Disaster recovery plan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Given organizations' increasing dependency on information technology to run their operations,
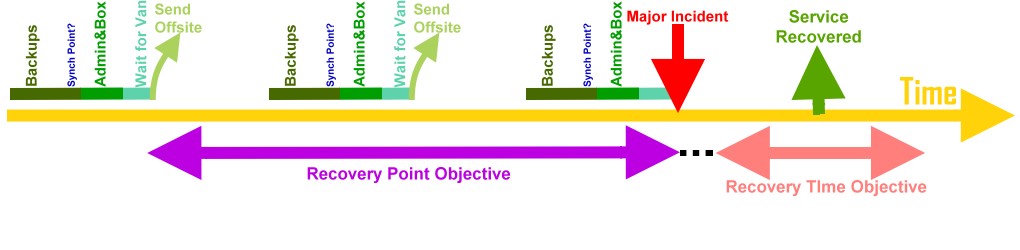 Minimizing downtime and data loss during disaster recovery is measured in terms of two concepts:
* Recovery Time Objective (RTO), time until a system is completely up and running
* Recovery Point Objective (RPO), a measure of the ability to recover files by specifying a point in time restore of the backup copy.
Minimizing downtime and data loss during disaster recovery is measured in terms of two concepts:
* Recovery Time Objective (RTO), time until a system is completely up and running
* Recovery Point Objective (RPO), a measure of the ability to recover files by specifying a point in time restore of the backup copy.
Business continuity planning
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning (or business continuity a ...
covers the entire organization, and Disaster recovery
Disaster recovery is the process of maintaining or reestablishing vital infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster, such as a storm or battle.It employs policies, tools, and procedures. Disaster recovery focuses on ...
focuses on ''IT''.
Auditing
An audit is an "independent examination of financial information of any entity, whether profit oriented or not, irrespective of its size or legal form when such an examination is conducted with a view to express an opinion thereon.” Auditing ...
of documents covering an organization's ''business continuity'' and ''disaster recovery'' plans provides a third-party validation to stakeholders that the documentation is complete and does not contain material
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geolo ...
misrepresentations.
Lack of completeness can result in overlooking secondary effects, such as when vastly increased work-at-home overloads incoming recovery site telecommunications capacity, and the bi-weekly payroll that was not critical within the first 48 hours is now causing perceived problems in ever recovering, complicated by governmental and possibly union reaction.
Overview
Often used together, the terms Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery are very different. Business Continuity refers to the ability of a business to continue critical functions and business processes after the occurrence of a disaster, whereas Disaster Recovery refers specifically to the Information Technology (IT) and data-centric functions of the business, and is a subset of Business Continuity.Metrics
The primary objective is to protect the organization in the event that all or part of its operations and/or computer services are rendered partially or completely unusable. Minimizing downtime and data loss during disaster recovery is measured in terms of two concepts:
* Recovery Time Objective (RTO), time until a system is completely up and running
* Recovery Point Objective (RPO), a measure of the ability to recover files by specifying a point in time restore of the backup copy.
Minimizing downtime and data loss during disaster recovery is measured in terms of two concepts:
* Recovery Time Objective (RTO), time until a system is completely up and running
* Recovery Point Objective (RPO), a measure of the ability to recover files by specifying a point in time restore of the backup copy.
The auditor's role
An auditor examines and assesses * the procedures stated in the BCP and DR plan are actually consistent with real practice * a specific individual within the organization, who may be referred to as the disaster recovery officer, the disaster recovery liaison, the DR coordinator, or some other similar title, has the technical skills, training, experience, and abilities to analyze the capabilities of the team members to complete assigned tasks * more than one individual is trained and capable of doing a particular function during the Disaster Recovery exercise. Tests and inquiries of personnel can help achieve this objective.Documentation
To maximize their effectiveness, disaster recovery plans are most effective when updated frequently, and should: * be an integral part of allbusiness analysis
Business analysis is a professional discipline of identifying business needs and determining solutions to business problems. Solutions often include a software-systems development component, but may also consist of process improvements, organiza ...
processes,
* be revisited at every major corporate acquisition, at every new product launch and at every new system development milestone.
Adequate records need to be retained by the organization. The auditor examines records, billings, and contracts to verify that records are being kept. One such record is a current list of the organization's hardware and software vendors. Such list is made and periodically updated to reflect changing business practice. Copies of it are stored on and off site and are made available or accessible to those who require them. An auditor tests the procedures used to meet this objective and determine their effectiveness.
Disaster recovery plan
A disaster recovery plan (DRP) is a documented process or set of procedures to execute an organization'sdisaster recovery
Disaster recovery is the process of maintaining or reestablishing vital infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster, such as a storm or battle.It employs policies, tools, and procedures. Disaster recovery focuses on ...
processes and recover and protect a business IT infrastructure in the event of a disaster
A disaster is a serious problem occurring over a short or long period of time that causes widespread human, material, economic or environmental loss which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources ...
. It is "a comprehensive statement of consistent actions to be taken before, during and after a disaster". The disaster could be natural
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans ar ...
, environmental
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scal ...
or man-made
Artificiality (the state of being artificial or manmade) is the state of being the product of intentional human manufacture, rather than occurring naturally through processes not involving or requiring human activity.
Connotations
Artificiality ...
. Man-made disasters could be intentional (for example, an act of a terrorist) or unintentional (that is, accidental, such as the breakage of a man-made dam or even "fat fingers" - or errant commands entered - on a computer system).
Types of plans
Although there is no one-size-fits-all plan, there are three basic strategies: # prevention, including proper backups, having surge protectors and generators # detection, a byproduct of routine inspections, which may discover new (potential) threats # correction The latter may include securing properinsurance policies
In insurance, the insurance policy is a contract (generally a standard form contract) between the insurer and the policyholder, which determines the claims which the insurer is legally required to pay. In exchange for an initial payment, known as ...
, and holding a "lessons learned" brainstorming session.
Relationship to the Business Continuity Plan
Disaster recovery is asubset
In mathematics, set ''A'' is a subset of a set ''B'' if all elements of ''A'' are also elements of ''B''; ''B'' is then a superset of ''A''. It is possible for ''A'' and ''B'' to be equal; if they are unequal, then ''A'' is a proper subset of ...
of business continuity. Where DRP encompasses the policies, tools and procedures to enable recovery of data following a catastrophic event, business continuity planning
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning (or business continuity a ...
(BCP) involves keeping all aspects of a business functioning regardless of potential disruptive events. As such, a business continuity plan is a comprehensive organizational strategy that includes the DRP as well as threat prevention, detection, recovery, and resumption of operations should a data breach or other disaster event occur. Therefore, BCP consists of five component plans:
* Business Resumption Plan
* Occupant Emergency Plan
* Continuity of Operations Plan
* Incident Management Plan
* Disaster Recovery Plan
The first three components (Business Resumption, Occupant Emergency, and Continuity of Operations Plans) do not deal with the IT infrastructure. The Incident Management Plan (IMP) does deal with the IT infrastructure, but since it establishes structure and procedures to address cyber attacks against an organization’s IT systems, it generally does not represent an agent for activating the Disaster Recovery Plan, leaving The Disaster Recovery Plan as the only BCP component of interest to IT.
Benefits
Like every insurance plan, there are benefits that can be obtained from proper business continuity planning, including: * Minimizing risk of delays * Guaranteeing the reliability of standby systems (even automating the failure detection and recovery in certain scenarios) * Providing a standard for testing the plan * Minimizing decision-making during a disaster * Reducing potential legal liabilities * Lowering unnecessarily stressful work environmentPlanning and testing methodology
According to Geoffrey H. Wold of the Disaster Recovery Journal, the entire process involved in developing a Disaster Recovery Plan consists of 10 steps: * Performing a risk assessment: The planning committee prepares a risk analysis and a business impact analysis (BIA) that includes a range of possible disasters. Each functional area of the organization is analyzed to determine potential consequences. Traditionally, fire has posed the greatest threat. A thorough plan provides for "worst case" situations, such as destruction of the main building. * Establishing priorities for processing and operations: Critical needs of each department are evaluated and prioritized. Writtenagreements Agreement may refer to:
Agreements between people and organizations
* Gentlemen's agreement, not enforceable by law
* Trade agreement, between countries
* Consensus, a decision-making process
* Contract, enforceable in a court of law
** Meeting of ...
for alternatives selected are prepared, with details specifying duration, termination conditions, system testing
System testing is testing conducted on a complete integrated system to evaluate the system's compliance with its specified requirements.
System testing takes, as its input, all of the integrated components that have passed integration testing. ...
, cost
In production, research, retail, and accounting, a cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in whic ...
, any special security procedures, procedure for the notification of system changes, hours of operation, the specific hardware and other equipment required for processing, personnel requirements, definition of the circumstances constituting an emergency
An emergency is an urgent, unexpected, and usually dangerous situation that poses an immediate risk to health, life, property, or environment and requires immediate action. Most emergencies require urgent intervention to prevent a worsening ...
, process to negotiate service extensions, guarantee of compatibility
Compatibility may refer to:
Computing
* Backward compatibility, in which newer devices can understand data generated by older devices
* Compatibility card, an expansion card for hardware emulation of another device
* Compatibility layer, compon ...
, availability
In reliability engineering, the term availability has the following meanings:
* The degree to which a system, subsystem or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at ...
, non-mainframe resource requirements, priorities, and other contractual issues.
* Collecting data: This includes various lists (employee backup position listing, critical telephone numbers list, master call list, master vendor list, notification checklist), inventories (communications equipment, documentation, office equipment, forms, insurance policies
In insurance, the insurance policy is a contract (generally a standard form contract) between the insurer and the policyholder, which determines the claims which the insurer is legally required to pay. In exchange for an initial payment, known as ...
, workgroup and data center computer hardware, microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PC ...
hardware and software, office supply, off-site storage location equipment, telephones, etc.), distribution register, software and data files backup/retention schedules, temporary location specifications, any other such lists, materials, inventories, and documentation. Pre-formatted forms are often used to facilitate the data gathering process.
* Organizing and documenting a written plan
* Developing testing criteria and procedures: reasons for testing include
** Determining the feasibility and compatibility of backup facilities and procedures.
** Identifying areas in the plan that need modification.
** Providing training to the team managers and team members.
** Demonstrating the ability of the organization to recover.
** Providing motivation for maintaining and updating the disaster recovery plan.
* Testing the plan: An initial "dry run
Dry run may refer to:
* Dry run (testing), a testing process
* Dry run (terrorism), a test by a terrorist organization to examine the reaction to an attempted attack
Places in the United States Settlements
* Dry Run, Ohio, a census-designated p ...
" of the plan is performed by conducting a structured walk-through test. An actual test-run must be performed. Problems are corrected.
Initial testing can be plan is done in sections and after normal business hours to minimize disruptions.
Subsequent tests occur during normal business hours.
Types of tests include: checklist tests, simulation tests, parallel tests, and full interruption tests.
Caveats/controversies
Due to high cost, various plans are not without critics.Dell
Dell is an American based technology company. It develops, sells, repairs, and supports computers and related products and services. Dell is owned by its parent company, Dell Technologies.
Dell sells personal computers (PCs), servers, data ...
has identified five "common mistakes" organizations often make related to BCP/DR planning:
* Lack of buy-in: When executive management sees DR planning as "just another fake earthquake drill" or CEOs fail to make DR planning and preparation a priority
* Incomplete RTOs and RPOs: Failure to include each and every important business process or a block of data. Ripples can extend a disaster's impact. Payroll may not initially be mission-critical, but left alone for several days, it can become more important than any of your initial problems.
* Systems myopia: A third point of failure involves focusing only on DR without considering the larger business continuity needs. Corporate office space lost to a disaster can result in an instant pool of teleworkers which, in turn, can overload a company's VPN
A virtual private network (VPN) extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network. The be ...
overnight, overwork the IT support staff at the blink of an eye and cause serious bottlenecks and monopolies with the dial-in PBX system.
* Lax security: When there is a disaster, an organization's data and business processes become vulnerable. As such, security can be more important than the raw speed involved in a disaster recovery plan's RTO. The most critical consideration then becomes securing the new data pipelines: from new VPNs to the connection from offsite backup services.
** In disasters, planning for post-mortem forensics
** Locking down or remotely wiping lost handheld devices
Decisions and strategies
* Site designation: hot site vs. cold site. A hot site is fully equipped to resume operations while a cold site does not have that capability. A warm site has the capability to resume some, but not all operations. : A cost-benefit analysis is needed. :* Occasional tests and trials verify the viability and effectiveness of the plan. An auditor looks into the probability that operations of the organization can be sustained at the level that is assumed in the plan, and the ability of the entity to actually establish operations at the site. :* The auditor can verify this through paper and paperless documentation and actual physical observation. Thesecurity" \n\n\nsecurity.txt is a proposed standard for websites' security information that is meant to allow security researchers to easily report security vulnerabilities. The standard prescribes a text file called \"security.txt\" in the well known locat ...
of the storage site is also confirmed.
* Data backup: An audit of backup processes determines if (a) they are effective, and (b) if they are actually being implemented by the involved personnel.Berman, Alan. : Constructing a Successful Business Continuity Plan. ''Business Insurance Magazine'', March 9, 2015. http://www.businessinsurance.com/article/20150309/ISSUE0401/303159991/constructing-a-successful-business-continuity-plan
:The disaster recovery plan also includes information on how best to recover any data that has not been copied. Controls and protections are put in place to ensure that data is not damaged, altered, or destroyed during this process.
* Drills: Practice drills conducted periodically to determine how effective the plan is and to determine what changes may be necessary. The auditor’s primary concern here is verifying that these drills are being conducted properly and that problems uncovered during these drills are addressed.
* Backup of key personnel - including periodic training
Training is teaching, or developing in oneself or others, any skills and knowledge or fitness that relate to specific useful competencies. Training has specific goals of improving one's capability, capacity, productivity and performance. I ...
, cross-training, and personnel redundancy.
Other considerations
Insurance issues
The auditor determines the adequacy of the company'sinsurance
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge ...
coverage (particularly property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, r ...
and casualty insurance Casualty insurance is a defined term which broadly encompasses insurance not directly concerned with life insurance, health insurance, or property insurance.
Casualty insurance is mainly liability coverage of an individual or organization for ne ...
) through a review of the company's insurance policies
In insurance, the insurance policy is a contract (generally a standard form contract) between the insurer and the policyholder, which determines the claims which the insurer is legally required to pay. In exchange for an initial payment, known as ...
and other research. Among the items that the auditor needs to verify are: the scope of the policy (including any stated exclusions), that the amount of coverage is sufficient to cover the organization’s needs, and that the policy is current and in force. The auditor also ascertains, through a review of the ratings assigned by independent rating agencies, that the insurance company or companies providing the coverage have the financial viability to cover the losses in the event of a disaster.
Effective DR plans take into account the extent of a company's responsibilities to other entities and its ability to fulfill those commitments despite a major disaster. A good DR audit will include a review of existing MOA
Moa are extinct giant flightless birds native to New Zealand.
The term has also come to be used for chicken in many Polynesian cultures and is found in the names of many chicken recipes, such as
Kale moa and Moa Samoa.
Moa or MOA may also refe ...
and contract
A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations between them. A contract typically involves the transfer of goods, services, money, or a promise to tr ...
s to ensure that the organization's legal liability for lack of performance in the event of disaster
A disaster is a serious problem occurring over a short or long period of time that causes widespread human, material, economic or environmental loss which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources ...
or any other unusual circumstance is minimized. Agreements pertaining to establishing support and assisting with recovery for the entity are also outlined. Techniques used for evaluating this area include an examination of the reasonableness of the plan, a determination of whether or not the plan takes all factors into account, and a verification of the contracts and agreements reasonableness through documentation and outside research.
Communication issues
The auditor must verify that planning ensures that bothmanagement
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includes the activitie ...
and the recovery team have effective communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inqui ...
hardware, contact information for both internal communication and external issues, such as business partners and key customers.
Audit techniques include
* testing of procedures, interviewing employees, making comparison against the plans of other company and against industry standards,
* examining company manuals and other written procedures.
* direct observation that emergency telephone numbers are listed and easily accessible in the event of a disaster.
Emergency procedures
Procedures to sustain staff during a round-the clock disaster recovery effort are included in any good disaster recovery plan. Procedures for the stocking of food and water, capabilities of administeringCPR
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spont ...
/first aid
First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person with either a minor or serious illness or injury, with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, or to promote recovery. It includes initial i ...
, and dealing with family emergencies are clearly written and tested. This can generally be accomplished by the company through good training
Training is teaching, or developing in oneself or others, any skills and knowledge or fitness that relate to specific useful competencies. Training has specific goals of improving one's capability, capacity, productivity and performance. I ...
programs and a clear definition of job responsibilities. A review of the readiness capacity of a plan often includes tasks such as inquires of personnel, direct physical observation, and examination of training records and any certifications.
Environmental issues
The auditor must review procedures that take into account the possibility of power failures or other situations that are of a non-IT nature. *Flashlight
A flashlight (American English, US, Canadian English, Canada) or torch (British English, UK, Australian English, Australia) is a portable hand-held electric lamp. Formerly, the light source typically was a miniature incandescent light bulb, b ...
s and candle
A candle is an ignitable wick embedded in wax, or another flammable solid substance such as tallow, that provides light, and in some cases, a fragrance. A candle can also provide heat or a method of keeping time.
A person who makes candle ...
s may be needed.
* Safety
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
There are two slightly di ...
procedures in case of gas leaks, fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames ...
s or other such phenomena and PPE may be needed.
See also
*Backup rotation scheme
A backup rotation scheme is a system of backing up data to computer media (such as tapes) that minimizes, by re-use, the number of media used. The scheme determines how and when each piece of removable storage is used for a backup job and how lo ...
* Information technology audit
An information technology audit, or information systems audit, is an examination of the management controls within an Information technology (IT) infrastructure and business applications. The evaluation of evidence obtained determines if the inform ...
* Comparison of backup software
* Comparison of online backup services
This is a comparison of online backup services.
Online backup is a special kind of online storage service; however, various products that are designed for file storage may not have features or characteristics that others designed for backup have ...
* Vulnerability (computing)
Vulnerabilities are flaws in a computer system that weaken the overall security of the device/system. Vulnerabilities can be weaknesses in either the hardware itself, or the software that runs on the hardware. Vulnerabilities can be exploited by ...
References
* *