Hydrolyzed on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for
 Upon hydrolysis, an
Upon hydrolysis, an
ATP + H2O -> ADP + P_
Secondly, the removal of a terminal diphosphate to yield adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and pyrophosphate. The latter usually undergoes further cleavage into its two constituent phosphates. This results in biosynthesis reactions, which usually occur in chains, that can be driven in the direction of synthesis when the phosphate bonds have undergone hydrolysis.
 Monosaccharides can be linked together by glycosidic bonds, which can be cleaved by hydrolysis. Two, three, several or many monosaccharides thus linked form disaccharides, trisaccharides,
Monosaccharides can be linked together by glycosidic bonds, which can be cleaved by hydrolysis. Two, three, several or many monosaccharides thus linked form disaccharides, trisaccharides,
M(H2O)_\mathit^ + H2O <=> M(H2O)_(OH)^ + H3O+
Thus the aqua cations behave as acids in terms of
 Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution
Substitution may refer to:
Arts and media
*Chord substitution, in music, swapping one chord for a related one within a chord progression
*Substitution (poetry), a variation in poetic scansion
* "Substitution" (song), a 2009 song by Silversun Pic ...
, elimination, and solvation
Solvation (or dissolution) describes the interaction of a solvent with dissolved molecules. Both ionized and uncharged molecules interact strongly with a solvent, and the strength and nature of this interaction influence many properties of t ...
reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may o ...
is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification.
Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water.
Types
Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. In such reactions, one fragment of the target molecule (or parent molecule) gains ahydrogen ion
A hydrogen ion is created when a hydrogen atom loses or gains an electron. A positively charged hydrogen ion (or proton) can readily combine with other particles and therefore is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearly particle ...
. It breaks a chemical bond in the compound.
Salts
A common kind of hydrolysis occurs when asalt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
of a weak acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions ...
or weak base (or both) is dissolved in water. Water spontaneously ionizes into hydroxide anions and hydronium cations. The salt also dissociates into its constituent anions and cations. For example, sodium acetate dissociates in water into sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
and acetate ions. Sodium ions react very little with the hydroxide ions whereas the acetate ions combine with hydronium ions to produce acetic acid. In this case the net result is a relative excess of hydroxide ions, yielding a basic solution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Solutio ...
.
Strong acids also undergo hydrolysis. For example, dissolving sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
() in water is accompanied by hydrolysis to give hydronium
In chemistry, hydronium (hydroxonium in traditional British English) is the common name for the aqueous cation , the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid ...
and bisulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
, the sulfuric acid's conjugate base
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid donates a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as in the reverse reaction it loses a ...
. For a more technical discussion of what occurs during such a hydrolysis, see Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory
The Brønsted–Lowry theory (also called proton theory of acids and bases) is an acid–base reaction theory which was proposed independently by Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923. The fundamental concept of this theory ...
.
Esters and amides
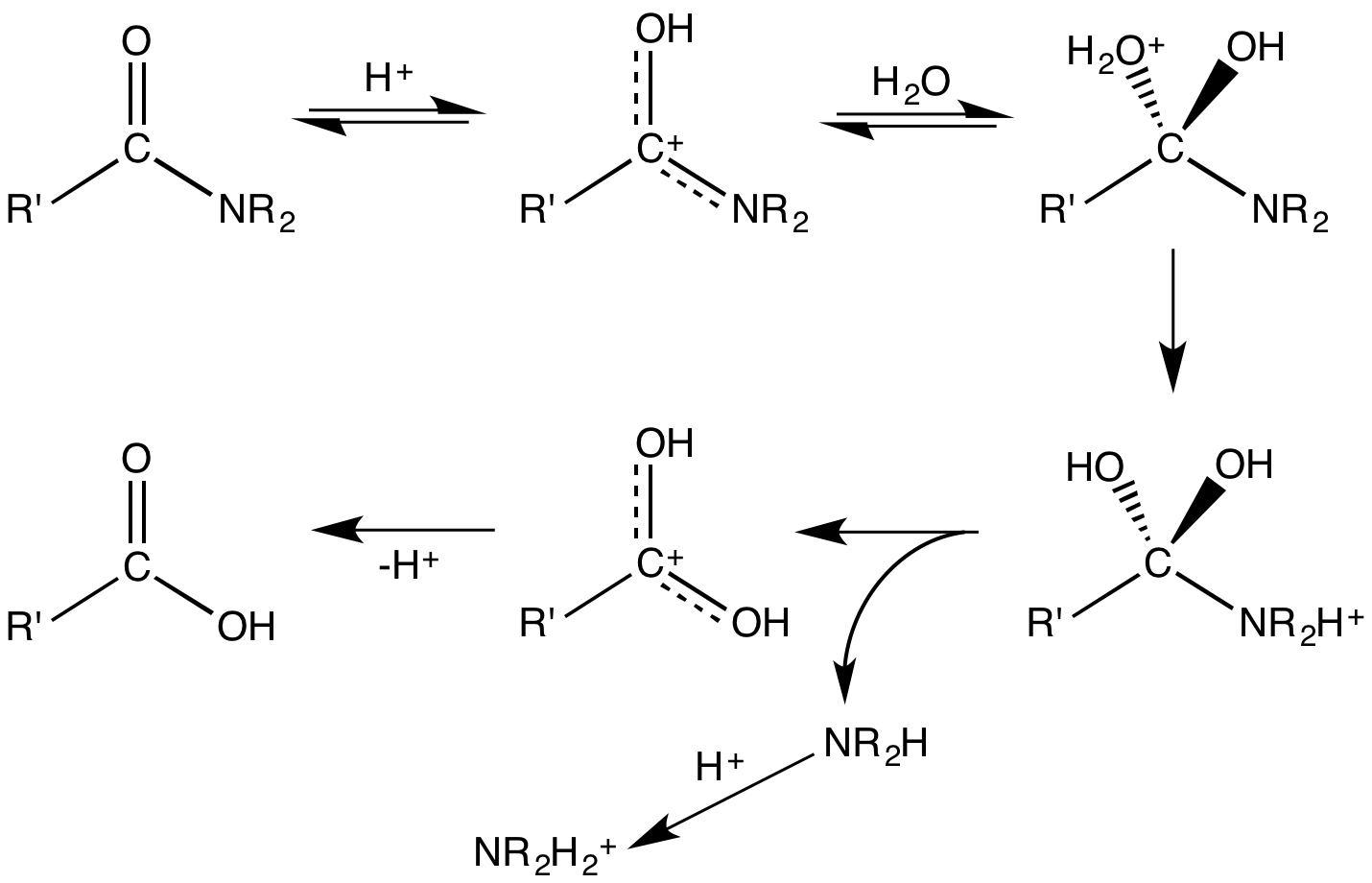
Acid–base-catalysed hydrolyses are very common; one example is the hydrolysis ofamide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it i ...
s or ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
s. Their hydrolysis occurs when the nucleophile (a nucleus-seeking agent, e.g., water or hydroxyl ion) attacks the carbon of the carbonyl group of the ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
or amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it i ...
. In an aqueous base, hydroxyl ions are better nucleophiles than polar molecules such as water. In acids, the carbonyl group becomes protonated, and this leads to a much easier nucleophilic attack. The products for both hydrolyses are compounds with carboxylic acid groups.
Perhaps the oldest commercially practiced example of ester hydrolysis is saponification (formation of soap). It is the hydrolysis of a triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as ...
(fat) with an aqueous base such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH). During the process, glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known ...
is formed, and the fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, f ...
s react with the base, converting them to salts. These salts are called soaps, commonly used in households.
In addition, in living systems, most biochemical reactions (including ATP hydrolysis) take place during the catalysis of enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s. The catalytic action of enzymes allows the hydrolysis of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s, fats, oils, and carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may o ...
s. As an example, one may consider protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
s (enzymes that aid digestion by causing hydrolysis of peptide bonds in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s). They catalyze the hydrolysis of interior peptide bonds in peptide chains, as opposed to exopeptidases (another class of enzymes, that catalyze the hydrolysis of terminal peptide bonds, liberating one free amino acid at a time).
However, proteases do not catalyze the hydrolysis of all kinds of proteins. Their action is stereo-selective: Only proteins with a certain tertiary structure are targeted as some kind of orienting force is needed to place the amide group in the proper position for catalysis. The necessary contacts between an enzyme and its substrates (proteins) are created because the enzyme folds in such a way as to form a crevice into which the substrate fits; the crevice also contains the catalytic groups. Therefore, proteins that do not fit into the crevice will not undergo hydrolysis. This specificity preserves the integrity of other proteins such as hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
s, and therefore the biological system continues to function normally.
 Upon hydrolysis, an
Upon hydrolysis, an amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it i ...
converts into a carboxylic acid and an amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent ...
or ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
(which in the presence of acid are immediately converted to ammonium salts). One of the two oxygen groups on the carboxylic acid are derived from a water molecule and the amine (or ammonia) gains the hydrogen ion. The hydrolysis of peptides gives amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
s.
Many polyamide
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds.
Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk. Artificially made polyamides can be made th ...
polymers such as nylon 6,6
Nylon 66 (loosely written nylon 6-6, nylon 6/6, nylon 6,6, or nylon 6:6) is a type of polyamide or nylon. It, and nylon 6, are the two most common for textile and plastic industries. Nylon 66 is made of two monomers each containing 6 carbon atoms ...
hydrolyze in the presence of strong acids. The process leads to depolymerization. For this reason nylon products fail by fracturing when exposed to small amounts of acidic water. Polyesters are also susceptible to similar polymer degradation reactions. The problem is known as environmental stress cracking.
ATP
Hydrolysis is related to energy metabolism and storage. All living cells require a continual supply of energy for two main purposes: the biosynthesis of micro and macromolecules, and the active transport of ions and molecules across cell membranes. The energy derived from theoxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or ...
of nutrients is not used directly but, by means of a complex and long sequence of reactions, it is channeled into a special energy-storage molecule, adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms ...
(ATP). The ATP molecule contains pyrophosphate linkages (bonds formed when two phosphate units are combined) that release energy when needed. ATP can undergo hydrolysis in two ways: Firstly, the removal of terminal phosphate to form adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate, with the reaction:
: Polysaccharides
oligosaccharide
An oligosaccharide (/ˌɑlɪgoʊˈsækəˌɹaɪd/; from the Greek ὀλίγος ''olígos'', "a few", and σάκχαρ ''sácchar'', "sugar") is a saccharide polymer containing a small number (typically two to ten) of monosaccharides (simple sug ...
s, or polysaccharides, respectively. Enzymes that hydrolyze glycosidic bonds are called "glycoside hydrolase
Glycoside hydrolases (also called glycosidases or glycosyl hydrolases) catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in complex sugars. They are extremely common enzymes with roles in nature including degradation of biomass such as cellulose (cel ...
s" or "glycosidases".
The best-known disaccharide is sucrose (table sugar). Hydrolysis of sucrose yields glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
and fructose. Invertase is a sucrase used industrially for the hydrolysis of sucrose to so-called invert sugar
Inverted sugar syrup, also called invert syrup, invert sugar, simple syrup, sugar syrup, sugar water, bar syrup, syrup USP, or sucrose inversion, is a syrup mixture of the monosaccharides glucose and fructose, that is made by hydrolytic s ...
. Lactase is essential for digestive hydrolysis of lactose in milk; many adult humans do not produce lactase and cannot digest the lactose in milk.
The hydrolysis of polysaccharides to soluble sugars can be recognized as saccharification. Malt made from barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
is used as a source of β-amylase to break down starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human die ...
into the disaccharide maltose, which can be used by yeast to produce beer. Other amylase enzymes may convert starch to glucose or to oligosaccharides. Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wa ...
is first hydrolyzed to cellobiose by cellulase
Cellulase (EC 3.2.1.4; systematic name 4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase) is any of several enzymes produced chiefly by fungi, bacteria, and protozoans that catalyze cellulolysis, the decomposition of cellulose and of some related polysaccha ...
and then cellobiose is further hydrolyzed to glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
by beta-glucosidase. Ruminants
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The ...
such as cows are able to hydrolyze cellulose into cellobiose and then glucose because of symbiotic bacteria that produce cellulases.
Metal aqua ions
Metal ions are Lewis acids, and in aqueous solution they form metal aquo complexes of the general formula . The aqua ions undergo hydrolysis, to a greater or lesser extent. The first hydrolysis step is given generically as :Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory
The Brønsted–Lowry theory (also called proton theory of acids and bases) is an acid–base reaction theory which was proposed independently by Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923. The fundamental concept of this theory ...
. This effect is easily explained by considering the inductive effect of the positively charged metal ion, which weakens the bond of an attached water molecule, making the liberation of a proton relatively easy.
The dissociation constant, pKa, for this reaction is more or less linearly related to the charge-to-size ratio of the metal ion. Ions with low charges, such as are very weak acids with almost imperceptible hydrolysis. Large divalent ions such as , , and have a pKa of 6 or more and would not normally be classed as acids, but small divalent ions such as undergo extensive hydrolysis. Trivalent ions like and are weak acids whose pKa is comparable to that of acetic acid. Solutions of salts such as or in water are noticeably acidic; the hydrolysis can be suppressed by adding an acid such as nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available ni ...
, making the solution more acidic.
Hydrolysis may proceed beyond the first step, often with the formation of polynuclear species via the process of olation In inorganic chemistry, olation is the process by which metal ions form polymeric oxides in aqueous solution. The phenomenon is important for understanding the relationship between metal aquo complexes and metal oxides, which are represented by man ...
. Some "exotic" species such as are well characterized. Hydrolysis tends to proceed as pH rises leading, in many cases, to the precipitation of a hydroxide such as or . These substances, major constituents of bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO ...
, are known as laterite
Laterite is both a soil and a rock type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by ...
s and are formed by leaching from rocks of most of the ions other than aluminium and iron and subsequent hydrolysis of the remaining aluminium and iron.
Mechanism strategies
Acetals, imines, and enamines can be converted back into ketones by treatment with excess water under acid-catalyzed conditions: ; ; .See also
* Acid hydrolysis *Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms ...
* Alkaline hydrolysis (body disposal)
Alkaline hydrolysis (also called biocremation, resomation, flameless cremation, aquamation or water cremation) is a process for the disposal of human and pet remains using lye and heat, and is an alternative to burial or cremation.
Process
The p ...
* Catabolism
* Condensation reaction
* Dehydration reaction
* Hydrolysis constant
* Inhibitor protein
The inhibitor protein (IP) is situated in the mitochondrial matrix and protects the cell against rapid ATP hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used ...
* Polymer degradation
* Proteolysis
* Saponification
* Sol–gel polymerisation
* Solvolysis
* Thermal hydrolysis
References
{{Authority control Chemical reactions Equilibrium chemistry