droplets on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A drop or droplet is a small column of
A drop or droplet is a small column of
 The classic shape associated with a drop (with a pointy end in its upper side) comes from the observation of a droplet clinging to a surface. The shape of a drop falling through a gas is actually more or less spherical for drops less than 2 mm in diameter. Larger drops tend to be flatter on the bottom part due to the pressure of the gas they move through. As a result, as drops get larger, a concave depression forms which leads to the eventual breakup of the drop.
The classic shape associated with a drop (with a pointy end in its upper side) comes from the observation of a droplet clinging to a surface. The shape of a drop falling through a gas is actually more or less spherical for drops less than 2 mm in diameter. Larger drops tend to be flatter on the bottom part due to the pressure of the gas they move through. As a result, as drops get larger, a concave depression forms which leads to the eventual breakup of the drop.
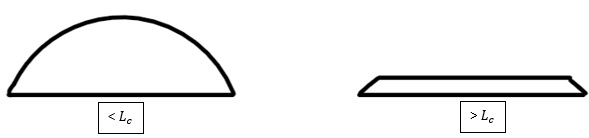
Image:Blue Droplet.jpg, Blue dye being dropped in a saucer of milk.
Image:2006-02-13 Drop-impact.jpg, Impact of a drop of water.
Image:2006-01-28 drop-impact backjet.jpg, Backjet from drop impact.
Image:Water splashes 001.jpg, A drop of water hitting a metal surface/ crown formation due to splashing of droplet.
Image:Post-splash with droplets.jpg, A drop of water hitting a wet metal surface and ejecting more droplets, which become water globules and skim across the surface of the water.
Image:Water drop on a leaf.jpg, A drop of water on a leaf /
Liquid Sculpture – pictures of drops
Liquid Art – Galleries of fine art droplet photography
* (Greatly varying) calculation of water waste from dripping tap
{{Authority control Liquids Fluid dynamics Articles containing video clips Alcohol measurement ps:څاڅکې

 A drop or droplet is a small column of
A drop or droplet is a small column of liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, ...
, bounded completely or almost completely by free surface
In physics, a free surface is the surface of a fluid that is subject to zero parallel shear stress,
such as the interface between two homogeneous fluids.
An example of two such homogeneous fluids would be a body of water (liquid) and the air i ...
s. A drop may form when liquid accumulates at the lower end of a tube or other surface boundary, producing a hanging drop called a pendant
A pendant is a loose-hanging piece of jewellery, generally attached by a small loop to a necklace, which may be known as a "pendant necklace". A pendant earring is an earring with a piece hanging down. Its name stems from the Latin word ...
drop. Drops may also be formed by the condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to ...
of a vapor
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (British English and Canadian English; see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical temperature,R. H. Petrucci, W. S. Harwood, and F. G. Her ...
or by atomization of a larger mass of solid. Water vapor will condense into droplets depending on the temperature. The temperature at which droplets form is called the dew point.
Surface tension
Liquid forms drops because it exhibitssurface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to ...
.
A simple way to form a drop is to allow liquid to flow slowly from the lower end of a vertical tube of small diameter. The surface tension of the liquid causes the liquid to hang from the tube, forming a pendant. When the drop exceeds a certain size it is no longer stable and detaches itself. The falling liquid is also a drop held together by surface tension.
Viscosity and pitch drop experiments
Some substances that appear to be solid, can be shown to instead be extremelyviscous
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inter ...
liquids, because they form drops and display droplet behavior. In the famous pitch drop experiment
A pitch drop experiment is a long-term experiment which measures the flow of a piece of pitch over many years. 'Pitch' is the name for any of a number of highly viscous liquids which appear solid, most commonly bitumen, also known as asphalt. ...
s, pitch – a substance somewhat like solid bitumen
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
– is shown to be a liquid in this way. Pitch in a funnel slowly forms droplets, each droplet taking about 10 years to form and break off.
Pendant drop test
In the pendant drop test, a drop of liquid is suspended from the end of a tube or by any surface bysurface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to ...
. The force due to surface tension is proportional to the length of the boundary between the liquid and the tube, with the proportionality constant usually denoted . Since the length of this boundary is the circumference of the tube, the force due to surface tension is given by
:
where ''d'' is the tube diameter.
The mass ''m'' of the drop hanging from the end of the tube can be found by equating the force due to gravity () with the component of the surface tension in the vertical direction () giving the formula
:
where α is the angle of contact with the tube's front surface, and ''g'' is the acceleration due to gravity.
The limit of this formula, as α goes to 90°, gives the maximum weight of a pendant drop for a liquid with a given surface tension, .
:
This relationship is the basis of a convenient method of measuring surface tension, commonly used in the petroleum industry. More sophisticated methods are available to take account of the developing shape of the pendant as the drop grows. These methods are used if the surface tension is unknown.
Drop adhesion to a solid
The dropadhesion
Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another ( cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another).
The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be ...
to a solid can be divided into two categories: lateral adhesion and normal adhesion. Lateral adhesion resembles friction (though tribologically lateral adhesion is a more accurate term) and refers to the force required to slide a drop on the surface, namely the force to detach the drop from its position on the surface only to translate it to another position on the surface. Normal adhesion is the adhesion required to detach a drop from the surface in the normal direction, namely the force to cause the drop to fly off from the surface. The measurement of both adhesion forms can be done with the Centrifugal Adhesion Balance (CAB). The CAB uses a combination of centrifugal and gravitational forces to obtain any ratio of lateral and normal forces. For example, it can apply a normal force at zero lateral force for the drop to fly off away from the surface in the normal direction or it can induce a lateral force at zero normal force (simulating zero gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the str ...
).
Droplet
The term droplet is a diminutive form of 'drop' – and as a guide is typically used for liquidparticle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from s ...
s of less than 500 μm diameter. In spray application, droplets are usually described by their perceived size (i.e., diameter) whereas the dose (or number of infective particles in the case of biopesticide
A Biopesticide is a biological substance or organism that damages, kills, or repels organisms seens as pests. Biological pest management intervention involves predatory, parasitic, or chemical relationships.
They are obtained from organisms inclu ...
s) is a function of their volume. This increases by a cubic function relative to diameter; thus a 50 μm droplet represents a dose in 65 pl and a 500 μm drop represents a dose in 65 nanometers.
Speed
A droplet with a diameter of 3mm has a terminal velocity of approximately 8 m/s. Drops smaller than in diameter will attain 95% of their terminal velocity within . But above this size the distance to get to terminal velocity increases sharply. An example is a drop with a diameter of that may achieve this at .Optics
Due to the differentrefractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, o ...
of water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
and air, refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomen ...
and reflection occur on the surfaces of rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water ...
drops, leading to rainbow
A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection, refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. Rainbo ...
formation.
Sound
The major source of sound when a droplet hits a liquid surface is the resonance of excited bubbles trapped underwater. These oscillating bubbles are responsible for most liquid sounds, such as running water or splashes, as they actually consist of many drop-liquid collisions."Dripping tap" noise prevention
Reducing the surface tension of a body of liquid makes possible to reduce or prevent noise due to droplets falling into it. This would involve addingsoap
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are used a ...
, detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are mor ...
or a similar substance to water. The reduced surface tension reduces the noise from dripping.
Shape
Capillary length
Thecapillary length
The capillary length or capillary constant, is a length scaling factor that relates gravity and surface tension. It is a fundamental physical property that governs the behavior of menisci, and is found when body forces (gravity) and surface forces ...
is a length scaling factor that relates gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the str ...
and surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to ...
, and is directly responsible for the shape a droplet for a specific fluid will take. The capillary length stems from the Laplace pressure
The Laplace pressure is the pressure difference between the inside and the outside of a curved surface that forms the boundary between two fluid regions. The pressure difference is caused by the surface tension of the interface between liquid and ...
, using the radius of the droplet.
Using the capillary length we can define microdrops and macrodrops. Microdrops are droplets with radius smaller than the capillary length, where the shape of the droplet is governed solely by surface tension and they form a spherical cap shape. If a droplet has a radius larger than the capillary length, they are known as macrodrops and the gravitational forces will dominate. Macrodrops will be 'flattened' by gravity and the height of the droplet will be reduced.

Size
Raindrop sizes typically range from 0.5 mm to 4 mm, with size distributions quickly decreasing past diameters larger than 2-2.5 mm. Scientists traditionally thought that the variation in the size of raindrops was due to collisions on the way down to the ground. In 2009, French researchers succeeded in showing that the distribution of sizes is due to the drops' interaction with air, which deforms larger drops and causes them to fragment into smaller drops, effectively limiting the largest raindrops to about 6 mm diameter. However, drops up to 10 mm (equivalent in volume to a sphere of radius 4.5 mm) are theoretically stable and could be levitated in a wind tunnel. The largest recorded raindrop was 8.8 mm in diameter, located at the base of acumulus congestus cloud
Cumulus congestus clouds, also known as towering cumulus, are a form of cumulus that can be based in the low or middle height ranges. They achieve considerable vertical development in areas of deep, moist convection. They are an intermediate stage ...
in the vicinity of Kwajalein Atoll
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marshallese: ) is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents (about 1,000 mostly U.S. civili ...
in July 1999. A raindrop of identical size was detected over northern Brazil in September 1995.
Standardized droplet sizes in medicine
Inmedicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care p ...
, this property is used to create droppers and IV infusion sets which have a standardized
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization ...
diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid ...
, in such a way that 1 millilitre
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American English spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3). ...
is equivalent to 20 drops
Drop, DROP, drops or DROPS may refer to:
* Drop (liquid) or droplet, a small volume of liquid
** Eye drops, saline (sometimes mydriatic) drops used as medication for the eyes
* Drop (unit), a unit of measure of volume
* Falling (physics), allowin ...
. When smaller amounts are necessary (such as paediatrics), microdroppers or paediatric infusion sets are used, in which 1 millilitre = 60 microdrops.
Gallery
Hydrophobic effect
The hydrophobic effect is the observed tendency of nonpolar substances to aggregate in an aqueous solution and exclude water molecules. The word hydrophobic literally means "water-fearing", and it describes the segregation of water and nonpolar ...
/ Partial Wetting
Wetting is the ability of a liquid to maintain contact with a solid surface, resulting from intermolecular interactions when the two are brought together. This happens in presence of a gaseous phase or another liquid phase not miscible with t ...
.
Image:Water droplet backjet.JPG, A triple backjet after impact.
Image:Raindrop on a fern frond.jpg, Photo of a raindrop on a fern frond.
Image:2006-01-21 Detaching drop.jpg, Detaching drop.
Image:Showerheadandwaterdroplets.jpg, Water droplets forming out of a shower head.
Image:Asteraceae03.JPG, A drop of water on an Asteraceae
The family Asteraceae, alternatively Compositae, consists of over 32,000 known species of flowering plants in over 1,900 genera within the order Asterales. Commonly referred to as the aster, daisy, composite, or sunflower family, Compositae ...
Image:A small flower refracted in rain droplets.jpg, Droplets of water refracting a small flower.
Image:Water Drop on rose leaf.JPG, A raindrop on a leaf
Image:Water_Droplets_Background.JPG, Water droplets on glass.
Image:Fountain water droplets.jpg, Fountain water droplets as seen in very short exposure
Image:Water drops on rose leaf.jpg, Rain droplets on Rose
A rose is either a woody perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred species and tens of thousands of cultivars. They form a group of plants that can be e ...
plant leaf
See also
*Pitch drop experiment
A pitch drop experiment is a long-term experiment which measures the flow of a piece of pitch over many years. 'Pitch' is the name for any of a number of highly viscous liquids which appear solid, most commonly bitumen, also known as asphalt. ...
* Rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water ...
* Splash (fluid dynamics)
* Water droplet erosion
References
External links
Liquid Sculpture – pictures of drops
Liquid Art – Galleries of fine art droplet photography
* (Greatly varying) calculation of water waste from dripping tap
{{Authority control Liquids Fluid dynamics Articles containing video clips Alcohol measurement ps:څاڅکې