color receptors on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cone cells, or cones, are
 Cone cells are somewhat shorter than rods, but wider and tapered, and are much less numerous than rods in most parts of the retina, but greatly outnumber rods in the fovea. Structurally, cone cells have a
Cone cells are somewhat shorter than rods, but wider and tapered, and are much less numerous than rods in most parts of the retina, but greatly outnumber rods in the fovea. Structurally, cone cells have a
 The difference in the signals received from the three cone types allows the brain to perceive a continuous range of colors, through the
The difference in the signals received from the three cone types allows the brain to perceive a continuous range of colors, through the
Cell Centered Database – Cone cell
NIF Search – Cone Cell
via the
Model and image of cone cell
{{Authority control Color vision Photoreceptor cells Human eye anatomy Human cells Neurons
photoreceptor cells
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiatio ...
in the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
s of vertebrate eyes including the human eye. They respond differently to light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
of different wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
s, and the combination of their responses is responsible for color vision. Cones function best in relatively bright light, called the photopic
Photopic vision is the vision of the eye under well-lit conditions (luminance levels from 10 to 108 cd/m2). In humans and many other animals, photopic vision allows color perception, mediated by cone cells, and a significantly higher visua ...
region, as opposed to rod cells, which work better in dim light, or the scotopic
In the study of human visual perception, scotopic vision (or scotopia) is the vision of the eye under low-light conditions. The term comes from Greek ''skotos'', meaning "darkness", and ''-opia'', meaning "a condition of sight". In the human eye, ...
region. Cone cells are densely packed in the fovea centralis
The fovea centralis is a small, central pit composed of closely packed cones in the eye. It is located in the center of the macula lutea of the retina.
The fovea is responsible for sharp central vision (also called foveal vision), which is ne ...
, a 0.3 mm diameter rod-free area with very thin, densely packed cones which quickly reduce in number towards the periphery of the retina. Conversely, they are absent from the optic disc, contributing to the blind spot. There are about six to seven million cones in a human eye (vs ~92 million rods), with the highest concentration being towards the macula
The macula (/ˈmakjʊlə/) or macula lutea is an oval-shaped pigmented area in the center of the retina of the human eye and in other animals. The macula in humans has a diameter of around and is subdivided into the umbo, foveola, foveal av ...
.
Cones are less sensitive to light than the rod cells in the retina (which support vision at low light levels), but allow the perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system ...
of color. They are also able to perceive finer detail and more rapid changes in images because their response times to stimuli
A stimulus is something that causes a physiological response. It may refer to:
* Stimulation
** Stimulus (physiology), something external that influences an activity
** Stimulus (psychology), a concept in behaviorism and perception
* Stimulus (eco ...
are faster than those of rods. Cones are normally one of three types: S-cones, M-cones and L-cones. Each type expresses a different opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become Retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most ...
: OPN1SW
Blue-sensitive opsin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''OPN1SW'' gene.
See also
* Opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When boun ...
, OPN1MW
Green-sensitive opsin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''OPN1MW'' gene.
OPN1MW2 is a similar opsin.
See also
* Opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, ...
, OPN1LW
OPN1LW is a gene on the X chromosome that encodes for long wave sensitive (LWS) opsin, or red cone photopigment. It is responsible for perception of visible light in the yellow-green range on the visible spectrum (around 500-570nm). The gene con ...
, respectively. These cones are sensitive to visible wavelengths of light that correspond to short-wavelength, medium-wavelength and longer-wavelength light respectively. Because humans usually have three kinds of cones with different photopsin
Vertebrate visual opsins are a subclass of ciliary opsins and mediate vision in vertebrates. They include the opsins in human rod and cone cells. They are often abbreviated to ''opsin'', as they were the first opsins discovered and are still t ...
s, which have different response curves and thus respond to variation in color in different ways, humans have trichromatic vision
Trichromacy or trichromatism is the possessing of three independent channels for conveying color information, derived from the three different types of cone cells in the eye. Organisms with trichromacy are called trichromats.
The normal exp ...
. Being color blind
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. It can impair tasks such as selecting ripe fruit, choosing clothing, and reading traffic lights. Color blindness may make some aca ...
can change this, and there have been some verified reports of people with four types of cones, giving them tetrachromat
Tetrachromacy (from Greek ''tetra'', meaning "four" and ''chromo'', meaning "color") is the condition of possessing four independent channels for conveying color information, or possessing four types of cone cell in the eye. Organisms with te ...
ic vision.
The three pigments responsible for detecting light have been shown to vary in their exact chemical composition due to genetic mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
; different individuals will have cones with different color sensitivity.
Structure
Types
Humans normally have three types of cones, usually designated L, M and S for long, medium and short wavelengths respectively. The first responds the most to light of the longer redwavelengths
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
, peaking at about 560 nm. The majority of the human cones are of the long type. The second most common type responds the most to light of yellow to green medium-wavelength, peaking at 530 nm. M cones make up about a third of cones in the human eye. The third type responds the most to blue short-wavelength light, peaking at 420 nm and make up only around 2% of the cones in the human retina. The three types have peak wavelengths in the range of 564–580 nm, 534–545 nm, and 420–440 nm, respectively, depending on the individual. Such a difference is caused by the different opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become Retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most ...
s they carry, OPN1LW
OPN1LW is a gene on the X chromosome that encodes for long wave sensitive (LWS) opsin, or red cone photopigment. It is responsible for perception of visible light in the yellow-green range on the visible spectrum (around 500-570nm). The gene con ...
, OPN1MW
Green-sensitive opsin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''OPN1MW'' gene.
OPN1MW2 is a similar opsin.
See also
* Opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, ...
, OPN1SW
Blue-sensitive opsin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''OPN1SW'' gene.
See also
* Opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When boun ...
, respectively, the forms of which affect the absorption of retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).
Some microorganisms use reti ...
. The CIE 1931 color space
The CIE 1931 color spaces are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that defin ...
is an often-used model of spectral sensitivities of the three cells of an average human.
While it has been discovered that there exists a mixed type of bipolar cells that bind to both rod and cone cells, bipolar cells still predominantly receive their input from cone cells.
Other animals might have different number of cone types, see Color vision.
Shape and arrangement
cone
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines con ...
-like shape at one end where a pigment filters incoming light, giving them their different response curves. They are typically 40–50 µm long, and their diameter varies from 0.5 to 4.0 µm, being smallest and most tightly packed at the center of the eye at the fovea. The S cone spacing is slightly larger than the others.
Photobleaching
In optics, photobleaching (sometimes termed fading) is the photochemical alteration of a dye or a fluorophore molecule such that it is permanently unable to fluoresce. This is caused by cleaving of covalent bonds or non-specific reactions between ...
can be used to determine cone arrangement. This is done by exposing dark-adapted retina to a certain wavelength of light that paralyzes the particular type of cone sensitive to that wavelength for up to thirty minutes from being able to dark-adapt making it appear white in contrast to the grey dark-adapted cones when a picture of the retina is taken. The results illustrate that S cones are randomly placed and appear much less frequently than the M and L cones. The ratio of M and L cones varies greatly among different people with regular vision (e.g. values of 75.8% L with 20.0% M versus 50.6% L with 44.2% M in two male subjects).
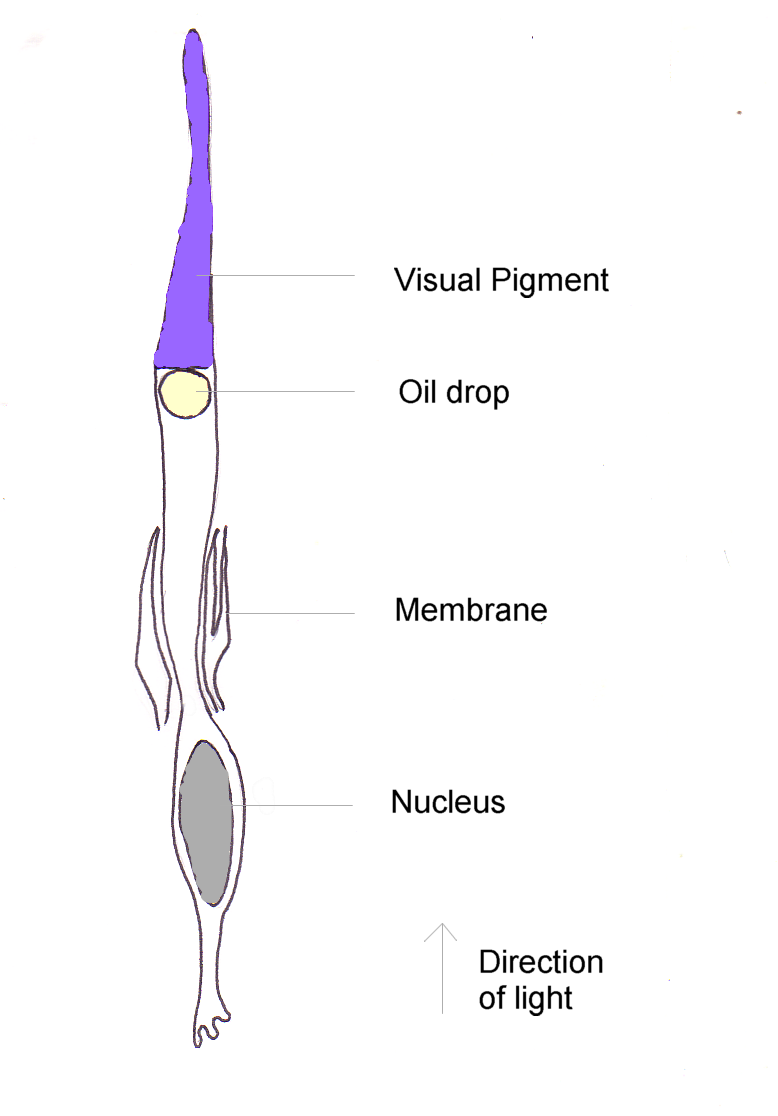
Like rods, each cone cell has a synaptic terminal, inner (nearer the brain) and outer segments, as well as an interior nucleus and various mitochondria. The synaptic terminal forms a synapse with a neuron bipolar cell
A bipolar neuron, or bipolar cell, is a type of neuron that has two extensions (one axon and one dendrite). Many bipolar cells are specialized sensory neurons for the transmission of sense. As such, they are part of the sensory pathways for smel ...
. The inner and outer segments are connected by a cilium
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike project ...
. The inner segment contains organelles and the cell's nucleus, while the outer segment contains the light-absorbing materials.
The outer segments of cones have invaginations of their cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
s that create stacks of membranous disks. Photopigments exist as transmembrane protein
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequent ...
s within these disks, which provide more surface area for light to affect the pigments. In cones, these disks are attached to the outer membrane, whereas they are pinched off and exist separately in rods. Neither rods nor cones divide, but their membranous disks wear out and are worn off at the end of the outer segment, to be consumed and recycled by phagocytic
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is c ...
cells.
Function
 The difference in the signals received from the three cone types allows the brain to perceive a continuous range of colors, through the
The difference in the signals received from the three cone types allows the brain to perceive a continuous range of colors, through the opponent process
The opponent process is a color theory that states that the human visual system interprets information about color by processing signals from photoreceptor cells in an antagonistic manner. The opponent-process theory suggests that there are th ...
of color vision. ( Rod cells have a peak sensitivity at 498 nm, roughly halfway between the peak sensitivities of the S and M cones.)
All of the receptors contain the protein photopsin
Vertebrate visual opsins are a subclass of ciliary opsins and mediate vision in vertebrates. They include the opsins in human rod and cone cells. They are often abbreviated to ''opsin'', as they were the first opsins discovered and are still t ...
, with variations in its conformation causing differences in the optimum wavelengths absorbed.
The color yellow, for example, is perceived when the L cones are stimulated slightly more than the M cones, and the color red is perceived when the L cones are stimulated significantly more than the M cones. Similarly, blue and violet hues are perceived when the S receptor is stimulated more. S Cones are most sensitive to light at wavelengths around 420 nm. However, the lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
and cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
of the human eye are increasingly absorptive to shorter wavelengths, and this sets the short wavelength limit of human-visible light to approximately 380 nm, which is therefore called 'ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
' light. People with aphakia
Aphakia is the absence of the lens of the eye, due to surgical removal, such as in cataract surgery, a perforating wound or ulcer, or congenital anomaly. It causes a loss of accommodation, high degree of farsightedness ( hyperopia), and a de ...
, a condition where the eye lacks a lens, sometimes report the ability to see into the ultraviolet range. At moderate to bright light levels where the cones function, the eye is more sensitive to yellowish-green light than other colors because this stimulates the two most common (M and L) of the three kinds of cones almost equally. At lower light levels, where only the rod cells function, the sensitivity is greatest at a blueish-green wavelength.
Cones also tend to possess a significantly elevated visual acuity because each cone cell has a lone connection to the optic nerve, therefore, the cones have an easier time telling that two stimuli are isolated. Separate connectivity is established in the
inner plexiform layer
The inner plexiform layer is an area of the retina that is made up of a dense reticulum of fibrils formed by interlaced dendrites of retinal ganglion cells and cells of the inner nuclear layer
The inner nuclear layer or layer of inner granules, o ...
so that each connection is parallel.
The response of cone cells to light is also directionally nonuniform, peaking at a direction that receives light from the center of the pupil; this effect is known as the Stiles–Crawford effect The Stiles–Crawford effect (subdivided into the Stiles–Crawford effect of the first and second kind) is a property of the human eye that refers to the directional sensitivity of the cone photoreceptors.
The Stiles–Crawford effect of the firs ...
.
It is possible that S cones may play a role in the regulation of the circadian system and the secretion of melatonin but this role is not clear yet. The exact contribution of S cone activation to circadian regulation is unclear but any potential role would be secondary to the better established role of melanopsin.
Color afterimage
Sensitivity to a prolonged stimulation tends to decline over time, leading toneural adaptation
Neural adaptation or sensory adaptation is a gradual decrease over time in the responsiveness of the sensory system to a constant stimulus. It is usually experienced as a change in the stimulus. For example, if a hand is rested on a table, the ta ...
. An interesting effect occurs when staring at a particular color for a minute or so. Such action leads to an exhaustion of the cone cells that respond to that color – resulting in the afterimage
AfterImage is a Filipino rock band formed in 1986, best known for their songs "Habang May Buhay", "Next in Line", and "Mangarap Ka". They disbanded in 1997 and became active again in 2008 after they reunited and released their fourth studio alb ...
. This vivid color aftereffect can last for a minute or more.Schacter, Daniel L. ''Psychology: the second edition.'' Chapter 4.9.
Associated Diseases
*Achromatopsia
Achromatopsia, also known as Rod monochromacy, is a medical syndrome that exhibits symptoms relating to five conditions, most notably monochromacy. Historically, the name referred to monochromacy in general, but now typically refers only to an a ...
(Rod Monochromacy) - a form of monochromacy
Monochromacy (from Greek ''mono'', meaning "one" and ''chromo'', meaning "color") is the ability of organisms or machines to perceive only light intensity, without respect to spectral composition (color). Organisms with monochromacy are called ...
with no functional cones
* Blue cone monochromacy
Blue-cone monochromacy (BCM) is an inherited eye disease that causes severe color blindness, poor visual acuity, nystagmus and photophobia due to the absence of functional red (L) and green (M) cone photoreceptor cells in the retina. BCM is a r ...
- a rare form of monochromacy
Monochromacy (from Greek ''mono'', meaning "one" and ''chromo'', meaning "color") is the ability of organisms or machines to perceive only light intensity, without respect to spectral composition (color). Organisms with monochromacy are called ...
with only functional S-cones
* Congenital red-green color blindness - partial color blindness include protanopia, deuteranopia, etc.
* Oligocone trichromacy - poor visual acuity and impairment of cone function according to ERG, but without significant color vision loss.
* Bradyopsia - photopic vision
Photopic vision is the vision of the eye under well-lit conditions (luminance levels from 10 to 108 cd/m2). In humans and many other animals, photopic vision allows color perception, mediated by cone cells, and a significantly higher visu ...
cannot respond quickly to stimuli.
* Bornholm eye disease - X-linked recessive myopia, astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at n ...
, impaired visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an examinee's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity is dependent on optical and neural factors, i.e. (1) the sharpness of the retinal ...
and red-green dichromacy
Dichromacy (from Greek ''di'', meaning "two" and ''chromo'', meaning "color") is the state of having two types of functioning photoreceptors, called cone cells, in the eyes. Organisms with dichromacy are called dichromats. Dichromats requir ...
.
* Cone dystrophy
A cone dystrophy is an inherited ocular disorder characterized by the loss of cone cells, the photoreceptors responsible for both central and color vision.
Presentation
The most common symptoms of cone dystrophy are vision loss (age of onset r ...
- a degenerative loss of cone cells
* Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and it is almost exclusively fo ...
- a type of cancer originating from cone precursor cells
See also
* Disc shedding * Double cones * RG color space *Tetrachromacy
Tetrachromacy (from Greek ''tetra'', meaning "four" and ''chromo'', meaning "color") is the condition of possessing four independent channels for conveying color information, or possessing four types of cone cell in the eye. Organisms with te ...
* Melanopsin
* Color vision
References
External links
Cell Centered Database – Cone cell
NIF Search – Cone Cell
via the
Neuroscience Information Framework
The Neuroscience Information Framework is a repository of global neuroscience web resources, including experimental, clinical, and translational neuroscience databases, knowledge bases, atlases, and genetic/genomic resources and provides many auth ...
Model and image of cone cell
{{Authority control Color vision Photoreceptor cells Human eye anatomy Human cells Neurons