economic indicator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An economic indicator is a
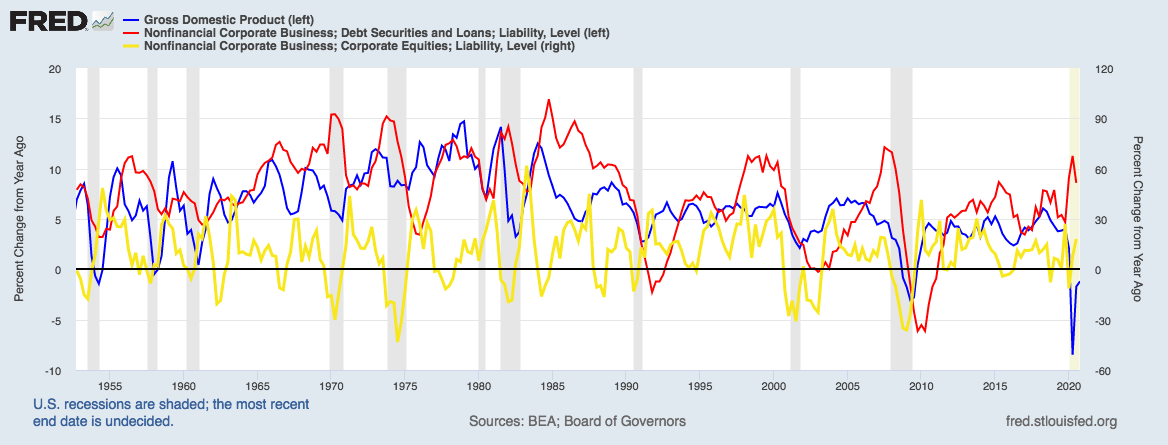 Economic indicators can be classified into three categories according to their usual timing in relation to the business cycle: leading indicators, lagging indicators, and coincident indicators.
Economic indicators can be classified into three categories according to their usual timing in relation to the business cycle: leading indicators, lagging indicators, and coincident indicators.
 Leading indicators are indicators that usually, but not always, change before the economy as a whole changes. They are therefore useful as short-term predictors of the economy. Leading indicators include the index of consumer expectations, building permits, and the money supply. The Conference Board publishes a composite Leading Economic Index consisting of ten indicators designed to predict activity in the U. S. economy six to nine months in future.
Components of the Conference Board's Leading Economic Indicators Index
#Average weekly hours (manufacturing) — Adjustments to the working hours of existing employees are usually made in advance of new hires or layoffs, which is why the measure of average weekly hours is a leading indicator for changes in unemployment.
#Average weekly initial jobless claims for unemployment insurance — The CB reverses the value of this component from positive to negative because a positive reading indicates a loss in jobs. The initial jobless-claims data is more sensitive to business conditions than other measures of unemployment, and as such leads the monthly unemployment data released by the U.S. Department of Labor.
#Manufacturers' new orders for consumer goods/materials — This component is considered a leading indicator because increases in new orders for consumer goods and materials usually mean positive changes in actual production. The new orders decrease inventory and contribute to unfilled orders, a precursor to future revenue.
#Vendor performance (slower deliveries diffusion index) — This component measures the time it takes to deliver orders to industrial companies. Vendor performance leads the business cycle because an increase in delivery time can indicate rising demand for manufacturing supplies. Vendor performance is measured by a monthly survey from the National Association of Purchasing Managers (NAPM). This diffusion index measures one-half of the respondents reporting no change and all respondents reporting slower deliveries.
#Manufacturers' new orders for non-defense
Leading indicators are indicators that usually, but not always, change before the economy as a whole changes. They are therefore useful as short-term predictors of the economy. Leading indicators include the index of consumer expectations, building permits, and the money supply. The Conference Board publishes a composite Leading Economic Index consisting of ten indicators designed to predict activity in the U. S. economy six to nine months in future.
Components of the Conference Board's Leading Economic Indicators Index
#Average weekly hours (manufacturing) — Adjustments to the working hours of existing employees are usually made in advance of new hires or layoffs, which is why the measure of average weekly hours is a leading indicator for changes in unemployment.
#Average weekly initial jobless claims for unemployment insurance — The CB reverses the value of this component from positive to negative because a positive reading indicates a loss in jobs. The initial jobless-claims data is more sensitive to business conditions than other measures of unemployment, and as such leads the monthly unemployment data released by the U.S. Department of Labor.
#Manufacturers' new orders for consumer goods/materials — This component is considered a leading indicator because increases in new orders for consumer goods and materials usually mean positive changes in actual production. The new orders decrease inventory and contribute to unfilled orders, a precursor to future revenue.
#Vendor performance (slower deliveries diffusion index) — This component measures the time it takes to deliver orders to industrial companies. Vendor performance leads the business cycle because an increase in delivery time can indicate rising demand for manufacturing supplies. Vendor performance is measured by a monthly survey from the National Association of Purchasing Managers (NAPM). This diffusion index measures one-half of the respondents reporting no change and all respondents reporting slower deliveries.
#Manufacturers' new orders for non-defense  #Money Supply (M2) — The
#Money Supply (M2) — The

 ;
;
OECD Economic IndicatorsEconomic Indicators Mobile AppU.S. Bureau of Labor StatisticsThe Conference Board - Economic IndicatorsFED101 - Economic IndicatorsInternational Conference on Indicators and Survey MethodologyEconomic Indicators
Monthly analysis from American Institute for Economic Research (AIER)
U.S. Economic Indicators United States Economic Indicators (current and historical, open data)
(quandl.com)
GPO Economic Indicators
{{DEFAULTSORT:Economic Indicator Indicators
statistic
A statistic (singular) or sample statistic is any quantity computed from values in a sample which is considered for a statistical purpose. Statistical purposes include estimating a population parameter, describing a sample, or evaluating a hypo ...
about an economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and prediction
A prediction (Latin ''præ-'', "before," and ''dicere'', "to say"), or forecast, is a statement about a future event or data. They are often, but not always, based upon experience or knowledge. There is no universal agreement about the exact ...
s of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic indicators include various indices, earnings reports, and economic summaries: for example, the unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refe ...
rate, quits rate (quit rate in American English), housing starts, consumer price index
A consumer price index (CPI) is a price index, the price of a weighted average market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households. Changes in measured CPI track changes in prices over time.
Overview
A CPI is a statisti ...
(a measure for inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
), Inverted yield curve, consumer leverage ratio, industrial production
Industrial production is a measure of output of the industrial sector of the economy. The industrial sector includes manufacturing, mining, and utilities. Although these sectors contribute only a small portion of gross domestic product (GDP), the ...
, bankruptcies
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor ...
, gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is of ...
, broadband internet penetration, retail sales
Retail is the sale of goods and services to consumers, in contrast to wholesaling, which is sale to business or institutional customers. A retailer purchases goods in large quantities from manufacturers, directly or through a wholesaler, and t ...
, price index, and money supply
In macroeconomics, the money supply (or money stock) refers to the total volume of currency held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several ways to define "money", but standard measures usually include currency in circu ...
changes.
The leading business cycle dating committee in the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
is the private National Bureau of Economic Research. The Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics and serves as a principal agency of ...
is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the field of labor economics and statistics. Other producers of economic indicators includes the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of th ...
and United States Bureau of Economic Analysis
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) of the United States Department of Commerce is a U.S. government agency that provides official macroeconomic and industry statistics, most notably reports about the gross domestic product (GDP) of the United ...
.
Classification by timing
 Economic indicators can be classified into three categories according to their usual timing in relation to the business cycle: leading indicators, lagging indicators, and coincident indicators.
Economic indicators can be classified into three categories according to their usual timing in relation to the business cycle: leading indicators, lagging indicators, and coincident indicators.
Leading indicators
 Leading indicators are indicators that usually, but not always, change before the economy as a whole changes. They are therefore useful as short-term predictors of the economy. Leading indicators include the index of consumer expectations, building permits, and the money supply. The Conference Board publishes a composite Leading Economic Index consisting of ten indicators designed to predict activity in the U. S. economy six to nine months in future.
Components of the Conference Board's Leading Economic Indicators Index
#Average weekly hours (manufacturing) — Adjustments to the working hours of existing employees are usually made in advance of new hires or layoffs, which is why the measure of average weekly hours is a leading indicator for changes in unemployment.
#Average weekly initial jobless claims for unemployment insurance — The CB reverses the value of this component from positive to negative because a positive reading indicates a loss in jobs. The initial jobless-claims data is more sensitive to business conditions than other measures of unemployment, and as such leads the monthly unemployment data released by the U.S. Department of Labor.
#Manufacturers' new orders for consumer goods/materials — This component is considered a leading indicator because increases in new orders for consumer goods and materials usually mean positive changes in actual production. The new orders decrease inventory and contribute to unfilled orders, a precursor to future revenue.
#Vendor performance (slower deliveries diffusion index) — This component measures the time it takes to deliver orders to industrial companies. Vendor performance leads the business cycle because an increase in delivery time can indicate rising demand for manufacturing supplies. Vendor performance is measured by a monthly survey from the National Association of Purchasing Managers (NAPM). This diffusion index measures one-half of the respondents reporting no change and all respondents reporting slower deliveries.
#Manufacturers' new orders for non-defense
Leading indicators are indicators that usually, but not always, change before the economy as a whole changes. They are therefore useful as short-term predictors of the economy. Leading indicators include the index of consumer expectations, building permits, and the money supply. The Conference Board publishes a composite Leading Economic Index consisting of ten indicators designed to predict activity in the U. S. economy six to nine months in future.
Components of the Conference Board's Leading Economic Indicators Index
#Average weekly hours (manufacturing) — Adjustments to the working hours of existing employees are usually made in advance of new hires or layoffs, which is why the measure of average weekly hours is a leading indicator for changes in unemployment.
#Average weekly initial jobless claims for unemployment insurance — The CB reverses the value of this component from positive to negative because a positive reading indicates a loss in jobs. The initial jobless-claims data is more sensitive to business conditions than other measures of unemployment, and as such leads the monthly unemployment data released by the U.S. Department of Labor.
#Manufacturers' new orders for consumer goods/materials — This component is considered a leading indicator because increases in new orders for consumer goods and materials usually mean positive changes in actual production. The new orders decrease inventory and contribute to unfilled orders, a precursor to future revenue.
#Vendor performance (slower deliveries diffusion index) — This component measures the time it takes to deliver orders to industrial companies. Vendor performance leads the business cycle because an increase in delivery time can indicate rising demand for manufacturing supplies. Vendor performance is measured by a monthly survey from the National Association of Purchasing Managers (NAPM). This diffusion index measures one-half of the respondents reporting no change and all respondents reporting slower deliveries.
#Manufacturers' new orders for non-defense capital goods
The economic concept of a capital good (also called complex product systems (CoPS),H. Rush, "Managing innovation in complex product systems (CoPS)," IEE Colloquium on EPSRC Technology Management Initiative (Engineering & Physical Sciences Researc ...
— As stated above, new orders lead the business cycle because increases in orders usually mean positive changes in actual production and perhaps rising demand. This measure is the producer's counterpart of new orders for consumer goods/materials component (#3).
#Building permits for new private housing units.
#Stock prices of 500 common stocks — Equity market returns are considered a leading indicator because changes in stock prices reflect investors' expectations for the future of the economy and interest rates.  #Money Supply (M2) — The
#Money Supply (M2) — The money supply
In macroeconomics, the money supply (or money stock) refers to the total volume of currency held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several ways to define "money", but standard measures usually include currency in circu ...
measures demand deposits, traveler's checks, savings deposits, currency, money market accounts, and small-denomination time deposits. Here, M2 is adjusted for inflation by means of the deflator published by the federal government in the GDP report. Bank lending, a factor contributing to account deposits, usually declines when inflation increases faster than the money supply, which can make economic expansion more difficult. Thus, an increase in demand deposits will indicate expectations that inflation will rise, resulting in a decrease in bank lending and an increase in savings.
#Interest rate spread (10-year Treasury vs. Federal Funds target) — The interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, t ...
spread is often referred to as the yield curve and implies the expected direction of short-, medium- and long-term interest rates. Changes in the yield curve have been the most accurate predictors of downturns in the economic cycle. This is particularly true when the curve becomes inverted, that is, when the longer-term returns are expected to be less than the short rates.
#Index of consumer expectations — This is the only component of the leading indicators that is based solely on expectations. This component leads the business cycle because consumer expectations can indicate future consumer spending or tightening. The data for this component comes from the University of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821)
, budget = $10.3 billion (2021)
, endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o ...
's Survey Research Center, and is released once a month.
Lagging indicators
Lagging indicators are indicators that usually change after the economy as a whole does. Typically the lag is a few quarters of a year. The unemployment rate is a lagging indicator: employment tends to increase two or three quarters after an upturn in the general economy.. In a performance measuring system, profit earned by a business is a lagging indicator as it reflects a historical performance; similarly, improved customer satisfaction is the result of initiatives taken in the past. The Index of Lagging Indicators is published monthly by The Conference Board, a non-governmental organization, which determines the value of the index from seven components. The Index tends to ''follow'' changes in the overall economy. The components on the Conference Board's index are: * The average duration ofunemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refe ...
(inverted)
* The value of outstanding commercial and industrial loan
In finance, a loan is the lending of money by one or more individuals, organizations, or other entities to other individuals, organizations, etc. The recipient (i.e., the borrower) incurs a debt and is usually liable to pay interest on that ...
s
* The change in the Consumer Price Index
A consumer price index (CPI) is a price index, the price of a weighted average market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households. Changes in measured CPI track changes in prices over time.
Overview
A CPI is a statisti ...
for services
* The change in labour cost per unit of output
* The ratio of manufacturing and trade inventories to sales
* The ratio of consumer credit outstanding to personal income
* The average prime rate
A prime rate or prime lending rate is an interest rate used by banks, usually the interest rate at which banks lend to customers with good credit. Some variable interest rates may be expressed as a percentage above or below prime rate.
Use in dif ...
charged by banks

Coincident indicators
Coincident indicators change at approximately the same time as the whole economy, thereby providing information about the current state of the economy. There are many coincident economic indicators, such asGross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is of ...
, industrial production, personal income and retail sales. A coincident index may be used to identify, after the fact, the dates of peaks and troughs in the business cycle.
There are four economic statistics comprising the Index of Coincident Economic Indicators:
* Number of employees on non-agricultural payrolls
* Personal income less transfer payments
* Industrial production
* Manufacturing and trade sale
A trade sale is a common means of exit to a trade buyer. This allows the management to withdraw from the business and may open up the prospect of collaboration on larger projects. The term trade sale is mostly used in the context of venture capital ...
The Philadelphia Federal Reserve produces state-level coincident indexes based on 4 state-level variables:
* Nonfarm payroll employment
* Average hours worked in manufacturing
* Unemployment rate
* Wage and salary disbursements deflated by the consumer price index (U.S. city average)
By direction
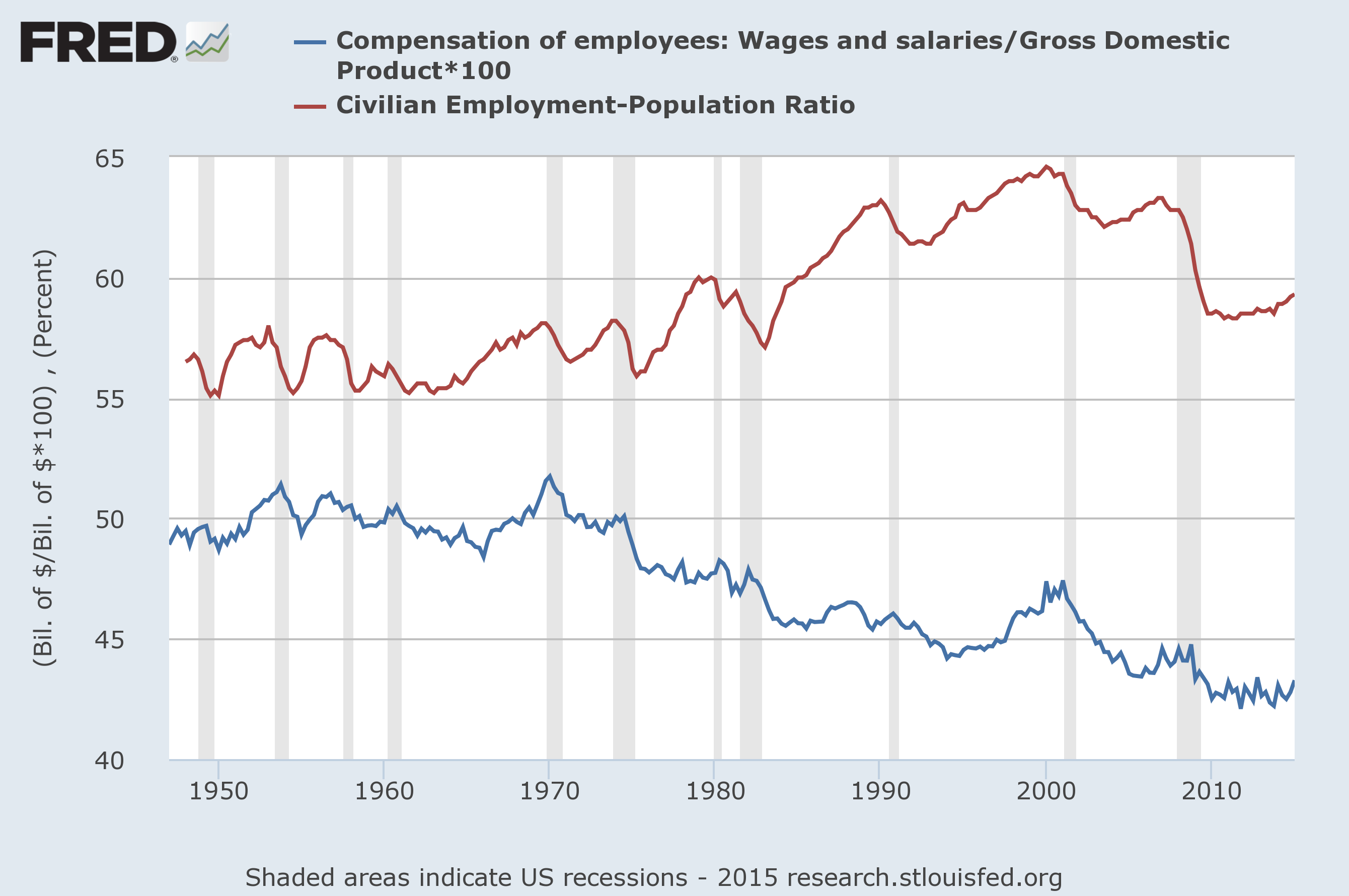
There are also three terms that describe an economic indicator's ''direction'' relative to the direction of the general economy: ;
;Procyclical
Procyclical and countercyclical variables are variables that fluctuate in a way that is positively or negatively correlated with business cycle fluctuations in gross domestic product (GDP). The scope of the concept may differ between the context ...
indicators: move in the same direction as the general economy: they increase when the economy is doing well; decrease when it is doing badly. Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is of ...
(GDP) is a procyclic indicator.
; Countercyclical indicators: move in the opposite direction to the general economy. The unemployment rate and the wage share are countercyclic: in the short run they rise when the economy is deteriorating.
; Acyclical indicators: are those with little or no correlation to the business cycle: they may rise or fall when the general economy is doing well, and may rise or fall when it is not doing well.
Local indicators
Local governments often need to project future tax revenues. The city of San Francisco, for example, uses the price of a one-bedroom apartment on Craigslist, weekend subway ridership numbers, parking garage usage, and monthly reports on passenger landings at the city's airport.See also
*Big Mac Index
The Big Mac Index is a price index published since 1986 by ''The Economist'' as an informal way of measuring the purchasing power parity (PPP) between two currencies and providing a test of the extent to which market exchange rates result ...
* Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics and serves as a principal agency of ...
* CAPRI model
* Consumer confidence index
* Consumer leverage ratio
* Consumer price index
A consumer price index (CPI) is a price index, the price of a weighted average market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households. Changes in measured CPI track changes in prices over time.
Overview
A CPI is a statisti ...
* Core inflation
* Economic data
Economic data are data describing an actual economy, past or present. These are typically found in time-series form, that is, covering more than one time period (say the monthly unemployment rate for the last five years) or in cross-sectional dat ...
* Fundamental analysis
* Genuine Progress Index
* Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is of ...
* Hemline index
* Inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
* Lipstick effect
* List of economic reports by U.S. government agencies
* Macroeconomic indicators
* Misery index (economics)
* Purchasing Managers' Index
* The Conference Board
References
External links
OECD Economic Indicators
Monthly analysis from American Institute for Economic Research (AIER)
U.S. Economic Indicators
(quandl.com)
GPO Economic Indicators
{{DEFAULTSORT:Economic Indicator Indicators