Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorder on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Circadian rhythm sleep disorders (CRSD), also known as circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders (CRSWD), are a family of sleep disorders which affect the timing of sleep. CRSDs arise from a persistent pattern of sleep/wake disturbances that can be caused either by dysfunction in one's biological clock system, or by misalignment between one's endogenous oscillator and externally imposed cues. As a result of this mismatch, those affected by circadian rhythm sleep disorders have a tendency to fall asleep at unconventional time points in the day. These occurrences often lead to recurring instances of disturbed rest, where individuals affected by the disorder are unable to go to sleep and awaken at "normal" times for work, school, and other social obligations. Delayed sleep phase disorder,
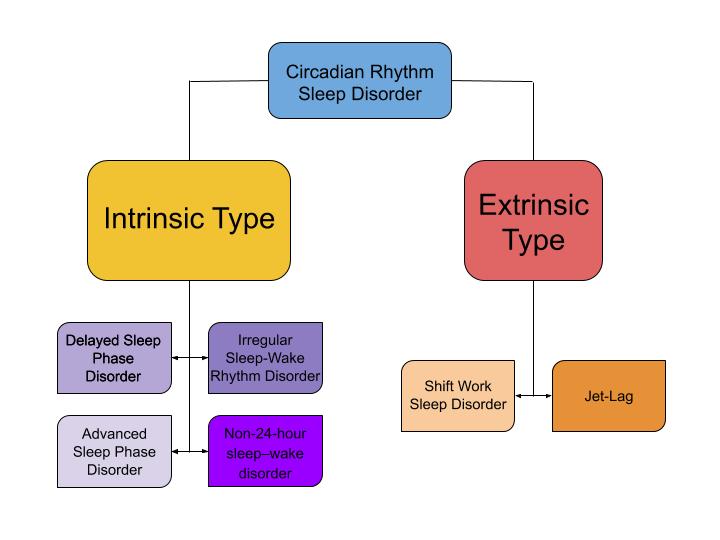 Currently, the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-3) lists 6 disorders under the category of circadian rhythm sleep disorders.
CRSDs can be categorized into two groups based on their underlying mechanisms: The first category is composed of disorders where the endogenous oscillator has been altered, known as intrinsic type disorders. The second category consists of disorders in which the external environment and the endogenous circadian clock are misaligned, called extrinsic type CRSDs.
Currently, the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-3) lists 6 disorders under the category of circadian rhythm sleep disorders.
CRSDs can be categorized into two groups based on their underlying mechanisms: The first category is composed of disorders where the endogenous oscillator has been altered, known as intrinsic type disorders. The second category consists of disorders in which the external environment and the endogenous circadian clock are misaligned, called extrinsic type CRSDs.
Circadian Sleep Disorders Network
An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Review: ''Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders: Part I, Basic Principles, Shift Work and Jet Lag Disorders.'' PDF, 24 pages. November 2007.
An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Review: ''Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders: Part II, Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder, Delayed Sleep Phase Disorder, Free-Running Disorder, and Irregular Sleep–Wake Rhythm.'' PDF, 18 pages. November 2007.
An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Report: ''Practice Parameters for the Clinical Evaluation and Treatment of Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders, November 1, 2007
{{DEFAULTSORT:Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorder Sleep disorders Circadian rhythm Neurophysiology Sleep physiology
advanced sleep phase disorder
Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder (ASPD), also known as the advanced sleep-phase type (ASPT) of circadian rhythm sleep disorder, is a condition that is characterized by a recurrent pattern of early evening (e.g. 7-9 PM) sleepiness and very early morn ...
, non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder and irregular sleep–wake rhythm disorder represents the four main types of CRSD.
Overview
Humans, like most living organisms, have various biological rhythms. These biological clocks control processes that fluctuate daily (e.g., body temperature, alertness, hormone secretion), generatingcircadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to ...
s. Among these physiological characteristics, the sleep-wake propensity can also be considered one of the daily rhythms regulated by the biological clock system. Human's sleeping cycles are tightly regulated by a series of circadian processes working in tandem, allowing for the experience of moments of consolidated sleep during the night and a long wakeful moment during the day. Conversely, disruptions to these processes and the communication pathways between them can lead to problems in sleeping patterns, which are collectively referred to as circadian rhythm sleep disorders.
Normal rhythm
Acircadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to ...
is an entrainable, endogenous, biological activity that has a period of roughly twenty-four hours. This internal time-keeping mechanism is centralized in the suprachiasmatic nucleus
The suprachiasmatic nucleus or nuclei (SCN) is a tiny region of the brain in the hypothalamus, situated directly above the optic chiasm. It is responsible for controlling circadian rhythms. The neuronal and hormonal activities it generates regula ...
(SCN) of humans, and allows for the internal physiological mechanisms underlying sleep and alertness to become synchronized to external environmental cues, like the light-dark cycle. The SCN also sends signals to peripheral clocks in other organs, like the liver, to control processes such as glucose metabolism. Although these rhythms will persist in constant light or dark conditions, different Zeitgeber
A zeitgeber () is any external or environmental cue that entrains or synchronizes an organism's biological rhythms, usually naturally occurring and serving to entrain to the Earth's 24-hour light/dark and 12-month cycles.
History
The term ' (; ) ...
s (time givers such as the light-dark cycle) give context to the clock and allow it to entrain and regulate expression of physiological processes to adjust to the changing environment. Genes that help control light-induced entrainment
Entrainment may refer to:
* Air entrainment, the intentional creation of tiny air bubbles in concrete
* Brainwave entrainment, the practice of entraining one's brainwaves to a desired frequency
* Entrainment (biomusicology), the synchronization of ...
include positive regulators BMAL1
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1 (ARNTL) or brain and muscle ARNT-Like 1 (BMAL1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene on chromosome 11, region p15.3. It's also known as ''BMAL1'', ''MOP3'', and, less com ...
and CLOCK
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the ...
and negative regulators PER1
The PER1 gene encodes the period circadian protein homolog 1 protein in humans.
Function
The PER1 protein is important to the maintenance of circadian rhythms in cells, and may also play a role in the development of cancer. This gene is a mem ...
and CRY
Crying is the dropping of tears (or welling of tears in the eyes) in response to an emotional state, or pain. Emotions that can lead to crying include sadness, anger, and even happiness. The act of crying has been defined as "a complex secreto ...
. A full circadian cycle can be described as a twenty-four hour circadian day, where circadian time zero (CT 0) marks the beginning of a subjective day for an organism and CT 12 marks the start of subjective night.
Humans with regular circadian function have been shown to maintain regular sleep schedules, regulate daily rhythms in hormone secretion, and sustain oscillations in core body temperature. Even in the absence of Zeitgebers, humans will continue to maintain a roughly 24-hour rhythm in these biological activities. Regarding sleep, normal circadian function allows people to maintain balance rest and wakefulness that allows people to work and maintain alertness during the day's activities, and rest at night.
Some misconceptions regarding circadian rhythms and sleep commonly mislabel irregular sleep as a circadian rhythm sleep disorder. In order to be diagnosed with CRSD, there must be either a misalignment between the timing of the circadian oscillator and the surrounding environment, or failure in the clock entrainment pathway. Among people with typical circadian clock function, there is variation in chronotype
A chronotype is the behavioral manifestation of underlying circadian rhythm's myriad of physical processes. A person's chronotype is the propensity for the individual to sleep at a particular time during a 24-hour period. ''Eveningness'' (delayed ...
s, or preferred wake and sleep times, of individuals. Although chronotype varies from individual to individual, as determined by rhythmic expression of clock genes
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the ...
, people with typical circadian clock function will be able to entrain to environmental cues. For example, if a person wishes to shift the onset of a biological activity, like waking time, light exposure during the late subjective night or early subjective morning can help advance one's circadian cycle earlier in the day, leading to an earlier wake time.
Diagnosis
TheInternational Classification of Sleep Disorders
The International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD) is "a primary diagnostic, epidemiological and coding resource for clinicians and researchers in the field of sleep and sleep medicine". The ICSD was produced by the American Academy of Slee ...
classifies Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorder as a type of sleep dyssomnia. Although studies suggest that 3% of the adult population has a CRSD, many people are often misdiagnosed with insomnia instead of a CRSD. Of adults diagnosed with sleep disorders, an estimated 10% have a CRSD and of adolescents with sleep disorders, an estimated 16% may have a CRSD. Patients diagnosed with circadian rhythm sleep disorders typically express a pattern of disturbed sleep, whether that be excessive sleep that intrudes on working schedules and daily functions, or insomnia at desired times of sleep. Note that having a preference for extreme early or late wake times are not related to a circadian rhythm sleep disorder diagnosis. There must be distinct impairment of biological rhythms that affects the person's desired work and daily behavior. For a CRSD diagnosis, a sleep specialist gathers the history of a patient's sleep and wake habits, body temperature patterns, and dim-light melatonin onset (DLMO). Gathering this data gives insight into the patient's current schedule, as well as the physiological phase markers of the patient's biological clock.
The start of the CRSD diagnostic process is a thorough sleep history assessment. A standard questionnaire is used to record the sleep habits of the patient, including typical bedtime, sleep duration, sleep latency
In sleep science, sleep onset latency (SOL) is the length of time that it takes to accomplish the transition from full wakefulness to sleep, normally to the lightest of the non-REM sleep stages.
Sleep latency studies
Pioneering Stanford Universi ...
, and instances of waking up. The professional will further inquire about other external factors that may impact sleep. Prescription drugs that treat mood disorders like tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracell ...
s and other antidepressants are associated with abnormal sleep behaviors. Other daily habits like work schedule and timing of exercise are also recorded—because they may impact an individual's sleep and wake patterns. To measure sleep variables candidly, patients wear actigraphy
Actigraphy is a non-invasive method of monitoring human rest/activity cycles. A small actigraph unit, also called an actimetry sensor, is worn for a week or more to measure gross motor activity. The unit is usually in a wristwatch-like package wo ...
watches that record sleep onset, wake time, and many other physiological variables. Patients are similarly asked to self-report their sleep habits with a week-long sleep diary to document when they go to bed, when they wake up, etc. to supplement the actigraphy data. Collecting this data allows sleep professionals to carefully document and measure patient's sleep habits and confirm patterns described in their sleep history.
Other additional ways to classify the nature of a patient's sleep and biological clock are the morningness-eveningness questionnaire (MEQ) and the Munich ChronoType Questionnaire, both of which have fairly strong correlations with accurately reporting phase advanced or delayed sleep. Questionnaires like the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) and the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) help gauge the severity of sleep disruption. Specifically, these questionnaires can help the professional assess the patient's problems with sleep latency, undesired early-morning wakefulness, and problems with falling or staying asleep.
Tayside children's sleep questionnaire is a ten-item questionnaire for sleep disorders in children aged between one and five years old.
Types
 Currently, the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-3) lists 6 disorders under the category of circadian rhythm sleep disorders.
CRSDs can be categorized into two groups based on their underlying mechanisms: The first category is composed of disorders where the endogenous oscillator has been altered, known as intrinsic type disorders. The second category consists of disorders in which the external environment and the endogenous circadian clock are misaligned, called extrinsic type CRSDs.
Currently, the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-3) lists 6 disorders under the category of circadian rhythm sleep disorders.
CRSDs can be categorized into two groups based on their underlying mechanisms: The first category is composed of disorders where the endogenous oscillator has been altered, known as intrinsic type disorders. The second category consists of disorders in which the external environment and the endogenous circadian clock are misaligned, called extrinsic type CRSDs.
Intrinsic
* Delayed sleep phase disorder (DSPD): Individuals who have been diagnosed with delayed sleep phase disorder have sleep-wake times which are delayed when compared to normal functioning individuals. People with DSPD typically have very long periods of sleep latency when they attempt to go to sleep during conventional sleeping times. Similarly, they also have trouble waking up at conventional times. *Advanced sleep phase disorder
Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder (ASPD), also known as the advanced sleep-phase type (ASPT) of circadian rhythm sleep disorder, is a condition that is characterized by a recurrent pattern of early evening (e.g. 7-9 PM) sleepiness and very early morn ...
(ASPD): People with advanced sleep phase disorder exhibit characteristics opposite to those with delayed sleep phase disorder. These individuals have advanced sleep wake times, so they tend to go to bed and wake up much earlier as compared to normal individuals. ASPD is less common than DSPD, and is most prevalent within older populations.
** Familial Advanced Sleep Phase Syndrome (FASPS) is linked to an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. It is associated with a missense mutation in human PER2
PER2 is a protein in mammals encoded by the ''PER2'' gene. ''PER2'' is noted for its major role in circadian rhythms.
Discovery
The ''per ''gene'' ''was first discovered using forward genetics in '' Drosophilla melanogaster'' in 1971. Mammali ...
that replaces Serine for a Glycine at position 662 (S662G). Families that have this mutation in PER2 experience extreme phase advances in sleep, waking up around 2 AM and going to bed around 7 PM.
* Irregular sleep–wake rhythm disorder (ISWRD) is characterized by a normal 24-hr sleeping period. However, individuals with this disorder experience fragmented and highly disorganized sleep that can manifest in the form of waking frequently during the night and taking naps during the day, yet still maintaining sufficient total time asleep. People with ISWRD often experience a range of symptoms from insomnia to excessive daytime sleepiness.
* Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder (N24SWD): Most common in individuals that are blind and unable to detect light, is characterized by chronic patterns of sleep/wake cycles which are not entrained to the 24-hr light-dark environmental cycle. As a result of this, individuals with this disorder will usually experience a gradual yet predictable delay of sleep onset and waking times. Patients with DSPD may develop this disorder if their condition is untreated.
Extrinsic
* Shift work sleep disorder (SWSD): Approximately 9% of Americans who work night or irregular work shifts are believed to experience shift work sleep disorder. Night shift work directly opposes the environmental cues that entrain our biological clock, so this disorder arises when an individual's clock is unable to adjust to the socially imposed work schedule. Shift work sleep disorder can lead to severe cases of insomnia as well as excessive daytime sleepiness. *Jet lag
Jet lag is a physiological condition that results from alterations to the body's circadian rhythms caused by rapid long-distance trans-meridian (east–west or west–east) travel. For example, someone flying from New York to London, i.e. from ...
: Jet lag is best characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep as a result of misalignment between one's internal circadian system and external, or environmental cues. It is typically associated with rapid travel across multiple time zones.
Alzheimer's disease
CRSD has been frequently associated with excessive daytime sleepiness and nighttime insomnia in patients diagnosed withAlzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As ...
(AD), representing a common characteristic among AD patients as well as a risk factor of progressive functional impairments.Malkani, R., & Attarian, H. (2015). Sleep in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Current Sleep Medicine Reports, 1(2), 81-90.Dick-Muehlke, C. (2015). Psychosocial studies of the individual's changing perspectives in Alzheimer's disease (Premier Reference Source). Hershey, PA: Medical Information Science Reference. On one hand, it has been stated that people with AD have melatonin alteration and high irregularity in their circadian rhythm that lead to a disrupted sleep-wake cycle, probably due to damage on hypothalamic SCN regions typically observed in AD. On the other hand, disturbed sleep and wakefulness states have been related to worsening of an AD patient's cognitive abilities, emotional state and quality of life. Moreover, the abnormal behavioural symptoms of the disease negatively contribute to overwhelming patient's relatives and caregivers as well.
However, the impact of sleep-wake disturbances on the subjective experience of a person with AD is not yet fully understood. Therefore, further studies exploring this field have been highly recommended, mainly considering the increasing life expectancy and significance of neurodegenerative diseases in clinical practices.
Treatment
Possible treatments for circadian rhythm sleep disorders include: * Chronotherapy, best shown to effectively treat delayed sleep phase disorder, acts by systematically delaying an individual's bedtime until their sleep-wake times coincide with the conventional 24-hr day. * Light therapy utilizes bright light exposure to induce phase advances and delays in sleep and wake times. This therapy requires 30–60 minutes of exposure to a bright (5,000–10,000 lux) white, blue, or natural light at a set time until the circadian clock is aligned with the desired schedule. Treatment is initially administered either upon awakening or before sleeping, and if successful may be continued indefinitely or performed less frequently. Though proven very effective in the treatment of individuals with DSPD and ASPD, the benefits of light therapy on N24SWD, shift work disorder, and jet lag have not been studied as extensively. * Hypnotics have also been used clinically alongside bright light exposure therapy and pharmacotherapy for the treatment of CRSDs such as Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder. Additionally, in conjunction with cognitive behavioral therapy, short-acting hypnotics also present an avenue for treating co-morbid insomnia in patients with circadian sleep disorders. * Melatonin, a naturally occurring biological hormone with circadian rhythmicity, has been shown to promote sleep and entrainment to external cues when administered in drug form (0.5–5.0 mg). Melatonin administered in the evening causes phase advances in sleep-wake times while maintaining duration and quality of sleep. Similarly, when administered in the early morning, melatonin can cause phase delays. It has been shown most effective in cases of shift work sleep disorder and delayed phase sleep disorder, but has not been proven particularly useful in cases of jet lag. *Dark therapy
Dark therapy is the practice of keeping people in complete darkness for extended periods of time in an attempt to treat psychological conditions. The human body produces the melatonin hormone, which is responsible for supporting the circadian rhy ...
, for example, the use of blue-blocking goggles, is used to block blue and blue-green wavelength light from reaching the eye during evening hours so as not to hinder melatonin production.
See also
*Chronobiology
Chronobiology is a field of biology that examines timing processes, including periodic (cyclic) phenomena in living organisms, such as their adaptation to solar- and lunar-related rhythms. These cycles are known as biological rhythms. Chronob ...
* Familial sleep traits
Familial sleep traits are heritable variations in sleep patterns, resulting in abnormal sleep-wake times and/or abnormal sleep length.
Circadian rhythms are coordinated physiological and biological changes that oscillate on an approximately 24-h ...
* Light effects on circadian rhythm
Light effects on circadian rhythm are the effects that light has on circadian rhythm.
Most animals and other organisms have "built-in clocks" in their brains that regulate the timing of biological processes and daily behavior. These "clocks" are ...
* Phase response curve
* Sleep diary
* Sleep medicine
Sleep medicine is a medical specialty or subspecialty devoted to the diagnosis and therapy of sleep disturbances and disorders. From the middle of the 20th century, research has provided increasing knowledge and answered many questions about ...
References
External links
Circadian Sleep Disorders Network
An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Review: ''Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders: Part I, Basic Principles, Shift Work and Jet Lag Disorders.'' PDF, 24 pages. November 2007.
An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Review: ''Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders: Part II, Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder, Delayed Sleep Phase Disorder, Free-Running Disorder, and Irregular Sleep–Wake Rhythm.'' PDF, 18 pages. November 2007.
An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Report: ''Practice Parameters for the Clinical Evaluation and Treatment of Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders, November 1, 2007
{{DEFAULTSORT:Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorder Sleep disorders Circadian rhythm Neurophysiology Sleep physiology