group 7 element on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Group 7, numbered by
 The most important manganese ore is pyrolusite ( MnO2). Other economically important manganese ores usually show a close spatial relation to the iron ores, such as
The most important manganese ore is pyrolusite ( MnO2). Other economically important manganese ores usually show a close spatial relation to the iron ores, such as  A more progressive extraction process involves directly reducing (a low grade) manganese ore in a heap leach. This is done by percolating natural gas through the bottom of the heap; the natural gas provides the heat (needs to be at least 850 °C) and the reducing agent (carbon monoxide). This reduces all of the manganese ore to manganese oxide (MnO), which is a leachable form. The ore then travels through a
A more progressive extraction process involves directly reducing (a low grade) manganese ore in a heap leach. This is done by percolating natural gas through the bottom of the heap; the natural gas provides the heat (needs to be at least 850 °C) and the reducing agent (carbon monoxide). This reduces all of the manganese ore to manganese oxide (MnO), which is a leachable form. The ore then travels through a
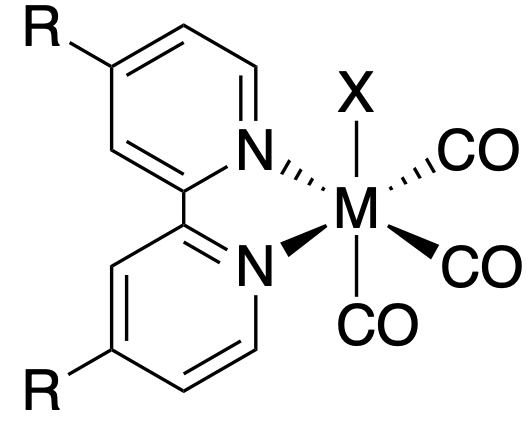 The ''facial'' isomer of both rhenium and manganese 2,2'-bipyridyl tricarbonyl halide complexes have been extensively researched as catalysts for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction due to their high selectivity and stability. They are commonly abbreviated as M(R-bpy)(CO)3X where M = Mn, Re; R-bpy = 4,4'-disubstituted 2,2'-bipyridine; and X = Cl, Br.
The ''facial'' isomer of both rhenium and manganese 2,2'-bipyridyl tricarbonyl halide complexes have been extensively researched as catalysts for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction due to their high selectivity and stability. They are commonly abbreviated as M(R-bpy)(CO)3X where M = Mn, Re; R-bpy = 4,4'-disubstituted 2,2'-bipyridine; and X = Cl, Br.
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
nomenclature, is a group of elements
Element or elements may refer to:
Science
* Chemical element, a pure substance of one type of atom
* Heating element, a device that generates heat by electrical resistance
* Orbital elements, parameters required to identify a specific orbit of o ...
in the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of ...
. They are manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial all ...
(Mn), technetium
Technetium is a chemical element with the symbol Tc and atomic number 43. It is the lightest element whose isotopes are all radioactive. All available technetium is produced as a synthetic element. Naturally occurring technetium is a spontaneou ...
(Tc), rhenium
Rhenium is a chemical element with the symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-gray, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an estimated average concentration of 1 part per billion (ppb), rhenium is ...
(Re), and bohrium
Bohrium is a Synthetic element, synthetic chemical element with the Chemical symbol, symbol Bh and atomic number 107. It is named after Danish physicist Niels Bohr. As a synthetic element, it can be created in a laboratory but is not found in nat ...
(Bh). All known elements of group 7 are transition metals.
Like other groups, the members of this family show patterns in their electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon at ...
s, especially the outermost shells resulting in trends in chemical behavior.
Chemistry
Like other groups, the members of this family show patterns in itselectron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon at ...
, especially the outermost shells:
Bohrium has not been isolated in pure form.
History
Manganese was discovered much earlier than the other group 7 elements owing to its much larger abundance in nature. While Johan Gottlieb Gahn is credited with the isolation of manganese in 1774, Ignatius Kaim reported his production of manganese in his dissertation in 1771. Group 7 contains the two naturally occurring transition metals discovered last: technetium and rhenium. Rhenium was discovered when Masataka Ogawa found what he thought was element 43 in thorianite, but this was dismissed; recent studies by H. K. Yoshihara suggest that he discovered rhenium instead, a fact not realized at the time. Walter Noddack, Otto Berg, and Ida Tacke were the first to conclusively identify rhenium; it was thought they discovered element 43 as well, but as the experiment could not be replicated, it was dismissed. Technetium was formally discovered in December 1936 byCarlo Perrier Carlo Perrier (born July 7, 1886 in Turin , † May 22, 1948 in Genoa ) was an Italian mineralogist and chemist who did extensive research on the element technetium. With the discovery of technetium in 1937, he and Emilio Segrè filled the long-s ...
and Emilio Segré, who discovered technetium-95 and technetium-97
Technetium (43Tc) is one of the two elements with that have no stable isotopes; the other such element is promethium. – Elements marked with a * have no stable isotope: 43, 61, and 83 and up. It is primarily artificial, with only trace q ...
. Bohrium was discovered in 1981 by a team led by Peter Armbruster and Gottfried Münzenburg by bombarding bismuth-209 with chromium-54.
Occurrence and production
Manganese
Manganese comprises about 1000 ppm (0.1%) of theEarth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. ...
, the 12th most abundant of the crust's elements. Soil contains 7–9000 ppm of manganese with an average of 440 ppm. The atmosphere contains 0.01 μg/m3. Manganese occurs principally as pyrolusite
Pyrolusite is a mineral consisting essentially of manganese dioxide ( Mn O2) and is important as an ore of manganese.. It is a black, amorphous appearing mineral, often with a granular, fibrous, or columnar structure, sometimes forming reniform ...
( MnO2), braunite
Braunite is a silicate mineral containing both di- and tri- valent manganese with the chemical formula:
Mn2+Mn3+6 SiO4 Common impurities include iron, calcium, boron, barium, titanium, aluminium, and magnesium.
Braunite forms grey/black tetrago ...
(Mn2+Mn3+6)(SiO12), psilomelane , and to a lesser extent as rhodochrosite
Rhodochrosite is a manganese carbonate mineral with chemical composition MnCO3. In its (rare) pure form, it is typically a rose-red color, but impure specimens can be shades of pink to pale brown. It streaks white, and its Mohs hardness varies be ...
( MnCO3).
sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in sedimentary exhalative, Mississippi- ...
. Land-based resources are large but irregularly distributed. About 80% of the known world manganese resources are in South Africa; other important manganese deposits are in Ukraine, Australia, India, China, Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, ...
and Brazil. According to 1978 estimate, the ocean floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most ...
has 500 billion tons of manganese nodule
Polymetallic nodules, also called manganese nodules, are mineral concretions on the sea bottom formed of concentric layers of iron and manganese hydroxides around a core. As nodules can be found in vast quantities, and contain valuable metals, ...
s. Attempts to find economically viable methods of harvesting manganese nodules were abandoned in the 1970s.
In South Africa, most identified deposits are located near Hotazel in the Northern Cape Province, with a 2011 estimate of 15 billion tons. In 2011 South Africa produced 3.4 million tons, topping all other nations.
Manganese is mainly mined in South Africa, Australia, China, Gabon, Brazil, India, Kazakhstan, Ghana, Ukraine and Malaysia.
For the production of ferromanganese, the manganese ore is mixed with iron ore and carbon, and then reduced either in a blast furnace or in an electric arc furnace. The resulting ferromanganese has a manganese content of 30 to 80%. Pure manganese used for the production of iron-free alloys is produced by leaching manganese ore with sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
and a subsequent electrowinning process.
 A more progressive extraction process involves directly reducing (a low grade) manganese ore in a heap leach. This is done by percolating natural gas through the bottom of the heap; the natural gas provides the heat (needs to be at least 850 °C) and the reducing agent (carbon monoxide). This reduces all of the manganese ore to manganese oxide (MnO), which is a leachable form. The ore then travels through a
A more progressive extraction process involves directly reducing (a low grade) manganese ore in a heap leach. This is done by percolating natural gas through the bottom of the heap; the natural gas provides the heat (needs to be at least 850 °C) and the reducing agent (carbon monoxide). This reduces all of the manganese ore to manganese oxide (MnO), which is a leachable form. The ore then travels through a grinding
Grind is the cross-sectional shape of a blade.
Grind, grinds, or grinding may also refer to:
Grinding action
* Grinding (abrasive cutting), a method of crafting
* Grinding (dance), suggestive club dancing
* Grinding (video gaming), repetitive an ...
circuit to reduce the particle size of the ore to between 150 and 250 μm, increasing the surface area to aid leaching. The ore is then added to a leach tank of sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
and ferrous iron (Fe2+) in a 1.6:1 ratio. The iron reacts with the manganese dioxide
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-cel ...
(MnO2) to form iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH)) and elemental manganese (Mn):
This process yields approximately 92% recovery of the manganese. For further purification, the manganese can then be sent to an electrowinning facility.
In 1972 the CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
's Project Azorian, through billionaire Howard Hughes
Howard Robard Hughes Jr. (December 24, 1905 – April 5, 1976) was an American business magnate, record-setting pilot, engineer, film producer, and philanthropist, known during his lifetime as one of the most influential and richest people in th ...
, commissioned the ship '' Hughes Glomar Explorer'' with the cover story of harvesting manganese nodules from the sea floor. That triggered a rush of activity to collect manganese nodules, which was not actually practical. The real mission of ''Hughes Glomar Explorer'' was to raise a sunken Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
submarine, the K-129, with the goal of retrieving Soviet code books.
An abundant resource of manganese in the form of Mn nodules found on the ocean floor. These nodules, which are composed of 29% manganese, are located along the ocean floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most ...
and the potential impact of mining these nodules is being researched. Physical, chemical, and biological environmental impacts can occur due to this nodule mining disturbing the seafloor and causing sediment plumes to form. This suspension includes metals and inorganic nutrients, which can lead to contamination of the near-bottom waters from dissolved toxic compounds. Mn nodules are also the grazing grounds, living space, and protection for endo- and epifaunal systems. When theses nodules are removed, these systems are directly affected. Overall, this can cause species to leave the area or completely die off. Prior to the commencement of the mining itself, research is being conducted by United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
affiliated bodies and state-sponsored companies in an attempt to fully understand environmental impacts in the hopes of mitigating these impacts.
Technetium
Technetium was created by bombardingmolybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lea ...
atoms with deuteron
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium ato ...
s that had been accelerated by a device called a cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: Jan ...
. Technetium occurs naturally in the Earth's crust in minute concentrations of about 0.003 parts per trillion. Technetium is so rare because the half-lives
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable at ...
of 97Tc and 98Tc are only 4.2 million years. More than a thousand of such periods have passed since the formation of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
, so the probability of survival of even one atom of primordial technetium is effectively zero. However, small amounts exist as spontaneous fission product
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release ...
s in uranium ore
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within the Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the more common elements in the Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than gold. It ...
s. A kilogram of uranium contains an estimated 1 nanogram
To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following lists describe various mass levels between 10−59 kg and 1052 kg. The least massive thing listed here is a graviton, and the most massive thing is the observable universe. ...
(10−9 g) equivalent to ten trillion atoms of technetium. Some red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around o ...
stars with the spectral types S-, M-, and N contain a spectral absorption line indicating the presence of technetium. These red giants are known informally as technetium stars.
Rhenium
Rhenium is one of the rarest elements inEarth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. ...
with an average concentration of 1 ppb; other sources quote the number of 0.5 ppb making it the 77th most abundant element in Earth's crust. Rhenium is probably not found free in nature (its possible natural occurrence is uncertain), but occurs in amounts up to 0.2% in the mineral molybdenite
Molybdenite is a mineral of molybdenum disulfide, Mo S2. Similar in appearance and feel to graphite, molybdenite has a lubricating effect that is a consequence of its layered structure. The atomic structure consists of a sheet of molybdenum at ...
(which is primarily molybdenum disulfide
Molybdenum disulfide (or moly) is an inorganic compound composed of molybdenum and sulfur. Its chemical formula is .
The compound is classified as a transition metal dichalcogenide. It is a silvery black solid that occurs as the mineral molybdeni ...
), the major commercial source, although single molybdenite samples with up to 1.88% have been found. Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
has the world's largest rhenium reserves, part of the copper ore deposits, and was the leading producer as of 2005. It was only recently that the first rhenium mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ...
was found and described (in 1994), a rhenium sulfide mineral
The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S2−) or disulfide (S22−) as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, t ...
(ReS2) condensing from a fumarole
A fumarole (or fumerole) is a vent in the surface of the Earth or other rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcan ...
on Kudriavy volcano, Iturup
, other_names = russian: Итуру́п; ja, 択捉島
, location = Sea of Okhotsk
, coordinates =
, archipelago = Kuril Islands
, total_islands =
, major_islands =
, area_km2 = 3139
, length_km = 200
, width_km = 27
, coastline =
, highest_moun ...
island, in the Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the ...
. Kudriavy discharges up to 20–60 kg rhenium per year mostly in the form of rhenium disulfide. Named rheniite, this rare mineral commands high prices among collectors.
Most of the rhenium extracted comes from porphyry molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lea ...
deposits. These ores typically contain 0.001% to 0.2% rhenium. Roasting the ore volatilizes rhenium oxides. Rhenium(VII) oxide
Rhenium(VII) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Re2 O7. This yellowish solid is the anhydride of HOReO3. Perrhenic acid, Re2O7·2H2O, is closely related to Re2O7. Re2O7 is the raw material for all rhenium compounds, being the volat ...
and perrhenic acid readily dissolve in water; they are leached from flue dusts and gasses and extracted by precipitating with potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosphe ...
or ammonium chloride as the perrhenate The perrhenate ion is the anion with the formula , or a compound containing this ion. The perrhenate anion is tetrahedral, being similar in size and shape to perchlorate and the valence isoelectronic permanganate. The perrhenate anion is stable ove ...
salts, and purified by recrystallization. Total world production is between 40 and 50 tons/year; the main producers are in Chile, the United States, Peru, and Poland. Recycling of used Pt-Re catalyst and special alloys allow the recovery of another 10 tons per year. Prices for the metal rose rapidly in early 2008, from $1000–$2000 per kg in 2003–2006 to over $10,000 in February 2008. The metal form is prepared by reducing ammonium perrhenate
Ammonium perrhenate (APR) is the ammonium salt of perrhenic acid, NH4ReO4. It is the most common form in which rhenium is traded. It is a white salt; soluble in ethanol and water, and mildly soluble in NH4Cl. It was first described soon after the ...
with hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxi ...
at high temperatures:Glemser, O. (1963) "Ammonium Perrhenate" in ''Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry'', 2nd ed., G. Brauer (ed.), Academic Press, NY., Vol. 1, pp. 1476–85.
:2 NH4ReO4 + 7 H2 → 2 Re + 8 H2O + 2 NH3
:There are technologies for the associated extraction of rhenium from productive solutions of underground leaching of uranium ores.
Bohrium
Bohrium is a synthetic element that does not occur in nature. Very few atoms have been synthesized, and also due to its radioactivity, only limited research has been conducted. Bohrium is only produced in nuclear reactors and has never been isolated in pure form.Applications
 The ''facial'' isomer of both rhenium and manganese 2,2'-bipyridyl tricarbonyl halide complexes have been extensively researched as catalysts for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction due to their high selectivity and stability. They are commonly abbreviated as M(R-bpy)(CO)3X where M = Mn, Re; R-bpy = 4,4'-disubstituted 2,2'-bipyridine; and X = Cl, Br.
The ''facial'' isomer of both rhenium and manganese 2,2'-bipyridyl tricarbonyl halide complexes have been extensively researched as catalysts for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction due to their high selectivity and stability. They are commonly abbreviated as M(R-bpy)(CO)3X where M = Mn, Re; R-bpy = 4,4'-disubstituted 2,2'-bipyridine; and X = Cl, Br.
Rhenium
The catalytic activity of Re(bpy)(CO)3Cl for carbon dioxide reduction was first studied by Lehn et al. and Meyer et al. in 1984 and 1985, respectively. Re(R-bpy)(CO)3X complexes exclusively produce CO from CO2 reduction with Faradaic efficiencies of close to 100% even in solutions with high concentrations of water or Brønsted acids. The catalytic mechanism of Re(R-bpy)(CO)3X involves reduction of the complex twice and loss of the X ligand to generate a five-coordinate active species which binds CO2. These complexes will reduce CO2 both with and without an additional acid present; however, the presence of an acid increases catalytic activity. The high selectivity of these complexes to CO2 reduction over the competinghydrogen evolution reaction
Hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) is a chemical reaction that yields H2. The conversion of protons to H2 requires reducing equivalents and usually a catalyst. In nature, HER is catalyzed by hydrogenase enzymes. Commercial electrolyzers typically e ...
has been shown by density functional theory
Density-functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-body ...
studies to be related to the faster kinetics of CO2 binding compared to H+ binding.
Manganese
The rarity of rhenium has shifted research toward the manganese version of these catalysts as a more sustainable alternative. The first reports of catalytic activity of Mn(R-bpy)(CO)3Br towards CO2 reduction came from Chardon-Noblat and coworkers in 2011. Compared to Re analogs, Mn(R-bpy)(CO)3Br shows catalytic activity at lower overpotentials. The catalytic mechanism for Mn(R-bpy)(CO)3X is complex and depends on the steric profile of the bipyridine ligand. When R is not bulky, the catalyst dimerizes to form n(R-bpy)(CO)3sub>2 before forming the active species. When R is bulky, however, the complex forms the active species without dimerizing, reducing the overpotential of CO2 reduction by 200-300 mV. Unlike Re(R-bpy)(CO)3X, Mn(R-bpy)(CO)3X only reduces CO2 in the presence of an acid.Technetium

Technetium-99m
Technetium-99m (99mTc) is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99 (itself an isotope of technetium), symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical ...
("m" indicates that this is a metastable
In chemistry and physics, metastability denotes an intermediate energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's state of least energy.
A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of metastability. If the ball ...
nuclear isomer) is used in radioactive isotope medical tests
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic ...
. For example, Technetium-99m is a radioactive tracer
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tr ...
that medical imaging equipment tracks in the human body. It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 140 keV Kev can refer to:
Given name
* Kev Adams, French comedian, actor, screenwriter and film producer born Kevin Smadja in 1991
* Kevin Kev Carmody (born 1946), Indigenous Australian singer-songwriter
* Kev Coghlan (born 1988), Scottish Grand Prix mo ...
gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
s, and its half-life is 6.01 hours (meaning that about 94% of it decays to technetium-99 in 24 hours). The chemistry of technetium allows it to be bound to a variety of biochemical compounds, each of which determines how it is metabolized and deposited in the body, and this single isotope can be used for a multitude of diagnostic tests. More than 50 common radiopharmaceuticals
Radiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is ...
are based on technetium-99m for imaging and functional studies of the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in ...
, heart muscle, thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
, lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of ...
, liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
, gall bladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, althoug ...
, kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s, skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
, blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in th ...
, and tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s. Technetium-99m is also used in radioimaging.
The longer-lived isotope, technetium-95m with a half-life of 61 days, is used as a radioactive tracer
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tr ...
to study the movement of technetium in the environment and in plant and animal systems.
Technetium-99 decays almost entirely by beta decay, emitting beta particles with consistent low energies and no accompanying gamma rays. Moreover, its long half-life means that this emission decreases very slowly with time. It can also be extracted to a high chemical and isotopic purity from radioactive waste. For these reasons, it is a National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sc ...
(NIST) standard beta emitter, and is used for equipment calibration. Technetium-99 has also been proposed for optoelectronic devices and nanoscale
The nanoscopic scale (or nanoscale) usually refers to structures with a length scale applicable to nanotechnology, usually cited as 1–100 nanometers (nm). A nanometer is a billionth of a meter. The nanoscopic scale is (roughly speaking) a ...
nuclear batteries.
Like rhenium
Rhenium is a chemical element with the symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-gray, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an estimated average concentration of 1 part per billion (ppb), rhenium is ...
and palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself ...
, technetium can serve as a catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recy ...
. In processes such as the dehydrogenation
In chemistry, dehydrogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the removal of hydrogen, usually from an organic molecule. It is the reverse of hydrogenation. Dehydrogenation is important, both as a useful reaction and a serious problem. At ...
of isopropyl alcohol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. As an isopropyl group linked to a hydroxyl group (chemical formula ) it is the simple ...
, it is a far more effective catalyst than either rhenium or palladium. However, its radioactivity is a major problem in safe catalytic applications.
When steel is immersed in water, adding a small concentration (55 ppm) of potassium pertechnetate(VII) to the water protects the steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resist ...
from corrosion, even if the temperature is raised to . For this reason, pertechnetate has been used as an anodic corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engin ...
inhibitor for steel, although technetium's radioactivity poses problems that limit this application to self-contained systems. While (for example) can also inhibit corrosion, it requires a concentration ten times as high. In one experiment, a specimen of carbon steel was kept in an aqueous solution of pertechnetate for 20 years and was still uncorroded. The mechanism by which pertechnetate prevents corrosion is not well understood, but seems to involve the reversible formation of a thin surface layer ( passivation). One theory holds that the pertechnetate reacts with the steel surface to form a layer of technetium dioxide which prevents further corrosion; the same effect explains how iron powder can be used to remove pertechnetate from water. The effect disappears rapidly if the concentration of pertechnetate falls below the minimum concentration or if too high a concentration of other ions is added.
As noted, the radioactive nature of technetium (3 MBq/L at the concentrations required) makes this corrosion protection impractical in almost all situations. Nevertheless, corrosion protection by pertechnetate ions was proposed (but never adopted) for use in boiling water reactor
A boiling water reactor (BWR) is a type of light water nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. It is a design different from a Soviet graphite-moderated RBMK. It is the second most common type of electricity-generating nu ...
s.
Bohrium
Bohrium is a synthetic element and is too radioactive to be used in anything.Precautions
Although being an essential trace element in the human body, manganese can be somewhat toxic if ingested in higher amounts than normal. Technetium should be handled with care due to its radioactivity.Biological role and precautions
Only manganese has a role in the human body. It is an essential trace nutrient, with the body containing approximately 10milligram
The kilogram (also kilogramme) is the unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), having the unit symbol kg. It is a widely used measure in science, engineering and commerce worldwide, and is often simply called a kilo colloquiall ...
s at any given time, being mainly in the liver and kidneys. Many enzymes contain manganese, making it essential for life, and is also found in chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s. Technetium, rhenium, and bohrium have no known biological roles. Technetium is, however, used in radioimaging.
References
Bibliography
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Group 07 Groups (periodic table)