Diverticulitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Diverticulitis, specifically colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by
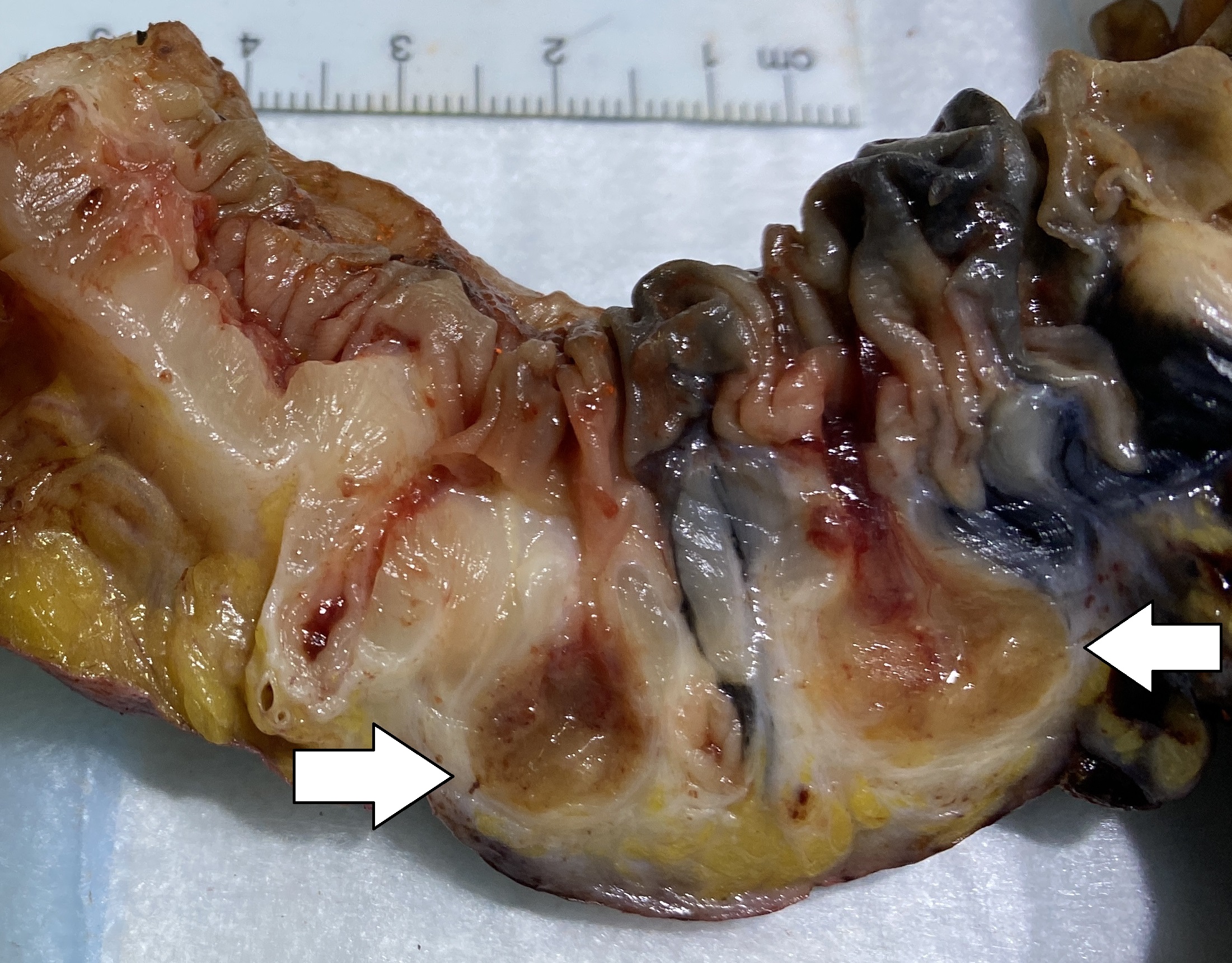 In complicated diverticulitis, an inflamed diverticulum can rupture, allowing
In complicated diverticulitis, an inflamed diverticulum can rupture, allowing


 People with the above symptoms are commonly studied with computed tomography, or a CT scan. Ultrasound can provide preliminary investigation for diverticulitis. Amongst the findings that can be seen on ultrasound is non-compressing outpouching of bowel wall, hypoechoic and thickened wall, or there is obstructive
People with the above symptoms are commonly studied with computed tomography, or a CT scan. Ultrasound can provide preliminary investigation for diverticulitis. Amongst the findings that can be seen on ultrasound is non-compressing outpouching of bowel wall, hypoechoic and thickened wall, or there is obstructive
Berger D, Erstad D J. Laparoscopic Low Anterior Resection for Diverticulitis. J Med Ins. 2015;2015(87) doi:https://jomi.com/article/87 With abscess confirmed by CT scan, some evidence and clinical guidelines tentatively support the use of oral or IV antibiotics for smaller abscesses (<5 cm) without systemic inflammation, but percutaneous or laparoscopic drainage may be necessary for larger abscesses (>5 cm). Emergency surgery is required for perforated diverticulitis with peritonitis.
Diverticulosis and diverticulitis
at NIDDK
Diverticulitis
at Mayo Clinic
Staging of Acute Diverticulitis
archive of link above {{Gastroenterology Diseases of intestines Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate
inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
of abnormal pouches— diverticula—which can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lower abdominal pain of sudden onset, but the onset may also occur over a few days. There may also be nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of th ...
; and diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
or constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel moveme ...
. Fever or blood in the stool suggests a complication. Repeated attacks may occur.
The causes of diverticulitis are unclear. Risk factors may include obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
, lack of exercise, smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have b ...
, a family history of the disease, and use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The role of a low fiber diet as a risk factor is unclear. Having pouches in the large intestine that are not inflamed is known as diverticulosis
Diverticulosis is the condition of having multiple pouches ( diverticula) in the colon that are not inflamed. These are outpockets of the colonic mucosa and submucosa through weaknesses of muscle layers in the colon wall. Diverticula do not ...
. Inflammation occurs in between 10% and 25% at some point in time, and is due to a bacterial infection. Diagnosis is typically by CT scan, though blood tests, colonoscopy, or a lower gastrointestinal series may also be supportive. The differential diagnoses include irritable bowel syndrome.
Preventive measures include altering risk factors such as obesity, inactivity, and smoking. Mesalazine and rifaximin appear useful for preventing attacks in those with diverticulosis. Avoiding nuts and seeds as a preventive measure is no longer recommended since there is no evidence these play a role in initiating inflammation in diverticula. For mild diverticulitis, antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s by mouth and a liquid diet are recommended. For severe cases, intravenous antibiotics, hospital admission, and complete bowel rest may be recommended. Probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host i ...
s are of unclear value. Complications such as abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
formation, fistula formation, and perforation of the colon may require surgery.
The disease is common in the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
and uncommon in Africa and Asia. In the Western world about 35% of people have diverticulosis while it affects less than 1% of those in rural Africa, and 4 to 15% of those may go on to develop diverticulitis. In North America and Europe the abdominal pain is usually on the left lower side ( sigmoid colon), while in Asia it is usually on the right ( ascending colon). The disease becomes more frequent with age, ranging from 5% for those under 40 years of age to 50% over the age of 60. It has also become more common in all parts of the world. In 2003 in Europe, it resulted in approximately 13,000 deaths. It is the most frequent anatomic disease of the colon. Costs associated with diverticular disease were around US $2.4 billion a year in the United States in 2013.
Signs and symptoms
Diverticulitis typically presents with lower quadrant abdominal pain of a sudden onset. Patients commonly have elevated C-reactive protein and a high white blood cell count. In North America and Europe the abdominal pain is usually on the left lower side (sigmoid colon), while in Asia it is usually on the right (ascending colon). There may also befever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of th ...
, diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
or constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel moveme ...
, and blood in the stool.
Complications
 In complicated diverticulitis, an inflamed diverticulum can rupture, allowing
In complicated diverticulitis, an inflamed diverticulum can rupture, allowing bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
to subsequently infect externally from the colon. If the infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
spreads to the lining of the abdominal cavity (the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mes ...
), peritonitis results. Sometimes, inflamed diverticula can cause narrowing of the bowel, leading to an obstruction. In some cases, the affected part of the colon adheres to the bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine en ...
or other organs in the pelvic cavity, causing a fistula, or creating an abnormal connection between an organ and adjacent structure or another organ (in the case of diverticulitis, the colon, and an adjacent organ).Related pathologies may include:
* Bowel obstruction
* Peritonitis
* Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
* Fistula
* Bleeding
* Strictures
Causes
The causes of diverticulitis are poorly understood, with approximately 40 percent due to genes and 60 percent due to environmental factors. Conditions that increase the risk of developing diverticulitis include arterial hypertension and immunosuppression.Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
is another risk factor. Low levels of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of Lipophilicity, fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group ar ...
are associated with an increased risk of diverticulitis.
Diet
It is unclear what roledietary fiber
Dietary fiber (in British English fibre) or roughage is the portion of plant-derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Dietary fibers are diverse in chemical composition, and can be grouped generally by t ...
plays in diverticulitis. It is often stated that a diet low in fiber is a risk factor; however, the evidence to support this is unclear. There is no evidence to suggest that the avoidance of nuts and seeds prevents the progression of diverticulosis to an acute case of diverticulitis. In fact, it appears that a higher intake of nuts and corn could help to avoid diverticulitis in adult males.
Pathology
Right-sided diverticula are micro-hernias of the colonic mucosa and submucosa through the colonic muscular layer where blood vessels penetrate it. Left-sided diverticula are pseudodiverticula, since the herniation is not through all the layers of the colon. Diverticulitis is postulated to develop because of changes inside the colon, including high pressures because of abnormally vigorous contractions.Diagnosis


 People with the above symptoms are commonly studied with computed tomography, or a CT scan. Ultrasound can provide preliminary investigation for diverticulitis. Amongst the findings that can be seen on ultrasound is non-compressing outpouching of bowel wall, hypoechoic and thickened wall, or there is obstructive
People with the above symptoms are commonly studied with computed tomography, or a CT scan. Ultrasound can provide preliminary investigation for diverticulitis. Amongst the findings that can be seen on ultrasound is non-compressing outpouching of bowel wall, hypoechoic and thickened wall, or there is obstructive fecalith
A fecalith is a stone made of feces. It is a hardening of feces into lumps of varying size and may occur anywhere in the intestinal tract but is typically found in the colon. It is also called appendicolith when it occurs in the appendix and is ...
at the bowel wall. Besides, bowel wall oedema with adjacent hyperechoic mesentery
The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intesti ...
can also be seen on ultrasound. However, CT scan is the mainstay of diagnosing diverticulitis and its complications. The diagnosis of acute diverticulitis is made confidently when the involved segment contains diverticula. CT images reveal localized colon wall thickening, with inflammation extending into the fat surrounding the colon. Amongst the complications that can be seen on CT scan are: abscesses, perforation, pylephlebitis, intestinal obstruction, bleeding, and fistula.
Barium enema and colonoscopy are contraindicated in the acute phase of diverticulitis because of the risk of perforation.
Classification by severity
Four classifications by severity have been published recently in the literature. The most recent and widely accepted is as follows: * Stage 0 – asymptomatic diverticulosis * Stage 1a – uncomplicated diverticulitis * Stage 1b – diverticulitis with phlegmonous peridiverticulitis * Stage 2a – diverticulitis with concealed perforation, and abscess with a diameter of one centimeter or less * Stage 2b – diverticulitis with abscess greater than one centimeter * Stage 3a – diverticulitis with symptoms but without complications * Stage 3b – relapsing diverticulitis without complications * Stage 3c – relapsing diverticulitis with complications The severity of diverticulitis can be radiographically graded by the Hinchey Classification.Differential diagnoses
The differential diagnoses includecolon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowe ...
, inflammatory bowel disease, ischemic colitis
Ischemic colitis (also spelled ischaemic colitis) is a medical condition in which inflammation and injury of the large intestine result from inadequate blood supply. Although uncommon in the general population, ischemic colitis occurs with greater ...
, and irritable bowel syndrome, as well as a number of urological and gynecological processes. In those with uncomplicated diverticulitis, cancer is present in less than 1% of people.
Treatment
Most cases of simple, uncomplicated diverticulitis respond to conservative therapy with bowel rest.Diet
People may be placed on alow-fiber diet
A low-residue diet is a diet intended to reduce certain constituents of the bowel, often with consequence for functional behaviour of the bowel. It may be prescribed for patients with ailments or functional gastrointestinal disorders mitigated ...
. It was previously thought that a low-fiber diet gives the colon adequate time to heal. Evidence tends to run counter to this, with a 2011 review finding no evidence for the superiority of low-fiber diets in treating diverticular disease, and that a high-fiber diet may prevent diverticular disease. A systematic review published in 2012 found no high-quality studies, but found that some studies and guidelines favour a high-fiber diet for the treatment of symptomatic disease. While it has been suggested that probiotics may be useful for treatment, the evidence currently neither supports nor refutes this claim.
Antibiotics
Mild uncomplicated diverticulitis without systemic inflammation should not be treated with antibiotics. For mild, uncomplicated, and non-purulent cases of acute diverticulitis, symptomatic treatment, IV fluids, and bowel rest have no worse outcome than surgical intervention in the short and medium term, and appear to have the same outcomes at 24 months.Berger D, Erstad D J. Laparoscopic Low Anterior Resection for Diverticulitis. J Med Ins. 2015;2015(87) doi:https://jomi.com/article/87 With abscess confirmed by CT scan, some evidence and clinical guidelines tentatively support the use of oral or IV antibiotics for smaller abscesses (<5 cm) without systemic inflammation, but percutaneous or laparoscopic drainage may be necessary for larger abscesses (>5 cm). Emergency surgery is required for perforated diverticulitis with peritonitis.
Surgery
Indications for surgery areabscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
or fistula formation; and intestinal rupture with peritonitis. These, however, rarely occur. Surgery for abscess or fistula is indicated either urgently or electively. The timing of the elective surgery is determined by evaluating factors such as the stage of the disease, the age of the person, their general medical condition, the severity and frequency of the attacks, and whether symptoms persist after the first acute (medicine), acute episode. In most cases, elective surgery is deemed to be indicated when the risks of the surgery are less than the risks of the complications of diverticulitis. Elective surgery is not indicated until at least six weeks after recovery from the acute event. Emergency surgery is indicated for an intestinal rupture with peritonitis.
Technique
The first surgical approach consists of resection and primary anastomosis. This first stage of surgery is performed on people if they have a well-vascularized, nonedematous, and tension-free bowel. The proximal margin should be an area of the pliable colon without hypertrophy or inflammation. The distal margin should extend to the upper third of the rectum where the taenia coalesces. Not all of the diverticula-bearing colon must be removed, since diverticula proximal to the descending or sigmoid colon are unlikely to result in further symptoms.Approach
Diverticulitis surgery consists of a bowel resection with or without colostomy. Either may be done by the traditionallaparotomy
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a surgical incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as a celiotomy.
Origins and history
The first successful laparotomy was performed without ane ...
or by laparoscopic surgery. The traditional bowel resection is made using an open surgical approach, called colectomy. During a colectomy, the person is placed under general anesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general ...
. A surgeon performing a colectomy will make a lower midline incision in the abdomen or a lateral lower transverse incision. The diseased section of the large intestine is removed, and then the two healthy ends are sewn or stapled back together. A colostomy may be performed when the bowel has to be relieved of its normal digestive work as it heals. A colostomy implies creating a temporary opening of the colon on the skin surface, and the end of the colon is passed through the abdominal wall with a removable bag attached to it. The waste is collected in the bag.
However, most surgeons prefer performing the bowel resection laparoscopically, mainly because postoperative pain is reduced with faster recovery. Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure in which three to four smaller incisions are made in the abdomen or navel
The navel (clinically known as the umbilicus, commonly known as the belly button or tummy button) is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord. All placental mammals have a navel, altho ...
. After incisions into the abdomen are done, placement of trocars occurs which allows a camera and other equipment entry into the peritoneal cavity. The greater omentum is reflected and the affected section of the bowel is mobilized. Alternately, laparoscopic sigmoid resection (LSR) compared to open sigmoid resection (OSR) showed that LSR is not superior over OSR for acute symptomatic diverticulitis. Furthermore, laparoscopic lavage was as safe as resection for perforated diverticulitis with peritonitis.
Maneuvers
All colon surgery involves only three maneuvers that may vary in complexity depending on the region of the bowel and the nature of the disease. The maneuvers are the retraction of the colon, the division of the attachments to the colon, and the dissection of themesentery
The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intesti ...
. After the resection of the colon, the surgeon normally divides the attachments to the liver and the small intestine. After the mesenteric vessels are dissected, the colon is divided with special surgical staplers that close off the bowel while cutting between the staple lines. After resection of the affected bowel segment, an anvil and spike are used to anastomose the remaining segments of the bowel. Anastomosis is confirmed by filling the cavity with normal saline and checking for any air bubbles.
Bowel resection with colostomy
When excessive inflammation of the colon renders primary bowel resection too risky, bowel resection with colostomy remains an option. Also known as the Hartmann's operation, this is a more complicated surgery typically reserved for life-threatening cases. The bowel resection with colostomy implies a temporary colostomy which is followed by a second operation to reverse the colostomy. The surgeon makes an opening in the abdominal wall (a colostomy) which helps clear the infection and inflammation. The colon is brought through the opening and all waste is collected in an external bag. The colostomy is usually temporary, but it may be permanent, depending on the severity of the case. In most cases several months later, after the inflammation has healed, the person undergoes another major surgery, during which the surgeon rejoins the colon and rectum and reverses the colostomy.Epidemiology
Diverticulitis most often affects the elderly. In Western countries, diverticular disease most commonly involves the sigmoid colon (95 percent of people with diverticulitis). Diverticulosis affects 5% to 45% of individuals with the prevalence of diverticulosis increasing with age from under 20% of individuals affected at age 40 up to 60% of individuals affected by age 60. Left-sided diverticular disease (involving the sigmoid colon) is most common in the West, while right-sided diverticular disease (involving the ascending colon) is more common in Asia and Africa. Among people with diverticulosis, 4 to 15% may go on to develop diverticulitis.References
External links
Diverticulosis and diverticulitis
at NIDDK
Diverticulitis
at Mayo Clinic
Staging of Acute Diverticulitis
archive of link above {{Gastroenterology Diseases of intestines Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate