compound of two tetrahedra on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
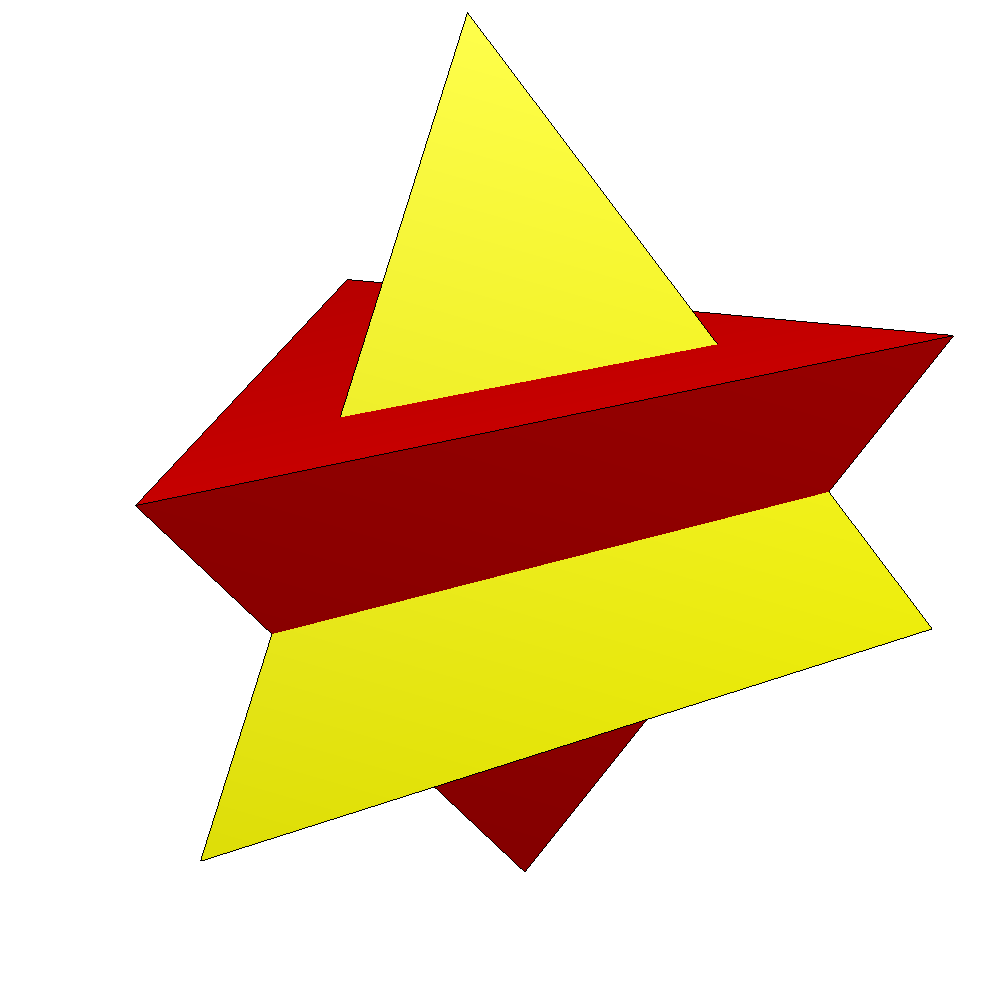 Other orientations can be chosen as 2 tetrahedra within the compound of five tetrahedra and
Other orientations can be chosen as 2 tetrahedra within the compound of five tetrahedra and 
Compounds of Polyhedra
VRML model
Polyhedral compounds
 In
In geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
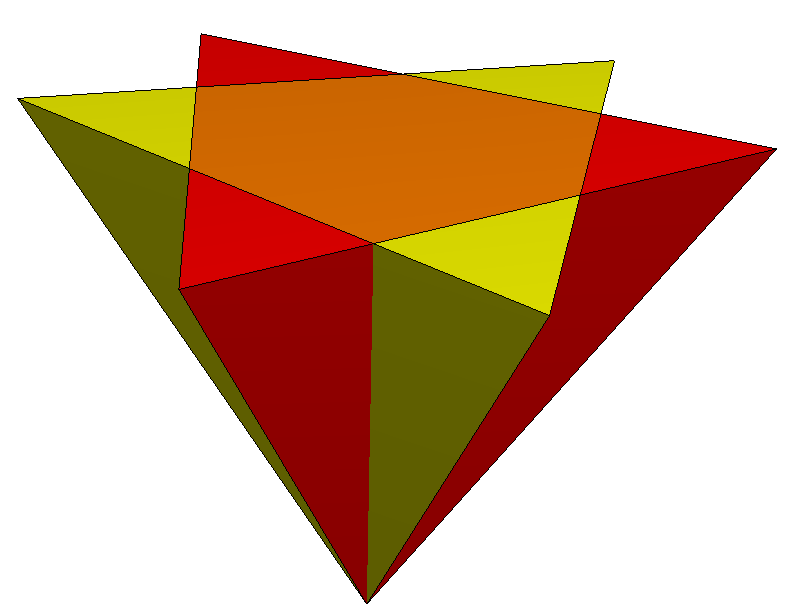
, a compound of two tetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all th ...
is constructed by two overlapping tetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all th ...
, usually implied as regular tetrahedra.
Stellated octahedron
There is only one uniform polyhedral compound, thestellated octahedron
The stellated octahedron is the only stellation of the octahedron. It is also called the stella octangula (Latin for "eight-pointed star"), a name given to it by Johannes Kepler in 1609, though it was known to earlier geometers. It was depic ...
, which has octahedral symmetry
A regular octahedron has 24 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and 48 symmetries altogether. These include transformations that combine a reflection and a rotation. A cube has the same set of symmetries, since it is the polyhedr ...
, order 48. It has a regular octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
core, and shares the same 8 vertices with the cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the only ...
.
If the edge crossings were treated as their own vertices, the compound would have identical surface topology to the rhombic dodecahedron; were face crossings also considered edges of their own the shape would effectively become a nonconvex triakis octahedron.
Lower symmetry constructions
There are lower symmetry variations on this compound, based on lower symmetry forms of the tetrahedron. * A facetting of a rectangular cuboid, creating compounds of two tetragonal or two rhombicdisphenoid
In geometry, a disphenoid () is a tetrahedron whose four faces are congruent acute-angled triangles. It can also be described as a tetrahedron in which every two edges that are opposite each other have equal lengths. Other names for the same ...
s, with a bipyramid
A (symmetric) -gonal bipyramid or dipyramid is a polyhedron formed by joining an -gonal pyramid and its mirror image base-to-base. An -gonal bipyramid has triangle faces, edges, and vertices.
The "-gonal" in the name of a bipyramid does ...
or rhombic fusil cores. This is first in a set of uniform compound of two antiprisms.
* A facetting of a trigonal trapezohedron
In geometry, a trigonal trapezohedron is a rhombohedron (a polyhedron with six rhombus-shaped faces) in which, additionally, all six faces are congruent. Alternative names for the same shape are the ''trigonal deltohedron'' or ''isohedral rh ...
creates a compound of two right triangular pyramids with a triangular antiprism
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
core. This is first in a set of compounds of two pyramids positioned as point reflection
In geometry, a point reflection (point inversion, central inversion, or inversion through a point) is a type of isometry of Euclidean space. An object that is invariant under a point reflection is said to possess point symmetry; if it is invari ...
s of each other.
Other compounds
If two regular tetrahedra are given the same orientation on the 3-fold axis, a different compound is made, with D3h, ,2symmetry, order 12. : Other orientations can be chosen as 2 tetrahedra within the compound of five tetrahedra and
Other orientations can be chosen as 2 tetrahedra within the compound of five tetrahedra and compound of ten tetrahedra
The compound of ten tetrahedra is one of the five regular polyhedral compounds. This polyhedron can be seen as either a stellation of the icosahedron or a compound. This compound was first described by Edmund Hess in 1876.
It can be seen as a ...
the latter of which can be seen as a hexagram
, can be seen as a compound composed of an upwards (blue here) and downwards (pink) facing equilateral triangle, with their intersection as a regular hexagon (in green).
A hexagram ( Greek language, Greek) or sexagram ( Latin) is a six-pointe ...
mic pyramid:
:

See also
*Compound of cube and octahedron
The compound of cube and octahedron is a polyhedron which can be seen as either a polyhedral stellation or a compound. Construction
The 14 Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of the compound are.
: 6: (±2, 0, 0), ( 0, ±2, 0), ( 0, 0, ±2)
: ...
* Compound of dodecahedron and icosahedron
In geometry, this polyhedron can be seen as either a polyhedral stellation or a compound.
As a compound
It can be seen as the compound of an icosahedron and dodecahedron. It is one of four compounds constructed from a Platonic solid or Ke ...
* Compound of small stellated dodecahedron and great dodecahedron
* Compound of great stellated dodecahedron and great icosahedron
There are two different compounds of great icosahedron and great stellated dodecahedron: one is a dual compound and a stellation of the great icosidodecahedron, the other is a stellation of the icosidodecahedron.
Dual compound
It can be seen as ...
References
* Cundy, H. and Rollett, A. "Five Tetrahedra in a Dodecahedron". §3.10.8 in ''Mathematical Models
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used in the natural sciences (such as physi ...
'', 3rd ed. Stradbroke, England: Tarquin Pub., pp. 139-141, 1989.
External links
* {{mathworld , urlname = Tetrahedron2-Compound , title = Compound of two tetrahedraCompounds of Polyhedra
VRML model
Polyhedral compounds