Field emission gun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
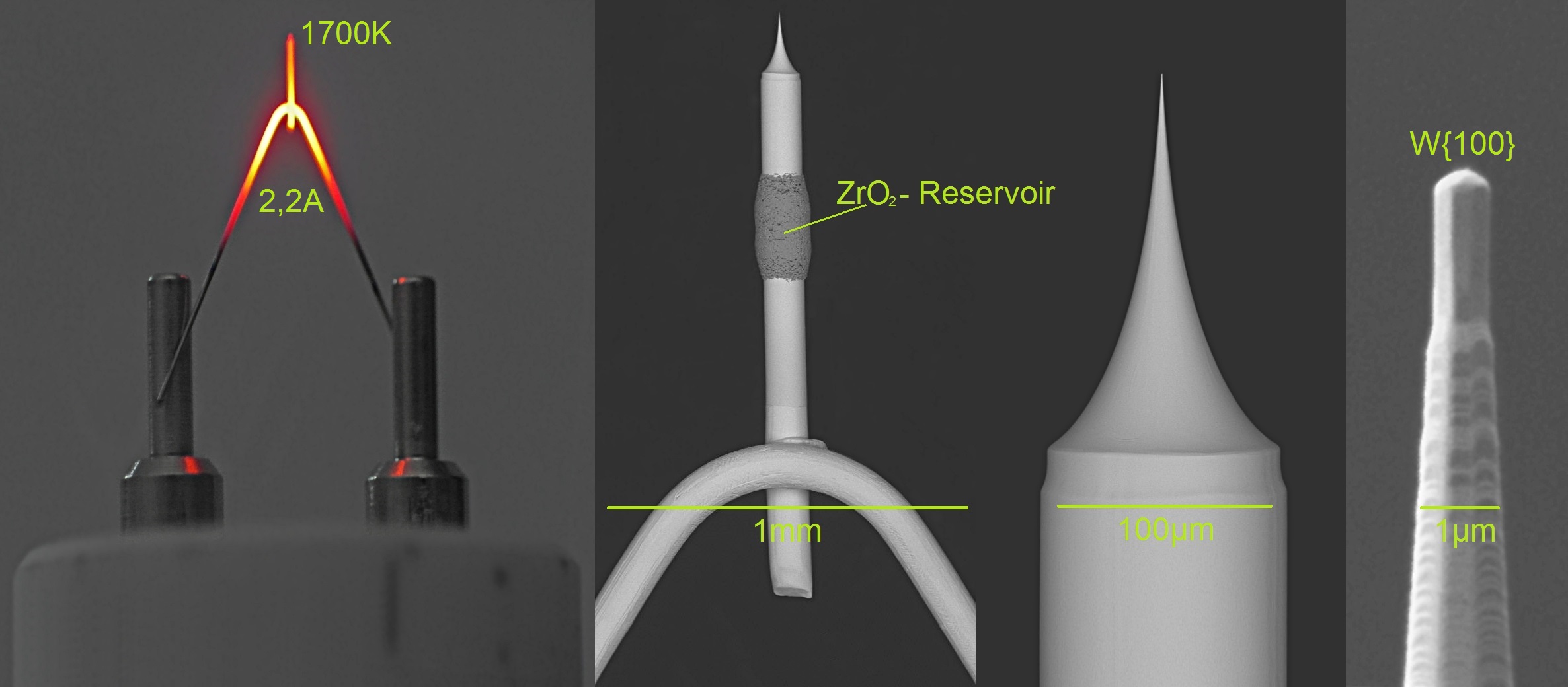 A field emission gun (FEG) is a type of
A field emission gun (FEG) is a type of
 A field emission gun (FEG) is a type of
A field emission gun (FEG) is a type of electron gun
An electron gun (also called electron emitter) is an electrical component in some vacuum tubes that produces a narrow, collimated electron beam that has a precise kinetic energy. The largest use is in cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), used in nearly ...
in which a sharply pointed Müller-type emitter is held at several kilovolts negative potential
Potential generally refers to a currently unrealized ability. The term is used in a wide variety of fields, from physics to the social sciences to indicate things that are in a state where they are able to change in ways ranging from the simple r ...
relative to a nearby electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials d ...
, so that there is sufficient potential gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p is the "direction and rate of fastest increase". If the gr ...
at the emitter surface to cause field electron emission. Emitters are either of cold-cathode
A cold cathode is a cathode that is not electrically heated by a filament.A negatively charged electrode emits electrons or is the positively charged terminal. For more, see field emission. A cathode may be considered "cold" if it emits more ele ...
type, usually made of single crystal tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
sharpened to a tip radius of about 100 nm, or of the Schottky type, in which thermionic emission
Thermionic emission is the liberation of electrons from an electrode by virtue of its temperature (releasing of energy supplied by heat). This occurs because the thermal energy given to the charge carrier overcomes the work function of the mater ...
is enhanced by barrier lowering in the presence of a high electric field. Schottky emitters are made by coating a tungsten tip with a layer of zirconium oxide
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral baddeleyite. A dopant stabi ...
(ZrO2) decreasing the work function
In solid-state physics, the work function (sometimes spelt workfunction) is the minimum thermodynamic work (i.e., energy) needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point in the vacuum immediately outside the solid surface. Here "immediately" ...
of the tip by approximately 2.7 eV.
In electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
s, a field emission gun is used to produce an electron beam that is smaller in diameter, more coherent and with up to three orders of magnitude greater current density or brightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target. The perception is not linear to luminan ...
than can be achieved with conventional thermionic emitters such as tungsten or lanthanum hexaboride ()-tipped filaments. The result in both scanning and transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a g ...
is significantly improved signal-to-noise ratio and spatial resolution
In physics and geosciences, the term spatial resolution refers to distance between independent measurements, or the physical dimension that represents a pixel of the image. While in some instruments, like cameras and telescopes, spatial resolut ...
, and greatly increased emitter life and reliability compared with thermionic devices.
References
Vacuum tubes Tungsten {{tech-stub