Extrinsic Extensor Muscles Of The Hand on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The extrinsic extensor muscles of the hand are located in the back of the forearm and have long tendons connecting them to bones in the hand, where they exert their action. ''Extrinsic'' denotes their location ''outside'' the hand. ''Extensor'' denotes their action which is to ''
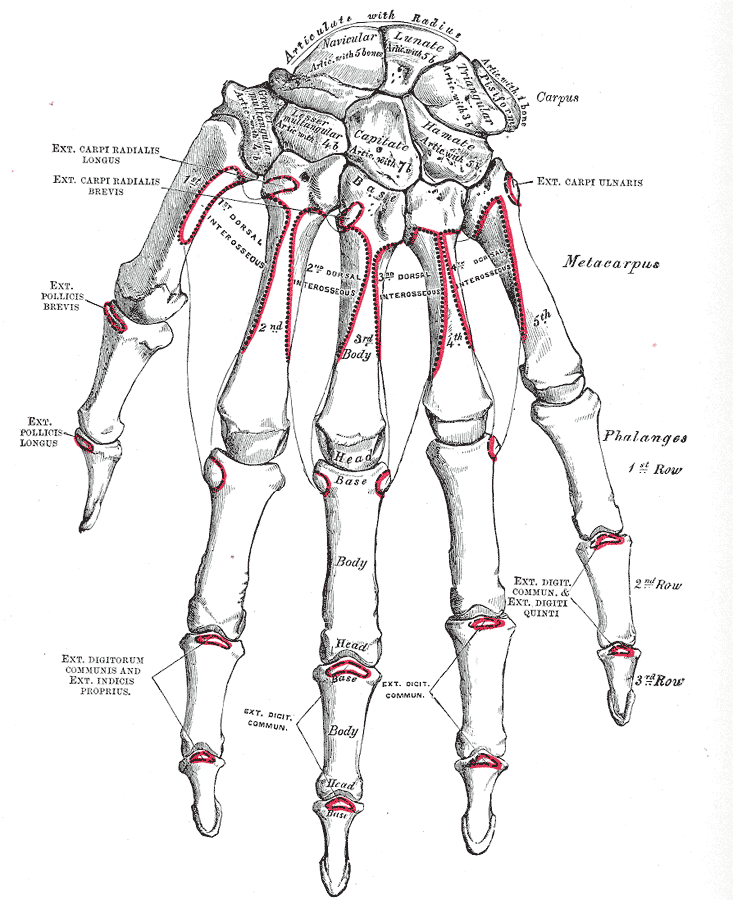 The ECRL inserts into the dorsal surface of the base of the
The ECRL inserts into the dorsal surface of the base of the
Extensor mechanism of fingers
at Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics {{Portal bar, Anatomy Muscles of the upper limb
extend
Extension, extend or extended may refer to:
Mathematics
Logic or set theory
* Axiom of extensionality
* Extensible cardinal
* Extension (model theory)
* Extension (predicate logic), the set of tuples of values that satisfy the predicate
* Ext ...
'', or open flat, joints in the hand. They include the extensor carpi radialis longus
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each ...
(ECRL), extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB), extensor digitorum (ED), extensor digiti minimi (EDM), extensor carpi ulnaris
In human anatomy, the extensor carpi ulnaris is a skeletal muscle located on the ulnar side of the forearm. The extensor carpi ulnaris acts to extend and adduct at the carpus/wrist from anatomical position.
Being an extensor muscle, extensor carp ...
(ECU), abductor pollicis longus
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox.
Structure
The abductor ...
(APL), extensor pollicis brevis
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis brevis is a skeletal muscle on the dorsal side of the forearm. It lies on the medial side of, and is closely connected with, the abductor pollicis longus. The extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) belongs to the ...
(EPB), extensor pollicis longus
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together ...
(EPL), and extensor indicis
In human anatomy, the extensor indicis roprius'' is a narrow, elongated skeletal muscle in the deep layer of the dorsal forearm, placed medial to, and parallel with, the extensor pollicis longus. Its tendon goes to the index finger, which it exte ...
(EI).

Origin
The extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) has the most proximal origin of the extrinsic hand extensors. It originates just distal to the brachioradialis at thelateral supracondylar ridge
The lateral supracondylar ridge is a prominent, rough margin on the lower part of the lateral border of the humerus. It presents an anterior lip for the origin of forearm extensors, including the brachioradialis muscle above, and the extensor car ...
of the humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a r ...
, the lateral intermuscular septum, and by a few fibers at the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. Distal to this, the extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB), extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, and extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) originate from the lateral epicondyle via the . The ECRB has additional origins from the radial collateral ligament, the ECU from the dorsal border of the ulna (shared with the flexor carpi ulnaris
The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a muscle of the forearm that flexes and adducts at the wrist joint.
Structure Origin
The flexor carpi ulnaris has two heads; a humeral head and ulnar head. The humeral head originates from the medial epicondyle of ...
and flexor digitorum profundus
The flexor digitorum profundus is a muscle in the forearm of humans that flexes the fingers (also known as digits). It is considered an extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on the hand while its muscle belly is located in the forearm.
Togeth ...
), and all four also originate from various fascia. Moving distally, there are the abductor pollicis longus (APL), extensor pollicis brevis (EPB), extensor pollicis longus (EPL), and extensor indicis (EI). The APL originates from the lateral part of the dorsal surface of the body of the ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
below the insertion of the anconeus and from the middle third of the dorsal surface of the body of the radius
In classical geometry, a radius (plural, : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', ...
. The EPB arises from the radius
In classical geometry, a radius (plural, : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', ...
distal to the APL and from the dorsal surface of the radius
In classical geometry, a radius (plural, : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', ...
. The EPL arises from the dorsal surface of the ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
and the EI from the distal third of the dorsal part of the body of ulna. The APL, EPB, EPL, and EI all have an additional origin at the interosseus membrane.
Course
The ECRL and ECRB, (with thebrachioradialis
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way ...
) form the lateral compartment. Their muscle fibers end at the upper third and the mid forearm respectively, continuing as flat tendons along the lateral border of the radius, beneath the APL and EPB. They then pass beneath the extensor retinaculum and dorsal carpal ligament, where they lie in a groove on the back of the radius, immediately behind the styloid process, and continue into the second tendon compartment. The ED divides into four tendons which, with the EI tendons, go through the fourth tendon compartment of the dorsal carpal ligament. On the back of the hand, the ED tendons diverge to follow the fingers and the EI tendon joins the ulnar side of one of the ED tendons along the back of the index finger. The EDM takes a similar course as the EI except it follows the ED tendon along the little finger. The ECU crosses from the lateral to the medial side of the forearm. The APL and EPB pass obliquely down and lateral, ending in tendons which run through a groove on the lateral side of the lower end of the radius. The EPL tendon passes through the third compartment and lies in a narrow, oblique groove on the back of the lower end of the radius.
Extensor digitorum tendons
The ED tendons are more complex in their course. Opposite the metacarpophalangeal joint each tendon is bound byfasciculi
Fascicle or ''fasciculus'' may refer to:
Anatomy and histology
* Muscle fascicle, a bundle of skeletal muscle fibers
* Nerve fascicle, a bundle of axons (nerve fibers)
** Superior longitudinal fasciculus
*** Arcuate fasciculus
** Gracile fasci ...
to the collateral ligaments and serves as the dorsal ligament of this joint; after having crossed the joint, it spreads out into a broad aponeurosis, which covers the dorsal surface of the first phalanx
The phalanx ( grc, φάλαγξ; plural phalanxes or phalanges, , ) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar pole weapons. The term is particularly ...
and is reinforced, in this situation, by the tendons of the Interossei {{short description, Muscles between certain bones
Interossei refer to muscles between certain bones. There are many interossei in a human body. Specific interossei include:
On the hands
* Dorsal interossei muscles of the hand
* Palmar interosse ...
and Lumbricalis.
Opposite the first interphalangeal joints this aponeurosis divides into three slips; an intermediate and two collateral: the former is inserted into the base of the second phalanx; and the two collateral, which are continued onward along the sides of the second phalanx, unite by their contiguous margins, and are inserted into the dorsal surface of the last phalanx. As the tendons cross the interphalangeal joints, they furnish them with dorsal ligaments. The tendon to the index finger is accompanied by the EI, which lies on its ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
r side. On the back of the hand, the tendons to the middle, ring, and little fingers are connected by two obliquely placed bands, one from the third tendon passing downward and lateralward to the second tendon, and the other passing from the same tendon downward and medialward to the fourth.
Occasionally the first tendon is connected to the second by a thin transverse band. Collectively, these are known as the sagittal bands; they serve to maintain the central alignment of the extensor tendons over the metacarpal head, thus increasing the available lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '' fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is d ...
age. Injuries (such as by an external flexion force during active extension) may allow the tendon to dislocate into the intermetacarpal space; the extensor tendon then acts as a flexor and the finger may no longer be actively extended. This may be corrected surgically by using a slip of the extensor tendon to replace the damaged ligamentous band
Anatomical snuff box
The EPL tendon crosses obliquely the tendons of the ECRL and ECRB, and is separated from the EPB by a triangular interval, the anatomical snuff box, in which theradial artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.
Structure
The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the f ...
is found.
Insertion and action
 The ECRL inserts into the dorsal surface of the base of the
The ECRL inserts into the dorsal surface of the base of the second metacarpal bone
The second metacarpal bone (metacarpal bone of the index finger) is the longest, and its base the largest, of all the metacarpal bones.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). See infobox.
Human anatomy
Its base is prolonged upward and medialward, forming a ...
on its radial side to extend and abduct the wrist.Platzer 2004, p 164 The ECRB inserts into the lateral dorsal surface of the base of the third metacarpal bone
The third metacarpal bone (metacarpal bone of the middle finger) is a little smaller than the second.
The dorsal aspect of its base presents on its radial side a pyramidal eminence, the styloid process, which extends upward behind the capitate ...
, with a few fibres inserting into the medial dorsal surface of the second metacarpal bone
The second metacarpal bone (metacarpal bone of the index finger) is the longest, and its base the largest, of all the metacarpal bones.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). See infobox.
Human anatomy
Its base is prolonged upward and medialward, forming a ...
, also to extend and abduct the wrist. The ED inserts into the middle and distal phalanges to extend the fingers and wrist. Opposite the head of the second metacarpal
The second metacarpal bone (metacarpal bone of the index finger) is the longest, and its base the largest, of all the metacarpal bones.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). See infobox.
Human anatomy
Its base is prolonged upward and medialward, forming a ...
bone, the EI joins the ulnar side of the ED tendon to extend the index finger. The EDM has a similar role for the little finger. The ECU inserts at the base of the 5th metacarpal to extend and adduct the wrist. The APL inserts into the radial side of the base of the first metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist, which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones ar ...
bone to abduct the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.
The CMC joint of the thumb or the first CMC joint, also known as the trapeziometaca ...
and may continue to abduct the wrist. The EPB inserts into the base of the first phalanx of the thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb ...
to extend and abduct the thumb at the carpometacarpal and MCP joints.
The EPL inserts on the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb. It uses the dorsal tubercle on the radius as fulcrum to help the EPB with its action as well as extending the distal phalanx of the thumb. Because the index finger and little finger have separate extensors, these fingers can be moved more independently than the other fingers.
Neurovascular supply
The ECU is supplied by theulnar artery
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial ar ...
. The APL, EPB, EPL, EI, ED, and EDM are supplied by the Posterior interosseous artery
The posterior interosseous artery (dorsal interosseous artery) is an artery of the forearm. It is a branch of the common interosseous artery, which is a branch of the ulnar artery.
Structure
The posterior interosseous artery passes backward be ...
, a branch of the ulnar artery. The ECRL and ECRB receive blood from the radial artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.
Structure
The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the f ...
.
The ECRL is supplied by the radial nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial comp ...
and the ECRB by its deep branch. The remaining extrinsic hand extensors are supplied by the posterior interosseus nerve
The posterior interosseous nerve (or dorsal interosseous nerve) is a nerve in the forearm. It is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve, after this has crossed the supinator muscle. It is considerably diminished in size compared t ...
, another branch of the radial nerve.
Summary table
See also
*Extensor digitorum reflex The extensor digitorum reflex is tested as part of the neurological examination to assess the sensory and motor pathways within the C6 and C7 spinal nerves. It is also known as Braunecker-Effenberg reflex, or BER.
Testing
The test is performed by ...
References
* * *External links
Extensor mechanism of fingers
at Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics {{Portal bar, Anatomy Muscles of the upper limb