Hearing protection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A hearing protection device, also known as a HPD, is an
A hearing protection device, also known as a HPD, is an
 Types of ear protection include:
*
Types of ear protection include:
*

 Canal caps are similar to earplugs in that they consists of soft tip that is inserted into the opening of the ear canal. Some styles are inserted slightly into the ear canal while others sit in place at the opening of the ear canal. In this case, the tips or caps are connected by a lightweight band which also serves to hold them in position.
Canal caps are similar to earplugs in that they consists of soft tip that is inserted into the opening of the ear canal. Some styles are inserted slightly into the ear canal while others sit in place at the opening of the ear canal. In this case, the tips or caps are connected by a lightweight band which also serves to hold them in position.

 A hearing protection device, also known as a HPD, is an
A hearing protection device, also known as a HPD, is an ear protection
Ear protection refers to devices used to protect the ear, either externally from elements such as cold, intrusion by water and other environmental conditions, debris. High levels of exposure to noise may result in noise-induced hearing loss
...
device worn in or over the ears while exposed to hazardous noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference aris ...
and provide hearing protection to help prevent noise-induced hearing loss
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a hearing impairment resulting from exposure to loud sound. People may have a loss of perception of a narrow range of frequencies or impaired perception of sound including sensitivity to sound or ringing i ...
. HPDs reduce the level of the noise entering the ear. HPDs can also protect against other effects of noise exposure such as tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearin ...
and hyperacusis
Hyperacusis is the increased sensitivity to sound and a low tolerance for environmental noise. Definitions of hyperacusis can vary significantly; it can refer to normal noises being perceived as: loud, annoying, painful, fear-inducing, or a combina ...
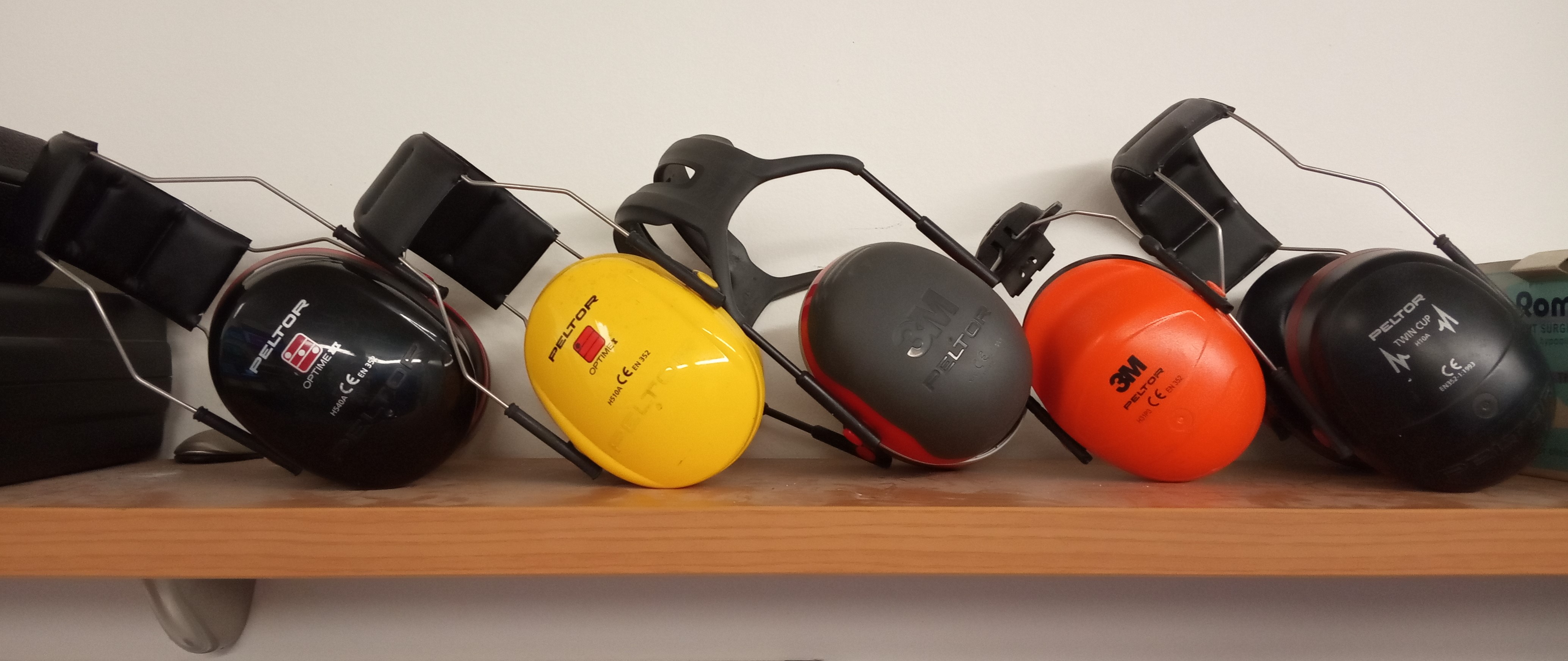
. There are many different types of HPDs available for use, including earmuffs
Earmuffs are clothing accessories or personal protective equipment designed to cover a person's ears for hearing protection or warmth. They consist of a thermoplastic or metal head-band that fits over the top or back of the head, and a cushi ...
, earplug
An earplug is a device that is inserted in the ear canal to protect the user's ears from loud noises, intrusion of water, foreign bodies, dust or excessive wind. Since they reduce the sound volume, earplugs are often used to help prevent heari ...
s, electronic hearing protection devices, and semi-insert devices.
The use of the HPD without individual selection, training and fit testing does not significantly reduce the risk of hearing loss. For example, one study covered more than 19 thousand workers, some of whom usually used hearing protective devices, and some did not use them at all. There was no statistically significant difference in the risk of noise-induced hearing loss.
Exposure limits
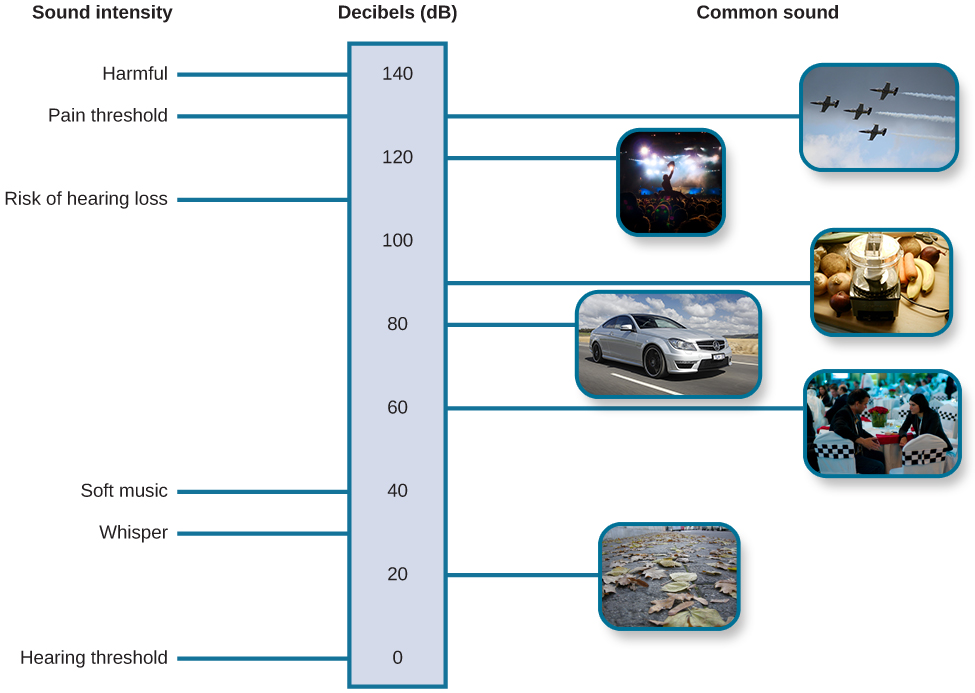
In the context of work, adequate hearing protection is that which reduces noise exposure to below 85 dBA over the course of an average work shift of eight hours. When sounds exceed 80 dBA, it becomes dangerous to the ears. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has standards that show how long a person can be in different loudness levels before the person reaches their maximum daily dose and becomes damaging to their hearing. These standards can give individuals an idea of when hearing protection should be considered. The maximum daily dose with the corresponding decibel level is shown below. Decibel Level with the time reaching maximum daily dose (dBA): * 8 hours at 85 dB(A) * 4 hours at 88 dB(A) * 2 hours at 91 dB(A) * 60 minutes at 94 dB(A) * 30 minutes at 97 dB(A) * 15 minutes at 100 dB(A) Different types of hearing protection may be utilized to maximize hearing protection. OSHA regulations dictate whether hearing protection is required and if the company must participate in ahearing conservation program
Hearing conservation programs are designed to prevent hearing loss due to noise. Hearing conservation programs require knowledge about risk factors such as noise and ototoxicity, hearing, hearing loss, protective measures to prevent hearing loss ...
.
Hunting and firearms
The shooting of guns for recreational use can lead to hearing loss in the high frequencies. The shooting of firearms can cause damage to a variety of cochlear structures due to the high peak sound pressure levels that they generate. This can range from 140 to 175 dB. Along with the passive noise reduction options usually used vocationally (such as earmuffs and earplugs) there are also active noise reduction devices available. Active noise reduction technology is used to provide noise protection like passive options, but also use circuitry to give audibility to sounds that are below a dangerous level (about 85 db) and try to limit the average output level to about 82 to 85 dB to keep the exposure at a safe level. Strategies to help protect your hearing from firearms also include using muzzle brakes and suppressors, shooting fewer rounds, and avoiding using a firearm with a short barrel. It is recommended to shoot outdoors or in a sound-treated environment, rather than a reverberant environment (an enclosed area with sound-reflecting surfaces). If there are multiple people shooting, make sure there is a large distance between the shooters and that they are not firing at the same time.Types
 Types of ear protection include:
*
Types of ear protection include:
*Earmuffs
Earmuffs are clothing accessories or personal protective equipment designed to cover a person's ears for hearing protection or warmth. They consist of a thermoplastic or metal head-band that fits over the top or back of the head, and a cushi ...
, external: This ear protection fits snug around the person's external ear.
*Earplug
An earplug is a device that is inserted in the ear canal to protect the user's ears from loud noises, intrusion of water, foreign bodies, dust or excessive wind. Since they reduce the sound volume, earplugs are often used to help prevent heari ...
s, internal: These are ear protection that fit inside of the person's ear canal. There are many different types of ear plugs. The most commonly known are foam, musician
A musician is a person who composes, conducts, or performs music. According to the United States Employment Service, "musician" is a general term used to designate one who follows music as a profession. Musicians include songwriters who wr ...
, or custom earplugs that are made from a mold of a person's ear.
*Helmet
A helmet is a form of protective gear worn to protect the head. More specifically, a helmet complements the skull in protecting the human brain. Ceremonial or symbolic helmets (e.g., a policeman's helmet in the United Kingdom) without protect ...
, covering various parts of the head, including the ears
In some occasions, multiple types of ear protection can be used together to increase the NRR. For example, foam earplugs can be worn in-conjunction with earmuffs.
Each type of ear protection has what is called a noise reduction rating (NRR). This gives the consumer an estimate of how much noise is being reduced before reaching the individual's ear. It is important for the consumer to know that this is only a single number estimate derived from a laboratory experiment, and the NRR will vary per individual wearing the hearing protection. NIOSH and OSHA have derating values to help give the person an idea of how much sound is being attenuated while wearing the hearing protection. OSHA uses a half derating, while NIOSH uses 70% for pre-formed earplugs, 50% for formable earplugs, and 25% for earmuffs.
Earmuffs

Earmuff
Earmuffs are clothing accessories or personal protective equipment designed to cover a person's ears for hearing protection or warmth. They consist of a thermoplastic or metal head-band that fits over the top or back of the head, and a cushion o ...
style hearing protection devices are designed to fit over the outer ear, or pinna. Earmuff HPDs typically consist of two ear cups and a head band. Ear cups are usually lined with a sound-absorbing material, such as foam. The cups should be fit so that the center of the ear canal aligns with the ear canal opening. The soft cushions seal around the pinna of the ears. The head band, centered at the top of the head, applies force/pressure to seal the ear cups over the ears.
Earplugs
Earplug
An earplug is a device that is inserted in the ear canal to protect the user's ears from loud noises, intrusion of water, foreign bodies, dust or excessive wind. Since they reduce the sound volume, earplugs are often used to help prevent heari ...
style hearing protection devices are designed to fit in the ear canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna (anatomy), pinna to the eardrum and is about in length and in di ...
. Earplugs come in a variety of different subtypes. The attenuation offered by these devices can be measured through hearing protection fit testing.
* Pre-molded earplugs have a preformed shape and a push-to-fit design.
* Formable earplugs are pliable and take the form of an individual's ear canal.
* Roll-down foam earplugs are one of the most commonly used earplugs, and are made from slow recovery foam which expands after it has been "rolled-down" and inserted in the ear canal, creating a tighter seal.
* Custom earplugs are made individually for each user following earmold impressions. Typically custom earplugs are purchased from an audiology clinic or hearing healthcare professional.
Electronic hearing protection devices
Some HPDs reduce the sound reaching theeardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the ...
through a combination of electronic and structural components. Electronic HPDs are available in both earmuff
Earmuffs are clothing accessories or personal protective equipment designed to cover a person's ears for hearing protection or warmth. They consist of a thermoplastic or metal head-band that fits over the top or back of the head, and a cushion o ...
and custom earplug
An earplug is a device that is inserted in the ear canal to protect the user's ears from loud noises, intrusion of water, foreign bodies, dust or excessive wind. Since they reduce the sound volume, earplugs are often used to help prevent heari ...
styles. Electronic microphones, circuitry, and receivers perform active noise reduction
Active may refer to:
Music
* ''Active'' (album), a 1992 album by Casiopea
* Active Records, a record label
Ships
* ''Active'' (ship), several commercial ships by that name
* HMS ''Active'', the name of various ships of the British Royal ...
, also known as noise-cancelling, in which a signal that is 180-degrees out-of-phase of the noise is presented, which in theory cancels the noise.
Some electronic HPDs, known as Hearing Enhancement Protection Systems, provide hearing protection from high-level sounds while allowing transmission of other sounds like speech. Some also have the ability to amplify low-level sounds. This type may be beneficial for users who are in noisy environments, but still need access to lower level sounds. For example, soldier
A soldier is a person who is a member of an army. A soldier can be a Conscription, conscripted or volunteer Enlisted rank, enlisted person, a non-commissioned officer, or an Officer (armed forces), officer.
Etymology
The word ''soldier'' deri ...
s who need to protect their hearing but also need to be able to identify enemy forces and communicate in noise, hunters
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
who rely on detecting and localizing soft sounds of wildlife
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted ...
but still wish to protect their hearing from recreational firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
blasts, as well as users with pre-existing hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken l ...
who are in noisy environments may all benefit from In Ear Electronic Hearing Enhancement Protection Systems.
Electronic HPDs require the use of batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
and are typically more expensive than non-electronic types.
Semi-insert devices (canal caps)
 Canal caps are similar to earplugs in that they consists of soft tip that is inserted into the opening of the ear canal. Some styles are inserted slightly into the ear canal while others sit in place at the opening of the ear canal. In this case, the tips or caps are connected by a lightweight band which also serves to hold them in position.
Canal caps are similar to earplugs in that they consists of soft tip that is inserted into the opening of the ear canal. Some styles are inserted slightly into the ear canal while others sit in place at the opening of the ear canal. In this case, the tips or caps are connected by a lightweight band which also serves to hold them in position.
Dual hearing protection
Dual hearing protection refers to the use of earplugs under ear muffs. This type of hearing protection is particularly recommended for workers in the mining industry because they are exposed to extremely high noise levels, such as an 105 dBA TWA." /> Fortunately, there is an option of adding electronic features to dual hearing protectors. These features help with communication by making speech more clear, especially for those workers who already have hearing loss. The sound attenuation of a dual hearing protector is generally lower than the algebra sum of the attenuation of each single hearing protector.Berger, E. H.; Kieper, R. W.; Gauger, D. (2003). "Hearing protection: surpassing the limits to attenuation imposed by the bone-conduction pathways". The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 114 (4): 1955–1967. doi: 10.1121/1.1605415. PMID 14587596 This phenomenon can be caused by the mechanical coupling between the earplug and earmuff through the human tissues, the vibration of the ear canal wall, or the bone conducted sound travelling from the head and body directly to the middle and inner ears. As a rule of thumb, the noise reduction rating of a dual hearing protector can be estimated by adding a 5 dB correction factor to the higher noise reduction rating of the two single hearing protectors.Hygiene and care
In order to prevent irritation or infection of the ear, reusable HPDs should be cleaned on a regular basis. Before using any HPD, it should be inspected for damage or dirt to ensure that it is safe to use. Single-use, disposable earplugs are available in addition to reusable options. Earplugs intended for single-use should not be washed for reuse as this degrades the material and reduces effectiveness. Most reusable earplugs can be cleaned using mild soap and warm water between uses and should be replaced every 2–4 weeks.Earmuff
Earmuffs are clothing accessories or personal protective equipment designed to cover a person's ears for hearing protection or warmth. They consist of a thermoplastic or metal head-band that fits over the top or back of the head, and a cushion o ...
cups and cushions should be cleaned regularly with soap and water, and be replaced if they become cracked or otherwise compromised. Ear cushions can last from 3–8 months depending on use. Use of a clean, protective case to store HPDs when not in use is recommended to prevent damage or contamination.
Any damage to a HPD can compromise its integrity, thus reducing its effectiveness. Damaged HPDs should not be used.
Recommended use
Many countries require several interventions to control risks from exposures to loud noise in the workplace. In the US, theOccupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration'' (OSHA ) is a large regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. Congress established the agen ...
requires hearing conservation program
Hearing conservation programs are designed to prevent hearing loss due to noise. Hearing conservation programs require knowledge about risk factors such as noise and ototoxicity, hearing, hearing loss, protective measures to prevent hearing loss ...
s which include the provision of hearing protection devices. It is also recommended by the U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the C ...
, audiologists
Audiology (from Latin , "to hear"; and from Greek , ''-logia'') is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various ...
and other hearing healthcare professionals when one works exposed to noise levels that exceed 85 dB. NIOSH and OSHA base their recommendations for use of hearing protection by a calculation called time-weighted average (TWA). A time-weighted average is the average noise level a worker is exposed to over a period of time. NIOSH recommends that OSHA use an 85 dBA time-weighted average during an 8-hour period as their exposure limit. An 85 dBA time-weighted average means that HPD use is recommended if an employee is exposed to an average noise level of 85 dBA or more during an 8-hour work day. NIOSH also uses a 3 dB exchange rate for time-weighted averages. A 3 dB exchange rate means that for every 3 dB increase in the average level of noise the recommended time being exposed to that level of noise is cut in half. For example, for a worker who is exposed to 88 dBA, it's recommended he/she only be exposed to that level of noise for 4 hours. These levels of noise may be encountered in both occupational and recreational settings. HPDs are recommended for use in settings where it is difficult to control the noise level, and the person exposed to the noise cannot be removed from the environment.
The amount of protection from noise can vary based on the physical fit of the device and the skill of the worker. Hearing protection devices with accurate placement (an airtight seal) and/or accurate insertion (deep into the ear canal) will provide the most attenuation of noise. There are many challenges to achieving the needed protection from the device, from barriers to adequate use, to issues related to comfort, convenience, lack of training, to beliefs and attitudes towards its use.
Noise reduction ratings
Hearing protection device manufacturers in the United States are required by theEPA
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it be ...
to label HPDs with a noise reduction rating, or NRR. The NRR estimates how much noise is reduced by a hearing protection device, measured in decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a ...
s.
The NRR is measured by manufacturers using American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The orga ...
(ANSI) specified procedures in a laboratory environment. The NRR tends to overestimate the amount of protection the HPDs provide in real-world conditions. These differences are most likely attributed to incorrect insertion or poor earplug fit. Because the actual amount of attenuation is typically less than the labeled NRR, the U.S. Department of Labor
The United States Department of Labor (DOL) is one of the United States federal executive departments, executive departments of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government. It is responsible for the administration of fede ...
/OSHA suggest "derating" or reducing the NRR when using it to evaluate total noise exposure when wearing the HPD. OSHA's training manual has uses a 7 dBA correction factor: NRR- 7dBA= estimated noise exposure
in the late 1990s the US National Institute for Occupational Health and Safety (NIOSH) recommended a different derating scheme for HPDs but now encourages the hearing protection fit-testing. Hearing protection fit-testing
Hearing protector fit-testing, also known as field attenuation estimation system (FAES), determines how effective a hearing protection device is for an individual when worn correctly. This is typically carried out using one of the available fit-tes ...
has been developed in order to determine the actual attenuation of the device as it is worn for an individual. These tests for checking attenuation values summarize the real-world attenuation in a personal attenuation rating (PAR). The PAR is unique to the HPD tested and the individual wearing the protection. When obtaining a PAR, it is recommended to test both ears individually as there may be asymmetry between ears. This asymmetry can be caused by anatomical differences between ears or improper fit of the HPD and could lead to a unilateral threshold shift. A PAR can be reported as C-weighted values, A-weighted values, or attenuation values for specific frequencies. The PAR can then be used to determine if the HPD is providing adequate attenuation so that an individual's noise exposure does not exceed the recommended limits set forth by regulatory agencies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration'' (OSHA ) is a large regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. Congress established the agen ...
(OSHA).
Regulations and standards
United States
*Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration'' (OSHA ) is a large regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. Congress established the agen ...
(1983; 29 CFR 1910.95) requires the use of HPDs in occupational settings when the noise exposure levels are equal to or above an 8-hour time-weighted average of 90 dB-A.
* Mine Safety and Health Administration
The Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) () is a large agency of the United States Department of Labor which administers the provisions of the Federal Mine Safety and Health Act of 1977 (Mine Act) to enforce compliance with mandatory safe ...
(1999; 30 CFR Part 62) provides similar regulations as OSHA (above), but further requires simultaneous use of both earplugs and earmuffs when exposure levels exceed a time-weighted average of 105 dB-A.
* U.S. Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national secur ...
(2004; Instruction 6055.12, Hearing Conservation Program, March 5, 2004)
* U.S. Navy and Marine Corps Public Health Center (2008; TM 6260.51.99-2)
* European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
Directive 2003/10/EC (European Parliament and Council, 2003)
* American National Standard for Construction Workers (American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The orga ...
/American Society of Safety Engineers
American Society of Safety Professionals (ASSP), formerly known as American Society of Safety Engineers (ASSE) until June 2018, is a global organization of more than 37,000 occupational safety and health (OSH) professional members who manage, ...
, 2007; A10.46)
References
Further reading
* {{Authority control Occupational safety and health Noise control Hearing loss Protective gear