Clone (plant) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cloning is the process of producing individual
Cloning is the process of producing individual
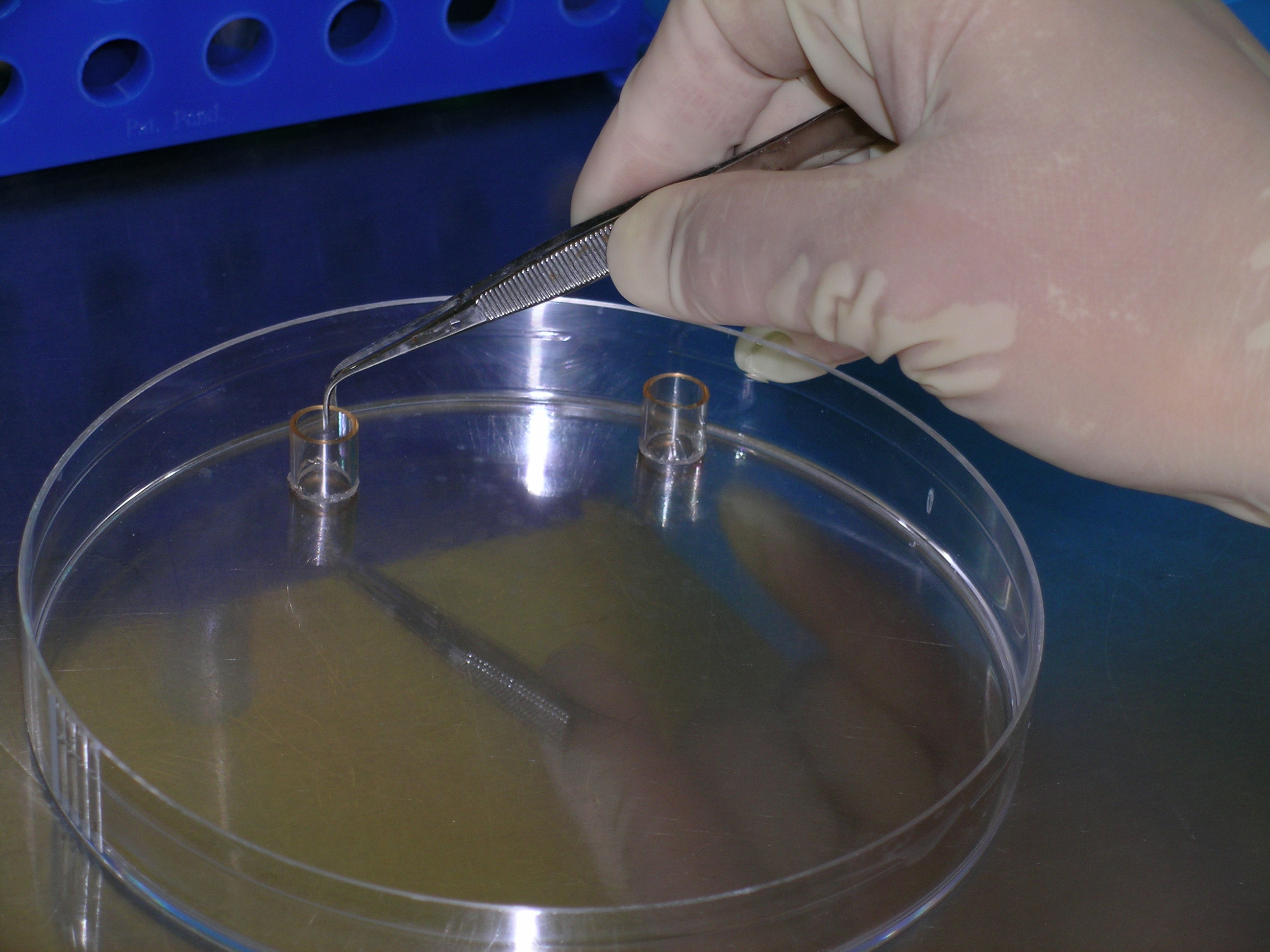 Cloning a cell means to derive a population of cells from a single cell. In the case of unicellular organisms such as bacteria and yeast, this process is remarkably simple and essentially only requires the
Cloning a cell means to derive a population of cells from a single cell. In the case of unicellular organisms such as bacteria and yeast, this process is remarkably simple and essentially only requires the
 The term ''clone'' is used in horticulture to refer to descendants of a single plant which were produced by
The term ''clone'' is used in horticulture to refer to descendants of a single plant which were produced by
"Birds Do It. Bees Do It. Dragons Don't Need To"
''

 Dolly, a Finn-Dorset ewe, was the first mammal to have been successfully cloned from an adult somatic cell. Dolly was formed by taking a cell from the udder of her 6-year-old biological mother. Dolly's embryo was created by taking the cell and inserting it into a sheep ovum. It took 435 attempts before an embryo was successful. The embryo was then placed inside a female sheep that went through a normal pregnancy. She was cloned at the
Dolly, a Finn-Dorset ewe, was the first mammal to have been successfully cloned from an adult somatic cell. Dolly was formed by taking a cell from the udder of her 6-year-old biological mother. Dolly's embryo was created by taking the cell and inserting it into a sheep ovum. It took 435 attempts before an embryo was successful. The embryo was then placed inside a female sheep that went through a normal pregnancy. She was cloned at the
BBC On This Day: 1997: Dolly the sheep is cloned
/ref>
Wildlife conservation and reproductive cloning
Reproduction, 126. This is also referred to as "Conservation cloning". In 2001, a cow named Bessie gave birth to a cloned Asian
("When the Mammoths Return"), 5 February 2015 (retrieved 6 September 2015) Another problem is the survival of the reconstructed mammoth:
 Discussion of cloning in the popular media often presents the subject negatively. In an article in the 8 November 1993 article of ''
Discussion of cloning in the popular media often presents the subject negatively. In an article in the 8 November 1993 article of ''
organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells ( cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fu ...
s with identical or virtually identical DNA, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the ...
. In the field of biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used ...
, cloning is the process of creating cloned organisms (copies) of cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
s and of DNA fragments (molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word '' cloning'' refers to the fact that the meth ...
).
Etymology
Coined byHerbert J. Webber
Herbert John Webber (December 27, 1865 – January 18, 1946) was an American plant physiologist, professor emeritus of sub-tropical horticulture, first director of the University of California Citrus Experiment Station, and the third curator of th ...
, the term clone derives from the Ancient Greek word (), ''twig'', which is the process whereby a new plant is created from a twig. In botany, the term ''lusus'' was used. In horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
, the spelling ''clon'' was used until the early twentieth century; the final ''e'' came into use to indicate the vowel is a "long o" instead of a "short o". Since the term entered the popular lexicon in a more general context, the spelling ''clone'' has been used exclusively.
Natural cloning
Cloning is a natural form of reproduction that has allowed life forms to spread for hundreds of millions of years. It is a reproduction method used by plants, fungi, and bacteria, and is also the way that clonal colonies reproduce themselves. Examples of these organisms include blueberry plants,Hazel
The hazel (''Corylus'') is a genus of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K. (1999). ...
trees, the Pando trees, the Kentucky coffeetree
The Kentucky coffeetree (''Gymnocladus dioicus''), also known as American coffee berry, Kentucky mahogany, nicker tree, and stump tree, is a tree in the subfamily Caesalpinioideae of the legume family Fabaceae, native to the Midwest, Upper South, ...
, ''Myrica
''Myrica'' is a genus of about 35–50 species of small trees and shrubs in the family Myricaceae, order Fagales. The genus has a wide distribution, including Africa, Asia, Europe, North America and South America, and missing only from Austra ...
'', and the American sweetgum.
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning refers to the process of making multiple molecules. Cloning is commonly used to amplify DNA fragments containing wholegenes
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
, but it can also be used to amplify any DNA sequence such as promoters, non-coding sequences and randomly fragmented DNA. It is used in a wide array of biological experiments and practical applications ranging from genetic fingerprinting
DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting) is the process of determining an individual's DNA characteristics. DNA analysis intended to identify a species, rather than an individual, is called DNA barcoding.
DNA profiling is a forensic t ...
to large scale protein production. Occasionally, the term cloning is misleadingly used to refer to the identification of the chromosomal
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
location of a gene associated with a particular phenotype of interest, such as in positional cloning
A genetic screen or mutagenesis screen is an experimental technique used to identify and select individuals who possess a phenotype of interest in a mutagenized population. Hence a genetic screen is a type of phenotypic screen. Genetic screens c ...
. In practice, localization of the gene to a chromosome or genomic region does not necessarily enable one to isolate or amplify the relevant genomic sequence. To amplify any DNA sequence in a living organism, that sequence must be linked to an origin of replication
The origin of replication (also called the replication origin) is a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated. Propagation of the genetic material between generations requires timely and accurate duplication of DNA by se ...
, which is a sequence of DNA capable of directing the propagation of itself and any linked sequence. However, a number of other features are needed, and a variety of specialised cloning vector
A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA that can be stably maintained in an organism, and into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted for cloning purposes. The cloning vector may be DNA taken from a virus, the cell of a higher organism, ...
s (small piece of DNA into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted) exist that allow protein production
Protein production is the biotechnological process of generating a specific protein. It is typically achieved by the manipulation of gene expression in an organism such that it expresses large amounts of a recombinant gene. This includes the t ...
, affinity tag
Protein tags are peptide sequences genetically grafted onto a recombinant protein. Tags are attached to proteins for various purposes. They can be added to either end of the target protein, so they are either C-terminus or N-terminus specific or a ...
ging, single-stranded RNA or DNA production and a host of other molecular biology tools.
Cloning of any DNA fragment essentially involves four steps
# fragmentation - breaking apart a strand of DNA
# ligation
Ligation may refer to:
* Ligation (molecular biology), the covalent linking of two ends of DNA or RNA molecules
* In medicine, the making of a ligature (tie)
* Chemical ligation, the production of peptides from amino acids
* Tubal ligation, a meth ...
– gluing together pieces of DNA in a desired sequence
# transfection
Transfection is the process of deliberately introducing naked or purified nucleic acids into eukaryotic cells. It may also refer to other methods and cell types, although other terms are often preferred: " transformation" is typically used to des ...
– inserting the newly formed pieces of DNA into cells
# screening/selection – selecting out the cells that were successfully transfected with the new DNA
Although these steps are invariable among cloning procedures a number of alternative routes can be selected; these are summarized as a ''cloning strategy''.
Initially, the DNA of interest needs to be isolated to provide a DNA segment of suitable size. Subsequently, a ligation procedure is used where the amplified fragment is inserted into a vector
Vector most often refers to:
*Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
*Vector (epidemiology), an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematic ...
(piece of DNA). The vector (which is frequently circular) is linearised using restriction enzyme
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or'' restrictase '' is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class ...
s, and incubated with the fragment of interest under appropriate conditions with an enzyme called DNA ligase
DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, () that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living orga ...
. Following ligation, the vector with the insert of interest is transfected into cells. A number of alternative techniques are available, such as chemical sensitisation of cells, electroporation
Electroporation, or electropermeabilization, is a microbiology technique in which an electrical field is applied to cells in order to increase the permeability of the cell membrane, allowing chemicals, drugs, electrode arrays or DNA to be introd ...
, optical injection
Optical transfection is a biomedical technique that entails introducing nucleic acids (i.e. genetic material such as DNA) into cells using light. All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane, which prevents many substances from entering or exiti ...
and biolistics. Finally, the transfected cells are cultured. As the aforementioned procedures are of particularly low efficiency, there is a need to identify the cells that have been successfully transfected with the vector construct containing the desired insertion sequence in the required orientation. Modern cloning vectors include selectable antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
resistance markers, which allow only cells in which the vector has been transfected, to grow. Additionally, the cloning vectors may contain colour selection markers, which provide blue/white screening (alpha-factor complementation) on X-gal medium. Nevertheless, these selection steps do not absolutely guarantee that the DNA insert is present in the cells obtained. Further investigation of the resulting colonies must be required to confirm that cloning was successful. This may be accomplished by means of PCR, restriction fragment analysis and/or DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. T ...
.
Cell cloning
Cloning unicellular organisms
 Cloning a cell means to derive a population of cells from a single cell. In the case of unicellular organisms such as bacteria and yeast, this process is remarkably simple and essentially only requires the
Cloning a cell means to derive a population of cells from a single cell. In the case of unicellular organisms such as bacteria and yeast, this process is remarkably simple and essentially only requires the inoculation
Inoculation is the act of implanting a pathogen or other microorganism. It may refer to methods of artificially inducing immunity against various infectious diseases, or it may be used to describe the spreading of disease, as in "self-inoculati ...
of the appropriate medium. However, in the case of cell cultures from multi-cellular organisms, cell cloning is an arduous task as these cells will not readily grow in standard media.
A useful tissue culture technique used to clone distinct lineages of cell lines involves the use of cloning rings (cylinders). In this technique a single-cell suspension of cells that have been exposed to a mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer i ...
ic agent or drug used to drive selection
Selection may refer to:
Science
* Selection (biology), also called natural selection, selection in evolution
** Sex selection, in genetics
** Mate selection, in mating
** Sexual selection in humans, in human sexuality
** Human mating strateg ...
is plated at high dilution to create isolated colonies, each arising from a single and potentially clonal distinct cell. At an early growth stage when colonies consist of only a few cells, sterile polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the Aromatic hydrocarbon, aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin pe ...
rings (cloning rings), which have been dipped in grease, are placed over an individual colony and a small amount of trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting these long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the d ...
is added. Cloned cells are collected from inside the ring and transferred to a new vessel for further growth.
Cloning stem cells
Somatic-cell nuclear transfer
In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. The technique consists of taking an enucleated oocyte (egg cell) and implantin ...
, popularly known as SCNT, can also be used to create embryos for research or therapeutic purposes. The most likely purpose for this is to produce embryos for use in stem cell research
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
. This process is also called "research cloning" or "therapeutic cloning". The goal is not to create cloned human beings (called "reproductive cloning"), but rather to harvest stem cells that can be used to study human development and to potentially treat disease. While a clonal human blastocyst has been created, stem cell lines are yet to be isolated from a clonal source.
Therapeutic cloning is achieved by creating embryonic stem cells in the hopes of treating diseases such as diabetes and Alzheimer's. The process begins by removing the nucleus (containing the DNA) from an egg cell and inserting a nucleus from the adult cell to be cloned. In the case of someone with Alzheimer's disease, the nucleus from a skin cell of that patient is placed into an empty egg. The reprogrammed cell begins to develop into an embryo because the egg reacts with the transferred nucleus. The embryo will become genetically identical to the patient. The embryo will then form a blastocyst which has the potential to form/become any cell in the body.
The reason why SCNT is used for cloning is because somatic cells can be easily acquired and cultured in the lab. This process can either add or delete specific genomes of farm animals. A key point to remember is that cloning is achieved when the oocyte maintains its normal functions and instead of using sperm and egg genomes to replicate, the donor's somatic cell nucleus is inserted into the oocyte. The oocyte will react to the somatic cell nucleus, the same way it would to a sperm cell's nucleus.
The process of cloning a particular farm animal using SCNT is relatively the same for all animals. The first step is to collect the somatic cells from the animal that will be cloned. The somatic cells could be used immediately or stored in the laboratory for later use. The hardest part of SCNT is removing maternal DNA from an oocyte at metaphase II. Once this has been done, the somatic nucleus can be inserted into an egg cytoplasm. This creates a one-cell embryo. The grouped somatic cell and egg cytoplasm are then introduced to an electrical current. This energy will hopefully allow the cloned embryo to begin development. The successfully developed embryos are then placed in surrogate recipients, such as a cow or sheep in the case of farm animals.
SCNT is seen as a good method for producing agriculture animals for food consumption. It successfully cloned sheep, cattle, goats, and pigs. Another benefit is SCNT is seen as a solution to clone endangered species that are on the verge of going extinct. However, stresses placed on both the egg cell and the introduced nucleus can be enormous, which led to a high loss in resulting cells in early research. For example, the cloned sheep Dolly was born after 277 eggs were used for SCNT, which created 29 viable embryos. Only three of these embryos survived until birth, and only one survived to adulthood. As the procedure could not be automated, and had to be performed manually under a microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
, SCNT was very resource intensive. The biochemistry involved in reprogramming the differentiated somatic cell nucleus and activating the recipient egg was also far from being well understood. However, by 2014 researchers were reporting cloning success rates of seven to eight out of ten and in 2016, a Korean Company Sooam Biotech was reported to be producing 500 cloned embryos per day.
In SCNT, not all of the donor cell's genetic information is transferred, as the donor cell's mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
that contain their own mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
are left behind. The resulting hybrid cells retain those mitochondrial structures which originally belonged to the egg. As a consequence, clones such as Dolly that are born from SCNT are not perfect copies of the donor of the nucleus.
Organism cloning
Organism cloning (also called reproductive cloning) refers to the procedure of creating a new multicellular organism, genetically identical to another. In essence this form of cloning is an asexual method of reproduction, where fertilization or inter-gamete contact does not take place. Asexual reproduction is a naturally occurring phenomenon in many species, including most plants and some insects. Scientists have made some major achievements with cloning, including the asexual reproduction of sheep and cows. There is a lot of ethical debate over whether or not cloning should be used. However, cloning, or asexual propagation, has been common practice in the horticultural world for hundreds of years.Horticultural
vegetative reproduction
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or spe ...
or apomixis
In botany, apomixis is asexual reproduction without fertilization. Its etymology is Greek for "away from" + "mixing". This definition notably does not mention meiosis. Thus "normal asexual reproduction" of plants, such as propagation from cuttin ...
. Many horticultural plant cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture ...
s are clones, having been derived from a single individual, multiplied by some process other than sexual reproduction. As an example, some European cultivars of grapes represent clones that have been propagated for over two millennia. Other examples are potato and banana.
Grafting
Grafting or graftage is a horticultural technique whereby tissues of plants are joined so as to continue their growth together. The upper part of the combined plant is called the scion () while the lower part is called the rootstock. The succ ...
can be regarded as cloning, since all the shoots and branches coming from the graft are genetically a clone of a single individual, but this particular kind of cloning has not come under ethical
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concerns ma ...
scrutiny and is generally treated as an entirely different kind of operation.
Many trees, shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from tree ...
s, vine
A vine (Latin ''vīnea'' "grapevine", "vineyard", from ''vīnum'' "wine") is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themsel ...
s, fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes exce ...
s and other herbaceous perennial
A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives more than two years. The term ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the years") is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. The term is also wide ...
s form clonal colonies naturally. Parts of an individual plant may become detached by fragmentation and grow on to become separate clonal individuals. A common example is in the vegetative reproduction of moss and liverwort gametophyte clones by means of gemmae. Some vascular plants e.g. dandelion
''Taraxacum'' () is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, which consists of species commonly known as dandelions. The scientific and hobby study of the genus is known as taraxacology. The genus is native to Eurasia and Nor ...
and certain viviparous
Among animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the parent. This is opposed to oviparity which is a reproductive mode in which females lay developing eggs that complete their development and hatch externally from the ...
grasses also form seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosper ...
s asexually, termed apomixis
In botany, apomixis is asexual reproduction without fertilization. Its etymology is Greek for "away from" + "mixing". This definition notably does not mention meiosis. Thus "normal asexual reproduction" of plants, such as propagation from cuttin ...
, resulting in clonal populations of genetically identical individuals.
Parthenogenesis
Clonal derivation exists in nature in some animal species and is referred to asparthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and developmen ...
(reproduction of an organism by itself without a mate). This is an asexual form of reproduction that is only found in females of some insects, crustaceans, nematodes, fish (for example the hammerhead shark
The hammerhead sharks are a group of sharks that form the family Sphyrnidae, so named for the unusual and distinctive structure of their heads, which are flattened and laterally extended into a "hammer" shape called a cephalofoil. Most hammerhe ...
Shubin, Neil (24 February 2008)"Birds Do It. Bees Do It. Dragons Don't Need To"
''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
''. Retrieved 21 February 2014), and lizards including the Komodo dragon
The Komodo dragon (''Varanus komodoensis''), also known as the Komodo monitor, is a member of the monitor lizard family Varanidae that is endemic to the Indonesian islands of Komodo, Rinca, Flores, and Gili Motang. It is the largest extant ...
and several whiptails. The growth and development occurs without fertilization by a male. In plants, parthenogenesis means the development of an embryo from an unfertilized egg cell, and is a component process of apomixis. In species that use the XY sex-determination system
The XY sex-determination system is a sex-determination system used to classify many mammals, including humans, some insects (''Drosophila''), some snakes, some fish ( guppies), and some plants ('' Ginkgo'' tree). In this system, the sex of an i ...
, the offspring will always be female. An example is the little fire ant (''Wasmannia auropunctata
The little fire ant (''Wasmannia auropunctata''), also known as the electric ant, is a small (approx long), light to golden brown (ginger) social ant native to Central and South America, now spread to parts of Africa (including Gabon and Camer ...
''), which is native to Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and South America but has spread throughout many tropical environments.
Artificial cloning of organisms
Artificial cloning of organisms may also be called ''reproductive cloning''.First steps
Hans Spemann
Hans Spemann (; 27 June 1869 – 9 September 1941) was a German embryologist who was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1935 for his student Hilde Mangold's discovery of the effect now known as embryonic induction, an influence, ...
, a German embryologist
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, '' -logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos ...
was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordi ...
in 1935 for his discovery of the effect now known as embryonic induction, exercised by various parts of the embryo, that directs the development of groups of cells into particular tissues and organs. In 1924 he and his student, Hilde Mangold, were the first to perform somatic-cell nuclear transfer
In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. The technique consists of taking an enucleated oocyte (egg cell) and implantin ...
using amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbo ...
embryos – one of the first steps towards cloning.
Methods
Reproductive cloning generally uses " somatic cell nuclear transfer" (SCNT) to create animals that are genetically identical. This process entails the transfer of a nucleus from a donor adult cell (somatic cell) to an egg from which the nucleus has been removed, or to a cell from ablastocyst
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryonic development of mammals. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM) also known as the ''embryoblast'' which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of trophoblast cells called th ...
from which the nucleus has been removed. If the egg begins to divide normally it is transferred into the uterus of the surrogate mother. Such clones are not strictly identical since the somatic cells may contain mutations in their nuclear DNA. Additionally, the mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
also contains DNA and during SCNT this mitochondrial DNA is wholly from the cytoplasmic donor's egg, thus the mitochondrial
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used t ...
genome is not the same as that of the nucleus donor cell from which it was produced. This may have important implications for cross-species nuclear transfer in which nuclear-mitochondrial incompatibilities may lead to death.
Artificial ''embryo splitting'' or ''embryo twinning'', a technique that creates monozygotic twins from a single embryo, is not considered in the same fashion as other methods of cloning. During that procedure, a donor embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
is split in two distinct embryos, that can then be transferred via embryo transfer
Embryo transfer refers to a step in the process of assisted reproduction in which embryos are placed into the uterus of a female with the intent to establish a pregnancy. This technique (which is often used in connection with in vitro fertilizati ...
. It is optimally performed at the 6- to 8-cell stage, where it can be used as an expansion of IVF
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating an individual's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) f ...
to increase the number of available embryos. If both embryos are successful, it gives rise to monozygotic (identical) twins.
Dolly the sheep

Roslin Institute
The Roslin Institute is an animal sciences research institute at Easter Bush, Midlothian, Scotland, part of the University of Edinburgh, and is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council.
It is best known for creati ...
in Scotland by British scientists Sir Ian Wilmut
Sir Ian Wilmut, OBE FRS -- FMedSci FRSE (born 7 July 1944) is an English embryologist and Chair of the Scottish Centre for Regenerative Medicine at the University of Edinburgh. He is best known as the leader of the research group that in 1996 ...
and Keith Campbell and lived there from her birth in 1996 until her death in 2003 when she was six. She was born on 5 July 1996 but not announced to the world until 22 February 1997. Her stuffed remains were placed at Edinburgh's Royal Museum
The National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland, was formed in 2006 with the merger of the new Museum of Scotland, with collections relating to Scottish antiquities, culture and history, and the adjacent Royal Scottish Museum (opened ...
, part of the National Museums of Scotland
National Museums Scotland (NMS; gd, Taighean-tasgaidh Nàiseanta na h-Alba) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government. It runs the national museums of Scotland.
NMS is one of the country's National Collections, ...
.
Dolly was publicly significant because the effort showed that genetic material from a specific adult cell, designed to express only a distinct subset of its genes, can be redesigned to grow an entirely new organism. Before this demonstration, it had been shown by John Gurdon that nuclei from differentiated cells could give rise to an entire organism after transplantation into an enucleated egg. However, this concept was not yet demonstrated in a mammalian system.
The first mammalian cloning (resulting in Dolly) had a success rate of 29 embryos per 277 fertilized eggs, which produced three lambs at birth, one of which lived. In a bovine experiment involving 70 cloned calves, one-third of the calves died quite young. The first successfully cloned horse, Prometea
Prometea (born May 28, 2003), a Haflinger foal, is the first cloned horse and the first to be born from and carried by its cloning mother. Her birth was announced publicly on August 6, 2003. Born 36 kilogram after a natural delivery and a full-te ...
, took 814 attempts. Notably, although the first clones were frogs, no adult cloned frog has yet been produced from a somatic adult nucleus donor cell.
There were early claims that Dolly had pathologies resembling accelerated aging. Scientists speculated that Dolly's death in 2003 was related to the shortening of telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature mos ...
s, DNA-protein complexes that protect the end of linear chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
s. However, other researchers, including Ian Wilmut
Sir Ian Wilmut, OBE FRS -- FMedSci FRSE (born 7 July 1944) is an English embryologist and Chair of the Scottish Centre for Regenerative Medicine at the University of Edinburgh. He is best known as the leader of the research group that in 1996 ...
who led the team that successfully cloned Dolly, argue that Dolly's early death due to respiratory infection was unrelated to problems with the cloning process. This idea that the nuclei have not irreversibly aged was shown in 2013 to be true for mice.
Dolly was named after performer Dolly Parton
Dolly Rebecca Parton (born January 19, 1946) is an American singer-songwriter, actress, philanthropist, and businesswoman, known primarily for her work in country music. After achieving success as a songwriter for others, Parton made her album ...
because the cells cloned to make her were from a mammary gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in ...
cell, and Parton is known for her ample cleavage.BBC. 22 February 2008.BBC On This Day: 1997: Dolly the sheep is cloned
/ref>
Species cloned
The modern cloning techniques involvingnuclear transfer
Nuclear transfer is a form of cloning. The step involves removing the DNA from an oocyte (unfertilised egg), and injecting the nucleus which contains the DNA to be cloned. In rare instances, the newly constructed cell will divide normally, rep ...
have been successfully performed on several species. Notable experiments include:
* Tadpole
A tadpole is the larval stage in the biological life cycle of an amphibian. Most tadpoles are fully aquatic, though some species of amphibians have tadpoles that are terrestrial. Tadpoles have some fish-like features that may not be found ...
: (1952) Robert Briggs and Thomas J. King had successfully cloned northern leopard frogs: thirty-five complete embryos and twenty-seven tadpoles from one-hundred and four successful nuclear transfers.
* Carp
Carp are various species of oily freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large group of fish native to Europe and Asia. While carp is consumed in many parts of the world, they are generally considered an invasive species in parts of ...
: (1963) In China, embryologist
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, '' -logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos ...
Tong Dizhou Tong may refer to:
Chinese
* Tang Dynasty, a dynasty in Chinese history when transliterated from Cantonese
* Tong (organization), a type of social organization found in Chinese immigrant communities
*''tong'', pronunciation of several Chinese ch ...
produced the world's first cloned fish by inserting the DNA from a cell of a male carp into an egg from a female carp. He published the findings in a Chinese science journal.
* Zebrafish
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a freshwater fish belonging to the minnow family (Cyprinidae) of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (and thus often ca ...
: The first vertebrate cloned (1981) by George Streisinger ()
*Sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticate ...
: Marked the first mammal being cloned (1984) from early embryonic cells by Steen Willadsen
Steen Malte Willadsen (born 1943 in Copenhagen, Denmark) is a Danish biologist credited with being the first to cloning, clone a mammal using nuclear transfer.
Willadsen graduated from the Royal Veterinary College of Copenhagen (1969), and recei ...
. Megan and Morag cloned from differentiated embryonic cells in June 1995 and Dolly from a somatic cell in 1996.
* Mice: (1986) A mouse was successfully cloned from an early embryonic cell. Soviet scientists Chaylakhyan, Veprencev, Sviridova, and Nikitin had the mouse "Masha" cloned. Research was published in the magazine ''Biofizika'' volume ХХХII, issue 5 of 1987.
* Rhesus monkey
The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally ...
: Tetra
Terrestrial Trunked Radio (TETRA; formerly known as Trans-European Trunked Radio), a European standard for a trunked radio system, is a professional mobile radio and two-way transceiver specification. TETRA was specifically designed for use by ...
(January 2000) from embryo splitting and not nuclear transfer. More akin to artificial formation of twins.
* Pig: the first cloned pigs (March 2000). By 2014, BGI in China was producing 500 cloned pigs a year to test new medicines.
* Gaur
The gaur (''Bos gaurus''; ), also known as the Indian bison, is a bovine native to South Asia and Southeast Asia, and has been listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 1986. The global population was estimated at a maximum of 21,000 m ...
: (2001) was the first endangered species cloned.
* Cattle: Alpha and Beta (males, 2001) and (2005) Brazil
* Cat: CopyCat
Copycat refers to a person who copies some aspect of some thing or somebody else.
Copycat may also refer to:
Intellectual property rights
* Copyright infringement, use of another’s ideas or words without permission
* Patent infringement, a v ...
"CC" (female, late 2001), Little Nicky
''Little Nicky'' is a 2000 American fantasy comedy film directed by Steven Brill, written by Brill, Adam Sandler, and Tim Herlihy, and starring Sandler in the title role, Patricia Arquette, Harvey Keitel, Rhys Ifans, Tommy "Tiny" Lister Jr., ...
, 2004, was the first cat cloned for commercial reasons
* Rat: Ralph
Ralph (pronounced ; or ,) is a male given name of English, Scottish and Irish origin, derived from the Old English ''Rædwulf'' and Radulf, cognate with the Old Norse ''Raðulfr'' (''rað'' "counsel" and ''ulfr'' "wolf").
The most common forms ...
, the first cloned rat (2003)
* Mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two po ...
: Idaho Gem
The mule Idaho Gem (born May 4, 2003) is the first cloned equine and first cloned mule.
He is the result of the collaboration of Dr. Gordon Woods and Dr. Dirk Vanderwall of the Northwest Equine Reproduction Laboratory at the University of Idaho a ...
, a john mule born 4 May 2003, was the first horse-family clone.
* Horse: Prometea
Prometea (born May 28, 2003), a Haflinger foal, is the first cloned horse and the first to be born from and carried by its cloning mother. Her birth was announced publicly on August 6, 2003. Born 36 kilogram after a natural delivery and a full-te ...
, a Haflinger female born 28 May 2003, was the first horse clone.
* Dog: Snuppy, a male Afghan hound
The Afghan Hound is a hound that is distinguished by its thick, fine, silky coat and its tail with a ring curl at the end. The breed is selectively bred for its unique features in the cold mountains of Afghanistan. Its local name is ( ps, تاژ ...
was the first cloned dog (2005). In 2017, the world's first gene-editing clone dog, Apple, was created by Sinogene Biotechnology. Sooam Biotech, South Korea, was reported in 2015 to have cloned 700 dogs to date for their owners, including two Yakutian Laika
The Yakutian Laika (russian: Якутская лайка) is an ancient working dog breed that originated in the Arctic seashore of the Sakha (Yakutia) Republic. Yakutian Laikas are multipurpose laikas, with many lineages able to herd reindeer, ...
hunting dogs, which are seriously endangered due to crossbreeding.
* Wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
: Snuwolf and Snuwolffy, the first two cloned female wolves (2005).
* Water buffalo
The water buffalo (''Bubalus bubalis''), also called the domestic water buffalo or Asian water buffalo, is a large bovid originating in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Today, it is also found in Europe, Australia, North America, So ...
: Samrupa was the first cloned water buffalo. It was born on 6 February 2009, at India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
's Karnal National Diary Research Institute but died five days later due to lung infection.
* Pyrenean ibex (2009) was the first extinct animal to be cloned back to life; the clone lived for seven minutes before dying of lung defects.
* Camel: (2009) Injaz
Injaz ( ar, إنجاز, meaning "achievement"; born April 8, 2009- died 12 January 2020) was a female dromedary camel, credited with being the world's first cloned camel. Dr. Nisar Ahmad Wani, a reproductive biologist and head of the research tea ...
, was the first cloned camel.
* Pashmina goat: (2012) Noori
Noori ( ) is a Pakistani rock band from Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan, formed in 1996. The group was formed by songwriter, lead vocalist, and guitarist, Ali Noor, along with his younger brother Ali Hamza, who were soon joined by bassist Muhammad ...
, is the first cloned pashmina goat. Scientists at the faculty of veterinary sciences and animal husbandry of Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir
Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir is an agricultural university located in Shalimar, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India. With its main campus and Faculty of Horticulture in Shalimar, Srinagar, the uni ...
successfully cloned the first Pashmina goat (Noori) using the advanced reproductive techniques under the leadership of Riaz Ahmad Shah.
* Goat: (2001) Scientists of Northwest A&F University
Northwest A&F University (NWAFU; ) is a key national public research university in Xianyang, Shaanxi, China, under the administration of the Ministry of Education.
NWAFU is a member of "Project 985" club, which is an origanization of 39 the mos ...
successfully cloned the first goat which use the adult female cell.
* Gastric brooding frog: (2013) The gastric brooding frog, ''Rheobatrachus silus'', thought to have been extinct since 1983 was cloned in Australia, although the embryos died after a few days.
* Macaque
The macaques () constitute a genus (''Macaca'') of gregarious Old World monkeys of the subfamily Cercopithecinae. The 23 species of macaques inhabit ranges throughout Asia, North Africa, and (in one instance) Gibraltar. Macaques are principall ...
monkey: (2017) First successful cloning of a primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter includin ...
species using nuclear transfer
Nuclear transfer is a form of cloning. The step involves removing the DNA from an oocyte (unfertilised egg), and injecting the nucleus which contains the DNA to be cloned. In rare instances, the newly constructed cell will divide normally, rep ...
, with the birth of two live clones named Zhong Zhong and Hua Hua
Zhong Zhong (, born 27 November 2017) and Hua Hua (, born 5 December 2017) are a pair of identical crab-eating macaques (also referred to as cynomolgus monkeys) that were created through somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), the same cloning te ...
. Conducted in China in 2017, and reported in January 2018. In January 2019, scientists in China reported the creation of five identical cloned
Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical or virtually identical DNA, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction. In the field of biotechnology, ...
gene-edited monkeys, using the same cloning technique that was used with Zhong Zhong and Hua Hua and Dolly the sheep
Dolly (5 July 1996 – 14 February 2003) was a female Finnish Dorset sheep and the first mammal cloned from an adult somatic cell. She was cloned by associates of the Roslin Institute in Scotland, using the process of nuclear transfer from a ...
, and the gene-editing Crispr
CRISPR () (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bact ...
-Cas9
Cas9 (CRISPR associated protein 9, formerly called Cas5, Csn1, or Csx12) is a 160 kilodalton protein which plays a vital role in the immunological defense of certain bacteria against DNA viruses and plasmids, and is heavily utilized in gene ...
technique allegedly used by He Jiankui
He Jiankui (; ; born 1984) is a Chinese biophysics researcher who was an associate professor in the Department of Biology of the Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech) in Shenzhen, China. Earning his Ph.D. from Rice University ...
in creating the first ever gene-modified human babies Lulu and Nana. The monkey clones were made to study several medical diseases.
*Black-footed ferret
The black-footed ferret (''Mustela nigripes''), also known as the American polecatHeptner, V. G. (Vladimir Georgievich); Nasimovich, A. A; Bannikov, Andrei Grigorovich; Hoffmann, Robert S. (2001)''Mammals of the Soviet Union''Volume: v. 2, pt. 1 ...
: (2020) In 2020, a team of scientists cloned a female named Willa, who died in the mid-1980s and left no living descendants. Her clone, a female named Elizabeth Ann, was born on 10 December. Scientists hope that the contribution of this individual will alleviate the effects of inbreeding and help black-footed ferrets better cope with plague. Experts estimate that this female's genome contains three times as much genetic diversity as any of the modern black-footed ferrets.
Human cloning
Human cloning is the creation of a genetically identical copy of a human. The term is generally used to refer to artificial human cloning, which is the reproduction of human cells and tissues. It does not refer to the natural conception and delivery of identicaltwins
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two em ...
. The possibility of human cloning has raised controversies
Controversy is a state of prolonged public dispute or debate, usually concerning a matter of conflicting opinion or point of view. The word was coined from the Latin ''controversia'', as a composite of ''controversus'' – "turned in an opposite d ...
. These ethical concerns have prompted several nations to pass legislation regarding human cloning and its legality. As of right now, scientists have no intention of trying to clone people and they believe their results should spark a wider discussion about the laws and regulations the world needs to regulate cloning.
Two commonly discussed types of theoretical human cloning are ''therapeutic cloning'' and ''reproductive cloning''. Therapeutic cloning would involve cloning cells from a human for use in medicine and transplants, and is an active area of research, but is not in medical practice anywhere in the world, . Two common methods of therapeutic cloning that are being researched are somatic-cell nuclear transfer
In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. The technique consists of taking an enucleated oocyte (egg cell) and implantin ...
and, more recently, pluripotent stem cell induction. Reproductive cloning would involve making an entire cloned human, instead of just specific cells or tissues.
Ethical issues of cloning
There are a variety ofethical
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concerns ma ...
positions regarding the possibilities of cloning, especially human cloning
Human cloning is the creation of a genetically identical copy (or clone) of a human. The term is generally used to refer to artificial human cloning, which is the reproduction of human cells and tissue. It does not refer to the natural concept ...
. While many of these views are religious in origin, the questions raised by cloning are faced by secular perspectives as well. Perspectives on human cloning are theoretical, as human therapeutic and reproductive cloning are not commercially used; animals are currently cloned in laboratories and in livestock production.
Advocates support development of therapeutic cloning to generate tissues and whole organs to treat patients who otherwise cannot obtain transplants, to avoid the need for immunosuppressive drugs
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into ...
, and to stave off the effects of aging.de Grey, Aubrey; Rae, Michael (September 2007). ''Ending Aging: The Rejuvenation Breakthroughs that Could Reverse Human Aging in Our Lifetime''. New York, NY: St. Martin's Press, 416 pp. . Advocates for reproductive cloning believe that parents who cannot otherwise procreate should have access to the technology.
Opponents of cloning have concerns that technology is not yet developed enough to be safe and that it could be prone to abuse (leading to the generation of humans from whom organs and tissues would be harvested), as well as concerns about how cloned individuals could integrate with families and with society at large.
Religious groups are divided, with some opposing the technology as usurping "God's place" and, to the extent embryos are used, destroying a human life; others support therapeutic cloning's potential life-saving benefits.
Cloning of animals is opposed by animal-groups due to the number of cloned animals that suffer from malformations before they die, and while food from cloned animals has been approved by the US FDA, its use is opposed by groups concerned about food safety.
Cloning extinct and endangered species
Cloning, or more precisely, the reconstruction of functional DNA fromextinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
species has, for decades, been a dream. Possible implications of this were dramatized in the 1984 novel '' Carnosaur'' and the 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later also referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton and centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of cloned dinosaurs. It began in 1990 when ...
''. The best current cloning techniques have an average success rate of 9.4 percent (and as high as 25 percent) when working with familiar species such as mice, while cloning wild animals is usually less than 1 percent successful.
Several tissue banks have come into existence, including the "Frozen zoo
A frozen zoo is a storage facility in which genetic materials taken from animals (e.g. DNA, sperm, eggs, embryos and live tissue) are stored at very low temperatures (−196 °C) in tanks of liquid nitrogen. Material preserved in this way c ...
" at the San Diego Zoo
The San Diego Zoo is a zoo in Balboa Park, San Diego, California, housing 4000 animals of more than 650 species and subspecies on of Balboa Park leased from the City of San Diego. Its parent organization, San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance, is a p ...
, to store frozen tissue from the world's rarest and most endangered species.Holt, W. V., Pickard, A. R., & Prather, R. S. (2004Wildlife conservation and reproductive cloning
Reproduction, 126. This is also referred to as "Conservation cloning". In 2001, a cow named Bessie gave birth to a cloned Asian
gaur
The gaur (''Bos gaurus''; ), also known as the Indian bison, is a bovine native to South Asia and Southeast Asia, and has been listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 1986. The global population was estimated at a maximum of 21,000 m ...
, an endangered species, but the calf died after two days. In 2003, a banteng
The banteng (''Bos javanicus''; ), also known as tembadau, is a species of cattle found in Southeast Asia. The head-and-body length is between . Wild banteng are typically larger and heavier than their domesticated counterparts, but are otherw ...
was successfully cloned, followed by three African wildcat
The African wildcat (''Felis lybica'') is a small wildcat species native to Africa, West and Central Asia up to Rajasthan in India and Xinjiang in China. It has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List in 2022.
In Cyprus, an African wil ...
s from a thawed frozen embryo. These successes provided hope that similar techniques (using surrogate mothers of another species) might be used to clone extinct species. Anticipating this possibility, tissue samples from the last ''bucardo'' ( Pyrenean ibex) were frozen in liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen—LN2—is nitrogen in a liquid state at low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, low viscosity liquid that is wid ...
immediately after it died in 2000. Researchers are also considering cloning endangered species such as the Giant panda
The giant panda (''Ailuropoda melanoleuca''), also known as the panda bear (or simply the panda), is a bear species endemic to China. It is characterised by its bold black-and-white coat and rotund body. The name "giant panda" is sometimes u ...
and Cheetah
The cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus'') is a large cat native to Africa and central Iran. It is the fastest land animal, estimated to be capable of running at with the fastest reliably recorded speeds being , and as such has evolved specialized ...
.
In 2002, geneticists at the Australian Museum
The Australian Museum is a heritage-listed museum at 1 William Street, Sydney central business district, New South Wales, Australia. It is the oldest museum in Australia,Design 5, 2016, p.1 and the fifth oldest natural history museum in the ...
announced that they had replicated DNA of the thylacine
The thylacine ( , or , also ) (''Thylacinus cynocephalus'') is an extinct carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmania and New Guinea. The last known live animal was captured in 1930 in Tasma ...
(Tasmanian tiger), at the time extinct for about 65 years, using polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
. However, on 15 February 2005 the museum announced that it was stopping the project after tests showed the specimens' DNA had been too badly degraded by the (ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
) preservative. On 15 May 2005 it was announced that the thylacine project would be revived, with new participation from researchers in New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
and Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
.
In 2003, for the first time, an extinct animal, the Pyrenean ibex mentioned above was cloned, at the Centre of Food Technology and Research of Aragon, using the preserved frozen cell nucleus of the skin samples from 2001 and domestic goat egg-cells. The ibex died shortly after birth due to physical defects in its lungs.
One of the most anticipated targets for cloning was once the woolly mammoth
The woolly mammoth (''Mammuthus primigenius'') is an extinct species of mammoth that lived during the Pleistocene until its extinction in the Holocene epoch. It was one of the last in a line of mammoth species, beginning with '' Mammuthus s ...
, but attempts to extract DNA from frozen mammoths have been unsuccessful, though a joint Russo-Japanese team is currently working toward this goal. In January 2011, it was reported by Yomiuri Shimbun that a team of scientists headed by Akira Iritani of Kyoto University had built upon research by Dr. Wakayama, saying that they will extract DNA from a mammoth carcass that had been preserved in a Russian laboratory and insert it into the egg cells of an Asian elephant
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus '' Elephas'' and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in t ...
in hopes of producing a mammoth embryo. The researchers said they hoped to produce a baby mammoth within six years. It was noted, however that the result, if possible, would be an elephant-mammoth hybrid rather than a true mammoth."Когда вернутся мамонты"("When the Mammoths Return"), 5 February 2015 (retrieved 6 September 2015) Another problem is the survival of the reconstructed mammoth:
ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The ...
s rely on a symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or para ...
with specific microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found ...
in their stomachs for digestion.
Scientists at the University of Newcastle and University of New South Wales
The University of New South Wales (UNSW), also known as UNSW Sydney, is a public research university based in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. It is one of the founding members of Group of Eight, a coalition of Australian research-intensiv ...
announced in March 2013 that the very recently extinct gastric-brooding frog
The gastric-brooding frogs or platypus frogs (''Rheobatrachus'') is a genus of extinct ground-dwelling frogs native to Queensland in eastern Australia. The genus consisted of only two species, both of which became extinct in the mid-1980s. The ...
would be the subject of a cloning attempt to resurrect the species.
Many such "De-extinction" projects are described in the Long Now Foundation
The Long Now Foundation, established in 1996, is an American non-profit organization based in San Francisco that seeks to start and promote a long-term cultural institution. It aims to provide a counterpoint to what it views as today's "faster ...
's Revive and Restore Project.
Lifespan
After an eight-year project involving the use of a pioneering cloning technique, Japanese researchers created 25 generations of healthy cloned mice with normal lifespans, demonstrating that clones are not intrinsically shorter-lived than naturally born animals. Other sources have noted that the offspring of clones tend to be healthier than the original clones and indistinguishable from animals produced naturally. Some posited that Dolly the sheep may have aged more quickly than naturally born animals, as she died relatively early for a sheep at the age of six. Ultimately, her death was attributed to a respiratory illness, and the "advanced aging" theory is disputed. A detailed study released in 2016 and less detailed studies by others suggest that once cloned animals get past the first month or two of life they are generally healthy. However, early pregnancy loss and neonatal losses are still greater with cloning than natural conception or assisted reproduction (IVF). Current research is attempting to overcome these problems.History
In popular culture
 Discussion of cloning in the popular media often presents the subject negatively. In an article in the 8 November 1993 article of ''
Discussion of cloning in the popular media often presents the subject negatively. In an article in the 8 November 1993 article of ''Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and event (philosophy), events that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various me ...
'', cloning was portrayed in a negative way, modifying Michelangelo's ''Creation of Adam
Creation may refer to:
Religion
*''Creatio ex nihilo'', the concept that matter was created by God out of nothing
*Creation myth, a religious story of the origin of the world and how people first came to inhabit it
*Creationism, the belief that ...
'' to depict Adam with five identical hands. ''Newsweek
''Newsweek'' is an American weekly online news magazine co-owned 50 percent each by Dev Pragad, its president and CEO, and Johnathan Davis (businessman), Johnathan Davis, who has no operational role at ''Newsweek''. Founded as a weekly print m ...
'' 10 March 1997 issue also critiqued the ethics of human cloning, and included a graphic depicting identical babies in beakers.
The concept of cloning, particularly human cloning, has featured a wide variety of science fiction works. An early fictional depiction of cloning is Bokanovsky's Process
''Brave New World'' is a dystopian novel by English author Aldous Huxley, written in 1931 and published in 1932. Largely set in a futuristic World State, whose citizens are environmentally engineered into an intelligence-based social hierarch ...
which features in Aldous Huxley
Aldous Leonard Huxley (26 July 1894 – 22 November 1963) was an English writer and philosopher. He wrote nearly 50 books, both novels and non-fiction works, as well as wide-ranging essays, narratives, and poems.
Born into the prominent Huxle ...
's 1931 dystopian novel ''Brave New World
''Brave New World'' is a dystopian novel by English author Aldous Huxley, written in 1931 and published in 1932. Largely set in a futuristic World State, whose citizens are environmentally engineered into an intelligence-based social hiera ...
''. The process is applied to fertilized human eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology a ...
'', causing them to split into identical genetic copies of the original. Following renewed interest in cloning in the 1950s, the subject was explored further in works such as Poul Anderson
Poul William Anderson (November 25, 1926 – July 31, 2001) was an American fantasy and science fiction author who was active from the 1940s until the 21st century. Anderson wrote also historical novels. His awards include seven Hugo Awards and ...
's 1953 story ''UN-Man'', which describes a technology called "exogenesis", and Gordon Rattray Taylor's book '' The Biological Time Bomb'', which popularised the term "cloning" in 1963.
Cloning is a recurring theme in a number of contemporary science fiction films, ranging from action films such as ''Anna to the Infinite Power
''Anna to the Infinite Power'' is a 1982 science-fiction thriller film about a young teenager who learns that she was the product of a cloning experiment. The film was based on the 1981 novel of the same name by Mildred Ames. It was produced by ...
'', '' The Boys from Brazil'', ''Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later also referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton and centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of cloned dinosaurs. It began in 1990 when ...
'' (1993), ''Alien Resurrection
''Alien Resurrection'' is a 1997 American science fiction horror film, directed by Jean-Pierre Jeunet, written by Joss Whedon, and starring Sigourney Weaver and Winona Ryder. It is the fourth installment of the ''Alien'' franchise, and wa ...
'' (1997), ''The 6th Day
''The 6th Day'' is a 2000 American science fiction action film directed by Roger Spottiswoode and starring Arnold Schwarzenegger, Tony Goldwyn, Michael Rapaport, and Robert Duvall. In the film, a family man of the future is illegally cloned ...
'' (2000), ''Resident Evil
''Resident Evil'', known in Japan as is a Japanese horror game series and media franchise created by Capcom. It consists of survival horror, third-person shooter and first-person shooter games, with players typically surviving in environments ...
'' (2002), '' Star Wars: Episode II – Attack of the Clones'' (2002), '' The Island'' (2005) and ''Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
'' (2009) to comedies such as Woody Allen
Heywood "Woody" Allen (born Allan Stewart Konigsberg; November 30, 1935) is an American film director, writer, actor, and comedian whose career spans more than six decades and multiple Academy Award-winning films. He began his career writing ...
's 1973 film '' Sleeper''.
The process of cloning is represented variously in fiction. Many works depict the artificial creation of humans by a method of growing cells from a tissue or DNA sample; the replication may be instantaneous, or take place through slow growth of human embryos in artificial womb
An artificial womb or artificial uterus is a device that would allow for extracorporeal pregnancy by growing a fetus outside the body of an organism that would normally carry the fetus to term.
An artificial uterus, as a replacement organ, w ...
s. In the long-running British television series ''Doctor Who
''Doctor Who'' is a British science fiction television series broadcast by the BBC since 1963. The series depicts the adventures of a Time Lord called the Doctor, an extraterrestrial being who appears to be human. The Doctor explores the ...
'', the Fourth Doctor
The Fourth Doctor is an incarnation of the Doctor, the protagonist of the BBC science fiction television series ''Doctor Who''. He is portrayed by Tom Baker.
Within the series' narrative, the Doctor is a centuries-old alien Time Lord from the ...
and his companion Leela were cloned in a matter of seconds from DNA samples (" The Invisible Enemy", 1977) and then – in an apparent homage
Homage (Old English) or Hommage (French) may refer to:
History
*Homage (feudal) /ˈhɒmɪdʒ/, the medieval oath of allegiance
*Commendation ceremony, medieval homage ceremony Arts
*Homage (arts) /oʊˈmɑʒ/, an allusion or imitation by one arti ...
to the 1966 film '' Fantastic Voyage'' – shrunk to microscopic size to enter the Doctor's body to combat an alien virus. The clones in this story are short-lived, and can only survive a matter of minutes before they expire. Science fiction films such as ''The Matrix
''The Matrix'' is a 1999 science fiction action film written and directed by the Wachowskis. It is the first installment in ''The Matrix'' film series, starring Keanu Reeves, Laurence Fishburne, Carrie-Anne Moss, Hugo Weaving, and Joe Pantolia ...
'' and ''Star Wars: Episode II – Attack of the Clones'' have featured scenes of human foetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal develo ...
es being cultured on an industrial scale in mechanical tanks.
Cloning humans from body parts is also a common theme in science fiction. Cloning features strongly among the science fiction conventions parodied in Woody Allen's ''Sleeper'', the plot of which centres around an attempt to clone an assassinated dictator from his disembodied nose. In the 2008 ''Doctor Who'' story " Journey's End", a duplicate version of the Tenth Doctor
The Tenth Doctor is an incarnation of the Doctor, the main protagonist of the BBC science fiction television franchise ''Doctor Who''. He is played by David Tennant in three series as well as nine specials. As with previous incarnations of ...
spontaneously grows from his severed hand, which had been cut off in a sword fight during an earlier episode.
Another example is the 2021 film ''Girl Next
''Girl Next'' is a 2021 American horror film directed by Larry Wade Carrell and written by Zeph E. Daniel. It stars Lacey Cofran as Lorian West, a woman who is abducted, drugged, and taken to a secluded Texas ranch where young women are tortured ...
'' in which a woman is abducted, drugged and brainwashed into becoming an obedient, living sex doll. It is later proved that she is a clone of a clone designed to assassinate the traffickers.
After the death of her beloved 14-year-old Coton de Tulear
The Coton de Tuléar is a breed of small dog named for the city of Tuléar (also known as Toliara) in Madagascar. This breed is thought to have originated from a group of small white dogs that swam across the Malagasy channel following a shipwrec ...
named Samantha in late 2017, Barbra Streisand
Barbara Joan "Barbra" Streisand (; born April 24, 1942) is an American singer, actress and director. With a career spanning over six decades, she has achieved success in multiple fields of entertainment, and is among the few performers awar ...
announced that she had cloned the dog, and was now "waiting for he two cloned pupsto get older so hecan see if they have amantha'sbrown eyes and her seriousness". The operation cost $50,000 through the pet cloning company ViaGen
ViaGen Pets, based in Cedar Park, Texas, is a division of TransOva Genetics, that offers animal cloning services to pet owners. ViaGen Pets division was launched in 2016.
ViaGen Pets offers cloning as well as DNA preservation services, sometim ...
.
Cloning and identity
Science fiction has used cloning, most commonly and specificallyhuman cloning
Human cloning is the creation of a genetically identical copy (or clone) of a human. The term is generally used to refer to artificial human cloning, which is the reproduction of human cells and tissue. It does not refer to the natural concept ...
, to raise the controversial questions of identity. ''A Number
''A Number'' is a 2002 English play by Caryl Churchill. The story, set in the near future, is structured around the conflict between a father (Salter) and his sons (Bernard 1, Bernard 2, and Michael Black) – two of whom are clones of the first ...
'' is a 2002 play by English playwright Caryl Churchill
Caryl Lesley Churchill (born 3 September 1938) is a British playwright known for dramatising the abuses of power, for her use of non- naturalistic techniques, and for her exploration of sexual politics and feminist themes.
which addresses the subject of human cloning and identity, especially nature and nurture
Nature versus nurture is a long-standing debate in biology and society about the balance between two competing factors which determine fate: genetics (nature) and environment (nurture). The alliterative expression "nature and nurture" in English h ...
. The story, set in the near future, is structured around the conflict between a father (Salter) and his sons (Bernard 1, Bernard 2, and Michael Black) – two of whom are clones of the first one. ''A Number'' was adapted by Caryl Churchill for television, in a co-production between the BBC and HBO Films
HBO Films (formerly called HBO Premiere Films and HBO Pictures) is an American production and distribution company, a division of the cable television network HBO that produces feature films and miniseries. The division produces fiction and non- ...
.
In 2012, a Japanese television series named "Bunshin" was created. The story's main character, Mariko, is a woman studying child welfare in Hokkaido. She grew up always doubtful about the love from her mother, who looked nothing like her and who died nine years before. One day, she finds some of her mother's belongings at a relative's house, and heads to Tokyo to seek out the truth behind her birth. She later discovered that she was a clone.
In the 2013 television series ''Orphan Black
''Orphan Black'' is a Canadian science-fiction thriller television series created by screenwriter Graeme Manson and director John Fawcett and starring Tatiana Maslany. The series focuses on Sarah Manning, one of several genetically identical ...
'', cloning is used as a scientific study on the behavioral adaptation of the clones. In a similar vein, the book '' The Double'' by Nobel Prize winner José Saramago
José de Sousa Saramago, GColSE ComSE GColCa (; 16 November 1922 – 18 June 2010), was a Portuguese writer and recipient of the 1998 Nobel Prize in Literature for his "parables sustained by imagination, compassion and irony ith which hecon ...
explores the emotional experience of a man who discovers that he is a clone.
Cloning as resurrection
Cloning has been used in fiction as a way of recreating historical figures. In the 1976Ira Levin
Ira Marvin Levin (August 27, 1929 – November 12, 2007) was an American novelist, playwright, and songwriter. His works include the novels '' A Kiss Before Dying'' (1953), '' Rosemary's Baby'' (1967), ''The Stepford Wives'' (1972), '' This Perfe ...
novel '' The Boys from Brazil'' and its 1978 film adaptation, Josef Mengele
, allegiance =
, branch = Schutzstaffel
, serviceyears = 1938–1945
, rank = '' SS''-'' Hauptsturmführer'' (Captain)
, servicenumber =
, battles =
, unit =
, awards =
, commands =
, ...
uses cloning to create copies of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
.
In Michael Crichton
John Michael Crichton (; October 23, 1942 – November 4, 2008) was an American author and filmmaker. His books have sold over 200 million copies worldwide, and over a dozen have been adapted into films. His literary works heavily feature tech ...
's 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later also referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton and centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of cloned dinosaurs. It began in 1990 when ...
'', which spawned a series of ''Jurassic Park'' feature films, the bioengineering company InGen develops a technique to resurrect extinct species of dinosaurs by creating cloned creatures using DNA extracted from fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s. The cloned dinosaurs are used to populate the Jurassic Park wildlife park for the entertainment of visitors. The scheme goes disastrously wrong when the dinosaurs escape their enclosures. Despite being selectively cloned as females to prevent them from breeding, the dinosaurs develop the ability to reproduce through parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and developmen ...
.
Cloning for warfare
The use of cloning for military purposes has also been explored in several fictional works. In ''Doctor Who'', an alien race of armour-clad, warlike beings calledSontaran
The Sontarans ( ) are a fictional race of extraterrestrial humanoids principally portrayed in the British science fiction television programme ''Doctor Who''. A warrior race characterised by their ruthlessness and fearlessness of death, they we ...
s was introduced in the 1973 serial " The Time Warrior". Sontarans are depicted as squat, bald creatures who have been genetically engineered for combat. Their weak spot is a "probic vent", a small socket at the back of their neck which is associated with the cloning process. The concept of cloned soldiers being bred for combat was revisited in " The Doctor's Daughter" (2008), when the Doctor's DNA is used to create a female warrior called Jenny
Jenny may refer to:
* Jenny (given name), a popular feminine name and list of real and fictional people
* Jenny (surname), a family name
Animals
* Jenny (donkey), a female donkey
* Jenny (gorilla), the oldest gorilla in captivity at the time of h ...
.
The 1977 film ''Star Wars
''Star Wars'' is an American epic space opera multimedia franchise created by George Lucas, which began with the eponymous 1977 film and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has been expanded into various film ...
'' was set against the backdrop of a historical conflict called the Clone Wars. The events of this war were not fully explored until the prequel films ''Attack of the Clones
Attack may refer to:
Warfare and combat
* Offensive (military)
* Charge (warfare)
* Attack (fencing)
* Strike (attack)
* Attack (computing)
* Attack aircraft
Books and publishing
* ''The Attack'' (novel), a book
* ''Attack No. 1'', comic an ...
'' (2002) and ''Revenge of the Sith
Revenge is committing a harmful action against a person or group in response to a grievance, be it real or perceived. Francis Bacon described revenge as a kind of "wild justice" that "does... offend the law ndputteth the law out of office." P ...
'' (2005), which depict a space war
''Space War'' is a video game cartridge released by Atari, Inc. in 1978 for the Atari Video Computer System (renamed to the Atari 2600 in 1982). The game is a version of ''Spacewar!'', the 1962 computer game by Steve Russell. It was released ...
waged by a massive army of heavily armoured clone trooper
Clone troopers are fictional characters in the ''Star Wars'' franchise created by George Lucas. They have been featured in a number of ''Star Wars'' media, including the live-action films '' Episode II: Attack of the Clones'' (2002) and '' ...
s that leads to the foundation of the Galactic Empire
Galactic empires are a common trope used in science fantasy and science fiction, particularly in works known as 'space operas'. Many authors have either used a galaxy-spanning empire as background or written about the growth and/or decline of ...
. Cloned soldiers are "manufactured" on an industrial scale, genetically conditioned for obedience and combat effectiveness. It is also revealed that the popular character Boba Fett
Boba Fett ( ) is a fictional character in the '' Star Wars'' franchise. First appearing in the ''Star Wars Holiday Special'' (1978), where he was voiced by Don Francks, he is an armored bounty hunter featured in both the original and prequel ...
originated as a clone of Jango Fett
Jango Fett is a fictional character in the '' Star Wars'' franchise, created by George Lucas. He first appeared as an antagonist in the 2002 film '' Star Wars: Episode II – Attack of the Clones'', played by Temuera Morrison. The character ...
, a mercenary who served as the genetic template for the clone troopers.
Cloning for exploitation
A recurring sub-theme of cloning fiction is the use of clones as a supply of organs for transplantation. The 2005Kazuo Ishiguro
Sir Kazuo Ishiguro ( ; born 8 November 1954) is a British novelist, screenwriter, musician, and short-story writer. Ishiguro was born in Nagasaki, Japan, and moved to Britain in 1960 with his parents when he was five.
He is one of the most cr ...
novel '' Never Let Me Go'' and the 2010 film adaption are set in an alternate history
Alternate history (also alternative history, althist, AH) is a genre of speculative fiction of stories in which one or more historical events occur and are resolved differently than in real life. As conjecture based upon historical fact, alte ...
in which cloned humans are created for the sole purpose of providing organ donations to naturally born humans, despite the fact that they are fully sentient and self-aware. The 2005 film '' The Island'' revolves around a similar plot, with the exception that the clones are unaware of the reason for their existence.
The exploitation of human clones for dangerous and undesirable work was examined in the 2009 British science fiction film ''Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
''. In the futuristic novel '' Cloud Atlas'' and subsequent film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmospher ...
, one of the story lines focuses on a genetically engineered fabricant clone named Sonmi~451, one of millions raised in an artificial "wombtank", destined to serve from birth. She is one of thousands created for manual and emotional labor
Emotional labor is the process of managing feelings and expressions to fulfill the emotional requirements of a job. More specifically, workers are expected to regulate their emotions during interactions with customers, co-workers, clients and man ...
; Sonmi herself works as a server in a restaurant. She later discovers that the sole source of food for clones, called 'Soap', is manufactured from the clones themselves.
In the film '' Us'', at some point prior to the 1980s, the US Government creates clones of every citizen of the United States with the intention of using them to control their original counterparts, akin to voodoo doll
The term Voodoo doll commonly describes an effigy into which pins are inserted. Such practices are found in various forms in the magical traditions of many cultures around the world.
Despite its name, the dolls are not prominent in Haitian Vodo ...
s. This fails, as they were able to copy bodies, but unable to copy the souls of those they cloned. The project is abandoned and the clones are trapped exactly mirroring their above-ground counterparts' actions for generations. In the present day, the clones launch a surprise attack and manage to complete a mass-genocide of their unaware counterparts.
In the series of ''A Certain Magical Index
is a Japanese light novel series written by Kazuma Kamachi and illustrated by Kiyotaka Haimura, which has been published by ASCII Media Works under their Dengeki Bunko imprint since April 2004 in a total of three sepa ...
'' and ''A Certain Scientific Railgun
is a Japanese manga series written by Kazuma Kamachi and illustrated by Motoi Fuyukawa, which began serialization in the April 2007 issue of ASCII Media Works' ''Dengeki Daioh'' magazine. The manga is a spin-off of Kamachi's ''A Certa ...
'', one of the espers, Mikoto Misaka
is a fictional character created by Kazuma Kamachi and first illustrated by Kiyotaka Haimura. She is a major character in the ''A Certain Magical Index'' light novel series and the main protagonist of its manga spin-off series ''A Certain Sci ...
, had DNA was harvested unknowingly, creating 20,000 exact but not equally powerful clones for an experiment. They were used as target practice by Accelerator, just to level up, as killing the original multiple times is impossible. The experiment ended when Toma Kamijo saved and foiled the experiment. The remaining clones have been dispersed everywhere in the world to conduct further experiments to expand their lifespans, save for at least 10 who remained in Academy City, and the last clone, who was not fully developed when the experiment stopped.
See also
* Frozen Ark *The President's Council on Bioethics
The President's Council on Bioethics (PCBE) was a group of individuals appointed by United States President George W. Bush to advise his administration on bioethics. Established on November 28, 2001, by Executive Order 13237, the council was dire ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*Guo, Owen. "World's Biggest Animal Cloning Center Set for '16 in a Skeptical China". ''The New York Times'', 26 November 2015 *Lerner, K. Lee. "Animal cloning". ''TheGale
A gale is a strong wind; the word is typically used as a descriptor in nautical contexts. The U.S. National Weather Service defines a gale as sustained surface winds moving at a speed of between 34 and 47 knots (, or ).link
*Dutchen, Stephanie (11 July 2018)
"Rise of the Clones"
Harvard Medical School.
Cloning Fact Sheet
from Human Genome Project Information website.
'Cloning'
Freeview video by the Vega Science Trust and the BBC/OU
Cloning in Focus
an accessible and comprehensive look at cloning research from the University of Utah's Genetic Science Learning Center
Click and Clone
Try it yourself in the virtual mouse cloning laboratory, from the
"Cloning Addendum: A statement on the cloning report issues by the President's Council on Bioethics"
. ''
*Dutchen, Stephanie (11 July 2018)
"Rise of the Clones"
Harvard Medical School.
External links
*Cloning Fact Sheet
from Human Genome Project Information website.
'Cloning'
Freeview video by the Vega Science Trust and the BBC/OU
Cloning in Focus
an accessible and comprehensive look at cloning research from the University of Utah's Genetic Science Learning Center
Click and Clone
Try it yourself in the virtual mouse cloning laboratory, from the
University of Utah
The University of Utah (U of U, UofU, or simply The U) is a public research university in Salt Lake City, Utah. It is the flagship institution of the Utah System of Higher Education. The university was established in 1850 as the University of De ...
's Genetic Science Learning Center
"Cloning Addendum: A statement on the cloning report issues by the President's Council on Bioethics"
. ''
National Review
''National Review'' is an American conservative editorial magazine, focusing on news and commentary pieces on political, social, and cultural affairs. The magazine was founded by the author William F. Buckley Jr. in 1955. Its editor-in-chief ...
'', 15 July 2002 8:45 am
{{Authority control
Molecular biology
Cryobiology
Applied genetics
Asexual reproduction