Heterochromatin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or '' condensed DNA'', which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continue between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a role in the expression of genes. Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed; however, according to Volpe et al. (2002), and many other papers since, much of this DNA is in fact transcribed, but it is continuously turned over via RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS). Recent studies with electron microscopy and OsO4 staining reveal that the dense packing is not due to the chromatin.
Constitutive heterochromatin can affect the genes near itself (e.g. position-effect variegation). It is usually repetitive and forms structural functions such as centromeres or telomeres, in addition to acting as an attractor for other gene-expression or repression signals.
Facultative heterochromatin is the result of genes that are silenced through a mechanism such as histone deacetylation or Piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) through RNAi. It is not repetitive and shares the compact structure of constitutive heterochromatin. However, under specific developmental or environmental signaling cues, it can lose its condensed structure and become transcriptionally active.
Heterochromatin has been associated with the di- and tri -methylation of H3K9 in certain portions of the human genome. H3K9me3-related


 Heterochromatin has been associated with several functions, from gene regulation to the protection of chromosome integrity; some of these roles can be attributed to the dense packing of DNA, which makes it less accessible to protein factors that usually bind DNA or its associated factors. For example, naked double-stranded DNA ends would usually be interpreted by the cell as damaged or viral DNA, triggering
Heterochromatin has been associated with several functions, from gene regulation to the protection of chromosome integrity; some of these roles can be attributed to the dense packing of DNA, which makes it less accessible to protein factors that usually bind DNA or its associated factors. For example, naked double-stranded DNA ends would usually be interpreted by the cell as damaged or viral DNA, triggering
methyltransferase
Methyltransferases are a large group of enzymes that all Methylation, methylate their substrates but can be split into several subclasses based on their structural features. The most common class of methyltransferases is class I, all of which co ...
s appear to have a pivotal role in modifying heterochromatin during lineage commitment at the onset of organogenesis and in maintaining lineage fidelity.
Structure
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important ...
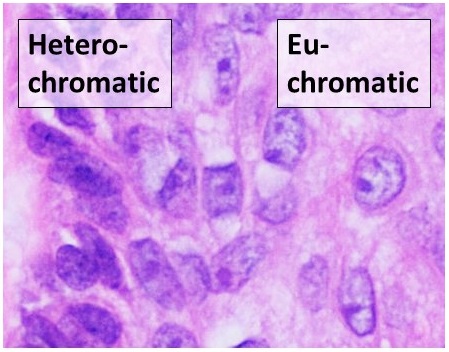
is found in two varieties: euchromatin and heterochromatin. Originally, the two forms were distinguished cytologically by how intensely they get stained – the euchromatin is less intense, while heterochromatin stains intensely, indicating tighter packing. Heterochromatin is usually localized to the periphery of the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
.
Despite this early dichotomy, recent evidence in both animals and plants has suggested that there are more than two distinct heterochromatin states, and it may in fact exist in four or five 'states', each marked by different combinations of epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are ...
marks.
Heterochromatin mainly consists of genetically inactive satellite sequences, and many genes are repressed to various extents, although some cannot be expressed in euchromatin at all. Both centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers ...
s and telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature mos ...
s are heterochromatic, as is the Barr body of the second, inactivated X-chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex- ...
in a female.
Function
 Heterochromatin has been associated with several functions, from gene regulation to the protection of chromosome integrity; some of these roles can be attributed to the dense packing of DNA, which makes it less accessible to protein factors that usually bind DNA or its associated factors. For example, naked double-stranded DNA ends would usually be interpreted by the cell as damaged or viral DNA, triggering
Heterochromatin has been associated with several functions, from gene regulation to the protection of chromosome integrity; some of these roles can be attributed to the dense packing of DNA, which makes it less accessible to protein factors that usually bind DNA or its associated factors. For example, naked double-stranded DNA ends would usually be interpreted by the cell as damaged or viral DNA, triggering cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
arrest, DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
or destruction of the fragment, such as by endonuclease
Endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain. Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically (without regard to sequence), while many, typically called restriction endonuclease ...
s in bacteria.
Some regions of chromatin are very densely packed with fibers that display a condition comparable to that of the chromosome at mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintai ...
. Heterochromatin is generally clonally inherited; when a cell divides, the two daughter cells typically contain heterochromatin within the same regions of DNA, resulting in epigenetic inheritance. Variations cause heterochromatin to encroach on adjacent genes or recede from genes at the extremes of domains. Transcribable material may be repressed by being positioned (in ''cis'') at these boundary domains. This gives rise to expression levels that vary from cell to cell, which may be demonstrated by position-effect variegation. Insulator sequences may act as a barrier in rare cases where constitutive heterochromatin and highly active genes are juxtaposed (e.g. the 5'HS4 insulator upstream of the chicken β-globin locus, and loci in two ''Saccharomyces
''Saccharomyces'' is a genus of fungi that includes many species of yeasts. ''Saccharomyces'' is from Greek σάκχαρον (sugar) and μύκης (fungus) and means ''sugar fungus''. Many members of this genus are considered very important in f ...
'' spp.).
Constitutive heterochromatin
All cells of a given species package the same regions of DNA in constitutive heterochromatin, and thus in all cells, any genes contained within the constitutive heterochromatin will be poorly expressed. For example, all human chromosomes 1, 9, 16, and theY-chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes ( allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or ...
contain large regions of constitutive heterochromatin. In most organisms, constitutive heterochromatin occurs around the chromosome centromere and near telomeres.
Facultative heterochromatin
The regions of DNA packaged in facultative heterochromatin will not be consistent between the cell types within a species, and thus a sequence in one cell that is packaged in facultative heterochromatin (and the genes within are poorly expressed) may be packaged in euchromatin in another cell (and the genes within are no longer silenced). However, the formation of facultative heterochromatin is regulated, and is often associated with morphogenesis or differentiation. An example of facultative heterochromatin is X chromosome inactivation in female mammals: oneX chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex ...
is packaged as facultative heterochromatin and silenced, while the other X chromosome is packaged as euchromatin and expressed.
Among the molecular components that appear to regulate the spreading of heterochromatin are the Polycomb-group proteins and non-coding genes such as Xist. The mechanism for such spreading is still a matter of controversy. The polycomb repressive complexes PRC1 and PRC2 regulate chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important ...
compaction and gene expression and have a fundamental role in developmental processes. PRC-mediated epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are ...
aberrations are linked to genome instability
Genome instability (also genetic instability or genomic instability) refers to a high frequency of mutations within the genome of a cellular lineage. These mutations can include changes in nucleic acid sequences, chromosomal rearrangements or ane ...
and malignancy and play a role in the DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
response, DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
and in the fidelity of replication.
Yeast heterochromatin
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have b ...
'', or budding yeast, is a model eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
and its heterochromatin has been defined thoroughly. Although most of its genome can be characterized as euchromatin, ''S. cerevisiae'' has regions of DNA that are transcribed very poorly. These loci are the so-called silent mating type loci (HML and HMR), the rDNA (encoding ribosomal RNA), and the sub-telomeric regions.
Fission yeast ('' Schizosaccharomyces pombe'') uses another mechanism for heterochromatin formation at its centromeres. Gene silencing at this location depends on components of the RNAi pathway. Double-stranded RNA is believed to result in silencing of the region through a series of steps.
In the fission yeast ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', two RNAi complexes, the RITS complex and the RNA-directed RNA polymerase complex (RDRC), are part of an RNAi machinery involved in the initiation, propagation and maintenance of heterochromatin assembly. These two complexes localize in a siRNA-dependent manner on chromosomes, at the site of heterochromatin assembly. RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of euka ...
synthesizes a transcript that serves as a platform to recruit RITS, RDRC and possibly other complexes required for heterochromatin assembly. Both RNAi and an exosome-dependent RNA degradation process contribute to heterochromatic gene silencing. These mechanisms of ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' may occur in other eukaryotes. A large RNA structure called RevCen has also been implicated in the production of siRNAs to mediate heterochromatin formation in some fission yeast.
See also
* Centric heterochromatinReferences
External links
* * * * {{Authority control Molecular genetics Nuclear organization