global maximum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In

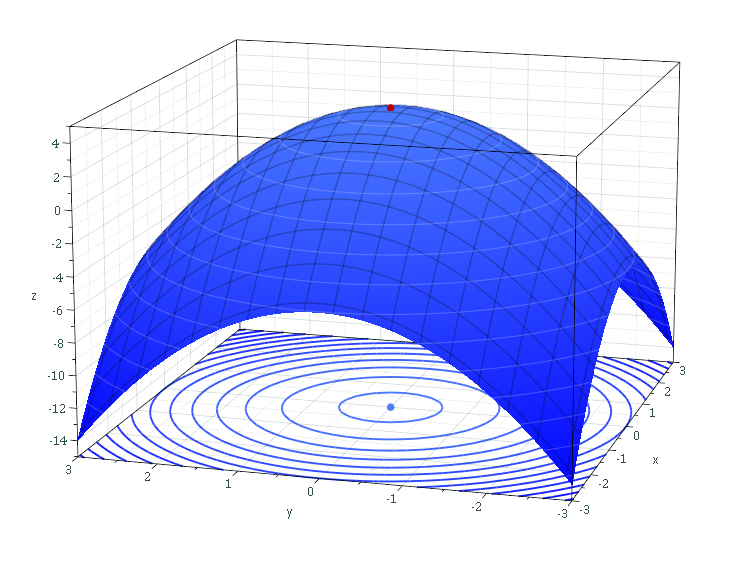
 For functions of more than one variable, similar conditions apply. For example, in the (enlargeable) figure on the right, the necessary conditions for a ''local'' maximum are similar to those of a function with only one variable. The first partial derivatives as to ''z'' (the variable to be maximized) are zero at the maximum (the glowing dot on top in the figure). The second partial derivatives are negative. These are only necessary, not sufficient, conditions for a local maximum, because of the possibility of a saddle point. For use of these conditions to solve for a maximum, the function ''z'' must also be differentiable throughout. The second partial derivative test can help classify the point as a relative maximum or relative minimum.
In contrast, there are substantial differences between functions of one variable and functions of more than one variable in the identification of global extrema. For example, if a bounded differentiable function ''f'' defined on a closed interval in the real line has a single critical point, which is a local minimum, then it is also a global minimum (use the intermediate value theorem and Rolle's theorem to prove this by
For functions of more than one variable, similar conditions apply. For example, in the (enlargeable) figure on the right, the necessary conditions for a ''local'' maximum are similar to those of a function with only one variable. The first partial derivatives as to ''z'' (the variable to be maximized) are zero at the maximum (the glowing dot on top in the figure). The second partial derivatives are negative. These are only necessary, not sufficient, conditions for a local maximum, because of the possibility of a saddle point. For use of these conditions to solve for a maximum, the function ''z'' must also be differentiable throughout. The second partial derivative test can help classify the point as a relative maximum or relative minimum.
In contrast, there are substantial differences between functions of one variable and functions of more than one variable in the identification of global extrema. For example, if a bounded differentiable function ''f'' defined on a closed interval in the real line has a single critical point, which is a local minimum, then it is also a global minimum (use the intermediate value theorem and Rolle's theorem to prove this by
Thomas Simpson's work on Maxima and Minima
a
ConvergenceApplication of Maxima and Minima with sub pages of solved problems
* {{Calculus topics Calculus Mathematical analysis Mathematical optimization Superlatives
mathematical analysis
Analysis is the branch of mathematics dealing with continuous functions, limits, and related theories, such as differentiation, integration, measure, infinite sequences, series, and analytic functions.
These theories are usually studied ...
, the maxima and minima (the respective plurals of maximum and minimum) of a function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
, known collectively as extrema (the plural of extremum), are the largest and smallest value of the function, either within a given range
Range may refer to:
Geography
* Range (geographic), a chain of hills or mountains; a somewhat linear, complex mountainous or hilly area (cordillera, sierra)
** Mountain range, a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
* Range, a term used to i ...
(the ''local'' or ''relative'' extrema), or on the entire domain (the ''global'' or ''absolute'' extrema). Pierre de Fermat was one of the first mathematicians to propose a general technique, adequality Adequality is a technique developed by Pierre de Fermat in his treatise ''Methodus ad disquirendam maximam et minimam''
, for finding the maxima and minima of functions.
As defined in set theory, the maximum and minimum of a set
Set, The Set, SET or SETS may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Mathematics
*Set (mathematics), a collection of elements
*Category of sets, the category whose objects and morphisms are sets and total functions, respectively
Electro ...
are the greatest and least elements
In mathematics, especially in order theory, the greatest element of a subset S of a partially ordered set (poset) is an element of S that is greater than every other element of S. The term least element is defined dually, that is, it is an el ...
in the set, respectively. Unbounded infinite sets, such as the set of real numbers, have no minimum or maximum.
Definition
A real-valuedfunction
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
''f'' defined on a domain ''X'' has a global (or absolute) maximum point at ''x''∗, if for all ''x'' in ''X''. Similarly, the function has a global (or absolute) minimum point at ''x''∗, if for all ''x'' in ''X''. The value of the function at a maximum point is called the of the function, denoted , and the value of the function at a minimum point is called the of the function. Symbolically, this can be written as follows:
: is a global maximum point of function if
The definition of global minimum point also proceeds similarly.
If the domain ''X'' is a metric space
In mathematics, a metric space is a set together with a notion of '' distance'' between its elements, usually called points. The distance is measured by a function called a metric or distance function. Metric spaces are the most general set ...
, then ''f'' is said to have a local (or relative) maximum point at the point ''x''∗, if there exists some ''ε'' > 0 such that for all ''x'' in ''X'' within distance ''ε'' of ''x''∗. Similarly, the function has a local minimum point at ''x''∗, if ''f''(''x''∗) ≤ ''f''(''x'') for all ''x'' in ''X'' within distance ''ε'' of ''x''∗. A similar definition can be used when ''X'' is a topological space
In mathematics, a topological space is, roughly speaking, a geometrical space in which closeness is defined but cannot necessarily be measured by a numeric distance. More specifically, a topological space is a set whose elements are called po ...
, since the definition just given can be rephrased in terms of neighbourhoods. Mathematically, the given definition is written as follows:
:Let be a metric space and function . Then is a local maximum point of function if such that
The definition of local minimum point can also proceed similarly.
In both the global and local cases, the concept of a can be defined. For example, ''x''∗ is a if for all ''x'' in ''X'' with , we have , and ''x''∗ is a if there exists some such that, for all ''x'' in ''X'' within distance ''ε'' of ''x''∗ with , we have . Note that a point is a strict global maximum point if and only if it is the unique global maximum point, and similarly for minimum points.
A continuous real-valued function with a compact
Compact as used in politics may refer broadly to a pact or treaty; in more specific cases it may refer to:
* Interstate compact
* Blood compact, an ancient ritual of the Philippines
* Compact government, a type of colonial rule utilized in Britis ...
domain always has a maximum point and a minimum point. An important example is a function whose domain is a closed and bounded interval of real numbers (see the graph above).
Search
Finding global maxima and minima is the goal of mathematical optimization. If a function is continuous on a closed interval, then by theextreme value theorem
In calculus, the extreme value theorem states that if a real-valued function f is continuous on the closed interval ,b/math>, then f must attain a maximum and a minimum, each at least once. That is, there exist numbers c and d in ,b/math> suc ...
, global maxima and minima exist. Furthermore, a global maximum (or minimum) either must be a local maximum (or minimum) in the interior of the domain, or must lie on the boundary of the domain. So a method of finding a global maximum (or minimum) is to look at all the local maxima (or minima) in the interior, and also look at the maxima (or minima) of the points on the boundary, and take the largest (or smallest) one.
For differentiable functions
In mathematics, a differentiable function of one real variable is a function whose derivative exists at each point in its domain. In other words, the graph of a differentiable function has a non- vertical tangent line at each interior point in i ...
, Fermat's theorem states that local extrema in the interior of a domain must occur at critical points (or points where the derivative equals zero). However, not all critical points are extrema. One can distinguish whether a critical point is a local maximum or local minimum by using the first derivative test
In calculus, a derivative test uses the derivatives of a function to locate the critical points of a function and determine whether each point is a local maximum, a local minimum, or a saddle point. Derivative tests can also give information abou ...
, second derivative test
In calculus, a derivative test uses the derivatives of a function to locate the critical points of a function and determine whether each point is a local maximum, a local minimum, or a saddle point. Derivative tests can also give information abou ...
, or higher-order derivative test
In calculus, a derivative test uses the derivatives of a function to locate the critical points of a function and determine whether each point is a local maximum, a local minimum, or a saddle point. Derivative tests can also give information abou ...
, given sufficient differentiability.
For any function that is defined piecewise
In mathematics, a piecewise-defined function (also called a piecewise function, a hybrid function, or definition by cases) is a function defined by multiple sub-functions, where each sub-function applies to a different interval in the domain. ...
, one finds a maximum (or minimum) by finding the maximum (or minimum) of each piece separately, and then seeing which one is largest (or smallest).
Examples
For a practical example, assume a situation where someone has feet of fencing and is trying to maximize the square footage of a rectangular enclosure, where is the length, is the width, and is the area: : : : : : The derivative with respect to is: : Setting this equal to : : : reveals that is our only critical point. Now retrieve the endpoints by determining the interval to which is restricted. Since width is positive, then , and since that implies that Plug in critical point as well as endpoints and into and the results are and respectively. Therefore, the greatest area attainable with a rectangle of feet of fencing isFunctions of more than one variable


 For functions of more than one variable, similar conditions apply. For example, in the (enlargeable) figure on the right, the necessary conditions for a ''local'' maximum are similar to those of a function with only one variable. The first partial derivatives as to ''z'' (the variable to be maximized) are zero at the maximum (the glowing dot on top in the figure). The second partial derivatives are negative. These are only necessary, not sufficient, conditions for a local maximum, because of the possibility of a saddle point. For use of these conditions to solve for a maximum, the function ''z'' must also be differentiable throughout. The second partial derivative test can help classify the point as a relative maximum or relative minimum.
In contrast, there are substantial differences between functions of one variable and functions of more than one variable in the identification of global extrema. For example, if a bounded differentiable function ''f'' defined on a closed interval in the real line has a single critical point, which is a local minimum, then it is also a global minimum (use the intermediate value theorem and Rolle's theorem to prove this by
For functions of more than one variable, similar conditions apply. For example, in the (enlargeable) figure on the right, the necessary conditions for a ''local'' maximum are similar to those of a function with only one variable. The first partial derivatives as to ''z'' (the variable to be maximized) are zero at the maximum (the glowing dot on top in the figure). The second partial derivatives are negative. These are only necessary, not sufficient, conditions for a local maximum, because of the possibility of a saddle point. For use of these conditions to solve for a maximum, the function ''z'' must also be differentiable throughout. The second partial derivative test can help classify the point as a relative maximum or relative minimum.
In contrast, there are substantial differences between functions of one variable and functions of more than one variable in the identification of global extrema. For example, if a bounded differentiable function ''f'' defined on a closed interval in the real line has a single critical point, which is a local minimum, then it is also a global minimum (use the intermediate value theorem and Rolle's theorem to prove this by contradiction
In traditional logic, a contradiction occurs when a proposition conflicts either with itself or established fact. It is often used as a tool to detect disingenuous beliefs and bias. Illustrating a general tendency in applied logic, Aristotle's ...
). In two and more dimensions, this argument fails. This is illustrated by the function
:
whose only critical point is at (0,0), which is a local minimum with ''f''(0,0) = 0. However, it cannot be a global one, because ''f''(2,3) = −5.
Maxima or minima of a functional
If the domain of a function for which an extremum is to be found consists itself of functions (i.e. if an extremum is to be found of afunctional
Functional may refer to:
* Movements in architecture:
** Functionalism (architecture)
** Form follows function
* Functional group, combination of atoms within molecules
* Medical conditions without currently visible organic basis:
** Functional sy ...
), then the extremum is found using the calculus of variations
The calculus of variations (or Variational Calculus) is a field of mathematical analysis that uses variations, which are small changes in functions
and functionals, to find maxima and minima of functionals: mappings from a set of functions t ...
.
In relation to sets
Maxima and minima can also be defined for sets. In general, if an ordered set ''S'' has a greatest element ''m'', then ''m'' is a maximal element of the set, also denoted as . Furthermore, if ''S'' is a subset of an ordered set ''T'' and ''m'' is the greatest element of ''S'' with (respect to order induced by ''T''), then ''m'' is a least upper bound of ''S'' in ''T''. Similar results hold for least element, minimal element and greatest lower bound. The maximum and minimum function for sets are used in databases, and can be computed rapidly, since the maximum (or minimum) of a set can be computed from the maxima of a partition; formally, they are self-decomposable aggregation function
In database management, an aggregate function or aggregation function is a function where the values of multiple rows are grouped together to form a single summary value.
Common aggregate functions include:
* Average (i.e., arithmetic mean)
* ...
s.
In the case of a general partial order, the least element (i.e., one that is smaller than all others) should not be confused with a minimal element (nothing is smaller). Likewise, a greatest element of a partially ordered set
In mathematics, especially order theory, a partially ordered set (also poset) formalizes and generalizes the intuitive concept of an ordering, sequencing, or arrangement of the elements of a set. A poset consists of a set together with a binary ...
(poset) is an upper bound
In mathematics, particularly in order theory, an upper bound or majorant of a subset of some preordered set is an element of that is greater than or equal to every element of .
Dually, a lower bound or minorant of is defined to be an eleme ...
of the set which is contained within the set, whereas a maximal element ''m'' of a poset ''A'' is an element of ''A'' such that if ''m'' ≤ ''b'' (for any ''b'' in ''A''), then ''m'' = ''b''. Any least element or greatest element of a poset is unique, but a poset can have several minimal or maximal elements. If a poset has more than one maximal element, then these elements will not be mutually comparable.
In a totally ordered set, or ''chain'', all elements are mutually comparable, so such a set can have at most one minimal element and at most one maximal element. Then, due to mutual comparability, the minimal element will also be the least element, and the maximal element will also be the greatest element. Thus in a totally ordered set, we can simply use the terms ''minimum'' and ''maximum''.
If a chain is finite, then it will always have a maximum and a minimum. If a chain is infinite, then it need not have a maximum or a minimum. For example, the set of natural numbers has no maximum, though it has a minimum. If an infinite chain ''S'' is bounded, then the closure ''Cl''(''S'') of the set occasionally has a minimum and a maximum, in which case they are called the greatest lower bound and the least upper bound of the set ''S'', respectively.
See also
* Arg max *Derivative test
In calculus, a derivative test uses the derivatives of a function to locate the critical points of a function and determine whether each point is a local maximum, a local minimum, or a saddle point. Derivative tests can also give information abou ...
*Infimum and supremum
In mathematics, the infimum (abbreviated inf; plural infima) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is a greatest element in P that is less than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. Consequently, the term ''greatest lo ...
* Limit superior and limit inferior
* Mechanical equilibrium
*Mex (mathematics) In mathematics, the mex of a subset of a well-ordered set is the smallest value from the whole set that does not belong to the subset. That is, it is the minimum value of the complement set. The name "mex" is shorthand for "''m''inimum ''ex''cluded ...
* Sample maximum and minimum
* Saddle point
References
External links
Thomas Simpson's work on Maxima and Minima
a
Convergence
* {{Calculus topics Calculus Mathematical analysis Mathematical optimization Superlatives