Chromium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chromium is a
 Chromium is extremely hard, and is the third hardest element behind carbon ( diamond) and
Chromium is extremely hard, and is the third hardest element behind carbon ( diamond) and
 Chromium is a member of
Chromium is a member of
 Chromium(II) compounds are uncommon, in part because they readily oxidize to chromium(III) derivatives in air. Water-stable
Chromium(II) compounds are uncommon, in part because they readily oxidize to chromium(III) derivatives in air. Water-stable
 A large number of chromium(III) compounds are known, such as chromium(III) nitrate, chromium(III) acetate, and
A large number of chromium(III) compounds are known, such as chromium(III) nitrate, chromium(III) acetate, and
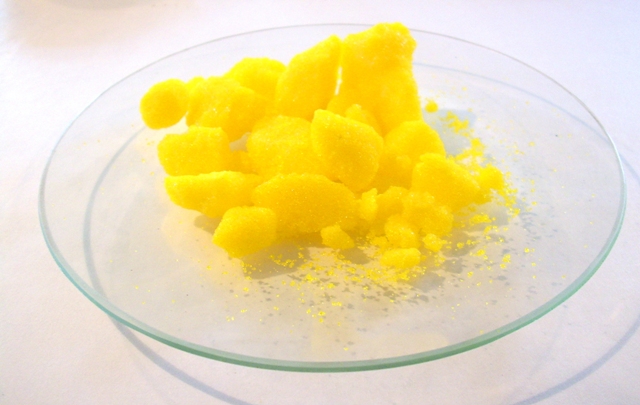
 Chromium(VI) compounds in solution can be detected by adding an acidic hydrogen peroxide solution. The unstable dark blue
Chromium(VI) compounds in solution can be detected by adding an acidic hydrogen peroxide solution. The unstable dark blue


 Chromium is the 21st most abundant element in Earth's crust with an average concentration of 100 ppm. Chromium compounds are found in the environment from the erosion of chromium-containing rocks, and can be redistributed by volcanic eruptions. Typical background concentrations of chromium in environmental media are: atmosphere <10 ng/m3; soil <500 mg/kg; vegetation <0.5 mg/kg; freshwater <10 μg/L; seawater <1 μg/L; sediment <80 mg/kg. Chromium is mined as chromite (FeCr2O4) ore.
About two-fifths of the chromite ores and concentrates in the world are produced in South Africa, about a third in Kazakhstan, while India, Russia, and Turkey are also substantial producers. Untapped chromite deposits are plentiful, but geographically concentrated in Kazakhstan and southern Africa. Although rare, deposits of
Chromium is the 21st most abundant element in Earth's crust with an average concentration of 100 ppm. Chromium compounds are found in the environment from the erosion of chromium-containing rocks, and can be redistributed by volcanic eruptions. Typical background concentrations of chromium in environmental media are: atmosphere <10 ng/m3; soil <500 mg/kg; vegetation <0.5 mg/kg; freshwater <10 μg/L; seawater <1 μg/L; sediment <80 mg/kg. Chromium is mined as chromite (FeCr2O4) ore.
About two-fifths of the chromite ores and concentrates in the world are produced in South Africa, about a third in Kazakhstan, while India, Russia, and Turkey are also substantial producers. Untapped chromite deposits are plentiful, but geographically concentrated in Kazakhstan and southern Africa. Although rare, deposits of
 In 1794, Louis Nicolas Vauquelin received samples of crocoite
In 1794, Louis Nicolas Vauquelin received samples of crocoite


 Approximately 28.8 million metric tons (Mt) of marketable chromite ore was produced in 2013, and converted into 7.5 Mt of ferrochromium. According to John F. Papp, writing for the USGS, "Ferrochromium is the leading end use of chromite ore, ndstainless steel is the leading end use of ferrochromium."
The largest producers of chromium ore in 2013 have been South Africa (48%), Kazakhstan (13%), Turkey (11%), and India (10%), with several other countries producing the rest of about 18% of the world production.
The two main products of chromium ore refining are
Approximately 28.8 million metric tons (Mt) of marketable chromite ore was produced in 2013, and converted into 7.5 Mt of ferrochromium. According to John F. Papp, writing for the USGS, "Ferrochromium is the leading end use of chromite ore, ndstainless steel is the leading end use of ferrochromium."
The largest producers of chromium ore in 2013 have been South Africa (48%), Kazakhstan (13%), Turkey (11%), and India (10%), with several other countries producing the rest of about 18% of the world production.
The two main products of chromium ore refining are  For the production of pure chromium, the iron must be separated from the chromium in a two step roasting and leaching process. The chromite ore is heated with a mixture of calcium carbonate and sodium carbonate in the presence of air. The chromium is oxidized to the hexavalent form, while the iron forms the stable Fe2O3. The subsequent leaching at higher elevated temperatures dissolves the
For the production of pure chromium, the iron must be separated from the chromium in a two step roasting and leaching process. The chromite ore is heated with a mixture of calcium carbonate and sodium carbonate in the presence of air. The chromium is oxidized to the hexavalent form, while the iron forms the stable Fe2O3. The subsequent leaching at higher elevated temperatures dissolves the
 The strengthening effect of forming stable metal carbides at grain boundaries, and the strong increase in corrosion resistance made chromium an important alloying material for steel. High-speed tool steels contain between 3 and 5% chromium. Stainless steel, the primary corrosion-resistant metal alloy, is formed when chromium is introduced to iron in concentrations above 11%. For stainless steel's formation, ferrochromium is added to the molten iron. Also, nickel-based alloys have increased strength due to the formation of discrete, stable, metal, carbide particles at the grain boundaries. For example, Inconel 718 contains 18.6% chromium. Because of the excellent high-temperature properties of these nickel superalloys, they are used in jet engines and gas turbines in lieu of common structural materials.
The strengthening effect of forming stable metal carbides at grain boundaries, and the strong increase in corrosion resistance made chromium an important alloying material for steel. High-speed tool steels contain between 3 and 5% chromium. Stainless steel, the primary corrosion-resistant metal alloy, is formed when chromium is introduced to iron in concentrations above 11%. For stainless steel's formation, ferrochromium is added to the molten iron. Also, nickel-based alloys have increased strength due to the formation of discrete, stable, metal, carbide particles at the grain boundaries. For example, Inconel 718 contains 18.6% chromium. Because of the excellent high-temperature properties of these nickel superalloys, they are used in jet engines and gas turbines in lieu of common structural materials.  The high hardness and corrosion resistance of unalloyed chromium makes it a reliable metal for surface coating; it is still the most popular metal for sheet coating, with its above-average durability, compared to other coating metals. A layer of chromium is deposited on pretreated metallic surfaces by electroplating techniques. There are two deposition methods: thin, and thick. Thin deposition involves a layer of chromium below 1 µm thickness deposited by
The high hardness and corrosion resistance of unalloyed chromium makes it a reliable metal for surface coating; it is still the most popular metal for sheet coating, with its above-average durability, compared to other coating metals. A layer of chromium is deposited on pretreated metallic surfaces by electroplating techniques. There are two deposition methods: thin, and thick. Thin deposition involves a layer of chromium below 1 µm thickness deposited by
 Chromium(III) ions present in
Chromium(III) ions present in
European Food Safety Authority EFSA J 2010;8(10)1732. Given the evidence for chromium deficiency causing problems with glucose management in the context of intravenous nutrition products formulated without chromium, research interest turned to whether chromium supplementation would benefit people who have type 2 diabetes but are not chromium deficient. Looking at the results from four meta-analyses, one reported a statistically significant decrease in fasting
ATSDR Case Studies in Environmental Medicine: Chromium Toxicity
U.S.
IARC Monograph "Chromium and Chromium compounds"
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health – Chromium Page
at ''
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
with the symbol Cr and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
24. It is the first element in group 6 Group 6 may refer to:
*Group 6 element
Group 6, numbered by IUPAC style, is a group of elements in the periodic table. Its members are chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), tungsten (W), and seaborgium (Sg). These are all transition metals and chromiu ...
. It is a steely-grey, lustrous
Lustre (British English) or luster (American English; see spelling differences) is the way light interacts with the surface of a crystal, rock, or mineral. The word traces its origins back to the Latin ''lux'', meaning "light", and generally im ...
, hard, and brittle transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...
.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
resistance and hardness. A major development in steel production was the discovery that steel could be made highly resistant to corrosion and discoloration by adding metallic chromium to form stainless steel. Stainless steel and chrome plating
Chrome plating (less commonly chromium plating) is a technique of electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object. A chrome-plated item is called ''chrome''. The chromed layer can be decorative, provide corrosion resistance, ease o ...
( electroplating with chromium) together comprise 85% of the commercial use. Chromium is also greatly valued as a metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typica ...
that is able to be highly polished while resisting tarnish
Tarnish is a thin layer of corrosion that forms over copper, brass, aluminum, magnesium, neodymium and other similar metals as their outermost layer undergoes a chemical reaction. Tarnish does not always result from the sole effects of oxygen in ...
ing. Polished chromium reflects almost 70% of the visible spectrum, and almost 90% of infrared light
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from ...
. The name of the element is derived from the Greek word χρῶμα, ''chrōma'', meaning color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associa ...
, because many chromium compounds are intensely colored.
Industrial production of chromium proceeds from chromite
Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of FeCr2O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The element magnesium can su ...
ore (mostly FeCr2O4) to produce ferrochromium
Ferrochrome, or ferrochromium (FeCr) is a type of ferroalloy, that is, an alloy of chromium and iron, generally containing 50 to 70% chromium by weight.
Ferrochrome is produced by electric arc carbothermic reduction of chromite. Most of the gl ...
, an iron-chromium alloy, by means of aluminothermic or silicothermic reaction
Silicothermic reactions are thermic chemical reactions using silicon as the reducing agent at high temperature (800-1400°C). The most prominent example is the Pidgeon process for reducing magnesium metal from ores. Other processes include the B ...
s. Ferrochromium is then used to produce alloys such as stainless steel. Pure chromium metal is produced by a different process: roasting and leaching of chromite to separate it from iron, followed by reduction with carbon and then aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
.
In the United States, trivalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.
Description
The combining capacity, or affinity of an ...
chromium (Cr(III)) ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conv ...
is considered an essential nutrient in humans for insulin, sugar, and lipid metabolism. However, in 2014, the European Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, ...
, acting for the European Union, concluded that there was insufficient evidence for chromium to be recognized as essential.
While chromium metal and Cr(III) ions are considered non-toxic, hexavalent chromium, Cr(VI), is toxic and carcinogenic
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substan ...
. According to the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), chromium trioxide
Chromium trioxide (also known as chromium(VI) oxide or chromic anhydride) is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO3. It is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid, and is sometimes marketed under the same name.
This compound is a dark-purple s ...
that is used in industrial electroplating processes is a "substance of very high concern" (SVHC).
Abandoned chromium production sites often require environmental cleanup
Environmental remediation deals with the removal of pollution or contaminants from environmental media such as soil, groundwater, sediment, or surface water. Remedial action is generally subject to an array of regulatory requirements, and may als ...
.
Physical properties
Atomic
Chromium is the fourthtransition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...
found on the periodic table, and has an electron configuration of Ar.html" ;"title="argon.html" ;"title="nowiki/>argon">Ar">argon.html" ;"title="nowiki/>argon">Ar3d5 4s1. It is also the first element in the periodic table whose ground-state electron configuration violates the Aufbau principle. This occurs again later in the periodic table with other elements and their electron configurations, such as copper, niobium, and molybdenum. This occurs because electrons in the same orbital repel each other due to their like charges. In the previous elements, the energetic cost of promoting an electron to the next higher energy level is too great to compensate for that released by lessening inter-electronic repulsion. However, in the 3d transition metals, the energy gap between the 3d and the next-higher 4s subshell is very small, and because the 3d subshell is more compact than the 4s subshell, inter-electron repulsion is smaller between 4s electrons than between 3d electrons. This lowers the energetic cost of promotion and increases the energy released by it, so that the promotion becomes energetically feasible and one or even two electrons are always promoted to the 4s subshell. (Similar promotions happen for every transition metal atom but one, palladium.)
Chromium is the first element in the 3d series where the 3d electrons start to sink into the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
; they thus contribute less to metallic bonding, and hence the melting and boiling points and the enthalpy of atomisation
In chemistry, the enthalpy of atomization (also atomisation in British English) is the enthalpy change that accompanies the total separation of all atoms in a chemical substance (either an element or a compound). This is often represented by th ...
of chromium are lower than those of the preceding element vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer ( pass ...
. Chromium(VI) is a strong oxidising agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxid ...
in contrast to the molybdenum(VI) and tungsten(VI) oxides.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1004–5
Bulk
 Chromium is extremely hard, and is the third hardest element behind carbon ( diamond) and
Chromium is extremely hard, and is the third hardest element behind carbon ( diamond) and boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has th ...
. Its Mohs hardness
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by ...
is 8.5, which means that it can scratch samples of quartz and topaz, but can be scratched by corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the pre ...
. Chromium is highly resistant to tarnish
Tarnish is a thin layer of corrosion that forms over copper, brass, aluminum, magnesium, neodymium and other similar metals as their outermost layer undergoes a chemical reaction. Tarnish does not always result from the sole effects of oxygen in ...
ing, which makes it useful as a metal that preserves its outermost layer from corroding
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
, unlike other metals such as copper, magnesium, and aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
.
Chromium has a melting point of 1907 °C (3465 °F), which is relatively low compared to the majority of transition metals. However, it still has the second highest melting point out of all the Period 4 elements, being topped by vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer ( pass ...
by 3 °C (5 °F) at 1910 °C (3470 °F). The boiling point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding envi ...
of 2671 °C (4840 °F), however, is comparatively lower, having the fourth lowest boiling point out of the Period 4 transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...
s alone behind copper, manganese and zinc.The melting/boiling point of transition metals are usually higher compared to the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, and nonmetals, which is why the range of elements compared to chromium differed between comparisons The electrical resistivity of chromium at 20 °C is 125 nanoohm- meters.
Chromium has a high specular reflection in comparison to other transition metals. In infrared, at 425 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Uni ...
, chromium has a maximum reflectance of about 72%, reducing to a minimum of 62% at 750 μm before rising again to 90% at 4000 μm. When chromium is used in stainless steel alloys and polished, the specular reflection decreases with the inclusion of additional metals, yet is still high in comparison with other alloys. Between 40% and 60% of the visible spectrum is reflected from polished stainless steel. The explanation on why chromium displays such a high turnout of reflected photon waves in general, especially the 90% in infrared, can be attributed to chromium's magnetic properties. Chromium has unique magnetic properties - chromium is the only elemental solid that shows antiferromagnetic
In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins (on different sublattices) pointing in opposite directions. ...
ordering at room temperature and below. Above 38 °C, its magnetic ordering becomes paramagnetic. The antiferromagnetic properties, which cause the chromium atoms to temporarily ionize and bond with themselves, are present because the body-centric cubic's magnetic properties are disproportionate to the lattice periodicity. This is due to the magnetic moments at the cube's corners and the unequal, but antiparallel, cube centers. From here, the frequency-dependent relative permittivity of chromium, deriving from Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits. ...
and chromium's antiferromagnetism
In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins (on different sublattices) pointing in opposite directions. ...
, leaves chromium with a high infrared and visible light reflectance.
Passivation
Chromium metal left standing in air is passivated - it forms a thin, protective, surface layer of oxide. This layer has aspinel
Spinel () is the magnesium/aluminium member of the larger spinel group of minerals. It has the formula in the cubic crystal system. Its name comes from the Latin word , which means ''spine'' in reference to its pointed crystals.
Properties
S ...
structure a few atomic layers thick; it is very dense and inhibits the diffusion of oxygen into the underlying metal. In contrast, iron forms a more porous oxide through which oxygen can migrate, causing continued rust
Rust is an iron oxide, a usually reddish-brown oxide formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the catalytic presence of water or air moisture. Rust consists of hydrous iron(III) oxides (Fe2O3·nH2O) and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH) ...
ing. Passivation can be enhanced by short contact with oxidizing acid
An oxidizing acid is a Brønsted acid that is a strong oxidizing agent. Most Brønsted acids can act as oxidizing agents, because the acidic proton can be reduced to hydrogen gas. Some acids contain other structures that act as stronger oxidizing ...
s like nitric acid. Passivated chromium is stable against acids. Passivation can be removed with a strong reducing agent that destroys the protective oxide layer on the metal. Chromium metal treated in this way readily dissolves in weak acids.
Chromium, unlike iron and nickel, does not suffer from hydrogen embrittlement
Hydrogen embrittlement (HE), also known as hydrogen-assisted cracking or hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC), is a reduction in the ductility of a metal due to absorbed hydrogen. Hydrogen atoms are small and can permeate solid metals. Once absorbe ...
. However, it does suffer from nitrogen embrittlement, reacting with nitrogen from air and forming brittle nitrides at the high temperatures necessary to work the metal parts.
Isotopes
Naturally occurring chromium is composed of three stable isotopes; 52Cr, 53Cr and 54Cr, with 52Cr being the most abundant (83.789% natural abundance). 19radioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
s have been characterized, with the most stable being 50Cr with a half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
of (more than) 1.8 years, and 51Cr with a half-life of 27.7 days. All of the remaining radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
isotopes have half-lives that are less than 24 hours and the majority less than 1 minute. Chromium also has two metastable
In chemistry and physics, metastability denotes an intermediate energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's state of least energy.
A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of metastability. If the ball i ...
nuclear isomers.
53Cr is the radiogenic decay product of 53 Mn (half-life = 3.74 million years). Chromium isotopes are typically collocated (and compounded) with manganese isotopes. This circumstance is useful in isotope geology
Isotope geochemistry is an aspect of geology based upon the study of natural variations in the relative abundances of isotopes of various elements. Variations in isotopic abundance are measured by isotope ratio mass spectrometry, and can reveal ...
. Manganese-chromium isotope ratios reinforce the evidence from 26 Al and 107 Pd concerning the early history of the Solar System. Variations in 53Cr/52Cr and Mn/Cr ratios from several meteorites indicate an initial 53Mn/55Mn ratio that suggests Mn-Cr isotopic composition must result from in-situ decay of 53Mn in differentiated planetary bodies. Hence 53Cr provides additional evidence for nucleosynthetic
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons (protons and neutrons) and nuclei. According to current theories, the first nuclei were formed a few minutes after the Big Bang, through nuclear reactions in ...
processes immediately before coalescence of the Solar System.
The isotopes of chromium range in atomic mass
The atomic mass (''m''a or ''m'') is the mass of an atom. Although the SI unit of mass is the kilogram (symbol: kg), atomic mass is often expressed in the non-SI unit dalton (symbol: Da) – equivalently, unified atomic mass unit (u). 1&nbs ...
from 43 u (43Cr) to 67 u (67Cr). The primary decay mode
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
before the most abundant stable isotope, 52Cr, is electron capture and the primary mode after is beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For e ...
. 53Cr has been posited as a proxy for atmospheric oxygen concentration.
Chemistry and compounds
 Chromium is a member of
Chromium is a member of group 6 Group 6 may refer to:
*Group 6 element
Group 6, numbered by IUPAC style, is a group of elements in the periodic table. Its members are chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), tungsten (W), and seaborgium (Sg). These are all transition metals and chromiu ...
, of the transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...
s. The +3 and +6 states occur most commonly within chromium compounds, followed by +2; charges of +1, +4 and +5 for chromium are rare, but do nevertheless occasionally exist.
Common oxidation states
Chromium(0)
Many Cr(0) complexes are known.Bis(benzene)chromium
Bis(benzene)chromium is the organometallic compound with the formula Cr( η6-C6H6)2. It is sometimes called dibenzenechromium. The compound played an important role in the development of sandwich compounds in organometallic chemistry and is the ...
and chromium hexacarbonyl
Chromium carbonyl, also known as chromium hexacarbonyl, is the chemical compound with the formula Cr( CO)6. At room temperature the solid is stable to air, although it does have a high vapor pressure and sublimes readily. Cr(CO)6 is zerovalent, ...
are highlights in organochromium chemistry Organochromium chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic compounds containing a chromium to carbon bond and their reactions. The field is of some relevance to organic synthesis. The relevant oxidation states for organ ...
.
Chromium(II)
chromium(II) chloride
Chromium(II) chloride describes inorganic compounds with the formula Cr Cl2(H2O)n. The anhydrous solid is white when pure, however commercial samples are often grey or green; it is hygroscopic and readily dissolves in water to give bright blue a ...
that can be made by reducing chromium(III) chloride with zinc. The resulting bright blue solution created from dissolving chromium(II) chloride is stable at neutral pH. Some other notable chromium(II) compounds include chromium(II) oxide
Chromium(II) oxide (CrO) is an inorganic compound composed of chromium and oxygen. It is a black powder that crystallises in the rock salt structure.Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', Elsevier
Hypophosphites m ...
, and chromium(II) sulfate
Chromium(II) sulfate refers to inorganic compounds with the chemical formula CrSO4·n H2O. Several closely related hydrated salts are known. The pentahydrate is a blue solid that dissolves readily in water. Solutions of chromium(II) are easily ox ...
. Many chromium(II) carboxylates are known. The red chromium(II) acetate
Chromium(II) acetate hydrate, also known as chromous acetate, is the coordination compound with the formula Cr2(CH3CO2)4(H2O)2. This formula is commonly abbreviated Cr2(OAc)4(H2O)2. This red-coloured compound features a quadruple bond. The prepara ...
(Cr2(O2CCH3)4) is somewhat famous. It features a Cr-Cr quadruple bond
A quadruple bond is a type of chemical bond between two atoms involving eight electrons. This bond is an extension of the more familiar types double bonds and triple bonds. Stable quadruple bonds are most common among the transition metals in the ...
.
Chromium(III)
 A large number of chromium(III) compounds are known, such as chromium(III) nitrate, chromium(III) acetate, and
A large number of chromium(III) compounds are known, such as chromium(III) nitrate, chromium(III) acetate, and chromium(III) oxide
Chromium(III) oxide (or chromia) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of chromium and is used as a pigment. In nature, it occurs as the rare mineral eskolaite.
Structure and properties
has the corundum s ...
. Chromium(III) can be obtained by dissolving elemental chromium in acids like hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid, but it can also be formed through the reduction of chromium(VI) by cytochrome
Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with a central Fe atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in electron transport chain and redox catalysis. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of ...
c7. The ion has a similar radius (63 pm) to (radius 50 pm), and they can replace each other in some compounds, such as in chrome alum
Chrome alum or Chromium(III) potassium sulfate is the potassium double sulfate of chromium. Its chemical formula is KCr(SO4)2 and it is commonly found in its dodecahydrate form as KCr(SO4)2·12(H2O). It is used in leather tanning.
Production an ...
and alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double sulfate salt of aluminium with the general formula , where is a monovalent cation such as potassium or ammonium. By itself, "alum" often refers to potassium alum, with the ...
.
Chromium(III) tends to form octahedral
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
complexes. Commercially available chromium(III) chloride
Chromium(III) chloride (also called chromic chloride) describes any of several chemical compounds with the formula CrCl3, where can be 0, 5, and 6. The anhydrous compound with the formula CrCl3 is a violet solid. The most common form of the tric ...
hydrate is the dark green complex rCl2(H2O)4l. Closely related compounds are the pale green rCl(H2O)5l2 and violet r(H2O)6l3. If anhydrous violet chromium(III) chloride
Chromium(III) chloride (also called chromic chloride) describes any of several chemical compounds with the formula CrCl3, where can be 0, 5, and 6. The anhydrous compound with the formula CrCl3 is a violet solid. The most common form of the tric ...
is dissolved in water, the violet solution turns green after some time as the chloride in the inner coordination sphere
In coordination chemistry, the first coordination sphere refers to the array of molecules and ions (the ligands) directly attached to the central metal atom. The second coordination sphere consists of molecules and ions that attached in various ...
is replaced by water. This kind of reaction is also observed with solutions of chrome alum
Chrome alum or Chromium(III) potassium sulfate is the potassium double sulfate of chromium. Its chemical formula is KCr(SO4)2 and it is commonly found in its dodecahydrate form as KCr(SO4)2·12(H2O). It is used in leather tanning.
Production an ...
and other water-soluble chromium(III) salts. A tetrahedral
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ...
coordination of chromium(III)
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardne ...
has been reported for the Cr-centered Keggin anion �-CrW12O40sup>5–.
Chromium(III) hydroxide (Cr(OH)3) is amphoteric
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound () is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used.
One type of amphoteric species are amphiprot ...
, dissolving in acidic solutions to form r(H2O)6sup>3+, and in basic solutions to form . It is dehydrated by heating to form the green chromium(III) oxide (Cr2O3), a stable oxide with a crystal structure identical to that of corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the pre ...
.
Chromium(VI)
Chromium(VI) compounds
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardne ...
are oxidants at low or neutral pH. Chromate Chromate or chromat, and their derived terms, may refer to:
Chemistry
* Chromate and dichromate, ions
* Monochromate, an ion
* Trichromate, an ion
* Tetrachromate, an ion
* Chromate conversion coating, a method for passivating metals
Biology ...
anions () and dichromate (Cr2O72−) anions are the principal ions at this oxidation state. They exist at an equilibrium, determined by pH:
:2 rO4sup>2− + 2 H+ r2O7sup>2− + H2O
Chromium(VI) oxyhalides are known also and include chromyl fluoride
Chromyl fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a violet-red colored crystalline solid that melts to an orange-red liquid.Gard, G. L. (1986) "Chromium Difluoride Dioxide (Chromyl Fluoride)," '' Inorg. Synth.'', 24, 67-69, .
Stru ...
(CrO2F2) and chromyl chloride
Chromyl chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula CrO2Cl2. It is a reddish brown compound that is a volatile liquid at room temperature, which is unusual for transition metal complexes.
Preparation
Chromyl chloride can be prepared by th ...
(). However, despite several erroneous claims, chromium hexafluoride (as well as all higher hexahalides) remains unknown, as of 2020.

Sodium chromate
Sodium chromate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CrO4. It exists as a yellow hygroscopic solid, which can form tetra-, hexa-, and decahydrates. It is an intermediate in the extraction of chromium from its ores.
Production and react ...
is produced industrially by the oxidative roasting of chromite
Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of FeCr2O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The element magnesium can su ...
ore with sodium carbonate. The change in equilibrium is visible by a change from yellow (chromate) to orange (dichromate), such as when an acid is added to a neutral solution of potassium chromate
Potassium chromate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2 CrO4. This yellow solid is the potassium salt of the chromate anion. It is a common laboratory chemical, whereas sodium chromate is important industrially.
Structure
Two crysta ...
. At yet lower pH values, further condensation to more complex oxyanions of chromium is possible.
Both the chromate and dichromate
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ...
anions are strong oxidizing reagents at low pH:
: + 14 + 6 e− → 2 + 21 (ε0 = 1.33 V)
They are, however, only moderately oxidizing at high pH:
: + 4 + 3 e− → + 5 (ε0 = −0.13 V)
chromium(VI) peroxide
Chromium(VI) peroxide or chromium oxide peroxide is an unstable compound with the formula CrO5. This compound contains one oxo ligand and two peroxo ligands, making a total of five oxygen atoms per chromium atom.
Preparation and properties
Chromi ...
(CrO5) is formed, which can be stabilized as an ether adduct .
Chromic acid
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixtu ...
has the hypothetical formula . It is a vaguely described chemical, despite many well-defined chromates and dichromates being known. The dark red chromium(VI) oxide
Chromium trioxide (also known as chromium(VI) oxide or chromic anhydride) is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO3. It is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid, and is sometimes marketed under the same name.
This compound is a dark-purple s ...
, the acid anhydride
An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the p ...
of chromic acid, is sold industrially as "chromic acid". It can be produced by mixing sulfuric acid with dichromate and is a strong oxidizing agent.
Other oxidation states
Compounds of chromium(V) are rather rare; the oxidation state +5 is only realized in few compounds but are intermediates in many reactions involving oxidations by chromate. The only binary compound is the volatilechromium(V) fluoride
Chromium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF5. It is a red volatile solid that melts at 34 °C. It is the highest known chromium fluoride, since the hypothetical chromium hexafluoride has not yet been synt ...
(CrF5). This red solid has a melting point of 30 °C and a boiling point of 117 °C. It can be prepared by treating chromium metal with fluorine at 400 °C and 200 bar pressure. The peroxochromate(V) is another example of the +5 oxidation state. Potassium peroxochromate (K3 r(O2)4 is made by reacting potassium chromate with hydrogen peroxide at low temperatures. This red brown compound is stable at room temperature but decomposes spontaneously at 150–170 °C.
Compounds of chromium(IV) are slightly more common than those of chromium(V). The tetrahalides, CrF4, CrCl4, and CrBr4, can be produced by treating the trihalides () with the corresponding halogen at elevated temperatures. Such compounds are susceptible to disproportionation reactions and are not stable in water. Organic compounds containing Cr(IV) state such as chromium tetra ''t''-butoxide are also known.
Most chromium(I) compounds are obtained solely by oxidation of electron-rich, octahedral
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
chromium(0) complexes. Other chromium(I) complexes contain cyclopentadienyl Cyclopentadienyl can refer to
* Cyclopentadienyl anion, or cyclopentadienide,
** Cyclopentadienyl ligand
* Cyclopentadienyl radical, •
* Cyclopentadienyl cation,
See also
*Pentadienyl
In organic chemistry, pentadienyl refers to the organic ...
ligands. As verified by X-ray diffraction, a Cr-Cr quintuple bond
A quintuple bond in chemistry is an unusual type of chemical bond, first reported in 2005 for a dichromium compound. Single bonds, double bonds, and triple bonds are commonplace in chemistry. Quadruple bonds are rarer but are currently known only ...
(length 183.51(4) pm) has also been described. Extremely bulky monodentate ligands stabilize this compound by shielding the quintuple bond from further reactions.

Occurrence

 Chromium is the 21st most abundant element in Earth's crust with an average concentration of 100 ppm. Chromium compounds are found in the environment from the erosion of chromium-containing rocks, and can be redistributed by volcanic eruptions. Typical background concentrations of chromium in environmental media are: atmosphere <10 ng/m3; soil <500 mg/kg; vegetation <0.5 mg/kg; freshwater <10 μg/L; seawater <1 μg/L; sediment <80 mg/kg. Chromium is mined as chromite (FeCr2O4) ore.
About two-fifths of the chromite ores and concentrates in the world are produced in South Africa, about a third in Kazakhstan, while India, Russia, and Turkey are also substantial producers. Untapped chromite deposits are plentiful, but geographically concentrated in Kazakhstan and southern Africa. Although rare, deposits of
Chromium is the 21st most abundant element in Earth's crust with an average concentration of 100 ppm. Chromium compounds are found in the environment from the erosion of chromium-containing rocks, and can be redistributed by volcanic eruptions. Typical background concentrations of chromium in environmental media are: atmosphere <10 ng/m3; soil <500 mg/kg; vegetation <0.5 mg/kg; freshwater <10 μg/L; seawater <1 μg/L; sediment <80 mg/kg. Chromium is mined as chromite (FeCr2O4) ore.
About two-fifths of the chromite ores and concentrates in the world are produced in South Africa, about a third in Kazakhstan, while India, Russia, and Turkey are also substantial producers. Untapped chromite deposits are plentiful, but geographically concentrated in Kazakhstan and southern Africa. Although rare, deposits of native
Native may refer to:
People
* Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Native Americans (disambiguation)
In arts and entert ...
chromium exist. The Udachnaya Pipe
The Udachnaya pipe (russian: тру́бка Уда́чная, literally ''lucky pipe'') is a diamond deposit in the Daldyn- Alakit kimberlite field in Sakha Republic, Russia. It is an open-pit mine, and is located just outside the Arctic ...
in Russia produces samples of the native metal. This mine is a kimberlite pipe, rich in diamonds, and the reducing environment
A reducing atmosphere is an atmospheric condition in which oxidation is prevented by removal of oxygen and other oxidizing gases or vapours, and which may contain actively reducing gases such as hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and gases such as hydro ...
helped produce both elemental chromium and diamonds.
The relation between Cr(III) and Cr(VI) strongly depends on pH and oxidative
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
properties of the location. In most cases, Cr(III) is the dominating species, but in some areas, the ground water can contain up to 39 µg/L of total chromium, of which 30 µg/L is Cr(VI).
History
Early applications
Chromium minerals as pigments came to the attention of the west in the eighteenth century. On 26 July 1761, Johann Gottlob Lehmann found an orange-red mineral in the Beryozovskoye mines in the Ural Mountains which he named ''Siberian red lead''. Though misidentified as a lead compound with selenium and iron components, the mineral was in factcrocoite
Crocoite is a mineral consisting of lead chromate, Pb Cr O4, and crystallizing in the monoclinic crystal system. It is identical in composition with the artificial product chrome yellow used as a paint pigment.
Description
Crocoite is comm ...
with a formula of PbCrO4. In 1770, Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussian zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia between 1767 and 1810.
Life and work
Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, the son of Professor of Surgery Si ...
visited the same site as Lehmann and found a red lead mineral that was discovered to possess useful properties as a pigment in paints. After Pallas, the use of Siberian red lead as a paint pigment began to develop rapidly throughout the region. Crocoite would be the principal source of chromium in pigments until the discovery of chromite
Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of FeCr2O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The element magnesium can su ...
many years later.
 In 1794, Louis Nicolas Vauquelin received samples of crocoite
In 1794, Louis Nicolas Vauquelin received samples of crocoite ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 April ...
. He produced chromium trioxide
Chromium trioxide (also known as chromium(VI) oxide or chromic anhydride) is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO3. It is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid, and is sometimes marketed under the same name.
This compound is a dark-purple s ...
(CrO3) by mixing crocoite with hydrochloric acid. In 1797, Vauquelin discovered that he could isolate metallic chromium by heating the oxide in a charcoal oven, for which he is credited as the one who truly discovered the element. Vauquelin was also able to detect traces of chromium in precious gemstones, such as ruby and emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr. and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991) ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. ...
.
During the nineteenth century, chromium was primarily used not only as a component of paints, but in tanning salts as well. For quite some time, the crocoite found in Russia was the main source for such tanning materials. In 1827, a larger chromite deposit was discovered near Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
, United States, which quickly met the demand for tanning salts much more adequately than the crocoite that had been used previously. This made the United States the largest producer of chromium products until the year 1848, when larger deposits of chromite were uncovered near the city of Bursa
( grc-gre, Προῦσα, Proûsa, Latin: Prusa, ota, بورسه, Arabic:بورصة) is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in the ...
, Turkey. With the development of metallurgy and chemical industries in the Western world, the need for chromium increased.
Chromium is also famous for its reflective, metallic luster when polished. It is used as a protective and decorative coating on car parts, plumbing fixtures, furniture parts and many other items, usually applied by electroplating. Chromium was used for electroplating as early as 1848, but this use only became widespread with the development of an improved process in 1924.
Production

 Approximately 28.8 million metric tons (Mt) of marketable chromite ore was produced in 2013, and converted into 7.5 Mt of ferrochromium. According to John F. Papp, writing for the USGS, "Ferrochromium is the leading end use of chromite ore, ndstainless steel is the leading end use of ferrochromium."
The largest producers of chromium ore in 2013 have been South Africa (48%), Kazakhstan (13%), Turkey (11%), and India (10%), with several other countries producing the rest of about 18% of the world production.
The two main products of chromium ore refining are
Approximately 28.8 million metric tons (Mt) of marketable chromite ore was produced in 2013, and converted into 7.5 Mt of ferrochromium. According to John F. Papp, writing for the USGS, "Ferrochromium is the leading end use of chromite ore, ndstainless steel is the leading end use of ferrochromium."
The largest producers of chromium ore in 2013 have been South Africa (48%), Kazakhstan (13%), Turkey (11%), and India (10%), with several other countries producing the rest of about 18% of the world production.
The two main products of chromium ore refining are ferrochromium
Ferrochrome, or ferrochromium (FeCr) is a type of ferroalloy, that is, an alloy of chromium and iron, generally containing 50 to 70% chromium by weight.
Ferrochrome is produced by electric arc carbothermic reduction of chromite. Most of the gl ...
and metallic chromium. For those products the ore smelter process differs considerably. For the production of ferrochromium, the chromite ore (FeCr2O4) is reduced in large scale in electric arc furnace or in smaller smelters with either aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
or silicon in an aluminothermic reaction
Aluminothermic reactions are exothermic chemical reactions using aluminum as the reducing agent at high temperature. The process is industrially useful for production of alloys of iron. The most prominent example is the thermite reaction between i ...
.
chromates
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ...
and leaves the insoluble iron oxide. The chromate is converted by sulfuric acid into the dichromate.
:4 FeCr2O4 + 8 Na2CO3 + 7 O2 → 8 Na2CrO4 + 2 Fe2O3 + 8 CO2
:2 Na2CrO4 + H2SO4 → Na2Cr2O7 + Na2SO4 + H2O
The dichromate is converted to the chromium(III) oxide by reduction with carbon and then reduced in an aluminothermic reaction to chromium.
:Na2Cr2O7 + 2 C → Cr2O3 + Na2CO3 + CO
:Cr2O3 + 2 Al → Al2O3 + 2 Cr
Applications
The creation of metal alloys account for 85% of the available chromium's usage. The remainder of chromium is used in the chemical,refractory
In materials science, a refractory material or refractory is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat, pressure, or chemical attack, and retains strength and form at high temperatures. Refractories are polycrystalline, polyphase, ...
, and foundry industries.
Metallurgy
 The strengthening effect of forming stable metal carbides at grain boundaries, and the strong increase in corrosion resistance made chromium an important alloying material for steel. High-speed tool steels contain between 3 and 5% chromium. Stainless steel, the primary corrosion-resistant metal alloy, is formed when chromium is introduced to iron in concentrations above 11%. For stainless steel's formation, ferrochromium is added to the molten iron. Also, nickel-based alloys have increased strength due to the formation of discrete, stable, metal, carbide particles at the grain boundaries. For example, Inconel 718 contains 18.6% chromium. Because of the excellent high-temperature properties of these nickel superalloys, they are used in jet engines and gas turbines in lieu of common structural materials.
The strengthening effect of forming stable metal carbides at grain boundaries, and the strong increase in corrosion resistance made chromium an important alloying material for steel. High-speed tool steels contain between 3 and 5% chromium. Stainless steel, the primary corrosion-resistant metal alloy, is formed when chromium is introduced to iron in concentrations above 11%. For stainless steel's formation, ferrochromium is added to the molten iron. Also, nickel-based alloys have increased strength due to the formation of discrete, stable, metal, carbide particles at the grain boundaries. For example, Inconel 718 contains 18.6% chromium. Because of the excellent high-temperature properties of these nickel superalloys, they are used in jet engines and gas turbines in lieu of common structural materials. ASTM
ASTM International, formerly known as American Society for Testing and Materials, is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, an ...
B163 relies on Chromium for condenser and heat-exchanger tubes, while castings
In metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing ob ...
with high strength at elevated temperatures that contain Chromium are standardised with ASTM A567. AISI type 332 is used where high temperature would normally cause carburization
Carburising, carburizing (chiefly American English), or carburisation is a heat treatment process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon while the metal is heated in the presence of a carbon-bearing material, such as charcoal or carbon monoxide. ...
, oxidation or corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
. Incoloy 800 "is capable of remaining stable and maintaining its austenitic
Austenite, also known as gamma-phase iron (γ-Fe), is a metallic, non-magnetic allotrope of iron or a solid solution of iron with an alloying element. In plain-carbon steel, austenite exists above the critical eutectoid temperature of 1000 K ...
structure even after long time exposures to high temperatures". Nichrome is used as resistance wire for heating elements in things like toasters
A toaster is a small electric appliance that uses radiant heat to brown sliced bread into toast.
Types
Pop-up toaster
In pop-up or automatic toasters, a single vertical piece of bread is dropped into a slot on the top of the toaster ...
and space heaters. These uses make chromium a strategic material
Strategic material is any sort of raw material that is important to an individual's or organization's strategic plan and supply chain management. Lack of supply of strategic materials may leave an organization or government vulnerable to disru ...
. Consequently, during World War II, U.S. road engineers were instructed to avoid chromium in yellow road paint, as it "may become a critical material during the emergency." The United States likewise considered chromium "essential for the German war industry" and made intense diplomatic efforts to keep it out of the hands of Nazi Germany.
 The high hardness and corrosion resistance of unalloyed chromium makes it a reliable metal for surface coating; it is still the most popular metal for sheet coating, with its above-average durability, compared to other coating metals. A layer of chromium is deposited on pretreated metallic surfaces by electroplating techniques. There are two deposition methods: thin, and thick. Thin deposition involves a layer of chromium below 1 µm thickness deposited by
The high hardness and corrosion resistance of unalloyed chromium makes it a reliable metal for surface coating; it is still the most popular metal for sheet coating, with its above-average durability, compared to other coating metals. A layer of chromium is deposited on pretreated metallic surfaces by electroplating techniques. There are two deposition methods: thin, and thick. Thin deposition involves a layer of chromium below 1 µm thickness deposited by chrome plating
Chrome plating (less commonly chromium plating) is a technique of electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object. A chrome-plated item is called ''chrome''. The chromed layer can be decorative, provide corrosion resistance, ease o ...
, and is used for decorative surfaces. Thicker chromium layers are deposited if wear-resistant surfaces are needed. Both methods use acidic chromate or dichromate solutions. To prevent the energy-consuming change in oxidation state, the use of chromium(III) sulfate is under development; for most applications of chromium, the previously established process is used.
In the chromate conversion coating
Chromate conversion coating or alodine coating is a type of conversion coating used to passivate steel, aluminium, zinc, cadmium, copper, silver, titanium, magnesium, and tin alloys. The coating serves as a corrosion inhibitor, as a p ...
process, the strong oxidative properties of chromates are used to deposit a protective oxide layer on metals like aluminium, zinc, and cadmium. This passivation and the self-healing properties of the chromate stored in the chromate conversion coating, which is able to migrate to local defects, are the benefits of this coating method. Because of environmental and health regulations on chromates, alternative coating methods are under development.
Chromic acid anodizing
Anodizing is an electrolytic passivation process used to increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the surface of metal parts.
The process is called ''anodizing'' because the part to be treated forms the anode electrode of an electro ...
(or Type I anodizing) of aluminium is another electrochemical process that does not lead to the deposition of chromium, but uses chromic acid
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixtu ...
as an electrolyte in the solution. During anodization, an oxide layer is formed on the aluminium. The use of chromic acid, instead of the normally used sulfuric acid, leads to a slight difference of these oxide layers.
The high toxicity of Cr(VI) compounds, used in the established chromium electroplating process, and the strengthening of safety and environmental regulations demand a search for substitutes for chromium, or at least a change to less toxic chromium(III) compounds.
Pigment
The mineralcrocoite
Crocoite is a mineral consisting of lead chromate, Pb Cr O4, and crystallizing in the monoclinic crystal system. It is identical in composition with the artificial product chrome yellow used as a paint pigment.
Description
Crocoite is comm ...
(which is also lead chromate PbCrO4) was used as a yellow pigment shortly after its discovery. After a synthesis method became available starting from the more abundant chromite, chrome yellow
__NOTOC__
Chrome yellow is a yellow pigment in paints using monoclinic lead(II) chromate (PbCrO4). It occurs naturally as the mineral crocoite but the mineral ore itself was never used as a pigment for paint. After the French chemist Louis ...
was, together with cadmium yellow
Cadmium pigments are a class of pigments that contain cadmium. Most of the cadmium produced worldwide has been for use in rechargeable nickel–cadmium batteries, which have been replaced by other rechargeable nickel-chemistry cell varieties ...
, one of the most used yellow pigments. The pigment does not photodegrade, but it tends to darken due to the formation of chromium(III) oxide. It has a strong color, and was used for school buses in the United States and for the postal services (for example, the Deutsche Post) in Europe. The use of chrome yellow has since declined due to environmental and safety concerns and was replaced by organic pigments or other alternatives that are free from lead and chromium. Other pigments that are based around chromium are, for example, the deep shade of red pigment chrome red
Chrome orange is a mixed oxide with the chemical formula Pb2CrO5. It can be made by treating a lead(II) salt with an alkaline solution of a chromate or by treating chrome yellow (PbCrO4) with strongly basic solution..
Synthesis and nanopart ...
, which is simply lead chromate with lead(II) hydroxide
Lead(II) hydroxide, Pb(OH)2, is a hydroxide of lead, with lead in oxidation state +2. In 1964 it was believed that such a simple compound did not exist, as lead basic carbonate (2PbCO3·Pb(OH)2) or lead(II) oxide (PbO) was encountered where lead ...
(PbCrO4·Pb(OH)2). A very important chromate pigment, which was used widely in metal primer formulations, was zinc chromate, now replaced by zinc phosphate. A wash primer was formulated to replace the dangerous practice of pre-treating aluminium aircraft bodies with a phosphoric acid solution. This used zinc tetroxychromate dispersed in a solution of polyvinyl butyral
Polyvinyl butyral (or PVB) is a resin mostly used for applications that require strong binding, optical clarity, adhesion to many surfaces, toughness and flexibility. It is prepared from polyvinyl alcohol by reaction with butyraldehyde. The majo ...
. An 8% solution of phosphoric acid in solvent was added just before application. It was found that an easily oxidized alcohol was an essential ingredient. A thin layer of about 10–15 µm was applied, which turned from yellow to dark green when it was cured. There is still a question as to the correct mechanism. Chrome green is a mixture of Prussian blue and chrome yellow
__NOTOC__
Chrome yellow is a yellow pigment in paints using monoclinic lead(II) chromate (PbCrO4). It occurs naturally as the mineral crocoite but the mineral ore itself was never used as a pigment for paint. After the French chemist Louis ...
, while the chrome oxide green is chromium(III) oxide
Chromium(III) oxide (or chromia) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of chromium and is used as a pigment. In nature, it occurs as the rare mineral eskolaite.
Structure and properties
has the corundum s ...
.
Chromium oxides are also used as a green pigment in the field of glassmaking and also as a glaze for ceramics. Green chromium oxide is extremely lightfast
Lightfastness is a property of a colourant such as dye or pigment that describes its resistance to fading when exposed to light. Dyes and pigments are used for example for dyeing of fabrics, plastics or other materials and manufacturing paints ...
and as such is used in cladding coatings. It is also the main ingredient in infrared reflecting paints, used by the armed forces to paint vehicles and to give them the same infrared reflectance as green leaves.
Other uses
 Chromium(III) ions present in
Chromium(III) ions present in corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the pre ...
crystals (aluminium oxide) cause them to be colored red; when corundum appears as such, it is known as a ruby. If the corundum is lacking in chromium(III) ions, it is known as a sapphire.Any color of corundum (disregarding red) is known as a sapphire. If the corundum is red, then it is a ruby. Sapphires are not required to be blue corundum crystals, as sapphires can be other colors such as yellow and purple A red-colored artificial ruby may also be achieved by doping chromium(III) into artificial corundum crystals, thus making chromium a requirement for making synthetic rubies.When replaces in corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the pre ...
(aluminium oxide, Al2O3), pink sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sapphir ...
or ruby is formed, depending on the amount of chromium. Such a synthetic ruby crystal was the basis for the first laser
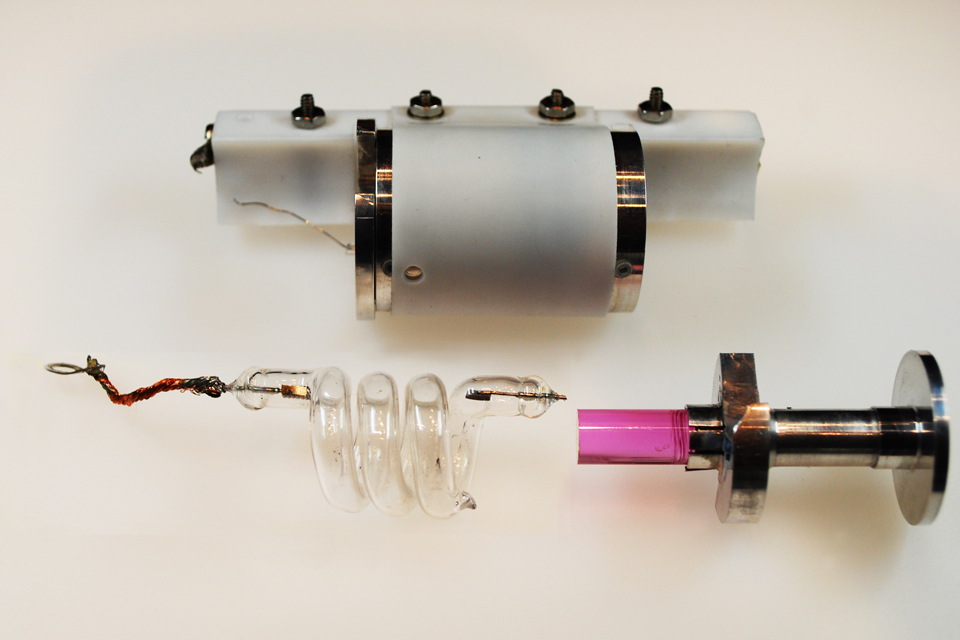
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...
, produced in 1960, which relied on stimulated emission of light from the chromium atoms in such a crystal. Ruby has a laser transition at 694.3 nanometers, in a deep red color.
Because of their toxicity, chromium(VI) salts are used for the preservation of wood. For example, chromated copper arsenate Chromated copper arsenate (CCA) is a wood preservative containing compounds of chromium, copper, and arsenic, in various proportions. It is used to impregnate timber and other wood products, especially those intended for outdoor use, in order to p ...
(CCA) is used in timber treatment to protect wood from decay fungi, wood-attacking insects, including termites
Termites are small insects that live in colonies and have distinct castes ( eusocial) and feed on wood or other dead plant matter. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blat ...
, and marine borers. The formulations contain chromium based on the oxide CrO3 between 35.3% and 65.5%. In the United States, 65,300 metric tons of CCA solution were used in 1996.
Chromium(III) salts, especially chrome alum
Chrome alum or Chromium(III) potassium sulfate is the potassium double sulfate of chromium. Its chemical formula is KCr(SO4)2 and it is commonly found in its dodecahydrate form as KCr(SO4)2·12(H2O). It is used in leather tanning.
Production an ...
and chromium(III) sulfate
Chromium(III) sulfate usually refers to the inorganic compounds with the formula Cr2(SO4)3.x(H2O), where x can range from 0 to 18. Additionally, ill-defined but commercially important "basic chromium sulfates" are known. These salts are usually eit ...
, are used in the tanning of leather. The chromium(III) stabilizes the leather by cross linking the collagen fibers. Chromium tanned leather can contain between 4 and 5% of chromium, which is tightly bound to the proteins. Although the form of chromium used for tanning is not the toxic hexavalent variety, there remains interest in management of chromium in the tanning industry. Recovery and reuse, direct/indirect recycling, and "chrome-less" or "chrome-free" tanning are practiced to better manage chromium usage.
The high heat resistivity and high melting point makes chromite
Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of FeCr2O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The element magnesium can su ...
and chromium(III) oxide a material for high temperature refractory applications, like blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric ...
s, cement kilns, molds for the firing of brick
A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured cons ...
s and as foundry sands for the casting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a ''casting'', which is ejected ...
of metals. In these applications, the refractory materials are made from mixtures of chromite and magnesite. The use is declining because of the environmental regulations due to the possibility of the formation of chromium(VI).
Several chromium compounds are used as catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the ...
s for processing hydrocarbons. For example, the Phillips catalyst
The Phillips catalyst, or the Phillips supported chromium catalyst, is the catalyst used to produce approximately half of the world's polyethylene. A heterogeneous catalyst, it consists of a chromium oxide supported on silica gel. Polyethylene, ...
, prepared from chromium oxides, is used for the production of about half the world's polyethylene. Fe-Cr mixed oxides are employed as high-temperature catalysts for the water gas shift reaction. Copper chromite
Copper chromite is an inorganic compound with the formula Cu2Cr2O5. It is a black solid that is used to catalyze reactions in organic synthesis.
History
The material was first described in 1908. The catalyst was developed in North America by Hom ...
is a useful hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic c ...
catalyst.
Chromates
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ...
of metals are used in humistor
A humistor is a type of variable resistor whose resistance varies based on humidity.
Construction
A humistor has a ceramic composition comprising at least one component having a spinel type cubic symmetry selected from the group consisting c ...
.
Uses of compounds
*Chromium(IV) oxide
Chromium dioxide or chromium(IV) oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO2. It is a black synthetic magnetic solid. It once was widely used in magnetic tape emulsion. With the increasing popularity of CDs and DVDs, the use of chromiu ...
(CrO2) is a magnetic
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles ...
compound. Its ideal shape anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the property of a material which allows it to change or assume different properties in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. It can be defined as a difference, when measured along different axes, in a material's physi ...
, which imparts high coercivity
Coercivity, also called the magnetic coercivity, coercive field or coercive force, is a measure of the ability of a ferromagnetic material to withstand an external magnetic field without becoming demagnetized. Coercivity is usually measured in ...
and remnant magnetization, made it a compound superior to γ-Fe2O3. Chromium(IV) oxide is used to manufacture magnetic tape used in high-performance audio tape and standard audio cassettes
The Compact Cassette or Musicassette (MC), also commonly called the tape cassette, cassette tape, audio cassette, or simply tape or cassette, is an analog magnetic tape recording format for audio recording and playback. Invented by Lou Otten ...
.
* Chromium(III) oxide
Chromium(III) oxide (or chromia) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of chromium and is used as a pigment. In nature, it occurs as the rare mineral eskolaite.
Structure and properties
has the corundum s ...
(Cr2O3) is a metal polish known as green rouge.
* Chromic acid
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixtu ...
is a powerful oxidizing agent and is a useful compound for cleaning laboratory glassware of any trace of organic compounds. It is prepared by dissolving potassium dichromate
Potassium dichromate, , is a common inorganic chemical reagent, most commonly used as an oxidizing agent in various laboratory and industrial applications. As with all hexavalent chromium compounds, it is acutely and chronically harmful to health ...
in concentrated sulfuric acid, which is then used to wash the apparatus. Sodium dichromate
Sodium dichromate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2 Cr2 O7. However, the salt is usually handled as its dihydrate Na2Cr2O7·2 H2O. Virtually all chromium ore is processed via conversion to sodium dichromate and virtually all compound ...
is sometimes used because of its higher solubility (50 g/L versus 200 g/L respectively). The use of dichromate cleaning solutions is now phased out due to the high toxicity and environmental concerns. Modern cleaning solutions are highly effective and chromium free.
* Potassium dichromate
Potassium dichromate, , is a common inorganic chemical reagent, most commonly used as an oxidizing agent in various laboratory and industrial applications. As with all hexavalent chromium compounds, it is acutely and chronically harmful to health ...
is a chemical reagent, used as a titrating agent.
* Chromate Chromate or chromat, and their derived terms, may refer to:
Chemistry
* Chromate and dichromate, ions
* Monochromate, an ion
* Trichromate, an ion
* Tetrachromate, an ion
* Chromate conversion coating, a method for passivating metals
Biology ...
s are added to drilling muds to prevent corrosion of steel under wet conditions.
* Chrome alum
Chrome alum or Chromium(III) potassium sulfate is the potassium double sulfate of chromium. Its chemical formula is KCr(SO4)2 and it is commonly found in its dodecahydrate form as KCr(SO4)2·12(H2O). It is used in leather tanning.
Production an ...
is Chromium(III) potassium sulfate
Chrome alum or Chromium(III) potassium sulfate is the potassium double sulfate of chromium. Its chemical formula is KCr(SO4)2 and it is commonly found in its dodecahydrate form as KCr(SO4)2·12(H2O). It is used in leather tanning.
Production an ...
and is used as a mordant
A mordant or dye fixative is a substance used to set (i.e. bind) dyes on fabrics by forming a coordination complex with the dye, which then attaches to the fabric (or tissue). It may be used for dyeing fabrics or for intensifying stains in ...
(i.e., a fixing agent) for dyes in fabric and in tanning.
Biological role
The biologically beneficial effects of chromium(III) are debated. Chromium is accepted by the U.S. National Institutes of Health as a trace element for its roles in the action of insulin, a hormone that mediates the metabolism and storage of carbohydrate, fat, and protein. The mechanism of its actions in the body, however, have not been defined, leaving in question the essentiality of chromium. In contrast, hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI) or Cr6+) is highly toxic and mutagenic. Ingestion of chromium(VI) in water has been linked to stomach tumors, and it may also cause allergiccontact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are ...
(ACD).
" Chromium deficiency", involving a lack of Cr(III) in the body, or perhaps some complex of it, such as glucose tolerance factor
Chromium deficiency is described as the consequence of an insufficient dietary intake of the mineral chromium. Chromium was first proposed as an essential element for normal glucose metabolism in 1959, and was widely accepted as being such by the ...
, is controversial. Some studies suggest that the biologically active form of chromium (III) is transported in the body via an oligopeptide called low-molecular-weight chromium-binding substance Low-molecular-weight chromium-binding substance (LMWCr; also known as chromodulin) is an oligopeptide that seems to transport chromium in the body. It consists of four amino acid residues; aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, and glycine, bonded with fou ...
(LMWCr), which might play a role in the insulin signaling pathway.
The chromium content of common foods is generally low (1-13 micrograms per serving). The chromium content of food varies widely, due to differences in soil mineral content, growing season, plant cultivar, and contamination during processing. Chromium (and nickel) leach into food cooked in stainless steel, with the effect being largest when the cookware is new. Acidic foods that are cooked for many hours also exacerbate this effect.
Dietary recommendations
There is disagreement on chromium's status as an essential nutrient. Governmental departments from Australia, New Zealand, India, Japan, and the United States consider chromium essential while theEuropean Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, ...
(EFSA) of the European Union does not.
The U.S. National Academy of Medicine
The National Academy of Medicine (NAM), formerly called the Institute of Medicine (IoM) until 2015, is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Medicine is a part of the National Academies of Sciences, Eng ...
(NAM) updated the Estimated Average Requirements
The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) is a system of nutrition recommendations from the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) of the National Academies (United States). It was introduced in 1997 in order to broaden the existing guidelines known as Rec ...
(EARs) and the Recommended Dietary Allowances
The Reference Daily Intake (RDI) used in nutrition labeling on food and dietary supplement products in the U.S. and Canada is the daily intake level of a nutrient that is considered to be sufficient to meet the requirements of 97–98% of healthy ...
(RDAs) for chromium in 2001. For chromium, there was insufficient information to set EARs and RDAs, so its needs are described as estimates for Adequate Intakes (AIs). The current AIs of chromium for women ages 14 through 50 is 25 μg/day, and the AIs for women ages 50 and above is 20 μg/day. The AIs for women who are pregnant are 30 μg/day, and for women who are lactating, the set AIs are 45 μg/day. The AIs for men ages 14 through 50 are 35 μg/day, and the AIs for men ages 50 and above are 30 μg/day. For children ages 1 through 13, the AIs increase with age from 0.2 μg/day up to 25 μg/day. As for safety, the NAM sets Tolerable Upper Intake Levels
The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) is a system of nutrition recommendations from the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) of the National Academies (United States). It was introduced in 1997 in order to broaden the existing guidelines known as Rec ...
(ULs) for vitamins and minerals when the evidence is sufficient. In the case of chromium, there is not yet enough information, hence no UL has been established. Collectively, the EARs, RDAs, AIs, and ULs are the parameters for the nutrition recommendation system known as Dietary Reference Intake
The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) is a system of nutrition recommendations from the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) of the National Academies (United States). It was introduced in 1997 in order to broaden the existing guidelines known as Reco ...
(DRI). Australia and New Zealand consider chromium to be an essential nutrient, with an AI of 35 μg/day for men, 25 μg/day for women, 30 μg/day for women who are pregnant, and 45 μg/day for women who are lactating. A UL has not been set due to the lack of sufficient data. India considers chromium to be an essential nutrient, with an adult recommended intake of 33 μg/day. Japan also considers chromium to be an essential nutrient, with an AI of 10 μg/day for adults, including women who are pregnant or lactating. A UL has not been set. The EFSA of the European Union however, does not consider chromium to be an essential nutrient; chromium is the only mineral for which the United States and the European Union disagree.
Labeling
For U.S. food and dietary supplement labeling purposes, the amount of the substance in a serving is expressed as a percent of the Daily Value (%DV). For chromium labeling purposes, 100% of the Daily Value was 120 μg. As of May 27, 2016, the percentage of daily value was revised to 35 μg to bring the chromium intake into a consensus with the officialRecommended Dietary Allowance
The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) is a system of nutrition recommendations from the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) of the National Academies (United States). It was introduced in 1997 in order to broaden the existing guidelines known as Rec ...
. A table of the old and new adult daily values is provided at Reference Daily Intake
The Reference Daily Intake (RDI) used in nutrition labeling on food and dietary supplement products in the U.S. and Canada is the daily intake level of a nutrient that is considered to be sufficient to meet the requirements of 97–98% of healt ...
.
Food sources
Food composition databases such as those maintained by the U.S. Department of Agriculture do not contain information on the chromium content of foods. A wide variety of animal and vegetable foods contain chromium. Content per serving is influenced by the chromium content of the soil in which the plants are grown, by foodstuffs fed to animals, and by processing methods, as chromium is leached into foods if processed or cooked in stainless steel equipment. One diet analysis study conducted in Mexico reported an average daily chromium intake of 30 micrograms. An estimated 31% of adults in the United States consume multi-vitamin/mineral dietary supplements, which often contain 25 to 60 micrograms of chromium.Supplementation
Chromium is an ingredient in total parenteral nutrition (TPN), because deficiency can occur after months of intravenous feeding with chromium-free TPN. It is also added to nutritional products forpreterm infant
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between ...
s. Although the mechanism of action in biological roles for chromium is unclear, in the United States chromium-containing products are sold as non-prescription dietary supplements in amounts ranging from 50 to 1,000 μg. Lower amounts of chromium are also often incorporated into multi-vitamin/mineral supplements consumed by an estimated 31% of adults in the United States. Chemical compounds used in dietary supplements include chromium chloride, chromium citrate, chromium(III) picolinate
Chromium(III) picolinate is a chemical compound with the formula Cr(C5H4N(CO2H))3, commonly abbreviated as CrPic3. It is sold as a nutritional supplement to treat type 2 diabetes and promote weight loss. This bright-red coordination compound is de ...
, chromium(III) polynicotinate, and other chemical compositions. The benefit of supplements has not been proven.
Approved and disapproved health claims
In 2005, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration had approved a qualified health claim for chromium picolinate with a requirement for very specific label wording: "One small study suggests that chromium picolinate may reduce the risk of insulin resistance, and therefore possibly may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. FDA concludes, however, that the existence of such a relationship between chromium picolinate and either insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes is highly uncertain." At the same time, in answer to other parts of the petition, the FDA rejected claims for chromium picolinate and cardiovascular disease, retinopathy or kidney disease caused by abnormally high blood sugar levels. In 2010, chromium(III) picolinate was approved by Health Canada to be used in dietary supplements. Approved labeling statements include: a factor in the maintenance of good health, provides support for healthy glucose metabolism, helps the body to metabolize carbohydrates and helps the body to metabolize fats. TheEuropean Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, ...
(EFSA) approved claims in 2010 that chromium contributed to normal macronutrient metabolism and maintenance of normal blood glucose concentration, but rejected claims for maintenance or achievement of a normal body weight, or reduction of tiredness or fatigue.Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to chromium and contribution to normal macronutrient metabolism (ID 260, 401, 4665, 4666, 4667), maintenance of normal blood glucose concentrations (ID 262, 4667), contribution to the maintenance or achievement of a normal body weight (ID 339, 4665, 4666), and reduction of tiredness and fatigue (ID 261) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006European Food Safety Authority EFSA J 2010;8(10)1732. Given the evidence for chromium deficiency causing problems with glucose management in the context of intravenous nutrition products formulated without chromium, research interest turned to whether chromium supplementation would benefit people who have type 2 diabetes but are not chromium deficient. Looking at the results from four meta-analyses, one reported a statistically significant decrease in fasting
plasma glucose
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
levels (FPG) and a non-significant trend in lower hemoglobin A1C
Glycated hemoglobin, also known as HbA1c, glycohemoglobin, hemoglobin A1c, A1C, is a form of hemoglobin (Hb) that is chemically linked to a sugar. Most monosaccharides, including glucose, galactose and fructose, spontaneously (i.e. non-enzymat ...
. A second reported the same, a third reported significant decreases for both measures, while a fourth reported no benefit for either. A review published in 2016 listed 53 randomized clinical trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical te ...
s that were included in one or more of six meta-analyses. It concluded that whereas there may be modest decreases in FPG and/or HbA1C that achieve statistical significance in some of these meta-analyses, few of the trials achieved decreases large enough to be expected to be relevant to clinical outcome.
Two systematic reviews looked at chromium supplements as a mean of managing body weight in overweight and obese people. One, limited to chromium picolinate
Chromium(III) picolinate is a chemical compound with the formula Cr(C5H4N(CO2H))3, commonly abbreviated as CrPic3. It is sold as a nutritional supplement to treat type 2 diabetes and promote weight loss. This bright-red coordination compound is de ...
, a popular supplement ingredient, reported a statistically significant −1.1 kg (2.4 lb) weight loss in trials longer than 12 weeks. The other included all chromium compounds and reported a statistically significant −0.50 kg (1.1 lb) weight change. Change in percent body fat did not reach statistical significance. Authors of both reviews considered the clinical relevance of this modest weight loss as uncertain/unreliable. The European Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, ...
reviewed the literature and concluded that there was insufficient evidence to support a claim.
Chromium is promoted as a sports performance dietary supplement, based on the theory that it potentiates insulin activity, with anticipated results of increased muscle mass, and faster recovery of glycogen storage during post-exercise recovery. A review of clinical trials reported that chromium supplementation did not improve exercise performance or increase muscle strength. The International Olympic Committee reviewed dietary supplements for high-performance athletes in 2018 and concluded there was no need to increase chromium intake for athletes, nor support for claims of losing body fat.
Fresh-water fish
Chromium is naturally present in the environment in trace amounts, but industrial use in rubber and stainless steel manufacturing, chrome plating, dyes for textiles, tanneries and other uses contaminates aquatic systems. InBangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
, rivers in or downstream from industrialized areas exhibit heavy metal contamination. Irrigation water standards for chromium are 0.1 mg/L, but some rivers are more than five times that amount. The standard for fish for human consumption is less than 1 mg/kg, but many tested samples were more than five times that amount. Chromium, especially hexavalent chromium, is highly toxic to fish because it is easily absorbed across the gills, readily enters blood circulation, crosses cell membranes and bioconcentrates up the food chain. In contrast, the toxicity of trivalent chromium is very low, attributed to poor membrane permeability and little biomagnification.
Acute and chronic exposure to chromium(VI) affects fish behavior, physiology, reproduction and survival. Hyperactivity and erratic swimming have been reported in contaminated environments. Egg hatching and fingerling survival are affected. In adult fish there are reports of histopathological damage to liver, kidney, muscle, intestines, and gills. Mechanisms include mutagenic gene damage and disruptions of enzyme functions.
There is evidence that fish may not require chromium, but benefit from a measured amount in diet. In one study, juvenile fish gained weight on a zero chromium diet, but the addition of 500 μg of chromium in the form of chromium chloride or other supplement types, per kilogram of food (dry weight), increased weight gain. At 2,000 μg/kg the weight gain was no better than with the zero chromium diet, and there were increased DNA strand breaks.
Precautions
Water-insoluble chromium(III) compounds and chromium metal are not considered a health hazard, while the toxicity and carcinogenic properties of chromium(VI) have been known for a long time. Because of the specifictransport
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelin ...
mechanisms, only limited amounts of chromium(III) enter the cells. Acute oral toxicity ranges between 50 and 150 mg/kg. A 2008 review suggested that moderate uptake of chromium(III) through dietary supplements poses no genetic-toxic risk. In the US, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has designated an air permissible exposure limit
The permissible exposure limit (PEL or OSHA PEL) is a legal limit in the United States for exposure of an employee to a chemical substance or physical agent such as high level noise. Permissible exposure limits are established by the Occupationa ...
(PEL) in the workplace as a time-weighted average (TWA) of 1 mg/m3. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the C ...
(NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit
A recommended exposure limit (REL) is an occupational exposure limit that has been recommended by the United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. The REL is a level that NIOSH believes would be protective of worker safety ...
(REL) of 0.5 mg/m3, time-weighted average. The IDLH
The term immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) is defined by the US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) as exposure to airborne contaminants that is "likely to cause death or immediate or delayed permanent advers ...
(immediately dangerous to life and health) value is 250 mg/m3.
Chromium(VI) toxicity
The acuteoral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
** Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or or ...
toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subs ...
for chromium(VI)
Hexavalent chromium (chromium(VI), Cr(VI), chromium 6) is chromium in any chemical compound that contains the element in the +6 oxidation state (thus hexavalent). Virtually all chromium ore is processed via hexavalent chromium, specifically the ...
ranges between 1.5 and 3.3 mg/kg. In the body, chromium(VI) is reduced by several mechanisms to chromium(III) already in the blood before it enters the cells. The chromium(III) is excreted from the body, whereas the chromate ion is transferred into the cell by a transport mechanism, by which also sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
and phosphate ions enter the cell. The acute toxicity of chromium(VI) is due to its strong oxidant properties. After it reaches the blood stream, it damages the kidneys, the liver and blood cells through oxidation reactions. Hemolysis, renal, and liver failure result. Aggressive dialysis can be therapeutic.
The carcinogenity
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substan ...
of chromate dust has been known for a long time, and in 1890 the first publication described the elevated cancer risk of workers in a chromate dye company. Three mechanisms have been proposed to describe the genotoxicity Genotoxicity is the property of chemical agents that damage the genetic information within a cell causing mutations, which may lead to cancer. While genotoxicity is often confused with mutagenicity, all mutagens are genotoxic, but some genotoxic ...
of chromium(VI). The first mechanism includes highly reactive hydroxyl radicals and other reactive radicals which are by products of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III). The second process includes the direct binding of chromium(V), produced by reduction in the cell, and chromium(IV) compounds to the DNA. The last mechanism attributed the genotoxicity to the binding to the DNA of the end product of the chromium(III) reduction.
Chromium salts (chromates) are also the cause of allergic reaction
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic derm ...
s in some people. Chromates are often used to manufacture, amongst other things, leather products, paints, cement, mortar and anti-corrosives. Contact with products containing chromates can lead to allergic contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are ...
and irritant dermatitis, resulting in ulceration of the skin, sometimes referred to as "chrome ulcers". This condition is often found in workers that have been exposed to strong chromate solutions in electroplating, tanning and chrome-producing manufacturers.
Environmental issues
Because chromium compounds were used indye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
s, paints, and leather tanning compounds, these compounds are often found in soil and groundwater at active and abandoned industrial sites, needing environmental cleanup
Environmental remediation deals with the removal of pollution or contaminants from environmental media such as soil, groundwater, sediment, or surface water. Remedial action is generally subject to an array of regulatory requirements, and may als ...
and remediation. Primer paint containing hexavalent chromium is still widely used for aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astr ...
and automobile refinishing applications.
In 2010, the Environmental Working Group
The Environmental Working Group (EWG) is an American activist group that specializes in research and advocacy in the areas of agricultural subsidies, toxic chemicals, drinking water pollutants, and corporate accountability. EWG is a nonprofit ...
studied the drinking water in 35 American cities in the first nationwide study. The study found measurable hexavalent chromium in the tap water of 31 of the cities sampled, with Norman, Oklahoma
Norman () is the third-largest city in the U.S. state of Oklahoma, with a population of 128,097 as of 2021. It is the largest city and the county seat of Cleveland County, and the second-largest city in the Oklahoma City metropolitan area, beh ...
, at the top of list; 25 cities had levels that exceeded California's proposed limit.
The more toxic hexavalent chromium form can be reduced to the less soluble trivalent oxidation state in soils by organic matter, ferrous iron, sulfides, and other reducing agents, with the rates of such reduction being faster under more acidic conditions than under more alkaline ones. In contrast, trivalent chromium can be oxidized to hexavalent chromium in soils by manganese oxides, such as Mn(III) and Mn(IV) compounds. Since the solubility and toxicity of chromium (VI) are greater that those of chromium (III), the oxidation-reduction conversions between the two oxidation states have implications for movement and bioavailability of chromium in soils, groundwater, and plants.
Notes
References
General bibliography
*External links
ATSDR Case Studies in Environmental Medicine: Chromium Toxicity
U.S.
Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
IARC Monograph "Chromium and Chromium compounds"
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health – Chromium Page
at ''
The Periodic Table of Videos
''Periodic Videos'' (also known as ''The Periodic Table of Videos'') is a video project and YouTube channel on chemistry. It consists of a series of videos about chemical elements and the periodic table, with additional videos on other topics i ...
'' (University of Nottingham)
*
{{Good article
Chemical elements
Dietary minerals
Native element minerals
Occupational safety and health
Chemical elements with body-centered cubic structure