Hot Cathode on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
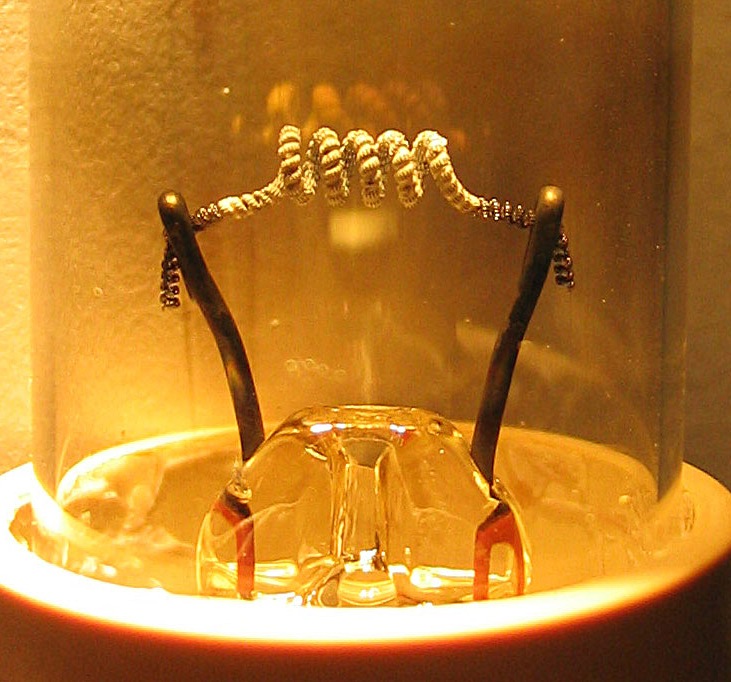 In
In



/ref>
John Harper (2003) ''Tubes 201 - How vacuum tubes really work'', John Harper's home page
* {{Thermionic valves Electrodes Gas discharge lamps Vacuum tubes Accelerator physics
 In
In vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
s and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
electrode which is heated to make it emit electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
s due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element. The heating element is usually an electrical filament
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxidat ...
heated by a separate electric current
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. The movi ...
passing through it. Hot cathodes typically achieve much higher power density than cold cathodes, emitting significantly more electrons from the same surface area. Cold cathodes rely on field electron emission
Field electron emission, also known as field emission (FE) and electron field emission, is emission of electrons induced by an electrostatic field. The most common context is field emission from a solid surface into a vacuum. However, field emissio ...
or secondary electron emission from positive ion bombardment, and do not require heating. There are two types of hot cathode. In a ''directly heated cathode'', the filament is the cathode and emits the electrons. In an ''indirectly heated cathode'', the filament or ''heater'' heats a separate metal cathode electrode which emits the electrons.
From the 1920s to the 1960s, a wide variety of electronic devices used hot-cathode vacuum tubes. Today, hot cathodes are used as the source of electrons in fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet, ult ...
s, vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
s, and the electron guns used in cathode ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms ( oscilloscope), ...
s and laboratory equipment such as electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
s.
Description
Acathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
electrode in a vacuum tube or other vacuum system is a metal surface which emits electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
s into the evacuated space of the tube. Since the negatively charged electrons are attracted to the positive nuclei of the metal atoms, they normally stay inside the metal and require energy to leave it.
This energy is called the ''work function
In solid-state physics, the work function (sometimes spelt workfunction) is the minimum thermodynamic work (i.e., energy) needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point in the vacuum immediately outside the solid surface. Here "immediately ...
'' of the metal. In a hot cathode, the cathode surface is induced to emit electrons by heating it with a filament
The word filament, which is descended from Latin ''filum'' meaning " thread", is used in English for a variety of thread-like structures, including:
Astronomy
* Galaxy filament, the largest known cosmic structures in the universe
* Solar filament ...
, a thin wire of refractory metal like tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
with current flowing through it.Ferris, Clifford "Electron tube fundamentals" in
The cathode is heated to a temperature that causes electrons to be 'boiled off' of its surface into the evacuated space in the tube, a process called '' thermionic emission''.
There are two types of hot cathodes:
;Directly heated cathode: In this type, the filament itself is the cathode and emits the electrons directly. Directly heated cathodes were used in the first vacuum tubes. Today, they are used in fluorescent tube
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet l ...
s and most high-power transmitting vacuum tubes.
;Indirectly heated cathode: In this type, the filament is not the cathode but rather heats a separate cathode consisting of a sheet metal cylinder surrounding the filament, and the cylinder emits electrons. Indirectly heated cathodes are used in most low power vacuum tubes. For example, in most vacuum tubes the cathode is a nickel tube, coated with metal oxides. It is heated by a tungsten filament inside it, and the heat from the filament causes the outside surface of the oxide coating to emit electrons. The filament of an indirectly heated cathode is usually called the ''heater''.
The main reason for using an indirectly heated cathode is to isolate the rest of the vacuum tube from the electric potential across the filament, allowing vacuum tubes to use alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in whic ...
to heat the filament. In a tube in which the filament itself is the cathode, the alternating electric field
An electric field (sometimes E-field) is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field ...
from the filament surface would affect the movement of the electrons and introduce hum into the tube output. It also allows the filaments in all the tubes in an electronic device to be tied together and supplied from the same current source, even though the cathodes they heat may be at different potentials.
To improve electron emission, cathodes are usually treated with chemicals, compounds of metals with a low work function
In solid-state physics, the work function (sometimes spelt workfunction) is the minimum thermodynamic work (i.e., energy) needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point in the vacuum immediately outside the solid surface. Here "immediately ...
. These form a metal layer on the surface which emits more electrons. Treated cathodes require less surface area, lower temperatures and less power to supply the same cathode current. The untreated thoriated tungsten filaments used in early vacuum tubes (called "bright emitters") had to be heated to 2500 °F (1400 °C), white-hot, to produce sufficient thermionic emission for use, while modern coated cathodes (called "dull emitters") produce far more electrons at a given temperature, so they only have to be heated to 800–1100 °F (425–600 °C).
Types
Oxide-coated cathodes
The most common type of indirectly heated cathode is the oxide-coated cathode, in which the nickel cathode surface has a coating of alkaline earth metal oxide to increase emission. One of the earliest materials used for this was barium oxide; it forms a monatomic layer ofbarium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
with an extremely low work function. More modern formulations utilize a mixture of barium oxide, strontium oxide
Strontium oxide or strontia, SrO, is formed when strontium reacts with oxygen. Burning strontium in air results in a mixture of strontium oxide and strontium nitride. It also forms from the decomposition of strontium carbonate SrCO3. It is a stro ...
and calcium oxide
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "'' lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic ...
. Another standard formulation is barium oxide, calcium oxide, and aluminium oxide in a 5:3:2 ratio. Thorium oxide may be used as well. Oxide-coated cathodes operate at about 800-1000 °C, orange-hot. They are used in most small glass vacuum tubes, but are rarely used in high-power tubes because the coating is degraded by positive ions that bombard the cathode, accelerated by the high voltage on the tube.
For manufacturing convenience, the oxide-coated cathodes are usually coated with carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate ...
s, which are then converted to oxides by heating. The activation may be achieved by microwave heating, direct electric current heating, or electron bombardment while the tube is on the exhausting machine, until the production of gases ceases. The purity of cathode materials is crucial for tube lifetime. The Ba content significantly increases on the surface layers of oxide cathodes down to several tens of nanometers in depth, after the cathode activation process. The lifetime of oxide cathodes can be evaluated with a stretched exponential function
The stretched exponential function f_\beta (t) = e^ is obtained by inserting a fractional power law into the exponential function.
In most applications, it is meaningful only for arguments between 0 and +∞. With , the usual exponential function ...
. The survivability of electron emission sources is significantly improved by high doping of high‐speed activator.
Barium oxide reacts with traces of silicon in the underlying metal, forming barium silicate (Ba2SiO4) layer. This layer has high electrical resistance, especially under discontinuous current load, and acts as a resistor in series with the cathode. This is particularly undesirable for tubes used in computer applications, where they can stay without conducting current for extended periods of time.Electron Tube Design, Radio Corporation of America, 1962
Barium also sublimates from the heated cathode, and deposits on nearby structures. For electron tubes, where the grid is subjected to high temperatures and barium contamination would facilitate electron emission from the grid itself, higher proportion of calcium is added to the coating mix (up to 20% of calcium carbonate).

Boride cathodes


Lanthanum hexaboride
Lanthanum hexaboride ( La B6, also called lanthanum boride and LaB) is an inorganic chemical, a boride of lanthanum. It is a refractory ceramic material that has a melting point of 2210 °C, and is insoluble in water and hydrochloric acid. ...
(LaB6) and cerium hexaboride
Cerium hexaboride ( Ce B6, also called cerium boride, CeBix, CEBIX, and (incorrectly) CeB) is an inorganic chemical, a boride of cerium. It is a refractory ceramic material. It has a low work function, one of the highest electron emissivities kno ...
(CeB6) are used as the coating of some high-current cathodes. Hexaborides show low work function, around 2.5 eV. They are also resistant to poisoning. Cerium boride cathodes show lower evaporation rate at 1700 K than lanthanum boride, but it becomes equal at 1850 K and higher. Cerium boride cathodes have one and a half times the lifetime of lanthanum boride, due to its higher resistance to carbon contamination. Boride cathodes are about ten times as "bright" as the tungsten ones and have 10-15 times longer lifetime. They are used e.g. in electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
s, microwave tube
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency rang ...
s, electron lithography
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no kno ...
, electron beam welding, X-Ray tubes, and free electron lasers. However these materials tend to be expensive.
Other hexaborides can be employed as well; examples are calcium hexaboride
Calcium hexaboride (sometimes calcium boride) is a compound of calcium and boron with the chemical formula CaB6. It is an important material due to its high electrical conductivity, hardness, chemical stability, and melting point. It is a black, lu ...
, strontium hexaboride, barium hexaboride
Barium hexaboride is a hard material with a high melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid ph ...
, yttrium hexaboride
Yttrium boride refers to a crystalline material composed of different proportions of yttrium and boron, such as YB2, YB4, YB6, YB12, YB25, YB50 and YB66. They are all gray-colored, hard solids having high melting temperatures. The most common form ...
, gadolinium hexaboride, samarium hexaboride, and thorium hexaboride.
Thoriated filaments
A common type of directly heated cathode, used in most high power transmitting tubes, is thethoriated tungsten
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as a ...
filament, discovered in 1914 and made practical by Irving Langmuir
Irving Langmuir (; January 31, 1881 – August 16, 1957) was an American chemist, physicist, and engineer. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1932 for his work in surface chemistry.
Langmuir's most famous publication is the 1919 ar ...
in 1923. A small amount of thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
is added to the tungsten of the filament. The filament is heated white-hot, at about 2400 °C, and thorium atoms migrate to the surface of the filament and form the emissive layer. Heating the filament in a hydrocarbon atmosphere carburizes the surface and stabilizes the emissive layer. Thoriated filaments can have very long lifetimes and are resistant to the ion bombardment that occurs at high voltages, because fresh thorium continually diffuses to the surface, renewing the layer. They are used in nearly all high-power vacuum tubes for radio transmitters, and in some tubes for hi-fi amplifiers. Their lifetimes tend to be longer than those of oxide cathodes.
Thorium alternatives
Due to concerns about thorium radioactivity and toxicity, efforts have been made to find alternatives. One of them is zirconiated tungsten, where zirconium dioxide is used instead of thorium dioxide. Other replacement materials are lanthanum(III) oxide,yttrium(III) oxide
Yttrium oxide, also known as yttria, is Y2 O3. It is an air-stable, white solid substance.
The thermal conductivity of yttrium oxide is 27 W/(m·K).
Uses Phosphors
Yttria is widely used to make Eu:YVO4 and Eu:Y2O3 phosphors that give the red ...
, cerium(IV) oxide, and their mixtures.Electron emission materials and components: United States Patent 5911919/ref>
Other materials
In addition to the listed oxides and borides, other materials can be used as well. Some examples arecarbide
In chemistry, a carbide usually describes a compound composed of carbon and a metal. In metallurgy, carbiding or carburizing is the process for producing carbide coatings on a metal piece.
Interstitial / Metallic carbides
The carbides of t ...
s and borides of transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...
s, e.g. zirconium carbide
Zirconium carbide ( Zr C) is an extremely hard refractory ceramic material, commercially used in tool bits for cutting tools. It is usually processed by sintering.
Properties
It has the appearance of a gray metallic powder with cubic crystal ...
, hafnium carbide
Hafnium carbide ( Hf C) is a chemical compound of hafnium and carbon. Previously the material was estimated to have a melting point of about 3,900 °C. More recent tests have been able to conclusively prove that the substance has an even hig ...
, tantalum carbide
Tantalum carbides (TaC) form a family of binary chemical compounds of tantalum and carbon with the empirical formula TaC''x'', where ''x'' usually varies between 0.4 and 1. They are extremely hard, brittle, refractory ceramic materials with metal ...
, hafnium diboride, and their mixtures. Metals from groups
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic ide ...
IIIB (scandium
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic d-block element. Historically, it has been classified as a rare-earth element, together with yttrium and the Lanthanides. It was discovered in ...
, yttrium, and some lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–71, from lanthanum through lutetium. These elements, along with the chemically similar elements scandium and yt ...
s, often gadolinium and samarium
Samarium is a chemical element with symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samar ...
) and IVB (hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri M ...
, zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name ''zirconium'' is taken from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian '' zargun'' (zircon; ''zar-gun'' ...
, titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion i ...
) are usually chosen.
In addition to tungsten, other refractory metals and alloys can be used, e.g. tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as ''tantalium'', it is named after Tantalus, a villain in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that ...
, molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ...
and rhenium and their alloys.
A barrier layer A diffusion barrier is a thin layer (usually micrometres thick) of metal usually placed between two other metals. It is done to act as a barrier to protect either one of the metals from corrupting the other..
Adhesion of a plated metal layer to it ...
of other material can be placed between the base metal and the emission layer, to inhibit chemical reaction between these. The material has to be resistant to high temperatures, have high melting point and very low vapor pressure, and be electrically conductive. Materials used can be e.g. tantalum diboride, titanium diboride, zirconium diboride, niobium diboride, tantalum carbide
Tantalum carbides (TaC) form a family of binary chemical compounds of tantalum and carbon with the empirical formula TaC''x'', where ''x'' usually varies between 0.4 and 1. They are extremely hard, brittle, refractory ceramic materials with metal ...
, zirconium carbide
Zirconium carbide ( Zr C) is an extremely hard refractory ceramic material, commercially used in tool bits for cutting tools. It is usually processed by sintering.
Properties
It has the appearance of a gray metallic powder with cubic crystal ...
, tantalum nitride
Tantalum nitride (TaN) is a chemical compound, a nitride of tantalum. There are multiple phases of compounds, stoichimetrically from Ta2N to Ta3N5, including TaN.
As a thin film TaN find use as a diffusion barrier and insulating layer between c ...
, and zirconium nitride
Zirconium nitride () is an inorganic compound used in a variety of ways due to its properties.
Properties
ZrN grown by physical vapor deposition (PVD) is a light gold color similar to elemental gold. ZrN has a room-temperature electrical resist ...
.
Cathode heater
A ''cathode heater'' is a heated wire filament used to heat thecathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
in a vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
or cathode ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms ( oscilloscope), ...
. The cathode element has to achieve the required temperature in order for these tubes to function properly. This is why older electronics often need some time to "warm up" after being powered on; this phenomenon can still be observed in the cathode ray tubes of some modern televisions and computer monitor
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.
The ...
s. The cathode heats to a temperature that causes electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
s to be 'boiled out' of its surface into the evacuated space in the tube, a process called thermionic emission. The temperature required for modern oxide-coated cathodes is around .
The cathode is usually in the form of a long narrow sheet metal cylinder at the center of the tube. The heater consists of a fine wire or ribbon, made of a high resistance metal alloy like nichrome
Nichrome (also known as NiCr, nickel-chromium or chromium-nickel) is a family of alloys of nickel, chromium, and often iron (and possibly other elements) commonly used as resistance wire, heating elements in devices like toasters, electrical kett ...
, similar to the heating element in a toaster but finer. It runs through the center of the cathode, often being coiled on tiny insulating supports or bent into hairpin-like shapes to give enough surface area to produce the required heat. Typical heaters have a ceramic coating on the wire. When it's bent sharply at the ends of the cathode sleeve, the wire is exposed.
The ends of the wire are electrically connected to two of the several pins protruding from the end of the tube. When current passes through the wire it becomes red hot, and the radiated heat strikes the inside surface of the cathode, heating it. The red or orange glow seen coming from operating vacuum tubes is produced by the heater.
There is not much room in the cathode, and the cathode is often built with the heater wire touching it. The inside of the cathode is insulated by a coating of alumina (aluminum oxide). This is not a very good insulator at high temperatures, therefore tubes have a rating for maximum voltage between cathode and heater, usually only 200 to 300 V.
Heaters require a low voltage, high current source of power. Miniature receiving tubes for line-operated equipment use on the order of 0.5 to 4 watts for heater power; high power tubes such as rectifiers or output tubes use on the order of 10 to 20 watts, and broadcast transmitter tubes might need a kilowatt or more to heat the cathode.
The voltage required is usually 5 or 6 volts AC. This is supplied by a separate 'heater winding' on the device's power supply transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
that also supplies the higher voltages required by the tubes' plates and other electrodes. One approach used in transformerless line-operated radio and television receivers such as the All American Five is to connect all the tube heaters in series across the supply line. Since all the heaters are rated at the same current, they would share voltage according to their heater ratings.
Battery-operated radio sets used direct-current power for the heaters (commonly known as filaments), and tubes intended for battery
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
sets were designed to use as little filament power as necessary, to economize on battery replacement. The final models of tube-equipped radio receivers were built with subminiature tubes using less than 50 mA for the heaters, but these types were developed at about the same time as transistors which replaced them.
Where leakage or stray fields from the heater circuit could potentially be coupled to the cathode, direct current is sometimes used for heater power. This eliminates a source of noise in sensitive audio or instrumentation circuits.
The majority of power required to operate low power tube equipment is consumed by the heaters. Transistors have no such power requirement, which is often a great advantage.
Failure modes
The emissive layers on coated cathodes degrade slowly with time, and much more quickly when the cathode is overloaded with too high current. The result is weakened emission and diminished power of the tubes, or in CRTs diminished brightness. The activated electrodes can be destroyed by contact withoxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
or other chemicals (e.g. aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
, or silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is a ...
s), either present as residual gases, entering the tube via leaks, or released by outgassing or migration from the construction elements. This results in diminished emissivity. This process is known as ''cathode poisoning''. High-reliability tubes had to be developed for the early Whirlwind computer, with filaments free of traces of silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
.
Slow degradation of the emissive layer and sudden burning and interruption of the filament are two main failure mode
Failure causes are defects in design, process, quality, or part application, which are the underlying cause of a failure or which initiate a process which leads to failure. Where failure depends on the user of the product or process, then human e ...
s of vacuum tubes.
Transmitting tube hot cathode characteristicsL.W. Turner,(ed), ''Electronics Engineer's Reference Book'', 4th ed. Newnes-Butterworth, London 1976 pg. 7-36
See also
*Hot filament ionization gauge
The hot-filament ionization gauge, sometimes called a hot-filament gauge or hot-cathode gauge, is the most widely used low-pressure (vacuum) measuring device for the region from 10−3 to 10−10 Torr. It is a triode, with the filament being th ...
References
External links
John Harper (2003) ''Tubes 201 - How vacuum tubes really work'', John Harper's home page
* {{Thermionic valves Electrodes Gas discharge lamps Vacuum tubes Accelerator physics