ...
and water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
. The pipes were covered by water and the solution was pumped through, freezing the water into ice. Gamgee discovered the process while attempting to develop a method to freeze meat for import from Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
, and patented it as early as 1870.
Gamgee operated the rink on a membership-only basis and attempted to attract a wealthy clientele, experienced in open-air ice skating during winters in the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
. He installed an orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families.
There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, c ...
gallery, which could also be used by spectators, and decorated the walls with views of the Swiss Alps
The Alpine region of Switzerland, conventionally referred to as the Swiss Alps (german: Schweizer Alpen, french: Alpes suisses, it, Alpi svizzere, rm, Alps svizras), represents a major natural feature of the country and is, along with the Swis ...
.
The rink initially proved a success, and Gamgee opened two further rinks later in the year: at Rusholme in Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The ...
and the "Floating Glaciarium" at Charing Cross in London, this last significantly larger at . The Southport Glaciarium opened in 1879, using Gamgee's method.
The Fens, England
In the marshlands ofThe Fens
The Fens, also known as the , in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a ...
, skating was developed early as a pastime during winter where there were plenty of natural ice surfaces. This is the origin of the Fen skating and is said to be the birthplace of bandy. The Great Britain Bandy Association
The Great Britain Bandy Association (GBBA) is the governing body of the sport of bandy in the United Kingdom. It is based in The Fens part of Cambridgeshire, East Anglia. Formerly, the federation was named Bandy Federation of England. After som ...
has its home in the area.
Germany
In Germany, the first ice skating rink opened in 1882 inFrankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
during a patent exhibition. It covered and operated for two months; the refrigeration system was designed by Jahre Linde, and was probably the first skating rink where ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
was used as a refrigerant. Ten years later, a larger rink was permanently installed on the same site.
United States
Early indoor ice rinks

 Ice skating quickly became a favorite pastime and craze in several American cities around the mid 1800s spawning a construction period of several ice rinks.
Two early indoor ice rinks made of mechanically frozen ice in the United States opened in 1894, the
Ice skating quickly became a favorite pastime and craze in several American cities around the mid 1800s spawning a construction period of several ice rinks.
Two early indoor ice rinks made of mechanically frozen ice in the United States opened in 1894, the North Avenue Ice Palace
The North Avenue Ice Palace in Baltimore, Maryland, United States was one of the first examples of an indoor artificial ice rink in North America. It was located on North Avenue between Charles Street and Lovegrove Alley and extended north to 20t ...
in Baltimore, Maryland
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore wa ...
, and the Ice Palace in New York.
The St. Nicholas Rink, ( "St. Nicholas Arena"), was an indoor ice rink in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
which existed from 1896 until its demolition in the 1980s. It was one of the earliest American indoor ice rinks made of mechanically frozen ice in North America and gave ice skaters the opportunity to enjoy an extended skating season. The rink was used for pleasure skating, ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
, and ice skating, and was an important rink involved in the development of the sports of ice hockey and boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
.
Oldest indoor artificial ice rink in use
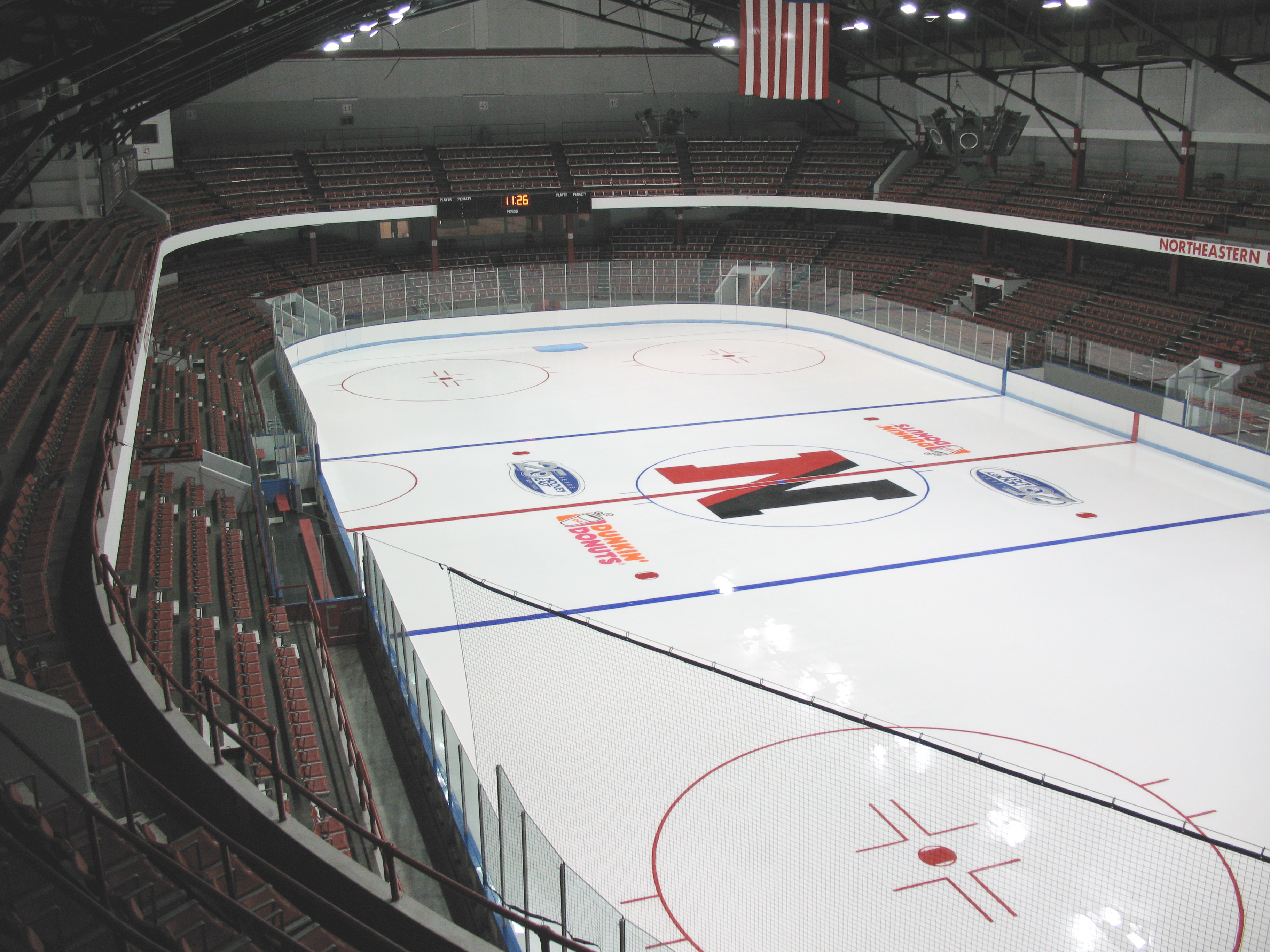
 The oldest indoor artificial ice rink still in use in the United States is Boston, Massachusetts's,
The oldest indoor artificial ice rink still in use in the United States is Boston, Massachusetts's, Matthews Arena
Matthews Arena (formerly Boston Arena) is a multi-purpose arena in Boston, Massachusetts. It is the world's oldest multi-purpose athletic building still in use, as well as the oldest arena in use for ice hockey.
The arena opened in 1910 on what ...
(formerly Boston Arena) which was built between 1909 and 1910. The rink is located on the campus of Northeastern University
Northeastern University (NU) is a private research university with its main campus in Boston. Established in 1898, the university offers undergraduate and graduate programs on its main campus as well as satellite campuses in Charlotte, North Ca ...
.
This American rink is the original home of the National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey sports league, league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranke ...
(NHL) Boston Bruins
The Boston Bruins are a professional ice hockey team based in Boston. The Bruins compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Atlantic Division in the Eastern Conference. The team has been in existence since 1924, making ...
. The Bruins are the only remaining NHL team who are members of the NHL's Original Six with their original home arena still in existence.
Contemporary
TheGuidant John Rose Minnesota Oval
The Guidant John Rose Minnesota Oval (officially stylized as OVAL), formerly the John Rose Minnesota Oval, is an outdoor ice rink in Roseville, Minnesota, United States. It is claimed to be the largest artificial outdoor skating surface in North ...
, (formerly the John Rose Minnesota Oval), is an outdoor ice rink in Roseville, Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over t ...
that is
large enough to allow ice skaters to play the sport of bandy. The facility was constructed from between June and December in 1993. It is the only regulation sized bandy field in North America and serves as the home of USA Bandy and its national bandy teams. The rink has been claimed to be the largest artificial outdoor ice skating surface in modern North America.
Canada
 The first building in
The first building in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
to be electrified was the Victoria Skating Rink which opened in 1862 in Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
, Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
, Canada. The rink was created using natural ice. At the start of the twentieth century it had been described as "one of the finest covered rinks in the world" and was used during winter for pleasure skating, ice hockey, and skating sports. In summer months, the building was used for various other events.
Types
Natural ice
 Many ice rinks consist of, or are found on, open bodies of water such as lakes, ponds, canals, and sometimes rivers; these can be used only in the
Many ice rinks consist of, or are found on, open bodies of water such as lakes, ponds, canals, and sometimes rivers; these can be used only in the winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultur ...
in climates where the surface freezes thickly enough to support human weight. Rinks can also be made in cold climates by enclosing a level area of ground, filling it with water, and letting it freeze. Snow may be packed to use as a containment material.
An example of this type of "rink", which is a body of water converted into a skating trail during winter, is the Rideau Canal Skateway in Ottawa, Ontario.
Artificial ice

 In any climate, an arena ice surface can be installed in a properly built space. This consists of a bed of sand or occasionally a slab of
In any climate, an arena ice surface can be installed in a properly built space. This consists of a bed of sand or occasionally a slab of concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
, through (or on top of) which pipes run. The pipes carry a chilled fluid (usually either a salt brine or water with antifreeze, or in the case of smaller rinks, refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated ...
) which can lower the temperature of the slab so that water placed atop will freeze. This method is known as 'artificial ice' to differentiate from ice rinks made by simply freezing water in a cold climate, indoors or outdoors, although both types are of frozen water. A more proper technical term is 'mechanically frozen' ice.
An example of this type of rink is the outdoor rink at Rockefeller Center in New York.
Construction
 Modern rinks have a specific procedure for preparing the surface. With the pipes cold, a thin layer of water is sprayed on the sand or concrete to seal and level it (or in the case of concrete, to keep it from being marked). This thin layer is painted white or pale blue for better contrast; markings necessary for hockey or curling are also placed, along with logos or other decorations. Another thin layer of water is sprayed on top of this. The ice is built up to a thickness of .
Modern rinks have a specific procedure for preparing the surface. With the pipes cold, a thin layer of water is sprayed on the sand or concrete to seal and level it (or in the case of concrete, to keep it from being marked). This thin layer is painted white or pale blue for better contrast; markings necessary for hockey or curling are also placed, along with logos or other decorations. Another thin layer of water is sprayed on top of this. The ice is built up to a thickness of .
Synthetic
Synthetic rinks are constructed from a solid polymer material designed for skating using normal metal-bladed ice skates. High density polyethelene (HDPE) and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMW) are the only materials that offer reasonable skating characteristics, with UHMW synthetic rinks offering the most ice-like skating but also being the most expensive. A typical synthetic rink will consist of many panels of thin surface material assembled on top of a sturdy, level and smooth sub-floor (anything from concrete to wood or even dirt or grass) to create a large skating area.Operation
Periodically after the ice has been used, it is resurfaced using a machine called an ice resurfacer (sometimes colloquially referred to as a Zamboni – referring to a major manufacturer of such machinery). For curling, the surface is 'pebbled' by allowing loose drops of cold water to fall onto the ice and freeze into rounded peaks. Between events, especially if the arena is being used without need for the ice surface, it is either covered with a heavily insulated floor or melted by allowing the fluid in the pipes below the ice to warm. A highly specialized form of rink is used forspeed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
; this is a large oval (or ''ring'') much like an athletic track. Because of their limited use, speed skating ovals are far less common than hockey or curling rinks.
Those skilled at preparing arena ice are often in demand for major events where ice quality is critical. The popularity of the sport of hockey in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
has led its icemakers to be particularly sought after. One such team of professionals was responsible for placing a loonie
The loonie (french: huard), formally the Canadian one-dollar coin, is a gold-coloured Canadian coin that was introduced in 1987 and is produced by the Royal Canadian Mint at its facility in Winnipeg. The most prevalent versions of the coin ...
coin under center ice at the 2002 Winter Olympics
The 2002 Winter Olympics, officially the XIX Olympic Winter Games and commonly known as Salt Lake 2002 ( arp, Niico'ooowu' 2002; Gosiute Shoshoni: ''Tit'-so-pi 2002''; nv, Sooléí 2002; Shoshoni: ''Soónkahni 2002''), was an internationa ...
in Salt Lake City, Utah
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the capital and most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, t ...
; as both Canadian teams (men's and women's) won their respective hockey gold medals, the coin was christened "lucky" and is now in the possession of the Hockey Hall of Fame after having been retrieved from beneath the ice.
Standard rink sizes
Bandy
In bandy, the size of the playing field is x . For internationals, the size must not be smaller than . The variety rink bandy is played on ice hockey rinks.Figure skating
 The size of figure skating rinks can be quite variable, but the
The size of figure skating rinks can be quite variable, but the International Skating Union
The International Skating Union (ISU) is the international governing body for competitive ice skating disciplines, including figure skating, synchronized skating, speed skating, and short track speed skating. It was founded in Scheveningen, N ...
prefers Olympic-sized rinks for figure skating competitions, particularly for major events. These are . The ISU specifies that competition rinks must not be larger than this and not smaller than .
Ice hockey
 Although there is a great deal of variation in the dimensions of actual ice rinks, there are basically two rink sizes in use at the highest levels of
Although there is a great deal of variation in the dimensions of actual ice rinks, there are basically two rink sizes in use at the highest levels of ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
. Historically, earlier ice rinks were smaller than today.
Official National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey sports league, league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranke ...
rinks are . The dimensions originate from the size of the Victoria Skating Rink in Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
Official Olympic
Olympic or Olympics may refer to
Sports
Competitions
* Olympic Games, international multi-sport event held since 1896
** Summer Olympic Games
** Winter Olympic Games
* Ancient Olympic Games, ancient multi-sport event held in Olympia, Greece bet ...
and International ice hockey rinks have dimensions of .
Para ice hockey
 Sledge hockey ( "Para ice hockey", or "sled hockey"), uses the same rink dimensions used by ice hockey rinks.
Sledge hockey ( "Para ice hockey", or "sled hockey"), uses the same rink dimensions used by ice hockey rinks.
Ringette
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
and Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bot ...
.
Playing area, size, lines and markings for the standard Canadian ringette rink are similar to the average ice hockey rink in Canada with certain modifications.
Early in its history, ringette was played mostly on rinks constructed for ice hockey, broomball, figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, when contested at the 1908 Olympics in London. The Olympic disciplines are me ...
, and recreational skating, and was mostly played on outdoor rinks since few indoor ice rinks were available at the time.
Broomball
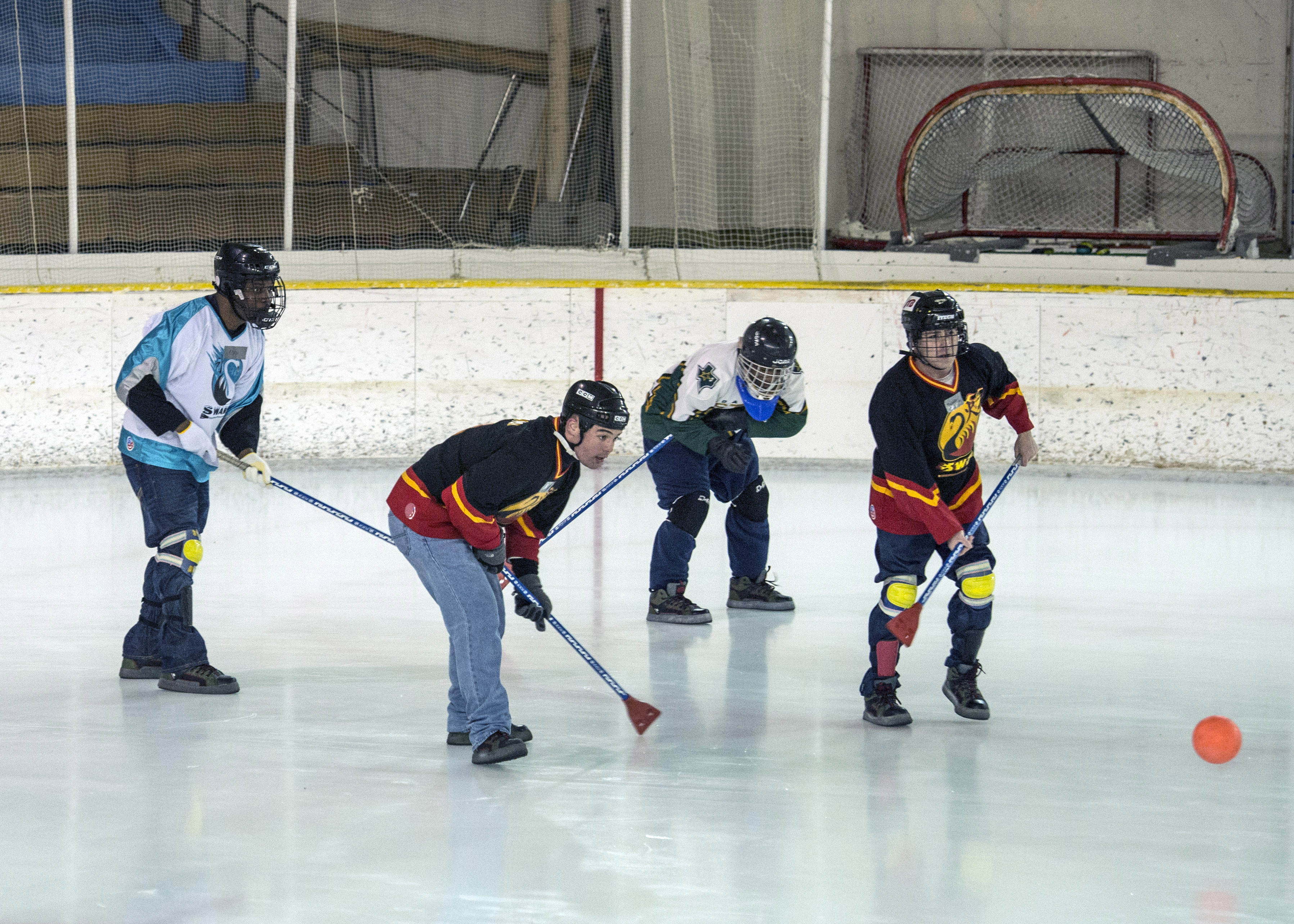
 The organized format of broomball uses the rink dimensions defined by a standard Canadian ice hockey rink.
The organized format of broomball uses the rink dimensions defined by a standard Canadian ice hockey rink.
Spongee
The sport of spongee, "sponge hockey", does not use ice skates. A skateless outdoor winter variant of ice hockey, spongee has its own rules codes and is played strictly within the Canadian city ofWinnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749 ...
as a cult sport. The sport generally uses the rink dimensions defined by a standard Canadian ice hockey rink.
Rinkball
Rinkball rinks today typically use the measurements of an ice hockey rink, though may be slightly larger due to the sport having originated in Europe where the bandy field influenced the size and development of smaller ice rinks.Tracks and trails
Tracks and trails are occasionally referred to as ice rinks in spite of their differences. Ice skating tracks and ice skating trails are used for recreational exercise and sporting activities during the winter season including distance ice skating. Ice trails are created by natural bodies of water such as rivers, which freeze during winter, though some trails are created by removing snow to create skating lanes on large frozen lakes for ice skaters. Ice trails are usually used for pleasure skating, though the sport and recreational activity of Tour skating can involve ice skaters passing over ice trails and open areas created by frozen lakes. To date,speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
and ice cross downhill are the only winter activities or sports whereby ice skaters use tracks and lanes designed to include bends rather than using a simple straightway. Some ice rinks are constructed in a manner allowing for a speed skating rink to be created around its outside perimeter.
Tracks
Speed skating track
speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
, for short track, the official Olympic
Olympic or Olympics may refer to
Sports
Competitions
* Olympic Games, international multi-sport event held since 1896
** Summer Olympic Games
** Winter Olympic Games
* Ancient Olympic Games, ancient multi-sport event held in Olympia, Greece bet ...
rink size is , with an oval ice track of in circumference.
In long track speed skating
Long-track speed skating, usually simply referred to as speed skating, is the Olympic discipline of speed skating where competitors are timed while crossing a set distance. It is also a sport for leisure. Sports such as ice skating marathon, ...
the oval ice track is usually in circumference.
Ice skating marathon tracks
An ice skating marathon is a long distance speed skating race which may be held on natural ice on canals and bodies of water such as lakes and rivers. Marathon is a discipline ofspeed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
, which is founded in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
.
The races concern speed skating by at least five skaters who start all together on an ice rink with a minimum length of 333.33 meters or on a track:
* Minimum distance longer than 6.4 kilometers and up to 200 kilometers for skaters who have reached the age of 17 prior to the skating season on July 1.
* Minimum distance longer than 4 kilometers and up to 20 kilometers for skaters who have reached the age of or the age of 13, but have not yet reached the age of 17 before July 1 preceding the skating season.
* Minimum distance of 2 kilometers and up to 10 kilometers for skaters who have not yet reached the age of 13 before July 1 preceding the skating season.
Dutch skating tracks
 The Netherlands is home of Elfstedentocht, a 200 km distance skating race of which the tracks leads through the 11 different cities in
The Netherlands is home of Elfstedentocht, a 200 km distance skating race of which the tracks leads through the 11 different cities in Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
which is a northern province of the Netherlands.
Skate tracks on natural ice are maintained by the towns and communities, who take care of the safety of the tracks.
Ice cross downhill tracks
 Ice cross downhill, (formerly known as "Red Bull Crashed Ice" or " Crashed Ice"), is a
Ice cross downhill, (formerly known as "Red Bull Crashed Ice" or " Crashed Ice"), is a winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultur ...
extreme sporting event involving direct competitive downhill skating. Skaters race down a walled track which features sharp turns and high vertical drops.
Trails
Rideau Canal Skateway
 An example of an ice skating trail, or "rink", is the Rideau Canal Skateway in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, estimated at and long, which is equivalent to 90 Olympic-size skating rinks.
The rink is prepared by lowering the canal's water level and letting the canal water freeze. The rink is then resurfaced nightly by cleaning the ice of snow and flooding it with water from below the ice. The rink is recognized as the "world's largest naturally frozen ice rink" by the Guinness Book of World Records because "its entire length receives daily maintenance such as sweeping, ice thickness checks and there are toilet and recreational facilities along its entire length".
An example of an ice skating trail, or "rink", is the Rideau Canal Skateway in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, estimated at and long, which is equivalent to 90 Olympic-size skating rinks.
The rink is prepared by lowering the canal's water level and letting the canal water freeze. The rink is then resurfaced nightly by cleaning the ice of snow and flooding it with water from below the ice. The rink is recognized as the "world's largest naturally frozen ice rink" by the Guinness Book of World Records because "its entire length receives daily maintenance such as sweeping, ice thickness checks and there are toilet and recreational facilities along its entire length".
Longest trail
The longest ice skating trail is in Invermere, British Columbia, Canada, onLake Windermere Whiteway
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
. The naturally frozen trail measures .
Combined
Outdoor ice skating activities and competitions involving a goal of distance travel for recreation, exercise, competition and adventure, can involve frozen lakes, rivers, and canals.Tour skating
The sport and recreational activity, Tour skating ( "Nordic skating" in North America), is strictly an outdoor activity for ice skaters. Nordic skating originated during the 1900s in Sweden. Ice skaters traverse naturally frozen bodies of water, which sometimes, but not always, includes interconnected ice trails as well as frozen ponds, lakes, and even marsh areas. Tour skaters use a special ice skate with long blades.Elfstedentocht (Eleven cities tour)
The Elfstedentocht (Eleven Cities Tour) is a long-distance tour skating event on natural ice, almost long, which is held both as aspeed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
competition (with 300 contestants) and a leisure tour (with 16,000 skaters). It is the biggest ice-skating tour in the world and held in the province of Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
in the north of the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
.
The event leads past all eleven historical cities of the province and is held at most once a year, only when the natural ice along the entire course is at least thick. It is sometimes held on consecutive years, while at other times, gaps between the touring years have exceeded 20 years. When the ice is suitable, the tour is announced and starts within 48 hours. The last Elfstedentocht was held in 1997.
Laneways
The sports ofcurling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
and Ice stock sport are played on either ice rinks or simple ice surfaces with lanes marked out for play.
Curling

curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
uses an ice rink known as a "curling rink" or curling sheet
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding he ...
. Curling does not involve ice skating. Curling uses lanes.
The curling sheet is a carefully prepared rectangular area of ice created to be as flat and level as possible. The ice surface dimensions are in length by in width. A curling sheet includes areas marked off in a manner specific to the sport, including the ''house'', the ''button'', ''hog lines'', ''hacks'', and shorter borders along the ends of the sheet called the backboards.
The dimensions of an official curling sheet is defined by the World Curling Federation
The World Curling Federation (WCF) is the world governing body for curling accreditation, with offices in Perth, Scotland. It was formed out of the International Curling Federation (ICF), when the push for Olympic Winter Sport status was made. ...
Rules of Curling. At major events, ice preparation and maintenance is extremely important. Curling clubs usually have an ice maker whose main job is to care for the ice.
Other
Crokicurl
 Crokicurl is a Canadian winter sport and is a large scale hybrid of
Crokicurl is a Canadian winter sport and is a large scale hybrid of curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
and the board game Crokinole. It is played outdoors by teams consisting of two players who take turns trying to score points on a quadrant shaped area with the playing area marked off on a sheet of ice. The quadrant includes posts, starting line, wooden edge side-rail, and a 20-point "button". Depending on the area involved, players can score 5, 10, or 15 points.
Outdoor ice
 Outdoor ice rinks and frozen ponds, rivers, and canals, serve several purposes, allowing for physical activities during the winter season such as recreational ice skating and
Outdoor ice rinks and frozen ponds, rivers, and canals, serve several purposes, allowing for physical activities during the winter season such as recreational ice skating and figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, when contested at the 1908 Olympics in London. The Olympic disciplines are me ...
, and also function as an affordable place for players to engage in team winter sports such as ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
, bandy, rinkball, ringette, broomball, and spongee, as a pastime.
These areas and facilities also help individuals, youth sporting organizations, and families, offset the expensive cost of indoor ice-time. They are also used as a part of outdoor winter festivals
A winter festival, winter carnival, snow festival, or frost fair is an outdoor cold weather celebration that occurs in wintertime.
Winter festivals are popular in D climates (see Köppen climate classification) where winter is particularly lon ...
and to host pond hockey tournaments and the like.
Decline
Rinks
The length of outdoor ice skating season began to experience a noticeable decline in North America in the early part of the 21st century. One of the correlated factors involved has been attributed toclimate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. One of the consequences involved includes reducing access to outdoor facilities needed by youth who require opportunities to participate in ice-based sports at length and with low-cost, a problematic development considering winter sports become increasingly expensive over time resulting in economic exclusion.
;RinkWatch
RinkWatchis a citizen science program in
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
run by researchers at Wilfrid Laurier University in Waterloo, Ontario. Beginning in 2013 the program started collecting data on outdoor rinks and frozen ponds across North America. The objective is to better understand how climate change may be impacting the outdoor skating season.
Tracks and trails
Elfstedentocht, the world's biggest ice-skating tour involving tour skating andspeed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
, has been declared to be in danger of "extinction" due to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. The last Elfstedentocht was held in 1997.
See also
* Bandy field * Figure skating rink * Ice hockey rink * Speed skating rink *Curling sheet
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding he ...
* Synthetic ice
*List of ice hockey arenas by capacity
The following is a list of ice hockey arenas by capacity. Only those arenas that regularly host ice hockey games with paid admission (e.g. professional, major junior, or university) are included. Outdoor stadiums that have hosted occasional hockey ...
References
External links
The Ice Rink – A Brief History
* RinkWatch'
is a citizen science research initiative that asks people to help environmental scientists monitor winter weather conditions and study the long-term impacts of climate change.
Comprehensive list of ice skating rinks
in the U.S. and Canada
Backyard Ice Rink Builder Community
{{Authority control Ice rinks, Playing field surfaces Sports venues Figure skating Bandy Ice hockey Sledge hockey Ringette Speed skating Broomball Sports rules and regulations