Domestic Duck on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The domestic duck or domestic mallard (''Anas platyrhynchos domesticus'') is a subspecies of
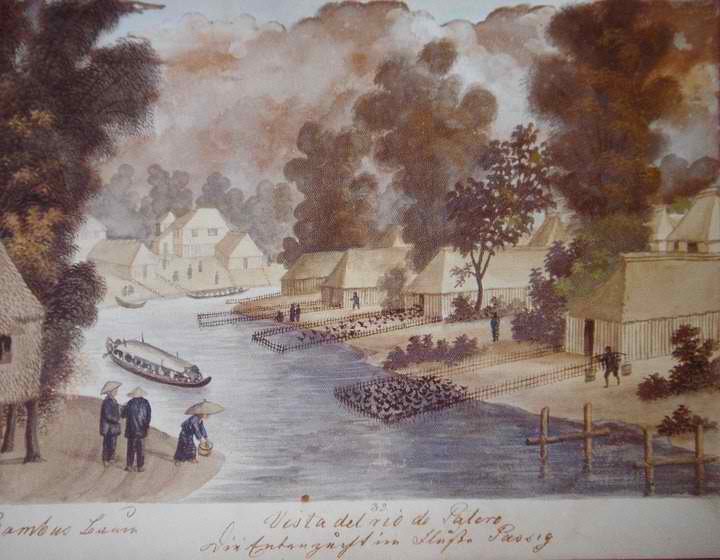 Ducks have been farmed for thousands of years. Approximately 3 billion ducks are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. In the
Ducks have been farmed for thousands of years. Approximately 3 billion ducks are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. In the  Ducks can be kept
Ducks can be kept
 The domestic duck has appeared numerous times in children's stories.
The domestic duck has appeared numerous times in children's stories.
Duck and Goose from Farm to Table
factsheet from
mallard
The mallard () or wild duck (''Anas platyrhynchos'') is a dabbling duck that breeds throughout the temperate and subtropical Americas, Eurasia, and North Africa, and has been introduced to New Zealand, Australia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay, Argen ...
that has been domesticated
Domestication is a sustained multi-generational relationship in which humans assume a significant degree of control over the reproduction and care of another group of organisms to secure a more predictable supply of resources from that group. A ...
by human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s and raised for meat
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chic ...
, eggs, and down feathers
The down of birds is a layer of fine feathers found under the tougher exterior feathers. Very young birds are clad only in down. Powder down is a specialized type of down found only in a few groups of birds. Down is a fine thermal insulator an ...
. A few are also kept for show, as pets, or for their ornamental value. Almost all varieties of domesticated ducks, apart from the domestic Muscovy duck (''Cairina moschata''), are descended from the mallard.
Domestication
Whole-genome sequencing indicate that domestic ducks originate from a single domestication event ofmallard
The mallard () or wild duck (''Anas platyrhynchos'') is a dabbling duck that breeds throughout the temperate and subtropical Americas, Eurasia, and North Africa, and has been introduced to New Zealand, Australia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay, Argen ...
s during the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
, followed by rapid selection for lineages favoring meat or egg production. They were likely domesticated in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
(most likely Southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
) by the rice paddy
A paddy field is a flooded field of arable land used for growing semiaquatic crops, most notably rice and taro. It originates from the Neolithic rice-farming cultures of the Yangtze River basin in southern China, associated with pre-Au ...
-farming ancestors of modern Southeast Asians. The date of domestication is unknown due to the scarcity of archaeological records. They spread outwards from the region, first being mentioned in Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
written records in central China
Central China () is a geographical and a loosely defined cultural region that includes the provinces of Henan, Hubei and Hunan. Jiangxi is sometimes also regarded to be part of this region. Central China is now officially part of South Cent ...
by around 500 BC. Duck farming for both meat and eggs is a widespread and ancient industry in Southeast Asia.
Wild ducks were hunted extensively in Ancient Egypt and other parts of the world in ancient times. But they were not domesticated. Ducks are also mentioned to be present in Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom ...
since at least the 2nd century BC. But based on descriptions (most notably by Columella
Lucius Junius Moderatus Columella (; Arabic: , 4 – ) was a prominent writer on agriculture in the Roman Empire.
His ' in twelve volumes has been completely preserved and forms an important source on Roman agriculture, together with the wo ...
), ducks in Roman agriculture were only tamed, not domesticated. Duck breeding did not exist in the Roman period, requiring the harvesting of eggs from wild ducks to start duck farms.
Almost all varieties of domestic duck except the muscovy have been derived from the mallard
The mallard () or wild duck (''Anas platyrhynchos'') is a dabbling duck that breeds throughout the temperate and subtropical Americas, Eurasia, and North Africa, and has been introduced to New Zealand, Australia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay, Argen ...
. Domestication has greatly altered their characteristics. Domestic ducks are mostly promiscuous
Promiscuity is the practice of engaging in sexual activity frequently with different partners or being indiscriminate in the choice of sexual partners. The term can carry a moral judgment. A common example of behavior viewed as promiscuous by ma ...
, where wild mallards are monogamous
Monogamy ( ) is a form of dyadic relationship in which an individual has only one partner during their lifetime. Alternately, only one partner at any one time ( serial monogamy) — as compared to the various forms of non-monogamy (e.g., pol ...
. Domestic ducks have lost the mallard's territorial behaviour, and are less aggressive than mallards. Despite these differences, domestic ducks frequently mate with wild mallards, producing fully fertile hybrid offspring.
Farming
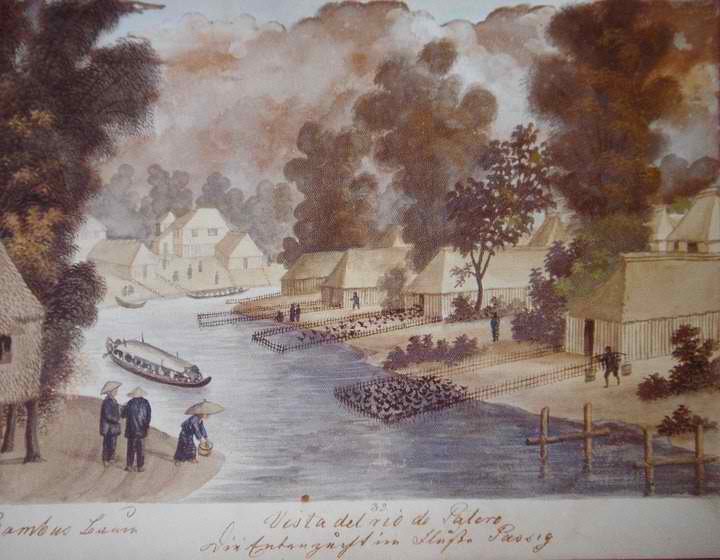 Ducks have been farmed for thousands of years. Approximately 3 billion ducks are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. In the
Ducks have been farmed for thousands of years. Approximately 3 billion ducks are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. In the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
, they are not as popular as the chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adu ...
, because chickens have much more white lean meat and are easier to keep confined, making the total price much lower for chicken meat, whereas duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
is comparatively expensive. While popular in ''haute cuisine
''Haute cuisine'' (; ) or ''grande cuisine'' is the cuisine of "high-level" establishments, gourmet restaurants, and luxury hotels. ''Haute cuisine'' is characterized by the meticulous preparation and careful presentation of food at a high pric ...
'', duck appears less frequently in the mass-market food industry and restaurants in the lower price range. However, ducks are more popular in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, and there they are raised extensively.
Ducks are farmed for their meat, eggs, and down. A minority of ducks are also kept for ''foie gras
Foie gras (, ; ) is a specialty food product made of the liver of a duck or goose. According to French law, foie gras is defined as the liver of a duck or goose fattened by gavage (force feeding).
Foie gras is a popular and well-known delica ...
'' production. The blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
of ducks slaughtered for meat is also collected in some regions and is used as an ingredient in many cultures' dishes. Their eggs are blue-green to white, depending on the breed.
 Ducks can be kept
Ducks can be kept free range
Free range denotes a method of farming husbandry where the animals, for at least part of the day, can roam freely outdoors, rather than being confined in an enclosure for 24 hours each day.
On many farms, the outdoors ranging area is fenced, ...
, in cages, in barns, or in batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
. Ducks enjoy access to swimming water, but do not require it to survive. They should be fed a grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legum ...
and insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pa ...
diet. It is a popular misconception that ducks should be fed bread
Bread is a staple food prepared from a dough of flour (usually wheat) and water, usually by baking. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cultures' diet. It is one of the oldest human-made f ...
; bread has limited nutritional value and can be deadly when fed to developing ducklings. Ducks should be monitored for avian influenza
Avian influenza, known informally as avian flu or bird flu, is a variety of influenza caused by viruses adapted to birds.
, as they are especially prone to infection with the dangerous H5N1
Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 (A/H5N1) is a subtype of the influenza A virus which can cause illness in humans and many other animal species. A bird-adapted strain of H5N1, called HPAI A(H5N1) for highly pathogenic avian influenza virus of type ...
strain.
The females of many breeds of domestic ducks are unreliable at sitting their eggs and raising their young. Exceptions include the Rouen duck
The Rouen is a heavyweight breed of domesticated duck raised primarily for decoration, exhibition or as general purpose ducks. Since they are not prolific egg layers, Rouen ducks are most commonly bred for their meat. The breed originated in ...
and especially the Muscovy duck. It has been a custom on farms for centuries to put duck eggs under broody hens for hatching; nowadays this role is often played by an incubator
An incubator is anything that performs or facilitates various forms of incubation, and may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* Incubator (culture), a device used to grow and maintain microbiological cultures or cell cultures
* Incubator (egg), a de ...
. However, young ducklings rely on their mothers for a supply of preen oil
The uropygial gland, informally known as the preen gland or the oil gland, is a bilobed sebaceous gland possessed by the majority of birds used to distribute the gland's oil through the plumage by means of preening. It is located dorsally at th ...
to make them waterproof; a chicken hen does not make as much preen oil as a female duck, and an incubator makes none. Once the duckling grows its own feathers, it produces preen oil from the sebaceous gland near the base of its tail.
Ducks are also kept for their ornamental value. Breeds have been developed with crests and tufts or striking plumage, for exhibition in competitions.
In culture
In children's stories
 The domestic duck has appeared numerous times in children's stories.
The domestic duck has appeared numerous times in children's stories. Beatrix Potter
Helen Beatrix Potter (, 28 July 186622 December 1943) was an English writer, illustrator, natural scientist, and conservationist. She is best known for her children's books featuring animals, such as '' The Tale of Peter Rabbit'', which was ...
's ''The Tale of Jemima Puddle-Duck
''The Tale of Jemima Puddle-Duck'' is a children's book written and illustrated by Beatrix Potter. It was first published by Frederick Warne & Co. in July 1908. Potter composed the book at Hill Top, a working farm in the Lake District sh ...
'' was published by Frederick Warne & Co
Frederick Warne & Co. is a British publisher founded in 1865. It is known for children's books, particularly those of Beatrix Potter, and for its Observer's Books.
Warne is an imprint of Penguin Random House, a subsidiary of German media cong ...
in 1908. One of Potter's best-known books, the tale was included in the Royal Ballet's ''The Tales of Beatrix Potter
''The Tales of Beatrix Potter'' (US title: ''Peter Rabbit and Tales of Beatrix Potter'') is a 1971 ballet film based on the children's stories of English author and illustrator Beatrix Potter. The film was directed by Reginald Mills, choreograp ...
.'' It is the story of how Jemima, a domestic duck, is saved from a cunning fox who plans to kill her, when she tries to find a safe place for her eggs to hatch.
''Make Way for Ducklings
''Make Way for Ducklings'' is a children's picture book written and illustrated by Robert McCloskey. First published in 1941 by the Viking Press, the book tells the story of a pair of mallards who raise their brood of ducklings on an island in t ...
'' is a children's picture book written and illustrated by Robert McCloskey. First published in 1941, the book tells the story of a pair of mallards who decide to raise their family on an island in the lagoon in Boston Public Garden, a park in the center of Boston. ''Make Way for Ducklings'' won the 1942 Caldecott Medal
The Randolph Caldecott Medal, frequently shortened to just the Caldecott, annually recognizes the preceding year's "most distinguished American picture book for children". It is awarded to the illustrator by the Association for Library Servic ...
for McCloskey's illustrations.
The Disney
The Walt Disney Company, commonly known as Disney (), is an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios complex in Burbank, California. Disney was originally founded on October ...
cartoon character Donald Duck
Donald Fauntleroy Duck is a cartoon character created by The Walt Disney Company. Donald is an anthropomorphic white duck with a yellow-orange bill, legs, and feet. He typically wears a sailor shirt and cap with a bow tie. Donald is known fo ...
, one of the world's most recognizable pop culture icons, is a domestic duck of the American Pekin
The Pekin or White Pekin is an American breed of domestic duck, raised primarily for meat. It derives from birds brought to the United States from China in the nineteenth century, and is now bred in many parts of the world. It is often known a ...
breed.
In music
The domestic duck features in the musical composition ''Peter and the Wolf
''Peter and the Wolf'' ( rus, Петя и Bолк, r="Pétya i volk", p=ˈpʲetʲə i volk, links=no) Op. 67, a "symphonic fairy tale for children", is a musical composition written by Sergei Prokofiev in 1936. The narrator tells a children's s ...
'', written by Sergei Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''., group=n (27 April .S. 15 April1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, ...
in 1936. The orchestra illustrates the children's story
"Children's Story" is a song recorded by British-American hip hop artist Slick Rick. Taken as the second single from his album ''The Great Adventures of Slick Rick'', the song was a Top 5 hit on both the Hot R&B Singles and the Hot Rap Tracks ...
while the narrator tells it. In this, a domestic duck and a little bird argue on each other's flight capabilities. The duck is represented by the oboe
The oboe ( ) is a type of double reed woodwind instrument. Oboes are usually made of wood, but may also be made of synthetic materials, such as plastic, resin, or hybrid composites. The most common oboe plays in the treble or soprano range.
...
. The story ends with the wolf eating the duck alive, its quack heard from inside the wolf's belly.
In art
Domestic ducks are frequently depicted in wall paintings and grave objects from ancient Egypt. They are featured in a range of ancient artefacts, which revealed that they were a fertility symbol.As food
Since ancient times, the duck has been eaten as food. Usually only the breast and thigh meat is eaten. It does not need to behung
Hung may refer to:
People
* Hung (surname), various Chinese surnames
* Hùng king, a king of Vietnam
People with the given name Hung include:
* Hung Huynh, Vietnamese-American chef, winner of the third season of the television show ''Top Chef''
...
before preparation, and is often braised or roasted, sometimes flavoured with bitter orange
Bitter orange, Seville orange, bigarade orange, or marmalade orange is the citrus tree ''Citrus'' × ''aurantium'' and its fruit. It is native to Southeast Asia and has been spread by humans to many parts of the world. It is probably a cross be ...
or with port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as H ...
. Peking duck
Peking duck is a dish from Beijing (Peking) that has been prepared since the Imperial era. The meat is characterized by its thin, crispy skin, with authentic versions of the dish serving mostly the skin and little meat, sliced in front of the di ...
is a dish of roast duck from Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the Capital city, capital of the China, People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's Li ...
, China, that has been prepared since medieval times. It is today traditionally served with spring pancake
The spring pancake () is a traditional Chinese food unique to the northern regions. People eat spring pancakes on the day called lichun to celebrate the beginning of the spring.
The spring pancake took its rise from the Jin dynasty and has pr ...
s, spring onion
Scallions (also known as spring onions or green onions) are vegetables derived from various species in the genus ''Allium''. Scallions generally have a milder taste than most onions and their close relatives include garlic, shallot, leek, chi ...
s and sweet bean sauce
Tianmian sauce (), also known as sweet bean sauce, sweet flour sauce or sweet wheat paste, is a thick, smooth, dark brown or black paste with either a mild, savory or sweet flavor. It is commonly used in Northern Chinese cuisine, Northeastern ...
.
See also
* Domestic Muscovy duckReferences
External links
Duck and Goose from Farm to Table
factsheet from
USDA
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of comme ...
{{Authority control
Domesticated birds
Ducks
Poultry
Birds described in 1758
Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus