Domestic Pig on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus scrofa'' (the wild boar or Eurasian boar) or a distinct
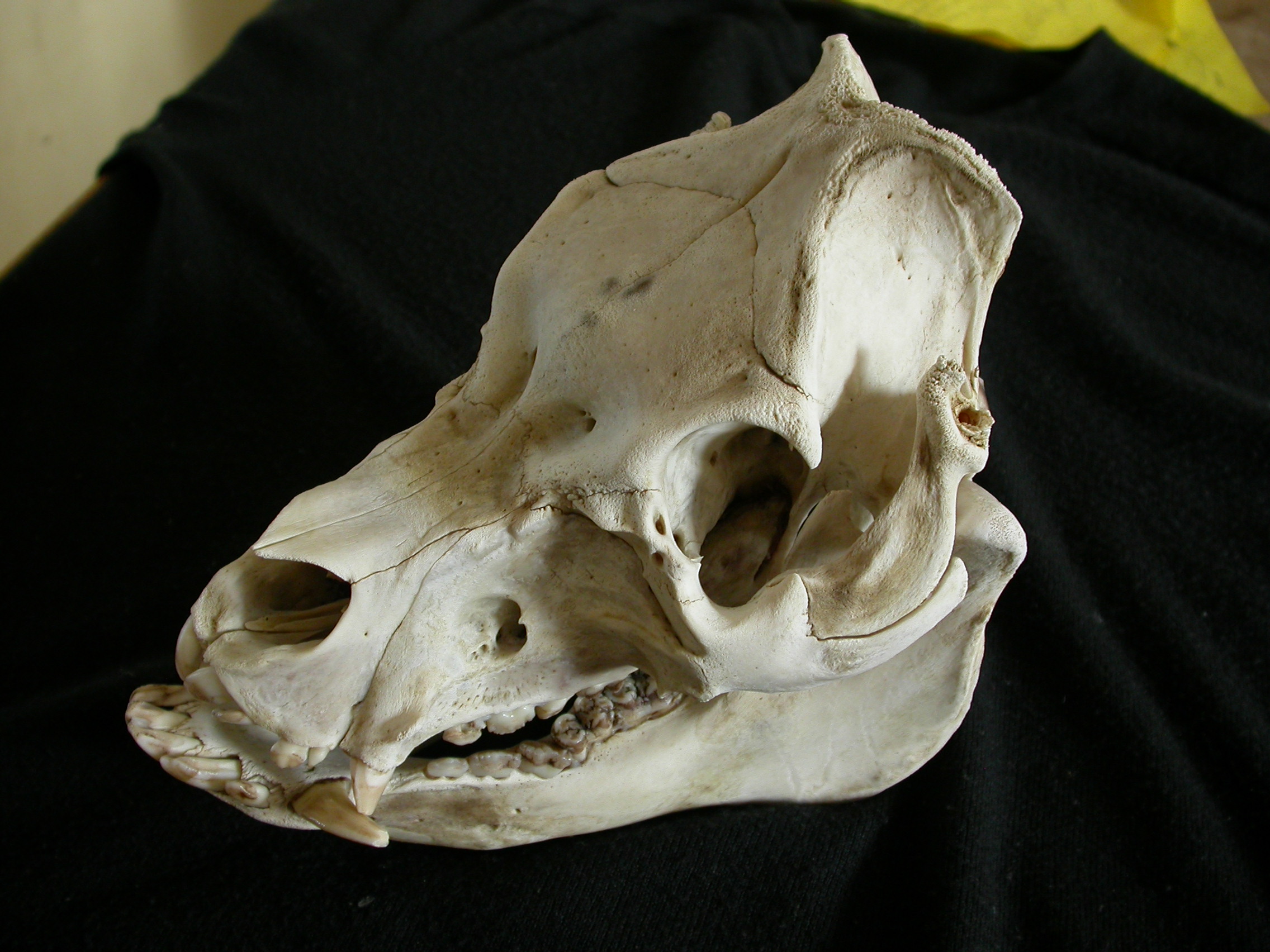

 The pig typically has a large head, with a long snout which is strengthened by a special prenasal bone and a disk of cartilage at the tip. The snout is used to dig into the soil to find food and is a very acute sense organ. The dental formula of adult pigs is , giving a total of 44 teeth. The rear teeth are adapted for crushing. In the male, the canine teeth can form tusks, which grow continuously and are sharpened by constantly being ground against each other.
Four hoofed toes are on each foot, with the two larger central toes bearing most of the weight, but the outer two also being used in soft ground.
Most pigs have rather a
The pig typically has a large head, with a long snout which is strengthened by a special prenasal bone and a disk of cartilage at the tip. The snout is used to dig into the soil to find food and is a very acute sense organ. The dental formula of adult pigs is , giving a total of 44 teeth. The rear teeth are adapted for crushing. In the male, the canine teeth can form tusks, which grow continuously and are sharpened by constantly being ground against each other.
Four hoofed toes are on each foot, with the two larger central toes bearing most of the weight, but the outer two also being used in soft ground.
Most pigs have rather a
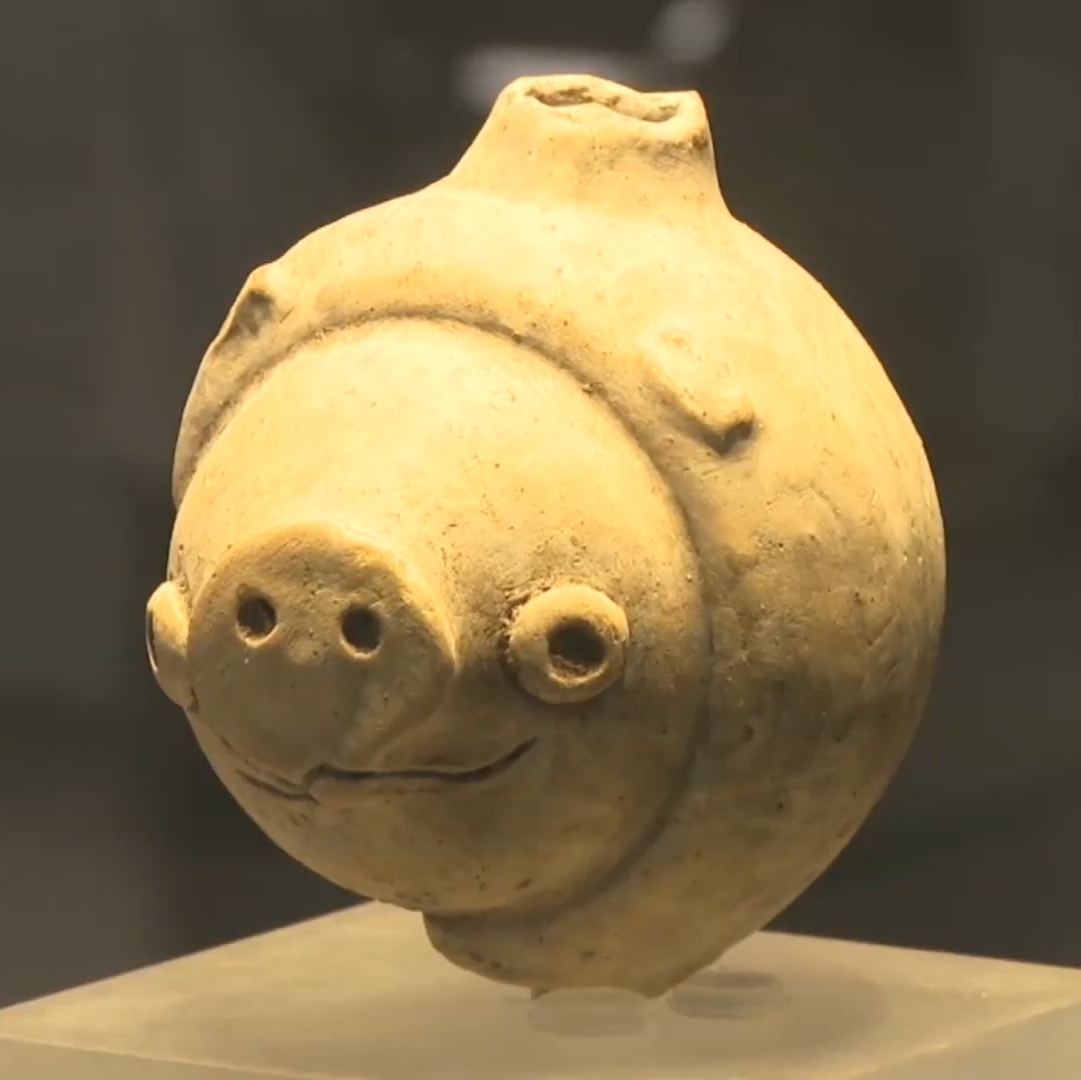

 Archaeological evidence suggests that pigs were domesticated from wild boar in the Near East in the Tigris Basin, Çayönü, Cafer Höyük,
Archaeological evidence suggests that pigs were domesticated from wild boar in the Near East in the Tigris Basin, Çayönü, Cafer Höyük,
 Estrus lasts two to three days, and the female's displayed receptiveness to mate is known as standing heat. Standing heat is a reflexive response that is stimulated when the female is in contact with the saliva of a sexually mature boar. Androstenol is one of the pheromones produced in the submaxillary salivary glands of boars that will trigger the female's response. The female cervix contains a series of five interdigitating pads, or folds, that will hold the boar's corkscrew-shaped penis during copulation. Females have bicornuate uteruses and two conceptuses must be present in both uterine horns for pregnancy to be established. Maternal recognition of pregnancy in pigs occurs on days 11 to 12 of pregnancy and is marked by progesterone production from a functioning corpus luteum (CL). To avoid luteolysis by PGF2α, rescuing of the CL must occur via embryonic signaling of estradiol 17β and PGE2. This signaling acts on both the endometrium and luteal tissue to prevent the regression of the CL by activation of genes that are responsible for CL maintenance. During mid to late pregnancy, the CL relies primarily on luteinizing hormone (LH) for maintenance until parturition. Animal nutrition is important prior to reproduction and during gestation to ensure optimum reproductive performance is achieved.
Archeological evidence indicates that medieval European pigs farrowed, or bore a litter of piglets, once per year. By the nineteenth century, European piglets routinely double-farrowed, or bore two litters of piglets per year. It is unclear when this shift occurred.
Estrus lasts two to three days, and the female's displayed receptiveness to mate is known as standing heat. Standing heat is a reflexive response that is stimulated when the female is in contact with the saliva of a sexually mature boar. Androstenol is one of the pheromones produced in the submaxillary salivary glands of boars that will trigger the female's response. The female cervix contains a series of five interdigitating pads, or folds, that will hold the boar's corkscrew-shaped penis during copulation. Females have bicornuate uteruses and two conceptuses must be present in both uterine horns for pregnancy to be established. Maternal recognition of pregnancy in pigs occurs on days 11 to 12 of pregnancy and is marked by progesterone production from a functioning corpus luteum (CL). To avoid luteolysis by PGF2α, rescuing of the CL must occur via embryonic signaling of estradiol 17β and PGE2. This signaling acts on both the endometrium and luteal tissue to prevent the regression of the CL by activation of genes that are responsible for CL maintenance. During mid to late pregnancy, the CL relies primarily on luteinizing hormone (LH) for maintenance until parturition. Animal nutrition is important prior to reproduction and during gestation to ensure optimum reproductive performance is achieved.
Archeological evidence indicates that medieval European pigs farrowed, or bore a litter of piglets, once per year. By the nineteenth century, European piglets routinely double-farrowed, or bore two litters of piglets per year. It is unclear when this shift occurred.
 In many ways pig behaviour appears to be intermediate between that of other artiodactyls and of carnivores.Clutton-Brock, J., (1987). A Natural History of Domesticated Mammals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge pp.73–74 Pigs seek out the company of other pigs and often huddle to maintain physical contact, although they do not naturally form large herds. They typically live in groups of about 8–10 adult sows, some young individuals, and some single males.
Because of their relative lack of sweat glands, pigs often control their body temperature using behavioural thermoregulation. Wallowing, which often consists of coating the body with mud, is a behaviour frequently exhibited by pigs. They do not submerge completely under the mud, but vary the depth and duration of wallowing depending on environmental conditions. Typically, adult pigs start wallowing once the ambient temperature is around 17–21 °C (63–70 °F). They cover themselves from head to toe in mud. Pigs may use mud as a sunscreen, or as a method of keeping parasites away. Most bristled pigs will "blow their coat", meaning that they shed most of the longer, coarser stiff hair once a year, usually in spring or early summer, to prepare for the warmer months ahead.
If conditions permit, pigs feed continuously for many hours and then sleep for many hours, in contrast to
In many ways pig behaviour appears to be intermediate between that of other artiodactyls and of carnivores.Clutton-Brock, J., (1987). A Natural History of Domesticated Mammals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge pp.73–74 Pigs seek out the company of other pigs and often huddle to maintain physical contact, although they do not naturally form large herds. They typically live in groups of about 8–10 adult sows, some young individuals, and some single males.
Because of their relative lack of sweat glands, pigs often control their body temperature using behavioural thermoregulation. Wallowing, which often consists of coating the body with mud, is a behaviour frequently exhibited by pigs. They do not submerge completely under the mud, but vary the depth and duration of wallowing depending on environmental conditions. Typically, adult pigs start wallowing once the ambient temperature is around 17–21 °C (63–70 °F). They cover themselves from head to toe in mud. Pigs may use mud as a sunscreen, or as a method of keeping parasites away. Most bristled pigs will "blow their coat", meaning that they shed most of the longer, coarser stiff hair once a year, usually in spring or early summer, to prepare for the warmer months ahead.
If conditions permit, pigs feed continuously for many hours and then sleep for many hours, in contrast to
 Rooting is an instinctual behavior in pigs that is characterized by a pig nudging its snout into something. Similar to a cat's kneading, rooting is found comforting. It first happens when piglets are born to obtain their mother's milk, and can become a habitual, obsessive behavior which is most prominent in animals weaned too early. Often, pigs will root and dig into the ground to forage for food. By means of rooting, pigs have been used to till farmland.
Rooting is known to also be used as a means of communication. Nose rings that pierce the septum of the nose discourage rooting because they make the behavior painful.
The breed known as the kunekune hardly ever roots, as it can sustain itself by feeding on nothing other than grass. Not having to root around in the soil to find underground food (e.g. tubers), it thus has evolved to, for the most part, not possess the instinct for rooting.
Rooting is an instinctual behavior in pigs that is characterized by a pig nudging its snout into something. Similar to a cat's kneading, rooting is found comforting. It first happens when piglets are born to obtain their mother's milk, and can become a habitual, obsessive behavior which is most prominent in animals weaned too early. Often, pigs will root and dig into the ground to forage for food. By means of rooting, pigs have been used to till farmland.
Rooting is known to also be used as a means of communication. Nose rings that pierce the septum of the nose discourage rooting because they make the behavior painful.
The breed known as the kunekune hardly ever roots, as it can sustain itself by feeding on nothing other than grass. Not having to root around in the soil to find underground food (e.g. tubers), it thus has evolved to, for the most part, not possess the instinct for rooting.

 Pigs display complex nursing and suckling behaviour. Nursing occurs every 50–60 minutes, and the sow requires stimulation from piglets before milk let-down. Sensory inputs (vocalisation, odours from mammary and birth fluids, and hair patterns of the sow) are particularly important immediately post-birth to facilitate teat location by the piglets. Initially, the piglets compete for position at the udder; then the piglets massage around their respective teats with their snouts, during which time the sow grunts at slow, regular intervals. Each series of grunts varies in frequency, tone and magnitude, indicating the stages of nursing to the piglets.
The phase of competition for teats and of nosing the udder lasts for about one minute and ends when milk flow begins. In the third phase, the piglets hold the teats in their mouths and suck with slow mouth movements (one per second), and the rate of the sow's grunting increases for approximately 20 seconds. The grunt peak in the third phase of suckling does not coincide with milk ejection, but rather the release of oxytocin from the pituitary into the bloodstream. Phase four coincides with the period of main milk flow (10–20 seconds) when the piglets suddenly withdraw slightly from the udder and start sucking with rapid mouth movements of about three per second. The sow grunts rapidly, lower in tone and often in quick runs of three or four, during this phase. Finally, the flow stops and so does the grunting of the sow. The piglets may then dart from teat to teat and recommence suckling with slow movements, or nosing the udder. Piglets massage and suckle the sow's teats after milk flow ceases as a way of letting the sow know their nutritional status. This helps her to regulate the amount of milk released from that teat in future sucklings. The more intense the post-feed massaging of a teat, the greater the future milk release from that teat will be.
Pigs display complex nursing and suckling behaviour. Nursing occurs every 50–60 minutes, and the sow requires stimulation from piglets before milk let-down. Sensory inputs (vocalisation, odours from mammary and birth fluids, and hair patterns of the sow) are particularly important immediately post-birth to facilitate teat location by the piglets. Initially, the piglets compete for position at the udder; then the piglets massage around their respective teats with their snouts, during which time the sow grunts at slow, regular intervals. Each series of grunts varies in frequency, tone and magnitude, indicating the stages of nursing to the piglets.
The phase of competition for teats and of nosing the udder lasts for about one minute and ends when milk flow begins. In the third phase, the piglets hold the teats in their mouths and suck with slow mouth movements (one per second), and the rate of the sow's grunting increases for approximately 20 seconds. The grunt peak in the third phase of suckling does not coincide with milk ejection, but rather the release of oxytocin from the pituitary into the bloodstream. Phase four coincides with the period of main milk flow (10–20 seconds) when the piglets suddenly withdraw slightly from the udder and start sucking with rapid mouth movements of about three per second. The sow grunts rapidly, lower in tone and often in quick runs of three or four, during this phase. Finally, the flow stops and so does the grunting of the sow. The piglets may then dart from teat to teat and recommence suckling with slow movements, or nosing the udder. Piglets massage and suckle the sow's teats after milk flow ceases as a way of letting the sow know their nutritional status. This helps her to regulate the amount of milk released from that teat in future sucklings. The more intense the post-feed massaging of a teat, the greater the future milk release from that teat will be.
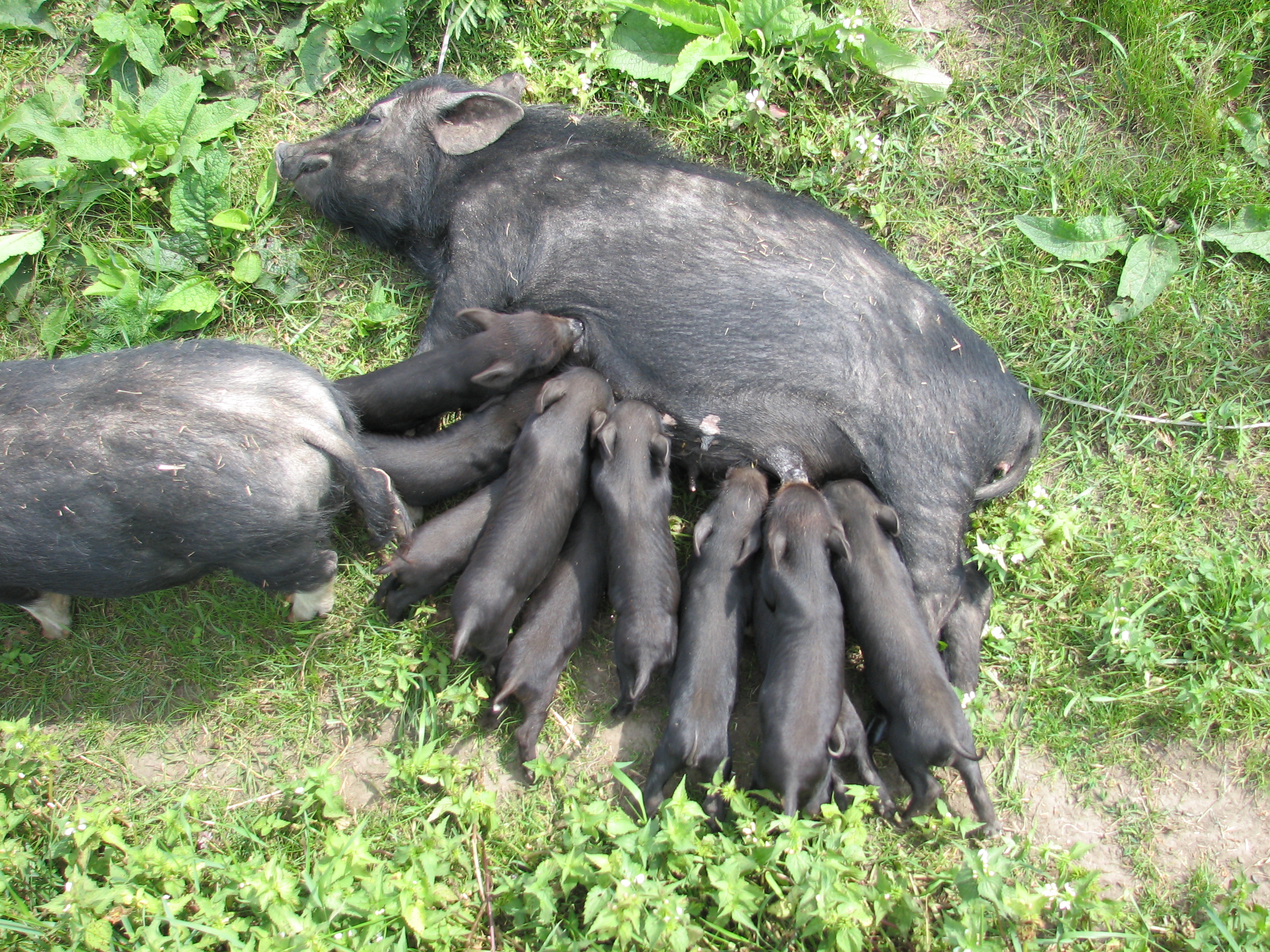 In pigs, dominance hierarchies can be formed at a very early age. Piglets are highly precocious and within minutes of being born, or sometimes seconds, will attempt to suckle. The piglets are born with sharp teeth and fight to develop a teat order as the anterior teats produce a greater quantity of milk. Once established, this teat order remains stable with each piglet tending to feed on a particular teat or group of teats. Stimulation of the anterior teats appears to be important in causing milk letdown, so it might be advantageous to the entire litter to have these teats occupied by healthy piglets.
Using an artificial sow to rear groups of piglets, recognition of a teat in a particular area of the udder depended initially on visual orientation by means of reference points on the udder to find the area, and then the olfactory sense for the more accurate search within that area.
In pigs, dominance hierarchies can be formed at a very early age. Piglets are highly precocious and within minutes of being born, or sometimes seconds, will attempt to suckle. The piglets are born with sharp teeth and fight to develop a teat order as the anterior teats produce a greater quantity of milk. Once established, this teat order remains stable with each piglet tending to feed on a particular teat or group of teats. Stimulation of the anterior teats appears to be important in causing milk letdown, so it might be advantageous to the entire litter to have these teats occupied by healthy piglets.
Using an artificial sow to rear groups of piglets, recognition of a teat in a particular area of the udder depended initially on visual orientation by means of reference points on the udder to find the area, and then the olfactory sense for the more accurate search within that area.
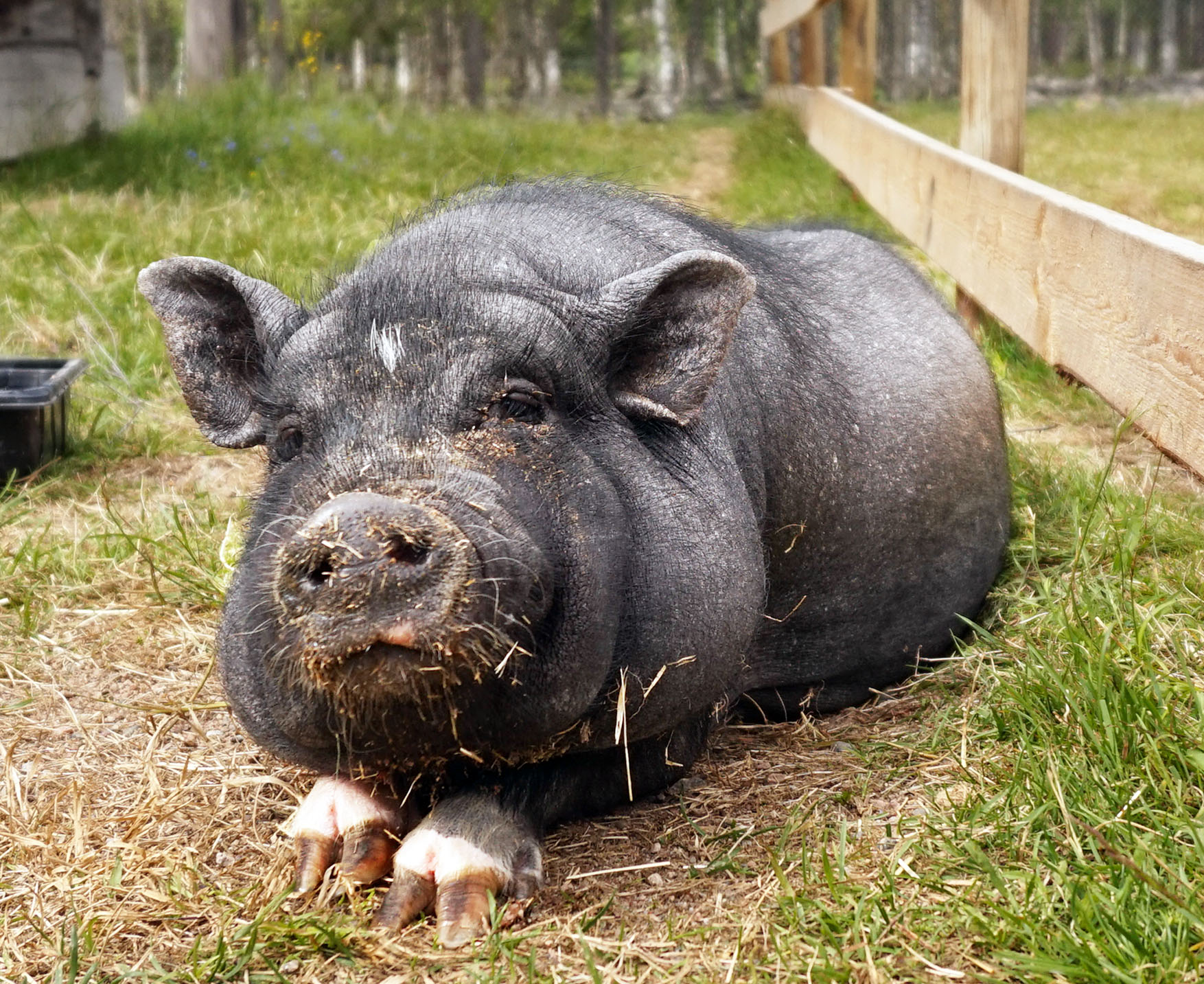 Vietnamese pot-bellied pigs, a miniature breed of pig, have made popular pets in the United States, beginning in the latter half of the 20th century.
In many respects, pot-bellied pigs are desirable and entertaining pets. They are considered intelligent, gregarious, and trainable. They lack the genetic hereditary weaknesses which commonly afflict certain pedigree cat and dog breeds, are generally quite sturdy, and have a reasonably affordable diet despite requiring large quantities of food. However, they can be strong-willed, defiant, and independent pets which will sometimes defy training. They require access to an outdoor space at all times, and depending on the individual pig, may become housebroken easily or never settle indoors. While hardy, an injured or sick pig will require costly surgery or larger than average quantities of medicine than most pets.
Pigs are highly intelligent, social creatures. They are considered
Vietnamese pot-bellied pigs, a miniature breed of pig, have made popular pets in the United States, beginning in the latter half of the 20th century.
In many respects, pot-bellied pigs are desirable and entertaining pets. They are considered intelligent, gregarious, and trainable. They lack the genetic hereditary weaknesses which commonly afflict certain pedigree cat and dog breeds, are generally quite sturdy, and have a reasonably affordable diet despite requiring large quantities of food. However, they can be strong-willed, defiant, and independent pets which will sometimes defy training. They require access to an outdoor space at all times, and depending on the individual pig, may become housebroken easily or never settle indoors. While hardy, an injured or sick pig will require costly surgery or larger than average quantities of medicine than most pets.
Pigs are highly intelligent, social creatures. They are considered 
Xenotransplantation
Emedicine.com Some obstacles to successful organ donation from a pig to a human arise from the response of the recipient's
Xenotransplantation Action Plan: FDA Approach to the Regulation of Xenotransplantation
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. Pig cells have been engineered to inactivate all 62 PERVs in the genome using CRISPR Cas9 genome editing technology, and eliminated infection from the pig to human cells in culture.
Animal Welfare AVMA Policy on Pregnant Sow Housing
*
CAST Scientific Assessment of the Welfare of Dry Sows kept in Individual Accommodations- March 2009
*
An introduction to pig keeping
British Pig Association
Globe and Mail article Canada's transgenic Enviropig is stuck in a genetic modification poke
Information on Micro Pigs
gilt pig breeders
JSR Genetics
Pig genetics company
Pig Sanctuary
Swine Care
Swine Study Guide
from
The process of pig slaughtery
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pig Mammals described in 1777 Mammals as pets Livestock Pork Taxa named by Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben Sus (genus)
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
. The pig's head-plus-body length ranges from , and adult pigs typically weigh between , with well-fed individuals even exceeding this range. The size and weight of hogs largely depends on their breed. Compared to other artiodactyls, a pig's head is relatively long and pointed. Most even-toed ungulates are herbivorous, but pigs are omnivores, like their wild relative. Pigs grunt and make snorting sounds.
When used as livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
, pigs are farmed
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
primarily for the production of meat, called pork. A group of pigs is called a ''passel'', a ''team'', or a ''sounder''. The animal's bones, hide, and bristles are also used in products. Pigs, especially miniature
A miniature is a small-scale reproduction, or a small version. It may refer to:
* Portrait miniature, a miniature portrait painting
* Miniature art, miniature painting, engraving and sculpture
* Miniature (chess), a masterful chess game or proble ...
breeds, are kept as pets.
Biology


 The pig typically has a large head, with a long snout which is strengthened by a special prenasal bone and a disk of cartilage at the tip. The snout is used to dig into the soil to find food and is a very acute sense organ. The dental formula of adult pigs is , giving a total of 44 teeth. The rear teeth are adapted for crushing. In the male, the canine teeth can form tusks, which grow continuously and are sharpened by constantly being ground against each other.
Four hoofed toes are on each foot, with the two larger central toes bearing most of the weight, but the outer two also being used in soft ground.
Most pigs have rather a
The pig typically has a large head, with a long snout which is strengthened by a special prenasal bone and a disk of cartilage at the tip. The snout is used to dig into the soil to find food and is a very acute sense organ. The dental formula of adult pigs is , giving a total of 44 teeth. The rear teeth are adapted for crushing. In the male, the canine teeth can form tusks, which grow continuously and are sharpened by constantly being ground against each other.
Four hoofed toes are on each foot, with the two larger central toes bearing most of the weight, but the outer two also being used in soft ground.
Most pigs have rather a bristle
A bristle is a stiff hair or feather (natural or artificial), either on an animal, such as a pig, a plant, or on a tool such as a brush or broom.
Synthetic types
Synthetic materials such as nylon are also used to make bristles in items such a ...
d sparse hair covering on their skin, although woolly-coated breeds such as the Mangalitsa exist.
Pigs possess both apocrine and eccrine sweat glands, although the latter appear limited to the snout and dorsonasal areas. Pigs, however, like other "hairless" mammals (e.g. elephants, rhinos, and mole-rats), do not use thermal sweat glands in cooling. Pigs are also less able than many other mammals to dissipate heat from wet mucous membranes in the mouth through panting. Their thermoneutral zone is . At higher temperatures, pigs lose heat by wallowing in mud or water via evaporative cooling, although it has been suggested that wallowing may serve other functions, such as protection from sunburn, ecto-parasite control, and scent-marking.
Pigs are one of four known mammalian species which possess mutations in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor that protect against snake venom. Mongooses, honey badgers, hedgehogs, and pigs all have modifications to the receptor pocket which prevents the snake venom α-neurotoxin from binding. These represent four separate, independent mutations.
Pigs have small lungs in relation to their body size, and are thus more susceptible than other domesticated animals to fatal bronchitis and pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
. Pigs have a maximum life span of about 27 years.
Genetics and genomics
The genome of the pig has been sequenced and contains about 22,342 protein-coding genes.Taxonomy
The pig is most often considered to be a subspecies of the wild boar, which was given the name ''Sus scrofa'' byCarl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
in 1758; following from this, the formal name of the pig is ''Sus scrofa domesticus''. However, in 1777, Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben
Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben was a German naturalist from Quedlinburg.
Erxleben was professor of physics and veterinary medicine at the University of Göttingen
The University of Göttingen, officially the Georg August University o ...
classified the pig as a separate species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
from the wild boar. He gave it the name ''Sus domesticus'', which is still used by some taxonomists. The American Society of Mammalogists considers it a separate species.
History

 Archaeological evidence suggests that pigs were domesticated from wild boar in the Near East in the Tigris Basin, Çayönü, Cafer Höyük,
Archaeological evidence suggests that pigs were domesticated from wild boar in the Near East in the Tigris Basin, Çayönü, Cafer Höyük, Nevalı Çori
Nevalı Çori ( tr, Nevali Çori, ku, Newala Çorî) was an early Neolithic settlement on the middle Euphrates, in Şanlıurfa Province, Southeastern Anatolia, Turkey. The site is known for having some of the world's oldest known temples and mon ...
being managed in the wild in a way similar to the way they are managed by some modern New Guineans. Remains of pigs have been dated to earlier than 11,400 years ago in Cyprus. Those animals must have been introduced from the mainland, which suggests domestication in the adjacent mainland by then. Pigs were separately domesticated in China beginning 8,000 years ago, and have been one of the most important domesticated animal there ever since.
In the Near East, pig husbandry spread for the next few millennia. It reduced gradually during the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, as rural populations focused instead on commodity-producing livestock. It was sustained in urbanized regions, however.
DNA evidence from subfossil remains of teeth and jawbones of Neolithic pigs shows that the first domestic pigs in Europe had been brought from the Near East. This stimulated the domestication of local European wild boar, resulting in a third domestication event with the Near Eastern genes dying out in European pig stock. Modern domesticated pigs have involved complex exchanges, with European domesticated lines being exported, in turn, to the ancient Near East. Historical records indicate that Asian pigs were introduced into Europe during the 18th and early 19th centuries.
In August 2015, a study looked at over 100 pig genome sequences to ascertain their process of domestication, which was assumed to have been initiated by humans, involved few individuals, and relied on reproductive isolation between wild and domestic forms. The study found that the assumption of reproductive isolation with population bottlenecks was not supported. The study indicated that pigs were domesticated separately in Western Asia and China, with Western Asian pigs introduced into Europe, where they crossed with wild boar. A model that fit the data included a mixture with a now extinct ghost population of wild pigs during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
. The study also found that despite back-crossing with wild pigs, the genomes of domestic pigs have strong signatures of selection at DNA loci that affect behavior and morphology. The study concluded that human selection for domestic traits likely counteracted the homogenizing effect of gene flow from wild boars and created domestication islands in the genome. The same process may also apply to other domesticated animals. In 2019, a study showed that the pig had arrived in Europe from the Near East 8,500 years ago. Over the next 3,000 years they then admixed with the European wild boar until their genome showed less than 5% Near Eastern ancestry, yet retained their domesticated features.
Among the animals that the Spanish introduced to the Chiloé Archipelago in the 16th century, pigs were the most successful to adapt. The pigs benefited from abundant shellfish and algae exposed by the large tides of the archipelago. Pigs were brought to southeastern North America from Europe by de Soto and other early Spanish explorers. Escaped pigs became feral and caused a great deal of disruption to Native Americans.
Feral pig populations in the southeastern United States have since migrated north and are a growing concern in the Midwest. Considered an invasive species, many state agencies have programs to trap or hunt feral pigs as means of removal. Domestic pigs have become feral in many other parts of the world (e.g. New Zealand and northern Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
) and have caused substantial environmental damage. Feral hybrids of the European wild boar with the domestic pig are also very disruptive to both environment and agriculture (among the 100 most damaging animal species), especially in southeastern South America from Uruguay to Brazil's Mato Grosso do Sul and São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaW ...
.
With around 1 billion individuals alive at any time, the domesticated pig is one of the most numerous large mammals on the planet.
Reproduction
Female pigs reach sexual maturity at 3–12 months of age and come into estrus every 18–24 days if they are not successfully bred. The variation in ovulation rate can be attributed to intrinsic factors such as age and genotype, as well as extrinsic factors like nutrition, environment, and the supplementation of exogenous hormones. The gestation period averages 112–120 days. Estrus lasts two to three days, and the female's displayed receptiveness to mate is known as standing heat. Standing heat is a reflexive response that is stimulated when the female is in contact with the saliva of a sexually mature boar. Androstenol is one of the pheromones produced in the submaxillary salivary glands of boars that will trigger the female's response. The female cervix contains a series of five interdigitating pads, or folds, that will hold the boar's corkscrew-shaped penis during copulation. Females have bicornuate uteruses and two conceptuses must be present in both uterine horns for pregnancy to be established. Maternal recognition of pregnancy in pigs occurs on days 11 to 12 of pregnancy and is marked by progesterone production from a functioning corpus luteum (CL). To avoid luteolysis by PGF2α, rescuing of the CL must occur via embryonic signaling of estradiol 17β and PGE2. This signaling acts on both the endometrium and luteal tissue to prevent the regression of the CL by activation of genes that are responsible for CL maintenance. During mid to late pregnancy, the CL relies primarily on luteinizing hormone (LH) for maintenance until parturition. Animal nutrition is important prior to reproduction and during gestation to ensure optimum reproductive performance is achieved.
Archeological evidence indicates that medieval European pigs farrowed, or bore a litter of piglets, once per year. By the nineteenth century, European piglets routinely double-farrowed, or bore two litters of piglets per year. It is unclear when this shift occurred.
Estrus lasts two to three days, and the female's displayed receptiveness to mate is known as standing heat. Standing heat is a reflexive response that is stimulated when the female is in contact with the saliva of a sexually mature boar. Androstenol is one of the pheromones produced in the submaxillary salivary glands of boars that will trigger the female's response. The female cervix contains a series of five interdigitating pads, or folds, that will hold the boar's corkscrew-shaped penis during copulation. Females have bicornuate uteruses and two conceptuses must be present in both uterine horns for pregnancy to be established. Maternal recognition of pregnancy in pigs occurs on days 11 to 12 of pregnancy and is marked by progesterone production from a functioning corpus luteum (CL). To avoid luteolysis by PGF2α, rescuing of the CL must occur via embryonic signaling of estradiol 17β and PGE2. This signaling acts on both the endometrium and luteal tissue to prevent the regression of the CL by activation of genes that are responsible for CL maintenance. During mid to late pregnancy, the CL relies primarily on luteinizing hormone (LH) for maintenance until parturition. Animal nutrition is important prior to reproduction and during gestation to ensure optimum reproductive performance is achieved.
Archeological evidence indicates that medieval European pigs farrowed, or bore a litter of piglets, once per year. By the nineteenth century, European piglets routinely double-farrowed, or bore two litters of piglets per year. It is unclear when this shift occurred.
Behavior
 In many ways pig behaviour appears to be intermediate between that of other artiodactyls and of carnivores.Clutton-Brock, J., (1987). A Natural History of Domesticated Mammals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge pp.73–74 Pigs seek out the company of other pigs and often huddle to maintain physical contact, although they do not naturally form large herds. They typically live in groups of about 8–10 adult sows, some young individuals, and some single males.
Because of their relative lack of sweat glands, pigs often control their body temperature using behavioural thermoregulation. Wallowing, which often consists of coating the body with mud, is a behaviour frequently exhibited by pigs. They do not submerge completely under the mud, but vary the depth and duration of wallowing depending on environmental conditions. Typically, adult pigs start wallowing once the ambient temperature is around 17–21 °C (63–70 °F). They cover themselves from head to toe in mud. Pigs may use mud as a sunscreen, or as a method of keeping parasites away. Most bristled pigs will "blow their coat", meaning that they shed most of the longer, coarser stiff hair once a year, usually in spring or early summer, to prepare for the warmer months ahead.
If conditions permit, pigs feed continuously for many hours and then sleep for many hours, in contrast to
In many ways pig behaviour appears to be intermediate between that of other artiodactyls and of carnivores.Clutton-Brock, J., (1987). A Natural History of Domesticated Mammals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge pp.73–74 Pigs seek out the company of other pigs and often huddle to maintain physical contact, although they do not naturally form large herds. They typically live in groups of about 8–10 adult sows, some young individuals, and some single males.
Because of their relative lack of sweat glands, pigs often control their body temperature using behavioural thermoregulation. Wallowing, which often consists of coating the body with mud, is a behaviour frequently exhibited by pigs. They do not submerge completely under the mud, but vary the depth and duration of wallowing depending on environmental conditions. Typically, adult pigs start wallowing once the ambient temperature is around 17–21 °C (63–70 °F). They cover themselves from head to toe in mud. Pigs may use mud as a sunscreen, or as a method of keeping parasites away. Most bristled pigs will "blow their coat", meaning that they shed most of the longer, coarser stiff hair once a year, usually in spring or early summer, to prepare for the warmer months ahead.
If conditions permit, pigs feed continuously for many hours and then sleep for many hours, in contrast to ruminants
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The ...
which tend to feed for a short time and then sleep for a short time. Pigs are omnivorous, and are highly versatile in their feeding behaviour. As they are foraging animals, they primarily eat leaves, stems, roots, fruits, and flowers. Pigs play an important role in regions where pig toilet
A pig toilet (sometimes called a "pig sty latrine") is a simple type of dry toilet consisting of an outhouse mounted over a pigsty, with a chute or hole connecting the two. The pigs consume the feces of the users of the toilet, as well as other ...
s are employed. Pigs are highly intelligent animals, on par with dogs, and according to David DiSalvo's writing in '' Forbes'', they are "widely considered the smartest domesticated animal in the world. Pigs have demonstrated the ability to move a cursor on a video screen with their snouts and understand what is happening onscreen, and have learned to distinguish between the scribbles they had seen before and those they were seeing for the first time."
Rooting
 Rooting is an instinctual behavior in pigs that is characterized by a pig nudging its snout into something. Similar to a cat's kneading, rooting is found comforting. It first happens when piglets are born to obtain their mother's milk, and can become a habitual, obsessive behavior which is most prominent in animals weaned too early. Often, pigs will root and dig into the ground to forage for food. By means of rooting, pigs have been used to till farmland.
Rooting is known to also be used as a means of communication. Nose rings that pierce the septum of the nose discourage rooting because they make the behavior painful.
The breed known as the kunekune hardly ever roots, as it can sustain itself by feeding on nothing other than grass. Not having to root around in the soil to find underground food (e.g. tubers), it thus has evolved to, for the most part, not possess the instinct for rooting.
Rooting is an instinctual behavior in pigs that is characterized by a pig nudging its snout into something. Similar to a cat's kneading, rooting is found comforting. It first happens when piglets are born to obtain their mother's milk, and can become a habitual, obsessive behavior which is most prominent in animals weaned too early. Often, pigs will root and dig into the ground to forage for food. By means of rooting, pigs have been used to till farmland.
Rooting is known to also be used as a means of communication. Nose rings that pierce the septum of the nose discourage rooting because they make the behavior painful.
The breed known as the kunekune hardly ever roots, as it can sustain itself by feeding on nothing other than grass. Not having to root around in the soil to find underground food (e.g. tubers), it thus has evolved to, for the most part, not possess the instinct for rooting.
Nest-building
A behavioural characteristic of pigs which they share with carnivores isnest-building
A nest is a structure built for certain animals to hold eggs or young. Although nests are most closely associated with birds, members of all classes of vertebrates and some invertebrates construct nests. They may be composed of organic materi ...
. Sows root in the ground to create depressions and then build nests in which to give birth. First, the sow digs a depression about the size of her body. She then collects twigs and leaves, and carries these in her mouth to the depression, building them into a mound. She distributes the softer, finer material to the centre of the mound using her feet. When the mound reaches the desired height, she places large branches, up to 2 metres in length, on the surface. She enters into the mound and roots around to create a depression within the gathered material. She then gives birth in a lying position, which, again, is different from other artiodactyls, which usually give birth in a standing position.
Nest-building behaviour is an important part in the process of pre and post-partum maternal behaviour. Nest-building will occur during the last 24 hours before the onset of farrowing and becomes most intense during 12 to 6 hours before farrowing. Nest-building is divided into two phases: one of which is the initial phase of rooting in the ground while the second phase is the collecting, carrying and arranging of the nest material. The sow will separate from the group and seek a suitable nest site with some shelter from rain and wind that has well-drained soil. This nest-building behaviour is performed to provide the offspring with shelter, comfort, and thermoregulation. The nest will provide protection against weather and predators while keeping the piglets close to the sow and away from the rest of the herd. This ensures they do not get trampled on and that other piglets are not stealing milk from the sow. Nest-building can be influenced by internal and external stimuli. Internal hormonal changes and the completion of one nesting phase are indicators of this maternal behaviour. The onset is triggered by the rise in prolactin levels, which is caused by a decrease in progesterone and an increase in prostaglandin, while the gathering of the nest material seems to be regulated more by external stimuli such as temperature. The longer time spent on nest-building will increase pre-partum oxytocin.
Nursing and suckling behaviour

 Pigs display complex nursing and suckling behaviour. Nursing occurs every 50–60 minutes, and the sow requires stimulation from piglets before milk let-down. Sensory inputs (vocalisation, odours from mammary and birth fluids, and hair patterns of the sow) are particularly important immediately post-birth to facilitate teat location by the piglets. Initially, the piglets compete for position at the udder; then the piglets massage around their respective teats with their snouts, during which time the sow grunts at slow, regular intervals. Each series of grunts varies in frequency, tone and magnitude, indicating the stages of nursing to the piglets.
The phase of competition for teats and of nosing the udder lasts for about one minute and ends when milk flow begins. In the third phase, the piglets hold the teats in their mouths and suck with slow mouth movements (one per second), and the rate of the sow's grunting increases for approximately 20 seconds. The grunt peak in the third phase of suckling does not coincide with milk ejection, but rather the release of oxytocin from the pituitary into the bloodstream. Phase four coincides with the period of main milk flow (10–20 seconds) when the piglets suddenly withdraw slightly from the udder and start sucking with rapid mouth movements of about three per second. The sow grunts rapidly, lower in tone and often in quick runs of three or four, during this phase. Finally, the flow stops and so does the grunting of the sow. The piglets may then dart from teat to teat and recommence suckling with slow movements, or nosing the udder. Piglets massage and suckle the sow's teats after milk flow ceases as a way of letting the sow know their nutritional status. This helps her to regulate the amount of milk released from that teat in future sucklings. The more intense the post-feed massaging of a teat, the greater the future milk release from that teat will be.
Pigs display complex nursing and suckling behaviour. Nursing occurs every 50–60 minutes, and the sow requires stimulation from piglets before milk let-down. Sensory inputs (vocalisation, odours from mammary and birth fluids, and hair patterns of the sow) are particularly important immediately post-birth to facilitate teat location by the piglets. Initially, the piglets compete for position at the udder; then the piglets massage around their respective teats with their snouts, during which time the sow grunts at slow, regular intervals. Each series of grunts varies in frequency, tone and magnitude, indicating the stages of nursing to the piglets.
The phase of competition for teats and of nosing the udder lasts for about one minute and ends when milk flow begins. In the third phase, the piglets hold the teats in their mouths and suck with slow mouth movements (one per second), and the rate of the sow's grunting increases for approximately 20 seconds. The grunt peak in the third phase of suckling does not coincide with milk ejection, but rather the release of oxytocin from the pituitary into the bloodstream. Phase four coincides with the period of main milk flow (10–20 seconds) when the piglets suddenly withdraw slightly from the udder and start sucking with rapid mouth movements of about three per second. The sow grunts rapidly, lower in tone and often in quick runs of three or four, during this phase. Finally, the flow stops and so does the grunting of the sow. The piglets may then dart from teat to teat and recommence suckling with slow movements, or nosing the udder. Piglets massage and suckle the sow's teats after milk flow ceases as a way of letting the sow know their nutritional status. This helps her to regulate the amount of milk released from that teat in future sucklings. The more intense the post-feed massaging of a teat, the greater the future milk release from that teat will be.
Teat order
 In pigs, dominance hierarchies can be formed at a very early age. Piglets are highly precocious and within minutes of being born, or sometimes seconds, will attempt to suckle. The piglets are born with sharp teeth and fight to develop a teat order as the anterior teats produce a greater quantity of milk. Once established, this teat order remains stable with each piglet tending to feed on a particular teat or group of teats. Stimulation of the anterior teats appears to be important in causing milk letdown, so it might be advantageous to the entire litter to have these teats occupied by healthy piglets.
Using an artificial sow to rear groups of piglets, recognition of a teat in a particular area of the udder depended initially on visual orientation by means of reference points on the udder to find the area, and then the olfactory sense for the more accurate search within that area.
In pigs, dominance hierarchies can be formed at a very early age. Piglets are highly precocious and within minutes of being born, or sometimes seconds, will attempt to suckle. The piglets are born with sharp teeth and fight to develop a teat order as the anterior teats produce a greater quantity of milk. Once established, this teat order remains stable with each piglet tending to feed on a particular teat or group of teats. Stimulation of the anterior teats appears to be important in causing milk letdown, so it might be advantageous to the entire litter to have these teats occupied by healthy piglets.
Using an artificial sow to rear groups of piglets, recognition of a teat in a particular area of the udder depended initially on visual orientation by means of reference points on the udder to find the area, and then the olfactory sense for the more accurate search within that area.
Senses
Pigs have panoramic vision of approximately 310° and binocular vision of 35° to 50°. It is thought they have no eye accommodation. Other animals that have no accommodation, e.g. sheep, lift their heads to see distant objects. The extent to which pigs have colour vision is still a source of some debate; however, the presence of cone cells in the retina with two distinct wavelength sensitivities (blue and green) suggests that at least some colour vision is present. Pigs have a well-developed sense of smell, and use is made of this in Europe where they are trained to locate underground truffles. Olfactory rather than visual stimuli are used in the identification of other pigs.Houpt, K.A., (1998). Domestic Animal Behavior for Veterinarians and Animal Scientists. 3rd edition. Iowa State University Press, Ames. Hearing is also well developed, and localisation of sounds is made by moving the head. Pigs use auditory stimuli extensively as a means of communication in all social activities.Gonyou, H.W., (2001). The social behaviour of pigs. In "Social Behaviour in Farm Animals", eds. Keeling, L.J., and Gonyou, H.W. CABI, Oxford. Alarm or aversive stimuli are transmitted to other pigs not only by auditory cues but also by pheromones. Similarly, recognition between the sow and her piglets is by olfactory and vocal cues.Breeds
Many breeds of pig exist, with different colors, shapes, and sizes. According to The Livestock Conservancy, as of 2016, three breeds of pig are critically rare (having a global population of fewer than 2000). They are the Choctaw hog, the Mulefoot, and the Ossabaw Island hog. The smallest known pig breed in the world is theGöttingen minipig
The Göttingen minipig (also known as the ''Göttinger'' or "Goettingen" minipig) is a breed of small swine. The Göttingen minipig is the smallest domestic pig breed known in the world; as an adult, they weigh around . Beside being known for the ...
, typically weighing about as a healthy, full-grown adult.
In agriculture
When in use as livestock, the pig is mostly farmed for its meat, pork. Other food products made from pigs include pork sausage (which includes casings that are made from the intestines), bacon, gammon, ham and pork rinds. The head of a pig can be used to make a preserved jelly calledhead cheese
Head cheese ( Dutch: ''hoofdkaas'') or brawn is a cold cut terrine or meat jelly that originated in Europe. It is made with flesh from the head of a calf or pig (less commonly a sheep or cow), typically set in aspic, and usually eaten cold, ...
, which is sometimes known as brawn. Liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
, chitterlings, blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
(for black pudding), and other offal from pigs are also widely used for food. In some religions, such as Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
and Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
, pork is a taboo food. Approximately 1.5 billion pigs are slaughtered each year for meat.
The use of pig milk
Pig milk is milk from pigs, and is typically consumed by piglets. It is similar in composition to cow's milk, though higher in fat and more watery. Pig milk is seldom obtained for human uses and is not considered to be a viable agricultural produc ...
for human consumption does take place, but as there are certain difficulties in obtaining it, there is little commercial production.
Livestock pigs are exhibited at agricultural shows, judged either as stud stock compared to the standard features of each pig breed, or in commercial classes where the animals are judged primarily on their suitability for slaughter to provide premium meat.
The skin of pigs is eaten and used to produce seat covers, apparel, and other items.
In some developing and developed nations, the pig is usually raised outdoors in yards or fields. In some areas, pigs are allowed to forage in woods where they may be taken care of by swineherds. In industrialized nations such as the United States, pig farming has switched from the traditional pig farm to large-scale intensive pig farms. This has resulted in lower production costs but can cause significant cruelty problems. As consumers have become concerned with the humane treatment of livestock, demand for pasture-raised pork in these nations has increased.
As pets
 Vietnamese pot-bellied pigs, a miniature breed of pig, have made popular pets in the United States, beginning in the latter half of the 20th century.
In many respects, pot-bellied pigs are desirable and entertaining pets. They are considered intelligent, gregarious, and trainable. They lack the genetic hereditary weaknesses which commonly afflict certain pedigree cat and dog breeds, are generally quite sturdy, and have a reasonably affordable diet despite requiring large quantities of food. However, they can be strong-willed, defiant, and independent pets which will sometimes defy training. They require access to an outdoor space at all times, and depending on the individual pig, may become housebroken easily or never settle indoors. While hardy, an injured or sick pig will require costly surgery or larger than average quantities of medicine than most pets.
Pigs are highly intelligent, social creatures. They are considered
Vietnamese pot-bellied pigs, a miniature breed of pig, have made popular pets in the United States, beginning in the latter half of the 20th century.
In many respects, pot-bellied pigs are desirable and entertaining pets. They are considered intelligent, gregarious, and trainable. They lack the genetic hereditary weaknesses which commonly afflict certain pedigree cat and dog breeds, are generally quite sturdy, and have a reasonably affordable diet despite requiring large quantities of food. However, they can be strong-willed, defiant, and independent pets which will sometimes defy training. They require access to an outdoor space at all times, and depending on the individual pig, may become housebroken easily or never settle indoors. While hardy, an injured or sick pig will require costly surgery or larger than average quantities of medicine than most pets.
Pigs are highly intelligent, social creatures. They are considered hypoallergenic
Hypoallergenic, meaning "below average" or "slightly" allergenic, is a term meaning that something (usually cosmetics, pets, textiles, food, etc.) causes fewer allergic reactions. The term was first used in 1953 in an advertising campaign for cos ...
, and are known to do quite well with people who have the usual animal allergies. Since these animals are known to have a life expectancy of 15 to 20 years, they require a long-term commitment.
Given pigs are bred primarily as livestock and have not been bred as companion animals for very long, selective breeding for a placid or biddable temperament is not well established. Pigs have radically different psychology to dogs and exhibit fight-or-flight instincts, independent nature, and natural assertiveness which can manifest as aggression towards children and a tendency to panic and lash out with little warning. Cats generally are safe around pigs as neither species has an incentive to express aggression or fear towards the other, although dogs will view pigs as prey animals and in turn, pigs will challenge dogs for food, leading to very violent fights.

Care
Male and female swine that have not been de-sexed may express unwanted aggressive behavior, and are prone to developing serious health issues. Regular trimming of the hooves is necessary; hooves left untreated cause major pain in the pig, can create malformations in bone structure and may cause the pig to be more susceptible to fungal growth between crevices of the hoof, or between the cracks in a split hoof. Male pigs, especially when left unaltered, can grow large, sharp tusks which may continue growing for years. Domestic owners may wish to keep their pigs' tusks trimmed back, or have them removed entirely. As prey animals, pigs' natural instinctive behavior causes them to have a strong fear of being picked up, resulting in the animal expressing stress through struggling and squealing, but they will usually calm down once placed back onto the ground. This instinctual fear may be lessened if the pig has been frequently held since infancy. When holding pigs, supporting them under the legs makes being held not as stressful for the animal. Pigs need enrichment activities to keep their intelligent minds occupied; if pigs get bored, they often become destructive. As rooting is found to be comforting, pigs kept in the house may root household objects, furniture or surfaces. While some owners are known to pierce their pigs' noses to discourage rooting behaviour, the efficacy and humaneness of this practice is questionable. Pet pigs should be let outside daily to allow them to fulfill their natural desire of rooting around.In human medical applications
Pigs, both as live animals and a source of post-mortem tissues, are one of the most valuable animal models used in biomedical research today, because of their biological, physiological, and anatomical similarities to human beings. For instance, human skin is very similar to the pigskin, therefore pigskin has been used in many preclinical studies. Porcine are used in finding treatments, cures for diseases, xenotransplantation, and for general education. They are also used in the development of medical instruments and devices, surgical techniques and instrumentation, and FDA-approved research. These animals contribute to the reduction methods for animal research, as they supply more information from fewer animals used, for a lower cost.Xenotransplantation
Pigs are currently thought to be the best non-human candidates for organ donation to humans, and to date they are the only animal that has successfully donated an organ to a human body. The first successful donation of a non-human organ to a human body was conducted on 15 September 2021, when a kidney from a pig was transplanted to a brain-dead human and immediately started functioning similarly to a human kidney. The procedure, led by Dr. Robert Montgomery, used a donor pig that was genetically engineered to not have a specific carbohydrate that the human body considers a threat– Galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. This followed an earlier major breakthrough when the carbohydrate was removed from genetically engineered mice. Besides similarity between pig and human organs, pigs are among the best animals suited for human donation due the lower risk of cross-species disease transmission. This is caused by pigs' increased phylogenetic distance from humans. Furthermore, they are readily available, and new infectious agents are less likely since they have been in close contact with humans through domestication for many generations.Taylor, L. (2007Xenotransplantation
Emedicine.com Some obstacles to successful organ donation from a pig to a human arise from the response of the recipient's
immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
—generally more extreme than in allotransplantation
Allotransplant (''allo-'' meaning "other" in Greek) is the transplantation of cells, tissues, or organs to a recipient from a genetically non-identical donor of the same species. The transplant is called an allograft, allogeneic transplant, o ...
s, ultimately results in rejection of the xenograft, and in some cases results in the death of the recipient—including hyperacute rejection, acute vascular rejection, cellular rejection, and chronic rejection.
Examples of viruses carried by pigs include porcine herpesvirus, rotavirus, parvovirus, and circovirus
''Circovirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family '' Circoviridae''. Birds (such as pigeons and ducks) and pigs serve as natural hosts, though dogs have been shown to be infected as well. It is a single stranded DNA virus (ssDNA). There are 49 ...
. Of particular concern are PERVs (porcine endogenous retroviruses), vertically transmitted viruses that embed in swine genomes. The risks with xenosis are twofold, as not only could the individual become infected, but a novel infection could initiate an epidemic in the human population. Because of this risk, the FDA has suggested any recipients of xenotransplants shall be closely monitored for the remainder of their life, and quarantined if they show signs of xenosis.FDA. (2006Xenotransplantation Action Plan: FDA Approach to the Regulation of Xenotransplantation
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. Pig cells have been engineered to inactivate all 62 PERVs in the genome using CRISPR Cas9 genome editing technology, and eliminated infection from the pig to human cells in culture.
Folklore
In the belief of traditional Irish fishermen, the pig is seen as a thing of bad luck and should not be mentioned.Glossary of terms
Because the pig is a major domesticated animal, English has many terms unique to the species: * ''barrow'' – a castrated male swine * ''boar'' – a mature male swine; often a wild or feral swine * '' boneen'' – a very young pig (Ireland) * ''farrow'' (noun) – a litter of piglets * ''farrow'' (verb) – to give birth to piglets * ''gilt'' – a female pig that has never been pregnant or is pregnant for the first time * ''hog'' – a domestic swine, especially a fully-grown specimen * ''parcel'' – collective noun for pigs * ''pig'' – strictly, an immature swine; more generally, any swine, especially of the domestic variety * ''piglet'' – a very young pig * ''queen'' – a female pig that has never been mated * '' savaging'' – the act of a sow attacking her own piglets, sometimes killing and cannibalising them * ''shoat'' – a young pig, especially one that has been weaned * ''sounder'' – collective noun for pigs * ''sow'' – a mature female swine * ''swine'' (singular and plural) – hogs collectively or generally; also a derogatory epithet Dictionary of Agriculture (2006), "swine," 240. "''noun'' a collective term for pigs" * '' swineherd'' – one who tends to swine raised as livestock; a pig farmerSee also
* Farming ** '' Mycoplasma hyorhinis'' ** Peccary (domestication) * List of individual pigs * Pet ** Pigs in culture ** Truffle hog ** Xenotransfusion * List of pig breedsFootnotes
References
Animal Welfare AVMA Policy on Pregnant Sow Housing
*
CAST Scientific Assessment of the Welfare of Dry Sows kept in Individual Accommodations- March 2009
*
External links
An introduction to pig keeping
British Pig Association
Globe and Mail article Canada's transgenic Enviropig is stuck in a genetic modification poke
Information on Micro Pigs
gilt pig breeders
JSR Genetics
Pig genetics company
Pig Sanctuary
Swine Care
Swine Study Guide
from
UC Davis
The University of California, Davis (UC Davis, UCD, or Davis) is a public land-grant research university near Davis, California. Named a Public Ivy, it is the northernmost of the ten campuses of the University of California system. The institu ...
The process of pig slaughtery
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pig Mammals described in 1777 Mammals as pets Livestock Pork Taxa named by Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben Sus (genus)