Enamel hypoplasia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the
 Enamel hypoplasia is believed to result from the dysfunction of
Enamel hypoplasia is believed to result from the dysfunction of
National Institute of Health (NIH)
Doctor Staci Whitman (2021)
 Enamel hypoplasia is a risk factor for dental caries in children including early childhood caries (ECC), which continues to be a burden for many children. This association has been identified as significant and independent, and is believed that the formation of pits and missing enamel provides a suitable local environment for adhesion and colonization of cariogenic bacteria. Historically, enamel hypoplasia has been under-appreciated as a risk factor for ECC.
Developmental defects in enamel that affect tooth appearance in the esthetic zone (i.e. upper front teeth) may cause individuals to experience social embarrassment or anxiety regarding the appearance of their teeth.
Enamel hypoplasia is a risk factor for dental caries in children including early childhood caries (ECC), which continues to be a burden for many children. This association has been identified as significant and independent, and is believed that the formation of pits and missing enamel provides a suitable local environment for adhesion and colonization of cariogenic bacteria. Historically, enamel hypoplasia has been under-appreciated as a risk factor for ECC.
Developmental defects in enamel that affect tooth appearance in the esthetic zone (i.e. upper front teeth) may cause individuals to experience social embarrassment or anxiety regarding the appearance of their teeth.
teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, t ...
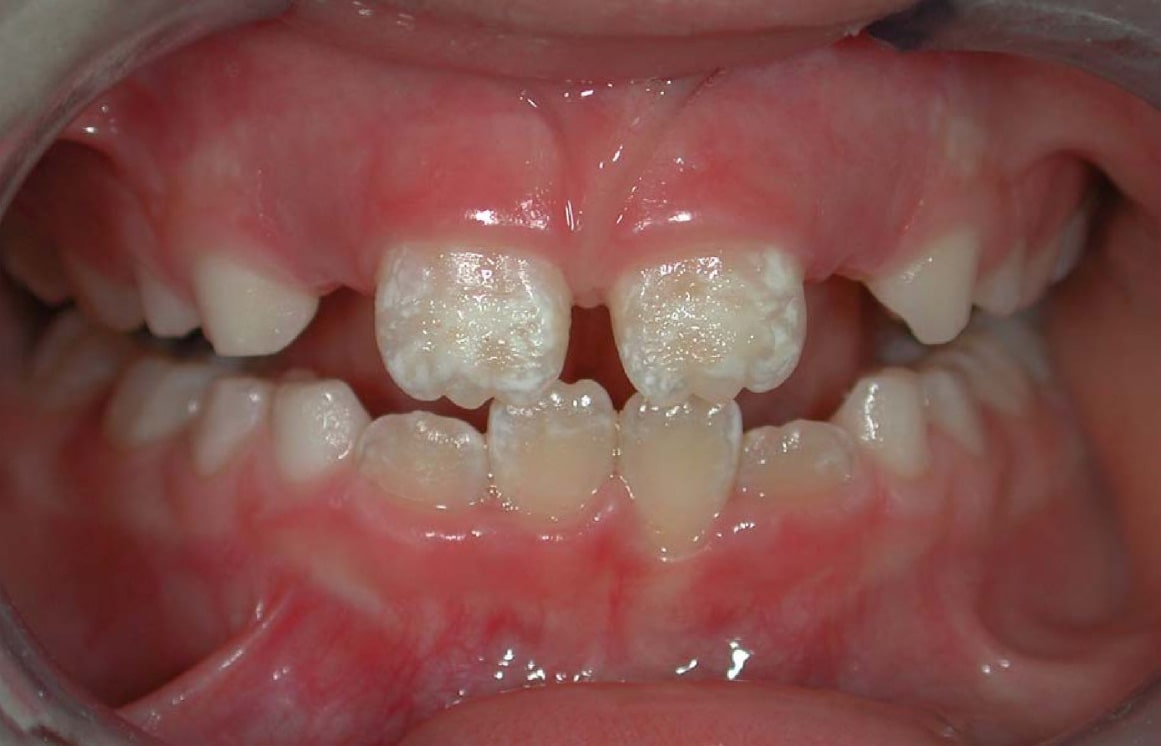
in which the enamel is deficient in quantity, caused by defective enamel matrix formation during enamel development, as a result of inherited and acquired systemic condition(s). It can be identified as missing tooth structure and may manifest as pits or grooves in the crown of the affected teeth, and in extreme cases, some portions of the crown of the tooth may have no enamel, exposing the dentin. It may be generalized across the dentition or localized to a few teeth. Defects are categorized by shape or location. Common categories are pit-form, plane-form, linear-form, and localised enamel hypoplasia. Hypoplastic lesions are found in areas of the teeth where the enamel was being actively formed during a systemic or local disturbance. Since the formation of enamel extends over a long period of time, defects may be confined to one well-defined area of the affected teeth. Knowledge of chronological development of deciduous and permanent teeth makes it possible to determine the approximate time at which the developmental disturbance occurred. Enamel hypoplasia varies substantially among populations and can be used to infer health and behavioural impacts from the past. Defects have also been found in a variety of non-human animals.
Causes
 Enamel hypoplasia is believed to result from the dysfunction of
Enamel hypoplasia is believed to result from the dysfunction of ameloblast
Ameloblasts are cells present only during tooth development that deposit tooth enamel, which is the hard outermost layer of the tooth forming the surface of the crown.
Structure
Each ameloblast is a columnar cell approximately 4 micrometers in ...
s—enamel-producing cells—either for a short period of time or throughout their lifespan. Enamel hypoplasia has a wide variety of known causes. Some causes are hereditary and others are from environmental exposure. The severity and localization of disease presentation is dependent on the timing and stage of tooth development in which the defective enamel formation occurred.
Hereditary causes of enamel hypoplasia include:
* Primary abnormalities in enamel development, such as amelogenesis imperfecta
Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) is a congenital disorder which presents with a rare abnormal formation of the enamel or external layer of the crown of teeth, unrelated to any systemic or generalized conditions. Enamel is composed mostly of mineral, ...
* Certain dermatological conditions, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
* Other complex hereditary conditions such as Usher syndrome
Usher syndrome, also known as Hallgren syndrome, Usher–Hallgren syndrome, retinitis pigmentosa–dysacusis syndrome or dystrophia retinae dysacusis syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder caused by a mutation in any one of at least 11 genes result ...
, Seckel syndrome
Seckel syndrome, or microcephalic primordial dwarfism (also known as bird-headed dwarfism, Harper's syndrome, Virchow–Seckel dwarfism and bird-headed dwarf of Seckel) is an extremely rare congenital nanosomic disorder. Inheritance is autosomal ...
, Treacher-Collins syndrome, Heimler syndrome & Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome
Environmental causes of enamel hypoplasia include:
* Nutritional deficits, such as Vitamin D, iron or calcium deficiency
* Birth injury or preterm birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 2 ...
* Smoking during pregnancy
* Trauma
* Radiation
* Certain infections (e.g. congenital syphilis, cytomegalovirus, congenital rubella)
* Certain diseases (such as undiagnosed and untreated celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
,Dental Enamel Defects and Celiac DiseaseNational Institute of Health (NIH)
chicken pox
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab ...
, congenital syphilis
Congenital syphilis is syphilis present ''in utero'' and at birth, and occurs when a child is born to a mother with syphilis. Untreated early syphilis infections results in a high risk of poor pregnancy outcomes, including saddle nose, lower extr ...
)
* High fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
* Hypoxia (i.e. from severe cardiac defect)
* Excessive fluoride exposure (dental fluorosis
Dental fluorosis is a common disorder, characterized by hypomineralization of tooth enamel caused by ingestion of excessive fluoride during enamel formation.
It appears as a range of visual changes in enamel causing degrees of intrinsic tooth d ...
)
* Tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis.
Common side effects in ...
* Vitamin A, C, or D deficiencyEnamel HypoplasiaDoctor Staci Whitman (2021)
Clinical relevance
 Enamel hypoplasia is a risk factor for dental caries in children including early childhood caries (ECC), which continues to be a burden for many children. This association has been identified as significant and independent, and is believed that the formation of pits and missing enamel provides a suitable local environment for adhesion and colonization of cariogenic bacteria. Historically, enamel hypoplasia has been under-appreciated as a risk factor for ECC.
Developmental defects in enamel that affect tooth appearance in the esthetic zone (i.e. upper front teeth) may cause individuals to experience social embarrassment or anxiety regarding the appearance of their teeth.
Enamel hypoplasia is a risk factor for dental caries in children including early childhood caries (ECC), which continues to be a burden for many children. This association has been identified as significant and independent, and is believed that the formation of pits and missing enamel provides a suitable local environment for adhesion and colonization of cariogenic bacteria. Historically, enamel hypoplasia has been under-appreciated as a risk factor for ECC.
Developmental defects in enamel that affect tooth appearance in the esthetic zone (i.e. upper front teeth) may cause individuals to experience social embarrassment or anxiety regarding the appearance of their teeth.
Guidelines for Treatment of Enamel Hypoplasia
Dental sealants may be indicated for the prevention of caries in hypoplastic pit & fissure systems. According to clinical trials, topical fluoride treatment in the form of gel or varnish is effective in preventing tooth decay in children with enamel defects. Treatment with other topical agents, such as calcium phosphate ( CPP-ACP), may also be effective in the remineralization of areas with congenital or carious enamel defects. In decayed teeth with enamel defects, only bonded restorations (e.g. glass ionomer, polyacid-modified composite resin and not amalgam) should be placed and cavity margins should not be placed in areas of defective enamel as this may lead to marginal leakage and recurrent decay. Stainless steel crowns with conservative preparation may be an effective method to eliminate sensitivity and prevent further breakdown in teeth with enamel defects requiring full-coverage crowns.Other conditions affecting enamel development
Hypomineralization or hypocalcification, as opposed to hypoplasia, refers to a decrease in the mineral content of the enamel, not the total amount present. It can vary in its presentation, and teeth may appear visually normal or highly translucent. Affected enamel is softer and more susceptible to acid, wear and decay.Molar-incisor hypomineralization
Molar-incisor hypomineralization (MIH) is a condition in which there are areas of hypomineralized or hypomatured enamel on the crowns of permanentmolars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
and incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wher ...
s. In these cases, teeth may lose their weakened enamel shortly after eruption and are highly susceptible to dental caries. Affected teeth are highly sensitive to chemical and thermal irritants, and may also be difficult to obtain anesthesia. The causes of MIH are thought to be similar to those of other forms of enamel hypoplasia, but occur concurrently with crown development in the permanent molars and incisors (birth to approximately 3 years of age).
Turner's hypoplasia
Turner's hypoplasia or Turner's tooth is a presentation of enamel hypoplasia that normally affects only a single tooth. Its causes can be the same as other forms of enamel hypoplasia, but it is most commonly associated with trauma to a primary maxillary central incisor and the subsequent developmental disturbance of the underlying permanent tooth. This may also result in dilaceration of the root of the permanent tooth.References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Enamel Hypoplasia Dental enamel Developmental tooth disorders