Culture Medium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or
A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or

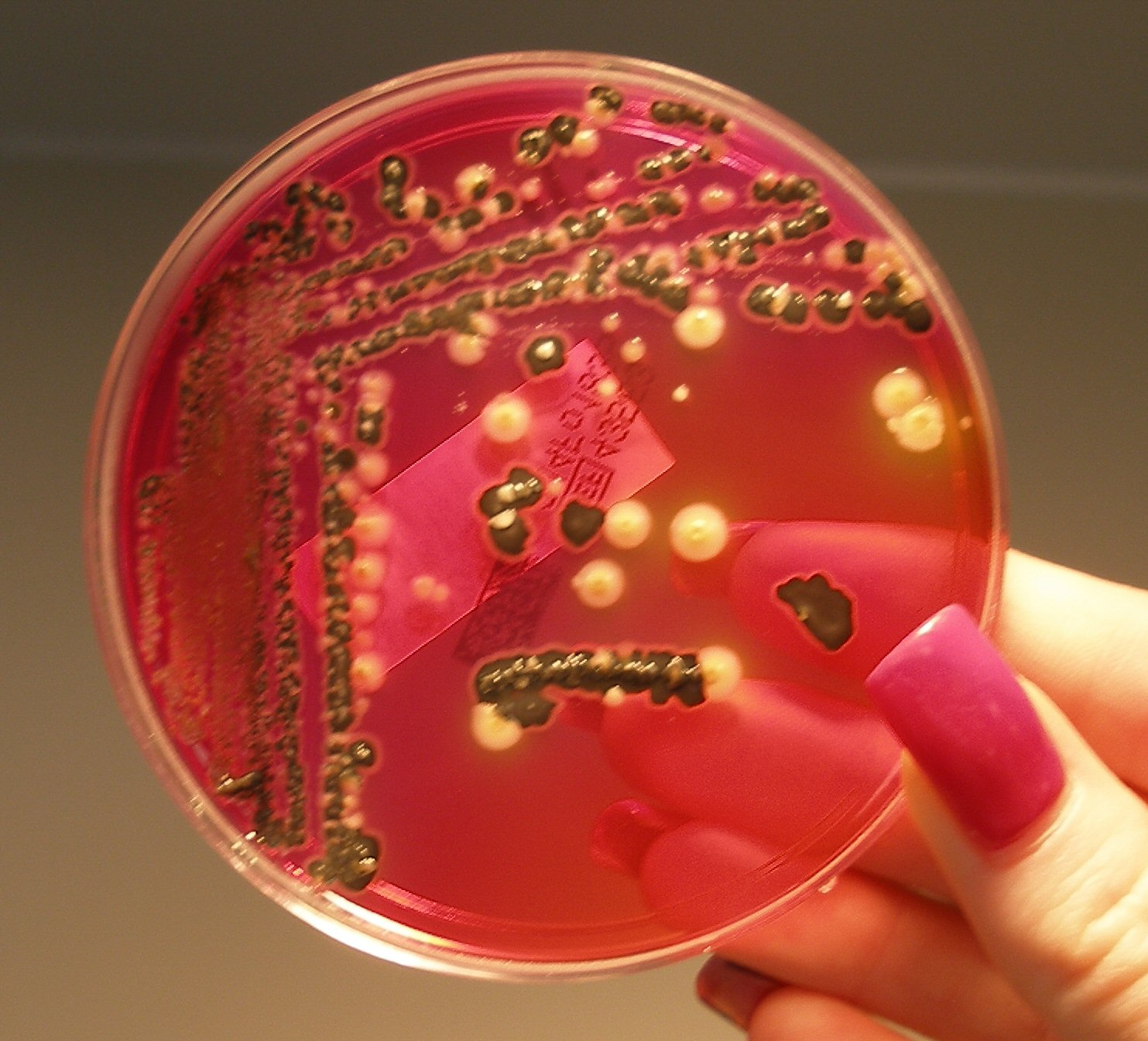 The most common growth media for microorganisms are nutrient broths (liquid nutrient medium) or
The most common growth media for microorganisms are nutrient broths (liquid nutrient medium) or
 An undefined medium (also known as a basal or complex medium) contains:
* a carbon source such as glucose
* water
* various salts
* a source of amino acids and nitrogen (e.g. beef, yeast extract)
This is an undefined medium because the amino-acid source contains a variety of compounds; the exact composition is unknown.
A defined medium (also known as
An undefined medium (also known as a basal or complex medium) contains:
* a carbon source such as glucose
* water
* various salts
* a source of amino acids and nitrogen (e.g. beef, yeast extract)
This is an undefined medium because the amino-acid source contains a variety of compounds; the exact composition is unknown.
A defined medium (also known as
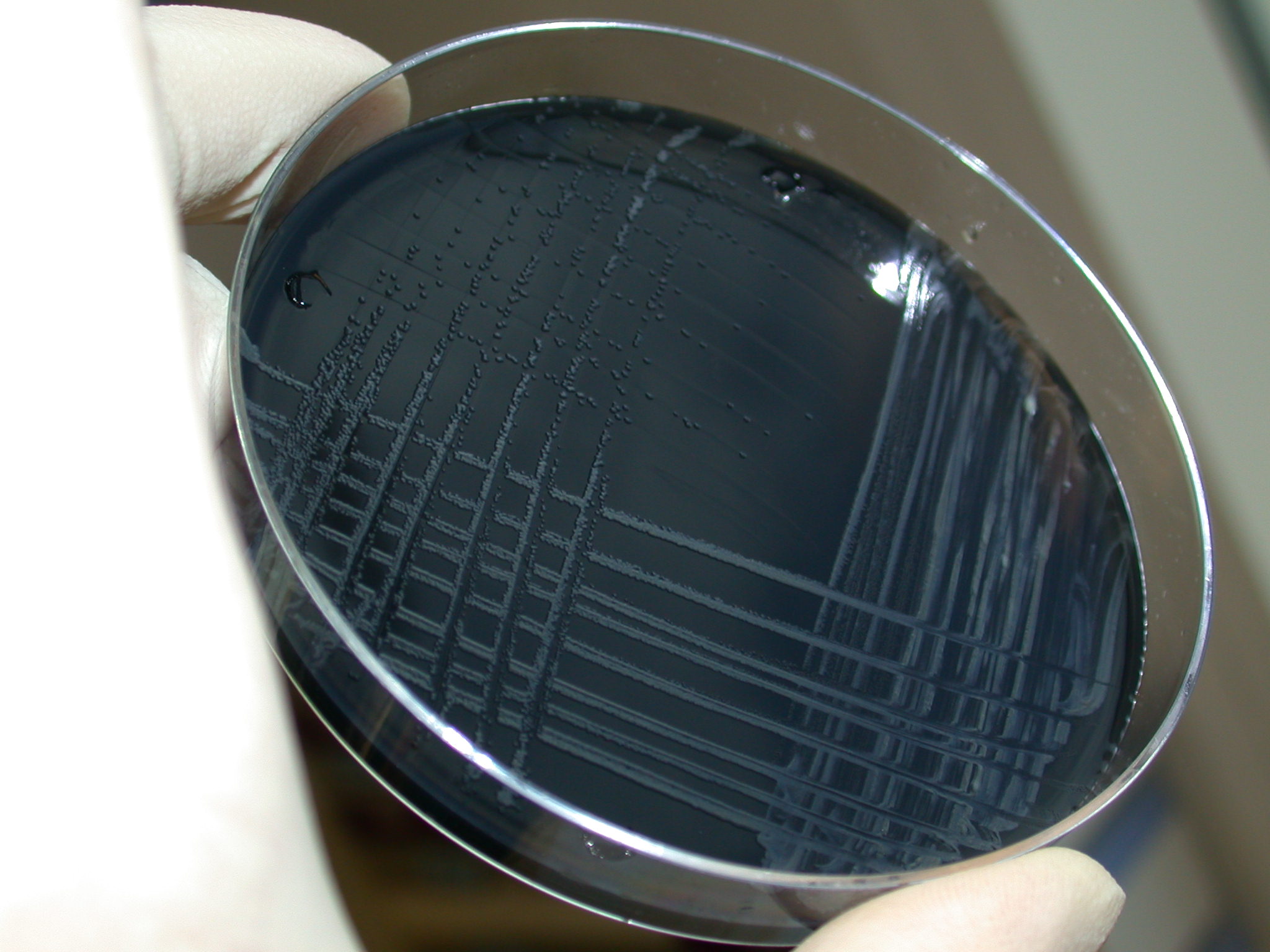
 Selective media are used for the growth of only selected microorganisms. For example, if a microorganism is resistant to a certain
Selective media are used for the growth of only selected microorganisms. For example, if a microorganism is resistant to a certain  Examples of selective media:
*
Examples of selective media:
*
 Differential or indicator media distinguish one microorganism type from another growing on the same medium. This type of media uses the biochemical characteristics of a microorganism growing in the presence of specific nutrients or indicators (such as neutral red,
Differential or indicator media distinguish one microorganism type from another growing on the same medium. This type of media uses the biochemical characteristics of a microorganism growing in the presence of specific nutrients or indicators (such as neutral red,
"The Nutrient Requirements of Cells"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Growth Medium Growth media Microbiological media
 A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or
A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
s via the process of cell proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation re ...
or small plants like the moss ''Physcomitrella patens
''Physcomitrium patens'', (synonym: ''Physcomitrella patens'' ) the spreading earthmoss, is a moss (bryophyte) used as a model organism for studies on plant evolution, development, and physiology.
Distribution and ecology
''Physcomitrella p ...
''. Different types of media are used for growing different types of cells.
The two major types of growth media are those used for cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This t ...
, which use specific cell types derived from plants or animals, and those used for microbiological culture
A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagn ...
, which are used for growing microorganisms such as bacteria or fungi. The most common growth media for microorganisms are nutrient broths and agar plate
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.
Individual microorganisms placed on the plate wi ...
s; specialized media are sometimes required for microorganism and cell culture growth. Some organisms, termed fastidious organisms, require specialized environments due to complex nutritional requirements. Viruses, for example, are obligate intracellular parasites and require a growth medium containing living cells.
Types

lysogeny broth
Lysogeny broth (LB) is a nutritionally rich medium primarily used for the growth of bacteria. Its creator, Giuseppe Bertani, intended LB to stand for lysogeny broth, but LB has also come to colloquially mean Luria broth, Lennox broth, life br ...
medium. Liquid media are often mixed with agar
Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from ogonori ('' Gracilaria'') and "tengusa" ('' Gelidiaceae''). As found in nature, agar ...
and poured via a sterile media dispenser
A media dispenser or a culture media dispenser is a device for repeatedly delivering small fixed volumes (typically between 1 ml and 50 ml) of liquid such as a laboratory growth medium like molten agar or caustic or volatile solvents li ...
into Petri dishes to solidify. These agar plate
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.
Individual microorganisms placed on the plate wi ...
s provide a solid medium on which microbes may be cultured. They remain solid, as very few bacteria are able to decompose agar (the exception being some species in the genera: ''Cytophaga
''Cytophaga'' is a genus of Gram-negative, gliding, rod-shaped bacteria. This bacterium is commonly found in soil, rapidly digests crystalline cellulose ''C. hutchinsonii'' is able to use its gliding motility to move quickly over surfaces. ...
'', ''Flavobacterium
''Flavobacterium'' is a genus of Gram-negative, nonmotile and motile, rod-shaped bacteria that consists of 130 recognized species. Flavobacteria are found in soil and fresh water in a variety of environments. Several species are known to caus ...
'', ''Bacillus
''Bacillus'' (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum ''Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural ''Bacill ...
'', ''Pseudomonas
''Pseudomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative, Gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae and containing 191 described species. The members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to ...
'', and ''Alcaligenes
''Alcaligenes'' is a genus of Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria. The species are motile with amphitrichous flagella and rarely nonmotile. It is a genus of non-fermenting bacteria (in the family Alcaligenaceae). Additionally, some st ...
''). Bacteria grown in liquid cultures often form colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend ...
al suspensions.
The difference between growth media used for cell culture and those used for microbiological culture is that cells derived from whole organisms and grown in culture often cannot grow without the addition of, for instance, hormones
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required fo ...
or growth factors
A growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cell proliferation, wound healing, and occasionally cellular differentiation. Usually it is a secreted protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for regu ...
which usually occur '' in vivo''. In the case of animal cells, this difficulty is often addressed by the addition of blood serum
Serum () is the fluid and solute component of blood which does not play a role in clotting. It may be defined as blood plasma without the clotting factors, or as blood with all cells and clotting factors removed. Serum includes all proteins not ...
or a synthetic serum replacement to the medium. In the case of microorganisms, no such limitations exist, as they are often unicellular organism
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
s. One other major difference is that animal cells in culture are often grown on a flat surface to which they attach, and the medium is provided in a liquid form, which covers the cells. In contrast, bacteria such as ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'' may be grown on solid or in liquid media.
An important distinction between growth media types is that of defined versus undefined media. A defined medium will have known quantities of all ingredients. For microorganisms, they consist of providing trace elements and vitamins required by the microbe and especially defined carbon and nitrogen sources. Glucose or glycerol are often used as carbon sources, and ammonium salts or nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insolubl ...
s as inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistr ...
nitrogen sources. An undefined medium has some complex ingredients, such as yeast extract or casein hydrolysate, which consist of a mixture of many chemical species in unknown proportions. Undefined media are sometimes chosen based on price and sometimes by necessity – some microorganisms have never been cultured on defined media.
A good example of a growth medium is the wort used to make beer. The wort contains all the nutrients required for yeast growth, and under anaerobic
Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to:
* Anaerobic adhesive, a bonding a ...
conditions, alcohol is produced. When the fermentation process is complete, the combination of medium and dormant microbes, now beer, is ready for consumption.
The main types are
*cultural media
*minimal media
*selective media
*differential media
*transport media
*indicator media
Culture media
Culture media contain all the elements that most bacteria need for growth and are not selective, so they are used for the general cultivation and maintenance of bacteria kept in laboratory culture collections. An undefined medium (also known as a basal or complex medium) contains:
* a carbon source such as glucose
* water
* various salts
* a source of amino acids and nitrogen (e.g. beef, yeast extract)
This is an undefined medium because the amino-acid source contains a variety of compounds; the exact composition is unknown.
A defined medium (also known as
An undefined medium (also known as a basal or complex medium) contains:
* a carbon source such as glucose
* water
* various salts
* a source of amino acids and nitrogen (e.g. beef, yeast extract)
This is an undefined medium because the amino-acid source contains a variety of compounds; the exact composition is unknown.
A defined medium (also known as chemically defined medium A chemically defined medium is a growth medium suitable for the in vitro cell culture of human or animal cells in which all of the chemical components are known. Standard cell culture media commonly consist of a basal medium supplemented with animal ...
or synthetic medium) is a medium in which
* all the chemicals used are known
* no yeast, animal, or plant tissue is present
Examples of nutrient media:
* nutrient agar
* plate count agar
Plate Count Agar (PCA), also called Standard Methods Agar (SMA), is a microbiological growth medium commonly used to assess or to monitor "total" or viable bacterial growth of a sample. PCA is not a selective medium.
The total number of living a ...
* trypticase soy agar
Trypticase soy agar or tryptone soya agar (TSA) and Trypticase soy broth or tryptone soya broth (TSB) with agar are growth media for the culturing of bacteria. They are general-purpose, nonselective media providing enough nutrients to allow fo ...
Minimal media
A defined medium that has just enough ingredients to support growth is called a "minimal medium". The number of ingredients that must be added to a minimal medium varies enormously depending on which microorganism is being grown. Minimal media are those that contain the minimum nutrients possible for colony growth, generally without the presence of amino acids, and are often used by microbiologists and geneticists to grow "wild-type" microorganisms. Minimal media can also be used to select for or against recombinants or exconjugants. Minimal medium typically contains: * a carbon source, which may be a sugar such as glucose, or a less energy-rich source such as succinate * various salts, which may vary among bacteria species and growing conditions; these generally provide essential elements such as magnesium, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur to allow the bacteria to synthesize protein and nucleic acids * water Supplementary minimal media are minimal media that also contains a single selected agent, usually an amino acid or a sugar. This supplementation allows for the culturing of specific lines ofauxotrophic
Auxotrophy ( grc, αὐξάνω "to increase"; ''τροφή'' "nourishment") is the inability of an organism to synthesize a particular organic compound required for its growth (as defined by IUPAC). An auxotroph is an organism that displays this ...
recombinants.
Selective media

 Selective media are used for the growth of only selected microorganisms. For example, if a microorganism is resistant to a certain
Selective media are used for the growth of only selected microorganisms. For example, if a microorganism is resistant to a certain antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
, such as ampicillin
Ampicillin is an antibiotic used to prevent and treat a number of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, salmonellosis, and endocarditis. It may also be used to prevent group B str ...
or tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis.
Common side effects in ...
, then that antibiotic can be added to the medium to prevent other cells, which do not possess the resistance, from growing. Media lacking an amino acid such as proline in conjunction with ''E. coli'' unable to synthesize it were commonly used by geneticists before the emergence of genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dim ...
to map bacterial chromosomes.
Selective growth media are also used in cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This t ...
to ensure the survival or proliferation of cells with certain properties, such as antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
or the ability to synthesize a certain metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
. Normally, the presence of a specific gene or an allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
of a gene confers upon the cell the ability to grow in the selective medium. In such cases, the gene is termed a marker.
Selective growth media for eukaryotic cells commonly contain neomycin to select cells that have been successfully transfected with a plasmid carrying the neomycin resistance gene as a marker. Gancyclovir is an exception to the rule, as it is used to specifically kill cells that carry its respective marker, the Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase.
 Examples of selective media:
*
Examples of selective media:
* Eosin methylene blue
Eosin methylene blue (EMB, also known as "Levine's formulation") is a selective stain for Gram-negative bacteria. EMB contains dyes that are toxic to Gram-positive bacteria. EMB is the selective and differential medium for coliforms. It is a blend ...
contains dyes that are toxic for Gram-positive bacteria. It is the selective and differential medium for coliforms.
* YM ( yeast extract agar) has a low pH, deterring bacterial growth.
* MEA (malt extract
Malt is germinated cereal grain that has been dried in a process known as "malting". The grain is made to germinate by soaking in water and is then halted from germinating further by drying with hot air.
Malted grain is used to make beer, whi ...
agar) has a low pH, deterring bacterial growth.
* MacConkey agar
MacConkey agar is a selective and differential culture medium for bacteria. It is designed to selectively isolate Gram-negative and enteric (normally found in the intestinal tract) bacteria and differentiate them based on lactose fermentation ...
is for Gram-negative bacteria.
* Hektoen enteric agar is selective for Gram-negative bacteria.
* HIS-selective medium HIS-selective medium is a type cell culture medium that lacks the amino acid histidine. It can be used with bacteria reliant on the expression of a gene encoding proteins involved in histidine expression in order to survive.Joung, J. K., E. I. Ramm ...
is a type cell culture medium that lacks the amino acid histidine.
* Mannitol salt agar
Mannitol salt agar or MSA is a commonly used selective and differential growth medium in microbiology. It encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others.
It contains a high concentration (about 7.5� ...
is selective for gram-positive bacteria and differential for mannitol.
* Xylose lysine deoxycholate is selective for Gram-negative bacteria.
* Buffered charcoal yeast extract agar Buffered charcoal yeast extract (BCYE) agar is a selective growth medium used to culture or grow certain types of bacteria, particularly the Gram-negative species ''Legionella pneumophila''. It has also been used for the laboratory diagnosis of ...
is selective for certain gram-negative bacteria, especially ''Legionella pneumophila
''Legionella pneumophila'' is a thin, aerobic, pleomorphic, flagellated, non-spore-forming, Gram-negative bacterium of the genus ''Legionella''. ''L. pneumophila'' is the primary human pathogenic bacterium in this group and is the causative age ...
''.
* Baird–Parker agar is for gram-positive staphylococci
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are faculta ...
.
* Sabouraud's agar
Sabouraud agar or Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) is a type of agar growth medium containing peptones. It is used to cultivate dermatophytes and other types of fungi, and can also grow filamentous bacteria such as ''Nocardia''. It has utility for ...
is selective to certain fungi due to its low pH (5.6) and high glucose concentration (3–4%).
* DRBC (dichloran rose bengal chloramphenicol agar) is a selective medium for the enumeration of moulds and yeasts in foods. Dichloran and rose bengal restrict the growth of mould colonies, preventing overgrowth of luxuriant species and assisting accurate counting of colonies.
Differential media
 Differential or indicator media distinguish one microorganism type from another growing on the same medium. This type of media uses the biochemical characteristics of a microorganism growing in the presence of specific nutrients or indicators (such as neutral red,
Differential or indicator media distinguish one microorganism type from another growing on the same medium. This type of media uses the biochemical characteristics of a microorganism growing in the presence of specific nutrients or indicators (such as neutral red, phenol red
Phenol red (also known as phenolsulfonphthalein or PSP) is a pH indicator frequently used in cell biology laboratories.
Chemical structure and properties
Phenol red exists as a red crystal that is stable in air. Its solubility is 0.77 grams per ...
, eosin y
Eosin Y, also called C.I. 45380 or C.I. Acid Red 87, is a member of the triarylmethane dyes. It is produced from fluorescein by bromination.
Use
Eosin Y is commonly used as the red dye in red inks.
It is commonly used in histology, most notabl ...
, or methylene blue
Methylthioninium chloride, commonly called methylene blue, is a salt used as a dye and as a medication. Methylene blue is a thiazine dye. As a medication, it is mainly used to treat methemoglobinemia by converting the ferric iron in hemoglobi ...
) added to the medium to visibly indicate the defining characteristics of a microorganism. These media are used for the detection of microorganisms and by molecular biologists to detect recombinant strains of bacteria.
Examples of differential media:
* Blood agar
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.
Individual microorganisms placed on the plate wi ...
(used in strep
The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the Europea ...
tests) contains bovine heart blood that becomes transparent in the presence of β-hemolytic organisms such as '' Streptococcus pyogenes'' and '' Staphylococcus aureus''.
* Eosin methylene blue
Eosin methylene blue (EMB, also known as "Levine's formulation") is a selective stain for Gram-negative bacteria. EMB contains dyes that are toxic to Gram-positive bacteria. EMB is the selective and differential medium for coliforms. It is a blend ...
is differential for lactose fermentation.
* Granada medium
Granada (,, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the foot of the Sierra Nevada mountains, at th ...
is selective and differential for '' Streptococcus agalactiae'' (group B streptococcus) which grows as distinctive red colonies in this medium.
* MacConkey agar
MacConkey agar is a selective and differential culture medium for bacteria. It is designed to selectively isolate Gram-negative and enteric (normally found in the intestinal tract) bacteria and differentiate them based on lactose fermentation ...
is differential for lactose fermentation.
* Mannitol salt agar
Mannitol salt agar or MSA is a commonly used selective and differential growth medium in microbiology. It encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others.
It contains a high concentration (about 7.5� ...
is differential for mannitol fermentation.
* X-gal plates are differential for lac operon mutants.
Transport media
Transport media should fulfill these criteria: * Temporary storage of specimens being transported to the laboratory for cultivation * Maintain the viability of all organisms in the specimen without altering their concentration * Contain only buffers and salt * Lack of carbon, nitrogen, and organic growth factors so as to prevent microbial multiplication * Transport media used in the isolation of anaerobes must be free of molecular oxygen. Examples of transport media: *Thioglycolate broth
Thioglycolate broth is a multipurpose, enrichment, differential medium used primarily to determine the oxygen requirements of microorganisms. Sodium thioglycolate in the medium consumes oxygen and permits the growth of obligate anaerobes. This, com ...
is for strict anaerobes
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenate ...
.
* Stuart transport medium is a non-nutrient soft agar gel containing a reducing agent to prevent oxidation, and charcoal to neutralize.
* Certain bacterial inhibitors are used for gonococci, and buffered glycerol saline for enteric bacilli.
* Venkataraman Ramakrishna (VR) medium is used for '' V. cholerae''.
Enriched media
Enriched media contain the nutrients required to support the growth of a wide variety of organisms, including some of the more fastidious ones. They are commonly used to harvest as many different types of microbes as are present in the specimen.Blood agar
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.
Individual microorganisms placed on the plate wi ...
is an enriched medium in which nutritionally rich whole blood supplements the basic nutrients. Chocolate agar
Chocolate agar (CHOC) or chocolate blood agar (CBA), is a nonselective, enriched growth medium used for isolation of pathogenic bacteria. It is a variant of the blood agar plate, containing red blood cells that have been lysed by slowly heating ...
is enriched with heat-treated blood (), which turns brown and gives the medium the color for which it is named.
Physiological relevance
The choice of culture medium might affect the physiological relevance of findings from tissue culture experiments, especially for metabolic studies. In addition, the dependence of acell line
An immortalised cell line is a population of cells from a multicellular organism which would normally not proliferate indefinitely but, due to mutation, have evaded normal cellular senescence and instead can keep undergoing division. The cell ...
on a metabolic gene was shown to be affected by the media type. When performing a study involving several cell lines, utilizing a uniform culture media for all cell lines might reduce the bias in the generated datasets. Using a growth medium that better represents the physiological levels of nutrients can improve the physiological relevance of in vitro studies and recently such media types, as Plasmax and human plasma-like medium (HPLM), were developed.
See also
*Cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This t ...
* Impedance microbiology Impedance microbiology is a microbiological technique used to measure the microbial number density (mainly bacteria but also yeasts) of a sample by monitoring the electrical parameters of the growth medium. The ability of microbial metabolism to ch ...
* Modified Chee's medium In cellular biology and microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-discipline ...
References
External links
"The Nutrient Requirements of Cells"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Growth Medium Growth media Microbiological media