Grey heron on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The grey heron (''Ardea cinerea'') is a long-legged wading

 Herons are a fairly ancient lineage and first appeared in the fossil record in the Paleogene period; very few fossil herons have been found, though. By seven million years ago (the late
Herons are a fairly ancient lineage and first appeared in the fossil record in the Paleogene period; very few fossil herons have been found, though. By seven million years ago (the late
 The grey heron is a large bird, standing up to tall and measuring long with a wingspan. The body weight can range from . The plumage is largely ashy-grey above, and greyish-white below with some black on the flanks. Adults have the head and neck white with a broad black supercilium that terminates in the slender, dangling crest, and bluish-black streaks on the front of the neck. The scapular feathers are elongated and the feathers at the base of the neck are also somewhat elongated. Immature birds lack the dark stripe on the head and are generally duller in appearance than adults, with a grey head and neck, and a small, dark grey crest. The pinkish-yellow beak is long, straight and powerful, and is brighter in colour in breeding adults. The
The grey heron is a large bird, standing up to tall and measuring long with a wingspan. The body weight can range from . The plumage is largely ashy-grey above, and greyish-white below with some black on the flanks. Adults have the head and neck white with a broad black supercilium that terminates in the slender, dangling crest, and bluish-black streaks on the front of the neck. The scapular feathers are elongated and the feathers at the base of the neck are also somewhat elongated. Immature birds lack the dark stripe on the head and are generally duller in appearance than adults, with a grey head and neck, and a small, dark grey crest. The pinkish-yellow beak is long, straight and powerful, and is brighter in colour in breeding adults. The
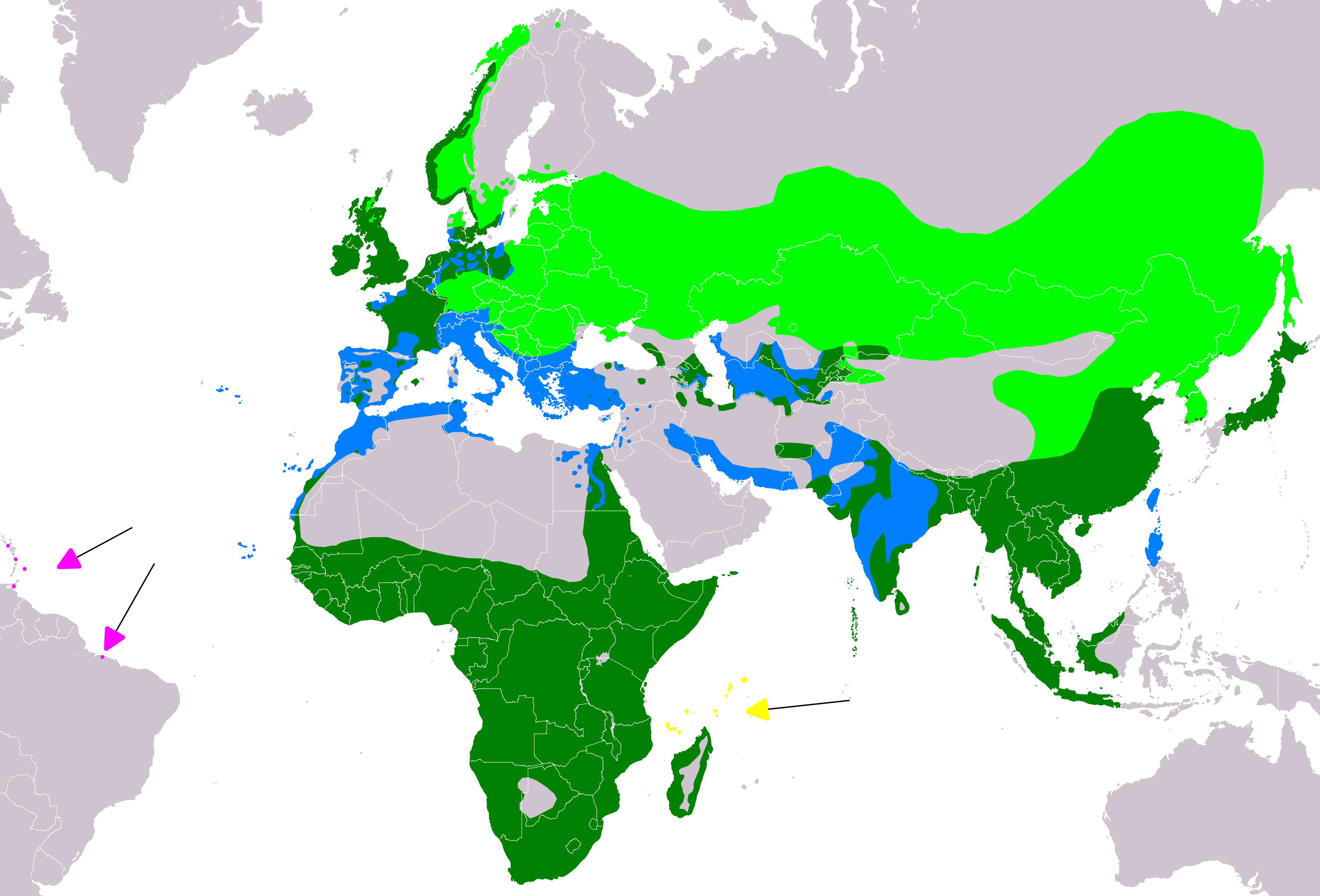 The grey heron has an extensive range throughout most of the
The grey heron has an extensive range throughout most of the
 Grey herons are
Grey herons are
 This species breeds in
This species breeds in  The clutch of eggs usually numbers three to five, though as few as two and as many as seven eggs have been recorded. The eggs have a matt surface and are greenish-blue, averaging . The eggs are normally laid at two-day intervals and incubation usually starts after the first or second egg has been laid. Both birds take part in incubation and the
The clutch of eggs usually numbers three to five, though as few as two and as many as seven eggs have been recorded. The eggs have a matt surface and are greenish-blue, averaging . The eggs are normally laid at two-day intervals and incubation usually starts after the first or second egg has been laid. Both birds take part in incubation and the
 In Ancient Egypt, the bird deity
In Ancient Egypt, the bird deity
bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
of the heron family, Ardeidae, native throughout temperate Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and also parts of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. It is resident in much of its range, but some populations from the more northern parts migrate southwards in autumn. A bird of wetland areas, it can be seen around lakes, rivers, ponds, marshes and on the sea coast. It feeds mostly on aquatic creatures which it catches after standing stationary beside or in the water or stalking its prey through the shallows.
Standing up to tall, adults weigh from . They have a white head and neck with a broad black stripe that extends from the eye to the black crest. The body and wings are grey above and the underparts are greyish-white, with some black on the flanks. The long, sharply pointed beak is pinkish-yellow and the legs are brown.
The birds breed colonially in spring in "heronries", usually building their nests high in trees. A clutch of usually three to five bluish-green eggs is laid. Both birds incubate the eggs for around 25 days, and then both feed the chicks, which fledge when 7-8 weeks old. Many juveniles do not survive their first winter, but if they do, they can expect to live for about 5 years.
In Ancient Egypt, the deity Bennu
Bennu is an ancient Egyptian deity linked with the Sun, creation, and rebirth. He may have been the original inspiration for the phoenix legends that developed in Greek mythology.
Roles
According to Egyptian mythology, Bennu was a self-create ...
was depicted as a heron in New Kingdom artwork.
In Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
, the heron was a bird of divination. Roast heron was once a specially prized dish; when George Neville became Archbishop of York
The archbishop of York is a senior bishop in the Church of England, second only to the archbishop of Canterbury. The archbishop is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of York and the metropolitan bishop of the province of York, which covers th ...
in 1465, 400 herons were served to the guests.
Taxonomy

 Herons are a fairly ancient lineage and first appeared in the fossil record in the Paleogene period; very few fossil herons have been found, though. By seven million years ago (the late
Herons are a fairly ancient lineage and first appeared in the fossil record in the Paleogene period; very few fossil herons have been found, though. By seven million years ago (the late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
), birds closely resembling modern forms and attributable to modern genera had appeared.
Herons are members of the family Ardeidae
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychu ...
, and the majority of extant species are in the subfamily Ardeinae and known as true or typical herons. This subfamily includes the herons and egret
Egrets ( ) are herons, generally long-legged wading birds, that have white or buff plumage, developing fine plumes (usually milky white) during the breeding season. Egrets are not a biologically distinct group from herons and have the same build ...
s, the green herons, the pond herons, the night herons, and a few other species. The grey heron belongs in this subfamily.
The grey heron was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his Nobility#Ennoblement, ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalise ...
in 1758 in the tenth edition of his '' Systema Naturae''. He placed it with the cattle egret and the great egret in the genus '' Ardea'' and coined the binomial name ''Ardea cinerea''. The scientific name comes the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''ardea'' meaning "heron" and ''cinereus'' meaning "ash-grey" or "ash-coloured".
Four subspecies are recognised:
* ''A. c. cinerea'' – Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
, 1758: nominate
Nomination is part of the process of selecting a candidate for either election to a public office, or the bestowing of an honor or award. A collection of nominees narrowed from the full list of candidates is a short list.
Political office
In the ...
, found in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, western Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
* ''A. c. jouyi'' – Clark, 1907: found in eastern Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
* ''A. c. firasa'' – Hartert, 1917: found in Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
* ''A. c. monicae'' – Jouanin & Roux, 1963: found on islands off Banc d'Arguin, Mauritania.
It is closely related and similar to the North American great blue heron (''Ardea herodias''), which differs in being larger, and having chestnut-brown flanks and thighs, and to the cocoi heron (''Ardea cocoi'') from South America with which it forms a superspecies. Some authorities believe that the subspecies ''A. c. monicae'' should be considered a separate species. It has been known to hybridise with the great egret (''Ardea alba''), the little egret (''Egretta garzetta''), the great blue heron and the purple heron (''Ardea purpurea''). The Australian white-faced heron
The white-faced heron (''Egretta novaehollandiae'') also known as the white-fronted heron, and incorrectly as the grey heron, or blue crane, is a common bird throughout most of Australasia, including New Guinea, the islands of Torres Strait, Ind ...
is often incorrectly called a grey heron. In Ireland, the grey heron is often colloquially called a "crane".
Description
 The grey heron is a large bird, standing up to tall and measuring long with a wingspan. The body weight can range from . The plumage is largely ashy-grey above, and greyish-white below with some black on the flanks. Adults have the head and neck white with a broad black supercilium that terminates in the slender, dangling crest, and bluish-black streaks on the front of the neck. The scapular feathers are elongated and the feathers at the base of the neck are also somewhat elongated. Immature birds lack the dark stripe on the head and are generally duller in appearance than adults, with a grey head and neck, and a small, dark grey crest. The pinkish-yellow beak is long, straight and powerful, and is brighter in colour in breeding adults. The
The grey heron is a large bird, standing up to tall and measuring long with a wingspan. The body weight can range from . The plumage is largely ashy-grey above, and greyish-white below with some black on the flanks. Adults have the head and neck white with a broad black supercilium that terminates in the slender, dangling crest, and bluish-black streaks on the front of the neck. The scapular feathers are elongated and the feathers at the base of the neck are also somewhat elongated. Immature birds lack the dark stripe on the head and are generally duller in appearance than adults, with a grey head and neck, and a small, dark grey crest. The pinkish-yellow beak is long, straight and powerful, and is brighter in colour in breeding adults. The iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
is yellow and the legs are brown and very long.
The main call is a loud croaking "fraaank", but a variety of guttural and raucous noises is heard at the breeding colony. The male uses an advertisement call to encourage a female to join him at the nest, and both sexes use various greeting calls after a pair bond has been established. A loud, harsh "schaah" is used by the male in driving other birds from the vicinity of the nest and a soft "gogogo" expresses anxiety, as when a predator is nearby or a human walks past the colony. The chicks utter loud chattering or ticking noises.
Distribution and habitat
 The grey heron has an extensive range throughout most of the
The grey heron has an extensive range throughout most of the Palearctic realm
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Sib ...
. The range of the nominate subspecies ''A. c. cinerea'' extends to 70° N in Norway and 66°N in Sweden, but otherwise its northerly limit is around 60°N across the rest of Europe and Asia eastwards as far as the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
. To the south, its range extends to northern Spain, France, central Italy, the Balkans, the Caucasus, Iraq, Iran, India, The Maldives and Myanmar (Burma). It is also present in Africa south of the Sahara Desert
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
, the Canary Islands, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and many of the Mediterranean Islands. It is replaced by ''A. c. jouyi'' in eastern Siberia, Mongolia, eastern China, Hainan, Japan, and Taiwan. In Madagascar and the Aldabra Islands, the subspecies ''A. c. firasa'' is found, while the subspecies ''A. c. monicae'' is restricted to Mauritania and offshore islands.
Over much of its range, the grey heron is resident, but birds from the more northerly parts of Europe migrate southwards, some remaining in Central and Southern Europe, others travelling on to Africa south of the Sahara Desert.
The grey heron is also known to be vagrant
Vagrancy is the condition of homelessness without regular employment or income. Vagrants (also known as bums, vagabonds, rogues, tramps or drifters) usually live in poverty and support themselves by begging, scavenging, petty theft, temporar ...
in the Caribbean, Bermuda, Iceland, Greenland, the Aleutian Islands, and Newfoundland, with a few confirmed sightings in other parts of North America including Nova Scotia and Nantucket.
Within its range, the grey heron can be found anywhere with suitable watery habitat that can supply its food. The water body needs to be either shallow enough, or have a shelving margin in it, which it can wade. Although most common in the lowlands, it also occurs in mountain tarns, lakes, reservoirs, large and small rivers, marshes, ponds, ditches, flooded areas, coastal lagoons, estuaries, and the sea shore. It sometimes forages away from water in pasture, and it has been recorded in desert areas, hunting for beetles and lizards. Breeding colonies are usually near feeding areas, but exceptionally may be up to away, and birds sometimes forage as much as from the nesting site.
Behaviour
The grey heron has a slow flight, with its long neck retracted (S-shaped). This is characteristic of herons andbittern
Bitterns are birds belonging to the subfamily Botaurinae of the heron family Ardeidae. Bitterns tend to be shorter-necked and more secretive than other members of the family. They were called ''hæferblæte'' in Old English; the word "bittern ...
s, and distinguishes them from storks, cranes, and spoonbills, which extend their necks. It flies with slow wing-beats and sometimes glides for short distances. It sometimes soars, circling to considerable heights, but not as often as the stork. In spring, and occasionally in autumn, birds may soar high above the heronry and chase each other, undertake aerial manoeuvres or swoop down towards the ground. The birds often perch in trees, but spend much time on the ground, striding about or standing still for long periods with an upright stance, often on a single leg.Diet and feeding
 Grey herons are
Grey herons are apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the highest trophic lev ...
in the aquatic ecosystems. Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
, amphibians, small mammals, crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can ...
s, and insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three ...
s are taken in shallow water with the heron's long bill. It has also been observed catching and killing juvenile birds such as duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
lings, and occasionally takes birds up to the size of a water rail
The water rail (''Rallus aquaticus'') is a bird of the Rallidae, rail family which breeds in well-vegetated wetlands across Europe, Asia and North Africa. Northern and eastern populations are bird migration, migratory, but this species is a perma ...
and white-throated rail. It may stand motionless in the shallows, or on a rock or sandbank beside the water, waiting for prey to come within striking distance. Alternatively, it moves slowly and stealthily through the water with its body less upright than when at rest and its neck curved in an "S". It is able to straighten its neck and strike with its bill very quickly.
Small fish are swallowed head first, and larger prey and eels are carried to the shore where they are subdued by being beaten on the ground or stabbed by the bill. They are then swallowed, or have hunks of flesh torn off. For prey such as small mammals and birds or ducklings, the prey is held by the neck and either drowned, suffocated, having its neck snapped with the heron's beak or by being bludgeoned against the ground or a nearby rock, before being swallowed whole. The bird regurgitates pellets of indigestible material such as fur, bones and the chitinous remains of insects. The main periods of hunting are around dawn and dusk, but it is also active at other times of day. At night it roosts in trees or on cliffs, where it tends to be gregarious.
Breeding
 This species breeds in
This species breeds in colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
known as heronries
A heronry, sometimes called a heron rookery, is a breeding ground for herons.
Notable heronries
Although their breeding territories are often on more protected small islands in lakes or retention ponds, herons breed in heronries (or also calle ...
, usually in high trees close to lakes, the seashore, or other wetlands. Other sites are sometimes chosen, and these include low trees and bushes, bramble patches, reed beds, heather clumps and cliff ledges. The same nest is used year after year until blown down; it starts as a small platform of sticks but expands into a bulky nest as more material is added in subsequent years. It may be lined with smaller twigs, strands of root or dead grasses, and in reed beds, it is built from dead reeds. The male usually collects the material, while the female constructs the nest. Breeding activities take place between February and June. When a bird arrives at the nest, a greeting ceremony occurs in which each partner raises and lowers its wings and plumes. In continental Europe, and elsewhere, nesting colonies sometimes include nests of the purple heron and other heron species.
Courtship involves the male calling from his chosen nesting site. On the arrival of the female, both birds participate in a stretching ceremony, in which each bird extends its neck vertically before bringing it backwards and downwards with the bill remaining vertical, simultaneously flexing its legs, before returning to its normal stance. The snapping ceremony is another behaviour where the neck is extended forward, the head is lowered to the level of the feet, and the mandibles are vigorously snapped together. This may be repeated 20-40 times. When the pairing is settled, the birds may caress each other by attending to the other bird's plumage. The male may then offer the female a stick, which she incorporates into the nest. At this, the male becomes excited, further preening the female and copulation takes place.
 The clutch of eggs usually numbers three to five, though as few as two and as many as seven eggs have been recorded. The eggs have a matt surface and are greenish-blue, averaging . The eggs are normally laid at two-day intervals and incubation usually starts after the first or second egg has been laid. Both birds take part in incubation and the
The clutch of eggs usually numbers three to five, though as few as two and as many as seven eggs have been recorded. The eggs have a matt surface and are greenish-blue, averaging . The eggs are normally laid at two-day intervals and incubation usually starts after the first or second egg has been laid. Both birds take part in incubation and the period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
lasts about 25 days. Both parents bring food for the young. At first, the chicks seize the adult's bill from the side and extract regurgitated food from it. Later, the adult disgorges the food at the nest and the chicks squabble for possession. They fledge at 7-8 weeks. Usually, a single brood is raised each year, but two broods have been recorded.
The oldest recorded bird lived for 23 years, but the average life expectancy in the wild is about 5 years. Only about a third of juveniles survive into their second year, many falling victim to predation.
City life
Grey herons have the ability to live in cities where habitats and nesting space are available. In theNetherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, it has established itself over the past decades in great numbers in urban environments. In cities such as Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
, they are ever present and well adapted to modern city life. They hunt as usual, but also visit street markets and snackbars. Some individuals make use of people feeding them at their homes or share the catch of recreational fishermen. Similar behaviour on a smaller scale has been reported in Ireland. Garden ponds stocked with ornamental fish are attractive to herons, and may provide young birds with a learning opportunity on how to catch easy prey.
Herons have been observed visiting water enclosures in zoos, such as spaces for penguins, otters, pelicans, and seals, and taking food meant for the animals on display.
Predators and parasites
Being large birds with powerful beaks, grey herons have few predators as adults, but the eggs and young are more vulnerable. The adult birds do not usually leave the nest unattended, but may be lured away by maraudingcrows
The Common Remotely Operated Weapon Station (CROWS) is a series of remote weapon stations used by the US military on its armored vehicles and ships. It allows weapon operators to engage targets without leaving the protection of their vehicle. ...
or kites
A kite is a tethered heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create lift and drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. Kites often have a bridle and tail to guide the face ...
. A dead grey heron found in the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
is thought to have been killed by an otter. The bird may have been weakened by harsh winter weather causing scarcity of its prey.
A study suggested that Central European grey herons host 29 species of parasitic worms
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as sc ...
. The dominant species consisted of ''Apharyngostrigea cornu'' (67% prevalence), ''Posthodiplostomum cuticola'' (41% prevalence), ''Echinochasmus beleocephalus'' (39% prevalence), ''Uroproctepisthmium bursicola'' (36% prevalence), ''Neogryporhynchus cheilancristrotus'' (31% prevalence), ''Desmidocercella numidica'' (29% prevalence), and ''Bilharziella polonica'' (5% prevalence). Juvenile grey herons were shown to host fewer species, but the intensity of infection was higher in the juveniles than in the adult herons. Of the digenean flatworms found in Central European grey herons, 52% of the species likely infected their definitive hosts outside Central Europe itself, in the premigratory, migratory, or wintering quarters, despite the fact that a substantial proportion of grey herons does not migrate to the south.
In human culture
 In Ancient Egypt, the bird deity
In Ancient Egypt, the bird deity Bennu
Bennu is an ancient Egyptian deity linked with the Sun, creation, and rebirth. He may have been the original inspiration for the phoenix legends that developed in Greek mythology.
Roles
According to Egyptian mythology, Bennu was a self-create ...
, associated with the sun, creation, and rebirth, was depicted as a heron in New Kingdom artwork.
In Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
, the heron was a bird of divination that gave an augury (sign of a coming event) by its call, like the raven, stork, and owl.
Roast heron was once a specially prized dish in Britain for special occasions such as state banquets. For the appointment of George Neville as Archbishop of York
The archbishop of York is a senior bishop in the Church of England, second only to the archbishop of Canterbury. The archbishop is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of York and the metropolitan bishop of the province of York, which covers th ...
in 1465, 400 herons were served to the guests. Young birds were still being shot and eaten in Romney Marsh
Romney Marsh is a sparsely populated wetland area in the counties of Kent and East Sussex in the south-east of England. It covers about . The Marsh has been in use for centuries, though its inhabitants commonly suffered from malaria until th ...
in 1896. Two grey herons feature in a stained-glass window of the church in Selborne, Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
.
The English surnames Earnshaw, Hernshaw, Herne, and Heron all derive from the heron, the suffix -shaw meaning a wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
, referring to a place where herons nested.
References
External links
* * {{Authority control grey heron grey heron Birds of Africa Birds of Eurasia grey heron grey heron Articles containing video clips Birds of Nepal ga:Corr réisc