higher plants on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the
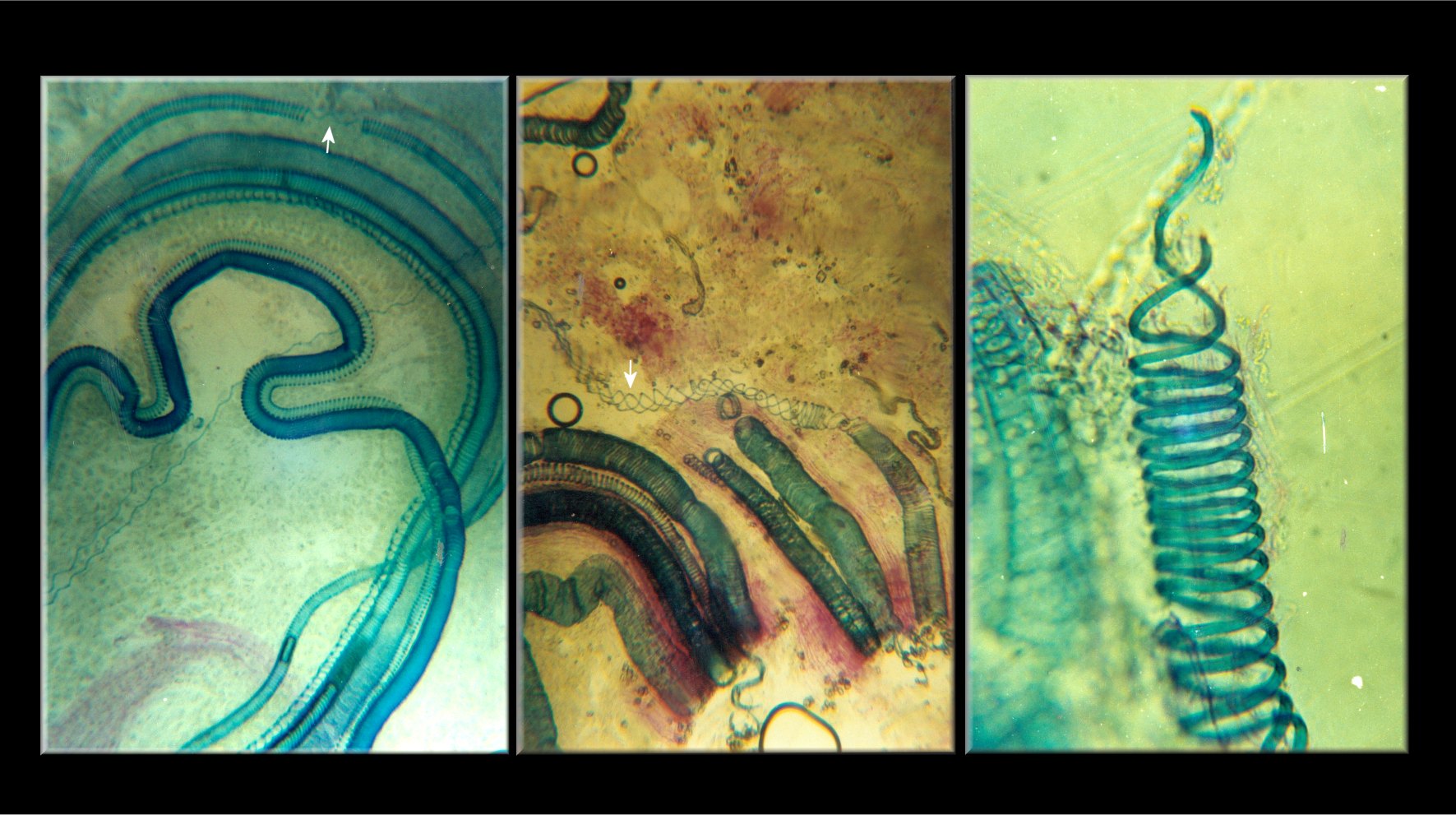 Water and nutrients in the form of inorganic solutes are drawn up from the soil by the roots and transported throughout the plant by the
Water and nutrients in the form of inorganic solutes are drawn up from the soil by the roots and transported throughout the plant by the
“Higher plants” or “vascular plants”?
{{Authority control Plants Extant Silurian first appearances
xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem. The basic function of xylem is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves, but it also transports nutrients. The word ''xylem'' is derived from ...
) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem
Phloem (, ) is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as ''photosynthates'', in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant. This transport process is c ...
) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmoss
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants known as lycopods, lycophytes or other terms including the component lyco-. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching ...
es, horsetails
''Equisetum'' (; horsetail, snake grass, puzzlegrass) is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of ferns, which reproduce by spores rather than seeds.
''Equisetum'' is a " living fossil", the only living genus of the entire subclass ...
, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophyte
The rhyniophytes are a group of extinct early vascular plants that are considered to be similar to the genus '' Rhynia'', found in the Early Devonian (around ). Sources vary in the name and rank used for this group, some treating it as the class ...
s) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones.
Historically, vascular plants were known as "higher plants", as it was believed that they were further evolved than other plants due to being more complex organisms. However, this is an antiquated remnant of the obsolete scala naturae, and the term is generally considered to be unscientific.
Characteristics
Botanists define vascular plants by three primary characteristics: # Vascular plants havevascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. The ...
s which distribute resources through the plant. Two kinds of vascular tissue occur in plants: xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem. The basic function of xylem is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves, but it also transports nutrients. The word ''xylem'' is derived from ...
and phloem
Phloem (, ) is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as ''photosynthates'', in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant. This transport process is c ...
. Phloem and xylem are closely associated with one another and are typically located immediately adjacent to each other in the plant. The combination of one xylem and one phloem strand adjacent to each other is known as a vascular bundle. The evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
of vascular tissue in plants allowed them to evolve to larger sizes than non-vascular plants, which lack these specialized conducting tissues and are thereby restricted to relatively small sizes.
# In vascular plants, the principal generation or phase is the '' sporophyte'', which produces spores and is diploid (having two sets of chromosomes per cell). (By contrast, the principal generation phase in non-vascular plants is the ''gametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternating multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the ...
'', which produces gametes
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce ...
and is haploid - with one set of chromosomes per cell.)
# Vascular plants have true roots, leaves, and stems, even if some groups have secondarily lost one or more of these traits.
Cavalier-Smith (1998) treated the Tracheophyta as a phylum or botanical division encompassing two of these characteristics defined by the Latin phrase "facies diploida xylem et phloem instructa" (diploid phase with xylem and phloem).
One possible mechanism for the presumed evolution from emphasis on haploid generation to emphasis on diploid generation is the greater efficiency in spore dispersal with more complex diploid structures. Elaboration of the spore stalk enabled the production of more spores and the development of the ability to release them higher and to broadcast them farther. Such developments may include more photosynthetic area for the spore-bearing structure, the ability to grow independent roots, woody structure for support, and more branching.
Phylogeny
A proposed phylogeny of the vascular plants after Kenrick and Crane 1997 is as follows, with modification to the gymnosperms from Christenhusz ''et al.'' (2011a), Pteridophyta from Smith ''et al.'' and lycophytes and ferns by Christenhusz ''et al.'' (2011b) The cladogram distinguishes therhyniophyte
The rhyniophytes are a group of extinct early vascular plants that are considered to be similar to the genus '' Rhynia'', found in the Early Devonian (around ). Sources vary in the name and rank used for this group, some treating it as the class ...
s from the "true" tracheophytes, the eutracheophytes.
This phylogeny is supported by several molecular studies. Other researchers state that taking fossils into account leads to different conclusions, for example that the ferns (Pteridophyta) are not monophyletic.
Hao and Xue presented an alternative phylogeny in 2013 for pre-euphyllophyte
The euphyllophytes are a clade of plants within the tracheophytes (the vascular plants). The group may be treated as an unranked clade, a division
Division or divider may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multipli ...
plants.
Nutrient distribution
 Water and nutrients in the form of inorganic solutes are drawn up from the soil by the roots and transported throughout the plant by the
Water and nutrients in the form of inorganic solutes are drawn up from the soil by the roots and transported throughout the plant by the xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem. The basic function of xylem is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves, but it also transports nutrients. The word ''xylem'' is derived from ...
. Organic compounds such as sucrose produced by photosynthesis in leaves are distributed by the phloem
Phloem (, ) is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as ''photosynthates'', in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant. This transport process is c ...
sieve-tube elements.
The xylem consists of vessels in flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s and of tracheid
A tracheid is a long and tapered lignified cell in the xylem of vascular plants. It is a type of conductive cell called a tracheary element. Angiosperms use another type of tracheary element, called vessel elements, to transport water through th ...
s in other vascular plants. Xylem cells are dead hard-walled hollow cells arranged to form files of tubes that function in the transport of water. A tracheid cell-wall usually contains the polymer lignin.
The phloem, on the other hand, consists of living cells called sieve-tube members. Between the sieve-tube members are sieve plates, which have pores to allow molecules to pass through. Sieve-tube members lack such organs as nuclei or ribosomes, but cells next to them, the companion cells, function to keep the sieve-tube members alive.
Transpiration
The most abundantcompound
Compound may refer to:
Architecture and built environments
* Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall
** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive struc ...
in all plants, as in all cellular organisms, is water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
, which has an important structural role and a vital role in plant metabolism
Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), phytochemistry (bio ...
. Transpiration is the main process of water movement within plant tissues. Plants constantly transpire water through their stomata to the atmosphere and replace that water with soil moisture taken up by their roots. The movement of water out of the leaf stomata sets up a transpiration pull or tension in the water-column in the xylem vessels or tracheids. The pull is the result of water surface tension within the cell walls of the mesophyll cells, from the surfaces of which evaporation takes place when the stomata are open. Hydrogen bonds exist between water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
s, causing them to line up; as the molecules at the top of the plant evaporate, each pulls the next one up to replace it, which in turn pulls on the next one in line. The draw of water upwards may be entirely passive and can be assisted by the movement of water into the roots via osmosis. Consequently, transpiration requires the plant to expend very little energy on water movement. Transpiration assists the plant in absorbing nutrients from the soil as soluble salts
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively c ...
.
Absorption
Living root cells passively absorb water in the absence of transpiration pull via osmosis creating root pressure. It is possible for there to be no evapotranspiration and therefore no pull of water towards the shoots and leaves. This is usually due to high temperatures, high humidity, darkness or drought.Conduction
Xylem andphloem
Phloem (, ) is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as ''photosynthates'', in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant. This transport process is c ...
tissues each play a part in the conduction processes within plants. Sugars are conducted throughout the plant in the phloem; water and other nutrients through the xylem. Conduction occurs from a source to a sink for each separate nutrient. Sugars are produced in the leaves (a source) by photosynthesis and transported to the growing shoots and roots (sinks) for use in growth, cellular respiration or storage. Minerals are absorbed in the roots (a source) and transported to the shoots to allow cell division and growth.
See also
* Fern allies *Bryophyte
The Bryophyta s.l. are a proposed taxonomic division containing three groups of non-vascular land plants (embryophytes): the liverworts, hornworts and mosses. Bryophyta s.s. consists of the mosses only. They are characteristically limited in s ...
s
* Non-vascular plant
* Pteridophyte
References
Bibliography
* * * * , inExternal links
“Higher plants” or “vascular plants”?
{{Authority control Plants Extant Silurian first appearances