command-line argument on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive
A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive
 Compared with a graphical user interface, a command-line interface requires fewer system resources to implement. Since options to commands are given in a few characters in each command line, an experienced user often finds the options easier to access. Automation of repetitive tasks is simplified by line editing and history mechanisms for storing frequently used sequences; this may extend to a
Compared with a graphical user interface, a command-line interface requires fewer system resources to implement. Since options to commands are given in a few characters in each command line, an experienced user often finds the options easier to access. Automation of repetitive tasks is simplified by line editing and history mechanisms for storing frequently used sequences; this may extend to a
 Application programs (as opposed to operating systems) may also have command-line interfaces.
An application program may support none, any, or all of these three major types of command-line interface mechanisms:
* ''Parameters'': Most command-line interfaces support a means to pass additional information to a program when it is launched.
* ''Interactive command-line sessions'': After launch, a program may provide an operator with an independent means to enter commands.
* ''Inter-process communication'': Most operating systems support means of
Application programs (as opposed to operating systems) may also have command-line interfaces.
An application program may support none, any, or all of these three major types of command-line interface mechanisms:
* ''Parameters'': Most command-line interfaces support a means to pass additional information to a program when it is launched.
* ''Interactive command-line sessions'': After launch, a program may provide an operator with an independent means to enter commands.
* ''Inter-process communication'': Most operating systems support means of
 The first
The first
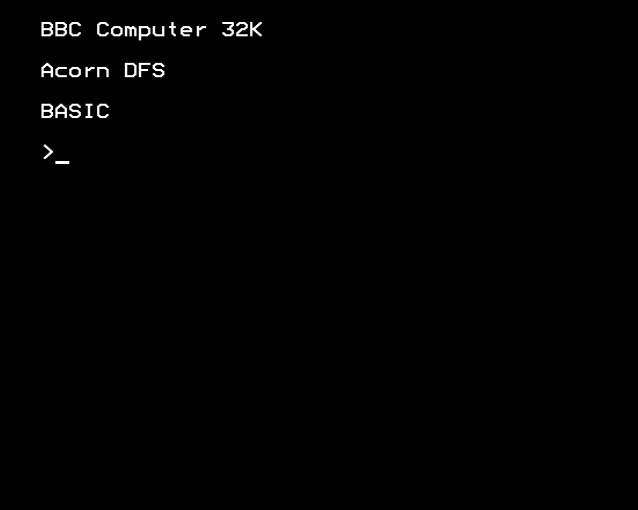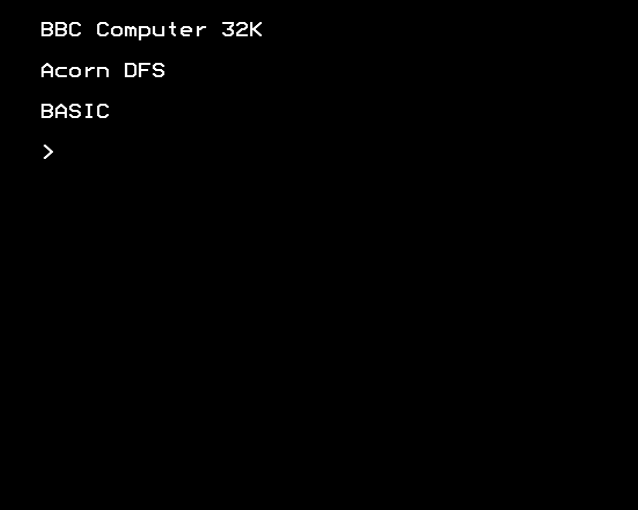 A command prompt (or just ''prompt'') is a sequence of (one or more) characters used in a command-line interface to indicate readiness to accept commands. It literally prompts the user to take action. A prompt usually ends with one of the characters
A command prompt (or just ''prompt'') is a sequence of (one or more) characters used in a command-line interface to indicate readiness to accept commands. It literally prompts the user to take action. A prompt usually ends with one of the characters export PS1=' t\u@\H: \W $'
In
 A command-line argument or
A command-line argument or
rm file.s
"file.s" is a command-line argument which tells the program rm to remove the file "file.s".
Some programming languages, such as C,
to separate options at the end of the command from the other arguments. For example, in the following command the options indicate that the target file should be replaced if it exists, and the date and time of the source file should be retained on the copy:
 If more detailed help is necessary than provided by a program's built-in internal help, many systems support a dedicated external "
If more detailed help is necessary than provided by a program's built-in internal help, many systems support a dedicated external "

 The earliest computers did not support interactive input/output devices, often relying on sense switches and lights to communicate with the
The earliest computers did not support interactive input/output devices, often relying on sense switches and lights to communicate with the
DuckDuckGo TTY
/ref> There are also Web-based SSH applications, that allow to give access to server command line interface from a browser. Many
The Roots of DOS
David Hunter, ''Softalk for the IBM Personal Computer'' March 1983. Archived at Patersontech.com sinc
Command-Line Reference
Microsoft TechNet Database "Command-Line Reference" {{DEFAULTSORT:Command-Line Interface History of human–computer interaction Software architecture User interface techniques User interfaces

 A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive
A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive command
Command may refer to:
Computing
* Command (computing), a statement in a computer language
* COMMAND.COM, the default operating system shell and command-line interpreter for DOS
* Command key, a modifier key on Apple Macintosh computer keyboards
* ...
s from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and providing information to them as to what actions they are to perform. In some cases the invocation is conditional based on conditions established by the user or previous executables. Such access was first provided by computer terminals starting in the mid-1960s. This provided an interactive environment not available with punched cards
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a piece of stiff paper that holds digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Punched cards were once common in data processing applications or to di ...
or other input methods.
Today, many users rely upon graphical user interface
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows User (computing), users to Human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through graphical icon (comp ...
s and menu-driven interactions. However, some programming and maintenance tasks may not have a graphical user interface and use a command line.
Alternatives to the command-line interface include text-based user interface
In computing, text-based user interfaces (TUI) (alternately terminal user interfaces, to reflect a dependence upon the properties of computer terminals and not just text), is a retronym describing a type of user interface (UI) common as an ...
menus (for example, IBM AIX SMIT
The System Management Interface Tool (SMIT) is a menu-based management tool for the IBM AIX operating system.
It allows a user to navigate a menu hierarchy of commands, rather than using the command line.
See also
* Object Data Manager
* IB ...
), keyboard shortcut
computing, a keyboard shortcut also known as hotkey is a series of one or several keys to quickly invoke a software program or perform a preprogrammed action. This action may be part of the standard functionality of the operating system or ...
s, and various desktop metaphor
In computing, the desktop metaphor is an interface metaphor which is a set of unifying concepts used by graphical user interfaces to help users interact more easily with the computer. The desktop metaphor treats the computer monitor as if it is t ...
s centered on the pointer (usually controlled with a mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
). Examples of this include the Microsoft Windows, DOS Shell
DOS Shell is a file manager that debuted in MS-DOS and PC DOS version 4.0, released in June 1988. It was discontinued in MS-DOS version 6.22, but remained part of the Supplemental Disk. The Supplemental Disk could be ordered or could be do ...
, and Mouse Systems PowerPanel. Command-line interfaces are often implemented in terminal devices that are also capable of screen-oriented text-based user interfaces that use cursor addressing to place symbols on a display screen.
Programs with command-line interfaces are generally easier to automate via scripting.
Many software systems implement command-line interfaces for control and operation. This includes programming environments and utility programs.
Comparison to graphical user interfaces
 Compared with a graphical user interface, a command-line interface requires fewer system resources to implement. Since options to commands are given in a few characters in each command line, an experienced user often finds the options easier to access. Automation of repetitive tasks is simplified by line editing and history mechanisms for storing frequently used sequences; this may extend to a
Compared with a graphical user interface, a command-line interface requires fewer system resources to implement. Since options to commands are given in a few characters in each command line, an experienced user often finds the options easier to access. Automation of repetitive tasks is simplified by line editing and history mechanisms for storing frequently used sequences; this may extend to a scripting language
A scripting language or script language is a programming language that is used to manipulate, customize, and automate the facilities of an existing system. Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled.
A scriptin ...
that can take parameters and variable options. A command-line history can be kept, allowing review or repetition of commands.
A command-line system may require paper or online manuals for the user's reference, although often a "help" option provides a concise review of the options of a command. The command-line environment may not provide graphical enhancements such as different fonts or extended edit windows found in a GUI. It may be difficult for a new user to become familiar with all the commands and options available, compared with the icons
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. They are not simply artworks; "an icon is a sacred image used in religious devotion". The most ...
and drop-down menu
A drop-down list (abbreviated drop-down, or DDL; also known as a drop-down menu, drop menu, pull-down list, picklist) is a graphical control element, similar to a list box, that allows the user to choose one value from a list. When a drop-down ...
s of a graphical user interface, without reference to manuals.
Types
Operating system command-line interfaces
Operating system (OS) command-line interfaces are usually distinct programs supplied with the operating system. A program that implements such a text interface is often called a command-line interpreter, command processor orshell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard o ...
.
Examples of command-line interpreters include DEC's DIGITAL Command Language
DIGITAL Command Language (DCL) is the standard command language adopted by many of the operating systems created by Digital Equipment Corporation. DCL had its roots in IAS, TOPS-20, and RT-11 and was implemented as a standard across most of Digital ...
(DCL) in OpenVMS
OpenVMS, often referred to as just VMS, is a multi-user, multiprocessing and virtual memory-based operating system. It is designed to support time-sharing, batch processing, transaction processing and workstation applications. Customers using Op ...
and RSX-11
RSX-11 is a discontinued family of multi-user real-time operating systems for PDP-11 computers created by Digital Equipment Corporation. In widespread use through the late 1970s and early 1980s, RSX-11 was influential in the development of later ...
, the various Unix shell
A Unix shell is a command-line interpreter or shell that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command language and a scripting language, and is used by the operating system to ...
s ( sh, ksh, csh, tcsh
tcsh ( “tee-see-shell”, “tee-shell”, or as “tee see ess aitch”, tcsh) is a Unix shell based on and backward compatible with the C shell (csh).
Shell
It is essentially the C shell with programmable command-line completion, command-l ...
, zsh
The Z shell (Zsh) is a Unix shell that can be used as an interactive login shell and as a command interpreter for shell scripting. Zsh is an extended Bourne shell with many improvements, including some features of Bash, ksh, and tcsh.
Histo ...
, Bash, etc.), CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/ 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initially ...
's CCP, DOS
DOS is shorthand for the MS-DOS and IBM PC DOS family of operating systems.
DOS may also refer to:
Computing
* Data over signalling (DoS), multiplexing data onto a signalling channel
* Denial-of-service attack (DoS), an attack on a communicatio ...
' COMMAND.COM, as well as the OS/2
OS/2 (Operating System/2) is a series of computer operating systems, initially created by Microsoft and IBM under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci. As a result of a feud between the two companies over how to position OS/2 re ...
and the Windows CMD.EXE programs, the latter groups being based heavily on DEC's RSX-11 and RSTS CLIs. Under most operating systems, it is possible to replace the default shell program with alternatives; examples include 4DOS
4DOS is a command-line interpreter by JP Software, designed to replace the default command interpreter COMMAND.COM in Microsoft DOS and Windows. It was written by Rex C. Conn and Tom Rawson and first released in 1989. Compared to the default, ...
for DOS, 4OS2
4OS2 is the OS/2 analogue of 4NT and 4DOS by JP Software, Inc. JP Software discontinued 4OS2, TCMDOS2 and TCMD16, making version 3.0, 2.0, 2.0 the final version of these. The code for 4OS2 has been released, and is maintained, first by SciTec ...
for OS/2, and 4NT / Take Command for Windows.
Although the term 'shell' is often used to describe a command-line interpreter, strictly speaking, a 'shell' can be any program that constitutes the user-interface, including fully graphically oriented ones. For example, the default Windows GUI is a shell program named EXPLORER.EXE
File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing the file ...
, as defined in the SHELL=EXPLORER.EXE line in the WIN.INI configuration file. These programs are shells, but not CLIs.
Application command-line interfaces
 Application programs (as opposed to operating systems) may also have command-line interfaces.
An application program may support none, any, or all of these three major types of command-line interface mechanisms:
* ''Parameters'': Most command-line interfaces support a means to pass additional information to a program when it is launched.
* ''Interactive command-line sessions'': After launch, a program may provide an operator with an independent means to enter commands.
* ''Inter-process communication'': Most operating systems support means of
Application programs (as opposed to operating systems) may also have command-line interfaces.
An application program may support none, any, or all of these three major types of command-line interface mechanisms:
* ''Parameters'': Most command-line interfaces support a means to pass additional information to a program when it is launched.
* ''Interactive command-line sessions'': After launch, a program may provide an operator with an independent means to enter commands.
* ''Inter-process communication'': Most operating systems support means of inter-process communication
In computer science, inter-process communication or interprocess communication (IPC) refers specifically to the mechanisms an operating system provides to allow the processes to manage shared data. Typically, applications can use IPC, categor ...
(for example, standard streams
In computer programming, standard streams are interconnected input and output communication channels between a computer program and its environment when it begins execution. The three input/output (I/O) connections are called standard input (std ...
or named pipe
In computing, a named pipe (also known as a FIFO for its behavior) is an extension to the traditional pipe concept on Unix and Unix-like systems, and is one of the methods of inter-process communication (IPC). The concept is also found in OS/2 a ...
s). Command lines from client processes may be redirected to a CLI program by one of these methods.
Some applications support a CLI, presenting their own prompt to the user and accepting command lines. Other programs support both a CLI and a GUI. In some cases, a GUI is simply a wrapper around a separate CLI executable file
In computing, executable code, an executable file, or an executable program, sometimes simply referred to as an executable or binary, causes a computer "to perform indicated tasks according to encoded instructions", as opposed to a data file ...
. In other cases, a program may provide a CLI as an optional alternative to its GUI. CLIs and GUIs often support different functionality. For example, all features of MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementatio ...
, a numerical analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of numerical methods t ...
computer program, are available via the CLI, whereas the MATLAB GUI exposes only a subset of features.
In Colossal Cave Adventure
''Colossal Cave Adventure'' (also known as ''Adventure'' or ''ADVENT'') is a text-based adventure game, released in 1976 by developer Will Crowther for the PDP-10 mainframe computer. It was expanded upon in 1977 by Don Woods. In the game, the pl ...
from 1975, the user uses a CLI to enter one or two words to explore a cave system.
History
The command-line interface evolved from a form of communication conducted by people overteleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Initi ...
(TTY) machines. Sometimes these involved sending an order or a confirmation using telex
The telex network is a station-to-station switched network of teleprinters similar to a telephone network, using telegraph-grade connecting circuits for two-way text-based messages. Telex was a major method of sending written messages electroni ...
. Early computer systems often used teleprinter as the means of interaction with an operator.
The mechanical teleprinter was replaced by a "glass tty", a keyboard and screen emulating the teleprinter. "Smart" terminals permitted additional functions, such as cursor movement over the entire screen, or local editing of data on the terminal for transmission to the computer. As the microcomputer revolution
The history of the personal computer as a mass-market consumer electronic device began with the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s. A personal computer is one intended for interactive individual use, as opposed to a mainframe computer where ...
replaced the traditionalminicomputer + terminalstime sharing
In computing, time-sharing is the sharing of a computing resource among many users at the same time by means of multiprogramming and multi-tasking.DEC Timesharing (1965), by Peter Clark, The DEC Professional, Volume 1, Number 1
Its emergence ...
architecture, hardware terminals were replaced by terminal emulator
A terminal emulator, or terminal application, is a computer program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term ''terminal'' covers all remote termi ...
s — PC software that interpreted terminal signals sent through the PC's serial port
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication interface through which information transfers in or out sequentially one bit at a time. This is in contrast to a parallel port, which communicates multiple bits simultaneously in parallel. T ...
s. These were typically used to interface an organization's new PC's with their existing mini- or mainframe computers, or to connect PC to PC. Some of these PCs were running Bulletin Board System software.
Early operating system CLIs were implemented as part of resident monitor
In computing, a resident monitor is a type of system software program that was used in many early computers from the 1950s to 1970s. It can be considered a precursor to the operating system. The name is derived from a program which is always pre ...
programs, and could not easily be replaced. The first implementation of the shell as a replaceable component was part of the Multics
Multics ("Multiplexed Information and Computing Service") is an influential early time-sharing operating system based on the concept of a single-level memory.Dennis M. Ritchie, "The Evolution of the Unix Time-sharing System", Communications of t ...
time-sharing
In computing, time-sharing is the sharing of a computing resource among many users at the same time by means of multiprogramming and multi-tasking.DEC Timesharing (1965), by Peter Clark, The DEC Professional, Volume 1, Number 1
Its emergence a ...
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
. In 1964, MIT Computation Center The MIT Computation Center was organized in 1956 as a 10-year joint venture between the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and IBM to provide computing resources for New England universities. As part of the venture, IBM installed an IBM 704, whi ...
staff member Louis Pouzin
Louis Pouzin (April 20, 1931 in Chantenay-Saint-Imbert, Nièvre, France) is a French computer scientist. He designed an early packet communications network, CYCLADES.
This network was the first actual implementation of the pure datagram model, ...
developed the RUNCOM
RUNCOM is a CTSS macro command (script) processor.
History
Louis Pouzin created RUNCOM for CTSS circa 1963. He wrote a paper in 1965 describing a design for the Multics shell which includes a brief description of RUNCOM followed by a second p ...
tool for executing command scripts while allowing argument substitution. Pouzin coined the term "shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard o ...
" to describe the technique of using commands like a programming language, and wrote a paper about how to implement the idea in the Multics
Multics ("Multiplexed Information and Computing Service") is an influential early time-sharing operating system based on the concept of a single-level memory.Dennis M. Ritchie, "The Evolution of the Unix Time-sharing System", Communications of t ...
operating system. Pouzin returned to his native France in 1965, and the first Multics shell was developed by Glenda Schroeder
Glenda Schroeder is an American software engineer noted for implementing the first command-line user interface shell and publishing one of the earliest research papers describing electronic mail systems while working as a member of the staff at th ...
.
 The first
The first Unix shell
A Unix shell is a command-line interpreter or shell that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command language and a scripting language, and is used by the operating system to ...
, the V6 shell, was developed by Ken Thompson
Kenneth Lane Thompson (born February 4, 1943) is an American pioneer of computer science. Thompson worked at Bell Labs for most of his career where he designed and implemented the original Unix operating system. He also invented the B programm ...
in 1971 at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
and was modeled after Schroeder's Multics shell. The Bourne shell
The Bourne shell (sh) is a shell command-line interpreter for computer operating systems.
The Bourne shell was the default shell for Version 7 Unix. Unix-like systems continue to have /bin/sh—which will be the Bourne shell, or a symbolic ...
was introduced in 1977 as a replacement for the V6 shell. Although it is used as an interactive command interpreter, it was also intended as a scripting language and contains most of the features that are commonly considered to produce structured programs. The Bourne shell led to the development of the KornShell
KornShell (ksh) is a Unix shell which was developed by David Korn at Bell Labs in the early 1980s and announced at USENIX on July 14, 1983. The initial development was based on Bourne shell source code. Other early contributors were Bell L ...
(ksh), Almquist shell (ash), and the popular Bourne-again shell
Bash is a Unix shell and command language written by Brian Fox for the GNU Project as a free software replacement for the Bourne shell. First released in 1989, it has been used as the default login shell for most Linux distributions. Bash was ...
(or Bash).
Early microcomputers themselves were based on a command-line interface such as CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/ 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initially ...
, DOS
DOS is shorthand for the MS-DOS and IBM PC DOS family of operating systems.
DOS may also refer to:
Computing
* Data over signalling (DoS), multiplexing data onto a signalling channel
* Denial-of-service attack (DoS), an attack on a communicatio ...
or AppleSoft BASIC
Applesoft BASIC is a dialect of Microsoft BASIC, developed by Marc McDonald and Ric Weiland, supplied with the Apple II series of computers. It supersedes Integer BASIC and is the BASIC in ROM in all Apple II series computers after the origina ...
. During the 1980s and 1990s, the introduction of the Apple Macintosh
The Mac (known as Macintosh until 1999) is a family of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc. Macs are known for their ease of use and minimalist designs, and are popular among students, creative professionals, and software en ...
and of Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for se ...
on PCs saw the command line interface as the primary user interface replaced by the Graphical User Interface
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows User (computing), users to Human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through graphical icon (comp ...
. The command line remained available as an alternative user interface, often used by system administrators
A system administrator, or sysadmin, or admin is a person who is responsible for the upkeep, configuration, and reliable operation of computer systems, especially multi-user computers, such as servers. The system administrator seeks to ens ...
and other advanced users for system administration, computer programming and batch processing.
In November 2006, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washingt ...
released version 1.0 of Windows PowerShell
PowerShell is a task automation and configuration management program from Microsoft, consisting of a command-line shell and the associated scripting language. Initially a Windows component only, known as Windows PowerShell, it was made open-sourc ...
(formerly codenamed ''Monad''), which combined features of traditional Unix shells with their proprietary object-oriented .NET Framework
The .NET Framework (pronounced as "''dot net"'') is a proprietary software framework developed by Microsoft that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. It was the predominant implementation of the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) until bein ...
. MinGW
MinGW ("Minimalist GNU for Windows"), formerly mingw32, is a free and open source software development environment to create Microsoft Windows applications.
MinGW includes a port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), GNU Binutils for Windows ( ...
and Cygwin
Cygwin ( ) is a POSIX-compatible programming and runtime environment that runs natively on Microsoft Windows. Under Cygwin, source code designed for Unix-like operating systems may be compiled with minimal modification and executed.
The Cygwin i ...
are open-source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open-source model is a decentralized sof ...
packages for Windows that offer a Unix-like CLI. Microsoft provides MKS Inc.
MKS, Inc (formerly called Mortice Kern Systems) is a subsidiary of PTC, Inc. It was previously a multinational independent software vendor that was acquired by Parametric Technology Corporation (now PTC) on May 31, 2011. MKS operated in the A ...
's ksh implementation ''MKS Korn shell'' for Windows through their Services for UNIX add-on.
Since 2001, the Macintosh
The Mac (known as Macintosh until 1999) is a family of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc. Macs are known for their ease of use and minimalist designs, and are popular among students, creative professionals, and software en ...
operating system macOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and lap ...
has been based on a Unix-like operating system called Darwin. On these computers, users can access a Unix-like command-line interface by running the terminal emulator
A terminal emulator, or terminal application, is a computer program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term ''terminal'' covers all remote termi ...
program called Terminal, which is found in the Utilities sub-folder of the Applications folder, or by remotely logging into the machine using ssh
The Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Its most notable applications are remote login and command-line execution.
SSH applications are based on a ...
. Z shell
The Z shell (Zsh) is a Unix shell that can be used as an interactive login shell and as a command interpreter for shell scripting. Zsh is an extended Bourne shell with many improvements, including some features of Bash, ksh, and tcsh.
Histor ...
is the default shell for macOS; Bash, tcsh
tcsh ( “tee-see-shell”, “tee-shell”, or as “tee see ess aitch”, tcsh) is a Unix shell based on and backward compatible with the C shell (csh).
Shell
It is essentially the C shell with programmable command-line completion, command-l ...
, and the KornShell
KornShell (ksh) is a Unix shell which was developed by David Korn at Bell Labs in the early 1980s and announced at USENIX on July 14, 1983. The initial development was based on Bourne shell source code. Other early contributors were Bell L ...
are also provided. Before macOS Catalina
macOS Catalina (version 10.15) is the sixteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop operating system for Macintosh computers. It is the successor to macOS Mojave and was announced at WWDC 2019 on June 3, 2019 and released to the publi ...
, Bash was the default.
Usage
A CLI is used whenever a large vocabulary of commands or queries, coupled with a wide (or arbitrary) range of options, can be entered more rapidly as text than with a pure GUI. This is typically the case with operating system command shells. CLIs are also used by systems with insufficient resources to support a graphical user interface. Some computer language systems (such asPython
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (pr ...
, Forth
Forth or FORTH may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''forth'' magazine, an Internet magazine
* ''Forth'' (album), by The Verve, 2008
* ''Forth'', a 2011 album by Proto-Kaw
* Radio Forth, a group of independent local radio stations in Scotl ...
, LISP
A lisp is a speech impairment in which a person misarticulates sibilants (, , , , , , , ). These misarticulations often result in unclear speech.
Types
* A frontal lisp occurs when the tongue is placed anterior to the target. Interdental lisping ...
, Rexx
Rexx (Restructured Extended Executor) is a programming language that can be interpreted or compiled. It was developed at IBM by Mike Cowlishaw. It is a structured, high-level programming language designed for ease of learning and reading. ...
, and many dialects of BASIC
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College i ...
) provide an interactive command-line mode to allow for rapid evaluation of code.
CLIs are often used by programmers and system administrators, in engineering and scientific environments, and by technically advanced personal computer users. CLIs are also popular among people with visual disabilities since the commands and responses can be displayed using refreshable Braille display
A refreshable braille display or braille terminal is an electro-mechanical device for displaying braille characters, usually by means of round-tipped pins raised through holes in a flat surface. Visually impaired computer users who cannot use a s ...
s.
Anatomy of a shell CLI
The general pattern of a command line interface is: Prompt command param1 param2 param3 … paramN * Prompt — generated by the program to provide context for the user. * Command — provided by the user. Commands are usually one of three classes: *# ''Internal'' commands are recognized and processed by the command line interpreter. *# ''Included'' commands run separate executables. *# ''External'' commands run executable files that may be included by other parties. * param1 …paramN — parameters provided by the user. The format and meaning of the parameters depends upon the command. In the case of Included or External commands, the values of the parameters are delivered to the program as it is launched by the OS. Parameters may be eitherArguments
An argument is a statement or group of statements called premises intended to determine the degree of truth or acceptability of another statement called conclusion. Arguments can be studied from three main perspectives: the logical, the dialectic ...
or Options.
In this format, the delimiters between command-line elements are whitespace character
In computer programming, whitespace is any character or series of characters that represent horizontal or vertical space in typography. When rendered, a whitespace character does not correspond to a visible mark, but typically does occupy an are ...
s and the end-of-line delimiter is the newline
Newline (frequently called line ending, end of line (EOL), next line (NEL) or line break) is a control character or sequence of control characters in character encoding specifications such as ASCII, EBCDIC, Unicode, etc. This character, or a ...
delimiter. This is a widely used (but not universal) convention.
A CLI can generally be considered as consisting of syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency ...
and semantics
Semantics (from grc, σημαντικός ''sēmantikós'', "significant") is the study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy, linguistics and compu ...
. The ''syntax'' is the grammar that all commands must follow. In the case of operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
s, DOS
DOS is shorthand for the MS-DOS and IBM PC DOS family of operating systems.
DOS may also refer to:
Computing
* Data over signalling (DoS), multiplexing data onto a signalling channel
* Denial-of-service attack (DoS), an attack on a communicatio ...
and Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and ot ...
each define their own set of rules that all commands must follow. In the case of embedded systems
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded'' a ...
, each vendor, such as Nortel
Nortel Networks Corporation (Nortel), formerly Northern Telecom Limited, was a Canadian multinational telecommunications and data networking equipment manufacturer headquartered in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It was founded in Montreal, Quebec, ...
, Juniper Networks
Juniper Networks, Inc. is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Sunnyvale, California. The company develops and markets networking products, including routers, switches, network management software, network security products, ...
or Cisco Systems, defines their own proprietary set of rules. These rules also dictate how a user navigates through the system of commands. The ''semantics'' define what sort of operations are possible, on what sort of data these operations can be performed, and how the grammar represents these operations and data—the symbolic meaning in the syntax.
Two different CLIs may agree on either syntax or semantics, but it is only when they agree on both that they can be considered sufficiently similar to allow users to use both CLIs without needing to learn anything, as well as to enable re-use of scripts.
A simple CLI will display a prompt, accept a "command line" typed by the user terminated by the Enter key
On computer keyboards, the enter key and return key are two closely related keys with overlapping and distinct functions dependent on operating system and application.
Functions
The return key has its origins in two typewriter functions: ca ...
, then execute the specified command and provide textual display of results or error messages. Advanced CLIs will validate, interpret and parameter-expand the command line before executing the specified command, and optionally capture or redirect its output.
Unlike a button or menu item in a GUI, a command line is typically self-documenting, stating exactly what the user wants done. In addition, command lines usually include many default
Default may refer to:
Law
* Default (law), the failure to do something required by law
** Default (finance), failure to satisfy the terms of a loan obligation or failure to pay back a loan
** Default judgment, a binding judgment in favor of ei ...
s that can be changed to customize the results. Useful command lines can be saved by assigning a character string
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation) ...
or alias to represent the full command, or several commands can be grouped to perform a more complex sequence – for instance, compile the program, install it, and run it — creating a single entity, called a command procedure or script which itself can be treated as a command. These advantages mean that a user must figure out a complex command or series of commands only once, because they can be saved, to be used again.
The commands given to a CLI shell are often in one of the following forms:
*
*
*
*
where ''doSomething'' is, in effect, a verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descri ...
, ''how'' an adverb An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, adjective, another adverb, determiner, clause, preposition, or sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, level of certainty, etc., answering que ...
(for example, should the command be executed "verbosely" or "quietly") and ''toFiles'' an object or objects (typically one or more files) on which the command should act. The > in the third example is a redirection operator
In computing, redirection is a form of interprocess communication, and is a function common to most command-line interpreters, including the various Unix shells that can redirect standard streams to user-specified locations.
In Unix-like oper ...
, telling the command-line interpreter to send the output of the command not to its own standard output (the screen) but to the named file. This will overwrite the file. Using >> will redirect the output and append it to the file. Another redirection operator is the vertical bar
The vertical bar, , is a glyph with various uses in mathematics, computing, and typography. It has many names, often related to particular meanings: Sheffer stroke (in logic), pipe, bar, or (literally the word "or"), vbar, and others.
Usage ...
(, ), which creates a pipeline
Pipeline may refer to:
Electronics, computers and computing
* Pipeline (computing), a chain of data-processing stages or a CPU optimization found on
** Instruction pipelining, a technique for implementing instruction-level parallelism within a s ...
where the output of one command becomes the input to the next command.
CLI and resource protection
One can modify the set of available commands by modifying which paths appear in thePATH
A path is a route for physical travel – see Trail.
Path or PATH may also refer to:
Physical paths of different types
* Bicycle path
* Bridle path, used by people on horseback
* Course (navigation), the intended path of a vehicle
* Desire p ...
environment variable. Under Unix, commands also need be marked as executable
In computing, executable code, an executable file, or an executable program, sometimes simply referred to as an executable or binary, causes a computer "to perform indicated tasks according to encoded instructions", as opposed to a data fil ...
files. The directories in the path variable are searched in the order they are given. By re-ordering the path, one can run e.g. \OS2\MDOS\E.EXE instead of \OS2\E.EXE, when the default is the opposite. Renaming of the executables also works: people often rename their favourite editor to EDIT, for example.
The command line allows one to restrict available commands, such as access to advanced internal commands. The Windows CMD.EXE does this. Often, shareware programs will limit the range of commands, including printing a command 'your administrator has disabled running batch files' from the prompt.
Some CLIs, such as those in network router
A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers perform the traffic directing functions between networks and on the global Internet. Data sent through a network, such as a web page or email, is ...
s, have a hierarchy of modes, with a different set of commands supported in each mode. The set of commands are grouped by association with security, system, interface, etc. In these systems the user might traverse through a series of sub-modes. For example, if the CLI had two modes called ''interface'' and ''system'', the user might use the command ''interface'' to enter the interface mode. At this point, commands from the system mode may not be accessible until the user exits the interface mode and enters the system mode.
Command prompt
 A command prompt (or just ''prompt'') is a sequence of (one or more) characters used in a command-line interface to indicate readiness to accept commands. It literally prompts the user to take action. A prompt usually ends with one of the characters
A command prompt (or just ''prompt'') is a sequence of (one or more) characters used in a command-line interface to indicate readiness to accept commands. It literally prompts the user to take action. A prompt usually ends with one of the characters $, %, #, :, > or - and often includes other information, such as the path of the current working directory
In computing, the working directory of a process is a directory of a hierarchical file system, if any, dynamically associated with each process. It is sometimes called the current working directory (CWD), e.g. the BSD getcwd function, or just cu ...
and the hostname
In computer networking, a hostname (archaically nodename) is a label that is assigned to a device connected to a computer network and that is used to identify the device in various forms of electronic communication, such as the World Wide Web. Hos ...
.
On many Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and ot ...
and derivative systems, the prompt commonly ends in $ or % if the user is a normal user, but in # if the user is a superuser
In computing, the superuser is a special user account used for system administration. Depending on the operating system (OS), the actual name of this account might be root, administrator, admin or supervisor. In some cases, the actual name of th ...
("root" in Unix terminology).
End-users can often modify prompts. Depending on the environment, they may include colors, special characters, and other elements (like variables and functions for the current time, user, shell number or working directory) in order, for instance, to make the prompt more informative or visually pleasing, to distinguish sessions on various machines, or to indicate the current level of nesting of commands. On some systems, special tokens in the definition of the prompt can be used to cause external programs to be called by the command-line interpreter while displaying the prompt.
In DOS' COMMAND.COM and in Windows NT's cmd.exe users can modify the prompt by issuing a PROMPT command or by directly changing the value of the corresponding %PROMPT% environment variable
An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. They are part of the environment in which a process runs. For example, a running process can query the value of the TEMP en ...
. The default of most modern systems, the C:\> style is obtained, for instance, with PROMPT $P$G. The default of older DOS systems, C> is obtained by just PROMPT, although on some systems this produces the newer C:\> style, unless used on floppy drives A: or B:; on those systems PROMPT $N$G can be used to override the automatic default and explicitly switch to the older style.
Many Unix systems feature the $PS1 variable (Prompt String 1), although other variables also may affect the prompt (depending on the shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard o ...
used). In the Bash shell, a prompt of the form:
ime
Ime is a village in Lindesnes municipality in Agder county, Norway. The village is located on the east side of the river Mandalselva, along the European route E39 highway. Ime is an eastern suburb of the town of Mandal. Ime might be considered to ...
user@host: work_dir $zsh
The Z shell (Zsh) is a Unix shell that can be used as an interactive login shell and as a command interpreter for shell scripting. Zsh is an extended Bourne shell with many improvements, including some features of Bash, ksh, and tcsh.
Histo ...
the $RPROMPT variable controls an optional "prompt" on the right-hand side of the display. It is not a real prompt in that the location of text entry does not change. It is used to display information on the same line as the prompt, but right-justified.
In RISC OS
RISC OS is a computer operating system originally designed by Acorn Computers Ltd in Cambridge, England. First released in 1987, it was designed to run on the ARM chipset, which Acorn had designed concurrently for use in its new line of Archi ...
the command prompt is a * symbol, and thus (OS) CLI commands are often referred to as "star commands". One can also access the same commands from other command lines (such as the BBC BASIC
BBC BASIC is a version of the BASIC programming language released in 1981 as the native programming language for the BBC Micro home/personal computer, providing a standardized language for a UK computer literacy project of the BBC. It was writ ...
command line), by preceding the command with a *.
Arguments
parameter
A parameter (), generally, is any characteristic that can help in defining or classifying a particular system (meaning an event, project, object, situation, etc.). That is, a parameter is an element of a system that is useful, or critical, when ...
is an item of information provided to a program when it is started. A program can have many command-line arguments that identify sources or destinations of information, or that alter the operation of the program.
When a command processor is active a program is typically invoked by typing its name followed by command-line arguments (if any). For example, in Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and ot ...
and Unix-like environments, an example of a command-line argument is:
C++
C, or c, is the third letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''cee'' (pronounced ), plural ''cees''.
History
"C" ...
and Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's most ...
, allow a program to interpret the command-line arguments by handling them as string parameters in the main function
In computer programming, an entry point is the place in a program where the execution of a program begins, and where the program has access to command line arguments.
To start a program's execution, the loader or operating system passes contr ...
. Other languages, such as Python
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (pr ...
, expose operating system specific API
An application programming interface (API) is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how ...
(functionality) through sys module, and in particular sys.argv for "command-line arguments".
In Unix-like operating system
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X or *nix) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-li ...
s, a single hyphen used in place of a file name is a special value specifying that a program should handle data coming from the standard input
In computer programming, standard streams are interconnected input and output communication channels between a computer program and its environment when it begins execution. The three input/output (I/O) connections are called standard input (stdi ...
or send data to the standard output
In computer programming, standard streams are interconnected input and output communication channels between a computer program and its environment when it begins execution. The three input/output (I/O) connections are called standard input (stdi ...
.
Command-line option
A command-line option or simply option (also known as a flag or switch) modifies the operation of a command; the effect is determined by the command's program. Options follow the command name on the command line, separated by spaces. A space before the first option is not always required, such asDir/? and DIR /? in DOS, which have the same effect of listing the DIR command's available options, whereas dir --help (in many versions of Unix) ''does'' require the option to be preceded by at least one space (and is case-sensitive).
The format of options varies widely between operating systems. In most cases the syntax is by convention rather than an operating system requirement; the entire command line is simply a string passed to a program, which can process it in any way the programmer wants, so long as the interpreter can tell where the command name ends and its arguments and options begin.
A few representative samples of command-line options, all relating to listing files in a directory, to illustrate some conventions:
=Abbreviating commands
= InMultics
Multics ("Multiplexed Information and Computing Service") is an influential early time-sharing operating system based on the concept of a single-level memory.Dennis M. Ritchie, "The Evolution of the Unix Time-sharing System", Communications of t ...
, command-line options and subsystem keywords may be abbreviated. This idea appears to derive from the PL/I programming language, with its shortened keywords (e.g., STRG for STRINGRANGE and DCL for DECLARE). For example, in the Multics "forum" subsystem, the ''-long_subject'' parameter can be abbreviated ''-lgsj''. It is also common for Multics commands to be abbreviated, typically corresponding to the initial letters of the words that are strung together with underscores to form command names, such as the use of ''did'' for ''delete_iacl_dir''.
In some other systems abbreviations are automatic, such as permitting enough of the first characters of a command name to uniquely identify it (such as SU as an abbreviation for SUPERUSER) while others may have some specific abbreviations pre-programmed (e.g. MD for MKDIR
The mkdir (make directory) command in the Unix, DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS operating systems is used to make a new directory. It is also available in the EFI shell and in the PHP scripting language. In DOS, OS ...
in COMMAND.COM) or user-defined via batch scripts and aliases (e.g. alias md mkdir in tcsh
tcsh ( “tee-see-shell”, “tee-shell”, or as “tee see ess aitch”, tcsh) is a Unix shell based on and backward compatible with the C shell (csh).
Shell
It is essentially the C shell with programmable command-line completion, command-l ...
).
=Option conventions in DOS, Windows, OS/2
= On DOS, OS/2 and Windows, different programs called from their COMMAND.COM or CMD.EXE (or internal their commands) may use different syntax within the same operating system. For example: * Options may be indicated by either of the "switch characters":/, -, or either may be allowed. See below.
* They may or may not be case-sensitive In computers, case sensitivity defines whether uppercase and lowercase letters are treated as distinct (case-sensitive) or equivalent (case-insensitive). For instance, when users interested in learning about dogs search an e-book, "dog" and "Dog" a ...
.
* Sometimes options and their arguments are run together, sometimes separated by whitespace, and sometimes by a character, typically : or =; thus Prog -fFilename, Prog -f Filename, Prog -f:Filename, Prog -f=Filename.
* Some programs allow single-character options to be combined; others do not. The switch -fA may mean the same as -f -A, or it may be incorrect, or it may even be a valid but different parameter.
In DOS
DOS is shorthand for the MS-DOS and IBM PC DOS family of operating systems.
DOS may also refer to:
Computing
* Data over signalling (DoS), multiplexing data onto a signalling channel
* Denial-of-service attack (DoS), an attack on a communicatio ...
, OS/2
OS/2 (Operating System/2) is a series of computer operating systems, initially created by Microsoft and IBM under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci. As a result of a feud between the two companies over how to position OS/2 re ...
and Windows
Windows is a group of several Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, W ...
, the forward slash (/) is most prevalent, although the hyphen-minus is also sometimes used. In many versions of DOS (MS-DOS/PC DOS 2.xx and higher, all versions of DR-DOS
DR-DOS (written as DR DOS, without a hyphen, in versions up to and including 6.0) is a disk operating system for IBM PC compatibles. Upon its introduction in 1988, it was the first DOS attempting to be compatible with IBM PC DOS and MS-DO ...
since 5.0, as well as PTS-DOS
PTS-DOS (aka PTS/DOS) is a disk operating system, a DOS clone, developed in Russia by PhysTechSoft and Paragon Technology Systems.
History and versions
PhysTechSoft was formed in 1991 in Moscow, Russia by graduates and members of MIPT, ...
, Embedded DOS
General Software was a Washington, USA based creator and supplier of system software headquartered in Bellevue, Washington. It was founded in 1989 by Steve Jones and later incorporated in 1990 as General Software, Inc. In 2008, the company was ...
, FreeDOS
FreeDOS (formerly Free-DOS and PD-DOS) is a free software operating system for IBM PC compatible computers. It intends to provide a complete MS-DOS-compatible environment for running legacy software and supporting embedded systems.
FreeDOS ca ...
and RxDOS
DOS is shorthand for the MS-DOS and IBM PC DOS family of operating systems.
DOS may also refer to:
Computing
* Data over signalling (DoS), multiplexing data onto a signalling channel
* Denial-of-service attack (DoS), an attack on a communicatio ...
) the switch character (sometimes abbreviated switchar or switchchar) to be used is defined by a value returned from a system call
In computing, a system call (commonly abbreviated to syscall) is the programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service from the operating system on which it is executed. This may include hardware-related services (for example, ac ...
( INT 21h/AX=3700h). The default character returned by this API is /, but can be changed to a hyphen-minus on the above-mentioned systems, except for under Datalight ROM-DOS and MS-DOS/PC DOS 5.0 and higher, which always return / from this call (unless one of many available TSRs to reenable the SwitChar feature is loaded). In some of these systems (MS-DOS/PC DOS 2.xx, DOS Plus 2.1, DR-DOS 7.02 and higher, PTS-DOS, Embedded DOS, FreeDOS and RxDOS), the setting can also be pre-configured by a SWITCHAR
A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and pro ...
directive in CONFIG.SYS
CONFIG.SYS is the primary configuration file for the DOS and OS/2 operating systems. It is a special ASCII text file that contains user-accessible setup or configuration directives evaluated by the operating system's DOS BIOS (typically residing ...
. General Software's Embedded DOS provides a SWITCH command for the same purpose, whereas 4DOS
4DOS is a command-line interpreter by JP Software, designed to replace the default command interpreter COMMAND.COM in Microsoft DOS and Windows. It was written by Rex C. Conn and Tom Rawson and first released in 1989. Compared to the default, ...
allows the setting to be changed via SETDOS /W:n. Under DR-DOS, if the setting has been changed from /, the first directory separator \ in the display of the PROMPT parameter $G will change to a forward slash / (which is also a valid directory separator in DOS, FlexOS, 4680 OS, 4690 OS, OS/2 and Windows) thereby serving as a visual clue to indicate the change. Also, the current setting is reflected also in the built-in help screens. Some versions of DR-DOS COMMAND.COM also support a PROMPT token $/ to display the current setting. COMMAND.COM since DR-DOS 7.02 also provides a pseudo-environment variable
An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. They are part of the environment in which a process runs. For example, a running process can query the value of the TEMP en ...
named %/% to allow portable batchjobs to be written. Several external DR-DOS commands additionally support an environment variable
An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. They are part of the environment in which a process runs. For example, a running process can query the value of the TEMP en ...
%SWITCHAR% to override the system setting.
However, many programs are hardwired to use / only, rather than retrieving the switch setting before parsing command-line arguments. A very small number, mainly ports from Unix-like systems, are programmed to accept "-" even if the switch character is not set to it (for example netstat
In computing, netstat (''network statistics'') is a command-line network utility that displays network connections for Transmission Control Protocol (both incoming and outgoing), routing tables, and a number of network interface (network inter ...
and ping
Ping may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Ping, a domesticated Chinese duck in the illustrated book '' The Story about Ping'', first published in 1933
* Ping, a minor character in ''Seinfeld'', an NBC sitcom
* Ping, a c ...
, supplied with Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for se ...
, will accept the /? option to list available options, and yet the list will specify the "-" convention).
=Option conventions in Unix-like systems
= In Unix-like systems, the ASCIIhyphen-minus
The hyphen-minus is the most commonly used type of hyphen, widely used in digital documents. It is the only character that looks like a minus sign or a dash in many character sets such as ASCII or on most keyboards, so it is also used as such. ...
begins options; the new (and GNU
GNU () is an extensive collection of free software (383 packages as of January 2022), which can be used as an operating system or can be used in parts with other operating systems. The use of the completed GNU tools led to the family of operat ...
) convention is to use ''two'' hyphens then a word (e.g. --create) to identify the option's use while the old convention (and still available as an option for frequently-used options) is to use one hyphen then one letter (e.g., -c); if one hyphen is followed by two or more letters it may mean two options are being specified, or it may mean the second and subsequent letters are a parameter (such as filename or date) for the first option.
Two hyphen-minus characters without following letters (--) may indicate that the remaining arguments should not be treated as options, which is useful for example if a file name itself begins with a hyphen, or if further arguments are meant for an inner command (e.g., sudo
sudo ( or ) is a program for Unix-like computer operating systems that enables users to run programs with the security privileges of another user, by default the superuser. It originally stood for "superuser do", as that was all it did, and it ...
). Double hyphen-minuses are also sometimes used to prefix "long options" where more descriptive option names are used. This is a common feature of GNU
GNU () is an extensive collection of free software (383 packages as of January 2022), which can be used as an operating system or can be used in parts with other operating systems. The use of the completed GNU tools led to the family of operat ...
software. The ''getopt
Getopt is a C library function used to parse command-line options of the Unix/POSIX style. It is a part of the POSIX specification, and is universal to Unix-like systems.
It is also the name of a Unix program for parsing command line arguments i ...
'' function and program, and the ''getopts
getopts is a built-in Unix shell command for parsing command-line arguments. It is designed to process command line arguments that follow the POSIX Utility Syntax Guidelines, based on the C interface of getopt.
The predecessor to was the ext ...
'' command are usually used for parsing command-line options.
Unix command names, arguments and options are case-sensitive (except in a few examples, mainly where popular commands from other operating systems have been ported to Unix).
=Option conventions in other systems
=FlexOS
FlexOS is a discontinued modular real-time multiuser multitasking operating system (RTOS) designed for computer-integrated manufacturing, laboratory, retail and financial markets. Developed by Digital Research's Flexible Automation Business U ...
, 4680 OS and 4690 OS
4690 Operating System (sometimes shortened to 4690 OS or 4690) is a specially designed point of sale (POS) operating system, originally sold by IBM. In 2012, IBM sold its retail business, including this product, to Toshiba, which assumed support. ...
use -.
CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/ 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initially ...
typically used /nowiki> COPY source file a target file b (REPLACE OLDDATE
Data General's CLI under their Data General RDOS, RDOS, Data General AOS, AOS, etc. operating systems, as well as the version of CLI that came with their Business Basic, uses only / as the switch character, is case-insensitive, and allows "local switches" on some arguments to control the way they are interpreted, such as MAC/U LIB/S A B C $LPT/L has the global option "U" to the macro assembler command to append user symbols, but two local switches, one to specify LIB should be skipped on pass 2 and the other to direct listing to the printer, $LPT.
Built-in usage help
One of the criticisms of a CLI is the lack of cues to the user as to the available actions. In contrast, GUIs usually inform the user of available actions with menus, icons, or other visual cues. To overcome this limitation, many CLI programs display ausage message
In computer programming, a usage message or help message refers to a brief message displayed by a program that utilizes a command-line interface for execution. This message usually consists of the correct command line usage for the program and inc ...
, typically when invoked with no arguments or one of ?, -?, -h, -H, /?, /h, /H, /Help, -help, or --help.
However, entering a program name without parameters in the hope that it will display usage help can be hazardous, as programs and scripts for which command line arguments are optional will execute without further notice.
Although desirable at least for the help parameter, programs may not support all option lead-in characters exemplified above.
Under DOS, where the default command-line option character can be changed from / to -, programs may query the SwitChar
A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and pro ...
API in order to determine the current setting. So, if a program is not hardwired to support them all, a user may need to know the current setting even to be able to reliably request help.
If the SwitChar has been changed to - and therefore the / character is accepted as alternative path delimiter also at the DOS command line, programs may misinterpret options like /h or /H as paths rather than help parameters. However, if given as first or only parameter, most DOS programs will, by convention, accept it as request for help regardless of the current SwitChar setting.
In some cases, different levels of help can be selected for a program. Some programs supporting this allow to give a verbosity level as an optional argument to the help parameter (as in /H:1, /H:2, etc.) or they give just a short help on help parameters with question mark and a longer help screen for the other help options.
Depending on the program, additional or more specific help on accepted parameters is sometimes available by either providing the parameter in question as an argument to the help parameter or vice versa (as in /H:W or in /W:? (assuming /W would be another parameter supported by the program)).
In a similar fashion to the help parameter, but much less common, some programs provide additional information about themselves (like mode, status, version, author, license or contact information) when invoked with an "about" parameter like -!, /!, -about, or --about.
Since the ? and ! characters typically also serve other purposes at the command line, they may not be available in all scenarios, therefore, they should not be the only options to access the corresponding help information.
 If more detailed help is necessary than provided by a program's built-in internal help, many systems support a dedicated external "
If more detailed help is necessary than provided by a program's built-in internal help, many systems support a dedicated external " help ''command''" command (or similar), which accepts a command name as calling parameter and will invoke an external help system.
In the DR-DOS family, typing /? or /H at the COMMAND.COM prompt instead of a command itself will display a dynamically generated list of available internal commands; 4DOS
4DOS is a command-line interpreter by JP Software, designed to replace the default command interpreter COMMAND.COM in Microsoft DOS and Windows. It was written by Rex C. Conn and Tom Rawson and first released in 1989. Compared to the default, ...
and NDOS
4DOS is a command-line interpreter by JP Software, designed to replace the default command interpreter COMMAND.COM in Microsoft DOS and Windows. It was written by Rex C. Conn and Tom Rawson and first released in 1989. Compared to the default, ...
support the same feature by typing ? at the prompt (which is also accepted by newer versions of DR-DOS COMMAND.COM); internal commands can be individually disabled or reenabled via SETDOS /I. In addition to this, some newer versions of DR-DOS COMMAND.COM also accept a ?% command to display a list of available built-in pseudo-environment variable
An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. They are part of the environment in which a process runs. For example, a running process can query the value of the TEMP en ...
s. Besides their purpose as quick help reference this can be used in batchjobs to query the facilities of the underlying command-line processor.
Command description syntax
Built-in usage help andman page
A man page (short for manual page) is a form of software documentation usually found on a Unix or Unix-like operating system. Topics covered include computer programs (including library and system calls), formal standards and conventions, and ...
s commonly employ a small syntax to describe the valid command form:
* angle brackets for ''required'' parameters: ping
* square brackets for ''optional'' parameters: mkdir p
* ellipses for ''repeated'' items: cp ource2…
* vertical bars for ''choice'' of items: netstat
Notice that these characters have different meanings than when used directly in the shell. Angle brackets may be omitted when confusing the parameter name with a literal string is not likely.
The space character
In many areas of computing, but particularly in the command line, thespace character
In computer programming, whitespace is any character or series of characters that represent horizontal or vertical space in typography. When rendered, a whitespace character does not correspond to a visible mark, but typically does occupy an ar ...
can cause problems as it has two distinct and incompatible functions: as part of a command or parameter, or as a parameter or name separator. Ambiguity can be prevented either by prohibiting embedded spaces in file and directory names in the first place (for example, by substituting them with underscores _), or by enclosing a name with embedded spaces between quote characters or using an escape character
In computing and telecommunication, an escape character is a character that invokes an alternative interpretation on the following characters in a character sequence. An escape character is a particular case of metacharacters. Generally, the ...
before the space, usually a backslash
The backslash is a typographical mark used mainly in computing and mathematics. It is the mirror image of the common slash . It is a relatively recent mark, first documented in the 1930s.
History
, efforts to identify either the origin ...
(\). For example
:Long path/Long program name Parameter one Parameter two …
is ambiguous (is "program name" part of the program name, or two parameters?); however
:Long_path/Long_program_name Parameter_one Parameter_two …,
:LongPath/LongProgramName ParameterOne ParameterTwo …,
:"Long path/Long program name" "Parameter one" "Parameter two" …
and
:Long\ path/Long\ program\ name Parameter\ one Parameter\ two …
are not ambiguous. Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and ot ...
-based operating systems minimize the use of embedded spaces to minimize the need for quotes. In Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for se ...
, one often has to use quotes because embedded spaces (such as in directory names) are common.
Command-line interpreter
The term command-line interpreter (CLI) is applied to computer programs designed tointerpret
Interpreting is a translational activity in which one produces a first and final target-language output on the basis of a one-time exposure to an expression in a source language.
The most common two modes of interpreting are simultaneous inter ...
a sequence of lines of text which may be entered by a user, read from a file
File or filing may refer to:
Mechanical tools and processes
* File (tool), a tool used to ''remove'' fine amounts of material from a workpiece
**Filing (metalworking), a material removal process in manufacturing
** Nail file, a tool used to gen ...
or another kind of data stream
In connection-oriented communication, a data stream is the transmission of a sequence of digitally encoded coherent signals to convey information. Typically, the transmitted symbols are grouped into a series of packets.
Data streaming has be ...
. The context of interpretation is usually one of a given operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
or programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Most programming languages are text-based formal languages, but they may also be graphical. They are a kind of computer language.
The description of a programming ...
.
Command-line interpreters allow users to issue various commands in a very efficient (and often terse) way. This requires the user to know the names of the commands and their parameters, and the syntax of the language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
that is interpreted.
The Unix #! mechanism and OS/2 EXTPROC command facilitate the passing of batch files to external processors. One can use these mechanisms to write specific command processors for dedicated uses, and process external data files which reside in batch files.
Many graphical interfaces, such as the OS/2 Presentation Manager Presentation Manager (PM) is the graphical user interface ( GUI) that IBM and Microsoft introduced in version 1.1 of their operating system OS/2 in late 1988.
History
Microsoft began developing a graphic user interface (GUI) in 1981. After it ...
and early versions of Microsoft Windows use command-lines to call helper programs to open documents and programs. The commands are stored in the graphical shell or in files like the registry or the OS/2
OS/2 (Operating System/2) is a series of computer operating systems, initially created by Microsoft and IBM under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci. As a result of a feud between the two companies over how to position OS/2 re ...
OS2USER.INI file.
Early history

 The earliest computers did not support interactive input/output devices, often relying on sense switches and lights to communicate with the
The earliest computers did not support interactive input/output devices, often relying on sense switches and lights to communicate with the computer operator
A computer operator is a role in IT which oversees the running of computer systems, ensuring that the machines, and computers are running properly. The job of a computer operator as defined by the United States Bureau of Labor Statistics is to ...
. This was adequate for batch systems that ran one program at a time, often with the programmer acting as operator. This also had the advantage of low overhead, since lights and switches could be tested and set with one machine instruction. Later a single system console
One meaning of system console, computer console, root console, operator's console, or simply console is the text entry and display device for system administration messages, particularly those from the BIOS or boot loader, the kernel, from the i ...
was added to allow the operator to communicate with the system.
From the 1960s onwards, user interaction with computers was primarily by means of command-line interfaces, initially on machines like the Teletype Model 33
The Teletype Model 33 is an electromechanical teleprinter designed for light-duty office use. It is less rugged and cost less than earlier Teletype machines. The Teletype Corporation introduced the Model 33 as a commercial product in 1963 after ...
ASR, but then on early CRT-based computer terminals
A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that can be used for entering data into, and transcribing data from, a computer or a computing system. The teletype was an example of an early-day hard-copy terminal ...
such as the VT52
The VT50 was a CRT-based computer terminal introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in July 1974. It provided a display with 12 rows and 80 columns of upper-case text, and used an expanded set of control characters and forward-only scro ...
.
All of these devices were purely text based, with no ability to display graphic or pictures. For business application programs, text-based menus were used, but for more general interaction the command line was the interface.
Around 1964 Louis Pouzin
Louis Pouzin (April 20, 1931 in Chantenay-Saint-Imbert, Nièvre, France) is a French computer scientist. He designed an early packet communications network, CYCLADES.
This network was the first actual implementation of the pure datagram model, ...
introduced the concept and the name ''shell'' in Multics
Multics ("Multiplexed Information and Computing Service") is an influential early time-sharing operating system based on the concept of a single-level memory.Dennis M. Ritchie, "The Evolution of the Unix Time-sharing System", Communications of t ...
, building on earlier, simpler facilities in the Compatible Time-Sharing System
The Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS) was the first general purpose time-sharing operating system. Compatible Time Sharing referred to time sharing which was compatible with batch processing; it could offer both time sharing and batch proces ...
(CTSS).
From the early 1970s the Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and ot ...
operating system adapted the concept of a powerful command-line environment, and introduced the ability to ''pipe
Pipe(s), PIPE(S) or piping may refer to:
Objects
* Pipe (fluid conveyance), a hollow cylinder following certain dimension rules
** Piping, the use of pipes in industry
* Smoking pipe
** Tobacco pipe
* Half-pipe and quarter pipe, semi-circul ...
'' the output of one command in as input to another. Unix also had the capability to save and re-run strings of commands as "shell scripts
A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by a Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be scripting languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file manip ...
" which acted like custom commands.
The command-line was also the main interface for the early home computers such as the Commodore PET
The Commodore PET is a line of personal computers produced starting in 1977 by Commodore International. A single all-in-one case combines a MOS Technology 6502 microprocessor, Commodore BASIC in read-only memory, keyboard, monochrome monitor, an ...
, Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-mol ...
and BBC Micro
The British Broadcasting Corporation Microcomputer System, or BBC Micro, is a series of microcomputers and associated peripherals designed and built by Acorn Computers in the 1980s for the BBC Computer Literacy Project. Designed with an emphas ...
– almost always in the form of a BASIC
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College i ...
interpreter. When more powerful business oriented microcomputers arrived with CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/ 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initially ...
and later DOS
DOS is shorthand for the MS-DOS and IBM PC DOS family of operating systems.
DOS may also refer to:
Computing
* Data over signalling (DoS), multiplexing data onto a signalling channel
* Denial-of-service attack (DoS), an attack on a communicatio ...
computers such as the IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team ...
, the command-line began to borrow some of the syntax and features of the Unix shells such as globbing
In computer programming, glob () patterns specify sets of filenames with wildcard characters. For example, the Unix Bash shell command mv *.txt textfiles/ moves (mv) all files with names ending in .txt from the current directory to the director ...
and piping
Within industry, piping is a system of pipes used to convey fluids (liquids and gases) from one location to another. The engineering discipline of piping design studies the efficient transport of fluid.
Industrial process piping (and accompan ...
of output.
The command-line was first seriously challenged by the PARC GUI
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, inst ...
approach used in the 1983 Apple Lisa
Lisa is a desktop computer developed by Apple, released on January 19, 1983. It is one of the first personal computers to present a graphical user interface (GUI) in a machine aimed at individual business users. Its development began in 1978. ...
and the 1984 Apple Macintosh
The Mac (known as Macintosh until 1999) is a family of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc. Macs are known for their ease of use and minimalist designs, and are popular among students, creative professionals, and software en ...
. A few computer users used GUIs such as GEOS and Windows 3.1
Windows 3.1 is a major release of Microsoft Windows. It was released to manufacturing on April 6, 1992, as a successor to Windows 3.0.
Like its predecessors, the Windows 3.1 series ran as a shell on top of MS-DOS. Codenamed Janus, Windows 3. ...
but the majority of IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team ...
users did not replace their COMMAND.COM shell with a GUI until Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of operating systems. The first operating system in the 9x family, it is the successor to Windows 3.1x, and was released to manufacturi ...
was released in 1995.
Modern usage as an operating system shell
While most non-expert computer users now use a GUI almost exclusively, more advanced users have access to powerful command-line environments: * The default VAX/VMS command shell, using theDCL
DCL or may refer to:
* 650 in Roman numerals, see 650 (disambiguation)
Computers
* Data Center Linux, see Open Source Development Labs
* Data Control Language, a subset of SQL
* Dialog Control Language, a language and interpreter within Aut ...
language, has been ported to Windows systems at least three times, including PC-DCL and Acceler8 DCL Lite. Unix command shells have been ported to VMS and DOS/Windows 95 and Windows NT types of operating systems.
* COMMAND.COM is the command-line interpreter of MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few oper ...
, IBM PC DOS
IBM PC DOS, an acronym for IBM Personal Computer Disk Operating System, is a discontinued disk operating system for IBM PC compatibles. It was manufactured and sold by IBM from the early 1980s into the 2000s. Developed by Microsoft, it was also ...
, and clones such as DR-DOS
DR-DOS (written as DR DOS, without a hyphen, in versions up to and including 6.0) is a disk operating system for IBM PC compatibles. Upon its introduction in 1988, it was the first DOS attempting to be compatible with IBM PC DOS and MS-DO ...
, SISNE plus
SISNE plus is a DOS 3.3 compatible clone created by Itautec and Scopus Tecnologia in Brazil prior to the end of the Market Reserve in 1991, which, at that time, forbade the importation of electronic equipment and software for general use. With ...
, PTS-DOS
PTS-DOS (aka PTS/DOS) is a disk operating system, a DOS clone, developed in Russia by PhysTechSoft and Paragon Technology Systems.
History and versions
PhysTechSoft was formed in 1991 in Moscow, Russia by graduates and members of MIPT, ...
, ROM-DOS
Datalight was a privately held software company specializing in power failsafe and high performance software for preserving data integrity in embedded systems. The company was founded in 1983 by Roy Sherrill, and is headquartered in Bothell, Washi ...
, and FreeDOS
FreeDOS (formerly Free-DOS and PD-DOS) is a free software operating system for IBM PC compatible computers. It intends to provide a complete MS-DOS-compatible environment for running legacy software and supporting embedded systems.
FreeDOS ca ...
.
* Windows Resource Kit Resource Kit is a term used by Microsoft for a set of software resources and documentation released for their software products, but which is not part of that product. Resource kits offer supplementary resources such as technical guidance, compatibi ...
and Windows Services for UNIX
Windows Services for UNIX (SFU) is a discontinued software package produced by Microsoft which provided a Unix environment on Windows NT and some of its immediate successor operating-systems.
SFU 1.0 and 2.0 used the MKS Toolkit; starting with ...
include Korn and the Bourne shells along with a Perl interpreter (Services for UNIX contains ActiveState
ActiveState Software Inc is a Canadian software company headquartered in Vancouver, British Columbia. It develops, sells, and supports cross-platform development tools for dynamic languages such as Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, and Tcl, as well a ...
ActivePerl in later versions and Interix
Interix was an optional, POSIX-conformant Unix subsystem for Windows NT operating systems. Interix was a component of Windows Services for UNIX, and a superset of the Microsoft POSIX subsystem. Like the POSIX subsystem, Interix was an environmen ...
for versions 1 and 2 and a shell compiled by Microsoft)
* IBM OS/2 (and derivatives such as eComStation
eComStation or eCS is an operating system based on OS/2 Warp for the 32-bit x86 architecture. It was originally developed by Serenity Systems and Mensys BV under license from IBM. It includes additional applications, and support for new hardwa ...
and ArcaOS
ArcaOS is an operating system based on OS/2, developed and marketed by Arca Noae, LLC under license from IBM. It was codenamed Blue Lion during its development. It builds on OS/2 Warp 4.52 by adding support for new hardware, fixing defects and l ...
) has the cmd.exe processor. This copies the COMMAND.COM commands, with extensions to REXX
Rexx (Restructured Extended Executor) is a programming language that can be interpreted or compiled. It was developed at IBM by Mike Cowlishaw. It is a structured, high-level programming language designed for ease of learning and reading. ...
.
* cmd.exe is part of the Windows NT stream of operating systems.
* Yet another cmd.exe is a stripped-down shell for Windows CE
Windows Embedded Compact, formerly Windows Embedded CE, Windows Powered and Windows CE, is an operating system subfamily developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows Embedded family of products.
Unlike Windows Embedded Standard, which is base ...
3.0.
* An MS-DOS type interpreter called PocketDOS has been ported to Windows CE machines; the most recent release is almost identical to MS-DOS 6.22 and can also run Windows 1, 2, and 3.0, QBasic
QBasic is an integrated development environment (IDE) and interpreter for a variety of dialects of BASIC which are based on QuickBASIC. Code entered into the IDE is compiled to an intermediate representation (IR), and this IR is immediately ex ...
and other development tools, 4NT and 4DOS. The latest release includes several shells, namely MS-DOS 6.22, PC DOS 7, DR DOS 3.xx, and others.
* Windows users might use the CScript interface to alternate programs, from command-line. PowerShell
PowerShell is a task automation and configuration management program from Microsoft, consisting of a command-line shell and the associated scripting language. Initially a Windows component only, known as Windows PowerShell, it was made open-sou ...
provides a command-line interface, but its applets are not written in Shell script
A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by a Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be scripting languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file mani ...
. Implementations of the Unix shell
A Unix shell is a command-line interpreter or shell that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command language and a scripting language, and is used by the operating system to ...
are also available as part of the POSIX sub-system, Cygwin
Cygwin ( ) is a POSIX-compatible programming and runtime environment that runs natively on Microsoft Windows. Under Cygwin, source code designed for Unix-like operating systems may be compiled with minimal modification and executed.
The Cygwin i ...
, MKS Toolkit
MKS Toolkit is a software package produced and maintained by PTC that provides a Unix-like environment for scripting, connectivity and porting Unix and Linux software to Microsoft Windows. It was originally created for MS-DOS, and OS/2 versions w ...
, UWIN
UWIN is a computer software package created by David Korn which allows programs written for the operating system Unix to be built and run on Microsoft Windows with few, if any, changes. Some of the software development was subcontracted to Wipr ...
, Hamilton C shell
Hamilton C shell is a clone of the Unix C shell and utilities
Early
for Microsoft Windows created by Nicole Hamilton at Hamilton Laboratories as a completely original work, not based on any prior code. It was first released on OS/2 on Dece ...
and other software packages. Available shells for these interoperability tools include csh, ksh, sh, Bash, rsh, tclsh
Tk is a free and open-source, cross-platform widget toolkit that provides a library of basic elements of GUI widgets for building a graphical user interface (GUI) in many programming languages.
Tk provides a number of widgets commonly needed t ...
and less commonly zsh
The Z shell (Zsh) is a Unix shell that can be used as an interactive login shell and as a command interpreter for shell scripting. Zsh is an extended Bourne shell with many improvements, including some features of Bash, ksh, and tcsh.
Histo ...
, psh
* Implementations of PHP
PHP is a general-purpose scripting language geared toward web development. It was originally created by Danish-Canadian programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1993 and released in 1995. The PHP reference implementation is now produced by The PHP Group. ...
have a shell for interactive use called php-cli.
* Standard Tcl/Tk
Tk is a free and open-source, cross-platform widget toolkit that provides a library of basic elements of GUI widgets for building a graphical user interface (GUI) in many programming languages.
Tk provides a number of widgets commonly needed t ...
has two interactive shells, Tclsh and Wish, the latter being the GUI version.
* Python
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (pr ...
, Ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sap ...
, Lua, XLNT
XLNT is a scripting language for Windows platforms based on the DCL language for OpenVMS systems.
Overview
Its proprietary implementation has been maintained by its originator, Advanced Systems Concepts, Inc., since 1997. The implementation c ...
, and other interpreters also have command shells for interactive use.
* FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), which was based on Research Unix. The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993. In 2005, FreeBSD was the most popular op ...
uses tcsh
tcsh ( “tee-see-shell”, “tee-shell”, or as “tee see ess aitch”, tcsh) is a Unix shell based on and backward compatible with the C shell (csh).
Shell
It is essentially the C shell with programmable command-line completion, command-l ...
as its default interactive shell for the superuser
In computing, the superuser is a special user account used for system administration. Depending on the operating system (OS), the actual name of this account might be root, administrator, admin or supervisor. In some cases, the actual name of th ...
, and ash as default scripting shell.
* Many Linux distribution
A Linux distribution (often abbreviated as distro) is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel and, often, a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one ...
s have the Bash implementation of the Unix shell
A Unix shell is a command-line interpreter or shell that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command language and a scripting language, and is used by the operating system to ...
.
*Apple macOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and lap ...
and some Linux distributions use zsh
The Z shell (Zsh) is a Unix shell that can be used as an interactive login shell and as a command interpreter for shell scripting. Zsh is an extended Bourne shell with many improvements, including some features of Bash, ksh, and tcsh.
Histo ...
. Previously, macOS used tcsh
tcsh ( “tee-see-shell”, “tee-shell”, or as “tee see ess aitch”, tcsh) is a Unix shell based on and backward compatible with the C shell (csh).
Shell
It is essentially the C shell with programmable command-line completion, command-l ...
and Bash.
* Embedded Linux
Operating systems based on the Linux kernel are used in embedded systems such as consumer electronics (eg. set-top boxes, smart TVs and personal video recorders (PVRs)), in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), networking equipment (such as routers, switc ...
(and other embedded Unix-like) devices often use the Ash implementation of the Unix shell, as part of Busybox
BusyBox is a software suite that provides several Unix utilities in a single executable file. It runs in a variety of POSIX environments such as Linux, Android, and FreeBSD, although many of the tools it provides are designed to work with inte ...
.
* Android uses the mksh shell, which replaces a shell derived from ash that was used in older Android versions, supplemented with commands from the separate ''toolbox'' binary.
* Routers with Cisco IOS
The Internetworking Operating System (IOS) is a family of proprietary network operating systems used on several router and network switch models manufactured by Cisco Systems. The system is a package of routing, switching, internetworking, an ...
, Junos
Junos OS (also known as Juniper Junos, Junos and JUNOS) is a FreeBSD-based network operating system used in Juniper Networks routing, switching and security devices.
Versioning
Junos OS was first made available on 7 July 1998, with new featur ...
and many others are commonly configured from the command line.
* The Plan 9 operating system uses the rc shell which is similar in design to the Bourne shell.
Scripting
Most command-line interpreters support scripting, to various extents. (They are, after all, interpreters of aninterpreted programming language
In computer science, an interpreter is a computer program that directly executes instructions written in a programming or scripting language, without requiring them previously to have been compiled into a machine language program. An interprete ...
, albeit in many cases the language is unique to the particular command-line interpreter.) They will interpret scripts (variously termed shell script
A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by a Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be scripting languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file mani ...
s or batch file
Batch may refer to:
Food and drink
* Batch (alcohol), an alcoholic fruit beverage
* Batch loaf, a type of bread popular in Ireland
* A dialect term for a bread roll used in North Warwickshire, Nuneaton and Coventry, as well as on the Wirral ...
s) written in the language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
that they interpret. Some command-line interpreters also incorporate the interpreter engines of other languages, such as REXX
Rexx (Restructured Extended Executor) is a programming language that can be interpreted or compiled. It was developed at IBM by Mike Cowlishaw. It is a structured, high-level programming language designed for ease of learning and reading. ...
, in addition to their own, allowing the executing of scripts, in those languages, directly within the command-line interpreter itself.
Conversely, scripting programming language
A scripting language or script language is a programming language that is used to manipulate, customize, and automate the facilities of an existing system. Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled.
A scriptin ...
s, in particular those with an eval
In some programming languages, eval , short for the English evaluate, is a function which evaluates a string as though it were an expression in the language, and returns a result; in others, it executes multiple lines of code as though they ha ...
function (such as REXX, Perl
Perl is a family of two high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming languages. "Perl" refers to Perl 5, but from 2000 to 2019 it also referred to its redesigned "sister language", Perl 6, before the latter's name was offic ...
, Python
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (pr ...
, Ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sap ...
or Jython
Jython is an implementation of the Python programming language designed to run on the Java platform. The implementation was formerly known as JPython until 1999.
Overview
Jython programs can import and use any Java class. Except for some standa ...
), can be used to implement command-line interpreters and filters. For a few operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
s, most notably DOS
DOS is shorthand for the MS-DOS and IBM PC DOS family of operating systems.
DOS may also refer to:
Computing
* Data over signalling (DoS), multiplexing data onto a signalling channel
* Denial-of-service attack (DoS), an attack on a communicatio ...
, such a command interpreter provides a more flexible command-line interface than the one supplied. In other cases, such a command interpreter can present a highly customised user interface employing the user interface and input/output facilities of the language.
Other command-line interfaces
The command line provides an interface between programs as well as the user. In this sense, a command line is an alternative to adialog box
The dialog box (also called dialogue box (non-U.S. English), message box or simply dialog) is a graphical control element in the form of a small window that communicates information to the user and prompts them for a response.
Dialog boxes are ...
. Editors and databases present a command line, in which alternate command processors might run. On the other hand, one might have options on the command line, which opens a dialog box. The latest version of 'Take Command' has this feature. DBase used a dialog box to construct command lines, which could be further edited before use.
Programs like BASIC, diskpart
In computing, diskpart is a command-line disk partitioning utility included in Windows 2000 and later Microsoft operating systems, replacing its predecessor, fdisk. The command is also available in ReactOS.
Overview
The diskpart is a uti ...
, Edlin, and QBASIC all provide command-line interfaces, some of which use the system shell. Basic is modeled on the default interface for 8-bit Intel computers. Calculators can be run as command-line or dialog interfaces.
Emacs
Emacs , originally named EMACS (an acronym for "Editor MACroS"), is a family of text editors that are characterized by their extensibility. The manual for the most widely used variant, GNU Emacs, describes it as "the extensible, customizable, se ...
provides a command-line interface in the form of its minibuffer. Commands and arguments can be entered using Emacs standard text editing support, and output is displayed in another buffer.
There are a number of text mode games, like ''Adventure
An adventure is an exciting experience or undertaking that is typically bold, sometimes risky. Adventures may be activities with danger such as traveling, exploring, skydiving, mountain climbing, scuba diving, river rafting, or other extreme sp ...
'' or '' King's Quest 1-3'', which relied on the user typing commands at the bottom of the screen. One controls the character by typing commands like 'get ring' or 'look'. The program returns a text which describes how the character sees it, or makes the action happen. The text adventure
''
Interactive fiction, often abbreviated IF, is software simulating environments in which players use text commands to control characters and influence the environment. Works in this form can be understood as literary narratives, either in the ...
''The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy
''The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy'' (sometimes referred to as ''HG2G'', ''HHGTTG'', ''H2G2'', or ''tHGttG'') is a comedy science fiction franchise created by Douglas Adams. Originally a 1978 radio comedy broadcast on BBC Radio 4, it ...
'', a piece of interactive fiction
''
Interactive fiction, often abbreviated IF, is software simulating environments in which players use text commands to control characters and influence the environment. Works in this form can be understood as literary narratives, either in the f ...
based on Douglas Adam's book of the same name, is a teletype-style command-line game.
The most notable of these interfaces is the standard streams
In computer programming, standard streams are interconnected input and output communication channels between a computer program and its environment when it begins execution. The three input/output (I/O) connections are called standard input (std ...
interface, which allows the output of one command to be passed to the input of another. Text files can serve either purpose as well. This provides the interfaces of piping, filters and redirection. Under Unix, devices are files too, so the normal type of file for the shell used for stdin,stdout and stderr is a tty
TTY may refer to:
Communications and technology
* Teleprinter or teletypewriter (TTY), an electromechanical typewriter paired with a communication channel
** Sometimes used more generally for any type of computer terminal
** Sometimes used for a v ...
device file.
Another command-line interface allows a shell program to launch helper programs, either to launch documents or start a program. The command is processed internally by the shell, and then passed on to another program to launch the document. The graphical interface of Windows and OS/2 rely heavily on command-lines passed through to other programs – console or graphical, which then usually process the command line without presenting a user-console.
Programs like the OS/2 E editor and some other IBM editors
Editing is the process of selecting and preparing written, photographic, visual, audible, or cinematic material used by a person or an entity to convey a message or information. The editing process can involve correction, condensation, org ...
, can process command-lines normally meant for the shell, the output being placed directly in the document window.
A web browser's URL input field can be used as a command line. It can be used to "launch" web app
A web application (or web app) is application software that is accessed using a web browser. Web applications are delivered on the World Wide Web to users with an active network connection.
History
In earlier computing models like client-serv ...
s, access browser configuration, as well as perform a search. Google
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. I ...
, which has been called "the command line of the internet" will perform a domain-specific search when it detects search parameters in a known format. This functionality is present whether the search is triggered from a browser field or on Google's website.
There are JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior, often ...
libraries that allow to write command line applications in browser as standalone Web apps or as part of bigger application. An example of such a website is the CLI interface to DuckDuckGo
DuckDuckGo (DDG) is an internet search engine that emphasizes protecting searchers' privacy and avoiding the filter bubble of personalized search results. DuckDuckGo does not show search results from content farms. It uses various APIs of ...
./ref> There are also Web-based SSH applications, that allow to give access to server command line interface from a browser. Many
video games
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This feedback ...
on the PC feature a command line interface often referred to as a console. It is typically used by the game developers during development and by mod developers for debugging purposes as well as for cheating or skipping parts of the game.
See also
*Comparison of command shells
A command shell is a command-line interface to interact with and manipulate a computer's operating system.
General characteristics
Interactive features
Background execution
Background execution allows a shell to run a command without use ...
* List of command-line interpreters
In computing, a command-line interpreter, or command language interpreter, is a blanket term for a certain class of programs designed to read lines of text entered by a user, thus implementing a command-line interface.
Operating system shells
...
* Console application
A console application is a computer program designed to be used via a text-only computer interface, such as a text terminal, the command-line interface of some operating systems (Unix, DOS, etc.) or the text-based interface included with most gra ...
* Interpreter directive
An interpreter directive is a computer language construct, that on some systems is better described as an aspect of the system's executable file format, that is used to control which interpreter parses and interprets the instructions in a compute ...
* Read-eval-print loop
* Shell script
A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by a Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be scripting languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file mani ...
* Run command
The Run command on an operating system such as Microsoft Windows and Unix-like systems is used to directly open an application or document whose path is known.
Overview
The command functions more or less like a single-line command-line interface ...
*
* '' In the Beginning... Was the Command Line''
Notes
References
External links
The Roots of DOS
David Hunter, ''Softalk for the IBM Personal Computer'' March 1983. Archived at Patersontech.com sinc
Command-Line Reference
Microsoft TechNet Database "Command-Line Reference" {{DEFAULTSORT:Command-Line Interface History of human–computer interaction Software architecture User interface techniques User interfaces