grand antiprism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
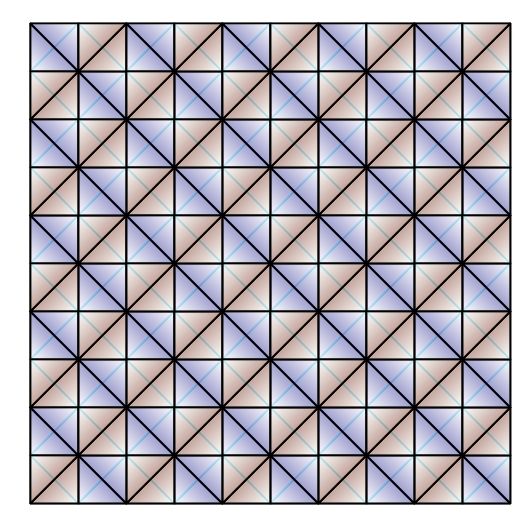 In addition the 300 tetrahedra can be partitioned into 10 disjoint Boerdijk–Coxeter helices of 30 cells each that close back on each other. The two pentagonal antiprism tubes, plus the 10 BC helices, form an irregular discrete
In addition the 300 tetrahedra can be partitioned into 10 disjoint Boerdijk–Coxeter helices of 30 cells each that close back on each other. The two pentagonal antiprism tubes, plus the 10 BC helices, form an irregular discrete
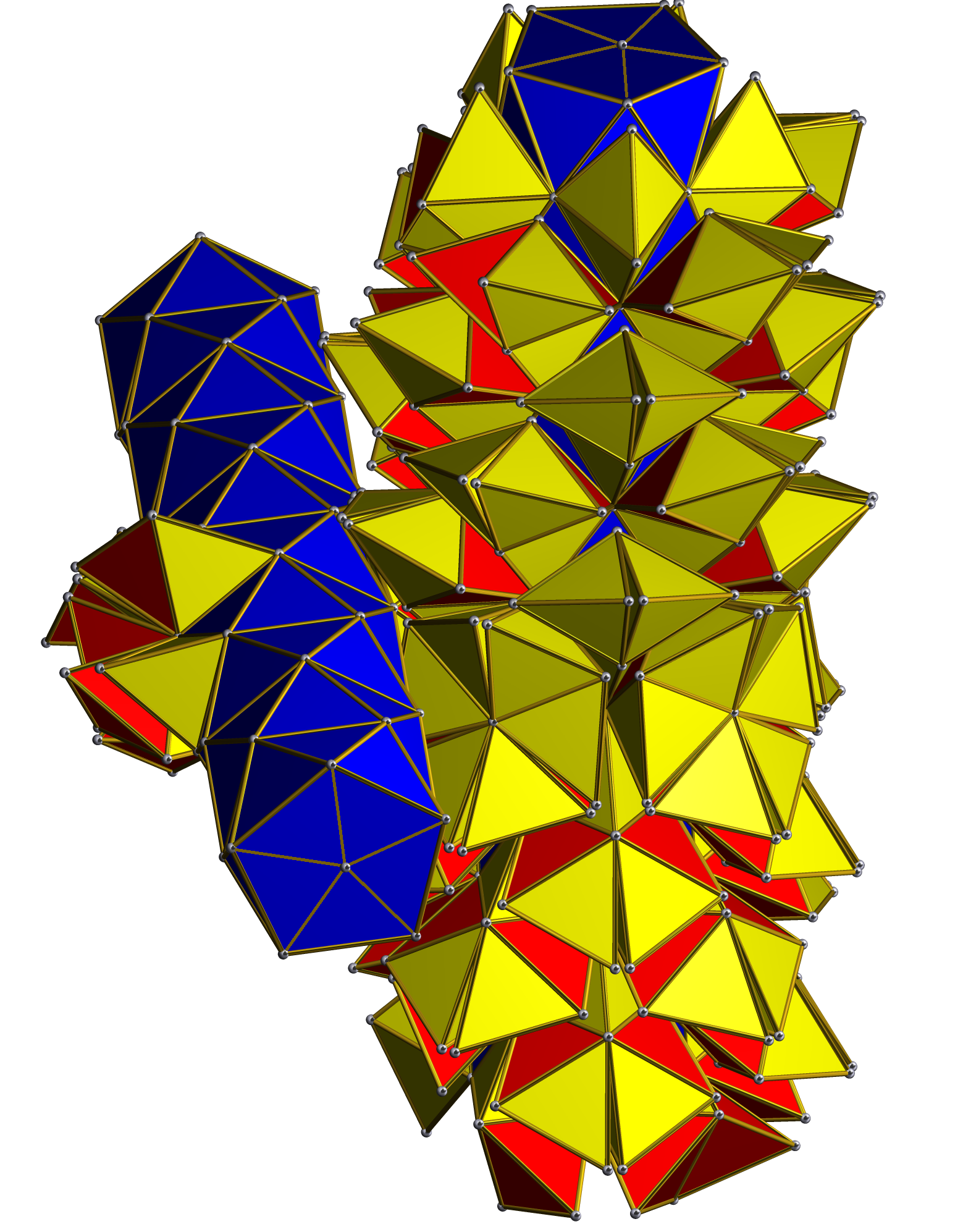 The grand antiprism can be constructed by ''diminishing'' the 600-cell: subtracting 20 pyramids whose bases are three-dimensional pentagonal antiprisms. Conversely, the two rings of pentagonal antiprisms in the grand antiprism may be triangulated by 10 tetrahedra joined to the triangular faces of each antiprism, and a circle of 5 tetrahedra between every pair of antiprisms, joining the 10 tetrahedra of each, yielding 150 tetrahedra per ring. These combined with the 300 tetrahedra that join the two rings together yield the 600 tetrahedra of the 600-cell.
This diminishing may be realized by removing two rings of 10 vertices from the 600-cell, each lying in mutually orthogonal planes. Each ring of removed vertices creates a stack of pentagonal antiprisms on the convex hull. This relationship is analogous to how a
The grand antiprism can be constructed by ''diminishing'' the 600-cell: subtracting 20 pyramids whose bases are three-dimensional pentagonal antiprisms. Conversely, the two rings of pentagonal antiprisms in the grand antiprism may be triangulated by 10 tetrahedra joined to the triangular faces of each antiprism, and a circle of 5 tetrahedra between every pair of antiprisms, joining the 10 tetrahedra of each, yielding 150 tetrahedra per ring. These combined with the 300 tetrahedra that join the two rings together yield the 600 tetrahedra of the 600-cell.
This diminishing may be realized by removing two rings of 10 vertices from the 600-cell, each lying in mutually orthogonal planes. Each ring of removed vertices creates a stack of pentagonal antiprisms on the convex hull. This relationship is analogous to how a
Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter
', edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ** (Paper 23) H.S.M. Coxeter, ''Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes II'', ath. Zeit. 188 (1985) 559-5912.8 The Grand Antiprism * * *
Grand Antiprism and Quaternions
Mehmet Koca, Mudhahir Al-Ajmi, Nazife Ozdes Koca (2009); Mehmet Koca et al. 2009 J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 42 495201
In the Belly of the Grand Antiprism
(middle section, describing the analogy with the icosahedron and the pentagonal antiprism) {{Polytopes 4-polytopes
geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
, the grand antiprism or pentagonal double antiprismoid is a uniform 4-polytope
In geometry, a uniform 4-polytope (or uniform polychoron) is a 4-dimensional polytope which is vertex-transitive and whose cells are uniform polyhedra, and faces are regular polygons.
There are 47 non-prismatic convex uniform 4-polytopes. There ...
(4-dimensional uniform polytope
In elementary geometry, a polytope is a geometric object with flat sides ('' faces''). Polytopes are the generalization of three-dimensional polyhedra to any number of dimensions. Polytopes may exist in any general number of dimensions as an ...
) bounded by 320 cells: 20 pentagonal antiprism
In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of 10 triangles for ...
s, and 300 tetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
. It is an anomalous, non-Wythoffian
In geometry, a Wythoff construction, named after mathematician Willem Abraham Wythoff, is a method for constructing a uniform polyhedron or plane tiling. It is often referred to as Wythoff's kaleidoscopic construction.
Construction process
...
uniform 4-polytope, discovered in 1965 by Conway and Guy. Topologically, under its highest symmetry, the pentagonal antiprism
In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of 10 triangles for ...
s have ''D5d'' symmetry and there are two types of tetrahedra, one with ''S4'' symmetry and one with ''Cs'' symmetry.
Alternate names
* Pentagonal double antiprismoid Norman W. Johnson * Gap (Jonathan Bowers: for grand antiprism)Structure
20 stacked pentagonal antiprisms occur in two disjoint rings of 10 antiprisms each. The antiprisms in each ring are joined to each other via their pentagonal faces. The two rings are mutually perpendicular, in a structure similar to aduoprism
In geometry of 4 dimensions or higher, a double prism or duoprism is a polytope resulting from the Cartesian product of two polytopes, each of two dimensions or higher. The Cartesian product of an -polytope and an -polytope is an -polytope, wher ...
.
The 300 tetrahedra join the two rings to each other, and are laid out in a 2-dimensional arrangement topologically equivalent to the 2-torus
In geometry, a torus (plural tori, colloquially donut or doughnut) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space about an axis that is coplanar with the circle.
If the axis of revolution does not tou ...
and the ridge of the duocylinder. These can be further divided into three sets. 100 face mate to one ring, 100 face mate to the other ring, and 100 are centered at the exact midpoint of the duocylinder and edge mate to both rings. This latter set forms a flat torus
In geometry, a torus (plural tori, colloquially donut or doughnut) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space about an axis that is coplanar with the circle.
If the axis of revolution does not tou ...
and can be "unrolled" into a flat 10×10 square array of tetrahedra that meet only at their edges and vertices. See figure below.  In addition the 300 tetrahedra can be partitioned into 10 disjoint Boerdijk–Coxeter helices of 30 cells each that close back on each other. The two pentagonal antiprism tubes, plus the 10 BC helices, form an irregular discrete
In addition the 300 tetrahedra can be partitioned into 10 disjoint Boerdijk–Coxeter helices of 30 cells each that close back on each other. The two pentagonal antiprism tubes, plus the 10 BC helices, form an irregular discrete Hopf fibration
In the mathematical field of differential topology, the Hopf fibration (also known as the Hopf bundle or Hopf map) describes a 3-sphere (a hypersphere in four-dimensional space) in terms of circles and an ordinary sphere. Discovered by Heinz H ...
of the grand antiprism that Hopf maps to the faces of a pentagonal antiprism. The two tubes map to the two pentagonal faces and the 10 BC helices map to the 10 triangular faces.
The structure of the grand antiprism is analogous to that of the 3-dimensional antiprism
In geometry, an antiprism or is a polyhedron composed of two parallel direct copies (not mirror images) of an polygon, connected by an alternating band of triangles. They are represented by the Conway notation .
Antiprisms are a subclass o ...
s. However, the grand antiprism is the only convex uniform analogue of the antiprism in 4 dimensions (although the 16-cell may be regarded as a regular analogue of the ''digonal antiprism
In geometry, an antiprism or is a polyhedron composed of two parallel direct copies (not mirror images) of an polygon, connected by an alternating band of triangles. They are represented by the Conway notation .
Antiprisms are a subclass o ...
''). The only nonconvex uniform 4-dimensional antiprism analogue uses pentagrammic crossed-antiprism
In geometry, the pentagrammic crossed-antiprism is one in an infinite set of nonconvex antiprisms formed by triangle sides and two regular star polygon caps, in this case two pentagrams.
It differs from the pentagrammic antiprism by having oppo ...
s instead of pentagonal antiprisms, and is called the '' pentagrammic double antiprismoid''.
Vertex figure
The vertex figure of the grand antiprism is asphenocorona
In geometry, the sphenocorona is one of the Johnson solids (). It is one of the elementary Johnson solids that do not arise from "cut and paste" manipulations of the Platonic and Archimedean solids.
Johnson uses the prefix ''spheno-'' to ref ...
or ''dissected regular icosahedron'': a regular icosahedron with two adjacent vertices removed. In their place 8 triangles are replaced by a pair of trapezoids, edge lengths φ, 1, 1, 1 (where φ is the golden ratio
In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Expressed algebraically, for quantities a and b with a > b > 0,
where the Greek letter phi ( ...
), joined together along their edge of length φ, to give a tetradecahedron
240px, A tetradecahedron with ''D2d'' symmetry, existing in the Weaire–Phelan structure
A tetradecahedron is a polyhedron with 14 faces. There are numerous topologically distinct forms of a tetradecahedron, with many constructible entirely wi ...
whose faces are the 2 trapezoid
A quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides is called a trapezoid () in American and Canadian English. In British and other forms of English, it is called a trapezium ().
A trapezoid is necessarily a Convex polygon, convex quadri ...
s and the 12 remaining equilateral triangle
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each oth ...
s.
Construction
 The grand antiprism can be constructed by ''diminishing'' the 600-cell: subtracting 20 pyramids whose bases are three-dimensional pentagonal antiprisms. Conversely, the two rings of pentagonal antiprisms in the grand antiprism may be triangulated by 10 tetrahedra joined to the triangular faces of each antiprism, and a circle of 5 tetrahedra between every pair of antiprisms, joining the 10 tetrahedra of each, yielding 150 tetrahedra per ring. These combined with the 300 tetrahedra that join the two rings together yield the 600 tetrahedra of the 600-cell.
This diminishing may be realized by removing two rings of 10 vertices from the 600-cell, each lying in mutually orthogonal planes. Each ring of removed vertices creates a stack of pentagonal antiprisms on the convex hull. This relationship is analogous to how a
The grand antiprism can be constructed by ''diminishing'' the 600-cell: subtracting 20 pyramids whose bases are three-dimensional pentagonal antiprisms. Conversely, the two rings of pentagonal antiprisms in the grand antiprism may be triangulated by 10 tetrahedra joined to the triangular faces of each antiprism, and a circle of 5 tetrahedra between every pair of antiprisms, joining the 10 tetrahedra of each, yielding 150 tetrahedra per ring. These combined with the 300 tetrahedra that join the two rings together yield the 600 tetrahedra of the 600-cell.
This diminishing may be realized by removing two rings of 10 vertices from the 600-cell, each lying in mutually orthogonal planes. Each ring of removed vertices creates a stack of pentagonal antiprisms on the convex hull. This relationship is analogous to how a pentagonal antiprism
In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of 10 triangles for ...
can be constructed from an icosahedron by removing two opposite vertices, thereby removing 5 triangles from the opposite 'poles' of the icosahedron, leaving the 10 equatorial triangles and two pentagons on the top and bottom.
(The snub 24-cell
In geometry, the snub 24-cell or snub disicositetrachoron is a convex uniform 4-polytope composed of 120 regular tetrahedral and 24 icosahedral cells. Five tetrahedra and three icosahedra meet at each vertex. In total it has 480 triangular faces ...
can also be constructed by another diminishing of the 600-cell, removing 24 icosahedral pyramids. Equivalently, this may be realized as taking the convex hull of the vertices remaining after 24 vertices, corresponding to those of an inscribed 24-cell, are removed from the 600-cell.)
Alternatively, it can also be constructed from the decagonal ditetragoltriate (the convex hull of two perpendicular nonuniform 10-10 duoprisms where the ratio of the two decagons are in the golden ratio
In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Expressed algebraically, for quantities a and b with a > b > 0,
where the Greek letter phi ( ...
) via an alternation process. The decagonal prism
In geometry, the decagonal prism is the eighth in the infinite set of prisms, formed by ten square side faces and two regular decagon caps. With twelve faces, it is one of many nonregular dodecahedra. The decagonal prism has 12 faces, 30 edges, an ...
s alternate into pentagonal antiprism
In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of 10 triangles for ...
s, the rectangular trapezoprisms alternate into tetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
with two new regular tetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
(representing a non-corealmic triangular bipyramid
In geometry, the triangular bipyramid (or dipyramid) is a type of hexahedron, being the first in the infinite set of face-transitive bipyramids. It is the dual of the triangular prism with 6 isosceles triangle faces.
As the name suggests, i ...
) created at the deleted vertices. This is the only uniform solution for the p-gonal double antiprismoids alongside its conjugate, the pentagrammic double antiprismoid from the decagrammic ditetragoltriate.
Projections
These are two perspective projections, projecting the polytope into ahypersphere
In mathematics, an -sphere or a hypersphere is a topological space that is homeomorphic to a ''standard'' -''sphere'', which is the set of points in -dimensional Euclidean space that are situated at a constant distance from a fixed point, call ...
, and applying a stereographic projection into 3-space.
See also
*600-cell
In geometry, the 600-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is also known as the C600, hexacosichoron and hexacosihedroid. It is also called a tetraplex (abbreviated from ...
* Snub 24-cell
In geometry, the snub 24-cell or snub disicositetrachoron is a convex uniform 4-polytope composed of 120 regular tetrahedral and 24 icosahedral cells. Five tetrahedra and three icosahedra meet at each vertex. In total it has 480 triangular faces ...
* Uniform 4-polytope
In geometry, a uniform 4-polytope (or uniform polychoron) is a 4-dimensional polytope which is vertex-transitive and whose cells are uniform polyhedra, and faces are regular polygons.
There are 47 non-prismatic convex uniform 4-polytopes. There ...
* Duoprism
In geometry of 4 dimensions or higher, a double prism or duoprism is a polytope resulting from the Cartesian product of two polytopes, each of two dimensions or higher. The Cartesian product of an -polytope and an -polytope is an -polytope, wher ...
* Duocylinder
The duocylinder, also called the double cylinder or the bidisc, is a geometric object embedded in 4- dimensional Euclidean space, defined as the Cartesian product of two disks of respective radii ''r''1 and ''r''2:
:D = \left\
It is analogo ...
Notes
References
*Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter
', edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ** (Paper 23) H.S.M. Coxeter, ''Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes II'', ath. Zeit. 188 (1985) 559-5912.8 The Grand Antiprism * * *
John H. Conway
John Horton Conway (26 December 1937 – 11 April 2020) was an English people, English mathematician active in the theory of finite groups, knot theory, number theory, combinatorial game theory and coding theory. He also made contributions to ...
, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strass, ''The Symmetries of Things'' 2008, (Chapter 26) The Grand Antiprism
Grand Antiprism and Quaternions
Mehmet Koca, Mudhahir Al-Ajmi, Nazife Ozdes Koca (2009); Mehmet Koca et al. 2009 J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 42 495201
External links
In the Belly of the Grand Antiprism
(middle section, describing the analogy with the icosahedron and the pentagonal antiprism) {{Polytopes 4-polytopes