dreams on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A dream is a succession of
A dream is a succession of
 Preserved writings from early Mediterranean civilizations indicate a relatively abrupt change in subjective dream experience between
Preserved writings from early Mediterranean civilizations indicate a relatively abrupt change in subjective dream experience between
Content Analysis Explained
Results indicated that participants from varying parts of the world demonstrated similarity in their dream content. The only residue of antiquity's authoritative dream figure in the Hall and Van de Castle listing of dream characters is the inclusion of God in the category of prominent persons. Hall's complete dream reports were made publicly available in the mid-1990s by his protégé In the Hall study, the most common emotion experienced in dreams was
In the Hall study, the most common emotion experienced in dreams was
 A turning point in theorizing about dream function came in 1953, when ''Science'' published the Aserinsky and Kleitman paper establishing
A turning point in theorizing about dream function came in 1953, when ''Science'' published the Aserinsky and Kleitman paper establishing
 In Judaism, dreams are considered part of the experience of the world that can be interpreted and from which lessons can be garnered. It is discussed in the Talmud, Tractate Berachot 55–60.
The ancient
In Judaism, dreams are considered part of the experience of the world that can be interpreted and from which lessons can be garnered. It is discussed in the Talmud, Tractate Berachot 55–60.
The ancient
 In Chinese history, people wrote of two vital aspects of the soul of which one is freed from the body during slumber to journey in a dream realm, while the other remained in the body. This belief and dream interpretation had been questioned since early times, such as by the philosopher Wang Chong ().
The Babylonians and Assyrians divided dreams into "good," which were sent by the gods, and "bad," sent by demons. A surviving collection of dream omens entitled '' Iškar Zaqīqu'' records various dream scenarios as well as prognostications of what will happen to the person who experiences each dream, apparently based on previous cases. Some list different possible outcomes, based on occasions in which people experienced similar dreams with different results. The Greeks shared their beliefs with the Egyptians on how to interpret good and bad dreams, and the idea of incubating dreams. Morpheus, the Greek god of dreams, also sent warnings and prophecies to those who slept at shrines and temples. The earliest Greek beliefs about dreams were that their gods physically visited the dreamers, where they entered through a keyhole, exiting the same way after the divine message was given.
In Chinese history, people wrote of two vital aspects of the soul of which one is freed from the body during slumber to journey in a dream realm, while the other remained in the body. This belief and dream interpretation had been questioned since early times, such as by the philosopher Wang Chong ().
The Babylonians and Assyrians divided dreams into "good," which were sent by the gods, and "bad," sent by demons. A surviving collection of dream omens entitled '' Iškar Zaqīqu'' records various dream scenarios as well as prognostications of what will happen to the person who experiences each dream, apparently based on previous cases. Some list different possible outcomes, based on occasions in which people experienced similar dreams with different results. The Greeks shared their beliefs with the Egyptians on how to interpret good and bad dreams, and the idea of incubating dreams. Morpheus, the Greek god of dreams, also sent warnings and prophecies to those who slept at shrines and temples. The earliest Greek beliefs about dreams were that their gods physically visited the dreamers, where they entered through a keyhole, exiting the same way after the divine message was given.
 Beginning in the late 19th century, Austrian neurologist
Beginning in the late 19th century, Austrian neurologist
File:Nicolas Dipre. Le songe de Jacob. c.1500 Avignon, Petit Palais..jpg, Nicolas Dipre. Le songe de Jacob. c.1500 Avignon, Petit Palais.
File:El sueño de Jacob, by José de Ribera, from Prado in Google Earth.jpg, José de Ribera (1591–1652). El sueño de Jacob, from Prado in Google Earth
File:Loggia_di_raffaello_08.jpg, Raphael. Jacob's Dream (1518)
File:Rembrandt Dream of Joseph.jpg, Rembrandt. Dream of Joseph (1645)
File:Mengs, Traum des hl. Joseph.jpg, Anton Raphael Mengs. Traum des Hl. Joseph (1773 or 1774)
Many later graphic artists have depicted dreams, including Japanese woodblock artist  Dreams have also featured in
Dreams have also featured in
 The recollection of dreams is extremely unreliable, though it is a skill that can be trained. Dreams can usually be recalled if a person is awakened while dreaming. Women tend to have more frequent dream recall than men. Dreams that are difficult to recall may be characterized by relatively little affect, and factors such as salience,
The recollection of dreams is extremely unreliable, though it is a skill that can be trained. Dreams can usually be recalled if a person is awakened while dreaming. Women tend to have more frequent dream recall than men. Dreams that are difficult to recall may be characterized by relatively little affect, and factors such as salience,
 A daydream is a visionary
A daydream is a visionary
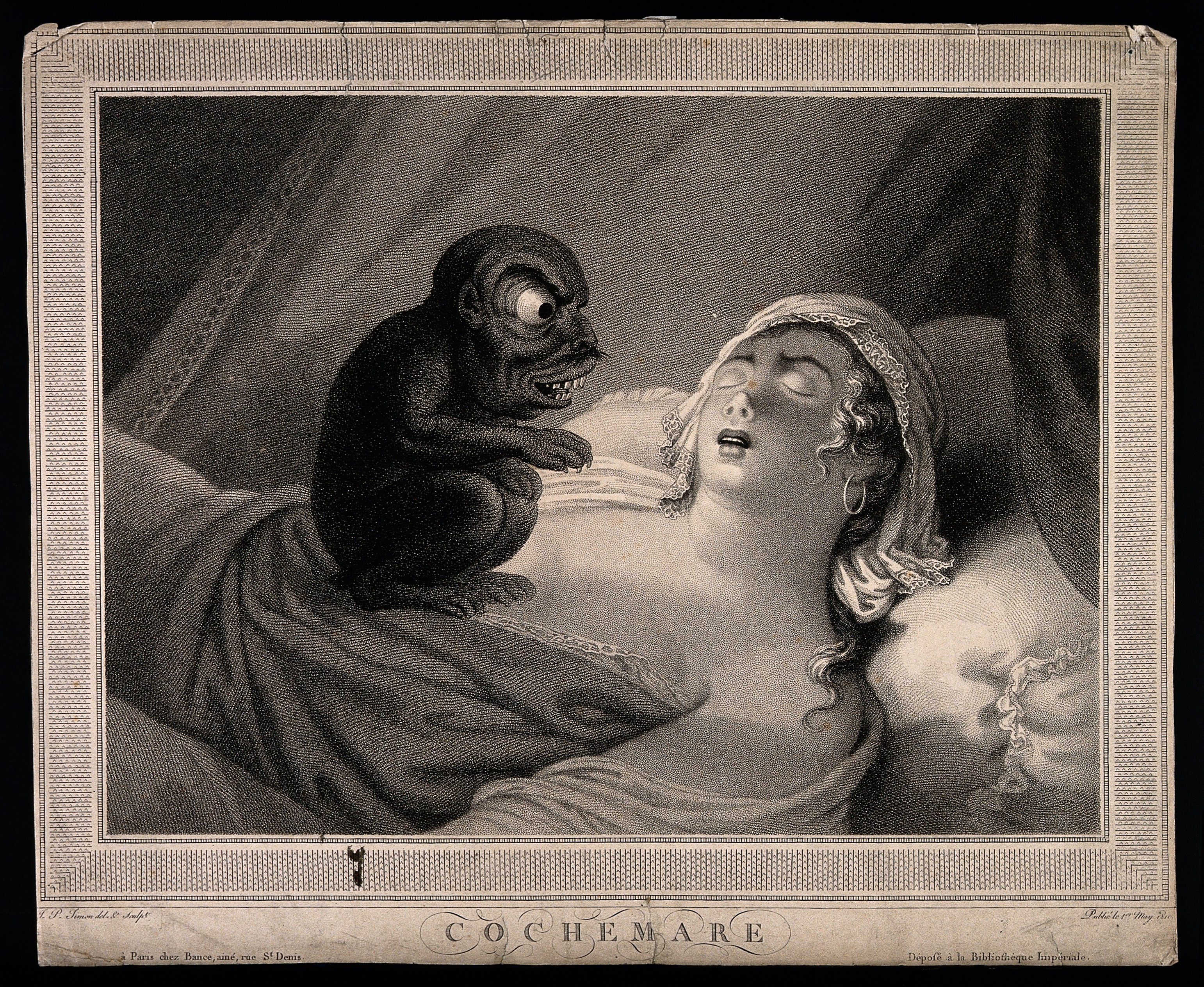 A nightmare is an unpleasant dream that can cause a strong negative emotional response from the mind, typically
A nightmare is an unpleasant dream that can cause a strong negative emotional response from the mind, typically
Archive for Research in Archetypal Symbolism website
The International Association for the Study of Dreams
* *
alt.dreams
A long-running USENET forum wherein readers post and analyze dreams
LSDBase
– online sleep research database documenting physiological effects of dreams through biofeedback {{Authority control Night Sleep Symbols
 A dream is a succession of
A dream is a succession of image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensio ...
s, idea
In common usage and in philosophy, ideas are the results of thought. Also in philosophy, ideas can also be mental representational images of some object. Many philosophers have considered ideas to be a fundamental ontological category of bei ...
s, emotions
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or displeasure. There is currently no scientific consensus on a definition. ...
, and sensations that usually occur involuntarily in the mind
The mind is the set of faculties responsible for all mental phenomena. Often the term is also identified with the phenomena themselves. These faculties include thought, imagination, memory, will, and sensation. They are responsible for various m ...
during certain stages of sleep
Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited Perception, sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefuln ...
. Humans spend about two hours dreaming per night, and each dream lasts around 5 to 20 minutes, although the dreamer may perceive the dream as being much longer than this.
The content and function of dreams have been topics of scientific, philosophical and religious interest throughout recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world his ...
. Dream interpretation
Dream interpretation is the process of assigning meaning to dreams. Although associated with some forms of psychotherapy, there is no reliable evidence that understanding or interpreting dreams has a positive impact on one's mental health.
In m ...
, practiced by the Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
ns in the third millennium BCE and even earlier by the ancient Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
ians, figures prominently in religious texts in several traditions, and has played a lead role in psychotherapy. The scientific study of dreams is called oneirology. Most modern dream study focuses on the neurophysiology of dreams and on proposing and testing hypotheses regarding dream function. It is not known where in the brain dreams originate, if there is a single origin for dreams or if multiple regions of the brain are involved, or what the purpose of dreaming is for the body or mind.
The human dream experience and what to make of it has undergone sizable shifts over the course of history. Long ago, according to writings from Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
and Ancient Egypt, dreams dictated post-dream behaviors to an extent sharply reduced in later millennia. These ancient writings about dreams highlight visitation dreams, where a dream figure, usually a deity or a prominent forebear, commands the dreamer to take specific actions and may predict future events. Framing the dream experience varies across cultures as well as through time.
Dreaming and sleep are intertwined. Dreams occur mainly in the rapid-eye movement (REM) stage of sleep—when brain activity
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocor ...
is high and resembles that of being awake. Because REM sleep is detectable in many species, and because research suggests that all mammals experience REM, linking dreams to REM sleep has led to conjectures that animals dream. However, humans dream during non-REM sleep, also, and not all REM awakenings elicit dream reports. To be studied, a dream must first be reduced to a verbal report, which is an account of the subject's memory of the dream, not the subject's dream experience itself. So, dreaming by non-humans is currently unprovable, as is dreaming by human fetuses and pre-verbal infants.
Subjective experience and content
 Preserved writings from early Mediterranean civilizations indicate a relatively abrupt change in subjective dream experience between
Preserved writings from early Mediterranean civilizations indicate a relatively abrupt change in subjective dream experience between Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
antiquity and the beginnings of the classical era.
In visitation dreams reported in ancient writings, dreamers were largely passive in their dreams, and visual content served primarily to frame authoritative auditory messaging. Gudea
Gudea ( Sumerian: , ''Gu3-de2-a'') was a ruler ('' ensi'') of the state of Lagash in Southern Mesopotamia, who ruled circa 2080–2060 BC (short chronology) or 2144-2124 BC ( middle chronology). He probably did not come from the city, but had mar ...
, the king of the Sumerian city-state of Lagash
Lagash (cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian: ''Lagaš''), was an ancient city state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Ash Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash (modern Al-Hiba) w ...
(reigned 2144–2124 BCE), rebuilt the temple of Ningirsu
, image= Cropped Image of Carving Showing the Mesopotamian God Ninurta.png
, caption= Assyrian stone relief from the temple of Ninurta at Kalhu, showing the god with his thunderbolts pursuing Anzû, who has stolen the Tablet of Destinies from E ...
as the result of a dream in which he was told to do so. After antiquity, the passive hearing of visitation dreams largely gave way to visualized narratives in which the dreamer becomes a character who actively participates.
From the 1940s to 1985, Calvin S. Hall collected more than 50,000 dream reports at Western Reserve University
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
* Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that i ...
. In 1966, Hall and Robert Van de Castle published ''The Content Analysis of Dreams'', in which they outlined a coding system to study 1,000 dream reports from college students.Hall, C., & Van de Castle, R. (1966). The Content Analysis of Dreams. New York: Appleton-Century-CroftsContent Analysis Explained
Results indicated that participants from varying parts of the world demonstrated similarity in their dream content. The only residue of antiquity's authoritative dream figure in the Hall and Van de Castle listing of dream characters is the inclusion of God in the category of prominent persons. Hall's complete dream reports were made publicly available in the mid-1990s by his protégé
William Domhoff
George William "Bill" Domhoff (born August 6, 1936) is a Distinguished Professor Emeritus and research professor of psychology and sociology at the University of California, Santa Cruz, and a founding faculty member of UCSC's Cowell College. He ...
. More recent studies of dream reports, while providing more detail, continue to cite the Hall study favorably.
anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
. Other emotions included abandonment, anger
Anger, also known as wrath or rage, is an intense emotional state involving a strong uncomfortable and non-cooperative response to a perceived provocation, hurt or threat.
A person experiencing anger will often experience physical effects, su ...
, fear
Fear is an intensely unpleasant emotion in response to perceiving or recognizing a danger or threat. Fear causes physiological changes that may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the threat. Fear ...
, joy, and happiness
Happiness, in the context of mental or emotional states, is positive or pleasant emotions ranging from contentment to intense joy. Other forms include life satisfaction, well-being, subjective well-being, flourishing and eudaimonia.
...
. Negative emotions were much more common than positive ones. The Hall data analysis showed that sexual dreams occur no more than 10% of the time and are more prevalent in young to mid-teens. Another study showed that 8% of both men's and women's dreams have sexual content. In some cases, sexual dreams may result in orgasm
Orgasm (from Greek , ; "excitement, swelling") or sexual climax is the sudden discharge of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, resulting in rhythmic, involuntary muscular contractions in the pelvic region chara ...
s or nocturnal emissions. These are colloquially known as "wet dreams".
The visual nature of dreams is generally highly phantasmagoric; that is, different locations and objects continuously blend into each other. The visuals (including locations, people, and objects) are generally reflective of a person's memories and experiences, but conversation can take on highly exaggerated and bizarre forms. Some dreams may even tell elaborate stories wherein the dreamer enters entirely new, complex worlds and awakes with ideas, thoughts and feelings never experienced prior to the dream.
People who are blind from birth do not have visual dreams. Their dream contents are related to other senses like hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is audit ...
, touch, smell and taste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception produced or stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste receptor ...
, whichever are present since birth.
Neurophysiology
Dream study is popular with scientists exploring the mind–brain problem. Some "propose to reduce aspects of dream phenomenology to neurobiology." But current science cannot specify dream physiology in detail. Protocols in most nations restrict human brain research to non-invasive procedures. In the United States, invasive brain procedures with a human subject are allowed only when these are deemed necessary in surgical treatment to address medical needs of the same human subject. Non-invasive measures of brain activity likeelectroencephalogram
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ...
(EEG) voltage averaging or cerebral blood flow
Cerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. A ...
cannot identify small but influential neuronal populations.Hobson, J. A., Pace-Schott, E. F., & Stickgold, R. (2000). "Dreaming and the brain: Toward a cognitive neuroscience of conscious states". ''Behavioral and Brain Sciences'', 23(6), 793–842. Also, fMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area ...
signals are too slow to explain how brains compute in real time.
Scientists researching some brain functions can work around current restrictions by examining animal subjects. As stated by the Society for Neuroscience, "Because no adequate alternatives exist, much of this research must be done on animal subjects." However, since animal dreaming can be only inferred, not confirmed, animal studies yield no hard facts to illuminate the neurophysiology of dreams. Examining human subjects with brain lesions can provide clues, but the lesion method cannot discriminate between the effects of destruction and disconnection and cannot target specific neuronal groups in heterogeneous regions like the brain stem.
Generation
Denied precision tools, obliged to depend on imaging, much dream research has succumbed to thelaw of the instrument
The law of the instrument, law of the hammer, Maslow's hammer (or gavel), or golden hammer is a cognitive bias that involves an over-reliance on a familiar tool. Abraham Maslow wrote in 1966, "If the only tool you have is a hammer, it is tempting t ...
. Studies detect an increase of blood flow in a specific brain region and then credit that region with a role in generating dreams. But pooling study results has led to the newer conclusion that dreaming involves large numbers of regions and pathways, which likely are different for different dream events.
Image creation in the brain involves significant neural activity downstream from eye intake, and it is theorized that "the visual imagery of dreams is produced by activation during sleep of the same structures that generate complex visual imagery in waking perception."
Dreams present a running narrative rather than exclusively visual imagery. Following their work with split-brain
Split-brain or callosal syndrome is a type of disconnection syndrome when the corpus callosum connecting the two hemispheres of the brain is severed to some degree. It is an association of symptoms produced by disruption of, or interference wit ...
subjects, Gazzaniga
Gazzaniga (Bergamasque: or ) is a '' comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Bergamo in the Italian region of Lombardy, located about northeast of Milan and northeast of Bergamo.
Gazzaniga borders the following municipalities: Albino, Avia ...
and LeDoux postulated, without attempting to specify the neural mechanisms, a "left-brain interpreter
The left-brain interpreter is a neuropsychological concept developed by the psychologist Michael S. Gazzaniga and the neuroscientist Joseph E. LeDoux. It refers to the construction of explanations by the left brain hemisphere in order to make se ...
" that seeks to create a plausible narrative from whatever electro-chemical signals reach the brain's left hemisphere. Sleep research has determined that some brain regions fully active during waking are, during REM sleep, activated only in a partial or fragmentary way. Drawing on this knowledge, textbook author James W. Kalat explains, " dream represents the brain's effort to make sense of sparse and distorted information.... The cortex combines this haphazard input with whatever other activity was already occurring and does its best to synthesize a story that makes sense of the information." Neuroscientist Indre Viskontas is even more blunt, calling often bizarre dream content "just the result of your interpreter trying to create a story out of random neural signaling."
Theories on function
For humans in the pre-classical era, and continuing for some non-literate populations into modern times, dreams are believed to have functioned as revealers of truths sourced during sleep from gods or other external entities. Ancient Egyptians believed that dreams were the best way to receive divine revelation, and thus they would induce (or "incubate") dreams. They went to sanctuaries and slept on special "dream beds" in hope of receiving advice, comfort, or healing from the gods. From a Darwinian perspective dreams would have to fulfill some kind of biological requirement, provide some benefit for natural selection to take place, or at least have no negative impact on fitness. Robert (1886), a physician from Hamburg, was the first who suggested that dreams are a need and that they have the function to erase (a) sensory impressions that were not fully worked up, and (b) ideas that were not fully developed during the day. In dreams, incomplete material is either removed (suppressed) or deepened and included into memory.Freud
Sigmund Freud ( , ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating pathologies explained as originating in conflicts i ...
, whose dream studies focused on interpreting dreams, not explaining how or why humans dream, disputed Robert's hypothesis and proposed that dreams preserve sleep by representing as fulfilled those wishes that otherwise would awaken the dreamer. Freud wrote that dreams "serve the purpose of prolonging sleep instead of waking up. ''Dreams are the'' GUARDIANS ''of sleep and not its disturbers.''"
 A turning point in theorizing about dream function came in 1953, when ''Science'' published the Aserinsky and Kleitman paper establishing
A turning point in theorizing about dream function came in 1953, when ''Science'' published the Aserinsky and Kleitman paper establishing REM sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream ...
as a distinct phase of sleep and linking dreams to REM sleep. Until and even after publication of the Solms 2000 paper that certified the separability of REM sleep and dream phenomena, many studies purporting to uncover the function of dreams have in fact been studying not dreams but measurable REM sleep.
Theories of dream function since the identification of REM sleep include:
Hobson's and McCarley's 1977 activation-synthesis hypothesis, which proposed "a functional role for dreaming sleep in promoting some aspect of the learning process...." In 2010 a Harvard study was published showing experimental evidence that dreams were correlated with improved learning.
Crick's and Mitchison's 1983 " reverse learning" theory, which states that dreams are like the cleaning-up operations of computers when they are offline, removing (suppressing) parasitic nodes and other "junk" from the mind during sleep.
Hartmann's 1995 proposal that dreams serve a "quasi-therapeutic" function, enabling the dreamer to process trauma in a safe place.
Revonsuo's 2000 threat simulation hypothesis, whose premise is that during much of human evolution, physical and interpersonal threats were serious, giving reproductive advantage to those who survived them. Dreaming aided survival by replicating these threats and providing the dreamer with practice in dealing with them.
Eagleman's and Vaughn's 2021 defensive activation theory, which says that, given the brain's neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity, or brain plasticity, is the ability of neural networks in the brain to change through growth and reorganization. It is when the brain is rewired to function in some way that differs from how it p ...
, dreams evolved as a visual hallucinatory activity during sleep's extended periods of darkness, busying the occipital lobe and thereby protecting it from possible appropriation by other, non-vision, sense operations.
Religious and other cultural contexts
Dreams figure prominently in major world religions. The dream experience for early humans, according to one interpretation, gave rise to the notion of a human "soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun '' soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest att ...
," a central element in much religious thought. J. W. Dunne
John William Dunne (2 December 1875 – 24 August 1949) was a British soldier, aeronautical engineer and philosopher. As a young man he fought in the Second Boer War, before becoming a pioneering aeroplane designer in the early years of the 20th ...
wrote: But there can be no reasonable doubt that the idea of a soul must have first arisen in the mind of primitive man as a result of observation of his dreams. Ignorant as he was, he could have come to no other conclusion but that, in dreams, he left his sleeping body in one universe and went wandering off into another. It is considered that, but for that savage, the idea of such a thing as a 'soul' would never have even occurred to mankind....
Hindu
In the Mandukya Upanishad, part of theVeda
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
scriptures of Indian Hinduism, a dream is one of three states that the soul experiences during its lifetime, the other two states being the waking state and the sleep state. The earliest Upanishads
The Upanishads (; sa, उपनिषद् ) are late Vedic Sanskrit texts that supplied the basis of later Hindu philosophy.Wendy Doniger (1990), ''Textual Sources for the Study of Hinduism'', 1st Edition, University of Chicago Press, , ...
, written before 300 BCE, emphasize two meanings of dreams. The first says that dreams are merely expressions of inner desires. The second is the belief of the soul leaving the body and being guided until awakened.
Abrahamic
 In Judaism, dreams are considered part of the experience of the world that can be interpreted and from which lessons can be garnered. It is discussed in the Talmud, Tractate Berachot 55–60.
The ancient
In Judaism, dreams are considered part of the experience of the world that can be interpreted and from which lessons can be garnered. It is discussed in the Talmud, Tractate Berachot 55–60.
The ancient Hebrews
The terms ''Hebrews'' (Hebrew: / , Modern: ' / ', Tiberian: ' / '; ISO 259-3: ' / ') and ''Hebrew people'' are mostly considered synonymous with the Semitic-speaking Israelites, especially in the pre-monarchic period when they were still ...
connected their dreams heavily with their religion, though the Hebrews were monotheistic
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxfor ...
and believed that dreams were the voice of one God alone. Hebrews also differentiated between good dreams (from God) and bad dreams (from evil spirits). The Hebrews, like many other ancient cultures, incubated dreams in order to receive a divine revelation. For example, the Hebrew prophet Samuel
Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the bib ...
would "lie down and sleep in the temple at Shiloh before the Ark and receive the word of the Lord". Most of the dreams in the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
are in the Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning" ...
.
Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ� ...
mostly shared the beliefs of the Hebrews and thought that dreams were of a supernatural character because the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
includes frequent stories of dreams with divine inspiration. The most famous of these dream stories was Jacob's dream of a ladder that stretches from Earth to Heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the belie ...
. Many Christians preach that God can speak to people through their dreams. The famous glossary, the Somniale Danielis, written in the name of Daniel
Daniel is a masculine given name and a surname of Hebrew origin. It means "God is my judge"Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 68. (cf. Gabriel—"God is my strength"), ...
, attempted to teach Christian populations to interpret their dreams.
Iain R. Edgar
Iain Edgar (6 June 1948 – 22 May 2021) was a social anthropologist at Durham University. He was an expert in the field of dreams and dreaming, and a specialist in altered states of consciousness and mental health. Starting his career in ...
has researched the role of dreams in Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
. He has argued that dreams play an important role in the history of Islam and the lives of Muslims, since dream interpretation is the only way that Muslims can receive revelations from God since the death of the last prophet, Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mon ...
. According to Edgar, Islam classifies three types of dreams. Firstly, there is the true dream (al-ru’ya), then the false dream, which may come from the devil ( shaytan), and finally, the meaningless everyday dream (hulm). This last dream could be brought forth by the dreamer's ego or base appetite based on what they experienced in the real world. The true dream is often indicated by Islam's hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approva ...
tradition. In one narration by Aisha
Aisha ( ar, , translit=ʿĀʾisha bint Abī Bakr; , also , ; ) was Muhammad's third and youngest wife. In Islamic writings, her name is thus often prefixed by the title "Mother of the Believers" ( ar, links=no, , ʾumm al- muʾminīn), referr ...
, the wife of the Prophet, it is said that the Prophet's dreams would come true like the ocean's waves. Just as in its predecessors, the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
also recounts the story of Joseph and his unique ability to interpret dreams.
Buddhist
In Buddhism, ideas about dreams are similar to the classical and folk traditions in South Asia. The same dream is sometimes experienced by multiple people, as in the case of the Buddha-to-be, before he is leaving his home. It is described in the '' Mahāvastu'' that several of the Buddha's relatives had premonitory dreams preceding this. Some dreams are also seen to transcend time: the Buddha-to-be has certain dreams that are the same as those of previous Buddhas, the '' Lalitavistara'' states. In Buddhist literature, dreams often function as a "signpost" motif to mark certain stages in the life of the main character. Buddhist views about dreams are expressed in the Pāli Commentaries and the Milinda Pañhā.Other
 In Chinese history, people wrote of two vital aspects of the soul of which one is freed from the body during slumber to journey in a dream realm, while the other remained in the body. This belief and dream interpretation had been questioned since early times, such as by the philosopher Wang Chong ().
The Babylonians and Assyrians divided dreams into "good," which were sent by the gods, and "bad," sent by demons. A surviving collection of dream omens entitled '' Iškar Zaqīqu'' records various dream scenarios as well as prognostications of what will happen to the person who experiences each dream, apparently based on previous cases. Some list different possible outcomes, based on occasions in which people experienced similar dreams with different results. The Greeks shared their beliefs with the Egyptians on how to interpret good and bad dreams, and the idea of incubating dreams. Morpheus, the Greek god of dreams, also sent warnings and prophecies to those who slept at shrines and temples. The earliest Greek beliefs about dreams were that their gods physically visited the dreamers, where they entered through a keyhole, exiting the same way after the divine message was given.
In Chinese history, people wrote of two vital aspects of the soul of which one is freed from the body during slumber to journey in a dream realm, while the other remained in the body. This belief and dream interpretation had been questioned since early times, such as by the philosopher Wang Chong ().
The Babylonians and Assyrians divided dreams into "good," which were sent by the gods, and "bad," sent by demons. A surviving collection of dream omens entitled '' Iškar Zaqīqu'' records various dream scenarios as well as prognostications of what will happen to the person who experiences each dream, apparently based on previous cases. Some list different possible outcomes, based on occasions in which people experienced similar dreams with different results. The Greeks shared their beliefs with the Egyptians on how to interpret good and bad dreams, and the idea of incubating dreams. Morpheus, the Greek god of dreams, also sent warnings and prophecies to those who slept at shrines and temples. The earliest Greek beliefs about dreams were that their gods physically visited the dreamers, where they entered through a keyhole, exiting the same way after the divine message was given.
Antiphon
An antiphon ( Greek ἀντίφωνον, ἀντί "opposite" and φωνή "voice") is a short chant in Christian ritual, sung as a refrain. The texts of antiphons are the Psalms. Their form was favored by St Ambrose and they feature prominentl ...
wrote the first known Greek book on dreams in the 5th century BCE. In that century, other cultures influenced Greeks to develop the belief that souls left the sleeping body. Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
() had a simple dream theory: during the day, the soul receives images; during the night, it produces images. Greek philosopher Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
(384–322 BCE) believed dreams caused physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemica ...
activity. He thought dreams could analyze illness and predict diseases. Marcus Tullius Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
, for his part, believed that all dreams are produced by thoughts and conversations a dreamer had during the preceding days. Cicero's '' Somnium Scipionis'' described a lengthy dream vision, which in turn was commented on by Macrobius
Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius, usually referred to as Macrobius (fl. AD 400), was a Roman provincial who lived during the early fifth century, during late antiquity, the period of time corresponding to the Later Roman Empire, and when Latin was ...
in his ''Commentarii in Somnium Scipionis''.
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
in his '' The Histories'', writes "The visions that occur to us in dreams are, more often than not, the things we have been concerned about during the day."
The Dreaming
The Dreaming, also referred to as Dreamtime, is a term devised by early anthropologists to refer to a religio-cultural worldview attributed to Australian Aboriginal beliefs. It was originally used by Francis Gillen, quickly adopted by his co ...
is a common term within the animist
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things— animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems ...
creation narrative of indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
for a personal, or group, creation
Creation may refer to:
Religion
*''Creatio ex nihilo'', the concept that matter was created by God out of nothing
*Creation myth, a religious story of the origin of the world and how people first came to inhabit it
*Creationism, the belief that ...
and for what may be understood as the "timeless time" of formative creation and perpetual creating.
Some Indigenous American tribes and Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
populations believe that dreams are a way of visiting and having contact with their ancestor
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from w ...
s. Some Native American tribes have used vision quests as a rite of passage, fasting and praying until an anticipated guiding dream was received, to be shared with the rest of the tribe upon their return.
Interpretation
 Beginning in the late 19th century, Austrian neurologist
Beginning in the late 19th century, Austrian neurologist Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( , ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating pathologies explained as originating in conflicts i ...
, founder of psychoanalysis
PsychoanalysisFrom Greek: + . is a set of theories and therapeutic techniques"What is psychoanalysis? Of course, one is supposed to answer that it is many things — a theory, a research method, a therapy, a body of knowledge. In what might ...
, theorized that dreams reflect the dreamer's unconscious mind and specifically that dream content is shaped by unconscious wish fulfillment. He argued that important unconscious desires often relate to early childhood memories and experiences. Carl Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, ph ...
and others expanded on Freud's idea that dream content reflects the dreamer's unconscious desires.
Dream interpretation can be a result of subjective ideas and experiences. One study found that most people believe that "their dreams reveal meaningful hidden truths". The researchers surveyed students in the United States, South Korea, and India, and found that 74% of Indians, 65% of South Koreans and 56% of Americans believed their dream content provided them with meaningful insight into their unconscious beliefs and desires. This Freudian view of dreaming was believed significantly more than theories of dreaming that attribute dream content to memory consolidation, problem-solving, or as a byproduct of unrelated brain activity. The same study found that people attribute more importance to dream content than to similar thought content that occurs while they are awake. Americans were more likely to report that they would intentionally miss their flight if they dreamt of their plane crashing than if they thought of their plane crashing the night before flying (while awake), and that they would be as likely to miss their flight if they dreamt of their plane crashing the night before their flight as if there was an actual plane crash on the route they intended to take. Participants in the study were more likely to perceive dreams to be meaningful when the content of dreams was in accordance with their beliefs and desires while awake. They were more likely to view a positive dream about a friend to be meaningful than a positive dream about someone they disliked, for example, and were more likely to view a negative dream about a person they disliked as meaningful than a negative dream about a person they liked.
According to surveys, it is common for people to feel their dreams are predicting subsequent life events. Psychologists have explained these experiences in terms of memory biases
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, ...
, namely a selective memory for accurate predictions and distorted memory so that dreams are retrospectively fitted onto life experiences. The multi-faceted nature of dreams makes it easy to find connections between dream content and real events. The term "veridical dream" has been used to indicate dreams that reveal or contain truths not yet known to the dreamer, whether future events or secrets.
In one experiment, subjects were asked to write down their dreams in a diary. This prevented the selective memory effect, and the dreams no longer seemed accurate about the future. Another experiment gave subjects a fake diary of a student with apparently precognitive dreams. This diary described events from the person's life, as well as some predictive dreams and some non-predictive dreams. When subjects were asked to recall the dreams they had read, they remembered more of the successful predictions than unsuccessful ones.
Images and literature
Graphic artists, writers and filmmakers all have found dreams to offer a rich vein for creative expression. In the West, artists' depictions of dreams in Renaissance and Baroque art often were related to Biblical narrative. Especially preferred by visual artists were theJacob's Ladder
Jacob's Ladder ( he, סֻלָּם יַעֲקֹב ) is a ladder leading to heaven that was featured in a dream the biblical Patriarch Jacob had during his flight from his brother Esau in the Book of Genesis (chapter 28).
The significance of th ...
dream in Genesis and St. Joseph's dreams in the Gospel according to Matthew.
Hokusai
, known simply as Hokusai, was a Japanese ukiyo-e artist of the Edo period, active as a painter and printmaker. He is best known for the woodblock print series '' Thirty-Six Views of Mount Fuji'', which includes the iconic print ''The Great W ...
(1760–1849) and Western European painters Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolu ...
(1844–1910), Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
(1881–1973), and Dali (1904–1989).
In literature, dream frames were frequently used in medieval allegory to justify the narrative; '' The Book of the Duchess'' and ''The Vision Concerning Piers Plowman
''Piers Plowman'' (written 1370–86; possibly ) or ''Visio Willelmi de Petro Ploughman'' (''William's Vision of Piers Plowman'') is a Middle English allegorical narrative poem by William Langland. It is written in un- rhymed, alliterati ...
'' are two such dream visions. Even before them, in antiquity, the same device had been used by Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
and Lucian of Samosata
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 – after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer who is best known for his characteristic tongue-in-cheek style, with which he frequently ridiculed superstiti ...
.
 Dreams have also featured in
Dreams have also featured in fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction involving magical elements, typically set in a fictional universe and sometimes inspired by mythology and folklore. Its roots are in oral traditions, which then became fantasy literature and d ...
and speculative fiction
Speculative fiction is a term that has been used with a variety of (sometimes contradictory) meanings. The broadest interpretation is as a category of fiction encompassing genres with elements that do not exist in reality, recorded history, nat ...
since the 19th century. One of the best-known dream worlds is Wonderland
Wonderland may refer to:
Places
Municipalities
* Wonderland, California, a ghost town in Plumas County
* Wonderland, Ohio, a ghost town in Columbus, Ohio, U.S.
Roads, streets, and trails
* Wonderland Avenue, a roadway in Laurel Canyon, Los A ...
from Lewis Carroll
Charles Lutwidge Dodgson (; 27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898), better known by his pen name Lewis Carroll, was an English author, poet and mathematician. His most notable works are '' Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865) and its sequ ...
's ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named Alice who falls through a rabbit hole into a fantasy world of anthropomorphic creature ...
'', as well as Looking-Glass Land
The looking-glass world is the setting for Lewis Carroll's 1871 children's novel ''Through the Looking-Glass''.
Geography
The entire country is divided into squares by a series of little brooks with hedges growing perpendicular to them.
Gover ...
from its sequel, ''Through the Looking-Glass
''Through the Looking-Glass, and What Alice Found There'' (also known as ''Alice Through the Looking-Glass'' or simply ''Through the Looking-Glass'') is a novel published on 27 December 1871 (though indicated as 1872) by Lewis Carroll and the ...
''. Unlike many dream worlds, Carroll's logic is like that of actual dreams, with transitions and flexible causality.
Other fictional dream worlds include the Dreamlands of H. P. Lovecraft's '' Dream Cycle'' and ''The Neverending Story
''The Neverending Story'' (german: Die unendliche Geschichte) is a fantasy novel by German writer Michael Ende, published in 1979. The first English translation, by Ralph Manheim, was published in 1983. The novel was later adapted into several ...
''s world of Fantastica, which includes places like the Desert of Lost Dreams, the Sea of Possibilities and the Swamps of Sadness. Dreamworlds, shared hallucinations and other alternate realities feature in a number of works by Philip K. Dick, such as ''The Three Stigmata of Palmer Eldritch
''The Three Stigmata of Palmer Eldritch'' is a 1964 science fiction novel by American writer Philip K. Dick. It was nominated for the Nebula Award for Best Novel in 1965. Like many of Dick's novels, it utilizes an array of science fiction conce ...
'' and '' Ubik''. Similar themes were explored by Jorge Luis Borges
Jorge Francisco Isidoro Luis Borges Acevedo (; ; 24 August 1899 – 14 June 1986) was an Argentine short-story writer, essayist, poet and translator, as well as a key figure in Spanish-language and international literature. His best-known b ...
, for instance in ''The Circular Ruins
"The Circular Ruins" (original Spanish title: "Las ruinas circulares") is a short story by Argentine author Jorge Luis Borges. First published in the literary journal '' Sur'' in December 1940, it was included in the 1941 collection ''The Garden ...
''.
Modern popular culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in a ...
often conceives of dreams, as did Freud, as expressions of the dreamer's deepest fears and desires. In speculative fiction, the line between dreams and reality may be blurred even more in service to the story.Van Riper, op. cit., p. 57. Dreams may be psychically invaded or manipulated ('' Dreamscape'', 1984; the '' Nightmare on Elm Street'' films, 1984–2010; '' Inception'', 2010) or even come literally true (as in ''The Lathe of Heaven
''The Lathe of Heaven'' is a 1971 science fiction novel by American writer Ursula K. Le Guin. The plot concerns a character whose dreams alter past and present reality. The story was serialized in the American science fiction magazine ''Amazing ...
'', 1971).
Lucidity
Lucid dreaming is the conscious perception of one's state while dreaming. In this state the dreamer may often have some degree of control over their own actions within the dream or even the characters and the environment of the dream. Dream control has been reported to improve with practiced deliberate lucid dreaming, but the ability to control aspects of the dream is not necessary for a dream to qualify as "lucid"—a lucid dream is any dream during which the dreamer knows they are dreaming. The occurrence of lucid dreaming has been scientifically verified. "Oneironaut
Oneironautics () refers to the ability to travel within a dream on a conscious basis. Such a traveler in a dream may be called an oneironaut.
Within one's dream
A lucid dream is one in which the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming. They are ...
" is a term sometimes used for those who lucidly dream.
In 1975, psychologist Keith Hearne successfully recorded a communication from a dreamer experiencing a lucid dream. On April 12, 1975, after agreeing to move his eyes left and right upon becoming lucid, the subject and Hearne's co-author on the resulting article, Alan Worsley, successfully carried out this task. Years later, psychophysiologist Stephen LaBerge conducted similar work including:
* Using eye signals to map the subjective sense of time in dreams.
* Comparing the electrical activity of the brain while singing awake and while dreaming.
* Studies comparing in-dream sex, arousal, and orgasm.
Communication between two dreamers has also been documented. The processes involved included EEG monitoring, ocular signaling, incorporation of reality in the form of red light stimuli and a coordinating website. The website tracked when both dreamers were dreaming and sent the stimulus to one of the dreamers where it was incorporated into the dream. This dreamer, upon becoming lucid, signaled with eye movements; this was detected by the website whereupon the stimulus was sent to the second dreamer, invoking incorporation into that dreamer's dream.
Recollection
 The recollection of dreams is extremely unreliable, though it is a skill that can be trained. Dreams can usually be recalled if a person is awakened while dreaming. Women tend to have more frequent dream recall than men. Dreams that are difficult to recall may be characterized by relatively little affect, and factors such as salience,
The recollection of dreams is extremely unreliable, though it is a skill that can be trained. Dreams can usually be recalled if a person is awakened while dreaming. Women tend to have more frequent dream recall than men. Dreams that are difficult to recall may be characterized by relatively little affect, and factors such as salience, arousal
Arousal is the physiological and psychological state of being awoken or of sense organs stimulated to a point of perception. It involves activation of the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) in the brain, which mediates wakefulness, th ...
, and interference play a role in dream recall. Often, a dream may be recalled upon viewing or hearing a random trigger or stimulus. The salience hypothesis proposes that dream content that is salient, that is, novel, intense, or unusual, is more easily remembered. There is considerable evidence that vivid, intense, or unusual dream content is more frequently recalled. A dream journal
A dream diary (or dream journal) is a diary in which dream experiences are recorded. A dream diary might include a record of nightly dreams, personal reflections and waking dream experiences. It is often used in the study of dreams and psycholo ...
can be used to assist dream recall, for personal interest or psychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase happiness, and overcome pro ...
purposes.
Adults report remembering around two dreams per week, on average. Unless a dream is particularly vivid and if one wakes during or immediately after it, the content of the dream is typically not remembered. Recording or reconstructing dreams may one day assist with dream recall. Using the permitted non-invasive technologies, functional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
(fMRI) and electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyo ...
(EMG), researchers have been able to identify basic dream imagery, dream speech activity and dream motor behavior (such as walking and hand movements).
In line with the salience hypothesis, there is considerable evidence that people who have more vivid, intense or unusual dreams show better recall. There is evidence that continuity of consciousness is related to recall. Specifically, people who have vivid and unusual experiences during the day tend to have more memorable dream content and hence better dream recall. People who score high on measures of personality traits associated with creativity, imagination, and fantasy, such as openness to experience
Openness to experience is one of the domains which are used to describe human personality in the Five Factor Model. Openness involves six facets, or dimensions: active imagination (fantasy), aesthetic sensitivity, attentiveness to inner feelings ...
, daydream
Daydreaming is the stream of consciousness that detaches from current, external tasks when attention drifts to a more personal and internal direction. This phenomenon is common in people's daily life shown by a large-scale study in which partici ...
ing, fantasy proneness, absorption
Absorption may refer to:
Chemistry and biology
*Absorption (biology), digestion
**Absorption (small intestine)
*Absorption (chemistry), diffusion of particles of gas or liquid into liquid or solid materials
*Absorption (skin), a route by which s ...
, and hypnotic susceptibility
Hypnotic susceptibility measures how easily a person can be hypnotized. Several types of scales are used; however, the most common are the Harvard Group Scale of Hypnotic Susceptibility and the Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scales.
The Harvard ...
, tend to show more frequent dream recall. There is also evidence for continuity between the bizarre aspects of dreaming and waking experience. That is, people who report more bizarre experiences during the day, such as people high in schizotypy
In psychology, schizotypy is a theoretical concept that posits a continuum of personality characteristics and experiences, ranging from normal dissociative, imaginative states to extreme states of mind related to psychosis, especially schizophr ...
(psychosis proneness), have more frequent dream recall and also report more frequent nightmare
A nightmare, also known as a bad dream, Retrieved 11 July 2016. is an unpleasant dream that can cause a strong emotional response from the mind, typically fear but also despair, anxiety or great sadness. The dream may contain situations of ...
s.
Miscellany
Illusion of reality
Some philosophers have proposed that what we think of as the "real world" could be or is an illusion (an idea known as theskeptical hypothesis
Philosophical skepticism ( UK spelling: scepticism; from Greek σκέψις ''skepsis'', "inquiry") is a family of philosophical views that question the possibility of knowledge. It differs from other forms of skepticism in that it even reject ...
about ontology
In metaphysics, ontology is the philosophy, philosophical study of being, as well as related concepts such as existence, Becoming (philosophy), becoming, and reality.
Ontology addresses questions like how entities are grouped into Category ...
). The first recorded mention of the idea was in the 4th century BCE by Zhuangzi, and in Eastern philosophy, the problem has been named the " Zhuangzi Paradox."
He who dreams of drinking wine may weep when morning comes; he who dreams of weeping may in the morning go off to hunt. While he is dreaming he does not know it is a dream, and in his dream he may even try to interpret a dream. Only after he wakes does he know it was a dream. And someday there will be a great awakening when we know that this is all a great dream. Yet the stupid believe they are awake, busily and brightly assuming they understand things, calling this man ruler, that one herdsman—how dense! Confucius and you are both dreaming! And when I say you are dreaming, I am dreaming, too. Words like these will be labeled the Supreme Swindle. Yet, after ten thousand generations, a great sage may appear who will know their meaning, and it will still be as though he appeared with astonishing speed.The idea also is discussed in Hindu and Buddhist writings. It was formally introduced to Western philosophy by Descartes in the 17th century in his '' Meditations on First Philosophy''.
Absent-minded transgression
Dreams of absent-minded transgression (DAMT) are dreams wherein the dreamer absent-mindedly performs an action that he or she has been trying to stop (one classic example is of a quitting smoker having dreams of lighting a cigarette). Subjects who have had DAMT have reported waking with intense feelings of guilt. One study found a positive association between having these dreams and successfully stopping the behavior.Non-REM dreams
Hypnogogic and hypnopompic dreams, dreamlike states shortly after falling asleep and shortly before awakening, and dreams during stage 2 of NREM-sleep, also occur, but are shorter than REM-dreams.Daydreams
 A daydream is a visionary
A daydream is a visionary fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction involving magical elements, typically set in a fictional universe and sometimes inspired by mythology and folklore. Its roots are in oral traditions, which then became fantasy literature and d ...
, especially one of happy, pleasant thoughts, hopes or ambitions, imagined as coming to pass, and experienced while awake.Klinger, Eric (October 1987). ''Psychology Today
''Psychology Today'' is an American media organization with a focus on psychology and human behavior. It began as a bimonthly magazine, which first appeared in 1967. The ''Psychology Today'' website features therapy and health professionals direc ...
''. There are many different types of daydreams, and there is no consistent definition amongst psychologists. The general public also uses the term for a broad variety of experiences. Research by Harvard psychologist Deirdre Barrett has found that people who experience vivid dreamlike mental image
A mental image is an experience that, on most occasions, significantly resembles the experience of 'perceiving' some object, event, or scene, but occurs when the relevant object, event, or scene is not actually present to the senses. There are ...
s reserve the word for these, whereas many other people refer to milder imagery, realistic future planning, review of memories or just "spacing out"—i.e. one's mind going relatively blank—when they talk about "daydreaming".
While daydreaming has long been derided as a lazy, non-productive pastime, it is now commonly acknowledged that daydreaming can be constructive in some contexts. There are numerous examples of people in creative or artistic careers, such as composers, novelists and filmmakers, developing new ideas through daydreaming. Similarly, research scientists, mathematicians and physicists have developed new ideas by daydreaming about their subject areas.
Hallucination
A hallucination, in the broadest sense of the word, is aperception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
in the absence of a stimulus. In a stricter sense, hallucinations are perceptions in a conscious and awake state, in the absence of external stimuli, and have qualities of real perception, in that they are vivid, substantial, and located in external objective space. The latter definition distinguishes hallucinations from the related phenomena of dreaming, which does not involve wakefulness.
Nightmare
 A nightmare is an unpleasant dream that can cause a strong negative emotional response from the mind, typically
A nightmare is an unpleasant dream that can cause a strong negative emotional response from the mind, typically fear
Fear is an intensely unpleasant emotion in response to perceiving or recognizing a danger or threat. Fear causes physiological changes that may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the threat. Fear ...
or horror, but also despair, anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
and great sadness
Sadness is an emotional pain associated with, or characterized by, feelings of disadvantage, loss, despair, grief, helplessness, disappointment and sorrow. An individual experiencing sadness may become quiet or lethargic, and withdraw them ...
. The dream may contain situations of danger, discomfort, psychological or physical terror. Sufferers usually awaken in a state of distress and may be unable to return to sleep
Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited Perception, sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefuln ...
for a prolonged period of time.
Night terror
A night terror, also known as a sleep terror or ''pavor nocturnus'', is a parasomniadisorder
Disorder may refer to randomness, non-order, or no intelligible pattern.
Disorder may also refer to:
Healthcare
* Disorder (medicine), a functional abnormality or disturbance
* Mental disorder or psychological disorder, a psychological pattern ...
that predominantly affects children, causing feelings of terror or dread. Night terrors should not be confused with nightmare
A nightmare, also known as a bad dream, Retrieved 11 July 2016. is an unpleasant dream that can cause a strong emotional response from the mind, typically fear but also despair, anxiety or great sadness. The dream may contain situations of ...
s, which are bad dreams that cause the feeling of horror or fear.
Déjà vu
One theory of déjà vu attributes the feeling of having previously seen or experienced something to having dreamed about a similar situation or place, and forgetting about it until one seems to be mysteriously reminded of the situation or the place while awake.See also
*Dream dictionary A dream dictionary (also known as oneirocritic literature) is a tool made for interpreting images in a dream. Dream dictionaries tend to include specific images which are attached to specific interpretations. However, dream dictionaries are generall ...
* Dream incubation
* Dream of Macsen Wledig
* Dream pop
Dream pop (also typeset as dreampop) is a subgenre of alternative rock and neo-psychedelia that emphasizes atmosphere and sonic texture as much as pop melody. Common characteristics include breathy vocals, dense productions, and effects such as ...
* Dream sequence
* Dream yoga
* Dreamcatcher
* Dreamwork
Dreamwork differs from classical dream interpretation in that the aim is to explore the various images and emotions that a dream presents and evokes, while not attempting to come up with a unique dream meaning. In this way the dream remains " ...
* False awakening
* ''Hatsuyume
In Japanese culture, a is the first dream one has in the new year. Traditionally, the contents of such a dream would foretell the luck of the dreamer in the ensuing year. In Japan, the night of December 31 was often passed without sleeping, so ...
''
* Incubus
* Lilith
Lilith ( ; he, לִילִית, Līlīṯ) is a female figure in Mesopotamian and Judaic mythology, alternatively the first wife of Adam and supposedly the primordial she-demon. Lilith is cited as having been "banished" from the Garden of Ed ...
, a Sumerian dream demoness
* List of dream diaries
* Mare (folklore)
A mare ( ang, mære, odt, mare, ; in Old High German, Old Norse, and Swedish) is a malicious entity in Germanic and Slavic folklore that rides on people's chests while they sleep, bringing on nightmares.Bjorvand and Lindeman (2007), pp. ...
* Mabinogion
The ''Mabinogion'' () are the earliest Welsh prose stories, and belong to the Matter of Britain. The stories were compiled in Middle Welsh in the 12th–13th centuries from earlier oral traditions. There are two main source manuscripts, creat ...
* Sleep in animals
* Sleep paralysis
* Spirit spouse The spirit spouse is a widespread element of shamanism, distributed through all continents and at all cultural levels. Often, these spirit husbands/wives are seen as the primary helping spirits of the shaman, who assist them in their work, and help ...
* Succubus
A succubus is a demon or supernatural entity in folklore, in female form, that appears in dreams to seduce men, usually through sexual activity. According to religious tradition, a succubus needs male semen to survive; repeated sexual activi ...
* Works based on dreams
On several occasions throughout history, dreams have been credited as the inspiration for creative works and scientific discoveries.
Books and poetry
''Kubla Khan''
Samuel Taylor Coleridge wrote ''Kubla Khan'' (completed in 1797 and published in ...
References
Further reading
* Dreaming (journal) * * * Harris, William V. (2009) ''Dreams and Еxperience in Classical Antiquity''. Cambridge, MA & London: Harvard University Press.External links
*Archive for Research in Archetypal Symbolism website
The International Association for the Study of Dreams
* *
alt.dreams
A long-running USENET forum wherein readers post and analyze dreams
LSDBase
– online sleep research database documenting physiological effects of dreams through biofeedback {{Authority control Night Sleep Symbols