early human migration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Early human migrations are the earliest migrations and expansions of archaic and modern humans across continents. They are believed to have begun approximately 2 million years ago with the early expansions out of Africa by ''
Early human migrations are the earliest migrations and expansions of archaic and modern humans across continents. They are believed to have begun approximately 2 million years ago with the early expansions out of Africa by ''
 Between 2 and less than a million years ago, ''
Between 2 and less than a million years ago, ''
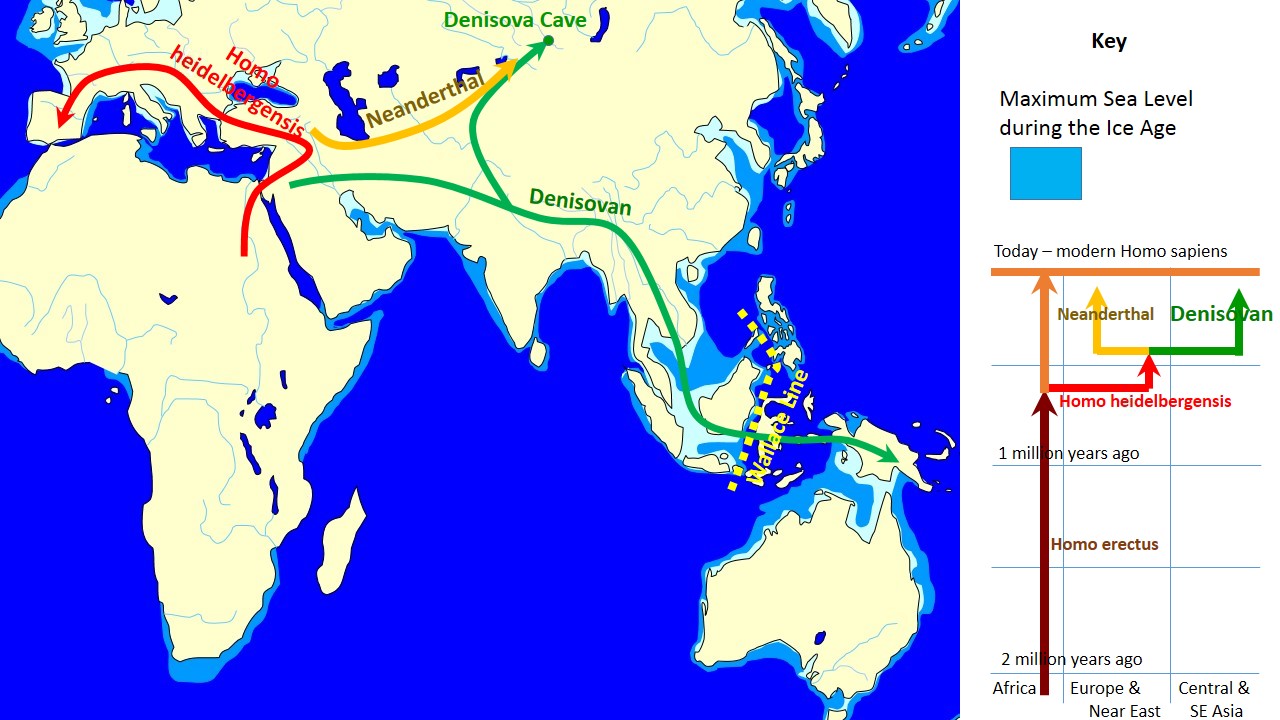
 One million years after its dispersal, ''H. erectus'' was diverging into new species. ''H. erectus'' is a chronospecies and was never extinct, so its "late survival" is a matter of taxonomic convention. Late forms of ''H. erectus'' are thought to have survived until after about 0.5 million ago to 143,000 years ago at the latest, with derived forms classified as ''
One million years after its dispersal, ''H. erectus'' was diverging into new species. ''H. erectus'' is a chronospecies and was never extinct, so its "late survival" is a matter of taxonomic convention. Late forms of ''H. erectus'' are thought to have survived until after about 0.5 million ago to 143,000 years ago at the latest, with derived forms classified as ''
 The so-called " recent dispersal" of modern humans took place about 70–50,000 years ago. It is this migration wave that led to the lasting spread of modern humans throughout the world.
A small group from a population in East Africa, bearing mitochondrial haplogroup L3 and numbering possibly fewer than 1,000 individuals, crossed the
The so-called " recent dispersal" of modern humans took place about 70–50,000 years ago. It is this migration wave that led to the lasting spread of modern humans throughout the world.
A small group from a population in East Africa, bearing mitochondrial haplogroup L3 and numbering possibly fewer than 1,000 individuals, crossed the
 During this time sea level was much lower and most of
During this time sea level was much lower and most of
 Around 20,000 years ago, approximately 5,000 years after the Neanderthal extinction, the
Around 20,000 years ago, approximately 5,000 years after the Neanderthal extinction, the
 The
The
 The first seaborne human migrations were by the
The first seaborne human migrations were by the
 The earliest inhabitants of North America's central and eastern Arctic are referred to as the
The earliest inhabitants of North America's central and eastern Arctic are referred to as the
Journey of Mankind – Genetic Map
–
Prehistoric Human Migration From Africa to World Video May 2015
{{Human Evolution Prehistoric migrations
 Early human migrations are the earliest migrations and expansions of archaic and modern humans across continents. They are believed to have begun approximately 2 million years ago with the early expansions out of Africa by ''
Early human migrations are the earliest migrations and expansions of archaic and modern humans across continents. They are believed to have begun approximately 2 million years ago with the early expansions out of Africa by ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
''. This initial migration was followed by other archaic humans
A number of varieties of ''Homo'' are grouped into the broad category of archaic humans in the period that precedes and is contemporary to the emergence of the earliest early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') around 300 ka. Omo-Kibish I (Omo I) f ...
including ''H. heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' in ...
'', which lived around 500,000 years ago and was the likely ancestor of Denisovan
The Denisovans or Denisova hominins ) are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human that ranged across Asia during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic. Denisovans are known from few physical remains and consequently, most of what is known ...
s and Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
s as well as modern humans. Early hominids had likely crossed land bridge
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regression, in which sea lev ...
s that have now sunk.
Within Africa, ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, a ...
'' dispersed around the time of its speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species. The biologist Orator F. Cook coined the term in 1906 for cladogenesis, the splitting of lineages, as opposed to anagenesis, phyletic evolution within ...
, roughly 300,000 years ago. The recent African origin
In paleoanthropology, the recent African origin of modern humans, also called the "Out of Africa" theory (OOA), recent single-origin hypothesis (RSOH), replacement hypothesis, or recent African origin model (RAO), is the dominant model of the ...
paradigm suggests that the anatomically modern humans outside of Africa descend from a population of ''Homo sapiens'' migrating from East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
roughly 70–50,000 years ago and spreading along the southern coast of Asia and to Oceania by about 50,000 years ago. Modern humans spread across Europe about 40,000 years ago.
Early Eurasian ''Homo sapiens'' fossils have been found in Palestine and Greece, dated to 194,000–177,000 and 210,000 years old respectively. These fossils seem to represent failed dispersal attempts by early ''Homo sapiens'', who were likely replaced by local Neanderthal populations.
The migrating modern human populations are known to have interbred with earlier local populations, so that contemporary human populations are descended in small part (below 10% contribution) from regional varieties of archaic humans.
After the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
, North Eurasian populations migrated to the Americas about 20,000 years ago. Northern Eurasia was peopled after 12,000 years ago, at the beginning of the Holocene period. Arctic Canada and Greenland were reached by the Paleo-Eskimo
The Paleo-Eskimo (also pre-Thule or pre-Inuit) were the peoples who inhabited the Arctic region from Chukotka (e.g., Chertov Ovrag) in present-day Russia across North America to Greenland prior to the arrival of the modern Inuit (Eskimo) and re ...
expansion around 4,000 years ago. Finally, Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
was populated within the past 2,000 years in the last wave of the Austronesian expansion
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrone ...
.
Early humans (before ''Homo sapiens'')
The earliest humans developed out ofaustralopithecine
Australopithecina or Hominina is a subtribe in the tribe Hominini. The members of the subtribe are generally ''Australopithecus'' (cladistically including the genera ''Homo'', ''Paranthropus'', and ''Kenyanthropus''), and it typically includes ...
ancestors about 3 million years ago, most likely in Eastern Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
, most likely in the area of the Kenyan Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is part of an intra-continental ridge system that runs through Kenya from north to south. It is part of the Gregory Rift, the eastern branch of the East African Rift, which starts in Tanzania to the south and continues no ...
, where the oldest known stone tools were found. Stone tools recently discovered at the Shangchen
Shangchen () is a Lower Palaeolithic archaeological site in Lantian County, Shaanxi, China, some 25 km south of Weinan.
It was discovered in 1964, and excavated during 2004 and 2017.
Stone tools found at the site were dated based on magne ...
site in China and dated to 2.12 million years ago are claimed to be the earliest known evidence of hominins outside Africa, surpassing Dmanisi
Dmanisi ( ka, დმანისი, tr, , az, Başkeçid) is a town and archaeological site in the Kvemo Kartli region of Georgia approximately 93 km southwest of the nation’s capital Tbilisi in the river valley of Mashavera. The hominin ...
in Georgia by 300,000 years.
''Homo erectus''
Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus ''Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely related ...
'' spread throughout East Africa and to Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number of ...
(''Homo ergaster
''Homo ergaster'' is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether ''H. ergaster'' constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into '' H. erectus'' is an ongoing and unresol ...
''), but not yet to West Africa. Around 1.8 million years ago, ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
'' migrated out of Africa via the Levantine corridor
The Levantine corridor is the relatively narrow strip between the Mediterranean Sea to the northwest and deserts to the southeast which connects Africa to Eurasia. This corridor is a land route of migrations of animals between Eurasia and Africa ...
and Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
to Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
. This migration has been proposed as being related to the operation of the Saharan pump, around 1.9 million years ago. ''Homo erectus'' dispersed throughout most of the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by th ...
, reaching as far as Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
. Its distribution is traced by the Oldowan
The Oldowan (or Mode I) was a widespread stone tool archaeological industry (style) in prehistory. These early tools were simple, usually made with one or a few flakes chipped off with another stone. Oldowan tools were used during the Lower ...
lithic industry, by 1.3 million years ago extending as far north as the 40th parallel (Xiaochangliang
Xiaochangliang () is the site of some of the earliest paleolithic remains in East Asia, located in the Nihewan (泥河灣) Basin in Yangyuan County, Hebei, China, most famous for the stone tools discovered there.
Stone tools
The tool forms disco ...
).
Key sites for this early migration out of Africa are Riwat in Pakistan (~2 Ma?), Ubeidiya in the Levant (1.5 Ma) and Dmanisi
Dmanisi ( ka, დმანისი, tr, , az, Başkeçid) is a town and archaeological site in the Kvemo Kartli region of Georgia approximately 93 km southwest of the nation’s capital Tbilisi in the river valley of Mashavera. The hominin ...
in the Caucasus (1.81 ± 0.03 Ma, p=0.05).
China shows evidence of Erectus from 2.12 Mya in Gongwangling in Lantian county.Zhu, Zhaoyu, Robin Dennell, Weiwen Huang, Yi Wu, Shifan Qiu, Shixia Yang, Zhiguo Rao, et al. 2018. “Hominin Occupation of the Chinese Loess Plateau since about 2.1 Million Years Ago.” Nature 559 (7715): 608–612. . Two ''Homo erectus'' incisors have been found near Yuanmou, south China, and are dated to 1.7 Mya, and a cranium from Lantian has been dated to 1.63 Ma. Artefacts from Majuangou III and Shangshazui in the Nihewan basin, north China, have been dated to 1.6–1.7 Ma. The archaeological site of Xihoudu () in Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level ...
Province is the earliest recorded use of fire by ''Homo erectus'', which is dated 1.27 million years ago.
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
(Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's most ...
) was reached about 1.7 million years ago (Meganthropus
''Meganthropus'' is an extinct genus of non-hominin hominid ape, known from the Pleistocene of Indonesia. It is known from a series of large jaw and skull fragments found at the Sangiran site near Surakarta in Central Java, Indonesia, alongside s ...
). Western Europe was first populated around 1.2 million years ago ( Atapuerca).
Robert G. Bednarik has suggested that ''Homo erectus'' may have built rafts and sailed oceans, a theory that has raised some controversy.
After ''H. erectus''

 One million years after its dispersal, ''H. erectus'' was diverging into new species. ''H. erectus'' is a chronospecies and was never extinct, so its "late survival" is a matter of taxonomic convention. Late forms of ''H. erectus'' are thought to have survived until after about 0.5 million ago to 143,000 years ago at the latest, with derived forms classified as ''
One million years after its dispersal, ''H. erectus'' was diverging into new species. ''H. erectus'' is a chronospecies and was never extinct, so its "late survival" is a matter of taxonomic convention. Late forms of ''H. erectus'' are thought to have survived until after about 0.5 million ago to 143,000 years ago at the latest, with derived forms classified as ''H. antecessor
''Homo antecessor'' ( Latin "pioneer man") is an extinct species of archaic human recorded in the Spanish Sierra de Atapuerca, a productive archaeological site, from 1.2 to 0.8 million years ago during the Early Pleistocene. Populations of thi ...
'' in Europe around 800,000 years ago and ''H. heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' in ...
'' in Africa around 600,000 years ago. ''H. heidelbergensis'' in its turn spread across East Africa (''H. rhodesiensis
''Homo rhodesiensis'' is the species name proposed by Arthur Smith Woodward (1921) to classify Kabwe 1 (the "Kabwe skull" or "Broken Hill skull", also "Rhodesian Man"), a Middle Stone Age fossil recovered from a cave at Broken Hill, or Kabwe, No ...
'') and to Eurasia, where it gave rise to Neanderthals
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While ...
and Denisovans
The Denisovans or Denisova hominins ) are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human that ranged across Asia during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic. Denisovans are known from few physical remains and consequently, most of what is known ...
.
''H. heidelbergensis'', Neanderthals and Denisovans expanded north beyond the 50th parallel ( Eartham Pit, Boxgrove 500kya, Swanscombe Heritage Park
Swanscombe Skull Site or Swanscombe Heritage Park is a geological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Swanscombe in north-west Kent, England. It contains two Geological Conservation Review sites and a National Nature Reserve. The park lies ...
400kya, Denisova Cave
Denisova Cave (russian: Денисова пещера, lit= the cave of Denis, translit= Denísova peshchéra; alt, Аю-Таш, lit= Bear Rock, translit= Ayu Tash) is a cave in the Bashelaksky Range of the Altai mountains, Siberia, Russia. Th ...
50 kya). It has been suggested that late Neanderthals may even have reached the boundary of the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
, by c. 32,000 years ago, when they were being displaced from their earlier habitats by ''H. sapiens'', based on 2011 excavations at the site of Byzovaya in the Urals
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
(Komi Republic
The Komi Republic (russian: Республика Коми; kv, Коми Республика), sometimes simply referred to as Komi, is a republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. Its capital is the city of Syktyvkar. The population of the ...
, ).
Other archaic human species are assumed to have spread throughout Africa by this time, although the fossil record is sparse. Their presence is assumed based on traces of admixture with modern humans found in the genome of African populations. ''Homo naledi
'' Homo naledi'' is an extinct species of archaic human discovered in 2013 in the Rising Star Cave, Cradle of Humankind, South Africa dating to the Middle Pleistocene 335,000–236,000 years ago. The initial discovery comprises 1,550 specime ...
'', discovered in South Africa in 2013 and tentatively dated to about 300,000 years ago, may represent fossil evidence of such an archaic human species.
Neanderthals spread across the Near East and Europe, while Denisovans appear to have spread across Central and East Asia and to Southeast Asia and Oceania. There is evidence that Denisovans interbred with Neanderthals in Central Asia where their habitats overlapped. Neanderthal evidence has also been found quite late at 33,000 years ago at the 65th latitude of the Byzovaya site in the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
. This is far outside of any otherwise known habitat, during a high ice cover period, and perhaps reflects a refugia of near extinction.
''Homo sapiens''
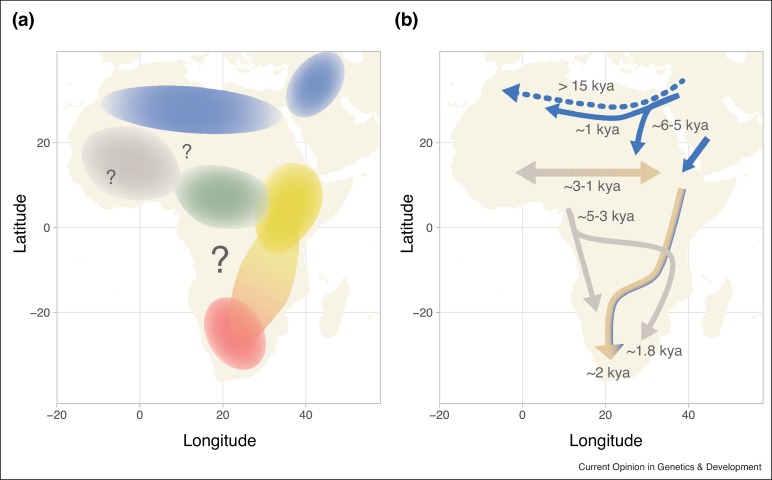
Dispersal throughout Africa
''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, a ...
'' are believed to have emerged in Africa about 300,000 years ago, based in part on thermoluminescence dating of artefacts and remains from Jebel Irhoud
Jebel Irhoud or Adrar n Ighoud ( zgh, ⴰⴷⵔⴰⵔ ⵏ ⵉⵖⵓⴷ, Adrar n Iɣud; ar, جبل إيغود, žbəl iġud), is an archaeological site located just north of the locality known as Tlet Ighoud, approximately south-east of the cit ...
, Morocco, published in 2017. The Florisbad Skull
The Florisbad Skull is an important human fossil of the early Middle Stone Age, representing either late ''Homo heidelbergensis'' or early ''Homo sapiens''.
It was discovered in 1932 by T. F. Dreyer at the Florisbad site, Free State Province, ...
from Florisbad, South Africa, dated to about 259,000 years ago, has also been classified as early ''Homo sapiens''. Previously, the Omo remains
The Omo remains are a collection of homininThis article quotes historic texts that use the terms 'hominid' and 'hominin' with meanings that may be different from their modern usages. This is because several revisions in classifying the great apes h ...
, excavated between 1967 and 1974 in Omo National Park
Omo National Park is a national park in Ethiopia founded in 1980. Located in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region on the west bank of the Omo River, the park covers approximately 4,068 square kilometers, about 870 kilometers so ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the no ...
, and dated to 200,000 years ago, were long held to be the oldest known fossils of ''Homo sapiens''.
In September 2019, scientists reported the computerized determination, based on 260 CT scans, of a virtual skull shape of the last common human ancestor to anatomically modern humans, representative of the earliest modern humans, and suggested that modern humans arose between 260,000 and 350,000 years ago through a merging of populations in East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
.
In July 2019, anthropologists reported the discovery of 210,000 year old remains of a ''H. sapiens'' and 170,000 year old remains of a ''H. neanderthalensis'' in Apidima Cave
The Apidima Cave (, ''Spilaio Apidima'') is a complex of five caves four small caves located on the western shore of Mani Peninsula in Southern Greece. A systematic investigation of the cave has yielded Neanderthal and ''Homo sapiens'' fossils ...
in southern Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, more than 150,000 years older than previous ''H. sapiens'' finds in Europe.
Early modern humans expanded to Western Eurasia and Central, Western and Southern Africa from the time of their emergence. While early expansions to Eurasia appear not to have persisted, expansions to Southern and Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, ...
resulted in the deepest temporal divergence in living human populations. Early modern human expansion in sub-Saharan Africa appears to have contributed to the end of late Acheulean
Acheulean (; also Acheulian and Mode II), from the French ''acheuléen'' after the type site of Saint-Acheul, is an archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture characterized by the distinctive oval and pear-shaped " hand axes" associate ...
(Fauresmith
Fauresmith is located 130 km south west of Bloemfontein, South Africa. The town, named after Rev Phillip Faure and Sir Harry Smith, is the second oldest town in the Free State.
Fauresmith is the only town in South Africa, and one of only ...
) industries at about 130,000 years ago, although very late coexistence of archaic and early modern humans, until as late as 12,000 years ago, has been argued for West Africa in particular.
The ancestors of the modern Khoi-San
Khoisan , or (), according to the contemporary Khoekhoegowab orthography, is a catch-all term for those indigenous peoples of Southern Africa who do not speak one of the Bantu languages, combining the (formerly "Khoikhoi") and the or ( in t ...
expanded to Southern Africa before 150,000 years ago, possibly as early as before 260,000 years ago, so that by the beginning of the MIS 5
Marine Isotope Stage 5 or MIS 5 is a marine isotope stage in the geologic temperature record, between 130,000 and 80,000 years ago. Sub-stage MIS 5e, called the Eemian or Ipswichian, covers the last major interglacial period before the Holocene, w ...
"megadrought
A megadrought (or mega-drought) is a prolonged drought lasting two decades or longer. Past megadroughts have been associated with persistent multiyear La Niña conditions (cooler than normal water temperatures in the tropical eastern Pacific Oce ...
", 130,000 years ago, there were two ancestral population clusters in Africa, bearers of mt-DNA haplogroup L0 in southern Africa, ancestral to the Khoi-San, and bearers of haplogroup L1-6 in central/eastern Africa, ancestral to everyone else. There was a significant back-migration of bearers of L0 towards eastern Africa between 120 and 75 kya.
Expansion to Central Africa by the ancestors of the Central African forager populations (African Pygmies) most likely took place before 130,000 years ago, and certainly before 60,000 years ago.
The situation in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, ...
is difficult to interpret due to a sparsity of fossil evidence. ''Homo sapiens'' seems to have reached the western Sahelian zone by 130,000 years ago, while tropical West African sites associated with ''H. sapiens'' are known only from after 130,000 years ago. Unlike elsewhere in Africa, archaic Middle Stone Age
The Middle Stone Age (or MSA) was a period of African prehistory between the Early Stone Age and the Late Stone Age. It is generally considered to have begun around 280,000 years ago and ended around 50–25,000 years ago. The beginnings of p ...
sites appear to persist until very late, down to the Holocene boundary (12,000 years ago), pointing to the possibility of late survival of archaic human
A number of varieties of ''Homo'' are grouped into the broad category of archaic humans in the period that precedes and is contemporary to the emergence of the earliest early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') around 300 ka. Omo-Kibish I (Omo I) f ...
s, and late hybridization with ''H. sapiens'' in West Africa.
Early northern Africa dispersal
Populations of ''Homo sapiens'' migrated to the Levant and to Europe between 130,000 and 115,000 years ago, and possibly in earlier waves as early as 185,000 years ago. A fragment of a jawbone with eight teeth found at Misliya Cave has been dated to around 185,000 years ago. Layers dating from between 250,000 and 140,000 years ago in the same cave contained tools of the Levallois type which could put the date of the first migration even earlier if the tools can be associated with the modern human jawbone finds. These early migrations do not appear to have led to lasting colonisation and receded by about 80,000 years ago. There is a possibility that this first wave of expansion may have reached China (or even North America) as early as 125,000 years ago, but would have died out without leaving a trace in the genome of contemporary humans. There is some evidence that modern humans left Africa at least 125,000 years ago using two different routes: through theNile Valley
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ...
heading to the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europea ...
, at least into modern Israel (Qafzeh
Mount Precipice ( he, הר הקפיצה, "''Har HaKfitsa''"; ar, جبل القفزة, "''Jebel al-Qafzeh''", "Mount of the Leap"), also known as Mount of Precipitation, Mount of the Leap of the Lord and Mount Kedumim is located just outside the ...
: 120,000–100,000 years ago); and a second route through the present-day Bab-el-Mandeb
The Bab-el-Mandeb (Arabic: , , ) is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
Name
The strait derives its name from the dangers attendin ...
Strait on the Red Sea (at that time, with a much lower sea level and narrower extension), crossing to the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
and settling in places like the present-day United Arab Emirates (125,000 years ago) and Oman (106,000 years ago), and possibly reaching the Indian Subcontinent (Jwalapuram
Jwalapuram (meaning "City of fire" in Telugu) is an archaeological site in the Kurnool district of Andhra Pradesh, southern India, which shows hominid habitation before and after the Toba event (73 kya) according to the Toba catastrophe theory. ...
: 75,000 years ago.) Although no human remains have yet been found in these three places, the apparent similarities between the stone tools found at Jebel Faya
Jebel Faya ( ar, جَبَل ٱلْفَايَة, Jabal Al-Fāyah; FAY-NE1) is an archaeological site and limestone hill or escarpment near Al Madam in the Emirate of Sharjah, the UAE, located about east of the city of Sharjah, and between the s ...
, those from Jwalapuram and some from Africa suggest that their creators were all modern humans. These findings might give some support to the claim that modern humans from Africa arrived at southern China about 100,000 years ago (Zhiren Cave
Zhiren Cave () is a karstic cave in the Mulan Mountains that overlooks the Hejiang River in Chongzuo, Guangxi, China. Zhiren Cave is an early Late Pleistocene site that has yielded the fossil remains of possibly anatomically modern humans with som ...
, Zhirendong
Zhiren Cave () is a karstic cave in the Mulan Mountains that overlooks the Hejiang River in Chongzuo, Guangxi, China. Zhiren Cave is an early Late Pleistocene site that has yielded the fossil remains of possibly anatomically modern humans with s ...
, Chongzuo
Chongzuo (; za, Cungzcoj) is a prefecture-level city in the south of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region near the Sino-Vietnamese border. It is home to one of China's largest Zhuang populations.
Geography and climate
Chongzuo is located in sout ...
City: 100,000 years ago; and the Liujiang hominid
The Liujiang men () are among the earliest modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') found in East Asia.
Their remains were discovered in the Tongtianyan Cave (通天岩) in Liujiang, Guangxi, China.
The remains were excavated in 1958. The remains con ...
(Liujiang County
Liujiang District (; Standard Zhuang: ) is under the administration of Liuzhou, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China, located on the southwest bank of the Liu River. It covers a land area of and had a population of 562,351 . The southernmost c ...
): controversially dated at 139,000–111,000 years ago ). Dating results of the Lunadong ( Bubing Basin, Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam ( ...
, southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
) teeth, which include a right upper second molar and a left lower second molar, indicate that the molars may be as old as 126,000 years. Since these previous exits from Africa did not leave traces in the results of genetic analyses based on the Y chromosome and on MtDNA (which represent only a small part of the human genetic material), it seems that those modern humans did not survive in large numbers and were assimilated by our major antecessors. An explanation for their extinction (or small genetic imprint) may be the Toba eruption (74,000 years ago), though some argue it scarcely affected human population.
Coastal migration
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
strait at Bab-el-Mandeb
The Bab-el-Mandeb (Arabic: , , ) is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
Name
The strait derives its name from the dangers attendin ...
, to what is now Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and sha ...
, after around 75,000 years ago. A recent review has also shown support for the northern route through Sinai/Israel/Syria (Levant). Their descendants spread along the coastal route around Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
to the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
before 55,000 years ago. Other research supports a migration out of Africa between about 65,000 and 50,000 years ago. The coastal migration between roughly 70,000 and 50,000 years ago is associated with mitochondrial haplogroups M and N, both derivative of L3.
Along the way ''H. sapiens'' interbred with Neanderthals and Denisovans, with Denisovan DNA making 0.2% of mainland Asian and Native American DNA.
Nearby Oceania
Migrations continued along the Asian coast to Southeast Asia and Oceania, colonising Australia by around 65,000–50,000 years ago. By reaching Australia, ''H. sapiens'' for the first time expanded its habitat beyond that of ''H. erectus''. Denisovan ancestry is shared byMelanesians
Melanesians are the predominant and indigenous inhabitants of Melanesia, in a wide area from Indonesia's New Guinea to as far East as the islands of Vanuatu and Fiji. Most speak either one of the many languages of the Austronesian language fa ...
, Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Island ...
, and smaller scattered groups of people in Southeast Asia, such as the Mamanwa
The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous people in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad (Literally: "indigenous people"), the autonym officially adopt ...
, a Negrito
The term Negrito () refers to several diverse ethnic groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia and the Andaman Islands. Populations often described as Negrito include: the Andamanese peoples (including the Great Andamanese, the Onge, ...
people in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, suggesting the interbreeding took place in Eastern Asia where the Denisovans lived. Denisovans may have crossed the Wallace Line
The Wallace Line or Wallace's Line is a faunal boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace and named by English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley that separates the biogeographical realms of Asia and Wallacea, a tra ...
, with Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of mainly Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as Lom ...
serving as their last refugium. ''Homo erectus'' had crossed the Lombok gap reaching as far as Flores, but never made it to Australia.
 During this time sea level was much lower and most of
During this time sea level was much lower and most of Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sou ...
formed one land mass known as Sunda. Migration continued Southeast on the coastal route to the strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean chann ...
s between Sunda and Sahul
__NOTOC__
Sahul (), also called Sahul-land, Meganesia, Papualand and Greater Australia, was a paleocontinent that encompassed the modern-day landmasses of mainland Australia, Tasmania, New Guinea, and the Aru Islands.
Sahul was in the south-we ...
, the continental land mass of present-day Australia and New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
. The gaps on the Weber Line
Max Carl Wilhelm Weber van Bosse or Max Wilhelm Carl Weber (5 December 1852, in Bonn – 7 February 1937, in Eerbeek) was a German-Dutch zoologist and biogeographer.
Weber studied at the University of Bonn, then at the Humboldt University in ...
are up to 90 km wide, so the migration to Australia and New Guinea would have required seafaring skills. Migration also continued along the coast eventually turning northeast to China and finally reaching Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
before turning inland. This is evidenced by the pattern of mitochondrial haplogroups descended from haplogroup M, and in Y-chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes ( allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abs ...
haplogroup C.
Sequencing of one Aboriginal genome from an old hair sample in Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...
revealed that the individual was descended from people who migrated into East Asia between 62,000 and 75,000 years ago. This supports the theory of a single migration into Australia and New Guinea before the arrival of Modern Asians (between 25,000 and 38,000 years ago) and their later migration into North America. This migration is believed to have happened around 50,000 years ago, before Australia and New Guinea were separated by rising sea levels approximately 8,000 years ago. This is supported by a date of 50,000–60,000 years ago for the oldest evidence of settlement in Australia, around 40,000 years ago for the oldest human remains, the earliest humans artifacts which are at least 65,000 years old and the extinction of the Australian megafauna
The term Australian megafauna refers to the megafauna in Australia during the Pleistocene Epoch. Most of these species became extinct during the latter half of the Pleistocene, and the roles of human and climatic factors in their extinction ar ...
by humans between 46,000 and 15,000 years ago argued by Tim Flannery, which is similar to what happened in the Americas. The continued use of Stone Age tools in Australia has been much debated.
Dispersal throughout Eurasia
The population brought toSouth Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;; ...
by coastal migration
In the context of the recent African origin of modern humans, the Southern Dispersal scenario (also the coastal migration or great coastal migration hypothesis) refers to the early migration along the southern coast of Asia, from the Arabian Pe ...
appears to have remained there for some time, during roughly 60,000 to 50,000 years ago, before spreading further throughout Eurasia. This dispersal of early humans, at the beginning of the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coi ...
, gave rise to the major population groups of the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by th ...
and the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with t ...
.
Towards the West, Upper Paleolithic populations associated with mitochondrial haplogroup R and its derivatives, spread throughout Asia and Europe, with a back-migration of M1 to North Africa and the Horn of Africa several millennia ago.
Presence in Europe is certain after 40,000 years ago, possibly as early as 43,000 years ago, rapidly replacing the Neanderthal population. Contemporary Europeans have Neanderthal ancestry, but it seems likely that substantial interbreeding with Neanderthals ceased before 47,000 years ago, i.e. took place before modern humans entered Europe.
There is evidence from mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DN ...
that modern humans have passed through at least one genetic bottleneck
A population bottleneck or genetic bottleneck is a sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events such as famines, earthquakes, floods, fires, disease, and droughts; or human activities such as specicide, widespread violen ...
, in which genome diversity was drastically reduced. Henry Harpending
Henry Cosad Harpending (January 13, 1944 – April 3, 2016) was an American anthropologist and writer. He was a distinguished professor at the University of Utah, and formerly taught at Penn State and the University of New Mexico. He was a member ...
has proposed that humans spread from a geographically restricted area about 100,000 years ago, the passage through the geographic bottleneck and then with a dramatic growth amongst geographically dispersed populations about 50,000 years ago, beginning first in Africa and thence spreading elsewhere. Climatological and geological evidence suggests evidence for the bottleneck. The explosion of Toba, the largest volcanic eruption of the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
, may have created a 1,000 year cold period, potentially reducing human populations to a few tropical refugia. It has been estimated that as few as 15,000 humans survived. In such circumstances genetic drift and founder effects may have been maximised. The greater diversity amongst African genomes may reflect the extent of African refugia during the Toba incident. However, a recent review highlights that the single-source hypothesis of non-African populations is less consistent with ancient DNA analysis than multiple sources with genetic mixing across Eurasia.
Europe
The recent expansion ofanatomically modern humans
Early modern human (EMH) or anatomically modern human (AMH) are terms used to distinguish ''Homo sapiens'' (the only extant Hominina species) that are anatomically consistent with the range of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans from extin ...
reached Europe around 40,000 years ago from Central Asia and the Middle East, as a result of cultural adaption to big game hunting of sub-glacial steppe fauna. Neanderthals
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While ...
were present both in the Middle East and in Europe, and the arriving populations of anatomically modern humans (also known as "Cro-Magnon
Early European modern humans (EEMH), or Cro-Magnons, were the first early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') to settle in Europe, migrating from Western Asia, continuously occupying the continent possibly from as early as 56,800 years ago. They i ...
" or European early modern humans
Early European modern humans (EEMH), or Cro-Magnons, were the first early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') to settle in Europe, migrating from Western Asia, continuously occupying the continent possibly from as early as 56,800 years ago. They i ...
) interbred with Neanderthal populations to a limited degree. Populations of modern humans and Neanderthal overlapped in various regions such as the Iberian peninsula and the Middle East. Interbreeding may have contributed Neanderthal genes to palaeolithic and ultimately modern Eurasians and Oceanians.
An important difference between Europe and other parts of the inhabited world was the northern latitude. Archaeological evidence suggests humans, whether Neanderthal or Cro-Magnon, reached sites in Arctic Russia by 40,000 years ago.
Cro-Magnon are considered the first anatomically modern humans in Europe. They entered Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
by the Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgr ...
(near present-day Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...
and eastern Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
) around 50,000 years ago, with one group rapidly settling coastal areas around the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
and another migrating north to the steppes of Central Asia. Modern human remains dating to 43,000–45,000 years ago have been discovered in Italy and Britain, as well as in the European Russian Arctic from 40,000 years ago.
Humans colonised the environment west of the Urals, hunting reindeer especially, but were faced with adaptive challenges; winter temperatures averaged from with fuel and shelter scarce. They travelled on foot and relied on hunting highly mobile herds for food. These challenges were overcome through technological innovations: tailored clothing from the pelts of fur-bearing animals; construction of shelters with hearths using bones as fuel; and digging "ice cellars" into the permafrost to store meat and bones.
A mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DN ...
sequence of two Cro-Magnons from the Paglicci Cave in Italy, dated to 23,000 and 24,000 years old (Paglicci 52 and 12), identified the mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA ...
as Haplogroup N, typical of the latter group.
The expansion of modern human population is thought to have begun 45,000 years ago, and it may have taken 15,000–20,000 years for Europe to be colonized.
During this time, the Neanderthals were slowly being displaced. Because it took so long for Europe to be occupied, it appears that humans and Neanderthals may have been constantly competing for territory. The Neanderthals had larger brains, and were larger overall, with a more robust or heavily built frame, which suggests that they were physically stronger than modern ''Homo sapiens''. Having lived in Europe for 200,000 years, they would have been better adapted to the cold weather. The anatomically modern humans known as the Cro-Magnons
Early European modern humans (EEMH), or Cro-Magnons, were the first early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') to settle in Europe, migrating from Western Asia, continuously occupying the continent possibly from as early as 56,800 years ago. They i ...
, with widespread trade networks, superior technology and bodies likely better suited to running, would eventually completely displace the Neanderthals, whose last refuge was in the Iberian peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
. After about 25,000 years ago the fossil record of the Neanderthals ends, indicating extinction. The last known population lived around a cave system on the remote south-facing coast of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
from 30,000 to 24,000 years ago.
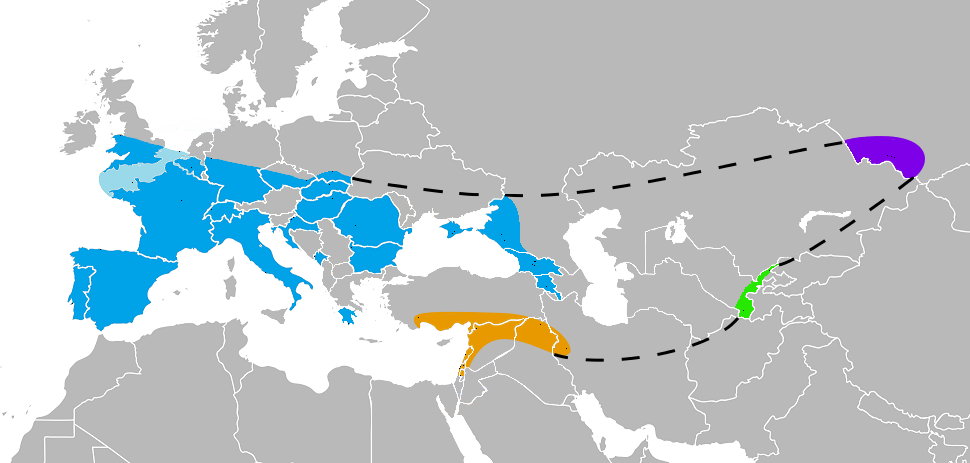
From the extent of linkage disequilibrium, it was estimated that the last Neanderthal gene flow into early ancestors of Europeans occurred 47,000–65,000 years BP. In conjunction with archaeological and fossil evidence, interbreeding is thought to have occurred somewhere in Western Eurasia, possibly the Middle East. Studies show a higher Neanderthal admixture in East Asians than in Europeans. North African groups share a similar excess of derived alleles with Neanderthals as non-African populations, whereas Sub-Saharan African groups are the only modern human populations with no substantial Neanderthal admixture. The Neanderthal-linked haplotype B006 of the dystrophin gene has also been found among nomadic pastoralist groups in the Sahel and Horn of Africa, who are associated with northern populations. Consequently, the presence of this B006 haplotype on the northern and northeastern perimeter of Sub-Saharan Africa is attributed to gene flow from a non-African point of origin.
East, Southeast and North Asia
"Tianyuan man
Tianyuan man ( zh, t=田園洞人, s=田园洞人, p=Tiányuándòng Rén) are the remains of one of the earliest modern humans to inhabit East Asia. In 2007, researchers found 34 bone fragments belonging to a single individual at the Tianyuan Ca ...
", an individual who lived in China c. 40,000 years ago, showed substantial Neanderthal admixture. A 2017 study of the ancient DNA of Tianyuan Man found that the individual is related to modern Asian and Native American populations. A 2013 study found Neanderthal introgression of 18 genes within the chromosome 3p21.31 region (HYAL region) of East Asians. The introgressive haplotypes were positively selected in only East Asian populations, rising steadily from 45,000 years ago until a sudden increase of growth rate around 5,000 to 3,500 years ago. They occur at very high frequencies among East Asian populations in contrast to other Eurasian populations (e.g. European and South Asian populations). The findings also suggest that this Neanderthal introgression occurred within the ancestral population shared by East Asians and Native Americans..
A 2016 study presented an analysis of the population genetics of the Ainu
Ainu or Aynu may refer to:
*Ainu people, an East Asian ethnic group of Japan and the Russian Far East
* Ainu languages, a family of languages
**Ainu language of Hokkaido
**Kuril Ainu language, extinct language of the Kuril Islands
**Sakhalin Ainu l ...
people of northern Japan as key to the reconstruction of the early peopling of East Asia. The Ainu were found to represent a more basal branch than the modern farming populations of East Asia, suggesting an ancient (pre-Neolithic) connection with northeast Siberians. A 2013 study associated several phenotypical
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological prope ...
traits associated with Mongoloids with a single mutation of the EDAR
Ectodysplasin A receptor (EDAR) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EDAR gene. EDAR is a cell surface receptor for ectodysplasin A which plays an important role in the development of ectodermal tissues such as the skin. It is structura ...
gene, dated to c. 35,000 years ago.
Mitochondrial haplogroups A, B and G originated about 50,000 years ago, and bearers subsequently colonized Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
, Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic of ...
and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, by about 35,000 years ago. Parts of these populations migrated to North America during the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
.
A review paper by Melinda A. Yang (in 2022) summarized and concluded that a distinctive "Basal-East Asian population" referred to as East- and Southeast Asian lineage''Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
ns, Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island South ...
, and Siberians
The Siberians, or Siberiaks, (russian: сибиряки, sibiryaki, ) are the majority inhabitants of Siberia, as well as the (sub)ethnic or ethnographic group of the Russians.
As demonym
The demonym ''Siberian'' can be restricted to either t ...
, originated in Mainland Southeast Asia
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
at ~50,000BC, and expanded through multiple migration waves southwards and northwards respectively. This ESEA lineage gave rise to various sublineages, and is also ancestral to the Hoabinhian hunter-gatherers of Southeast Asia and the ~40,000 year old Tianyuan lineage found in Northern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions within China. The exact boundary between these two regions is not precisely defined and only serve to depict where there appears to be regional differences between the climate ...
, but already differentiated and distinct from European-related and Australasian-related lineages, found in other regions of prehistoric Eurasia. The ESEA lineage trifurcated from an earlier East-Eurasian or "eastern non-African" (ENA) lineage somewhere in South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;; ...
, which also contributed to the formation of indigenous South Asian hunter-gatherers (AASI) as well as to Australasians.
Last Glacial Maximum
Eurasia
 Around 20,000 years ago, approximately 5,000 years after the Neanderthal extinction, the
Around 20,000 years ago, approximately 5,000 years after the Neanderthal extinction, the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
forced northern hemisphere inhabitants to migrate to several shelters ( refugia) until the end of this period. The resulting populations are presumed to have resided in such refuges during the LGM to ultimately reoccupy Europe, where archaic historical populations are considered their descendants. The composition of European populations was later altered by further migrations, notably the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
expansion from the Middle East, and still later the Chalcolithic population movements associated with Indo-European expansion
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially expla ...
. A Paleolithic site on the Yana River, Siberia, at 71°N, lies well above the Arctic Circle and dates to 27,000 radiocarbon years before present, during glacial times. This site shows that people adapted to this harsh, high-latitude, Late Pleistocene environment much earlier than previously thought.
Americas
Paleo-Indians originated from Central Asia, crossing the Beringia land bridge between eastern Siberia and present-day Alaska. Humans lived throughout the Americas by the end of the last glacial period, or more specifically what is known as thelate glacial maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eu ...
. Details of Paleo-Indian migration to and throughout the American continent, including the dates and the routes traveled, are subject to ongoing research and discussion.
Conventional estimates have it that humans reached North America at some point between 15,000 and 20,000 years ago. The traditional theory is that these early migrants moved when sea levels were significantly lowered due to the Quaternary glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial and interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Ma (million years ago) and is ongoing. Although geologists describe ...
, following herds of now-extinct pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
along ''ice-free corridors'' that stretched between the Laurentide
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.58 million years ...
and Cordilleran ice sheets. Another route proposed is that, either on foot or using primitive boats, they migrated down the Pacific coast to South America as far as Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
. Any archaeological evidence of coastal occupation during the last Ice Age would now have been covered by the sea level rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryo ...
, up to a hundred metres since then. The recent finding of indigenous Australasia
Australasia is a region that comprises Australia, New Zealand and some neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologi ...
n genetic markers in Amazonia supports that a coastal route and subsequent isolation did occur with some migrants.
Holocene migrations
The Holocene is taken to begin 12,000 years ago, after the end of theLast Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
. During the Holocene climatic optimum
The Holocene Climate Optimum (HCO) was a warm period that occurred in the interval roughly 9,000 to 5,000 years ago BP, with a thermal maximum around 8000 years BP. It has also been known by many other names, such as Altithermal, Climatic Optimu ...
, beginning about 9,000 years ago, human populations which had been geographically confined to refugia began to migrate. By this time, most parts of the globe had been settled by ''H. sapiens''; however, large areas that had been covered by glaciers
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such a ...
were now re-populated.
This period sees the transition from the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymousl ...
to the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
stage throughout the temperate zone
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
. The Neolithic subsequently gives way to the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
in Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by th ...
cultures and the gradual emergence of the historical record
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world hist ...
in the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
and China beginning around 4,000 years ago.
Large-scale migrations of the Mesolithic to Neolithic era are thought to have given rise to the pre-modern distribution of the world's major language families
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in hi ...
such as the Niger-Congo, Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. ...
, Afro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic su ...
, Uralic
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian lan ...
, Sino-Tibetan
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ...
or Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
phyla. The speculative Nostratic theory postulates the derivation of the major language families of Eurasia (excluding Sino-Tibetan) from a single proto-language spoken at the beginning of the Holocene period.
Eurasia
Evidence published in 2014 from genome analysis of ancient human remains suggests that the modern native populations of Europe largely descend from three distinct lineages: "Western Hunter-Gatherers
In archaeogenetics, the term Western Hunter-Gatherer (WHG), West European Hunter-Gatherer or Western European Hunter-Gatherer names a distinct ancestral component of modern Europeans, representing descent from a population of Mesolithic hunter-gat ...
", derivative of the Cro-Magnon population of Europe, Early European Farmers
Early European Farmers (EEF), First European Farmers (FEF), Neolithic European Farmers, Ancient Aegean Farmers, or Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (ANF) are names used to describe a distinct group of early Neolithic farmers who brought agriculture to E ...
introduced to Europe from the Near East during the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incr ...
and Ancient North Eurasians
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient North Eurasian (generally abbreviated as ANE) is the name given to an ancestral component that represents a lineage ancestral to the people of the Mal'ta–Buret' culture and populations closely related to the ...
which expanded to Europe in the context of the Indo-European expansion
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially expla ...
. The Ancient North Eurasian component was introduced to Western Europe by people related to the Yamnaya culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age arch ...
. Additional ANE ancestry is found in European populations through Paleolithic interactions with Eastern Hunter-Gatherer
In archaeogenetics, the term Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), sometimes East European Hunter-Gatherer, or Eastern European Hunter-Gatherer is the name given to a distinct ancestral component that represents descent from Mesolithic hunter-gatherers ...
s.
Sub-Saharan Africa
West-Eurasian back-migrations started in the early Holocene or already earlier in thePaleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος '' lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
period (30-15kya),followed by pre-Neolithic and Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
migration events from the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europea ...
, mostly affecting Northern Africa, the Horn of Africa, and wider regions of the Sahel zone and East Africa. The
The Nilotic peoples
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-s ...
are thought to be derived from an earlier undifferentiated Eastern Sudanic unity by the 3rd millennium BCE. The development of the Proto-Nilotes as a group may have been connected with their domestication of livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals raised in an agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is som ...
. The Eastern Sudanic unity must have been considerably earlier still, perhaps around the 5th millennium BCE (while the proposed Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. ...
unity would date to the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coi ...
about 15kya). The original locus of the early Nilotic speakers was presumably east of the Nile in what is now South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Con ...
. The Proto-Nilotes of the 3rd millennium BCE were pastoralists
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The animal ...
, while their neighbors, the Proto-Central Sudanic
Central Sudanic is a family of about sixty languages that have been included in the proposed Nilo-Saharan language family. Central Sudanic languages are spoken in the Central African Republic, Chad, South Sudan, Uganda, Congo (DRC), Nigeria and ...
peoples, were mostly agriculturalists.
The Niger-Congo phylum is thought to have emerged around 6,000 years ago in West or Central Africa. Its expansion may have been associated with the expansion of Sahel agriculture in the African Neolithic period, following the desiccation of the Sahara in c. 3900 BCE. The Bantu expansion
The Bantu expansion is a hypothesis about the history of the major series of migrations of the original Proto-Bantu-speaking group, which spread from an original nucleus around Central Africa across much of sub-Saharan Africa. In the process, ...
has spread the Bantu languages
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀) are a large family of languages spoken by the Bantu people of Central, Southern, Eastern africa and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages.
The ...
to Central, Eastern and Southern Africa, partly replacing the indigenous populations of these regions, including the African Pygmies
The African Pygmies (or Congo Pygmies, variously also Central African foragers, "African rainforest hunter-gatherers" (RHG) or "Forest People of Central Africa") are a group of ethnicities native to Central Africa, mostly the Congo Basin, tra ...
, Hadza people
The Hadza, or Hadzabe (''Wahadzabe'' in Swahili), are a Tanzanian indigenous ethnic group mostly based in southwest Karatu District of Arusha Region. They live around Lake Eyasi in the central Rift Valley and in the neighboring Serengeti Pl ...
and San people
The San peoples (also Saan), or Bushmen, are members of various Khoe, Tuu, or Kxʼa-speaking indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures that are the first cultures of Southern Africa, and whose territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia, ...
. Beginning about 3,000 years ago, it reached South Africa
about 1,700 years ago.
Some evidence (including a 2016 study by Busby et al.) suggests admixture from ancient and recent migrations from Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
into parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. Another study (Ramsay et al. 2018) also shows evidence that ancient Eurasians migrated into Africa and that Eurasian admixture in modern Sub-Saharan Africans ranges from 0% to 50%, varying by region and generally higher in the Horn of Africa and parts of the Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid cl ...
zone, and found to a lesser degree in certain parts of Western Africa, and Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number of ...
(excluding recent immigrants).
Indo-Pacific
Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrones ...
originating from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
known as the "Austronesian expansion
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrone ...
". Using advanced sailing technologies like catamaran
A Formula 16 beachable catamaran
Powered catamaran passenger ferry at Salem, Massachusetts, United States
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a multi-hulled watercraft featuring two parallel hulls of equal size. It is a geometry-sta ...
s, outrigger boat
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull. They can range from small dugout canoes to large plank-built vessels. Outrigger ...
s, and crab claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC. It is used in many traditional Austronesian cultures in Isla ...
s, they built the first sea-going ships and rapidly colonized Island Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sou ...
at around 3000 to 1500 BCE. From the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and Eastern Indonesia
This is a list of some of the regions of Indonesia. Many regions are defined in law or regulations by the central government. At different times of Indonesia's history, the nation has been designated as having regions that do not necessarily corr ...
they colonized Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, an ...
by 2200 to 1000 BCE.
A branch of the Austronesians reached Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
between 1600 and 1000 BCE, establishing the Lapita culture
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian peoples, Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from ...
(named after the archaeological site in Lapita, New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
, where their characteristic pottery was first discovered). They are the direct ancestors of the modern Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island South ...
. They ventured into Remote Oceania
Remote Oceania is the part of Oceania settled within the last 3,000 to 3,500 years, comprising south-eastern Island Melanesia and islands in the open Pacific east of the Solomon Islands: Fiji, Micronesia, New Caledonia, New Zealand, Polynesia, t ...
reaching Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (french: link=no, République de Vanuatu; bi, Ripablik blong Vanuatu), is an island country located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of no ...
, New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
, and Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
by 1200 BCE, and Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
and Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
by around 900 to 800 BCE. This was the furthest extent of the Lapita culture expansion. During a period of around 1,500 years, they gradually lost the technology for pottery (likely due to the lack of clay deposits in the islands), replacing it with carved wooden and bamboo containers. Back-migrations from the Lapita culture also merged back Island Southeast Asia in 1500 BCE, and into Micronesia at around 200 BCE. It was not until 700 CE when they started voyaging further into the Pacific Ocean, when they colonized the Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, langu ...
, the Society Islands
The Society Islands (french: Îles de la Société, officially ''Archipel de la Société;'' ty, Tōtaiete mā) are an archipelago located in the South Pacific Ocean. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country of the F ...
, and the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' ( North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in th ...
. From there, they further colonized Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is ...
by 900 CE, Rapa Nui
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
by 1000 CE, and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country ...
by 1200 CE.
In the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
, Austronesians from Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and ea ...
also colonized Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
and the Comoros Islands
The Comoro Islands or Comoros (Shikomori ''Komori''; ar, جزر القمر , ''Juzur al-qamar''; french: Les Comores) form an archipelago of volcanic islands situated off the southeastern coast of Africa, to the east of Mozambique and northwes ...
by around 500 CE. Austronesians remain the dominant ethnolinguistic group of the islands of the Indo-Pacific, and were the first to establish a maritime trade network reaching as far west as East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
and the Arabian peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
. They assimilated earlier Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
to early Holocene human overland migrations through Sundaland
Sundaland (also called Sundaica or the Sundaic region) is a biogeographical region of South-eastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It ...
like the Papuans
The indigenous peoples of West Papua in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands: a first wave from the Malay Arch ...
and the Negrito
The term Negrito () refers to several diverse ethnic groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia and the Andaman Islands. Populations often described as Negrito include: the Andamanese peoples (including the Great Andamanese, the Onge, ...
s in Island Southeast Asia. The Austronesian expansion was the last and the most far-reaching Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
human migration event.
Caribbean
TheCaribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean S ...
was one of the last places in the Americas that were settled by humans. The oldest remains are known from the Greater Antilles (Cuba and Hispaniola) dating between 4000 and 3500 BCE, and comparisons between tool-technologies suggest that these peoples moved across the Yucatán Channel from Central America. All evidence suggests that later migrants from 2000 BCE and onwards originated from South America, via the Orinoco region. The descendants of these migrants include the ancestors of the Taíno
The Taíno were a historic indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the late 15th century, they were the pri ...
and Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated languag ...
(Island Carib) peoples.
Arctic
Arctic small tool tradition The Arctic Small Tool tradition (ASTt) was a broad cultural entity that developed along the Alaska Peninsula, around Bristol Bay, and on the eastern shores of the Bering Strait around 2500 BC. ASTt groups were the first human occupants of Arctic C ...
(AST) and existed c. 2500 BCE. AST consisted of several Paleo-Eskimo
The Paleo-Eskimo (also pre-Thule or pre-Inuit) were the peoples who inhabited the Arctic region from Chukotka (e.g., Chertov Ovrag) in present-day Russia across North America to Greenland prior to the arrival of the modern Inuit (Eskimo) and re ...
cultures, including the Independence cultures and Pre-Dorset
The Pre-Dorset is a loosely defined term for a Paleo-Eskimo culture or group of cultures that existed in the Eastern Canadian Arctic from c. 3200 to 850 cal BC, and preceded the Dorset culture.
Due to its vast geographical expanse and to history ...
culture.Gibbon, pp. 28–31
The Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, and ...
are the descendants of the Thule culture
The Thule (, , ) or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit. They developed in coastal Alaska by the year 1000 and expanded eastward across northern Canada, reaching Greenland by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people o ...
, which emerged from western Alaska around CE 1000 and gradually displaced the Dorset culture.
See also
* List of first human settlements *Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleo ...
* Quaternary extinction
The Quaternary period (from 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present) has seen the extinctions of numerous predominantly megafaunal species, which have resulted in a collapse in faunal density and diversity and the extinction of key ecolog ...
* Timeline of human evolution
The timeline of human evolution outlines the major events in the evolutionary lineage of the modern human species, ''Homo sapiens'',
throughout the history of life, beginning some 4 billion years ago down to recent evolution within ''H. sapiens ...
* Timeline of maritime migration and exploration
Notes
References
Further reading
* * Diamond, Jared, '' Guns, germs and steel. A short history of everybody for the last 13,000 years'', 1997. * * ; *External links
Journey of Mankind – Genetic Map
–
Bradshaw Foundation
The Gwion Gwion rock paintings, Gwion figures, Kiro Kiro or Kujon (previously known as the Bradshaw rock paintings, Bradshaw rock art, Bradshaw figures and the Bradshaws) are one of the two major regional traditions of rock art found in the nort ...
Prehistoric Human Migration From Africa to World Video May 2015
{{Human Evolution Prehistoric migrations
Migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
Paleolithic
Early migration
Demographic history
Global events