cure for cancer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cancer research is
 Cancer research has been ongoing for centuries. Early research focused on the causes of cancer. Percivall Pott identified the first environmental trigger (chimney soot) for cancer in 1775 and cigarette smoking was identified as a cause of lung cancer in 1950. Early cancer treatment focused on improving surgical techniques for removing tumors. Radiation therapy took hold in the 1900s. Chemotherapeutics were developed and refined throughout the 20th century.
The U.S. declared a "
Cancer research has been ongoing for centuries. Early research focused on the causes of cancer. Percivall Pott identified the first environmental trigger (chimney soot) for cancer in 1775 and cigarette smoking was identified as a cause of lung cancer in 1950. Early cancer treatment focused on improving surgical techniques for removing tumors. Radiation therapy took hold in the 1900s. Chemotherapeutics were developed and refined throughout the 20th century.
The U.S. declared a "
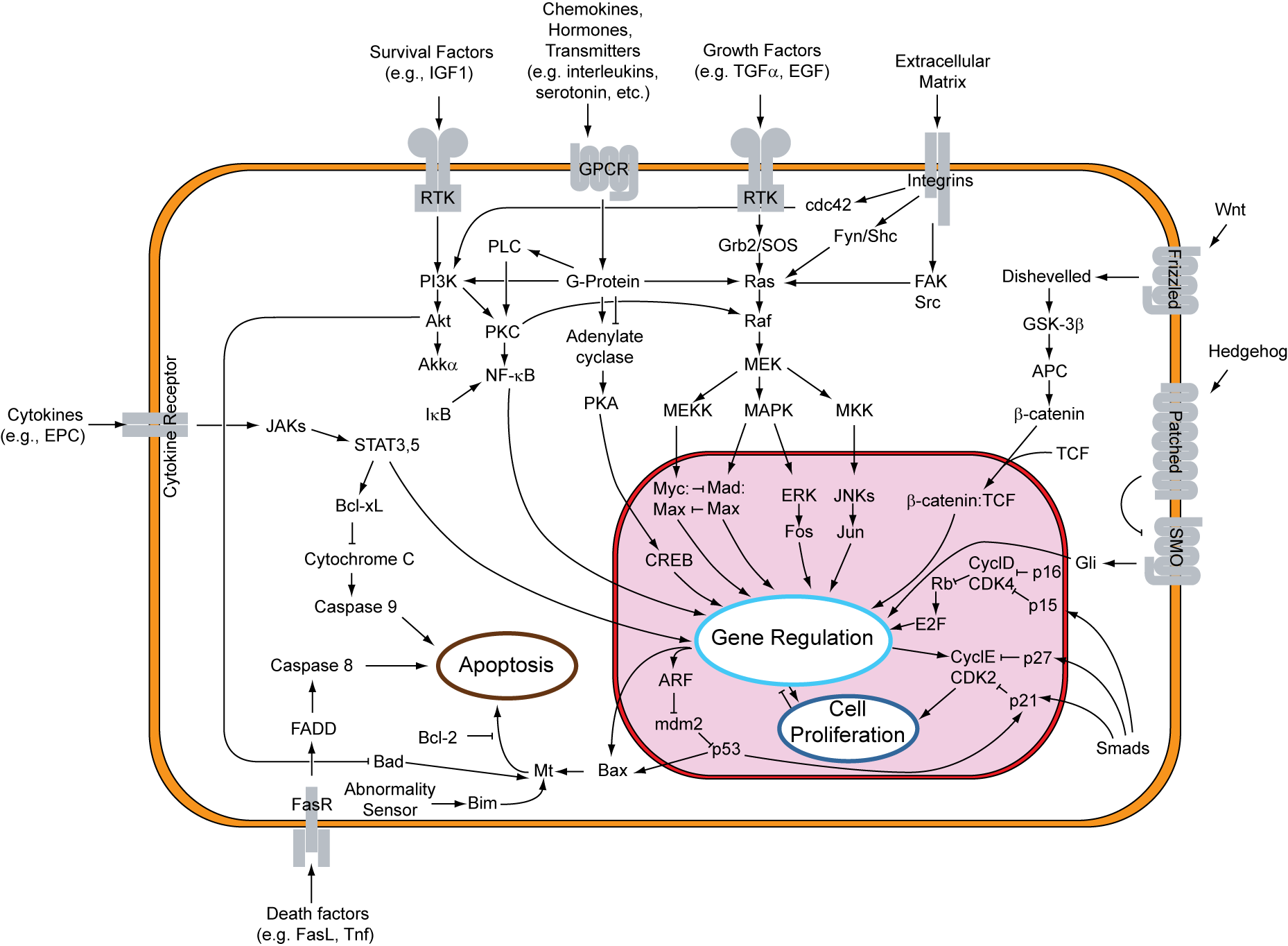 Research into the cause of cancer involves many different disciplines including genetics, diet, environmental factors (i.e. chemical
Research into the cause of cancer involves many different disciplines including genetics, diet, environmental factors (i.e. chemical
 Members of the public can also join
Members of the public can also join
 Organizations exist as associations for scientists participating in cancer research, such as the American Association for Cancer Research and
Organizations exist as associations for scientists participating in cancer research, such as the American Association for Cancer Research and
Cancer Genome Anatomy Project @ The NIH
The Integrative Cancer Biology Program @ National Cancer Institute
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cancer Research Cancer
research
Research is "creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness ...
into cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
to identify causes and develop strategies for prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and cure.
Cancer research ranges from epidemiology, molecular bioscience to the performance of clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, diet ...
s to evaluate and compare applications of the various cancer treatments. These applications include surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pa ...
, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Rad ...
, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemother ...
, hormone therapy, immunotherapy and combined treatment modalities such as chemo-radiotherapy. Starting in the mid-1990s, the emphasis in clinical cancer research shifted towards therapies derived from biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used ...
research, such as cancer immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy (sometimes called immuno-oncology) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer ...
and gene therapy
Gene therapy is a Medicine, medical field which focuses on the genetic modification of cells to produce a therapeutic effect or the treatment of disease by repairing or reconstructing defective genetic material. The first attempt at modifying ...
.
Cancer research is done in academia, research institutes, and corporate environments, and is largely government funded.
History
 Cancer research has been ongoing for centuries. Early research focused on the causes of cancer. Percivall Pott identified the first environmental trigger (chimney soot) for cancer in 1775 and cigarette smoking was identified as a cause of lung cancer in 1950. Early cancer treatment focused on improving surgical techniques for removing tumors. Radiation therapy took hold in the 1900s. Chemotherapeutics were developed and refined throughout the 20th century.
The U.S. declared a "
Cancer research has been ongoing for centuries. Early research focused on the causes of cancer. Percivall Pott identified the first environmental trigger (chimney soot) for cancer in 1775 and cigarette smoking was identified as a cause of lung cancer in 1950. Early cancer treatment focused on improving surgical techniques for removing tumors. Radiation therapy took hold in the 1900s. Chemotherapeutics were developed and refined throughout the 20th century.
The U.S. declared a "War on Cancer
The "war on cancer" is the effort to find a cure for cancer by increased research to improve the understanding of cancer biology and the development of more effective cancer treatments, such as targeted drug therapies. The aim of such efforts is ...
" in the 1970s, and increased the funding and support for cancer research.
Seminal papers
Some of the most highly cited and most influential research reports include: *'' The Hallmarks of Cancer'', published in 2000, and ''Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation'', published in 2011, by Douglas Hanahan and Robert Weinberg. Together, these articles have been cited in over 30,000 published papers.Types of research
Cancer research encompasses a variety of types and interdisciplinary areas of research. Scientists involved in cancer research may be trained in areas such aschemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, proper ...
, biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
, molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and phys ...
, physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemic ...
, medical physics
Medical physics deals with the application of the concepts and methods of physics to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of human diseases with a specific goal of improving human health and well-being. Since 2008, medical physics has been incl ...
, epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evi ...
, and biomedical engineering
Biomedical engineering (BME) or medical engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology for healthcare purposes (e.g., diagnostic or therapeutic). BME is also traditionally logical sciences ...
. Research performed on a foundational level is referred to as basic research and is intended to clarify scientific principles and mechanisms. Translational research aims to elucidate mechanisms of cancer development and progression and transform basic scientific findings into concepts that can be applicable to the treatment and prevention of cancer. Clinical research
Clinical research is a branch of healthcare science that determines the safety and effectiveness ( efficacy) of medications, devices, diagnostic products and treatment regimens intended for human use. These may be used for prevention, treat ...
is devoted to the development of pharmaceuticals, surgical procedures, and medical technologies for the eventual treatment of patients.
Prevention and epidemiology
Epidemiologic analysis indicates that at least 35% of all cancer deaths in the world could now be avoided by primary prevention.Song M, Vogelstein B, Giovannucci EL, Willett WC, Tomasetti C. Cancer prevention: Molecular and epidemiologic consensus. Science. 2018 Sep 28;361(6409):1317-1318. doi: 10.1126/science.aau3830. PMID: 30262488; PMCID: PMC6260589 According to a newer GBD systematic analysis, in 2019, ~44% of all cancer deaths – or ~4.5 M deaths or ~105 million lostdisability-adjusted life year
The disability-adjusted life year (DALY) is a measure of overall disease burden, expressed as the number of years lost due to ill-health, disability or early death. It was developed in the 1990s as a way of comparing the overall health and life ex ...
s – were due to known clearly preventable risk factors, led by smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have b ...
, alcohol use
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The cons ...
and high BMI. Furthermore, it is estimated that with further research cancer death rates could be reduced by 70% around the world even without the development of any new therapies. Cancer prevention research receives only 2 to 9% of global cancer research funding, albeit many of the options for prevention are already well-known without further cancer-specific research but are not reflected in economics and policy
Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an orga ...
.
Detection
Prompt detection of cancer is important, since it is usually more difficult to treat in later stages. Accurate detection of cancer is also important because false positives can cause harm from unnecessary medical procedures. Some screening protocols are currently not accurate (such as prostate-specific antigen testing). Others such as a colonoscopy or mammogram are unpleasant and as a result some patients may opt out. Active research is underway to address all these problems, to develop novel ways of cancer screening and to increase detection rates. For example, multimodal learning AI systems are being developed to help detect many cancer types via integrating different types of data.Treatment
Emerging topics of cancer treatment research include: * Anti-cancer vaccines ** Oncophage ** Sipuleucel-T (Provenge) is a prostate cancer vaccine * Newer forms ofchemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemother ...
*Gene therapy
Gene therapy is a Medicine, medical field which focuses on the genetic modification of cells to produce a therapeutic effect or the treatment of disease by repairing or reconstructing defective genetic material. The first attempt at modifying ...
* Photodynamic therapy
*Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Rad ...
* Reoviridae (Reolysin drug therapy)
* Targeted therapy
* Medical microbots and nanobots
Nanoid robotics, or for short, nanorobotics or nanobotics, is an emerging technology field creating machines or robots whose components are at or near the scale of a nanometer (10−9 meters). More specifically, nanorobotics (as opposed to mic ...
* Antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
* Photoimmunotherapy (for brain cancer
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and second ...
)
*Natural killer cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and repre ...
s can induce immunological memory. Research is being developed to modify their action against cancer.
*How treatments can best be combined (in combination therapies)
Cause and development of cancer
 Research into the cause of cancer involves many different disciplines including genetics, diet, environmental factors (i.e. chemical
Research into the cause of cancer involves many different disciplines including genetics, diet, environmental factors (i.e. chemical carcinogens
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive sub ...
). In regard to investigation of causes and potential targets for therapy, the route used starts with data obtained from clinical observations, enters basic research, and, once convincing and independently confirmed results are obtained, proceeds with clinical research, involving appropriately designed trials on consenting human subjects, with the aim to test safety and efficiency of the therapeutic intervention method.
An important part of basic research is characterization of the potential mechanisms of carcinogenesis, in regard to the types of genetic and epigenetic changes that are associated with cancer development. The mouse is often used as a mammalian model for manipulation of the function of genes that play a role in tumor formation, while basic aspects of tumor initiation, such as mutagenesis, are assayed on cultures of bacteria and mammalian cells.
Genes involved in cancer
The goal of oncogenomics is to identify newoncogenes
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.
or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers, and new targets for cancer therapies. As the Cancer Genome Project stated in a 2004 review article, "a central aim of cancer research has been to identify the mutated genes that are causally implicated in oncogenesis (''cancer genes'')." The Cancer Genome Atlas project is a related effort investigating the genomic changes associated with cancer, while the COSMIC cancer database documents acquired genetic mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
s from hundreds of thousands of human cancer samples.
These large scale projects, involving about 350 different types of cancer, have identified ~130,000 mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
s in ~3000 genes that have been mutated in the tumours. The majority occurred in 319 genes, of which 286 were tumour suppressor genes and 33 oncogenes.
Several hereditary factors can increase the chance of cancer-causing mutations, including the activation of oncogenes or the inhibition of tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or re ...
s. The functions of various onco- and tumor suppressor genes can be disrupted at different stages of tumor progression. Mutations in such genes can be used to classify the malignancy of a tumor.
In later stages, tumors can develop a resistance to cancer treatment. The identification of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes is important to understand tumor progression and treatment success. The role of a given gene in cancer progression may vary tremendously, depending on the stage and type of cancer involved.
Cancer epigenetics
Cancer growth
Diet and cancer
Research funding
Cancer research is funded by government grants, charitable foundations and pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. In the early 2000s, most funding for cancer research came from taxpayers and charities, rather than from corporations. In the US, less than 30% of all cancer research was funded by commercial researchers such as pharmaceutical companies. Per capita, public spending on cancer research by taxpayers and charities in the US was five times as much in 2002–03 as public spending by taxpayers and charities in the 15 countries that were full members of the European Union. As a percentage of GDP, the non-commercial funding of cancer research in the US was four times the amount dedicated to cancer research in Europe. Half of Europe's non-commercial cancer research is funded by charitable organizations. TheNational Cancer Institute
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) coordinates the United States National Cancer Program and is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which is one of eleven agencies that are part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. T ...
is the major funding institution in the United States. In the 2016 fiscal year, the NCI funded $5.2 billion in cancer research.
Difficulties
Difficulties inherent to cancer research are shared with many types of biomedical research. Cancer research processes have been criticised. These include, especially in the US, for the financial resources and positions required to conduct research. Other consequences of competition for research resources appear to be a substantial number of research publications whose results cannot be replicated.Replicability
Public participation
Distributed computing
One can share computer time for distributed cancer research projects like Help Conquer Cancer.World Community Grid
World Community Grid (WCG) is an effort to create the world's largest volunteer computing platform to tackle scientific research that benefits humanity. Launched on November 16, 2004, with proprietary Grid MP client from United Devices and addi ...
also had a project called Help Defeat Cancer. Other related projects include the Folding@home and Rosetta@home projects, which focus on groundbreaking protein folding
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein chain is translated to its native three-dimensional structure, typically a "folded" conformation by which the protein becomes biologically functional. Via an expeditious and reproduc ...
and protein structure prediction research. Vodafone
Vodafone Group plc () is a British multinational telecommunications company. Its registered office and global headquarters are in Newbury, Berkshire, England. It predominantly operates services in Asia, Africa, Europe, and Oceania.
, Vod ...
has also partnered with the Garvan Institute to create the DreamLab Project, which uses distributed computing via an app on cellphones to perform cancer research.
Clinical trials
 Members of the public can also join
Members of the public can also join clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, diet ...
s as healthy control subjects or for methods of cancer detection.
There could be software and data-related procedures that increase participation in trials and make them faster and less expensive. One open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open-source model is a decentralized so ...
platform matches genomically profiled cancer patients to precision medicine drug trials.
Dominance of cancer research
Cancer research has grown considerably as indicated by the number of records that have been indexed in theMEDLINE
MEDLINE (Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online, or MEDLARS Online) is a bibliographic database of life sciences and biomedical information. It includes bibliographic information for articles from academic journals covering med ...
database, in the 1950s the proportion of cancer-related entries was approximately 6% of all entries and this has risen to 16% in 2016. This rise may be attributed to the impact of scientific advances such as genomics, computing and mathematics, which have had a stronger influence in cancer than in other areas such as cardiovascular conditions.
Organizations
 Organizations exist as associations for scientists participating in cancer research, such as the American Association for Cancer Research and
Organizations exist as associations for scientists participating in cancer research, such as the American Association for Cancer Research and American Society of Clinical Oncology
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a professional organization representing physicians of all oncology sub-specialties who care for people with cancer. Founded in 1964 by Fred Ansfield, Harry Bisel, Herman Freckman, Arnoldus Go ...
, and as foundations for public awareness or raising funds for cancer research, such as Relay For Life and the American Cancer Society.
Awareness campaigns
Supporters of different types of cancer have adopted different colored awareness ribbons and promote months of the year as being dedicated to the support of specific types of cancer. The American Cancer Society began promoting October as Breast Cancer Awareness Month in the United States in the 1980s. Pink products are sold to both generate awareness and raise money to be donated for research purposes. This has led to pinkwashing, or the selling of ordinary products turned pink as a promotion for the company.See also
* .cancerresearch * ExposomeReferences
External links
Cancer Genome Anatomy Project @ The NIH
The Integrative Cancer Biology Program @ National Cancer Institute
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cancer Research Cancer