dual in-line memory module on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A DIMM () (Dual In-line
A DIMM () (Dual In-line
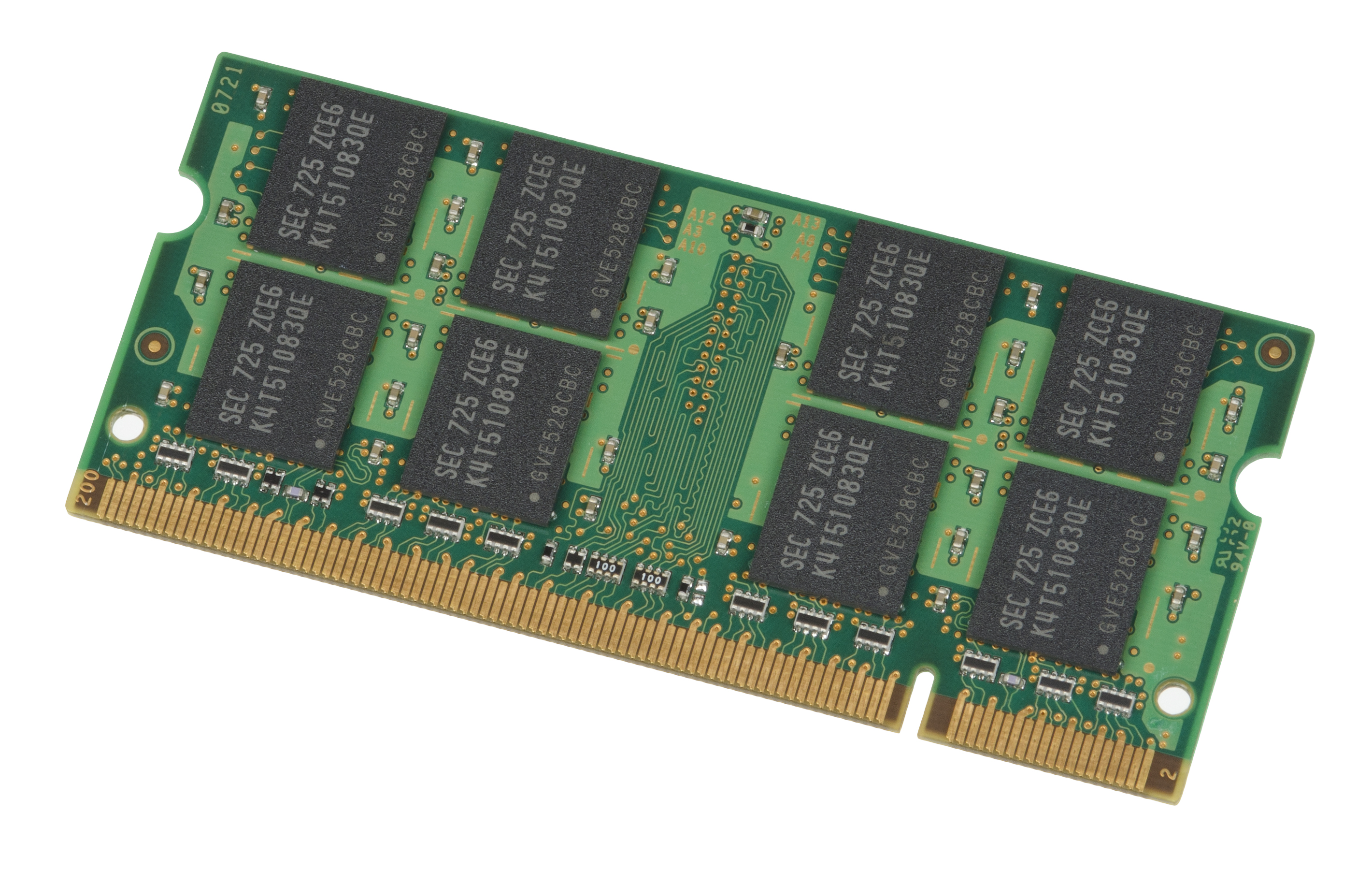

 A SO-DIMM (pronounced "so-dimm" , also spelled "SODIMM") or small outline DIMM, is a smaller alternative to a DIMM, being roughly half the physical size of a regular DIMM.
SO-DIMMs are often used in systems that have limited space, which include laptops,
A SO-DIMM (pronounced "so-dimm" , also spelled "SODIMM") or small outline DIMM, is a smaller alternative to a DIMM, being roughly half the physical size of a regular DIMM.
SO-DIMMs are often used in systems that have limited space, which include laptops,
 On the bottom edge of 168-pin DIMMs there are two notches, and the location of each notch determines a particular feature of the module. The first notch is the DRAM key position, which represents RFU (reserved future use), registered, and unbuffered DIMM types (left, middle and right position, respectively). The second notch is the voltage key position, which represents 5.0 V, 3.3 V, and RFU DIMM types (order is the same as above).
On the bottom edge of 168-pin DIMMs there are two notches, and the location of each notch determines a particular feature of the module. The first notch is the DRAM key position, which represents RFU (reserved future use), registered, and unbuffered DIMM types (left, middle and right position, respectively). The second notch is the voltage key position, which represents 5.0 V, 3.3 V, and RFU DIMM types (order is the same as above).
 DDR, DDR2,
DDR, DDR2,
 Several form factors are commonly used in DIMMs. Single Data Rate Synchronous DRAM (SDR SDRAM) DIMMs were primarily manufactured in and heights. When 1U rackmount servers started becoming popular, these form factor registered DIMMs had to plug into angled DIMM sockets to fit in the high box. To alleviate this issue, the next standards of DDR DIMMs were created with a "low profile" (LP) height of around . These fit into vertical DIMM sockets for a 1U platform.
With the advent of
Several form factors are commonly used in DIMMs. Single Data Rate Synchronous DRAM (SDR SDRAM) DIMMs were primarily manufactured in and heights. When 1U rackmount servers started becoming popular, these form factor registered DIMMs had to plug into angled DIMM sockets to fit in the high box. To alleviate this issue, the next standards of DDR DIMMs were created with a "low profile" (LP) height of around . These fit into vertical DIMM sockets for a 1U platform.
With the advent of ASUS DIMM.2 is a M.2 Riser Card.
accessed Jun. 4, 2020. Regular DIMMs are generally 133.35 mm in length, SO-DIMMs 67.6 mm.
How to Install PC Memory guides
Very Low Profile (VLP) DDR2 Whitepaper (PDF)
Is 4GB RAM Good For a Laptop?
{{DRAM Computer memory form factor
 A DIMM () (Dual In-line
A DIMM () (Dual In-line Memory Module
In computing, a memory module or RAM (random-access memory) stick is a printed circuit board on which memory integrated circuits are mounted. Memory modules permit easy installation and replacement in electronic systems, especially computers such ...
), commonly called a RAM stick, comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory
Dynamic random-access memory (dynamic RAM or DRAM) is a type of random-access semiconductor memory that stores each bit of data in a memory cell, usually consisting of a tiny capacitor and a transistor, both typically based on metal-ox ...
integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
s. These memory modules are mounted on a printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich str ...
and designed for use in personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or te ...
s, workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term ''workst ...
s, printers, and server
Server may refer to:
Computing
*Server (computing), a computer program or a device that provides functionality for other programs or devices, called clients
Role
* Waiting staff, those who work at a restaurant or a bar attending customers and su ...
s. They are the predominant method for adding memory into a computer system. The vast majority of DIMMs are standardized through JEDEC standards
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association is an independent semiconductor engineering trade organization and standardization body headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia, United States.
JEDEC has over 300 members, including some of the w ...
, although there are proprietary DIMMs. DIMMs come in a variety of speeds and sizes, but generally are one of two lengths - PC which are and laptop (SO-DIMM) which are about half the size at .
History
DIMMs (Dual In-line Memory Module) were a 1990s upgrade forSIMM
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module containing random-access memory used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It differs from a dual in-line memory module (DIMM), the most predominant form of memo ...
s (Single In-line Memory Modules) as Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 ser ...
P5-based Pentium
Pentium is a brand used for a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel. The original Pentium processor from which the brand took its name was first released on March 22, 1993. After that, the Pentium II and P ...
processors began to gain market share. The Pentium had a 64-bit bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
width, which would require SIMMs installed in matched pairs in order to populate the data bus. The processor would then access the two SIMMs in parallel.
DIMMs were introduced to eliminate this disadvantage. The contacts on SIMMs on both sides are redundant, while DIMMs have separate electrical contacts on each side of the module. This allowed them to double the SIMMs 32-bit data path into a 64-bit data path.
The name "DIMM" was chosen as an acronym for Dual In-line Memory Module symbolizing the split in the contacts of a SIMM into two independent rows. Many enhancements have occurred to the modules in the intervening years, but the word "DIMM" has remained as a generic term for computer memory modules.
Variants
Variants of DIMMs support DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5 RAM. Common types of DIMMs include the following: 70 to 200 pins * 72-pin SO-DIMM (not the same as a 72-pin SIMM), used for FPM DRAM andEDO
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
DRAM
* 100-pin DIMM, used for printer SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal.
DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the ...
* 144-pin SO-DIMM, used for SDR SDRAM (less frequently for DDR2 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It superseded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself superseded by DDR ...
)
* 168-pin DIMM, used for SDR SDRAM (less frequently for FPM/EDO DRAM in workstations/servers, may be 3.3 or 5 V)
* 172-pin MicroDIMM, used for DDR SDRAM
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 ...
* 184-pin DIMM, used for DDR SDRAM
* 200-pin SO-DIMM, used for DDR SDRAM and DDR2 SDRAM
* 200-pin DIMM, used for FPM/EDO DRAM in some Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
workstations and servers.
201 to 300 pins
* 204-pin SO-DIMM, used for DDR3 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-spe ...
* 214-pin MicroDIMM, used for DDR2 SDRAM
* 240-pin DIMM, used for DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM and FB-DIMM
Fully Buffered DIMM (or FB-DIMM) is a memory technology that can be used to increase reliability and density of memory systems. Unlike the parallel bus architecture of traditional DRAMs, an FB-DIMM has a serial interface between the memory contro ...
DRAM
* 244-pin MiniDIMM, used for DDR2 SDRAM
* 260-pin SO-DIMM, used for DDR4 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 4 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR4 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface.
Released to the market in 2014, it is a variant of dynamic r ...
* 260-pin SO-DIMM, with different notch position than on DDR4 SO-DIMMs, used for UniDIMM
UniDIMM (short for Universal DIMM) is a specification for dual in-line memory modules (DIMMs), which are printed circuit boards (PCBs) designed to carry dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) chips. UniDIMMs can be populated with either DDR3 or ...
s that can carry either DDR3 or DDR4 SDRAM
* 278-pin DIMM, used for HP high density SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal.
DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the ...
.
* 288-pin DIMM, used for DDR4 SDRAM and DDR5 SDRAM
SO-DIMM


 A SO-DIMM (pronounced "so-dimm" , also spelled "SODIMM") or small outline DIMM, is a smaller alternative to a DIMM, being roughly half the physical size of a regular DIMM.
SO-DIMMs are often used in systems that have limited space, which include laptops,
A SO-DIMM (pronounced "so-dimm" , also spelled "SODIMM") or small outline DIMM, is a smaller alternative to a DIMM, being roughly half the physical size of a regular DIMM.
SO-DIMMs are often used in systems that have limited space, which include laptops, notebooks
A notebook is a small book often used for writing.
Notebook or The Notebook may also refer to:
Computing
*Laptop, a type of personal computer
* Google Notebook, a discontinued online application
* Notebook interface, a type of programming envir ...
, small-footprint personal computers
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tec ...
such as those based on Nano-ITX
Nano-ITX is a computer motherboard form factor first proposed by VIA Technologies at CeBIT in March 2003, and implemented in late 2005. Nano-ITX boards measure , and are fully integrated, very low power consumption motherboards with many uses, but ...
motherboards
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
, high-end upgradable office printers, and networking hardware
Networking hardware, also known as network equipment or computer networking devices, are electronic devices which are required for communication and interaction between devices on a computer network. Specifically, they mediate data transmission in ...
such as routers and NAS
Nas (born 1973) is the stage name of American rapper Nasir Jones.
Nas, NaS, or NAS may also refer to:
Aviation
* Nasair, a low-cost airline carrier and subsidiary based in Eritrea
* National Air Services, an airline in Saudi Arabia
** Nas Air ...
devices. They are usually available with the same size data path and speed ratings of the regular DIMMs though normally with smaller capacities.
SDR 168-pin SDRAM
 On the bottom edge of 168-pin DIMMs there are two notches, and the location of each notch determines a particular feature of the module. The first notch is the DRAM key position, which represents RFU (reserved future use), registered, and unbuffered DIMM types (left, middle and right position, respectively). The second notch is the voltage key position, which represents 5.0 V, 3.3 V, and RFU DIMM types (order is the same as above).
On the bottom edge of 168-pin DIMMs there are two notches, and the location of each notch determines a particular feature of the module. The first notch is the DRAM key position, which represents RFU (reserved future use), registered, and unbuffered DIMM types (left, middle and right position, respectively). The second notch is the voltage key position, which represents 5.0 V, 3.3 V, and RFU DIMM types (order is the same as above).
DDR DIMMs
 DDR, DDR2,
DDR, DDR2, DDR3
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth ("double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed ...
, DDR4
Double Data Rate 4 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR4 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface.
Released to the market in 2014, it is a variant of dynamic ran ...
and DDR5
Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR5 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory. Compared to its predecessor DDR4 SDRAM, DDR5 was planned to reduce power consumption, while doubling bandwidth. Th ...
all have different pin counts and/or different notch positions. As of October 2022, DDR5 SDRAM is a modern emerging type of dynamic random access memory (DRAM) with a high-bandwidth ("double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2020. It is the higher-speed successor to DDR, DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4. DDR5 SDRAM is neither forward nor backward compatible with any earlier type of random access memory (RAM) because of different signalling voltages, timings, as well as other differing factors between the technologies and their implementation.
SPD EEPROM
A DIMM's capacity and other operational parameters may be identified withserial presence detect
In computing, serial presence detect (SPD) is a standardized way to automatically access information about a memory module. Earlier 72-pin SIMMs included five pins that provided five bits of ''parallel presence detect'' (PPD) data, but the 168-p ...
(SPD), an additional chip which contains information about the module type and timing for the memory controller to be configured correctly. The SPD EEPROM
EEPROM (also called E2PROM) stands for electrically erasable programmable read-only memory and is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or ...
connects to the System Management Bus The System Management Bus (abbreviated to SMBus or SMB) is a single-ended simple two-wire bus for the purpose of lightweight communication. Most commonly it is found in computer motherboards for communication with the power source for ON/OFF instru ...
and may also contain thermal sensors (''TS-on-DIMM'').
Error correction
ECC DIMMs are those that have extra data bits which can be used by the system memory controller to detect and correct errors. There are numerous ECC schemes, but perhaps the most common is Single Error Correct, Double Error Detect ( SECDED) which uses an extra byte per 64-bit word. ECC modules usually carry a multiple of 9 instead of a multiple of 8 chips.Ranking
Sometimes memory modules are designed with two or more independent sets of DRAM chips connected to the same address and data buses; each such set is called a rank. Ranks that share the same slot, only one rank may be accessed at any given time; it is specified by activating the corresponding rank's chip select (CS) signal. The other ranks on the module are deactivated for the duration of the operation by having their corresponding CS signals deactivated. DIMMs are currently being commonly manufactured with up to four ranks per module. Consumer DIMM vendors have recently begun to distinguish between single and dual ranked DIMMs. After a memory word is fetched, the memory is typically inaccessible for an extended period of time while the sense amplifiers are charged for access of the next cell. By interleaving the memory (e.g. cells 0, 4, 8, etc. are stored together in one rank), sequential memory accesses can be performed more rapidly because sense amplifiers have 3 cycles of idle time for recharging, between accesses. DIMMs are often referred to as "single-sided" or " double-sided" to describe whether the DRAM chips are located on one or both sides of the module'sprinted circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich str ...
(PCB). However, these terms may cause confusion, as the physical layout of the chips does not necessarily relate to how they are logically organized or accessed.
JEDEC
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association is an independent semiconductor engineering trade organization and standardization body headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia, United States.
JEDEC has over 300 members, including some of the w ...
decided that the terms "dual-sided", "double-sided", or "dual-banked" were not correct when applied to registered DIMMs (RDIMMs).
Organization
Most DIMMs are built using "×4" ("by four") or "×8" ("by eight") memory chips with nine chips per side; "×4" and "×8" refer to the data width of the DRAM chips in bits. In the case of "×4" registered DIMMs, the data width per side is 36 bits; therefore, thememory controller
The memory controller is a digital circuit that manages the flow of data going to and from the computer's main memory. A memory controller can be a separate chip or integrated into another chip, such as being placed on the same die or as an int ...
(which requires 72 bits) needs to address both sides at the same time to read or write the data it needs. In this case, the two-sided module is single-ranked. For "×8" registered DIMMs, each side is 72 bits wide, so the memory controller only addresses one side at a time (the two-sided module is dual-ranked).
The above example applies to ECC memory that stores 72 bits instead of the more common 64. There would also be one extra chip per group of eight, which is not counted.
Speeds
For various technologies, there are certain bus and device clock frequencies that are standardized; there is also a decided nomenclature for each of these speeds for each type. DIMMs based on Single Data Rate (SDR) DRAM have the same bus frequency for data, address and control lines. DIMMs based onDouble Data Rate
In computing, a computer bus operating with double data rate (DDR) transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in ...
(DDR) DRAM have data but not the strobe at double the rate of the clock; this is achieved by clocking on both the rising and falling edge of the data strobes. Power consumption and voltage gradually became lower with each generation of DDR-based DIMMs.
Another influence is Column Access Strobe (CAS) latency, or CL which affects memory access speed. This is the delay time between the READ command and the moment data is available. See main article CAS/CL
Form factors
blade server
A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, whi ...
s, angled slots have once again become common in order to accommodate LP form factor DIMMs in these space-constrained boxes. This led to the development of the Very Low Profile (VLP) form factor DIMM with a height of around . The DDR3 JEDEC standard for VLP DIMM height is around . These will fit vertically in ATCA systems.
Full-height 240-pin DDR2 and DDR3 DIMMs are all specified at a height of around by standards set by JEDEC. These form factors include 240-pin DIMM, SO-DIMM, Mini-DIMM and Micro-DIMM.
Full-height 288-pin DDR4 DIMMs are slightly taller than their DDR3 counterparts at . Similarly, VLP DDR4 DIMMs are also marginally taller than their DDR3 equivalent at nearly .
As of Q2 2017, Asus has had a PCI-E
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common m ...
based "DIMM.2", which has a similar socket to DDR3 DIMMs and is used to put in a module to connect up to two M.2
M.2, pronounced ''m dot two'' and formerly known as the Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF), is a specification for internally mounted computer expansion cards and associated connectors. M.2 replaces the mSATA standard, which uses the PCI Ex ...
NVMe
NVM Express (NVMe) or Non-Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification (NVMHCIS) is an open, logical-device interface specification for accessing a computer's non-volatile storage media usually attached via PCI Express (PCIe) bus. The ...
solid-state drives. However, it cannot use common DDR type ram and does not have much support other than Asus.accessed Jun. 4, 2020. Regular DIMMs are generally 133.35 mm in length, SO-DIMMs 67.6 mm.
See also
*Dual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL), is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board ( ...
(DIP)
* Memory scrambling
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, ...
* Memory geometry logical configuration of RAM modules (channels, ranks, banks, etc.)
* Motherboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
* NVDIMM non-volatile DIMM
* Row hammer
Row hammer (also written as rowhammer) is a security exploit that takes advantage of an unintended and undesirable side effect in dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) in which memory cells interact electrically between themselves by leaking thei ...
* Rambus in-line memory module (RIMM)
* Single in-line memory module (SIMM)
* Single in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL), is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (P ...
(SIP)
* Zig-zag in-line package
The zig-zag in-line package (ZIP) is a packaging technology for integrated circuits. It was intended as a replacement for dual in-line packaging (DIL or DIP). A ZIP is an integrated circuit encapsulated in a slab of plastic with 16, 20, 28 or 4 ...
(ZIP)
References
External links
How to Install PC Memory guides
Very Low Profile (VLP) DDR2 Whitepaper (PDF)
Is 4GB RAM Good For a Laptop?
{{DRAM Computer memory form factor