fraud on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
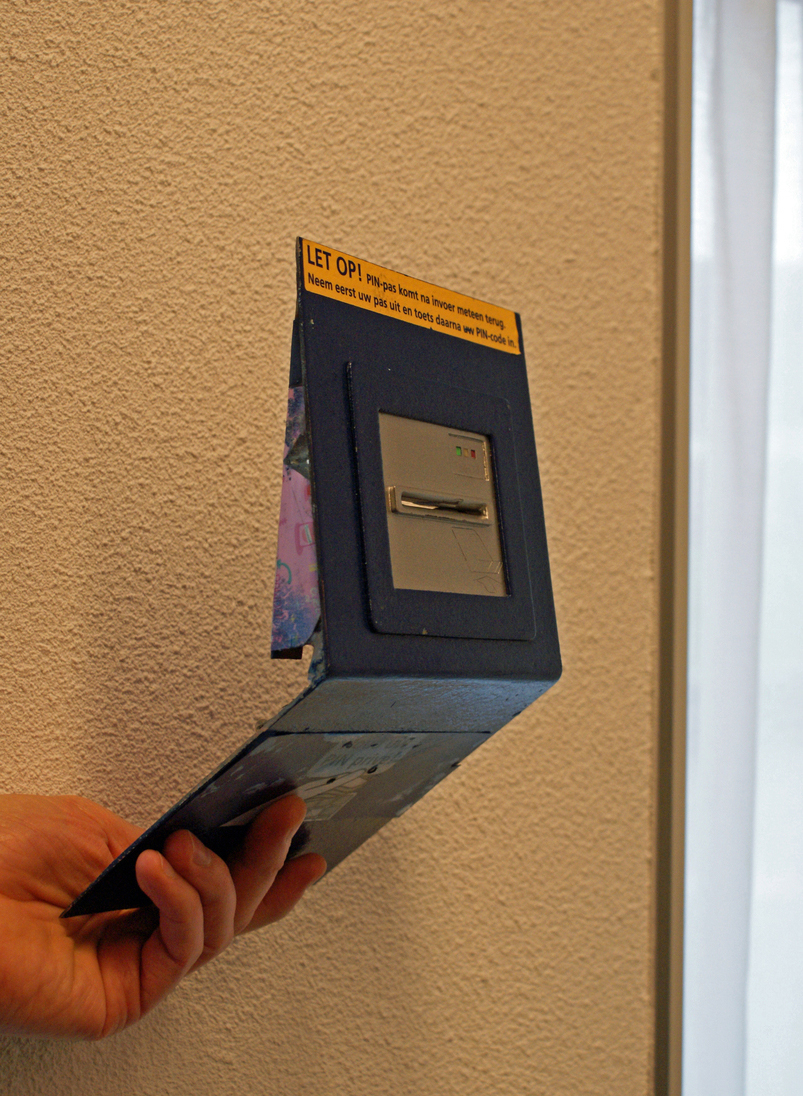 In
In
 The falsification of documents, known as forgery, and counterfeiting are types of fraud involved in physical duplication or fabrication. The "theft" of one's personal information or identity, like one finding out another's social security number and then using it as identification, is a type of fraud. Fraud can be committed through and across many media including
The falsification of documents, known as forgery, and counterfeiting are types of fraud involved in physical duplication or fabrication. The "theft" of one's personal information or identity, like one finding out another's social security number and then using it as identification, is a type of fraud. Fraud can be committed through and across many media including
 The detection of fraudulent activities on a large scale is possible with the harvesting of massive amounts of financial
The detection of fraudulent activities on a large scale is possible with the harvesting of massive amounts of financial
Review Fraud – Alex Copola
Podgor, Ellen S. ''Criminal Fraud'', (1999) Vol, 48, No. 4 American Law Review 1.
The Nature, Extent and Economic Impact of Fraud in the UK. February, 2007.
by Eamon Dillon, published September 2008 by Merlin Publishing * Zhang, Yingyu.
The Book of Swindles: Selections from a Late Ming Collection
'. Columbia University Press, 2017.
Association of Certified Fraud Examiners
Immigration Marriage Fraud Amendments of 1986
U.S. Department of Justice Fraud Section
{{Authority control Crimes Deception Tort law Property crimes Financial crimes
 In
In law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
, fraud is intentional
Intentions are mental states in which the agent commits themselves to a course of action. Having the plan to visit the zoo tomorrow is an example of an intention. The action plan is the ''content'' of the intention while the commitment is the ''a ...
deception to secure unfair or unlawful gain, or to deprive a victim of a legal right. Fraud can violate civil law (e.g., a fraud victim may sue the fraud perpetrator to avoid the fraud or recover monetary compensation) or criminal law (e.g., a fraud perpetrator may be prosecuted and imprisoned by governmental authorities), or it may cause no loss of money, property, or legal right but still be an element of another civil or criminal wrong. The purpose of fraud may be monetary gain or other benefits, for example by obtaining a passport, travel document, or driver's license, or mortgage fraud
Mortgage fraud refers to an intentional misstatement, misrepresentation, or omission of information relied upon by an underwriter or lender to fund, purchase, or insure a loan secured by real property.
Criminal offenses may be prosecuted in eith ...
, where the perpetrator may attempt to qualify for a mortgage by way of false statements.
Internal fraud, also known as "insider fraud", is fraud committed or attempted by someone within an organisation such as an employee.
A hoax is a distinct concept that involves deliberate deception without the intention of gain or of materially damaging or depriving a victim.
As a civil wrong
In common law jurisdictions, as a civil wrong, fraud is atort
A tort is a civil wrong that causes a claimant to suffer loss or harm, resulting in legal liability for the person who commits the tortious act. Tort law can be contrasted with criminal law, which deals with criminal wrongs that are punishable ...
. While the precise definitions and requirements of proof vary among jurisdictions, the requisite elements of fraud as a tort generally are the intentional misrepresentation or concealment of an important fact upon which the victim is meant to rely, and in fact does rely, to the harm of the victim. Proving fraud in a court of law is often said to be difficult as the intention to defraud is the key element in question. As such, proving fraud comes with a "greater evidentiary burden than other civil claims". This difficulty is exacerbated by the fact that some jurisdictions require the victim to prove fraud by clear and convincing evidence
In a legal dispute, one party has the burden of proof to show that they are correct, while the other party had no such burden and is presumed to be correct. The burden of proof requires a party to produce evidence to establish the truth of facts ...
.
The remedies for fraud may include rescission
Rescission is the noun form of the verb "to rescind." It may refer to:
* Rescission (contract law)
* Rescission bill, a procedure to rescind previously appropriated funding in the United States
* A synonym for repeal in parliamentary procedure
* ...
(i.e., reversal) of a fraudulently obtained agreement or transaction, the recovery of a monetary award to compensate for the harm caused, punitive damages
Punitive damages, or exemplary damages, are damages assessed in order to punish the defendant for outrageous conduct and/or to reform or deter the defendant and others from engaging in conduct similar to that which formed the basis of the lawsuit. ...
to punish or deter the misconduct, and possibly others.
In cases of a fraudulently induced contract, fraud may serve as a defense in a civil action
-
A lawsuit is a proceeding by a party or parties against another in the civil court of law. The archaic term "suit in law" is found in only a small number of laws still in effect today. The term "lawsuit" is used in reference to a civil act ...
for breach of contract or specific performance
Specific performance is an equitable remedy in the law of contract, whereby a court issues an order requiring a party to perform a specific act, such as to complete performance of the contract. It is typically available in the sale of land law, ...
of contract
A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations between them. A contract typically involves the transfer of goods, services, money, or a promise to tr ...
. Similarly, fraud may serve as a basis for a court to invoke its equitable jurisdiction
Equity is a particular body of law that was developed in the English Court of Chancery. Its general purpose is to provide a remedy for situations where the law is not flexible enough for the usual court system to deliver a fair resolution to a cas ...
.
As a criminal offense
In common law jurisdictions, as a criminal offense, fraud takes many different forms, some general (e.g., theft by false pretense) and some specific to particular categories of victims or misconduct (e.g., bank fraud, insurance fraud, forgery). The elements of fraud as a crime similarly vary. The requisite elements of perhaps the most general form of criminal fraud, theft by false pretense, are the intentional deception of a victim by false representation or pretense with the intent of persuading the victim to part with property and with the victim parting with property in reliance on the representation or pretense and with the perpetrator intending to keep the property from the victim.By region
North America
Canada
Section 380(1) of theCriminal Code
A criminal code (or penal code) is a document that compiles all, or a significant amount of a particular jurisdiction's criminal law. Typically a criminal code will contain offences that are recognised in the jurisdiction, penalties that might ...
provides the general definition for fraud in Canada:
In addition to the penalties outlined above, the court can also issue a prohibition order under s. 380.2 (preventing a person from "seeking, obtaining or continuing any employment, or becoming or being a volunteer in any capacity, that involves having authority over the real property, money or valuable security of another person"). It can also make a restitution order under s. 380.3.
The Canadian courts have held that the offence consists of two distinct elements:
:* A prohibited act of deceit, falsehood or other fraudulent means. In the absence of deceit or falsehood, the courts will look objectively for a "dishonest act"; and
:* The deprivation must be caused by the prohibited act, and deprivation must relate to property, money, valuable security, or any service.
The Supreme Court of Canada has held that deprivation is satisfied on proof of detriment, prejudice or risk of prejudice; it is not essential that there be actual loss. Deprivation of confidential information
Confidentiality involves a set of rules or a promise usually executed through confidentiality agreements that limits the access or places restrictions on certain types of information.
Legal confidentiality
By law, lawyers are often required ...
, in the nature of a trade secret
Trade secrets are a type of intellectual property that includes formulas, practices, processes, designs, instruments, patterns, or compilations of information that have inherent economic value because they are not generally known or readily ...
or copyrighted material that has commercial value, has also been held to fall within the scope of the offence.
United States
=Criminal fraud
= The proof requirements for criminal fraud charges in the United States are essentially the same as the requirements for other crimes: guilt must be proved beyond areasonable doubt
Beyond a reasonable doubt is a legal standard of proof required to validate a criminal conviction in most adversarial legal systems. It is a higher standard of proof than the balance of probabilities standard commonly used in civil cases, bec ...
. Throughout the United States fraud charges can be misdemeanours or felonies depending on the amount of loss involved. High value fraud can also trigger additional penalties. For example, in California, losses of $500,000 or more will result in an extra two, three, or five years in prison in addition to the regular penalty for the fraud.
The U.S. government's 2006 fraud review concluded that fraud is a significantly under-reported crime, and while various agencies and organizations were attempting to tackle the issue, greater co-operation was needed to achieve a real impact in the public sector. The scale of the problem pointed to the need for a small but high-powered body to bring together the numerous counter-fraud initiatives that existed.
= Civil fraud
= Although elements may vary by jurisdiction and the specific allegations made by a plaintiff who files a lawsuit that alleged fraud, typical elements of a fraud case in the United States are that: #Somebody misrepresents amaterial fact
A material fact is a fact that a reasonable person would recognize as relevant to a decision to be made, as distinguished from an insignificant, trivial, or unimportant detail. In other words, it is a fact, the suppression of which would reasonabl ...
in order to obtain action or forbearance by another person;
#The other person relies upon the misrepresentation; and
#The other person suffers injury as a result of the act or forbearance taken in reliance upon the misrepresentation.
To establish a civil claim of fraud, most jurisdictions in the United States require that each element of a fraud claim be pleaded with particularity and be proved by a preponderance of the evidence
In a legal dispute, one party has the burden of proof to show that they are correct, while the other party had no such burden and is presumed to be correct. The burden of proof requires a party to produce evidence to establish the truth of facts ...
, meaning that it is more likely than not that the fraud occurred. Some jurisdictions impose a higher evidentiary standard, such as Washington State's requirement that the elements of fraud be proved with clear, cogent, and convincing evidence (very probable evidence), or Pennsylvania's requirement that common law fraud be proved by clear and convincing evidence.
The measure of damages in fraud cases is normally computed using one of two rules:
#The "benefit of bargain" rule, which allows for recovery of damages in the amount of the difference between the value of the property had it been as represented and its actual value;
#Out-of-pocket loss, which allows for the recovery of damages in the amount of the difference between the value of what was given and the value of what was received.
Special damages
At common law, damages are a remedy in the form of a monetary award to be paid to a claimant as compensation for loss or injury. To warrant the award, the claimant must show that a breach of duty has caused foreseeable loss. To be recognised at ...
may be allowed if shown to have been proximately caused by defendant's fraud and the damage amounts are proved with specificity.
Many jurisdictions permit a plaintiff in a fraud case to seek punitive
Punishment, commonly, is the imposition of an undesirable or unpleasant outcome upon a group or individual, meted out by an authority—in contexts ranging from child discipline to criminal law—as a response and deterrent to a particular acti ...
or exemplary damages.
Asia
China
Zhang Yingyu's story collection ''The Book of Swindles
''The Book of Swindles'' (''Piàn jīng'' 騙經), also known by its longer title, ''A New Book for Foiling Swindlers, Based on Worldly Experience'' (''Jiānghú lìlǎn dùpiàn xīnshū'' 江湖歷覽杜騙新書), is said to be the first publi ...
'' (available here; ca. 1617) testifies to rampant commercial fraud, especially involving itinerant businessmen, in late Ming China. ''The Economist'', CNN, and other media outlets regularly report on incidents of fraud or bad faith in Chinese business and trade practices. ''Forbes'' cites cybercrime as a persistent and growing threat to Chinese consumers.
India
In India the criminal laws are enshrined in theIndian Penal Code
The Indian Penal Code (IPC) is the official criminal code of India. It is a comprehensive code intended to cover all substantive aspects of criminal law. The code was drafted on the recommendations of first law commission of India established ...
. It is supplemented by the Criminal Procedure Code
Criminal procedure is the adjudication process of the criminal law. While criminal procedure differs dramatically by jurisdiction, the process generally begins with a formal criminal charge with the person on trial either being free on bail or ...
and Indian Evidence Act
The Indian Evidence Act, originally passed in India by the Imperial Legislative Council in 1872, during the British Raj, contains a set of rules and allied issues governing admissibility of evidence in the Indian courts of law.
Importance
The ...
.
Europe
United Kingdom
In 2016 the estimated value lost through fraud in the UK was £193 billion a year. In January 2018 the ''Financial Times
The ''Financial Times'' (''FT'') is a British daily newspaper printed in broadsheet and published digitally that focuses on business and economic current affairs. Based in London, England, the paper is owned by a Japanese holding company, Ni ...
'' reported that the value of UK fraud hit a 15-year high of £2.11bn in 2017, according to a study. The article said that the accountancy firm BDO examined reported fraud cases worth more than £50,000 and found that the total number rose to 577 in 2017, compared with 212 in 2003. The study found that the average amount stolen in each incident rose to £3.66m, up from £1.5m in 2003.
As at November 2017, fraud is the most common criminal offence in the UK according to a study by Crowe Clark Whitehill, Experian and the Centre for Counter Fraud Studies. The study suggests the UK loses over £190 billion per year to fraud. £190 billion is more than 9% of the UK's projected GDP for 2017 ($2,496 (£2,080) billion according to ''Statistics Times''.) The estimate for fraud in the UK figure is more than the entire GDP of countries such as Romania, Qatar and Hungary.
According to another review by the UK anti-fraud charity Fraud Advisory Panel
The Fraud Advisory Panel is a UK charitable organisation. Incorporated in 2001, the Panel focuses on offering advice and education to the general public on how to mitigate and avoid fraud. Panel members have provided evidence to the House of Comm ...
(FAP), business fraud accounted for £144bn, while fraud against individuals was estimated at £9.7bn. The FAP has been particularly critical of the support available from the police to victims of fraud in the UK outside of London. Although victims of fraud are generally referred to the UK's national fraud and cyber crime reporting centre, Action Fraud
The National Fraud Intelligence Bureau is a police unit in the United Kingdom responsible for gathering and analysing intelligence relating to fraud and financially motivated cyber crime. The NFIB was created as part of the recommendations of the ...
, the FAP found that there was "little chance" that these crime reports would be followed up with any kind of substantive law enforcement action by UK authorities, according to the report.
In July 2016, it was reported that fraudulent activity levels in the UK increased in the 10 years leading up to 2016 from £52 billion to £193 bn. This figure would be a conservative estimate, since as the former commissioner of the City of London Police, Adrian Leppard, has said, only 1 in 12 such crimes are actually reported. Donald Toon, director of the NCA's economic crime command, stated in July 2016: "The annual losses to the UK from fraud are estimated to be more than £190bn". Figures released in October 2015 from the Crime Survey of England and Wales found that there had been 5.1 million incidents of fraud in England and Wales in the previous year, affecting an estimated one in 12 adults and making it the most common form of crime.
Also in July 2016, the Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; cy, Swyddfa Ystadegau Gwladol) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible for t ...
(ONS) stated "Almost six million fraud and cyber crimes were committed last year in England and Wales and estimated there were two million computer misuse offences and 3.8 million fraud offences in the 12 months to the end of March 2016." Fraud affects one in ten people in the UK. According to the ONS, most fraud relates to bank account fraud. These figures are separate from the headline estimate that another 6.3 million crimes (distinct from fraud) were perpetrated in the UK against adults in the year to March 2016.
Fraud was not included in a "Crime Harm Index" published by the Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; cy, Swyddfa Ystadegau Gwladol) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible for t ...
in 2016. Michael Levi, professor of criminology at Cardiff University, remarked in August 2016 that it was "deeply regrettable" that fraud was being left out of the first index despite being the most common crime reported to police in the UK. Levi said "If you've got some categories that are excluded, they are automatically left out of the police's priorities." The Chief of the National Audit Office (NAO), Sir Anyas Morse has also said "For too long, as a low-value but high-volume crime, online fraud has been overlooked by government, law enforcement and industry. It is now the most commonly experienced crime in England and Wales and demands an urgent response."
HM Treasury
His Majesty's Treasury (HM Treasury), occasionally referred to as the Exchequer, or more informally the Treasury, is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for developing and executing the government's public finance policy and ...
issued guidance to central government departments in January 2011 concerned with "Tackling Internal Fraud", concerned that economic pressures and potential staff redundancies at the time might lead those staff who "might be tempted" to commit fraud to make more of any opportunity which might arise, noting a possible shift in the balance between "the reward from fraud" and the risk of detection. An aspect of the guidance was to equip staff to look out for "fraud indicators": clues or hints that an individual member of staff, team or area of activity might need "a closer look".
=England, Wales, and Northern Ireland
= Since 2007, fraud inEngland and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is Eng ...
and Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
has been covered by the Fraud Act 2006
The Fraud Act 2006 (c 35) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which affects England and Wales and Northern Ireland. It was given royal assent on 8 November 2006, and came into effect on 15 January 2007.
Purpose
The Act gives a sta ...
. The Act was given Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in oth ...
on 8 November 2006, and came into effect on 15 January 2007.
The Act gives a statutory definition of the criminal offence of fraud, defining it in three classes—fraud by false representation, fraud by failing to disclose information, and fraud by abuse of position. It provides that a person found guilty of fraud is liable to a fine or imprisonment for up to twelve months on summary conviction (six months in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
), or a fine or imprisonment for up to ten years on conviction on indictment
An indictment ( ) is a formal accusation that a person has committed a crime. In jurisdictions that use the concept of felonies, the most serious criminal offence is a felony; jurisdictions that do not use the felonies concept often use that of a ...
. This Act largely replaces the laws relating to obtaining property by deception, obtaining a pecuniary advantage and other offences that were created under the Theft Act 1978
The Theft Act 1978 (c 31) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It supplemented the earlier deception offences contained in sections 15 and 16 of the Theft Act 1968 by reforming some aspects of those offences and adding new provis ...
.
=Scotland
= In Scots law, fraud is covered under the common law and a number of statutory offences. The main fraud offences are common law fraud, uttering, embezzlement, and statutory fraud. The Fraud Act 2006 does not apply in Scotland.=Governmental Organizations
= The Serious Fraud Office is an arm of the Government of the United Kingdom, accountable to the Attorney-General. The National Fraud Authority (NFA) was, until 2014, a government agency coordinating the counter-fraud response in the UK. Cifas is a British fraud prevention service, a not-for-profit membership organization for all sectors that enables organizations to share and access fraud data using their databases. Cifas is dedicated to the prevention of fraud, including internal fraud by staff, and the identification of financial and related crime.Cost
Participants of a 2010 survey by theAssociation of Certified Fraud Examiners
The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE) is a professional organization of fraud examiners. Its activities include producing fraud information, tools and training. Based in Austin, Texas, the ACFE was founded in 1988 by Joseph T. Wells ...
estimated that the typical organization loses five percent of its annual revenue to fraud, with a median loss of $160,000. Fraud committed by owners and executives were more than nine times as costly as employee fraud. The industries most commonly affected are banking, manufacturing, and government.
Types of fraudulent acts
 The falsification of documents, known as forgery, and counterfeiting are types of fraud involved in physical duplication or fabrication. The "theft" of one's personal information or identity, like one finding out another's social security number and then using it as identification, is a type of fraud. Fraud can be committed through and across many media including
The falsification of documents, known as forgery, and counterfeiting are types of fraud involved in physical duplication or fabrication. The "theft" of one's personal information or identity, like one finding out another's social security number and then using it as identification, is a type of fraud. Fraud can be committed through and across many media including mail
The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letters, and parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid-19th century, national postal sys ...
, wire
Overhead power cabling. The conductor consists of seven strands of steel (centre, high tensile strength), surrounded by four outer layers of aluminium (high conductivity). Sample diameter 40 mm
A wire is a flexible strand of metal.
Wire is c ...
, phone, and the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
( computer crime and Internet fraud
Internet fraud is a type of cybercrime fraud or deception which makes use of the Internet and could involve hiding of information or providing incorrect information for the purpose of tricking victims out of money, property, and inheritance. Int ...
).
Given the international nature of the web and ease with which users can hide their location, obstacles to checking identity and legitimacy online, and the variety of hacker techniques available to gain access to PII have all contributed to the very rapid growth of Internet fraud. In some countries, tax fraud is also prosecuted under false billing or tax forgery. There have also been fraudulent "discoveries", e.g., science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
, where the appetite is for prestige rather than immediate monetary gain.
Commodities fraud
The illegal act of obtaining (or the attempt of obtaining) a certain amount ofcurrency
A currency, "in circulation", from la, currens, -entis, literally meaning "running" or "traversing" is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins.
A more general def ...
in accordance with a contract
A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations between them. A contract typically involves the transfer of goods, services, money, or a promise to tr ...
that promises the later exchange
Exchange may refer to:
Physics
*Gas exchange is the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Places United States
* Exchange, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* ...
of equated assets
In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned or controlled by a business or an economic entity. It is anything (tangible or intangible) that can be used to produce positive economic value. Assets represent value of ownership that can ...
, which ultimately never arrive, is a type of fraud, known as commodities fraud. Alternatively, the term can relate to: the failure of registering in an exchange; the act of deliberately providing falsified information to clients; the action of executing transactions with the sole purpose of making a profit for the payee
A payment is the voluntary tender of money or its equivalent or of things of value by one party (such as a person or company) to another in exchange for goods, or services provided by them, or to fulfill a legal obligation. The party making the ...
; the theft of client funds.
Detection
 The detection of fraudulent activities on a large scale is possible with the harvesting of massive amounts of financial
The detection of fraudulent activities on a large scale is possible with the harvesting of massive amounts of financial data
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete Value_(semiotics), values that convey information, describing quantity, qualitative property, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of sy ...
paired with predictive analytics
Predictive analytics encompasses a variety of statistical techniques from data mining, predictive modeling, and machine learning that analyze current and historical facts to make predictions about future or otherwise unknown events.
In busine ...
or forensic analytics, the use of electronic data to reconstruct or detect financial fraud.
Using computer-based analytic methods in particular allows for surfacing of errors, anomalies, inefficiencies, irregularities, and biases which often refer to fraudsters gravitating to certain dollar amounts to get past internal control thresholds. These high-level tests include tests related to Benford's Law and possibly also those statistics known as descriptive statistics. High-level tests are always followed by more focused tests to look for small samples of highly irregular transactions. The familiar methods of correlation and time-series analysis
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Ex ...
can also be used to detect fraud and other irregularities.
Anti-fraud provisioning
Beyond laws that aim at prevention of fraud, there are also governmental and non-governmental organizations that aim to fight fraud. Between 1911 and 1933, 47 states adopted the so-calledBlue Sky Laws
A blue sky law is a state law in the United States that regulates the offering and sale of securities to protect the public from fraud. Though the specific provisions of these laws vary among states, they all require the registration of all se ...
status.
These laws were enacted and enforced at the state level and regulated the offering and sale of securities
A security is a tradable financial asset. The term commonly refers to any form of financial instrument, but its legal definition varies by jurisdiction. In some countries and languages people commonly use the term "security" to refer to any for ...
to protect the public from fraud. Though the specific provisions of these laws varied among states, they all required the registration of all securities offerings and sales, as well as of every U.S. stockbroker and brokerage firm. However, these Blue Sky laws were generally found to be ineffective. To increase public trust in the capital markets the President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
, Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
, established the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government, created in the aftermath of the Wall Street Crash of 1929. The primary purpose of the SEC is to enforce the law against market ...
(SEC). The main reason for the creation of the SEC was to regulate the stock market and prevent corporate abuses relating to the offering and sale of securities and corporate reporting. The SEC was given the power to license and regulate stock exchanges, the companies whose securities traded on them, and the brokers and dealers who conducted the trading.
Further reading
Apart from fraud, there are several related categories of intentional deceptions that may or may not include the elements of personal gain or damage to another individual: *Obstruction of justice
Obstruction of justice, in United States jurisdictions, is an act that involves unduly influencing, impeding, or otherwise interfering with the justice system, especially the legal and procedural tasks of prosecutors, investigators, or other gov ...
* which criminalizes false representation of having been awarded any decoration or medal authorized by Congress for the Armed Forces of the United States
See also
*Bait-and-switch
Bait-and-switch is a form of fraud used in retail sales but also employed in other contexts. First, customers are "baited" by merchants' advertising products or services at a low price, but when customers visit the store, they discover that the a ...
* Caper stories (such as ''The Sting
''The Sting'' is a 1973 American caper film set in September 1936, involving a complicated plot by two professional grifters (Paul Newman and Robert Redford) to con a mob boss ( Robert Shaw).'' Variety'' film review; December 12, 1973, pag ...
'')
* Contract fraud
* Corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense which is undertaken by a person or an organization which is entrusted in a position of authority, in order to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's personal gain. Corruption m ...
* Cramming (fraud)
* Creative accounting
* Crimestoppers
Crime Stoppers or Crimestoppers is a community program that helps people to provide anonymous information about criminal activity. Often managed by non-profit groups or the police, it operates separately from the emergency telephone number sy ...
* Deception
* Electoral fraud
* Embezzlement
* False Claims Act
The False Claims Act (FCA), also called the "Lincoln Law", is an American federal law that imposes liability on persons and companies (typically federal contractors) who defraud governmental programs. It is the federal government's primary litigat ...
* Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, ...
(FBI)
* Financial crimes
Financial crime is crime committed against property, involving the unlawful conversion of the ownership of property (belonging to one person) to one's own personal use and benefit. Financial crimes may involve fraud (cheque fraud, credit card f ...
* Forgery
* Fortune telling fraud
Fortune telling fraud, also called the bujo or egg curse scam, is a type of confidence trick, based on a claim of secret or occult information. The basic feature of the scam involves diagnosing the victim (the "mark") with some sort of secret ...
* Fraud deterrence Fraud deterrence has gained public recognition and spotlight since the 2002 inception of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. Of the many reforms enacted through Sarbanes-Oxley, one major goal was to regain public confidence in the reliability of financial mar ...
* Fraud in the factum
Fraud in the factum is a type of fraud where misrepresentation causes one to enter a transaction without accurately realizing the risks, duties, or obligations incurred.Black's Law Dictionary (2nd Pocket ed. 2001 pg. 293). This can be when the m ...
* Fraud in parapsychology
Parapsychology is the study of alleged psychic phenomena (extrasensory perception, telepathy, precognition, clairvoyance, psychokinesis (also called telekinesis), and psychometry) and other paranormal claims, for example, those related to near ...
* Fraud Squad (UK)
A Fraud squad is a police department which investigates fraud and other economic crimes, the largest of which in the United Kingdom is run by the City of London Police
City of London Police
This unit is responsible for policing London's and the ...
* Friendly fraud
Chargeback fraud, also known as friendly fraud, occurs when a consumer makes an online shopping purchase with their own credit card, and then requests a chargeback from the issuing bank after receiving the purchased goods or services. Once approve ...
* Front running
Front running, also known as tailgating, is the prohibited practice of entering into an equity ( stock) trade, option, futures contract, derivative, or security-based swap to capitalize on advance, nonpublic knowledge of a large ("block") pend ...
* Geneivat da'at
* Great Stock Exchange Fraud of 1814
The Great Stock Exchange Fraud of 1814 was a hoax or fraud centered on false information about the Napoleonic Wars, affecting the London Stock Exchange in 1814.
The du Bourg hoax
On the morning of Monday, 21 February 1814, a uniformed man posing ...
* Guinness share-trading fraud
The Guinness share-trading fraud was a major business scandal of the 1980s. It involved the manipulation of the London stock market to inflate the price of Guinness shares to thereby assist Guinness's £4 billion takeover bid for the Scottish d ...
, famous British business scandal of the 1980s
* Hoax
* Identity management
* Impersonator
* Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
* Internet fraud
Internet fraud is a type of cybercrime fraud or deception which makes use of the Internet and could involve hiding of information or providing incorrect information for the purpose of tricking victims out of money, property, and inheritance. Int ...
* Interpol
The International Criminal Police Organization (ICPO; french: link=no, Organisation internationale de police criminelle), commonly known as Interpol ( , ), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and cri ...
* Journalism fraud
* Mail and wire fraud
* Money laundering
* Misappropriation
In law, misappropriation is the unauthorized use of another's name, likeness, identity, property, discoveries, inventions, etc without that person's permission, resulting in harm to that person.
Another use of the word refers to intentional a ...
* The National Council Against Health Fraud
The National Council Against Health Fraud (NCAHF) was a not-for-profit, US-based organization, that described itself as a "private nonprofit, voluntary health agency that focuses upon health misinformation, fraud, and quackery as public health p ...
* Organized crime
Organized crime (or organised crime) is a category of transnational, national, or local groupings of highly centralized enterprises run by criminals to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally th ...
* Phishing
Phishing is a type of social engineering where an attacker sends a fraudulent (e.g., spoofed, fake, or otherwise deceptive) message designed to trick a person into revealing sensitive information to the attacker or to deploy malicious softwa ...
, attempt to fraudulently acquire sensitive information
* Placebo
A placebo ( ) is a substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like Saline (medicine), saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
In general ...
* Police impersonation Police impersonation is the act of falsely portraying oneself as a member of the police for the purpose of deception.
Typology and methods
Criminology research has developed a typology of police impersonators, categorizing offenders as
# "police ...
* Political corruption
* Push payment fraud
* Quackery
Quackery, often synonymous with health fraud, is the promotion of fraudulent or ignorant medical practices. A quack is a "fraudulent or ignorant pretender to medical skill" or "a person who pretends, professionally or publicly, to have skill, ...
* Quatloos.com
Quatloos.com is an anti-fraud website maintained by a non-profit corporation, Financial and Tax Fraud Education Associates, Inc. It evolved out of a basic educational website on the topic created in 1997 by Jay Adkisson, an attorney and stockbr ...
* Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act
The Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations (RICO) Act is a United States federal law that provides for extended criminal penalties and a civil cause of action for acts performed as part of an ongoing criminal organization.
RICO was en ...
(RICO)
* SAS 99 {{Short description, Statutory Auditor Coderal
Statement on Auditing Standards No. 99: Consideration of Fraud in a Financial Statement Audit, commonly abbreviated as SAS 99, is an auditing statement issued by the Auditing Standards Board of the Am ...
* Scam
A confidence trick is an attempt to defraud a person or group after first gaining their trust. Confidence tricks exploit victims using their credulity, naïveté, compassion, vanity, confidence, irresponsibility, and greed. Researchers hav ...
* Scientific misconduct
Scientific misconduct is the violation of the standard codes of scholarly conduct and ethical behavior in the publication of professional scientific research. A '' Lancet'' review on ''Handling of Scientific Misconduct in Scandinavian countrie ...
* Secret profit
In English law, a secret profit is a profit made by an employee who uses his employer's premises and business facilities in order to engage in unauthorised trade on his own behalf. A common example is a bar manager who purchases beer from a bre ...
s
* Shell company
* Swampland in Florida
''Swampland in Florida'' is a figure of speech referring to real estate scams in which a seller misrepresents unusable swampland as developable property. These types of unseen property scams became widely known in the United States in the 20th cen ...
* Tobashi scheme
A tobashi scheme is a financial fraud through creative accounting where a client's losses are hidden by an investment firm by shifting them between the portfolios of other (genuine or fake) clients. Any real client with portfolio losses can there ...
, concealing financial losses
* U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government, created in the aftermath of the Wall Street Crash of 1929. The primary purpose of the SEC is to enforce the law against market ...
(SEC)
* United States Postal Inspection Service
The United States Postal Inspection Service (USPIS), or the Postal Inspectors, is the law enforcement arm of the United States Postal Service. It supports and protects the U.S. Postal Service, its employees, infrastructure, and customers by enf ...
* United States Secret Service
The United States Secret Service (USSS or Secret Service) is a federal law enforcement agency under the Department of Homeland Security charged with conducting criminal investigations and protecting U.S. political leaders, their families, and ...
* White-collar crime
The term "white-collar crime" refers to financially motivated, nonviolent or non-directly violent crime committed by individuals, businesses and government professionals. It was first defined by the sociologist Edwin Sutherland in 1939 as "a ...
* Wood laundering
References
Further reading
* Edward J. Balleisen ''Fraud: An American History from Barnum to Madoff''. (2017). Princeton University Press. *Fred Cohen
Frederick B. Cohen (born 1956) is an American computer scientist and best known as the inventor of computer virus defense techniques. He gave the definition of "computer virus". Cohen is best known for his pioneering work on computer viruses, t ...
''Frauds, Spies, and Lies – and How to Defeat Them''. (2006). ASP Press.
* Green, Stuart P. ''Lying, Cheating, and Stealing: A Moral Theory of White Collar Crime''. Oxford University Press, 2006.
Review Fraud – Alex Copola
Podgor, Ellen S. ''Criminal Fraud'', (1999) Vol, 48, No. 4 American Law Review 1.
The Nature, Extent and Economic Impact of Fraud in the UK. February, 2007.
by Eamon Dillon, published September 2008 by Merlin Publishing * Zhang, Yingyu.
The Book of Swindles: Selections from a Late Ming Collection
'. Columbia University Press, 2017.
External links
*Association of Certified Fraud Examiners
Immigration Marriage Fraud Amendments of 1986
U.S. Department of Justice Fraud Section
{{Authority control Crimes Deception Tort law Property crimes Financial crimes