History of Chicago on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]



File:Chicago in 1812 Andreas.png, Retrospective map showing how Chicago may have appeared in 1812 (right is north, published in 1884)
File:Chicago in 1820.jpg, Chicago in 1820
 The first settler in Chicago was
The first settler in Chicago was
Chicago: 1929; Kessinger Publishing, LLC, reprint 2009, accessed 24 Aug 2010




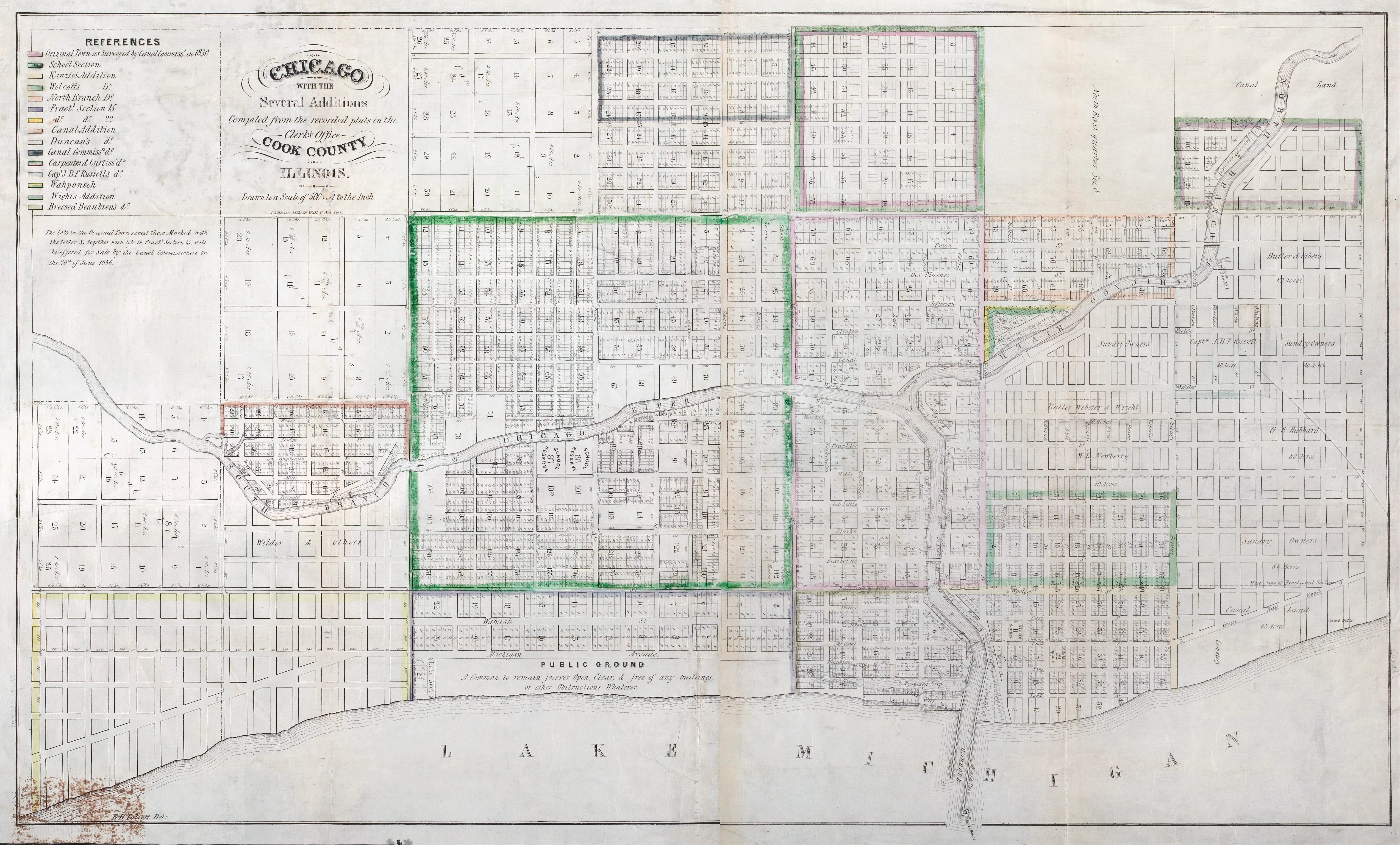
 In 1829, the Illinois legislature appointed commissioners to locate a canal and lay out the surrounding town. The commissioners employed James Thompson to survey and
In 1829, the Illinois legislature appointed commissioners to locate a canal and lay out the surrounding town. The commissioners employed James Thompson to survey and

 In 1848, the opening of the Illinois and Michigan Canal allowed shipping from the
In 1848, the opening of the Illinois and Michigan Canal allowed shipping from the
 Although originally settled by Yankees in the 1830s, the city in the 1840s had many
Although originally settled by Yankees in the 1830s, the city in the 1840s had many
 Most of the city burned in the 1871 Great Chicago Fire. The damage from the fire was immense since 300 people died, 18,000 buildings were destroyed, and nearly 100,000 of the city's 300,000 residents were left homeless. Several key factors exacerbated the spread of the fire. Most of Chicago's buildings and sidewalks were then constructed of wood. Also, the lack of attention to proper waste disposal practices, which was sometimes deliberate to favor certain industries, left an abundance of flammable pollutants in the Chicago River along which the fire spread from the south to the north. The fire led to the incorporation of stringent fire-safety codes, which included a strong preference for masonry construction.
The Danish immigrant Jens Jensen arrived in 1886 and soon became a successful and celebrated landscape designer. Jensen's work was characterized by a democratic approach to landscaping, which was informed by his interest in social justice and conservation, and a rejection of antidemocratic formalism. Among Jensen's creations were four Chicago city parks, most famously Columbus Park. His work also included garden design for some of the region's most influential millionaires.
The
Most of the city burned in the 1871 Great Chicago Fire. The damage from the fire was immense since 300 people died, 18,000 buildings were destroyed, and nearly 100,000 of the city's 300,000 residents were left homeless. Several key factors exacerbated the spread of the fire. Most of Chicago's buildings and sidewalks were then constructed of wood. Also, the lack of attention to proper waste disposal practices, which was sometimes deliberate to favor certain industries, left an abundance of flammable pollutants in the Chicago River along which the fire spread from the south to the north. The fire led to the incorporation of stringent fire-safety codes, which included a strong preference for masonry construction.
The Danish immigrant Jens Jensen arrived in 1886 and soon became a successful and celebrated landscape designer. Jensen's work was characterized by a democratic approach to landscaping, which was informed by his interest in social justice and conservation, and a rejection of antidemocratic formalism. Among Jensen's creations were four Chicago city parks, most famously Columbus Park. His work also included garden design for some of the region's most influential millionaires.
The
 Chicago became the center of the nation's advertising industry after New York City. Albert Lasker, known as the "father of modern advertising," made Chicago his base from 1898 to 1942. As head of the Lord and Thomas agency, Lasker devised a copywriting technique that appealed directly to the psychology of the consumer. Women, who seldom smoked cigarettes, were told that if they smoked Lucky Strikes, they could stay slender. Lasker's use of radio, particularly with his campaigns for Palmolive soap, Pepsodent toothpaste, Kotex products, and Lucky Strike cigarettes, not only revolutionized the advertising industry but also significantly changed popular culture.
Chicago became the center of the nation's advertising industry after New York City. Albert Lasker, known as the "father of modern advertising," made Chicago his base from 1898 to 1942. As head of the Lord and Thomas agency, Lasker devised a copywriting technique that appealed directly to the psychology of the consumer. Women, who seldom smoked cigarettes, were told that if they smoked Lucky Strikes, they could stay slender. Lasker's use of radio, particularly with his campaigns for Palmolive soap, Pepsodent toothpaste, Kotex products, and Lucky Strike cigarettes, not only revolutionized the advertising industry but also significantly changed popular culture.
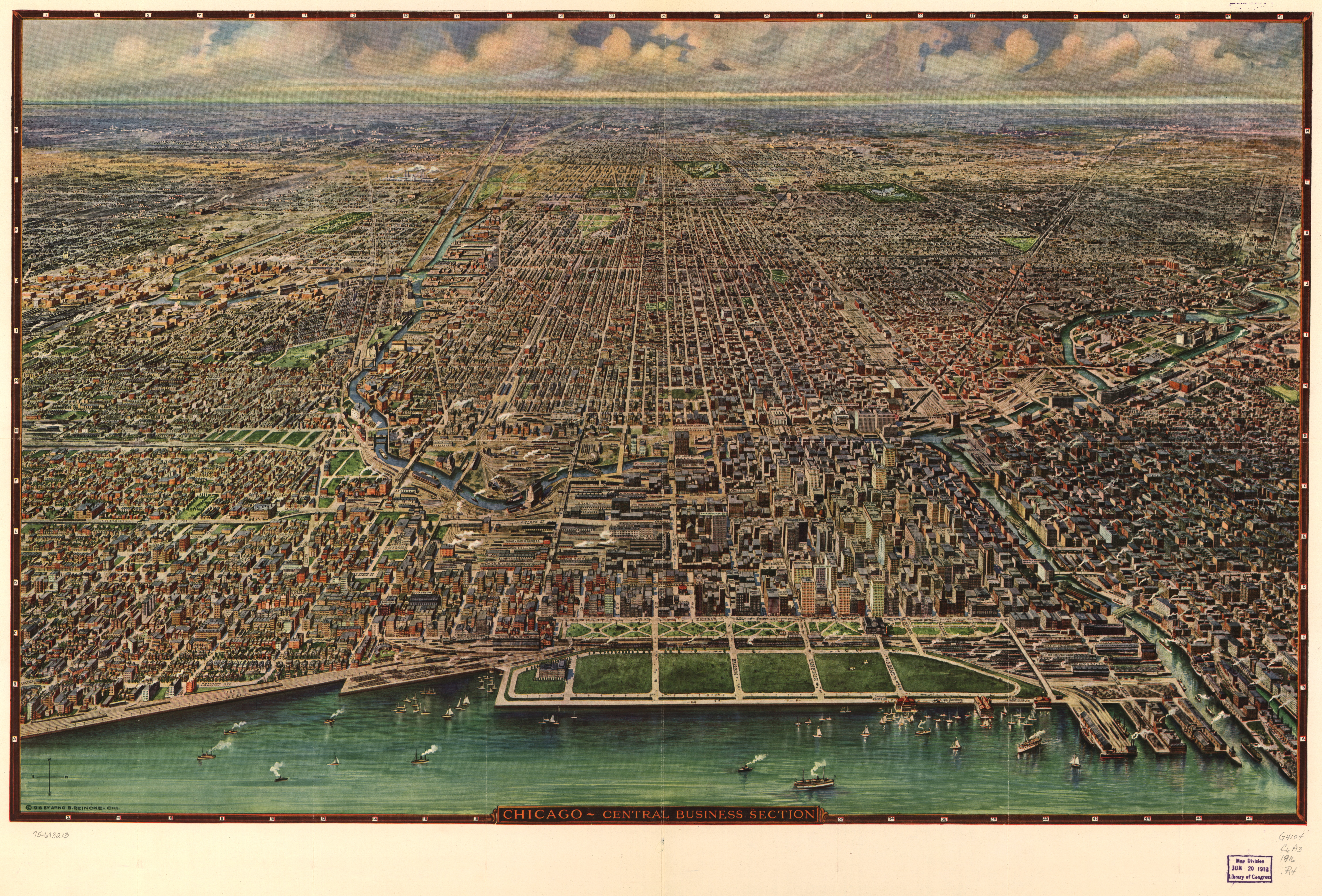
 Chicago's manufacturing and retail sectors, fostered by the expansion of railroads throughout the upper Midwest and East, grew rapidly and came to dominate the
Chicago's manufacturing and retail sectors, fostered by the expansion of railroads throughout the upper Midwest and East, grew rapidly and came to dominate the


 During the election of April 23, 1875, the voters of Chicago chose to operate under the Illinois
During the election of April 23, 1875, the voters of Chicago chose to operate under the Illinois
Image:StateStreetc1907.jpg, State Street c. 1907
File:International Ballooning Contest Aero Park Chicago July 4th 1908.jpg, International Ballooning Contest, Aero Park, Chicago, July 4, 1908
File:1938 Chicago Map.jpg, Bird's eye view of Chicago in 1938
File:Crowd of bathers on the Lake Michigan beach, ca. 1925 - NARA - 535893.jpg, Oak Street Beach, 1925
 After 1900 Chicago was a heavily unionized city, apart from the factories (which were non-union until the 1930s). The
After 1900 Chicago was a heavily unionized city, apart from the factories (which were non-union until the 1930s). The
File:HOUSE IN THE INNER CITY OF CHICAGO, ILLINOIS. THE INNER CITY TODAY IS AN ABSOLUTE CONTRADICTION TO THE MAIN STREAM... - NARA - 555949.jpg, House in Chicago's inner city, 1974. Photo by Danny Lyon.
Image:2004-09-07 1800x2400 chicago picasso.jpg,
''The Encyclopedia of Chicago''
(2004), with thorough coverage by scholars in 1120 pages of text, maps and photos. * Abu-Lughod, Janet L. ''New York, Chicago, Los Angeles: America's Global Cities'' (U of Minnesota Press, 1999), Compares the three cities in terms of geography, economics and race from 1800 to 1990 * Allswang, John. ''A House For All Peoples: Ethnic Politics In Chicago, 1890-1936''. (1973). 213 pp. * Andreas, A. T. ''History of Chicago. From the earliest period to the present time'' (1884
online v 1online v 2online v. 3
* Ascoli, Peter Max. ''Julius Rosenwald: The Man Who Built Sears, Roebuck and Advanced the Cause of Black Education in the American South'' (2006
excerpt and text search
* Avrich, Paul. ''The Haymarket Tragedy'' (1984
excerpt and text search
* Bales, Richard F. ''The Great Chicago Fire and the Myth of Mrs. O'Leary's Cow''. (2002). 338 pp. * Barnard, Harry. ''"Eagle Forgotten": The Life of John Peter Altgeld'' (1938) * Barrett, James. ''Work and Community in the Jungle: Chicago's Packinghouse Workers, 1894—1922'' (1987)
excerpt and text search
* Biles, Roger. ''Big City Boss in Depression and War: Mayor Edward J. Kelly of Chicago''. (1984). 219 pp. * Biles, Roger. ''Richard J. Daley: Politics, Race, and the Governing of Chicago''. (1995). 292 pp. * Bolotin, Norman and Laing, Christine. ''The World's Columbian Exposition: The Chicago World's Fair of 1893''. (1992). 166 pp. * Bonner, Thomas Neville. ''Medicine in Chicago, 1850-1950: A Chapter in the Social and Scientific Development of a City''. (1957, 2nd ed. 1991). 335 pp. * Brosnan, Kathleen A., William C. Barnett, and Ann Durkin Keating. ''City of Lake and Prairie: Chicago's Environmental History'' (U of Pittsburgh Press, 2020) * Bukowski, Douglas. ''Big Bill Thompson, Chicago, and the Politics of Image''. (1998). 273 pp
excerpt and text search
* Candeloro, Dominic. ''Italians in Chicago''. (1999). 128 pp. * Clavel, Pierre, and Robert Giloth, "Planning for Manufacturing: Chicago After 1983," ''Journal of Planning History'', 14#1 (Feb. 2015) pp: 19–37. * Cohen, Adam, and Elizabeth Taylor. ''American Pharaoh: Mayor Richard J. Daley - His Battle for Chicago and the Nation''. (2001). 614pp
excerpt and text search
* Cohen, Lizabeth. ''Making a New Deal: Industrial Workers in Chicago, 1919-1939''. (1990). 526 pp.
excerpt and text search
* Condit, Carl W. ''Chicago, 1910-29: Building, Planning, and Urban Technology''. (1973). 354 pp.; ''Chicago, 1930-70: Building, Planning, and Urban Technology''. (1974). 351 pp. * Connolly, Mary Beth Fraser. ''Women of Faith: The Chicago Sisters of Mercy and the Evolution of a Religious Community'' (Oxford University Press, 2014) * Cronon, William. ''Nature's Metropolis: Chicago and the Great West''. (1991). 530 pp.
excerpt and text search
* Cutler, Irving. ''The Jews of Chicago: From Shtetl to Suburb''. (1996). 316 pp. * Drake, St. Clair, and Horace R. Cayton. ''Black Metropolis: A Study of Negro Life in a Northern City'' (4th ed. 1945), classic sociological study * Duis, Perry R. ''The Saloon: Public Drinking in Chicago and Boston, 1880-1920'' (1983). * Emmet, Boris, and John E. Jeuck. ''Catalogues and Counters: A History of Sears, Roebuck & Company'' (1965), the standard corporate history * Fernandez, Lilia. ''Brown in the Windy City: Mexicans and Puerto Ricans in Postwar Chicago'' (2014) * Ferris, William G. ''The Grain Traders: The Story of the Chicago Board of Trade''. (1988). 221 pp. * Fine, Lisa M. ''The Souls of the Skyscraper: Female Clerical Workers in Chicago, 1870-1930''. (1990). 249 pp. * Fisher, Colin. ''Urban Green: Nature, Recreation, and the Working Class in Industrial Chicago'' (2015) * Green, Paul M. and Holli, Melvin G., eds. ''The Mayors: The Chicago Political Tradition'' (1995
online edition
I; essays by scholars covering important mayors before 1980 * Green, Paul M., and Melvin G. Holli. ''Chicago, World War II'' (2003
excerpt and text search
short and heavily illustrated * Grimshaw, William J. ''Bitter Fruit: Black Politics and the Chicago Machine, 1931-1991''. (1992). 248 pp. * Grossman, James R. ''Land of Hope: Chicago, Black Southerners, and the Great Migration''. (1989). 384 pp. * Gustaitis, Joseph. ''Chicago's Greatest Year, 1893: The White City and the Birth of a Modern Metropolis'' (2013) * Gustaitis, Joseph. ''Chicago Transformed: World War I and the Windy City'' (2016). * Hogan, David John. ''Class and Reform: School and Society in Chicago, 1880-1930''. (1985). 328 pp. * Holli, Melvin G. and Jones, Peter d'A., eds. Ethnic Chicago: A Multicultural Portrait''. (4th ed. 1995). 648 pp. essays by scholars on each major ethnic group * Jentz, John B. and Richard Schneirov. ''Chicago in the Age of Capital'' (2012) covers politics 1860 to 188
excerpt and text search
330pp; also —full text. * Kantowicz, Edward R. ''Corporation Sole: Cardinal Mundelein and Chicago Catholicism''. (1983). 295 pp. * Karamanski, Theodore J. ''Rally 'Round the Flag: Chicago and the Civil War''. (1993). 292 pp. * Keating, Ann Durkin. "In the Shadow of Chicago: Postwar Illinois Historiography." ''Journal of the Illinois State Historical Society'' 111.1-2 (2018): 120-136. . * Keating, Ann Durkin. "Chicagoland: More than the Sum of its Parts." ''Journal of Urban History'' 2004 30(2): 213-230. * Keating, Ann Durkin. ''Building Chicago: Suburban Developers and the Creation of Divided Metropolis'' (2002) * Keil, Hartmut and Jentz, John B., eds. ''German Workers in Industrial Chicago, 1850-1910: A Comparative Perspective''. (1983). 252 pp. * Kleppner, Paul. ''Chicago Divided: The Making of a Black Mayor''. (1985). 313 pp. * Lemann, Nicholas. ''The Promised Land: The Great Black Migration and How It Changed America''. (1991). 401 pp. * Longstreet, Stephen. ''Chicago: An Intimate Portrait of People, Pleasures, and Power, 1860–1919''. (1973). 547 pp. popular * Mayer, Harold M., and Richard C. Wade. ''Chicago: Growth of a Metropolis'' (1969) 510pp * McCaffrey, Lawrence J.; Skerrett, Ellen; Funchion, Michael F.; and Fanning, Charles. ''The Irish in Chicago''. (1987). 171 pp. * McDonald, Forrest. ''Insull: The Rise and Fall of a Billionaire Utility Tycoon'' (2004) * Miller, Donald L. ''City of the Century: The Epic of Chicago and the Making of America'' (1997), popular epic
excerpt and text search
* Miller, Ross. ''American Apocalypse: The Great Fire and the Myth of Chicago''. 1990. 287 pp. * Miller, Ross. ''The Great Chicago Fire'' (2000); 1st ed was ''American Apocalypse: The Great Chicago Fire and the Myth of Chicago'' 287 pp. * Nelli, Humbert S. ''The Italians in Chicago: A Study in Ethnic Mobility, 1880–1930''. (1970). 300 pp. * Pacyga, Dominic A. ''Polish Immigrants and Industrial Chicago: Workers on the South Side, 1880–1920''. (1991). 322 pp
excerpt and text search
* Pacyga, Dominic A. ''Chicago: A Biography'' (2011), 472pp; detailed history by a scholar, based on secondary sources
excerpt and text search
* Parot, Joseph John. ''Polish Catholics in Chicago, 1850-1920: A Religious History''. (1982) 298 pp. * Peterson, Paul E. ''The Politics of School Reform, 1870–1940''. (1985). 241 pp. * Pierce, Bessie Louise. ''A History of Chicago'' (3 vol., Volume I: ''The Beginning of a City 1673–1848'' (1937
excerpt and text search vol 1
Volume II: ''From Town to City 1848–1871'' (1940); Volume III: ''The Rise of a Modern City, 1871–1893'' (1957
excerpt and text search vol 3
; the major scholarly history * Pierce, Bessue Louise, ed. ''As Others See Chicago: Impressions of Visitors, 1673-1933''. (1937, reprinted 2004). 548 p
excerpt and text search
primary sources * Rivlin, Gary (1992). ''Fire on the Prairie: Chicago's Harold Washington and the Politics of Race''. 426 pp. * Sawyers, June Skinner. ''Chicago Portraits'' (2nd ed. Northwestern University Press, 2012), 250 short biographies * Schneirov, Richard; Stromquist, Shelton; and Salvatore, Nick, eds. ''The Pullman Strike and the Crisis of the 1890s: Essays on Labor and Politics''. (1999). 258 pp
excerpt and text search
* Shanabruch, Charles. ''Chicago's Catholics: The Evolution of an American Identity''. (1981). 296 pp. * Smith, Carl S. ''Chicago and the American Literary Imagination, 1880-1920''. (1984). 232 pp. * Smith, Richard Norton. ''The Colonel: The Life and Legend of Robert R. McCormick, 1880-1955''. (1997). 597 pp. publisher of ''Chicago Tribune'' * Spear, Allan. ''Black Chicago: The Making of a Negro Ghetto, 1890–1920'' (1967), * Spinney, Robert G. ''City of Big Shoulders: A History of Chicago'' (2000), popular epic
excerpt and text search
* Tuttle, William M., Jr. ''Race Riot: Chicago in the Red Summer of 1919''. (1970). 305 pp. * WPA. ''Illinois: A Descriptive and Historical Guide'' (1939) * Young, David M. ''Chicago Transit: An Illustrated History'' (1998). 213 pp.
In the Vicinity of Maxwell and Halsted Streets, 1890–1930
History of Chicago from its founding to the World's Fair at PBS.org
The Northwest Chicago Historical Society's official website
Chicago History
and other overlooked elements at
Chicago Foreign Language Press Survey English translations of 120,000 pages of news articles from the foreign language press from 1855 to 1938.
*
''Digital Research Library of Illinois History''
William Joseph Showalter, "Chicago Today and Tomorrow" '' National Geographic,'' January, 1919, pages 1-42 well illustrated
* * {{Authority control Articles containing video clips

Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
has played a central role in American economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with th ...
, cultural and political history
Political history is the narrative and survey of political events, ideas, movements, organs of government, voters, parties and leaders. It is closely related to other fields of history, including diplomatic history, constitutional history, social ...
. Since the 1850s Chicago has been one of the dominant metropolises in the Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
, and has been the largest city in the Midwest since the 1880 census
The United States census of 1880 conducted by the Census Bureau during June 1880 was the tenth United States census.Pottawatomie
The Potawatomi , also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American people of the western Great Lakes region, upper Mississippi River and Great Plains. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a ...
Native Americans. Jean Baptiste Point du Sable
Jean Baptiste Point du Sable (also spelled ''Point de Sable'', ''Point au Sable'', ''Point Sable'', ''Pointe DuSable'', ''Pointe du Sable''; before 1750 – 28 August 1818) is regarded as the first permanent non-Indigenous settler of what would ...
was the first permanent non-indigenous settler in the area, having a house at the mouth of the Chicago River
The Chicago River is a system of rivers and canals with a combined length of that runs through the city of Chicago, including its center (the Chicago Loop). Though not especially long, the river is notable because it is one of the reasons fo ...
in the late 18th century. There were small settlements and a U.S. Army fort, but the soldiers and settlers were all driven off in 1812. The modern city was incorporated in 1837 by Northern businessmen and grew rapidly from real estate speculation and the realization that it had a commanding position in the emerging inland transportation network, based on lake traffic and railroads, controlling access from the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
into the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest Drainage system (geomorphology), drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson B ...
basin.
Despite a fire in 1871 that destroyed the Central Business District
A central business district (CBD) is the commercial and business centre of a city. It contains commercial space and offices, and in larger cities will often be described as a financial district. Geographically, it often coincides with the "city ...
, the city grew exponentially, becoming the nation's rail center and the dominant Midwestern center for manufacturing, commerce, finance, higher education, religion, broadcasting, sports, jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a m ...
, and high culture. The city was a magnet for European immigrants—at first Germans, Irish and Scandinavians, then from the 1890s to 1914, Jews, Czechs, Poles and Italians. They were all absorbed in the city's powerful ward-based political machines. Many joined militant labor union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits (s ...
s, and Chicago became notorious for its violent strikes, but respected for its high wages.
Large numbers of African Americans migrated from the South starting in the World War I era as part of the Great Migration. Mexicans started arriving after 1910, and Puerto Ricans after 1945. The Cook County
Cook County is the most populous county in the U.S. state of Illinois and the second-most-populous county in the United States, after Los Angeles County, California. More than 40% of all residents of Illinois live within Cook County. As of 20 ...
suburbs grew rapidly after 1945, but the Democratic party machine kept both the city and suburbs under control, especially under mayor Richard J. Daley, who was chairman of the Cook County Democratic Party. Deindustrialization after 1970 closed the stockyards and most of the steel mills and factories, but the city retained its role as a financial and transportation hub. Increasingly it emphasized its service roles in medicine, higher education, and tourism. The city formed the political base for national leaders of the Democratic Party, especially Stephen A. Douglas in the 1850s, Adlai Stevenson in the 1950s, and Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Obama was the first Af ...
in recent years.
Pre-1830
Early native settlements
At its first appearance in records by explorers, the Chicago area was inhabited by a number ofAlgonquian peoples
The Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American native language groups. Historically, the peoples were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and into the interior along the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. T ...
, including the Mascouten and Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at ...
. The name "Chicago" is derived from a French rendering of the Native American word ''shikaakwa'', known to botanists as ''Allium tricoccum
''Allium tricoccum'' (commonly known as ramp, ramps, ramson, wild leek, wood leek, or wild garlic) is a North American species of wild onion or garlic widespread across eastern Canada and the eastern United States. Many of the common English n ...
'', from the Miami-Illinois language
Miami-Illinois (endonym: , ) also known as Irenwa, or Irenwe is an indigenous Algonquian language spoken in the United States, primarily in Illinois, Missouri, Indiana, western Ohio and adjacent areas along the Mississippi River by the Miami ...
. The first known reference to the site of the current city of Chicago as "Checagou" was by Robert de LaSalle
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honou ...
around 1679 in a memoir. Henri Joutel, in his journal of 1688, noted that the wild garlic, called "chicagoua", grew abundantly in the area. According to his diary of late September 1687:
The tribe was part of the Miami Confederacy, which included the Illini and Kickapoo. In 1671, Potawatomi guides first took the French trader Nicolas Perrot to the Miami villages near the site of present-day Chicago. Pierre François Xavier de Charlevoix
Pierre François Xavier de Charlevoix, S.J. ( la, Petrus Franciscus-Xaverius de Charlevoix; 24 or 29 October 1682 – 1 February 1761) was a French Jesuit priest, traveller, and historian, often considered the first historian of New France. He ha ...
would write in 1721 that the Miami had a settlement in what is now Chicago around 1670. Chicago's location at a short canoe portage (the Chicago Portage
The Chicago Portage was an ancient portage that connected the Great Lakes waterway system with the Mississippi River system. Connecting these two great water trails meant comparatively easy access from the mouth of the St Lawrence River on the Atl ...
) connecting the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
with the Mississippi River system
The Mississippi River System, also referred to as the Western Rivers, is a mostly riverine network of the United States which includes the Mississippi River and connecting waterways. The Mississippi River is the largest drainage basin in the Unit ...
attracted the attention of many French explorers, notably Louis Jolliet
Louis Jolliet (September 21, 1645after May 1700) was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to explore and ...
and Jacques Marquette
Jacques Marquette S.J. (June 1, 1637 – May 18, 1675), sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded Saint Ign ...
in 1673. ''The Jesuit Relations
''The Jesuit Relations'', also known as ''Relations des Jésuites de la Nouvelle-France'', are chronicles of the Jesuit missions in New France. The works were written annually and printed beginning in 1632 and ending in 1673.
Originally written ...
'' indicate that by this time, the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
tribes of New York had driven the Algonquian tribes entirely out of Lower Michigan and as far as this portage, during the later Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout t ...
.
René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle
René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle (; November 22, 1643 – March 19, 1687), was a 17th-century French explorer and fur trader in North America. He explored the Great Lakes region of the United States and Canada, the Mississippi River, ...
, who traversed the Kankakee and Illinois River
The Illinois River ( mia, Inoka Siipiiwi) is a principal tributary of the Mississippi River and is approximately long. Located in the U.S. state of Illinois, it has a drainage basin of . The Illinois River begins at the confluence of the ...
s south of Chicago in the winter of 1681–82, identified the Des Plaines River
The Des Plaines River () is a river that flows southward for U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed May 13, 2011 through southern Wisconsin and northern Illinois''American H ...
as the western boundary of the Miami. In 1683, La Salle built Fort St. Louis on the Illinois River. Almost two thousand Miami, including Weas and Piankeshaw
The Piankeshaw, Piankashaw or Pianguichia were members of the Miami tribe who lived apart from the rest of the Miami nation, therefore they were known as Peeyankihšiaki ("splitting off" from the others, Sing.: ''Peeyankihšia'' - "Piankeshaw Per ...
s, left the Chicago area to gather on the opposite shore at the Grand Village of the Illinois
The Grand Village of the Illinois, also called Old Kaskaskia Village, is a site significant for being the best documented historic Native American village in the Illinois River valley. It was a large agricultural and trading village of Native A ...
, seeking French protection from the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
. In 1696, French Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
s led by Jean-François Buisson de Saint-Cosme
Jean-François Buisson de Saint-Cosme (1667–1706) was a Canadian missionary, born in Quebec, ordained in 1690, and murdered while on a missionary trip.
Jean-François came from a family with a high level of devotion to the Catholic Church. His ...
built the Mission of the Guardian Angel
The Mission of the Guardian Angel () was a 17th-century Jesuit mission in the vicinity of what is now Chicago, Illinois. It was established in 1696 by Father François Pinet, a French Jesuit priest. The mission was abandoned by 1700; its exact lo ...
to Christianize the local Wea and Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at ...
people. Shortly thereafter, Augustin le Gardeur de Courtemanche visited the settlement on behalf of the French government, seeking peace between the Miami and Iroquois. Miami chief Chichikatalo accompanied de Courtemanche to Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
.
The Algonquian tribes began to retake the lost territory in the ensuing decades, and in 1701, the Iroquois formally abandoned their claim to their "hunting grounds" as far as the portage to England in the Nanfan Treaty
Deed from the Five Nations to the King, of their Beaver Hunting Ground, more commonly known as the Nanfan Treaty, was an agreement made between the representatives of the Iroquois Confederacy with John Nanfan, the acting colonial governor of New ...
, which was finally ratified in 1726. This was largely a political maneuver of little practicality, as the English then had no presence in the region whatsoever, the French and their Algonquian allies being the dominant force in the area. A writer in 1718 noted at the Was had a village in Chicago, but had recently fled due to concerns about approaching Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
s and Pottawatomi
The Potawatomi , also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American people of the western Great Lakes region, upper Mississippi River and Great Plains. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a me ...
s. The Iroquois and Meskwaki
The Meskwaki (sometimes spelled Mesquaki), also known by the European exonyms Fox Indians or the Fox, are a Native American people. They have been closely linked to the Sauk people of the same language family. In the Meskwaki language, th ...
probably drove out all Miami from the Chicago area by the end of the 1720s. The Pottawatomi assumed control of the area, but probably did not have any major settlements in Chicago. French and allied use of the Chicago portage was mostly abandoned during the 1720s because of continual Native American raids during the Fox Wars.
There was also a Michigamea Mitchigamea or Michigamea or Michigamie were a tribe in the Illinois Confederation. Not much is known about them and their origin is uncertain. Originally they were said to be from Lake Michigan, perhaps the Chicago area. Mitchie Precinct, Monroe C ...
chief named Chicago who may have lived in the region. In the 1680s, the Illinois River was called the Chicago River.
First non-native settlements
 The first settler in Chicago was
The first settler in Chicago was Jean Baptiste Point du Sable
Jean Baptiste Point du Sable (also spelled ''Point de Sable'', ''Point au Sable'', ''Point Sable'', ''Pointe DuSable'', ''Pointe du Sable''; before 1750 – 28 August 1818) is regarded as the first permanent non-Indigenous settler of what would ...
, a free black man, who built a farm at the mouth of the Chicago River
The Chicago River is a system of rivers and canals with a combined length of that runs through the city of Chicago, including its center (the Chicago Loop). Though not especially long, the river is notable because it is one of the reasons fo ...
in 1790. He left Chicago in 1800. In 1968, Point du Sable was honored at Pioneer Court
Pioneer Court is a plaza located near the junction of the Chicago River and Upper Michigan Avenue in Chicago's Magnificent Mile. It is believed to be the site of Jean Baptiste Point du Sable's original residence and trading post. In 1965, th ...
as the city's founder and featured as a symbol.
In 1795, following the Northwest Indian War
The Northwest Indian War (1786–1795), also known by other names, was an armed conflict for control of the Northwest Territory fought between the United States and a united group of Native American nations known today as the Northwestern ...
, some Native Americans ceded the area of Chicago to the United States for a military post in the Treaty of Greenville
The Treaty of Greenville, formally titled Treaty with the Wyandots, etc., was a 1795 treaty between the United States and indigenous nations of the Northwest Territory (now Midwestern United States), including the Wyandot and Delaware peoples ...
. The US built Fort Dearborn
Fort Dearborn was a United States fort built in 1803 beside the Chicago River, in what is now Chicago, Illinois. It was constructed by troops under Captain John Whistler and named in honor of Henry Dearborn, then United States Secretary of War ...
in 1803 on the Chicago River. It was destroyed by Indian forces during the War of 1812 in the Battle of Fort Dearborn, and many of the inhabitants were killed or taken prisoner. The fort had been ordered to evacuate. During the evacuation soldiers and civilians were overtaken near what is today Prairie Avenue
Prairie Avenue is a north–south street on the South Side of Chicago, which historically extended from 16th Street in the Near South Side to the city's southern limits and beyond. The street has a rich history from its origins as a major trail ...
. After the end of the war, the Potawatomi ceded the land to the United States in the 1816 Treaty of St. Louis. (Today, this treaty is commemorated in Indian Boundary Park
Indian Boundary Park is a urban park in the West Ridge neighborhood of North Side, Chicago, Illinois.
History
The park opened in 1922.Alice Sinkevitch, et al. ''AIA Guide to Chicago''. American Institute of Architects. 2004. 248. It is named aft ...
.) Fort Dearborn was rebuilt in 1818 and used until 1837.Lloyd Lewis and Henry Justin Smith, ''Chicago: The History of Its Reputation''Chicago: 1929; Kessinger Publishing, LLC, reprint 2009, accessed 24 Aug 2010
Growth of city





 In 1829, the Illinois legislature appointed commissioners to locate a canal and lay out the surrounding town. The commissioners employed James Thompson to survey and
In 1829, the Illinois legislature appointed commissioners to locate a canal and lay out the surrounding town. The commissioners employed James Thompson to survey and plat
In the United States, a plat ( or ) (plan) is a cadastral map, drawn to scale, showing the divisions of a piece of land. United States General Land Office surveyors drafted township plats of Public Lands Surveys to show the distance and bea ...
the town of Chicago, which at the time had a population of less than 100. Historians regard the August 4, 1830 filing of the plat as the official recognition of a location known as Chicago.
Yankee
The term ''Yankee'' and its contracted form ''Yank'' have several interrelated meanings, all referring to people from the United States. Its various senses depend on the context, and may refer to New Englanders, residents of the Northern United S ...
entrepreneurs saw the potential of Chicago as a transportation hub in the 1830s and engaged in land speculation to obtain the choicest lots. On August 12, 1833, the Town of Chicago was incorporated with a population of 350. On July 12, 1834, the ''Illinois'' from Sackets Harbor, New York
Sackets Harbor (earlier spelled Sacketts Harbor) is a village in Jefferson County, New York, United States, on Lake Ontario. The population was 1,450 at the 2010 census. The village was named after land developer and owner Augustus Sackett, who ...
, was the first commercial schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schoo ...
to enter the harbor, a sign of the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
trade that would benefit both Chicago and New York state. Chicago was granted a city charter
A city charter or town charter (generically, municipal charter) is a legal document ('' charter'') establishing a municipality such as a city or town. The concept developed in Europe during the Middle Ages.
Traditionally the granting of a charte ...
by the State of Illinois on March 4, 1837; it was part of the larger Cook County
Cook County is the most populous county in the U.S. state of Illinois and the second-most-populous county in the United States, after Los Angeles County, California. More than 40% of all residents of Illinois live within Cook County. As of 20 ...
. By 1840 the boom town had a population of over 4,000.
After 1830, the rich farmlands of northern Illinois attracted Yankee settlers. Yankee real estate operators created a city overnight in the 1830s. To open the surrounding farmlands to trade, the Cook County
Cook County is the most populous county in the U.S. state of Illinois and the second-most-populous county in the United States, after Los Angeles County, California. More than 40% of all residents of Illinois live within Cook County. As of 20 ...
commissioners built roads south and west. The latter crossed the "dismal Nine-mile Swamp," the Des Plaines River
The Des Plaines River () is a river that flows southward for U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed May 13, 2011 through southern Wisconsin and northern Illinois''American H ...
, and went southwest to Walker's Grove, now the Village of Plainfield. The roads enabled hundreds of wagons per day of farm produce to arrive and so the entrepreneurs built grain elevators and docks to load ships bound for points east through the Great Lakes. Produce was shipped through the Erie Canal and down the Hudson River to New York City; the growth of the Midwest farms expanded New York City as a port.
In 1837, Chicago held its first mayoral election and elected William B. Ogden
William Butler Ogden (June 15, 1805 – August 3, 1877) was an American politician and railroad executive who served as the first Mayor of Chicago. He was referred to as "the Astor of Chicago." He was, at one time, the city's richest citizen. ...
as its inaugural mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well ...
.
Emergence as transportation hub

 In 1848, the opening of the Illinois and Michigan Canal allowed shipping from the
In 1848, the opening of the Illinois and Michigan Canal allowed shipping from the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
through Chicago to the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest Drainage system (geomorphology), drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson B ...
and the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
. The first rail line to Chicago, the Galena & Chicago Union Railroad, was completed the same year. Chicago would go on to become the transportation hub of the United States, with its road, rail, water, and later air connections. Chicago also became home to national retailers offering catalog shopping such as Montgomery Ward
Montgomery Ward is the name of two successive U.S. retail corporations. The original Montgomery Ward & Co. was a world-pioneering mail-order business and later also a leading department store chain that operated between 1872 and 2001. The curr ...
and Sears, Roebuck and Company
Sears, Roebuck and Co. ( ), commonly known as Sears, is an American chain of department stores founded in 1892 by Richard Warren Sears and Alvah Curtis Roebuck and reincorporated in 1906 by Richard Sears and Julius Rosenwald, with what began ...
, which used the transportation lines to ship all over the nation.
By the 1850s, the construction of railroads
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
made Chicago a major hub and over 30 lines entered the city. The main lines from the East ended in Chicago, and those oriented to the West began in Chicago and so by 1860, the city had become the nation's trans-shipment and warehousing center. Factories were created, most famously the harvester factory that was opened in 1847 by Cyrus Hall McCormick
Cyrus Hall McCormick (February 15, 1809 – May 13, 1884) was an American inventor and businessman who founded the McCormick Harvesting Machine Company, which later became part of the International Harvester Company in 1902. Originally from the ...
. It was a processing center for natural resource commodities extracted in the West. The Wisconsin forests supported the millwork and lumber business; the Illinois hinterland provided the wheat. Hundreds of thousands of hogs and cattle were shipped to Chicago for slaughter, preserved in salt, and transported to eastern markets. By 1870, refrigerated
The term refrigeration refers to the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature.International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.phpASHRAE Terminology, ht ...
cars allowed the shipping of fresh meat to cities in the East.
The prairie bog nature of the area provided a fertile ground for disease-carrying insects. In springtime, Chicago was so muddy from the high water that horses could scarcely move. Comical signs proclaiming "Fastest route to China" or "No Bottom Here" were placed to warn people of the mud.
Travelers reported Chicago was the filthiest city in America. The city created a massive sewer system. In the first phase, sewage pipes were laid across the city above ground and used gravity to move the waste. The city was built in a low-lying area subject to flooding. In 1856, the city council decided that the entire city should be elevated four to five feet by using a newly available jacking-up process. In one instance, the five-story Brigg's Hotel, weighing 22,000 tons, was lifted while it continued to operate. Observing that such a thing could never have happened in Europe, the British historian Paul Johnson cites the astounding feat as a dramatic example of American determination and ingenuity based on the conviction that anything material is possible.
Immigration and population in 19th century
 Although originally settled by Yankees in the 1830s, the city in the 1840s had many
Although originally settled by Yankees in the 1830s, the city in the 1840s had many Irish Catholics
Irish Catholics are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland whose members are both Catholic and Irish. They have a large diaspora, which includes over 36 million American citizens and over 14 million British citizens (a quarter of the Briti ...
come as a result of the Great Famine. Later in the century, the railroads, stockyards, and other heavy industry of the late 19th century attracted a variety of skilled workers from Europe, especially Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
, Norwegians
Norwegians ( no, nordmenn) are a North Germanic peoples, North Germanic ethnic group and nation native to Norway, where they form the vast majority of the population. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegians a ...
, and Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
. A small African-American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ensl ...
community formed, led by activist leaders like John Jones and Mary Richardson Jones, who established Chicago as a stop on the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. ...
.
In 1840, Chicago was the 92nd city in the United States by population. Its population grew so rapidly that 20 years later, it was the ninth city. In the pivotal year of 1848, Chicago saw the completion of the Illinois and Michigan Canal, its first steam locomotives, the introduction of steam-powered grain elevators, the arrival of the telegraph, and the founding of the Chicago Board of Trade
The Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT), established on April 3, 1848, is one of the world's oldest futures and options exchanges. On July 12, 2007, the CBOT merged with the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) to form CME Group. CBOT and three other exch ...
. By 1857, Chicago was the largest city in what was then called the Northwest. In 20 years, Chicago grew from 4,000 people to over 90,000. Chicago surpassed St. Louis and Cincinnati as the major city in the West and gained political notice as the home of Stephen Douglas
Stephen Arnold Douglas (April 23, 1813 – June 3, 1861) was an American politician and lawyer from Illinois. A senator, he was one of two nominees of the badly split Democratic Party for president in the 1860 presidential election, which wa ...
, the 1860 presidential nominee of the Northern Democrats. The 1860 Republican National Convention
The 1860 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention that met May 16-18 in Chicago, Illinois. It was held to nominate the Republican Party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1860 election. The conve ...
in Chicago nominated the home-state candidate Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
. The city's government and voluntary societies gave generous support to soldiers during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
.
Many of the newcomers were Irish Catholic and German immigrants. Their neighborhood saloons, a center of male social life, were attacked in the mid-1850s by the local Know-Nothing Party
The Know Nothing party was a nativist political party and movement in the United States in the mid-1850s. The party was officially known as the "Native American Party" prior to 1855 and thereafter, it was simply known as the "American Party". ...
, which drew its strength from evangelical Protestants. The new party was anti-immigration and anti-liquor and called for the purification of politics by reducing the power of the saloonkeepers. In 1855, the Know-Nothings elected Levi Boone mayor, who banned Sunday sales of liquor and beer. His aggressive law enforcement sparked the Lager Beer Riot
The Lager Beer Riot occurred on April 21, 1855 in Chicago, Illinois, and was the first major civil disturbance in the city. Mayor Levi Boone, a Nativist politician, renewed enforcement of an old local ordinance mandating that taverns be clos ...
of April 1855, which erupted outside a courthouse in which eight Germans were being tried for liquor ordinance violations. After 1865, saloons became community centers only for local ethnic men, as reformers saw them as places that incited riotous behavior and moral decay. Salons were also sources of musical entertainment. Francis O'Neill
Francis O'Neill (August 28, 1848 – January 26, 1936) was an Irish-born American police officer and collector of Irish traditional music. His biographer Nicholas Carolan referred to him as "the greatest individual influence on the evolution o ...
, an Irish immigrant who later became police chief, published compendiums of Irish music that were largely collected from other newcomers playing in saloons.
By 1870, Chicago had grown to become the nation's second-largest city and one of the largest cities in the world. Between 1870 and 1900, Chicago grew from a city of 299,000 to nearly 1.7 million and was the fastest-growing city in world history. Chicago's flourishing economy attracted huge numbers of new immigrants from Eastern and Central Europe, especially Jews, Poles, and Italians, along with many smaller groups. Many businesspeople and professionals arrived from the eastern states. Relatively few new arrivals came from Chicago's rural hinterland. The exponential growth put increasing pollution on the environment, as hazards to public health impacted everyone.
Gilded Age

 Most of the city burned in the 1871 Great Chicago Fire. The damage from the fire was immense since 300 people died, 18,000 buildings were destroyed, and nearly 100,000 of the city's 300,000 residents were left homeless. Several key factors exacerbated the spread of the fire. Most of Chicago's buildings and sidewalks were then constructed of wood. Also, the lack of attention to proper waste disposal practices, which was sometimes deliberate to favor certain industries, left an abundance of flammable pollutants in the Chicago River along which the fire spread from the south to the north. The fire led to the incorporation of stringent fire-safety codes, which included a strong preference for masonry construction.
The Danish immigrant Jens Jensen arrived in 1886 and soon became a successful and celebrated landscape designer. Jensen's work was characterized by a democratic approach to landscaping, which was informed by his interest in social justice and conservation, and a rejection of antidemocratic formalism. Among Jensen's creations were four Chicago city parks, most famously Columbus Park. His work also included garden design for some of the region's most influential millionaires.
The
Most of the city burned in the 1871 Great Chicago Fire. The damage from the fire was immense since 300 people died, 18,000 buildings were destroyed, and nearly 100,000 of the city's 300,000 residents were left homeless. Several key factors exacerbated the spread of the fire. Most of Chicago's buildings and sidewalks were then constructed of wood. Also, the lack of attention to proper waste disposal practices, which was sometimes deliberate to favor certain industries, left an abundance of flammable pollutants in the Chicago River along which the fire spread from the south to the north. The fire led to the incorporation of stringent fire-safety codes, which included a strong preference for masonry construction.
The Danish immigrant Jens Jensen arrived in 1886 and soon became a successful and celebrated landscape designer. Jensen's work was characterized by a democratic approach to landscaping, which was informed by his interest in social justice and conservation, and a rejection of antidemocratic formalism. Among Jensen's creations were four Chicago city parks, most famously Columbus Park. His work also included garden design for some of the region's most influential millionaires.
The World's Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition (also known as the Chicago World's Fair) was a world's fair held in Chicago in 1893 to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492. The centerpiece of the Fair, hel ...
of 1893 was constructed on former wetlands
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The p ...
at the present location of Jackson Park along Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The land was reclaimed according to a design by the landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted
Frederick Law Olmsted (April 26, 1822August 28, 1903) was an American landscape architect, journalist, social critic, and public administrator. He is considered to be the father of landscape architecture in the USA. Olmsted was famous for co- ...
. The temporary pavilions, which followed a classical theme, were designed by a committee of the city's architects under the direction of Daniel Burnham
Daniel Hudson Burnham (September 4, 1846 – June 1, 1912) was an American architect and urban designer. A proponent of the '' Beaux-Arts'' movement, he may have been, "the most successful power broker the American architectural profession has ...
. It was called the "White City" for the appearance of its buildings.
The Exposition drew 27.5 million visitors; is considered among the most influential world's fairs in history; and affected art, architecture, and design throughout the nation. The classical architectural style contributed to a revival of '' Beaux Arts'' architecture that borrowed from historical styles, but Chicago was also developing the original skyscraper and organic forms based in new technologies. The fair featured the first and until recently the largest Ferris wheel
A Ferris wheel (also called a Giant Wheel or an observation wheel) is an amusement ride consisting of a rotating upright wheel with multiple passenger-carrying components (commonly referred to as passenger cars, cabins, tubs, gondolas, capsule ...
ever built.
The soft, swampy ground near the lake proved unstable ground for tall masonry buildings. That was an early constraint, but builders developed the innovative use of steel framing for support and invented the skyscraper
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ri ...
in Chicago, which became a leader in modern architecture and set the model nationwide for achieving vertical city densities.
Developers and citizens began immediate reconstruction on the existing Jeffersonian grid. The building boom that followed saved the city's status as the transportation and trade hub of the Midwest. Massive reconstruction using the newest materials and methods catapulted Chicago into its status as a city on par with New York and became the birthplace of modern architecture in the United States.
Rise of industry and commerce
 Chicago became the center of the nation's advertising industry after New York City. Albert Lasker, known as the "father of modern advertising," made Chicago his base from 1898 to 1942. As head of the Lord and Thomas agency, Lasker devised a copywriting technique that appealed directly to the psychology of the consumer. Women, who seldom smoked cigarettes, were told that if they smoked Lucky Strikes, they could stay slender. Lasker's use of radio, particularly with his campaigns for Palmolive soap, Pepsodent toothpaste, Kotex products, and Lucky Strike cigarettes, not only revolutionized the advertising industry but also significantly changed popular culture.
Chicago became the center of the nation's advertising industry after New York City. Albert Lasker, known as the "father of modern advertising," made Chicago his base from 1898 to 1942. As head of the Lord and Thomas agency, Lasker devised a copywriting technique that appealed directly to the psychology of the consumer. Women, who seldom smoked cigarettes, were told that if they smoked Lucky Strikes, they could stay slender. Lasker's use of radio, particularly with his campaigns for Palmolive soap, Pepsodent toothpaste, Kotex products, and Lucky Strike cigarettes, not only revolutionized the advertising industry but also significantly changed popular culture.
Gambling
In Chicago, like other rapidly growing industrial centers with large immigrant working-class neighborhoods, gambling was a major issue. The city's elite upper-class had private clubs and closely-supervised horse racing tracks. The middle-class reformers like Jane Addams focused on the workers, who discovered freedom and independence in gambling that were a world apart from their closely-supervised factory jobs and gambled to validate risk-taking aspect of masculinity, betting heavily on dice, card games, policy, and cock fights. By the 1850s, hundreds of saloons had offered gambling opportunities, including off-track betting on the horses. The historian Mark Holler argues that organized crime provided upward mobility to ambitious ethnics. The high-income, high-visibility vice lords, and racketeers built their careers and profits in ghetto neighborhoods and often branched into local politics to protect their domains. For example, in 1868 to 1888, Michael C. McDonald, "The Gambler King of Clark Street," kept numerous Democratic machine politicians in his city on expense account to protect his gambling empire and to keep the goo-goo reformers at bay. In large cities, illegal businesses like gambling and prostitution were typically contained in the geographically-segregated red light districts. The businessowners made regularly-scheduled payments to police and politicians, which they treated as licensing expenses. The informal rates became standardized. For example, in Chicago, they ranged from $20 a month for a cheap brothel to $1000 a month for luxurious operations in Chicago. Reform elements never accepted the segregated vice districts and wanted them all destroyed, but in large cities, the political machine was powerful enough to keep the reformers at bay. Finally, around 1900 to 1910, the reformers grew politically strong enough to shut down the system of vice segregation, and the survivors went underground.20th century

 Chicago's manufacturing and retail sectors, fostered by the expansion of railroads throughout the upper Midwest and East, grew rapidly and came to dominate the
Chicago's manufacturing and retail sectors, fostered by the expansion of railroads throughout the upper Midwest and East, grew rapidly and came to dominate the Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
and greatly influence the nation's economy. The Chicago Union Stock Yards dominated the packing trade. Chicago became the world's largest rail hub, and one of its busiest ports by shipping traffic on the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
. Commodity resources, such as lumber, iron and coal, were brought to Chicago and Ohio for processing, with products shipped both East and West to support new growth.
Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
—the primary source of fresh water for the city—became polluted from the rapidly growing industries in and around Chicago; a new way of procuring clean water was needed. In 1885 the civil engineer Lyman Edgar Cooley proposed the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal
The Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal, historically known as the Chicago Drainage Canal, is a canal system that connects the Chicago River to the Des Plaines River. It reverses the direction of the Main Stem and the South Branch of the Chicago R ...
. He envisioned a deep waterway that would dilute and divert the city's sewage by funneling water from Lake Michigan into a canal, which would drain into the Mississippi River via the Illinois River. Beyond presenting a solution for Chicago's sewage problem, Cooley's proposal appealed to the economic need to link the Midwest with America's central waterways to compete with East Coast shipping and railroad industries.
Strong regional support for the project led the Illinois legislature to circumvent the federal government and complete the canal with state funding. The opening in January 1900 met with controversy and a lawsuit against Chicago's appropriation of water from Lake Michigan. By the 1920s the lawsuit was divided between the states of the Mississippi River Valley, who supported the development of deep waterways linking the Great Lakes with the Mississippi, and the Great Lakes states, which feared sinking water levels might harm shipping in the lakes. In 1929 the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in support of Chicago's use of the canal to promote commerce, but ordered the city to discontinue its use for sewage disposal.
New construction boomed in the 1920s, with notable landmarks such as the Merchandise Mart
The Merchandise Mart (or the Merch Mart, or the Mart) is a commercial building located in downtown Chicago, Illinois. When it was opened in 1930, it was the largest building in the world, with of floor space. The Art Deco structure is loca ...
and art deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unit ...
Chicago Board of Trade Building
The Chicago Board of Trade Building is a 44-story, Art Deco skyscraper located in the Chicago Loop, standing at the foot of the LaSalle Street canyon. Built in 1930 for the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT), it has served as the primary trading ...
completed in 1930. The Wall Street Crash of 1929
The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Great Crash, was a major American stock market crash that occurred in the autumn of 1929. It started in September and ended late in October, when share prices on the New York Stock Exchange coll ...
, the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
and diversion of resources into World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
led to the suspension for years of new construction.
The Century of Progress
A Century of Progress International Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States, from 1933 to 1934. The fair, registered under the Bureau International des Expositi ...
International Exposition was the name of the World's Fair held on the Near South Side lakefront from 1933 to 1934 to celebrate the city's centennial. The theme of the fair was technological innovation over the century since Chicago's founding. More than 40 million people visited the fair, which symbolized for many hope for Chicago and the nation, then in the midst of the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
.
The demographics of the city were changing in the early 20th century as black southern families migrated out of the south, but while cities like Chicago empathized with the condition of impoverished white children, black children were mostly excluded from the private and religious institutions that provided homes for such children. Those that did take in black dependent children were overcrowded and underfunded because of institutional racism
Institutional racism, also known as systemic racism, is a form of racism that is embedded in the laws and regulations of a society or an organization. It manifests as discrimination in areas such as criminal justice, employment, housing, health ...
. Between 1899 and 1945 many of the city's black children found themselves in the juvenile court system. The 1899 Juvenile Court Act, supported by Progressive reformers, created a class of dependants for orphans and other children lacking "proper parental care or guardianship" but the court's designations of "delinquency" and "dependency" were racialized so black children were far more likely to be labeled as delinquents.
Politics in the late 19th and early 20th centuries

 During the election of April 23, 1875, the voters of Chicago chose to operate under the Illinois
During the election of April 23, 1875, the voters of Chicago chose to operate under the Illinois Cities and Villages Act of 1872
The Cities and Villages Act of 1872 was an act of the Illinois General Assembly governing the operation of incorporated municipalities. The act was an immediate source of political controversy. The legacy of the Act is that Illinois municipal e ...
. Chicago still operates under this act, in lieu of a charter. The Cities and Villages Act has been revised several times since, and may be found in Chapter 65 of the Illinois Compiled Statutes.
Late-19th-century big city newspapers such as the ''Chicago Daily News
The ''Chicago Daily News'' was an afternoon daily newspaper in the midwestern United States, published between 1875 and 1978 in Chicago, Illinois.
History
The ''Daily News'' was founded by Melville E. Stone, Percy Meggy, and William Doughert ...
'' - founded in 1875 by Melville Stone - ushered in an era of news reporting that was, unlike earlier periods, in tune with the particulars of community life in specific cities. Vigorous competition between older and newer-style city papers soon broke out, centered on civic activism
Activism (or Advocacy) consists of efforts to promote, impede, direct or intervene in social, political, economic or environmental reform with the desire to make changes in society toward a perceived greater good. Forms of activism range fro ...
and sensationalist reporting of urban political issues and the numerous problems associated with rapid urban growth. Competition was especially fierce between the ''Chicago Times
The ''Chicago Times'' was a newspaper in Chicago from 1854 to 1895, when it merged with the ''Chicago Herald'', to become the ''Chicago Times-Herald''. The ''Times-Herald'' effectively disappeared in 1901 when it merged with the ''Chicago Record ...
'' (Democratic), the ''Chicago Tribune
The ''Chicago Tribune'' is a daily newspaper based in Chicago, Illinois, United States, owned by Tribune Publishing. Founded in 1847, and formerly self-styled as the "World's Greatest Newspaper" (a slogan for which WGN radio and television ar ...
'' (Republican), and the ''Daily News'' (independent), with the latter becoming the city's most popular paper by the 1880s. The city's boasting lobbyists and politicians earned Chicago the nickname " Windy City" in the New York press. The city adopted the nickname as its own.
Polarized attitudes of labor and business in Chicago prompted a strike by workers' lobbying for an eight-hour work day
The eight-hour day movement (also known as the 40-hour week movement or the short-time movement) was a social movement to regulate the length of a working day, preventing excesses and abuses.
An eight-hour work day has its origins in the 1 ...
, later named the Haymarket affair
The Haymarket affair, also known as the Haymarket massacre, the Haymarket riot, the Haymarket Square riot, or the Haymarket Incident, was the aftermath of a bombing that took place at a labor demonstration on May 4, 1886, at Haymarket Square i ...
. A peaceful demonstration on May 4, 1886, at Haymarket near the west side was interrupted by a bomb thrown at police; seven police officers were killed. Widespread violence broke out. A group of anarchists
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not necessari ...
were tried for inciting the riot and convicted. Several were hanged and others were pardoned. The episode was a watershed moment in the labor movement
The labour movement or labor movement consists of two main wings: the trade union movement (British English) or labor union movement (American English) on the one hand, and the political labour movement on the other.
* The trade union movement ...
, and its history was commemorated in the annual May Day
May Day is a European festival of ancient origins marking the beginning of summer, usually celebrated on 1 May, around halfway between the spring equinox and summer solstice. Festivities may also be held the night before, known as May Eve. Tr ...
celebrations.
By 1900, Progressive Era
The Progressive Era (late 1890s – late 1910s) was a period of widespread social activism and political reform across the United States focused on defeating corruption, monopoly, waste and inefficiency. The main themes ended during Am ...
political and legal reformers initiated far-ranging changes in the American criminal justice system, with Chicago taking the lead.
The city became notorious worldwide for its rate of murders in the early 20th century, yet the courts failed to convict the killers. More than three-fourths of cases were not closed. Even when the police made arrests in cases where killers' identities were known, jurors typically exonerated or acquitted them. A blend of gender-, race-, and class-based notions of justice trumped the rule of law, producing low homicide conviction rates during a period of soaring violence.
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, rates of domestic murder tripled in Chicago. Domestic homicide was often a manifestation of strains in gender relations induced by urban and industrial change. At the core of such family murders were male attempts to preserve masculine authority. Yet, there were nuances in the motives for the murder of family members, and study of the patterns of domestic homicide among different ethnic groups reveals basic cultural differences. German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
male immigrants tended to murder over declining status and the failure to achieve economic prosperity. In addition, they were likely to kill all members of the family, and then commit suicide in the ultimate attempt at maintaining control. Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
men killed family members to save a gender-based ideal of respectability that entailed patriarchal control over women and family reputation. African American men, like the Germans, often murdered in response to economic conditions but not over desperation about the future. Like the Italians, the killers tended to be young, but family honor was not usually at stake. Instead, black men murdered to regain control of wives and lovers who resisted their patriarchal "rights".
Progressive reformers in the business community created the Chicago Crime Commission The Chicago Crime Commission is an independent, non-partisan civic watchdog organization of business leaders dedicated to educating the public about the dangers of organized criminal activity, especially organized crime, street gangs and the tool ...
(CCC) in 1919 after an investigation into a robbery at a factory showed the city's criminal justice system was deficient. The CCC initially served as a watchdog of the justice system. After its suggestion that the city's justice system begin collecting criminal records was rejected, the CCC assumed a more active role in fighting crime. The commission's role expanded further after Frank J. Loesch became president in 1928. Loesch recognized the need to eliminate the glamor that Chicago's media typically attributed to criminals. Determined to expose the violence of the crime world, Loesch drafted a list of "public enemies"; among them was Al Capone
Alphonse Gabriel Capone (; January 17, 1899 – January 25, 1947), sometimes known by the nickname "Scarface", was an American gangster and businessman who attained notoriety during the Prohibition era as the co-founder and boss of the ...
, whom he made a scapegoat for widespread social problems.
After the passage of Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholi ...
, the 1920s brought international notoriety to Chicago. Bootleggers and smugglers bringing in liquor from Canada formed powerful gangs. They competed with each other for lucrative profits, and to evade the police, to bring liquor to speakeasies
A speakeasy, also called a blind pig or blind tiger, is an illicit establishment that sells alcoholic beverages, or a retro style bar that replicates aspects of historical speakeasies.
Speakeasy bars came into prominence in the United States ...
and private clients. The most notorious was Al Capone.
Immigration and migration in the 20th century
From 1890 to 1914, migrations swelled, attracting to the city of mostly unskilled Catholic and Jewish immigrants from Southern and Eastern Europe, including Italians, Greeks, Czechs, Poles, Lithuanians, Ukrainians, Hungarians, and Slovaks. World War I cut off immigration from Europe, which brought hundreds of thousands of southern blacks and whites into Northern cities to fill in the labor shortages. TheImmigration Act of 1924
The Immigration Act of 1924, or Johnson–Reed Act, including the Asian Exclusion Act and National Origins Act (), was a United States federal law that prevented immigration from Asia and set quotas on the number of immigrants from the Eastern ...
restricted populations from southern and eastern Europe, apart from refugees after World War II. The heavy annual turnover of ethnic populations ended, and the groups stabilized, each favoring specific neighborhoods.
While whites from rural areas arrived and generally settled in the suburban parts of the city, large numbers of blacks from the South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
arrived as well. The near South Side of the city became the first Black residential area, as it had the oldest, less expensive housing. Although restricted by segregation and competing ethnic groups such as the Irish, gradually continued black migration caused this community to expand, as well as the black neighborhoods on the near West Side. These were ''de facto'' segregated areas (few blacks were tolerated in ethnic white neighborhoods); the Irish and ethnic groups who had been longer in the city began to move to outer areas and the suburbs. After World War II, the city built public housing for working-class families to upgrade residential quality. The high-rise design of such public housing proved a problem when industrial jobs left the city and poor families became concentrated in the facilities. After 1950, public housing high rises anchored poor black neighborhoods south and west of the Loop.
"Old stock" Americans who relocated to Chicago after 1900 preferred the outlying areas and suburbs, with their commutes eased by train lines, making Oak Park and Evanston enclaves of the upper middle class. In the 1910s, high-rise luxury apartments were constructed along the lakefront north of the Loop, continuing into the 21st century. They attracted wealthy residents but few families with children, as wealthier families moved to suburbs for the schools. There were problems in the public school system; mostly Catholic students attended schools in the large parochial system, which was of middling quality. There were a few private schools. The Latin School
The Latin school was the grammar school of 14th- to 19th-century Europe, though the latter term was much more common in England. Emphasis was placed, as the name indicates, on learning to use Latin. The education given at Latin schools gave gre ...
, Francis Parker and later The Bateman School The Bateman School was a well known private school located in Chicago's "Gold Coast." From 1950 onward, the school was housed in the historic Patterson-McCormick Mansion. The school closed doors in the mid-1970s by financial pressures.
The Bateman ...
, all centrally located served those who could afford to pay.
The northern and western suburbs developed some of the best public schools in the nation, which were strongly supported by their wealthier residents. The suburban trend accelerated after 1945, with the construction of highways and train lines that made commuting easier. Middle-class Chicagoans headed to the outlying areas of the city, and then into the Cook County and Dupage County suburbs. As ethnic Jews and Irish rose in economic class, they left the city and headed north. Well-educated migrants from around the country moved to the far suburbs.
Chicago's '' Polonia'' sustained diverse political cultures in the early twentieth century, each with its own newspaper. In 1920 the community had a choice of five daily papers – from the Socialist '' Dziennik Ludowy'' (People's Daily; 1907–1925) to the Polish Roman Catholic Union's ''Dziennik Zjednoczenia'' (Union Daily; 1921–1939). The decision to subscribe to a particular paper reaffirmed a particular ideology or institutional network based on ethnicity and class, which lent itself to different alliances and different strategies.
In 1926, the city hosted the 28th International Eucharistic Congress, a major event for the Catholic community of Chicago.
As the First World War cut off immigration, tens of thousands of African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
came north in the Great Migration out of the rural South. With new populations competing for limited housing and jobs, especially on the South Side, social tensions rose in the city. Postwar years were more difficult. Black veterans looked for more respect for having served their nation, and some whites resented it.
In 1919, the Chicago race riot
The Chicago race riot of 1919 was a violent racial conflict between white Americans and black Americans that began on the South Side of Chicago, Illinois, on July 27 and ended on August 3, 1919. During the riot, 38 people died (23 black and ...
erupted, in what became known as "Red Summer", when other major cities also suffered mass racial violence based in competition for jobs and housing as the country tried to absorb veterans in the postwar years. During the riot, thirty-eight people died (23 black and 15 white) and over five hundred were injured. Much of the violence against blacks in Chicago was led by members of ethnic Irish athletic clubs, who had much political power in the city and defended their "territory" against African Americans. As was typical in these occurrences, more blacks than whites died in the violence.
Concentrating the family resources to achieve home ownership was a common strategy in the ethnic European neighborhoods. It meant sacrificing current consumption, and pulling children out of school as soon as they could earn a wage. By 1900, working-class ethnic immigrants owned homes at higher rates than native-born people. After borrowing from friends and building associations, immigrants kept boarders, grew market gardens, and opened home-based commercial laundries, eroding home-work distinctions, while sending out women and children to work to repay loans. They sought not middle-class upward mobility but the security of home ownership. Many social workers wanted them to pursue upward job mobility (which required more education), but realtors asserted that houses were better than a bank for a poor man. With hindsight, and considering uninsured banks' precariousness, this appears to have been true. Chicago's workers made immense sacrifices for home ownership, contributing to Chicago's sprawling suburban geography and to modern myths about the American dream. The Jewish community, by contrast, rented apartments and maximized education and upward mobility for the next generation.
Beginning in the 1940s, waves of Hispanic immigrants began to arrive. The largest numbers were from Mexico and Puerto Rico, as well as Cuba during Fidel Castro
Fidel Alejandro Castro Ruz (; ; 13 August 1926 – 25 November 2016) was a Cuban revolutionary and politician who was the leader of Cuba from 1959 to 2008, serving as the prime minister of Cuba from 1959 to 1976 and president from 1976 to 20 ...
's rise. During the 1980s, Hispanic immigrants were more likely to be from Central and South America.
After 1965 and the change in US immigration laws, numerous Asian immigrants came; the largest proportion were well-educated Indians and Chinese, who generally settled directly in the suburbs. By the 1970s gentrification began in the city, in some cases with people renovating housing in old inner city
The term ''inner city'' has been used, especially in the United States, as a euphemism for majority-minority lower-income residential districts that often refer to rundown neighborhoods, in a downtown or city centre area. Sociologists some ...
neighborhoods, and attracting singles and gay people.
1930s
Labor unions
 After 1900 Chicago was a heavily unionized city, apart from the factories (which were non-union until the 1930s). The
After 1900 Chicago was a heavily unionized city, apart from the factories (which were non-union until the 1930s). The Industrial Workers of the World
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), members of which are commonly termed "Wobblies", is an international labor union that was founded in Chicago in 1905. The origin of the nickname "Wobblies" is uncertain. IWW ideology combines general ...
was founded in Chicago in June 1905 at a convention of 200 socialists, anarchists, and radical trade unionists from all over the United States. The Railroad brotherhoods were strong, as were the crafts unions affiliated with the American Federation of Labor
The American Federation of Labor (A.F. of L.) was a national federation of labor unions in the United States that continues today as the AFL-CIO. It was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1886 by an alliance of craft unions eager to provide mutua ...
. The AFL unions operated through the Chicago Federation of Labor to minimize jurisdictional conflicts, which caused many strikes as two unions battled to control a work site.
The unionized teamsters in Chicago enjoyed an unusually strong bargaining position when they contended with employers around the city, or supported another union in a specific strike. Their wagons could easily be positioned to disrupt streetcars and block traffic. In addition, their families and neighborhood supporters often surrounded and attacked the wagons of nonunion teamsters who were strikebreaking. When the teamsters used their clout to engage in sympathy strikes, employers decided to coordinate their antiunion efforts, claiming that the teamsters held too much power over commerce in their control of the streets. The teamsters' strike in 1905 represented a clash both over labor issues and the public nature of the streets. To the employers, the streets were arteries for commerce, while to the teamsters, they remained public spaces integral to their neighborhoods.
World War II
On December 2, 1942, the world's first controllednuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a transformatio ...
was conducted at the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the b ...
as part of the top secret Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
.
During World War II, the steel mills in the city of Chicago alone accounted for 20% of all steel production in the United States and 10% of global production. The city produced more steel than the United Kingdom during the war, and surpassed Nazi Germany's output in 1943 (after barely missing in 1942).
The city's diversified industrial base made it second only to Detroit in the value—$24 billion—of war goods produced. Over 1,400 companies produced everything from field rations to parachutes to torpedoes, while new aircraft plants employed 100,000 in the construction of engines, aluminum sheeting, bombsights, and other components. The Great Migration, which had been on pause due to the Depression, resumed at an even faster pace as the 1910 - 1930 period, as hundreds of thousands of black Americans arrived in the city to work in the steel mills, railroads, and shipping yards.
Postwar
Returning World War II veterans and immigrants from Europe (in particulardisplaced persons
Forced displacement (also forced migration) is an involuntary or coerced movement of a person or people away from their home or home region. The UNHCR defines 'forced displacement' as follows: displaced "as a result of persecution, conflict, g ...
from Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
) created a postwar economic boom and led to the development of huge housing tracts on Chicago's Northwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each s ...
and Southwest Sides. The city was extensively photographed during the postwar years by street photographers
A street is a public thoroughfare in a built environment. It is a public parcel of land adjoining buildings in an urban context, on which people may freely assemble, interact, and move about. A street can be as simple as a level patch of dirt ...
such as Richard Nickel and Vivian Maier
Vivian Dorothy Maier (February 1, 1926 – April 21, 2009) was an American street photographer whose work was discovered and recognized after her death. She worked for about 40 years as a nanny, mostly in Chicago's North Shore, while pursuin ...
.
In the 1950s, the postwar desire for new and improved housing, aided by new highways and commuter train lines, caused many middle and higher income Americans to begin to move from the inner-city of Chicago to the suburbs
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area, which may include commercial and mixed-use, that is primarily a residential area. A suburb can exist either as part of a larger city/urban area or as a separa ...
. Changes in industry after 1950, with restructuring of the stockyards and steel industries, led to massive job losses in the city for working-class people. The city population shrank by nearly 700,000. The City Council devised "Plan 21" to improve neighborhoods and focused on creating "Suburbs within the city" near downtown and the lakefront. It built public housing to try to improve housing standards in the city. As a result, many poor were uprooted from newly created enclaves of Black, Latino, and poor people in neighborhoods such as Near North, Wicker Park, Lakeview, Uptown, Cabrini–Green, West Town and Lincoln Park. The passage of civil rights laws in the 1960s also affected Chicago and other northern cities. In the 1960s and the 1970s, many middle- and upper-class Americans continued to move from the city for better housing and schools in the suburbs.
Office building resumed in the 1960s. When completed in 1974, the Sears Tower, now known as the Willis Tower
The Willis Tower (originally the Sears Tower) is a 108- story, skyscraper in the Loop community area of Chicago in Illinois, United States. Designed by architect Bruce Graham and engineer Fazlur Rahman Khan of Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM ...
, was at 1451 feet the world's tallest building. It was designed by the famous Chicago firm of Skidmore, Owings & Merrill
Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM) is an American architectural, urban planning and engineering firm. It was founded in 1936 by Louis Skidmore and Nathaniel A. Owings, Nathaniel Owings in Chicago, Illinois. In 1939, they were joined by engineer Jo ...
, which designed many of the city's other famous buildings.
Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
sculpture in Chicago, Illinois. The sculptor refused the $100,000 fee and donated it to the people of Chicago.
Politics in the 20th and 21st centuries
In the early 20th century, theChicago Traction Wars
The Chicago Traction Wars was a political conflict which took place in Chicago primarily from the mid-1890s through the early 1910s. It concerned the franchise and ownership of streetcar lines. At the time it was one of the dominant political iss ...
were a dominant controversy in Chicago politics.
Mayor Richard J. Daley served 1955–1976, dominating the city's machine politics by his control of the Cook County Democratic Central Committee, which selected party nominees, who were usually elected in the Democratic stronghold. Daley took credit for building four major expressways focused on the Loop, and city-owned O'Hare Airport (which became the world's busiest airport, displacing Midway Airport's prior claims). Several neighborhoods near downtown and the lakefront were gentrified and transformed into "suburbs within the city".
He held office during the unrest of the 1960s, some of which was provoked by the police department's discriminatory practices. In the Lincoln Park, Lakeview, Wicker Park and Humboldt Park communities, the Young Lords
The Young Lords, also known as the Young Lords Organization (YLO) or Young Lords Party (YLP), was a Chicago-based street gang that became a civil and human rights organization. The group aims to fight for neighborhood empowerment and self-det ...
under the leadership of Jose Cha Cha Jimenez
José Cha Cha Jiménez (born August 8, 1948) is a political activist and the founder of the Young Lords Organization, a Chicago-based street gang that became a civil and human rights organization. Started in September 23, 1968, it was most acti ...
marched and held sit ins to protest the displacement of Latinos
Hispanic and Latino Americans ( es, Estadounidenses hispanos y latinos; pt, Estadunidenses hispânicos e latinos) are Americans of Spaniards, Spanish and/or Latin Americans, Latin American ancestry. More broadly, these demographics include a ...
and the poor. After the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr., an African-American clergyman and civil rights leader, was fatally shot at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee, on April 4, 1968, at 6:01 p.m. CST. He was rushed to St. Joseph's Hospital, where he died at ...
in 1968, major riots of despair resulted in the burning down of sections of the black neighborhoods of the South and West sides. Protests against the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
at the 1968 Democratic National Convention
The 1968 Democratic National Convention was held August 26–29 at the International Amphitheatre in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Earlier that year incumbent President Lyndon B. Johnson had announced he would not seek reelection, thus maki ...
, held in Chicago, resulted in street violence, with televised broadcasts of the Chicago police's beating of unarmed protesters.
In 1979, Jane Byrne
Jane Margaret Byrne (née Burke; May 24, 1933November 14, 2014) was an American politician who was the first woman to be elected mayor of a major city in the United States. She served as the 50th Mayor of Chicago from April 16, 1979, until April ...
, the city's first woman mayor, was elected, winning the Democratic primary due to a citywide outrage about the ineffective snow removal across the city. In 1983, Harold Washington
Harold Lee Washington (April 15, 1922 – November 25, 1987) was an American lawyer and politician who was the 51st Mayor of Chicago. Washington became the first African American to be elected as the city's mayor in April 1983. He served as may ...
became the first black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
mayor of Chicago. Richard M. Daley
Richard Michael Daley (born April 24, 1942) is an American politician who served as the 54th mayor of Chicago, Illinois, from 1989 to 2011. Daley was elected mayor in 1989 and was reelected five times until declining to run for a seventh term ...
, son of Richard J. Daley, became mayor in 1989, and was repeatedly reelected until he declined to seek re-election in 2011. He sparked debate by demolishing many of the city's vast public housing
Public housing is a form of housing tenure in which the property is usually owned by a government authority, either central or local. Although the common goal of public housing is to provide affordable housing, the details, terminology, de ...
projects, which had deteriorated and were holding too many poor and dysfunctional families. Concepts for new affordable and public housing have changed to include many new features to make them more viable: smaller scale, environmental designs for public safety, mixed-rate housing, etc. New projects during Daley's administration have been designed to be environmentally sound, more accessible and better for their occupants. In 2011, Rahm Emanuel
Rahm Israel Emanuel (; born November 29, 1959) is an American politician and diplomat who is the current United States Ambassador to Japan. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served two terms as the 55th Mayor of Chicago from 2011 ...
was elected mayor of Chicago.
Since the 1990s, Chicago has seen a turnaround with many revitalized inner city neighborhoods. The city's diversity has grown with new immigrants, with larger percentages of ethnic groups such as Asians, Mexicans and Puerto Ricans. In the 1990s, Chicago gained 113,000 new inhabitants. Since the 1920s, the lakefront has been lined with high-rise apartment buildings for middle classes who work in the city. Chicago's 1996 Democratic National Convention sparked protests, such as the one whereby Civil Rights Movement historian Randy Kryn and 10 others were arrested by the Federal Protective Service.
Chicago earned the title of "City of the Year" in 2008 from '' GQ'' for contributions in architecture and literature, its world of politics, and the downtown's starring role in the Batman
Batman is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by DC Comics. The character was created by artist Bob Kane and writer Bill Finger, and debuted in the 27th issue of the comic book ''Detective Comics'' on March 30, 1939. I ...
movie ''The Dark Knight
''The Dark Knight'' is a 2008 superhero film directed by Christopher Nolan from a screenplay he co-wrote with his brother Jonathan Nolan, Jonathan. Based on the DC Comics superhero, Batman, it is the sequel to ''Batman Begins'' (2005) and t ...
''. The city was rated by Moody's as having the most balanced economy in the United States due to its high level of diversification.
Flag
Four historical events are commemorated by the four red stars on Chicago's flag: The United States'Fort Dearborn
Fort Dearborn was a United States fort built in 1803 beside the Chicago River, in what is now Chicago, Illinois. It was constructed by troops under Captain John Whistler and named in honor of Henry Dearborn, then United States Secretary of War ...
, established at the mouth of the Chicago River
The Chicago River is a system of rivers and canals with a combined length of that runs through the city of Chicago, including its center (the Chicago Loop). Though not especially long, the river is notable because it is one of the reasons fo ...
in 1803; the Great Chicago Fire
The Great Chicago Fire was a conflagration that burned in the American city of Chicago during October 8–10, 1871. The fire killed approximately 300 people, destroyed roughly of the city including over 17,000 structures, and left more than 1 ...
of 1871, which destroyed much of the city; the World Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition (also known as the Chicago World's Fair) was a world's fair held in Chicago in 1893 to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492. The centerpiece of the Fair, hel ...
of 1893, by which Chicago celebrated its recovery from the fire; and the Century of Progress
A Century of Progress International Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States, from 1933 to 1934. The fair, registered under the Bureau International des Expositi ...
World's Fair of 1933–1934, which celebrated the city's centennial. The flag's two blue stripes symbolize the north and south branches of the Chicago River, which flows through the city's downtown. The three white stripes represent the North, West and South sides of the city, Lake Michigan being the east side.
Major disasters
The most famous and serious disaster was theGreat Chicago Fire
The Great Chicago Fire was a conflagration that burned in the American city of Chicago during October 8–10, 1871. The fire killed approximately 300 people, destroyed roughly of the city including over 17,000 structures, and left more than 1 ...
of 1871.
On December 30, 1903, the "absolutely fireproof", five-week-old Iroquois Theater was engulfed by fire. The fire lasted less than thirty minutes; 602 people died as a result of being burned, asphyxiated, or trampled.
The S.S. ''Eastland'' was a cruise ship based in Chicago and used for tours. On 24 July 1915—a calm, sunny day—the ship was taking on passengers when it rolled over while tied to a dock in the Chicago River. A total of 844 passengers and crew were killed. An investigation found that the ''Eastland'' had become too heavy with rescue gear that had been ordered by Congress in the wake of the ''Titanic'' disaster.
On December 1, 1958, the Our Lady of the Angels School Fire occurred in the Humboldt Park area. The fire killed 92 students and three nuns; in response, fire safety improvements were made to public and private schools across the United States.
April 13, 1992, billions of dollars in damage was caused by the Chicago Flood, when a hole was accidentally drilled into the long-abandoned (and mostly forgotten) Chicago Tunnel system, which was still connected to the basements of numerous buildings in the Loop. It flooded the central business district with 250 million US gallons (950,000 m3) of water from the Chicago River
The Chicago River is a system of rivers and canals with a combined length of that runs through the city of Chicago, including its center (the Chicago Loop). Though not especially long, the river is notable because it is one of the reasons fo ...
.
A major environmental disaster occurred in July 1995, when a week of record high heat and humidity caused 739 heat-related deaths, mostly among isolated elderly poor and others without air conditioning.Christopher R. Browning et al. "Neighborhood Social Processes, Physical Conditions, and Disaster-related Mortality: the Case of the 1995 Chicago Heat Wave", ''American Sociological Review'' 2006 71(4): 661–678. .
See also
* American urban history * Bibliography of Chicago history * Chicago in the 1930s * Ethnic groups in Chicago; the larger groups have articles such as Poles in Chicago and History of African Americans in Chicago * Political history of Chicago *Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Chicago
The Archdiocese of Chicago ( la, Archidiœcesis Chicagiensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical jurisdiction or archdiocese of the Catholic Church located in Northeastern Illinois, in the United States. It was established as a diocese in 1843 a ...
* Timeline of Chicago history
Citations
Further reading
For many topics the easiest way to start is with Janice L. Reiff, Ann Durkin Keating and James R. Grossman, eds''The Encyclopedia of Chicago''
(2004), with thorough coverage by scholars in 1120 pages of text, maps and photos. * Abu-Lughod, Janet L. ''New York, Chicago, Los Angeles: America's Global Cities'' (U of Minnesota Press, 1999), Compares the three cities in terms of geography, economics and race from 1800 to 1990 * Allswang, John. ''A House For All Peoples: Ethnic Politics In Chicago, 1890-1936''. (1973). 213 pp. * Andreas, A. T. ''History of Chicago. From the earliest period to the present time'' (1884
online v 1
* Ascoli, Peter Max. ''Julius Rosenwald: The Man Who Built Sears, Roebuck and Advanced the Cause of Black Education in the American South'' (2006
excerpt and text search
* Avrich, Paul. ''The Haymarket Tragedy'' (1984
excerpt and text search
* Bales, Richard F. ''The Great Chicago Fire and the Myth of Mrs. O'Leary's Cow''. (2002). 338 pp. * Barnard, Harry. ''"Eagle Forgotten": The Life of John Peter Altgeld'' (1938) * Barrett, James. ''Work and Community in the Jungle: Chicago's Packinghouse Workers, 1894—1922'' (1987)
excerpt and text search
* Biles, Roger. ''Big City Boss in Depression and War: Mayor Edward J. Kelly of Chicago''. (1984). 219 pp. * Biles, Roger. ''Richard J. Daley: Politics, Race, and the Governing of Chicago''. (1995). 292 pp. * Bolotin, Norman and Laing, Christine. ''The World's Columbian Exposition: The Chicago World's Fair of 1893''. (1992). 166 pp. * Bonner, Thomas Neville. ''Medicine in Chicago, 1850-1950: A Chapter in the Social and Scientific Development of a City''. (1957, 2nd ed. 1991). 335 pp. * Brosnan, Kathleen A., William C. Barnett, and Ann Durkin Keating. ''City of Lake and Prairie: Chicago's Environmental History'' (U of Pittsburgh Press, 2020) * Bukowski, Douglas. ''Big Bill Thompson, Chicago, and the Politics of Image''. (1998). 273 pp
excerpt and text search
* Candeloro, Dominic. ''Italians in Chicago''. (1999). 128 pp. * Clavel, Pierre, and Robert Giloth, "Planning for Manufacturing: Chicago After 1983," ''Journal of Planning History'', 14#1 (Feb. 2015) pp: 19–37. * Cohen, Adam, and Elizabeth Taylor. ''American Pharaoh: Mayor Richard J. Daley - His Battle for Chicago and the Nation''. (2001). 614pp
excerpt and text search
* Cohen, Lizabeth. ''Making a New Deal: Industrial Workers in Chicago, 1919-1939''. (1990). 526 pp.
excerpt and text search
* Condit, Carl W. ''Chicago, 1910-29: Building, Planning, and Urban Technology''. (1973). 354 pp.; ''Chicago, 1930-70: Building, Planning, and Urban Technology''. (1974). 351 pp. * Connolly, Mary Beth Fraser. ''Women of Faith: The Chicago Sisters of Mercy and the Evolution of a Religious Community'' (Oxford University Press, 2014) * Cronon, William. ''Nature's Metropolis: Chicago and the Great West''. (1991). 530 pp.
excerpt and text search
* Cutler, Irving. ''The Jews of Chicago: From Shtetl to Suburb''. (1996). 316 pp. * Drake, St. Clair, and Horace R. Cayton. ''Black Metropolis: A Study of Negro Life in a Northern City'' (4th ed. 1945), classic sociological study * Duis, Perry R. ''The Saloon: Public Drinking in Chicago and Boston, 1880-1920'' (1983). * Emmet, Boris, and John E. Jeuck. ''Catalogues and Counters: A History of Sears, Roebuck & Company'' (1965), the standard corporate history * Fernandez, Lilia. ''Brown in the Windy City: Mexicans and Puerto Ricans in Postwar Chicago'' (2014) * Ferris, William G. ''The Grain Traders: The Story of the Chicago Board of Trade''. (1988). 221 pp. * Fine, Lisa M. ''The Souls of the Skyscraper: Female Clerical Workers in Chicago, 1870-1930''. (1990). 249 pp. * Fisher, Colin. ''Urban Green: Nature, Recreation, and the Working Class in Industrial Chicago'' (2015) * Green, Paul M. and Holli, Melvin G., eds. ''The Mayors: The Chicago Political Tradition'' (1995
online edition
I; essays by scholars covering important mayors before 1980 * Green, Paul M., and Melvin G. Holli. ''Chicago, World War II'' (2003
excerpt and text search
short and heavily illustrated * Grimshaw, William J. ''Bitter Fruit: Black Politics and the Chicago Machine, 1931-1991''. (1992). 248 pp. * Grossman, James R. ''Land of Hope: Chicago, Black Southerners, and the Great Migration''. (1989). 384 pp. * Gustaitis, Joseph. ''Chicago's Greatest Year, 1893: The White City and the Birth of a Modern Metropolis'' (2013) * Gustaitis, Joseph. ''Chicago Transformed: World War I and the Windy City'' (2016). * Hogan, David John. ''Class and Reform: School and Society in Chicago, 1880-1930''. (1985). 328 pp. * Holli, Melvin G. and Jones, Peter d'A., eds. Ethnic Chicago: A Multicultural Portrait''. (4th ed. 1995). 648 pp. essays by scholars on each major ethnic group * Jentz, John B. and Richard Schneirov. ''Chicago in the Age of Capital'' (2012) covers politics 1860 to 188
excerpt and text search
330pp; also —full text. * Kantowicz, Edward R. ''Corporation Sole: Cardinal Mundelein and Chicago Catholicism''. (1983). 295 pp. * Karamanski, Theodore J. ''Rally 'Round the Flag: Chicago and the Civil War''. (1993). 292 pp. * Keating, Ann Durkin. "In the Shadow of Chicago: Postwar Illinois Historiography." ''Journal of the Illinois State Historical Society'' 111.1-2 (2018): 120-136. . * Keating, Ann Durkin. "Chicagoland: More than the Sum of its Parts." ''Journal of Urban History'' 2004 30(2): 213-230. * Keating, Ann Durkin. ''Building Chicago: Suburban Developers and the Creation of Divided Metropolis'' (2002) * Keil, Hartmut and Jentz, John B., eds. ''German Workers in Industrial Chicago, 1850-1910: A Comparative Perspective''. (1983). 252 pp. * Kleppner, Paul. ''Chicago Divided: The Making of a Black Mayor''. (1985). 313 pp. * Lemann, Nicholas. ''The Promised Land: The Great Black Migration and How It Changed America''. (1991). 401 pp. * Longstreet, Stephen. ''Chicago: An Intimate Portrait of People, Pleasures, and Power, 1860–1919''. (1973). 547 pp. popular * Mayer, Harold M., and Richard C. Wade. ''Chicago: Growth of a Metropolis'' (1969) 510pp * McCaffrey, Lawrence J.; Skerrett, Ellen; Funchion, Michael F.; and Fanning, Charles. ''The Irish in Chicago''. (1987). 171 pp. * McDonald, Forrest. ''Insull: The Rise and Fall of a Billionaire Utility Tycoon'' (2004) * Miller, Donald L. ''City of the Century: The Epic of Chicago and the Making of America'' (1997), popular epic
excerpt and text search
* Miller, Ross. ''American Apocalypse: The Great Fire and the Myth of Chicago''. 1990. 287 pp. * Miller, Ross. ''The Great Chicago Fire'' (2000); 1st ed was ''American Apocalypse: The Great Chicago Fire and the Myth of Chicago'' 287 pp. * Nelli, Humbert S. ''The Italians in Chicago: A Study in Ethnic Mobility, 1880–1930''. (1970). 300 pp. * Pacyga, Dominic A. ''Polish Immigrants and Industrial Chicago: Workers on the South Side, 1880–1920''. (1991). 322 pp
excerpt and text search
* Pacyga, Dominic A. ''Chicago: A Biography'' (2011), 472pp; detailed history by a scholar, based on secondary sources
excerpt and text search
* Parot, Joseph John. ''Polish Catholics in Chicago, 1850-1920: A Religious History''. (1982) 298 pp. * Peterson, Paul E. ''The Politics of School Reform, 1870–1940''. (1985). 241 pp. * Pierce, Bessie Louise. ''A History of Chicago'' (3 vol., Volume I: ''The Beginning of a City 1673–1848'' (1937
excerpt and text search vol 1
Volume II: ''From Town to City 1848–1871'' (1940); Volume III: ''The Rise of a Modern City, 1871–1893'' (1957
excerpt and text search vol 3
; the major scholarly history * Pierce, Bessue Louise, ed. ''As Others See Chicago: Impressions of Visitors, 1673-1933''. (1937, reprinted 2004). 548 p
excerpt and text search
primary sources * Rivlin, Gary (1992). ''Fire on the Prairie: Chicago's Harold Washington and the Politics of Race''. 426 pp. * Sawyers, June Skinner. ''Chicago Portraits'' (2nd ed. Northwestern University Press, 2012), 250 short biographies * Schneirov, Richard; Stromquist, Shelton; and Salvatore, Nick, eds. ''The Pullman Strike and the Crisis of the 1890s: Essays on Labor and Politics''. (1999). 258 pp
excerpt and text search
* Shanabruch, Charles. ''Chicago's Catholics: The Evolution of an American Identity''. (1981). 296 pp. * Smith, Carl S. ''Chicago and the American Literary Imagination, 1880-1920''. (1984). 232 pp. * Smith, Richard Norton. ''The Colonel: The Life and Legend of Robert R. McCormick, 1880-1955''. (1997). 597 pp. publisher of ''Chicago Tribune'' * Spear, Allan. ''Black Chicago: The Making of a Negro Ghetto, 1890–1920'' (1967), * Spinney, Robert G. ''City of Big Shoulders: A History of Chicago'' (2000), popular epic
excerpt and text search
* Tuttle, William M., Jr. ''Race Riot: Chicago in the Red Summer of 1919''. (1970). 305 pp. * WPA. ''Illinois: A Descriptive and Historical Guide'' (1939) * Young, David M. ''Chicago Transit: An Illustrated History'' (1998). 213 pp.
External links
In the Vicinity of Maxwell and Halsted Streets, 1890–1930
History of Chicago from its founding to the World's Fair at PBS.org
The Northwest Chicago Historical Society's official website
Chicago History
and other overlooked elements at
Forgotten Chicago
Forgotten Chicago is an organization that seeks to discover and document little-known elements of Chicago's infrastructure, architecture, neighborhoods, and general cityscape, existing or historical.
The organization exposes many of these often ...
Chicago Foreign Language Press Survey English translations of 120,000 pages of news articles from the foreign language press from 1855 to 1938.
*
''Digital Research Library of Illinois History''
William Joseph Showalter, "Chicago Today and Tomorrow" '' National Geographic,'' January, 1919, pages 1-42 well illustrated
* * {{Authority control Articles containing video clips