Global Economy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The world economy or global economy is the

 * GDP (GWP) (gross world product): (purchasing power parity exchange rates) – $59.38 trillion (2005 est.), $51.48 trillion (2004), $23 trillion (2002). The GWP is the combined gross national income of all the countries in the world. When calculating the GWP, add GDP of all countries. Also, GWP shows that imports and exports are equal. Because imports and exports balance exactly when considering the whole world:, this also equals the total global gross domestic product (GDP). According to the World Bank, the 2013 nominal GWP was approximately US$75.59 trillion. In 2017, according to the CIA's World Factbook, the GWP was around US$80.27 trillion in nominal terms and totaled approximately 127.8 trillion international dollars in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). The per capita PPP GWP in 2017 was approximately Int$17,500 according to the World Factbook.
* GDP (GWP) ( gross world product): (market exchange rates) – $60.69 trillion (2008). The market exchange rates increased from 1990 to 2008. The reason for this increase is the world's advancement in terms of technology.
* GDP (real growth rate): The following part shows the GDP growth rate and the expected value after one year.
** Developed Economies. A developed country, industrialized country, more developed country (MDC), or more economically developed country (MEDC), is a sovereign state that has a developed economy and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. The GDP of the developed countries is predicted to fall from 2.2% in 2017 to 2.0% in 2018 due to the fall in dollar value.
** Developing Countries. A developing country is a country with a less developed industrial base (industries) and a low Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. A nation's GDP per capita, compared with other nations, can also be a reference point. In general, the United Nations accepts any country's claim of itself being "developing". The GDP of the developing countries is expected to rise from 4.3% in 2017 to 4.6% in 2018 due to political stability in those countries and advancement in technology.
** Least developed countries. The least developed countries (LDCs) is a list of developing countries that, according to the United Nations, exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development, with the lowest Human Development Index ratings of all countries in the world. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed by the UN in its resolution 2768 (XXVI) of 18 November 1971. This is a group of countries that are expected to improve their GDP from 4.8% in 2017 to 5.4% in 2018. The predicted growth is associated advancement in technology and industrialization of those countries for the past decade.
* GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $9,300, €7,500 (2005 est.), $8,200, €6,800 (92) (2003), $7,900, €5,000 (2002)
* World
* GDP (GWP) (gross world product): (purchasing power parity exchange rates) – $59.38 trillion (2005 est.), $51.48 trillion (2004), $23 trillion (2002). The GWP is the combined gross national income of all the countries in the world. When calculating the GWP, add GDP of all countries. Also, GWP shows that imports and exports are equal. Because imports and exports balance exactly when considering the whole world:, this also equals the total global gross domestic product (GDP). According to the World Bank, the 2013 nominal GWP was approximately US$75.59 trillion. In 2017, according to the CIA's World Factbook, the GWP was around US$80.27 trillion in nominal terms and totaled approximately 127.8 trillion international dollars in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). The per capita PPP GWP in 2017 was approximately Int$17,500 according to the World Factbook.
* GDP (GWP) ( gross world product): (market exchange rates) – $60.69 trillion (2008). The market exchange rates increased from 1990 to 2008. The reason for this increase is the world's advancement in terms of technology.
* GDP (real growth rate): The following part shows the GDP growth rate and the expected value after one year.
** Developed Economies. A developed country, industrialized country, more developed country (MDC), or more economically developed country (MEDC), is a sovereign state that has a developed economy and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. The GDP of the developed countries is predicted to fall from 2.2% in 2017 to 2.0% in 2018 due to the fall in dollar value.
** Developing Countries. A developing country is a country with a less developed industrial base (industries) and a low Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. A nation's GDP per capita, compared with other nations, can also be a reference point. In general, the United Nations accepts any country's claim of itself being "developing". The GDP of the developing countries is expected to rise from 4.3% in 2017 to 4.6% in 2018 due to political stability in those countries and advancement in technology.
** Least developed countries. The least developed countries (LDCs) is a list of developing countries that, according to the United Nations, exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development, with the lowest Human Development Index ratings of all countries in the world. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed by the UN in its resolution 2768 (XXVI) of 18 November 1971. This is a group of countries that are expected to improve their GDP from 4.8% in 2017 to 5.4% in 2018. The predicted growth is associated advancement in technology and industrialization of those countries for the past decade.
* GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $9,300, €7,500 (2005 est.), $8,200, €6,800 (92) (2003), $7,900, €5,000 (2002)
* World
* Derivatives exchange traded outstanding notional amount: $82 trillion (June 2011)
* Global

 *
*
 * Yearly
* Yearly
4,263,367,600 (2008) * Telephones – mobile cellular: 3,300,000,000 (Nov. 2007)global cellphone penetration reaches 50 percent
* Internet Service Providers (ISPs): 10,350 (2000 est.) *
, 360,985,492 (31 December 2000)
 * World military expenditure in 2018: estimated to $1.822 trillion
* Military expenditures – percent of GDP: roughly 2% of gross world product (1999).
* World military expenditure in 2018: estimated to $1.822 trillion
* Military expenditures – percent of GDP: roughly 2% of gross world product (1999).
, Alok Jha, Monday 28 March 2011, The Guardian In 2015,
 * Forests ( carbon sinks,
* Forests ( carbon sinks,
 One example for a comparable metric other than GDP are the OECD Better Life Index rankings for different aggregative domains.
The index includes 11 comparable "dimensions" of well-being:
#Housing:
One example for a comparable metric other than GDP are the OECD Better Life Index rankings for different aggregative domains.
The index includes 11 comparable "dimensions" of well-being:
#Housing:
OECD – Economic Outlook
* [http://www.imf.org/external/ns/cs.aspx?id=29 IMF – World Economic Outlook]
UN DESA – World Economy publications
CIA – The World Factbook – World
BBC News Special Report – Global Economy
Guardian Special Report – Global Economy
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics for World
{{DEFAULTSORT:World Economy World economy, Economics catchphrases Economic globalization
economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with th ...
of all humans of the world, referring to the global economic system
An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within a society or a given geographic area. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entit ...
, which includes all economic activities which are conducted both within and between nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective identity of a group of people understood as defined by th ...
s, including production, consumption, economic management, work in general, exchange of financial values and trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct exc ...
of goods and services. In some contexts, the two terms are distinct "international" or "global economy" being measured separately and distinguished from national economies, while the "world economy" is simply an aggregate of the separate countries' measurements. Beyond the minimum standard concerning value in production, use and exchange, the definitions, representations, models and valuations of the world economy vary widely. It is inseparable from the geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
and ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overl ...
of planet Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
.
It is common to limit questions of the world economy exclusively to human economic activity, and the world economy is typically judged in monetary
Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context. The primary functions which distinguish money are ...
terms, even in cases in which there is no efficient market to help valuate certain goods or services, or in cases in which a lack of independent research, genuine data or government cooperation makes establishing figures difficult. Typical examples are illegal drugs and other black market goods, which by any standard are a part of the world economy, but for which there is, by definition, no legal market of any kind.
However, even in cases in which there is a clear and efficient market to establish a monetary
Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context. The primary functions which distinguish money are ...
value
Value or values may refer to:
Ethics and social
* Value (ethics) wherein said concept may be construed as treating actions themselves as abstract objects, associating value to them
** Values (Western philosophy) expands the notion of value beyo ...
, economists do not typically use the current or official exchange rate to translate the monetary units of this market into a single unit for the world economy since exchange rates typically do not closely reflect world
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the worl ...
wide value, for example in cases where the volume or price of transactions is closely regulated by the government.
Rather, market valuations in a local currency are typically translated to a single monetary unit using the idea of purchasing power. This is the method used below, which is used for estimating worldwide economic activity in terms of real United States dollar
The United States dollar ( symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the officia ...
s or euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
s. However, the world economy can be evaluated and expressed in many more ways. It is unclear, for example, how many of the world's 7.8 billion people () have most of their economic activity reflected in these valuations.
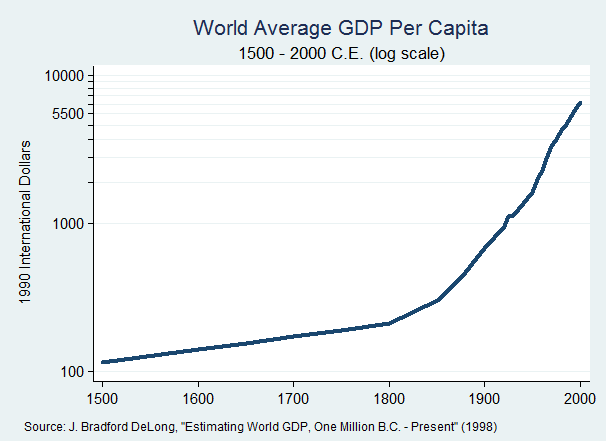
According to Maddison, until the middle of the 19th century, global output was dominated by China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
. Waves of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in Western Europe and Northern America shifted the shares to the Western Hemisphere. As of 2022, the following 18 countries or collectives have reached an economy of at least US$2 trillion
''Trillion'' is a number with two distinct definitions:
*1,000,000,000,000, i.e. one million million, or (ten to the twelfth power), as defined on the short scale. This is now the meaning in both American and British English.
* 1,000,000,000,00 ...
by GDP in nominal or PPP terms: Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
.
Despite high levels of government investment, the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
predicted that the global economy would decrease by 5.2 percent in 2020. Cities account for 80% of global GDP, thus they would face the brunt of this decline.
Overview
World economy by country groups
Current world economic league table of largest economies in the world by GDP and share of global economic growth
Twenty largest economies in the world by nominal GDP
Twenty largest economies in the world by GDP (PPP)
Statistical indicators
Finance
 * GDP (GWP) (gross world product): (purchasing power parity exchange rates) – $59.38 trillion (2005 est.), $51.48 trillion (2004), $23 trillion (2002). The GWP is the combined gross national income of all the countries in the world. When calculating the GWP, add GDP of all countries. Also, GWP shows that imports and exports are equal. Because imports and exports balance exactly when considering the whole world:, this also equals the total global gross domestic product (GDP). According to the World Bank, the 2013 nominal GWP was approximately US$75.59 trillion. In 2017, according to the CIA's World Factbook, the GWP was around US$80.27 trillion in nominal terms and totaled approximately 127.8 trillion international dollars in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). The per capita PPP GWP in 2017 was approximately Int$17,500 according to the World Factbook.
* GDP (GWP) ( gross world product): (market exchange rates) – $60.69 trillion (2008). The market exchange rates increased from 1990 to 2008. The reason for this increase is the world's advancement in terms of technology.
* GDP (real growth rate): The following part shows the GDP growth rate and the expected value after one year.
** Developed Economies. A developed country, industrialized country, more developed country (MDC), or more economically developed country (MEDC), is a sovereign state that has a developed economy and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. The GDP of the developed countries is predicted to fall from 2.2% in 2017 to 2.0% in 2018 due to the fall in dollar value.
** Developing Countries. A developing country is a country with a less developed industrial base (industries) and a low Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. A nation's GDP per capita, compared with other nations, can also be a reference point. In general, the United Nations accepts any country's claim of itself being "developing". The GDP of the developing countries is expected to rise from 4.3% in 2017 to 4.6% in 2018 due to political stability in those countries and advancement in technology.
** Least developed countries. The least developed countries (LDCs) is a list of developing countries that, according to the United Nations, exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development, with the lowest Human Development Index ratings of all countries in the world. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed by the UN in its resolution 2768 (XXVI) of 18 November 1971. This is a group of countries that are expected to improve their GDP from 4.8% in 2017 to 5.4% in 2018. The predicted growth is associated advancement in technology and industrialization of those countries for the past decade.
* GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $9,300, €7,500 (2005 est.), $8,200, €6,800 (92) (2003), $7,900, €5,000 (2002)
* World
* GDP (GWP) (gross world product): (purchasing power parity exchange rates) – $59.38 trillion (2005 est.), $51.48 trillion (2004), $23 trillion (2002). The GWP is the combined gross national income of all the countries in the world. When calculating the GWP, add GDP of all countries. Also, GWP shows that imports and exports are equal. Because imports and exports balance exactly when considering the whole world:, this also equals the total global gross domestic product (GDP). According to the World Bank, the 2013 nominal GWP was approximately US$75.59 trillion. In 2017, according to the CIA's World Factbook, the GWP was around US$80.27 trillion in nominal terms and totaled approximately 127.8 trillion international dollars in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). The per capita PPP GWP in 2017 was approximately Int$17,500 according to the World Factbook.
* GDP (GWP) ( gross world product): (market exchange rates) – $60.69 trillion (2008). The market exchange rates increased from 1990 to 2008. The reason for this increase is the world's advancement in terms of technology.
* GDP (real growth rate): The following part shows the GDP growth rate and the expected value after one year.
** Developed Economies. A developed country, industrialized country, more developed country (MDC), or more economically developed country (MEDC), is a sovereign state that has a developed economy and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. The GDP of the developed countries is predicted to fall from 2.2% in 2017 to 2.0% in 2018 due to the fall in dollar value.
** Developing Countries. A developing country is a country with a less developed industrial base (industries) and a low Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. A nation's GDP per capita, compared with other nations, can also be a reference point. In general, the United Nations accepts any country's claim of itself being "developing". The GDP of the developing countries is expected to rise from 4.3% in 2017 to 4.6% in 2018 due to political stability in those countries and advancement in technology.
** Least developed countries. The least developed countries (LDCs) is a list of developing countries that, according to the United Nations, exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development, with the lowest Human Development Index ratings of all countries in the world. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed by the UN in its resolution 2768 (XXVI) of 18 November 1971. This is a group of countries that are expected to improve their GDP from 4.8% in 2017 to 5.4% in 2018. The predicted growth is associated advancement in technology and industrialization of those countries for the past decade.
* GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $9,300, €7,500 (2005 est.), $8,200, €6,800 (92) (2003), $7,900, €5,000 (2002)
* World median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic f ...
income: purchasing power parity $1,041, €950 (1993)
* GDP – composition by sector: agriculture: 4%; industry: 32%; services: 64% (2004 est.)
* Inflation rate (consumer prices); In economics, inflation is a general rise in the price level in an economy over a period of time, resulting in a sustained drop in the purchasing power of money. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation reflects a reduction in the purchasing power per unit of money – a loss of real value in the medium of exchange and unit of account within the economy. The opposite of inflation is deflation, a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index, usually the consumer price index, over time. ''national inflation rates vary widely in individual cases, from declining prices in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
to hyperinflation (In economics, hyperinflation is very high and typically accelerating inflation) in several Third World
The term "Third World" arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Western European nations and their allies represented the " First ...
countries (2003)'':
** World 2.6% (2017), 2.8% (predicted 2018);
** Developed Economies 1% to 4% typically
** Developing Countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
5% to 60% typically
** Least developed countries 11.4% (2017), 8.3% (predicted 2018)
* Derivatives OTC outstanding notional amount: $601 trillion (Dec 2010)* Derivatives exchange traded outstanding notional amount: $82 trillion (June 2011)
* Global
debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money or other agreed-upon value to another party, the creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, which differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The ...
issuance: $5.187 trillion, €3 trillion (2004), $4.938 trillion, €3.98 trillion (2003), $3.938 trillion (2002) ( Thomson Financial League Tables)
* Global equity
Equity may refer to:
Finance, accounting and ownership
*Equity (finance), ownership of assets that have liabilities attached to them
** Stock, equity based on original contributions of cash or other value to a business
** Home equity, the diff ...
issuance: $505 billion, €450 billion (2004), $388 billion. €320 billion (2003), $319 billion, €250 trillion (2002) ( Thomson Financial League Tables)
Employment

 *
* Unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refe ...
rate: 8.7% (2009 est.). 30% (2007 est.) combined unemployment and underemployment
Underemployment is the underuse of a worker because a job does not use the worker's skills, is part-time, or leaves the worker idle. Examples include holding a part-time job despite desiring full-time work, and overqualification, in which the ...
in many non-industrialized countries; developed countries typically 4%–12% unemployment.
Industries
* Industrial production growth rate: 3% (2002 est.)Energy
electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describe ...
– production: 21,080,878 GWh (2011 est.), 15,850,000 GWh (2003 est.), 14,850,000 GWh (2001 est.)
* Yearly electricity – consumption: 14,280,000 GWh (2003 est.), 13,930,000 GWh (2001 est.)
* Oil – production: (2003 est.), (2001)
* Oil – consumption: (2003 est.), (2001)
* Oil – proved reserves: 1.025 trillion barrel ( (2001 est.)
* Natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
– production: (2012 est.), (2001 est.)
* Natural gas – consumption: (2001 est.)
* Natural gas – proved reserves: (1 January 2002)
Cross-border
* Yearly exports: $12.4 trillion, €11.05 trillion (2009 est.) * Exports – commodities: the whole range of industrial and agricultural goods and services * Exports – partners: US 12.7%, Germany 7.1%, China 6.2%, France 4.4%, Japan 4.2%, UK 4.1% (2008) * Yearly imports: $12.29 trillion, €10.95 trillion (2009 est.) * Imports – commodities: the whole range of industrial and agricultural goods and services * Imports – partners: China 10.3%, Germany 8.6%, US 8.1%, Japan 5% (2008) * Debt – external: $56.9 trillion, €40 trillion (31 December 2009 est.)Gift economy
* Yearly economic aid – recipient: netOfficial Development Assistance
Official development assistance (ODA) is a category used by the Development Assistance Committee (DAC) of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) to measure foreign aid. The DAC first adopted the concept in 1969. It ...
(ODA) of $135.2 billion (2014)
Communications
Telephones – main lines in use: 843,923,500 (2007)4,263,367,600 (2008) * Telephones – mobile cellular: 3,300,000,000 (Nov. 2007)global cellphone penetration reaches 50 percent
* Internet Service Providers (ISPs): 10,350 (2000 est.) *
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
users: 3,079,339,857 (31 December 201, 360,985,492 (31 December 2000)
Transport
Transportation infrastructure worldwide includes: *Airports
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surfac ...
** Total: 41,821 (2013)
* Roadways
** Total:
** Paved:
** Unpaved: (2002)
* Railways
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
** Total: includes about of electrified routes of which are in Europe, in the Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The t ...
, in Africa, in South America, and in North America.
Military
Science, research and development
TheRoyal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
in a 2011 report stated that in terms of number of papers the share of English-language scientific research papers the United States was first followed by China, the UK, Germany, Japan, France, and Canada.China poised to overhaul US as biggest publisher of scientific papers, Alok Jha, Monday 28 March 2011, The Guardian In 2015,
research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in Europe as research and technological development (RTD), is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products, and improving existi ...
constituted an average 2.2% of the global GDP according to the UNESCO Institute for Statistics
The UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) is the statistical office of UNESCO and is the UN depository for cross-nationally comparable statistics on education, science and technology, culture, and communication.
The UIS was established in 1999. ...
. Metrics and rankings of innovation include the Bloomberg Innovation Index, the Global Innovation Index
The Global Innovation Index is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for, and success in, innovation, published by the World Intellectual Property Organization. It was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a British m ...
and the share of Nobel laureates per capita.
Resources and environment
 * Forests ( carbon sinks,
* Forests ( carbon sinks, wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
, ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the many and varied benefits to humans provided by the natural environment and healthy ecosystems. Such ecosystems include, for example, agroecosystems, forest ecosystem, grassland ecosystems, and aquatic ecosystems. ...
, ...)
** Estimated number of trees that are net lost annually as of 2021: 10 billion
** Global annual deforested land in 2015–2020: 10 million hectares
** Global annual net forest area loss in 2000–2010 : 4.7 million hectares
* Other land degradation and land- and organisms-related ecosystem disturbances
** Soils (carbon sink, ecosystem services, food production, ...)
*** Soil erosion
Soil erosion is the denudation or wearing away of the upper layer of soil. It is a form of soil degradation. This natural process is caused by the dynamic activity of erosive agents, that is, water, ice (glaciers), snow, air (wind), plants, a ...
by water in 2012: almost 36 billion tons (based on a high resolution global potential soil erosion model developed in 2017)
*** Estimated annual loss of agricultural productivity due to soil erosion: 8 billion US dollars (based on the soil erosion data)
*** Soil erosion by water in 2015: approximately 43 billion tons (according to a 2020 study)
*** Environmental impact of pesticides
The environmental effects of pesticides describe the broad series of consequences of using pesticides. The unintended consequences of pesticides is one of the main drivers of the negative impact of modern industrial agriculture on the environme ...
**** Pesticide use in tonnes of active ingredient in Australia in 2016: ca. 62,500 tonnes
* Oceans (ecosystem services, food production, ...): Blue economy
* Waste and pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, th ...
(effects of economic mechanisms, effects on ecosystem services)
** As of 2018, about 380 million tonnes of plastic is produced worldwide each year. From the 1950s up to 2018, an estimated 6.3 billion tonnes of plastic has been produced worldwide, of which an estimated 9% has been recycled and another 12% has been incinerated with the rest reportedly being " dumped in landfills or the natural environment".
** Air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different type ...
*** Number of human deaths caused annually by air pollution worldwide: ca. 7 million
*** Estimated global annual cost of air pollution: $5 trillionStudy by the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington.
Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seatt ...
:
** Microplastic pollution
*** Estimated accumulated number of microplastic particles in the North Atlantic Ocean in 2014: 15 to 51 trillion particles, weighing between 93,000 and 236,000 metric tons
*** Estimated accumulated number of microplastic particles in the North Atlantic Ocean in 2020: 3700 microplastics per cubic meter
From the scientific perspective, economic activities are embedded in a web of dynamic, interrelated, and interdependent activities that constitute the natural system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and express ...
of Earth. Novel application of cybernetics in decision-making (such as in decision-making related to process- and product-design and related laws) and direction of human activity (such as economic activity) may make it easier to control modern ecological problems.
Historical development
 One example for a comparable metric other than GDP are the OECD Better Life Index rankings for different aggregative domains.
The index includes 11 comparable "dimensions" of well-being:
#Housing:
One example for a comparable metric other than GDP are the OECD Better Life Index rankings for different aggregative domains.
The index includes 11 comparable "dimensions" of well-being:
#Housing: housing
Housing, or more generally, living spaces, refers to the construction and assigned usage of houses or buildings individually or collectively, for the purpose of shelter. Housing ensures that members of society have a place to live, whether ...
conditions and spendings (e.g. real estate pricing)
#Income: household income (after taxes and transfers) and net financial wealth
#Jobs: earnings, job security and unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refe ...
#Community: quality of social support network
#Education: education and what one gets out of it
#Environment: quality of environment (e.g. environmental health
Environmental health is the branch of public health concerned with all aspects of the natural and built environment affecting human health. In order to effectively control factors that may affect health, the requirements that must be met in ...
)
#Governance: involvement in democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose g ...
#Health
#Life Satisfaction: level of happiness
Happiness, in the context of mental or emotional states, is positive or pleasant emotions ranging from contentment to intense joy. Other forms include life satisfaction, well-being, subjective well-being, flourishing and eudaimonia.
...
#Safety: murder and assault rates
# Work-life balance
Economic studies
To promote exports, many government agencies publish on the web economic studies by sector and country. Among these agencies include the USCS (US DoC) and Foreign Agricultural Service, FAS (USDA) in the United States, the Export Development Canada, EDC and Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, AAFC in Canada, Ubifrance in France, the UK Trade & Investment, UKTI in the United Kingdom, the Hong Kong Trade Development Council, HKTDC and Japan External Trade Organization, JETRO in Asia, Austrade and the New Zealand Trade and Enterprise, NZTE in Oceania. Through Partnership Agreements, the Federation of International Trade Associations publishes studies from several of these agencies (USCS, FAS, AAFC, UKTI, and HKTDC) as well as other non-governmental organizations on its website globaltrade.net.See also
* Anarchy (international relations) * Capitalism * ''Common Wealth: Economics for a Crowded Planet'' (book) * Economic bubble * Economic collapse * Emerging and growth-leading economies * Fourth Industrial Revolution * Global financial system * Global workforce * Globality * Globalization * International trade * Trade route * Overconsumption * Petrodollar recycling * ''World Trade Report'' * World history (field), World history ** Economic history of the world * World-systems theory Regional economies: * Economy of Africa * Economy of Asia * Economy of Europe * Economy of North America * Economy of Oceania * Economy of South America Events: * Great Recession * World oil market chronology from 2003 * 2007–2008 financial crisis * 2007–2008 world food price crisis * Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic Lists: * List of countries by GDP sector composition * List of countries by GDP (nominal), List of world's largest economies (nominal) – based on current currency market exchange rates * List of countries by GDP (PPP), List of world's largest economies (PPP) – based on purchasing power parity * List of regions by past GDP (PPP), Historical list of world's largest economies (PPP) – for the years between 1 and 1998References
External links
OECD – Economic Outlook
* [http://www.imf.org/external/ns/cs.aspx?id=29 IMF – World Economic Outlook]
UN DESA – World Economy publications
CIA – The World Factbook – World
BBC News Special Report – Global Economy
Guardian Special Report – Global Economy
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics for World
{{DEFAULTSORT:World Economy World economy, Economics catchphrases Economic globalization