Diode Bridge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A diode bridge is a bridge rectifier circuit of four
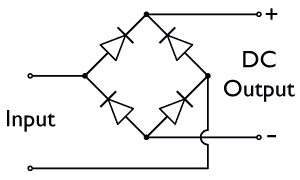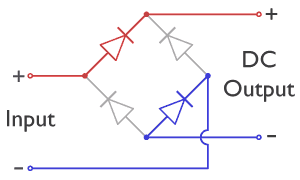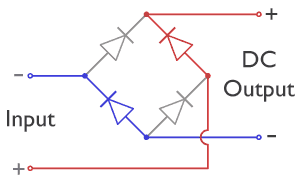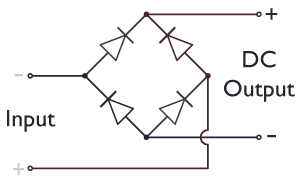 In each case, the upper right output remains positive, and lower right output negative. Since this is true whether the input is AC or DC, this circuit not only produces a DC output from an AC input, it can also provide what is sometimes called "reverse-polarity protection". That is, it permits normal functioning of DC-powered equipment when
In each case, the upper right output remains positive, and lower right output negative. Since this is true whether the input is AC or DC, this circuit not only produces a DC output from an AC input, it can also provide what is sometimes called "reverse-polarity protection". That is, it permits normal functioning of DC-powered equipment when

diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diod ...
s that is used in the process of converting alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which ...
(AC) from the input terminals to direct current (DC, i.e. fixed polarity
Polarity may refer to:
Science
*Electrical polarity, direction of electrical current
* Polarity (mutual inductance), the relationship between components such as transformer windings
* Polarity (projective geometry), in mathematics, a duality of or ...
) on the output terminals. Its function is to convert the negative-going AC pulses into positive going pulses, after which a low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filter de ...
can be used to smooth the result into DC.
When used in its most common application, for conversion of an alternating-current (AC) input into a direct-current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even ...
(DC) output, it is known as a bridge rectifier. A bridge rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an inver ...
provides full-wave rectification from a two-wire AC input, resulting in lower cost and weight as compared to a rectifier with a three-wire input from a transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's ...
with a center-tapped secondary winding.
The essential feature of a diode bridge is that the polarity of the output is the same regardless of the polarity at the input. The diode bridge circuit was invented by Polish electrotechnician Karol Pollak
Karol Franciszek Pollak (November 15, 1859 – December 17, 1928) was a Polish electrotechnician, inventor and businessman.
Early life
He was born in Sanok, Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, part of the Austrian Empire . His father was Karol ...
and patented in December 1895 in Great Britain and in January 1896 in Germany. In 1897, the German physicist Leo Graetz independently invented and published a similar circuit. Today the circuit is sometimes referred to as a Graetz circuit or Graetz bridge.
Prior to the availability of integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny M ...
s, a bridge rectifier was constructed from "discrete components", i.e., separate diodes. Since about 1950, a single four-terminal component containing the four diodes connected in a bridge configuration became a standard commercial component and is now available with various voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to mo ...
and current ratings.
Diodes are also used in bridge topologies along with capacitors as voltage multiplier 280px, Villard cascade voltage multiplier.
A voltage multiplier is an electrical circuit that converts AC electrical power from a lower voltage to a higher DC voltage, typically using a network of capacitors and diodes.
Voltage multipliers can be ...
s.
Current flow
According to the conventional model ofcurrent
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
flow (originally established by Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading intel ...
and still followed by most engineers today), current flows through electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. Electric current is gener ...
s from the ''positive'' to the ''negative'' pole (defined as "positive flow"). In actuality, free electrons in a conductor nearly always flow from the ''negative'' to the ''positive'' pole. In the vast majority of applications, however, the ''actual'' direction of current flow is irrelevant. Therefore, in the discussion below the conventional model is retained.
The fundamental characteristic of a diode is that current can flow only one way through it, which is defined as the forward direction. A diode bridge uses diodes as series components to allow current to pass in the forward direction during the positive part of the AC cycle and as shunt components to redirect current flowing in the reverse direction during the negative part of the AC cycle to the opposite rails.
Rectifier
In the diagrams below, when the input connected to the left corner of the diamond is ''positive'', and the input connected to the right corner is ''negative'', current flows from the ''upper'' supply terminal to the right along the ''red'' (positive) path to the output and returns to the lower supply terminal through the ''blue'' (negative) path. When the input connected to the left corner is ''negative'', and the input connected to the right corner is ''positive'', current flows from the ''lower'' supply terminal to the right along the ''red'' (positive) path to the output and returns to the upper supply terminal through the ''blue'' (negative) path.Sears, Francis W., Mark W. Zemansky and Hugh D. Young, ''University Physics'', Sixth Ed., Addison-Wesely Publishing Co., Inc., 1982, p. 685. In each case, the upper right output remains positive, and lower right output negative. Since this is true whether the input is AC or DC, this circuit not only produces a DC output from an AC input, it can also provide what is sometimes called "reverse-polarity protection". That is, it permits normal functioning of DC-powered equipment when
In each case, the upper right output remains positive, and lower right output negative. Since this is true whether the input is AC or DC, this circuit not only produces a DC output from an AC input, it can also provide what is sometimes called "reverse-polarity protection". That is, it permits normal functioning of DC-powered equipment when batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
have been installed backwards, or when the leads (wires) from a DC power source have been reversed, and protects the equipment from potential damage caused by reverse polarity.
Alternatives to the diode-bridge full-wave rectifiers are the center-tapped transformer and double-diode rectifier, and voltage doubler
A voltage doubler is an electronic circuit which charges capacitors from the input voltage and switches these charges in such a way that, in the ideal case, exactly twice the voltage is produced at the output as at its input.
The simplest of thes ...
rectifier using two diodes and two capacitors in a bridge topology.
Smoothing circuits
With AC input, the output of a diode bridge (called afull-wave rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an inver ...
for this purpose; there is also half-wave rectification, which does not use a diode bridge) is polarized pulsating non-sinusoidal voltage of the same amplitude but twice the frequency of the input. It may be considered as DC voltage upon which is superimposed a very large ripple voltage Ripple (specifically ripple voltage) in electronics is the residual periodic variation of the DC voltage within a power supply which has been derived from an alternating current (AC) source. This ripple is due to incomplete suppression of the alt ...
. This kind of electric power is not very usable, because ripple is dissipated as waste heat
Waste heat is heat that is produced by a machine, or other process that uses energy, as a byproduct of doing work. All such processes give off some waste heat as a fundamental result of the laws of thermodynamics. Waste heat has lower utility ( ...
in DC circuit components and may cause noise or distortion during circuit operation. So nearly all rectifiers are followed by a series of bandpass
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects (attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
Description
In electronics and signal processing, a filter is usually a two-po ...
or bandstop filters and/or a voltage regulator
A voltage regulator is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage. A voltage regulator may use a simple feed-forward design or may include negative feedback. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components ...
to convert most or all of the ripple voltage into a smoother and possibly higher DC output. A filter may be as simple as a single sufficiently large capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passivity (engineering), passive electronic component with two termi ...
or choke, but most power-supply filters have multiple alternating series and shunt components. When the ripple voltage rises, reactive power
Reactive may refer to:
*Generally, capable of having a reaction (disambiguation)
Reaction may refer to a process or to a response to an action, event, or exposure:
Physics and chemistry
*Chemical reaction
* Nuclear reaction
*Reaction (physics) ...
is stored in the filter components, reducing the voltage; when the ripple voltage falls, reactive power is discharged from the filter components, raising the voltage. The final stage of rectification may consist of a zener diode
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to reliably allow current to flow "backwards" (inverted polarity) when a certain set reverse voltage, known as the ''Zener voltage'', is reached.
Zener diodes are manufactured with a great var ...
-based voltage regulator, which almost completely eliminates any residual ripple.
Snubber circuits
Power-supply transformers have leakage inductance and parasitic capacitance. When the diodes in a bridge rectifier switch off, these "non-ideal" elements form a resonant circuit, which can oscillate at high frequency. This high-frequency oscillation can then couple into the rest of the circuitry. Snubber circuits are used in an attempt to mitigate this problem. A snubber circuit consists of either a very small capacitor or series capacitor and resistor across a diode.Polyphase diode bridges
The diode bridge can be generalized to rectify polyphase AC inputs. For example, for a three-phase AC input, a half-wave rectifier consists of three diodes, but a full-wave bridge rectifier consists of six diodes. A half-wave rectifier may be considered a wye connection (star connection), because it returns the current through the center (neutral) wire. A full-wave rectifier is more like adelta connection
Delta Connection is a regional airline brand name for Delta Air Lines, under which a number of individually owned regional airlines primarily operate short- and medium-haul routes. Mainline major air carriers often use regional airlines to oper ...
, although it can be connected to the three-phase source of either wye or delta and it does not use the center (neutral) wire.
See also
*1N400x general-purpose diodes
Woodbine Municipal Airport is a public use airport located two nautical miles (4 km) southeast of the central business district of Woodbine, in Cape May County, New Jersey, United States. The airport is owned by the Woodbine Port Auth ...
also called rectifier diodes
* Active rectification
Active rectification, or synchronous rectification, is a technique for improving the efficiency of rectification by replacing diodes with actively controlled switches, usually power MOSFETs or power bipolar junction transistors (BJT). Whereas nor ...
* HVDC converter An HVDC converter converts electric power from high voltage alternating current (AC) to high-voltage direct current (HVDC), or vice versa. HVDC is used as an alternative to AC for transmitting electrical energy over long distances or between AC powe ...
References
External links
{{Bridge circuits Bridge circuits Rectifiers