chocolates on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Chocolate is a
Chocolate is a
 Chocolate has been prepared as a drink for nearly all of its history. For example, one vessel found at an
Chocolate has been prepared as a drink for nearly all of its history. For example, one vessel found at an  An early Classic-period (460–480 AD) Maya tomb from the site in Rio Azul had vessels with the Maya glyph for cocoa on them with residue of a chocolate drink, suggests the Maya were drinking chocolate around 400 AD. Documents in Maya hieroglyphs stated chocolate was used for ceremonial purposes in addition to everyday life. The Maya grew cacao trees in their backyards and used the cocoa seeds the trees produced to make a frothy, bitter drink.
By the 15th century, the Aztecs had gained control of a large part of Mesoamerica and had adopted cocoa into their culture. They associated chocolate with
An early Classic-period (460–480 AD) Maya tomb from the site in Rio Azul had vessels with the Maya glyph for cocoa on them with residue of a chocolate drink, suggests the Maya were drinking chocolate around 400 AD. Documents in Maya hieroglyphs stated chocolate was used for ceremonial purposes in addition to everyday life. The Maya grew cacao trees in their backyards and used the cocoa seeds the trees produced to make a frothy, bitter drink.
By the 15th century, the Aztecs had gained control of a large part of Mesoamerica and had adopted cocoa into their culture. They associated chocolate with
 Until the 16th century, no European had ever heard of the popular drink from the
Until the 16th century, no European had ever heard of the popular drink from the  While Columbus had taken cocoa beans with him back to Spain, chocolate made no impact until Spanish friars introduced it to the Spanish court. After the Spanish conquest of the Aztecs, chocolate was imported to Europe. There, it quickly became a court favorite. It was still served as a beverage, but the Spanish added sugar, as well as honey (the original sweetener used by the Aztecs for chocolate), to counteract the natural bitterness.
While Columbus had taken cocoa beans with him back to Spain, chocolate made no impact until Spanish friars introduced it to the Spanish court. After the Spanish conquest of the Aztecs, chocolate was imported to Europe. There, it quickly became a court favorite. It was still served as a beverage, but the Spanish added sugar, as well as honey (the original sweetener used by the Aztecs for chocolate), to counteract the natural bitterness.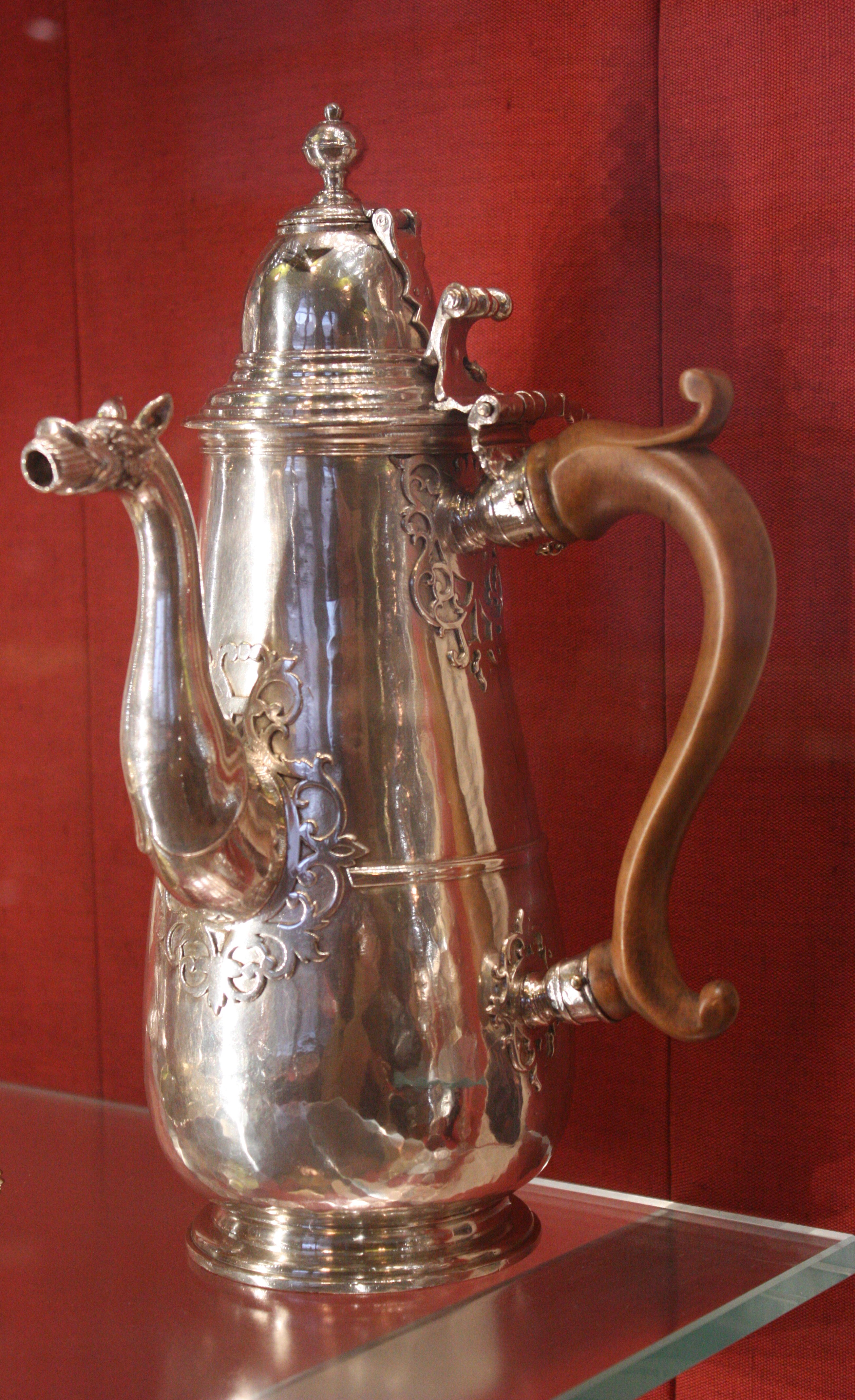 
 The new craze for chocolate brought with it a thriving slave market, as between the early 1600s and late 1800s, the laborious and slow processing of the cocoa bean was manual. Cocoa plantations spread, as the English, Dutch, and French colonized and planted. With the depletion of Mesoamerican workers, largely to disease, cocoa production was often the work of poor wage laborers and African slaves. Wind-powered and horse-drawn mills were used to speed production, augmenting human labor. Heating the working areas of the table-mill, an innovation that emerged in France in 1732, also assisted in extraction.
The new craze for chocolate brought with it a thriving slave market, as between the early 1600s and late 1800s, the laborious and slow processing of the cocoa bean was manual. Cocoa plantations spread, as the English, Dutch, and French colonized and planted. With the depletion of Mesoamerican workers, largely to disease, cocoa production was often the work of poor wage laborers and African slaves. Wind-powered and horse-drawn mills were used to speed production, augmenting human labor. Heating the working areas of the table-mill, an innovation that emerged in France in 1732, also assisted in extraction.
 Known as " Dutch cocoa", this machine-pressed chocolate was instrumental in the transformation of chocolate to its solid form when, in 1847, English chocolatier Joseph Fry discovered a way to make chocolate moldable when he mixed the ingredients of cocoa powder and sugar with melted cocoa butter. Subsequently, his chocolate factory, Fry's of
Known as " Dutch cocoa", this machine-pressed chocolate was instrumental in the transformation of chocolate to its solid form when, in 1847, English chocolatier Joseph Fry discovered a way to make chocolate moldable when he mixed the ingredients of cocoa powder and sugar with melted cocoa butter. Subsequently, his chocolate factory, Fry's of
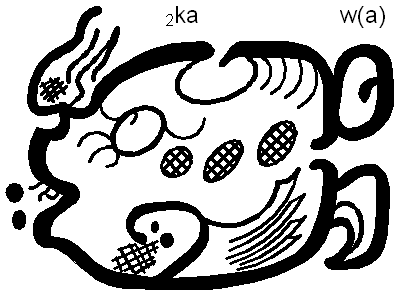 Cocoa, pronounced by the Olmecs as ''kakawa'', dates to 1000 BC or earlier. The word "chocolate" entered the English language from Spanish in about 1600. The word entered Spanish from the word ''chocolātl'' in
Cocoa, pronounced by the Olmecs as ''kakawa'', dates to 1000 BC or earlier. The word "chocolate" entered the English language from Spanish in about 1600. The word entered Spanish from the word ''chocolātl'' in
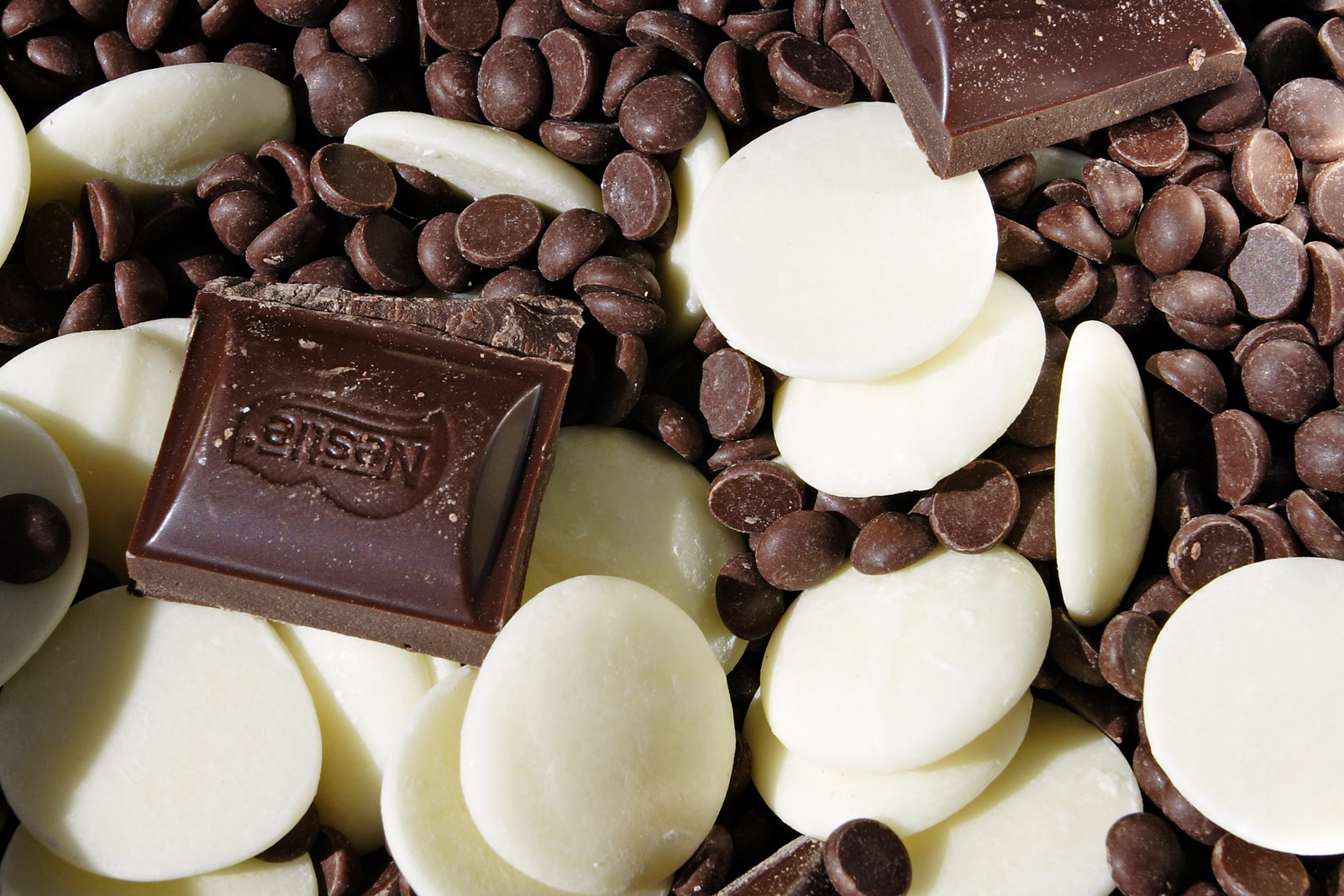
 Several types of chocolate can be distinguished. Pure, unsweetened chocolate, often called "baking chocolate", contains primarily
Several types of chocolate can be distinguished. Pure, unsweetened chocolate, often called "baking chocolate", contains primarily
 White chocolate, although similar in texture to that of milk and dark chocolate, does not contain any cocoa solids that impart a dark color. In 2002, the US
White chocolate, although similar in texture to that of milk and dark chocolate, does not contain any cocoa solids that impart a dark color. In 2002, the US
 Baking chocolate, or cooking chocolate, is chocolate intended to be used for baking and in sweet foods that may or may not be sweetened. Dark chocolate,
Baking chocolate, or cooking chocolate, is chocolate intended to be used for baking and in sweet foods that may or may not be sweetened. Dark chocolate,
 Roughly two-thirds of the entire world's cocoa is produced in West Africa, with 43% sourced from Côte d'Ivoire, where, , child labor is a common practice to obtain the product. According to the World Cocoa Foundation, in 2007 some 50 million people around the world depended on cocoa as a source of livelihood. in the UK, most chocolatiers purchase their chocolate from them, to melt, mold and package to their own design. According to the WCF's 2012 report, the
Roughly two-thirds of the entire world's cocoa is produced in West Africa, with 43% sourced from Côte d'Ivoire, where, , child labor is a common practice to obtain the product. According to the World Cocoa Foundation, in 2007 some 50 million people around the world depended on cocoa as a source of livelihood. in the UK, most chocolatiers purchase their chocolate from them, to melt, mold and package to their own design. According to the WCF's 2012 report, the
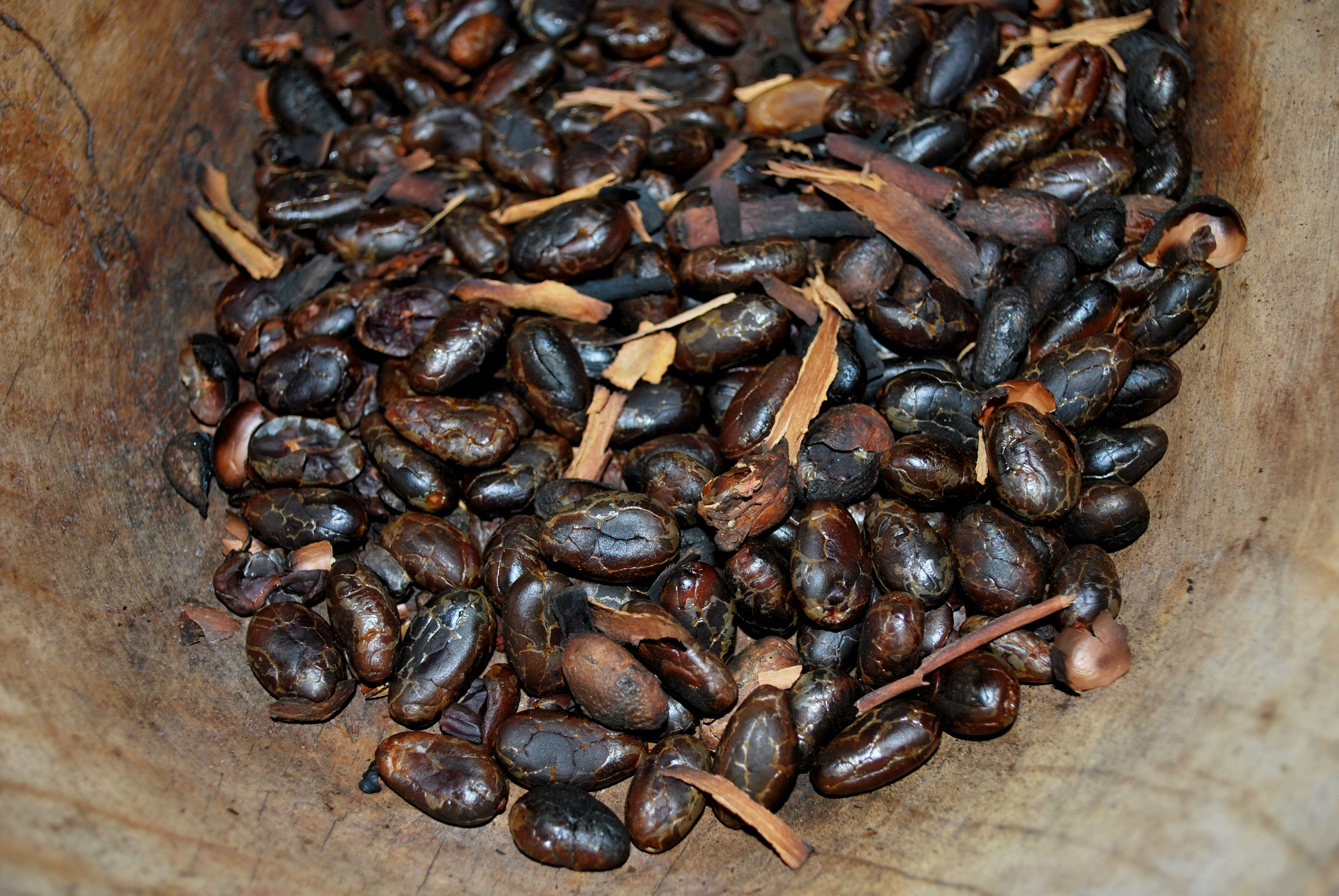 Chocolate is made from
Chocolate is made from
 * Dark chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, cocoa liquor, and (sometimes) vanilla
* Milk chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, cocoa liquor, milk or milk powder, and vanilla
* White chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, milk or milk powder, and vanilla
Usually, an
* Dark chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, cocoa liquor, and (sometimes) vanilla
* Milk chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, cocoa liquor, milk or milk powder, and vanilla
* White chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, milk or milk powder, and vanilla
Usually, an
 The penultimate process is called conching. A conche is a container filled with metal beads, which act as grinders. The refined and blended chocolate mass is kept in a liquid state by frictional heat. Chocolate before conching has an uneven and gritty texture. The conching process produces cocoa and sugar particles smaller than the tongue can detect (typically around 20
The penultimate process is called conching. A conche is a container filled with metal beads, which act as grinders. The refined and blended chocolate mass is kept in a liquid state by frictional heat. Chocolate before conching has an uneven and gritty texture. The conching process produces cocoa and sugar particles smaller than the tongue can detect (typically around 20
 As a solid piece of chocolate, the cocoa butter fat particles are in a crystalline rigid structure that gives the chocolate its solid appearance. Once heated, the crystals of the polymorphic cocoa butter can break apart from the rigid structure and allow the chocolate to obtain a more fluid consistency as the temperature increases – the melting process. When the heat is removed, the cocoa butter crystals become rigid again and come closer together, allowing the chocolate to solidify.
The temperature in which the crystals obtain enough energy to break apart from their rigid conformation would depend on the milk fat content in the chocolate and the shape of the fat molecules, as well as the form of the cocoa butterfat. Chocolate with a higher fat content will melt at a lower temperature.
Making chocolate considered "good" is about forming as many type V crystals as possible. This provides the best appearance and texture and creates the most stable crystals, so the texture and appearance will not degrade over time. To accomplish this, the temperature is carefully manipulated during the crystallization.
As a solid piece of chocolate, the cocoa butter fat particles are in a crystalline rigid structure that gives the chocolate its solid appearance. Once heated, the crystals of the polymorphic cocoa butter can break apart from the rigid structure and allow the chocolate to obtain a more fluid consistency as the temperature increases – the melting process. When the heat is removed, the cocoa butter crystals become rigid again and come closer together, allowing the chocolate to solidify.
The temperature in which the crystals obtain enough energy to break apart from their rigid conformation would depend on the milk fat content in the chocolate and the shape of the fat molecules, as well as the form of the cocoa butterfat. Chocolate with a higher fat content will melt at a lower temperature.
Making chocolate considered "good" is about forming as many type V crystals as possible. This provides the best appearance and texture and creates the most stable crystals, so the texture and appearance will not degrade over time. To accomplish this, the temperature is carefully manipulated during the crystallization.
 Generally, the chocolate is first heated to to melt all six forms of crystals. Next, the chocolate is cooled to about , which will allow crystal types IV and V to form. At this temperature, the chocolate is agitated to create many small crystal "seeds" which will serve as nuclei to create small crystals in the chocolate. The chocolate is then heated to about to eliminate any type IV crystals, leaving just type V. After this point, any excessive heating of the chocolate will destroy the temper and this process will have to be repeated. Other methods of chocolate tempering are used as well. The most common variant is introducing already tempered, solid "seed" chocolate. The temper of chocolate can be measured with a chocolate temper meter to ensure accuracy and consistency. A sample cup is filled with the chocolate and placed in the unit which then displays or prints the results.
Two classic ways of manually tempering chocolate are:
* Working the molten chocolate on a heat-absorbing surface, such as a stone slab, until thickening indicates the presence of sufficient crystal "seeds"; the chocolate is then gently warmed to working temperature.
* Stirring solid chocolate into molten chocolate to "inoculate" the liquid chocolate with crystals (this method uses the already formed crystals of the solid chocolate to "seed" the molten chocolate).
Chocolate tempering machines (or temperers) with computer controls can be used for producing consistently tempered chocolate. In particular,
Generally, the chocolate is first heated to to melt all six forms of crystals. Next, the chocolate is cooled to about , which will allow crystal types IV and V to form. At this temperature, the chocolate is agitated to create many small crystal "seeds" which will serve as nuclei to create small crystals in the chocolate. The chocolate is then heated to about to eliminate any type IV crystals, leaving just type V. After this point, any excessive heating of the chocolate will destroy the temper and this process will have to be repeated. Other methods of chocolate tempering are used as well. The most common variant is introducing already tempered, solid "seed" chocolate. The temper of chocolate can be measured with a chocolate temper meter to ensure accuracy and consistency. A sample cup is filled with the chocolate and placed in the unit which then displays or prints the results.
Two classic ways of manually tempering chocolate are:
* Working the molten chocolate on a heat-absorbing surface, such as a stone slab, until thickening indicates the presence of sufficient crystal "seeds"; the chocolate is then gently warmed to working temperature.
* Stirring solid chocolate into molten chocolate to "inoculate" the liquid chocolate with crystals (this method uses the already formed crystals of the solid chocolate to "seed" the molten chocolate).
Chocolate tempering machines (or temperers) with computer controls can be used for producing consistently tempered chocolate. In particular,
 Chocolate is very sensitive to temperature and humidity. Ideal storage temperatures are between , with a relative humidity of less than 50%. If refrigerated or frozen without containment, chocolate can absorb enough moisture to cause a whitish discoloration, the result of fat or sugar crystals rising to the surface. Various types of "blooming" effects can occur if chocolate is stored or served improperly.
Chocolate is very sensitive to temperature and humidity. Ideal storage temperatures are between , with a relative humidity of less than 50%. If refrigerated or frozen without containment, chocolate can absorb enough moisture to cause a whitish discoloration, the result of fat or sugar crystals rising to the surface. Various types of "blooming" effects can occur if chocolate is stored or served improperly.
 Chocolate manufacturers produce a range of products from chocolate bars to
Chocolate manufacturers produce a range of products from chocolate bars to
Human Trafficking – Promises
." conditions for the production of chocolate, and an increasing number of health-food and anti-slavery organisations are highlighting and campaigning against the use of trafficking in the chocolate industry. As of 2017, approximately 2.1 million children in Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire were involved in farming cocoa, carrying heavy loads, clearing forests, and being exposed to pesticides. According to Sona Ebai, the former secretary-general of the Alliance of Cocoa Producing Countries: "I think child labor cannot be just the responsibility of industry to solve. I think it's the proverbial all-hands-on-deck: government, civil society, the private sector. And there, you need leadership." Reported in 2018, a 3-year
 Chocolate is sold in
Chocolate is sold in
 Chocolate is used as a flavouring product in many
Chocolate is used as a flavouring product in many
 Chocolate is associated with festivals such as
Chocolate is associated with festivals such as
Chocolate Tempering
"Chocolate and Tea"
American Enterprise Exhibition, National Museum of American History (exhibit on 18th century American trade) {{Authority control Aphrodisiac foods Articles containing video clips Baking Candy Cooking Desserts Mesoamerican cuisine Snack foods
 Chocolate is a
Chocolate is a food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is in ...
made from roasted and ground cacao seed
The cocoa bean (technically cocoa seed) or simply cocoa (), also called the cacao bean (technically cacao seed) or cacao (), is the dried and fully fermented seed of ''Theobroma cacao'', from which cocoa solids (a mixture of nonfat substances ...
kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent
A flavoring (or flavouring), also known as flavor (or flavour) or flavorant, is a food additive used to improve the taste or smell of food. It changes the perceptual impression of food as determined primarily by the chemoreceptors of the gust ...
in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec
The Olmecs () were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that ...
civilization (19th-11th century BCE), and the majority of Mesoamerican
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Withi ...
people ─ including the Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popul ...
and Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
s ─ made chocolate beverages.
The seeds of the cacao tree
''Theobroma cacao'', also called the cacao tree and the cocoa tree, is a small ( tall) evergreen tree in the family Malvaceae. Its seeds, cocoa beans, are used to make chocolate liquor, cocoa solids, cocoa butter and chocolate. The largest p ...
have an intense bitter taste and must be fermented
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food p ...
to develop the flavor. After fermentation, the seeds are dried, cleaned, and roasted. The shell is removed to produce cocoa nibs, which are then ground to cocoa mass
Chocolate liquor (cocoa liquor) is pure cocoa mass (cocoa paste) in solid or semi-solid form. Like the cocoa beans (nibs) from which it is produced, it contains both cocoa solids and cocoa butter in roughly equal proportion.
It is produced f ...
, unadulterated chocolate in rough form. Once the cocoa mass is liquefied by heating, it is called chocolate liquor
Chocolate liquor (cocoa liquor) is pure cocoa mass (cocoa paste) in solid or semi-solid form. Like the cocoa beans (nibs) from which it is produced, it contains both cocoa solids and cocoa butter in roughly equal proportion.
It is produced fr ...
. The liquor may also be cooled and processed into its two components: cocoa solids
Dry cocoa solids are the components of cocoa beans remaining after cocoa butter, the fatty component of the bean, is extracted from chocolate liquor, roasted cocoa beans that have been ground into a liquid state. Cocoa butter is 46% to 57% of t ...
and cocoa butter
Cocoa butter, also called theobroma oil, is a pale-yellow, edible fat extracted from the cocoa bean. It is used to make chocolate, as well as some ointments, toiletries, and pharmaceuticals. Cocoa butter has a cocoa flavor and aroma. Its melt ...
. Baking chocolate
Baking chocolate, or cooking chocolate, is chocolate intended to be used for baking and in sweet foods that may or may not be sweetened. Dark chocolate, milk chocolate, and white chocolate, are produced and marketed as baking chocolate. Howe ...
, also called bitter chocolate, contains cocoa solids and cocoa butter in varying proportions, without any added sugar
Added sugars or free sugars are sugar carbohydrates (caloric sweeteners) added to food and beverages at some point before their consumption. These include added carbohydrates (monosaccharides and disaccharides), and more broadly, sugars na ...
. Powdered baking cocoa, which contains more fiber
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
than cocoa butter, can be processed with alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a ...
to produce dutch cocoa. Much of the chocolate consumed today is in the form of sweet chocolate
Chocolate is a food product made from roasted and ground cocoa pods mixed with fat (e.g. cocoa butter) and powdered sugar to produce a solid confectionery. There are several types of chocolate, classified primarily according to the proportion ...
, a combination of cocoa solids, cocoa butter or added vegetable oils, and sugar. Milk chocolate
Milk chocolate is a solid chocolate confectionery containing cocoa, sugar and milk. Chocolate was originally sold and consumed as a beverage in pre-Columbian times, and upon its introduction to Western Europe. Major milk chocolate producers incl ...
is sweet chocolate that additionally contains milk powder
Powdered milk, also called milk powder, dried milk, or dry milk, is a manufactured dairy product made by evaporating milk to dryness. One purpose of drying milk is to preserve it; milk powder has a far longer shelf life than liquid milk and do ...
or condensed milk
Condensed milk is cow's milk from which water has been removed (roughly 60% of it). It is most often found with sugar added, in the form of ''sweetened condensed milk'' (SCM), to the extent that the terms "condensed milk" and "sweetened condense ...
. White chocolate
White chocolate is a confectionery typically made of sugar, milk, and cocoa butter. It is pale ivory colored, and lacks many of the compounds found in milk and dark chocolates. It is solid at room temperature because the melting point of cocoa ...
contains cocoa butter, sugar, and milk, but no cocoa solids.
Chocolate is one of the most popular food types and flavors in the world, and many foodstuffs involving chocolate exist, particularly dessert
Dessert is a course that concludes a meal. The course consists of sweet foods, such as confections, and possibly a beverage such as dessert wine and liqueur. In some parts of the world, such as much of Greece and West Africa, and most parts o ...
s, including cakes
Cake is a flour confection made from flour, sugar, and other ingredients, and is usually baked. In their oldest forms, cakes were modifications of bread, but cakes now cover a wide range of preparations that can be simple or elaborate ...
, pudding
Pudding is a type of food. It can be either a dessert or a savoury (salty or spicy) dish served as part of the main meal.
In the United States, ''pudding'' means a sweet, milk-based dessert similar in consistency to egg-based custards, inst ...
, mousse
A mousse (; ; "foam") is a soft prepared food that incorporates air bubbles to give it a light and airy texture. Depending on preparation techniques, it can range from light and fluffy to creamy and thick. A mousse may be sweet or savory. as ...
, chocolate brownie
A chocolate brownie or simply a brownie is a chocolate baked confection. Brownies come in a variety of forms and may be either fudgy or cakey, depending on their density. Brownies often, but not always, have a glossy "skin" on their upper crust ...
s, and chocolate chip cookies. Many candies are filled with or coated with sweetened chocolate. Chocolate bar
A chocolate bar (Commonwealth English) or candy bar (some dialects of American English) is a confection containing chocolate, which may also contain layerings or mixtures that include nuts, fruit, caramel, nougat, and wafers. A flat, easily brea ...
s, either made of solid chocolate or other ingredients coated in chocolate, are eaten as snack
A snack is a small portion of food generally eaten between meals. Snacks come in a variety of forms including packaged snack foods and other processed foods, as well as items made from fresh ingredients at home.
Traditionally, snacks are ...
s. Gifts of chocolate molded into different shapes (such as eggs, hearts, coins) are traditional on certain Western holidays, including Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
, Easter
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the '' Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samue ...
, Valentine's Day
Valentine's Day, also called Saint Valentine's Day or the Feast of Saint Valentine, is celebrated annually on February 14. It originated as a Christian feast day honoring one or two early Christian martyrs named Saint Valentine and, thr ...
, and Hanukkah
or English translation: 'Establishing' or 'Dedication' (of the Temple in Jerusalem)
, nickname =
, observedby = Jews
, begins = 25 Kislev
, ends = 2 Tevet or 3 Tevet
, celebrations = Lighting candles each nig ...
. Chocolate is also used in cold and hot beverages, such as chocolate milk
Chocolate milk is a type of flavoured milk made by mixing cocoa solids with milk (either dairy or plant-based). It is a food pairing in which the milk's mouthfeel masks the dietary fibres of the cocoa solids.
Types
The liquid carbohy ...
and hot chocolate
Hot chocolate, also known as hot cocoa or drinking chocolate, is a heated drink consisting of shaved chocolate, melted chocolate or cocoa powder, heated milk or water, and usually a sweetener like whipped cream or marshmallows. Hot chocolate ...
, and in some alcoholic drinks, such as creme de cacao
Chocolate liqueur is a chocolate flavored liqueur made from a base liquor of whisky or vodka. Unlike chocolate liquor, chocolate liqueur does contain alcohol and is often used as a sweetening ingredient in mixology, baking, and cooking.
His ...
.
Although cocoa originated in the Americas, West African countries, particularly Côte d'Ivoire
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre ...
and Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and Tog ...
, are the leading producers of cocoa in the 21st century, accounting for some 60% of the world cocoa supply.
With some two million children involved in the farming of cocoa in West Africa, child slavery and trafficking associated with the cocoa trade remain major concerns. A 2018 report argued that international attempts to improve conditions for children were doomed to failure because of persistent poverty, absence of schools, increasing world cocoa demand, more intensive farming
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of ...
of cocoa, and continued exploitation of child labor.
History
Mesoamerican usage
 Chocolate has been prepared as a drink for nearly all of its history. For example, one vessel found at an
Chocolate has been prepared as a drink for nearly all of its history. For example, one vessel found at an Olmec
The Olmecs () were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that ...
archaeological site on the Gulf Coast of Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
, Mexico, dates chocolate's preparation by pre-Olmec peoples as early as 1750 BC. On the Pacific coast of Chiapas
Chiapas (; Tzotzil and Tzeltal: ''Chyapas'' ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas), is one of the states that make up the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 124 municipalities ...
, Mexico, a Mokaya archaeological site provides evidence of cocoa beverages dating even earlier to 1900 BC. The residues and the kind of vessel in which they were found indicate the initial use of cocoa was not simply as a beverage, but the white pulp around the cocoa beans was likely used as a source of fermentable sugars for an alcoholic drink.
 An early Classic-period (460–480 AD) Maya tomb from the site in Rio Azul had vessels with the Maya glyph for cocoa on them with residue of a chocolate drink, suggests the Maya were drinking chocolate around 400 AD. Documents in Maya hieroglyphs stated chocolate was used for ceremonial purposes in addition to everyday life. The Maya grew cacao trees in their backyards and used the cocoa seeds the trees produced to make a frothy, bitter drink.
By the 15th century, the Aztecs had gained control of a large part of Mesoamerica and had adopted cocoa into their culture. They associated chocolate with
An early Classic-period (460–480 AD) Maya tomb from the site in Rio Azul had vessels with the Maya glyph for cocoa on them with residue of a chocolate drink, suggests the Maya were drinking chocolate around 400 AD. Documents in Maya hieroglyphs stated chocolate was used for ceremonial purposes in addition to everyday life. The Maya grew cacao trees in their backyards and used the cocoa seeds the trees produced to make a frothy, bitter drink.
By the 15th century, the Aztecs had gained control of a large part of Mesoamerica and had adopted cocoa into their culture. They associated chocolate with Quetzalcoatl
Quetzalcoatl (, ; Spanish: ''Quetzalcóatl'' ; nci-IPA, Quetzalcōātl, ket͡saɬˈkoːaːt͡ɬ (Modern Nahuatl pronunciation), in honorific form: ''Quetzalcōātzin'') is a deity in Aztec culture and literature whose name comes from the Nah ...
, who, according to one legend, was cast away by the other gods for sharing chocolate with humans, and identified its extrication from the pod with the removal of the human heart in sacrifice. In contrast to the Maya, who liked their chocolate warm, the Aztecs drank it cold, seasoning it with a broad variety of additives, including the petals of the '' Cymbopetalum penduliflorum'' tree, chile pepper
Chili peppers (also chile, chile pepper, chilli pepper, or chilli), from Nahuatl '' chīlli'' (), are varieties of the berry-fruit of plants from the genus ''Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for t ...
, allspice
Allspice, also known as Jamaica pepper, myrtle pepper, pimenta, or pimento, is the dried unripe berry of ''Pimenta dioica'', a midcanopy tree native to the Greater Antilles, southern Mexico, and Central America, now cultivated in many warm par ...
, vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus '' Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla ('' V. planifolia'').
Pollination is required to make the plants produce the fruit from whic ...
, and honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
.
The Aztecs were unable to grow cocoa themselves, as their home in the Mexican highlands was unsuitable for it, so chocolate was a luxury imported into the empire. Those who lived in areas ruled by the Aztecs were required to offer cocoa seeds in payment of the tax they deemed "tribute". Cocoa beans were often used as currency. For example, the Aztecs used a system in which one turkey cost 100 cocoa beans and one fresh avocado
The avocado (''Persea americana'') is a medium-sized, evergreen tree in the laurel family ( Lauraceae). It is native to the Americas and was first domesticated by Mesoamerican tribes more than 5,000 years ago. Then as now it was prized for ...
was worth three beans.
The Maya and Aztecs associated cocoa with human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherei ...
, and chocolate drinks specifically with sacrificial human blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
.
The Spanish royal chronicler Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés
Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés (August 14781557), commonly known as Oviedo, was a Spanish soldier, historian, writer, botanist and colonist. Oviedo participated in the Spanish colonization of the West Indies, arriving in the first few year ...
described a chocolate drink he had seen in Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the coun ...
in 1528, mixed with achiote
''Bixa orellana'', also known as achiote, is a shrub native to Central America. ''Bixa orellana'' is grown in many countries worldwide.
The tree is best known as the source of annatto, a natural orange-red condiment (also called or ) obtained ...
: "because those people are fond of drinking human blood, to make this beverage seem like blood, they add a little achiote, so that it then turns red. ... and part of that foam is left on the lips and around the mouth, and when it is red for having achiote, it seems a horrific thing, because it seems like blood itself."
European adaptation
 Until the 16th century, no European had ever heard of the popular drink from the
Until the 16th century, no European had ever heard of the popular drink from the Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
n peoples. Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
and his son Ferdinand
Ferdinand is a Germanic name composed of the elements "protection", "peace" (PIE "to love, to make peace") or alternatively "journey, travel", Proto-Germanic , abstract noun from root "to fare, travel" (PIE , "to lead, pass over"), and "co ...
encountered the cocoa bean on Columbus's fourth mission to the Americas on 15 August 1502, when he and his crew stole a large native canoe that proved to contain cocoa beans among other goods for trade. Spanish conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, ...
Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of w ...
may have been the first European to encounter it, as the frothy drink was part of the after-dinner routine of Montezuma. José de Acosta
José de Acosta (1539 or 1540 in Medina del Campo, Spain – February 15, 1600 in Salamanca, Spain) was a sixteenth-century Spanish Jesuit missionary and naturalist in Latin America. His deductions regarding the ill effects of crossing over t ...
, a Spanish Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
missionary who lived in Peru and then Mexico in the later 16th century, wrote of its growing influence on the Spaniards:
Although bananas are more profitable, cocoa is more highly esteemed in Mexico. . . Cocoa is a smaller fruit than almonds and thicker, which toasted do not taste bad. It is so prized among the Indians and even among Spaniards. . . because since it is a dried fruit it can be stored for a long time without deterioration, and they brings ships loaded with them from the province of Guatemala. . . It also serves as currency, because with five cocoas you can buy one thing, with thirty another, and with a hundred something else, without there being contradiction; and they give these cocoas as alms to the poor who beg for them. The principal product of this cocoa is a concoction which they make that they call “chocolate,” which is a crazy thing treasured in that land, and those who are not accustomed are disgusted by it, because it has a foam on top and a bubbling like that of feces, which certainly takes a lot to put up with. Anyway, it is the prized beverage which the Indians offer to nobles who come to or pass through their lands; and the Spaniards, especially Spanish women born in those lands die for black chocolate. This aforementioned chocolate is said to be made in various forms and temperaments, hot, cold, and lukewarm. They are wont to use spices and much chili; they also make it into a paste, and it is said that it is a medicine to treat coughs, the stomach, and colds. Whatever may be the case, in fact those who have not been reared on this opinion are not appetized by it.
 While Columbus had taken cocoa beans with him back to Spain, chocolate made no impact until Spanish friars introduced it to the Spanish court. After the Spanish conquest of the Aztecs, chocolate was imported to Europe. There, it quickly became a court favorite. It was still served as a beverage, but the Spanish added sugar, as well as honey (the original sweetener used by the Aztecs for chocolate), to counteract the natural bitterness.
While Columbus had taken cocoa beans with him back to Spain, chocolate made no impact until Spanish friars introduced it to the Spanish court. After the Spanish conquest of the Aztecs, chocolate was imported to Europe. There, it quickly became a court favorite. It was still served as a beverage, but the Spanish added sugar, as well as honey (the original sweetener used by the Aztecs for chocolate), to counteract the natural bitterness. Vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus '' Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla ('' V. planifolia'').
Pollination is required to make the plants produce the fruit from whic ...
, another indigenous American introduction, was also a popular additive, with pepper and other spices sometimes used to give the illusion of a more potent vanilla flavor. Unfortunately, these spices tended to unsettle the European constitution; the ''Encyclopédie
''Encyclopédie, ou dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers'' (English: ''Encyclopedia, or a Systematic Dictionary of the Sciences, Arts, and Crafts''), better known as ''Encyclopédie'', was a general encyclopedia publis ...
'' states, "The pleasant scent and sublime taste it imparts to chocolate have made it highly recommended; but a long experience having shown that it could potentially upset one's stomach", which is why chocolate without vanilla was sometimes referred to as "healthy chocolate". By 1602, chocolate had made its way from Spain to Austria. By 1662, Pope Alexander VII
Pope Alexander VII ( it, Alessandro VII; 13 February 159922 May 1667), born Fabio Chigi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 April 1655 to his death in May 1667.
He began his career as a vice- papal legate, an ...
had declared that religious fasts were not broken by consuming chocolate drinks. Within about a hundred years, chocolate established a foothold throughout Europe.

 The new craze for chocolate brought with it a thriving slave market, as between the early 1600s and late 1800s, the laborious and slow processing of the cocoa bean was manual. Cocoa plantations spread, as the English, Dutch, and French colonized and planted. With the depletion of Mesoamerican workers, largely to disease, cocoa production was often the work of poor wage laborers and African slaves. Wind-powered and horse-drawn mills were used to speed production, augmenting human labor. Heating the working areas of the table-mill, an innovation that emerged in France in 1732, also assisted in extraction.
The new craze for chocolate brought with it a thriving slave market, as between the early 1600s and late 1800s, the laborious and slow processing of the cocoa bean was manual. Cocoa plantations spread, as the English, Dutch, and French colonized and planted. With the depletion of Mesoamerican workers, largely to disease, cocoa production was often the work of poor wage laborers and African slaves. Wind-powered and horse-drawn mills were used to speed production, augmenting human labor. Heating the working areas of the table-mill, an innovation that emerged in France in 1732, also assisted in extraction.
Solid chocolate
New processes that sped the production of chocolate emerged early in theIndustrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
. In 1815, Dutch chemist Coenraad van Houten introduced alkaline salts to chocolate, which reduced its bitterness. A few years thereafter, in 1828, he created a press to remove about half the natural fat (cocoa butter
Cocoa butter, also called theobroma oil, is a pale-yellow, edible fat extracted from the cocoa bean. It is used to make chocolate, as well as some ointments, toiletries, and pharmaceuticals. Cocoa butter has a cocoa flavor and aroma. Its melt ...
) from chocolate liquor, which made chocolate both cheaper to produce and more consistent in quality. This innovation introduced the modern era of chocolate.
Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city, Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Glouces ...
, England, began mass-producing chocolate bars, Fry's Chocolate Cream
Fry's Chocolate Cream is a chocolate bar developed by J. S. Fry & Sons and currently manufactured by Cadbury. Launched in 1866, Fry's Chocolate Cream is the first mass-produced chocolate bar and is the world's oldest chocolate bar brand.The fir ...
, launched in 1866, and they became very popular. Milk had sometimes been used as an addition to chocolate beverages since the mid-17th century, but in 1875 Swiss chocolatier Daniel Peter
Daniel Peter (9 March 1836 – 4 November 1919) was a Swiss chocolatier and entrepreneur who founded Peter's Chocolate. A neighbour of Henri Nestlé in Vevey, he was one of the first chocolatiers to make milk chocolate and is credited for inven ...
invented milk chocolate
Milk chocolate is a solid chocolate confectionery containing cocoa, sugar and milk. Chocolate was originally sold and consumed as a beverage in pre-Columbian times, and upon its introduction to Western Europe. Major milk chocolate producers incl ...
by mixing a powdered milk
Powdered milk, also called milk powder, dried milk, or dry milk, is a manufactured dairy product made by evaporating milk to dryness. One purpose of drying milk is to preserve it; milk powder has a far longer shelf life than liquid milk and do ...
developed by Henri Nestlé
Henri Nestlé () (born Heinrich Nestle; 10 August 1814 – 7 July 1890) was a German-Swiss confectioner and the founder of Nestlé, the world's largest food and beverage company.
Early life
Heinrich Nestle was born on 10 August 1814 in Frankfu ...
with the liquor. In 1879, the texture and taste of chocolate was further improved when Rudolphe Lindt invented the conching
upright=1.35, Conche (in the Imhoff-Schokoladenmuseum)
Conching is a process used in the manufacture of chocolate whereby a surface scraping mixer and agitator, known as a conche, evenly distributes cocoa butter within chocolate and may act as ...
machine.
Besides Nestlé
Nestlé S.A. (; ; ) is a Switzerland, Swiss multinational food and drink processing conglomerate corporation headquartered in Vevey, Vaud, Switzerland. It is the largest publicly held food company in the world, measured by revenue and other me ...
, several notable chocolate companies had their start in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Rowntree's
Rowntree's is a British confectionery brand and former business based in York, England. Rowntree developed the Kit Kat (introduced in 1935), Aero (introduced in 1935), Fruit Pastilles (introduced in 1881), Smarties (introduced in 1937) brands ...
of York set up and began producing chocolate in 1862, after buying out the Tuke family
The Tuke family of York were a family of Quaker innovators involved in establishing:
* Rowntree's Cocoa Works
* The Retreat Mental Hospital
*three Quaker schools - Ackworth, Bootham, and The Mount
They included four generations. The main Tukes ...
business. Cadbury
Cadbury, formerly Cadbury's and Cadbury Schweppes, is a British multinational confectionery company fully owned by Mondelez International (originally Kraft Foods) since 2010. It is the second largest confectionery brand in the world after Mar ...
was manufacturing boxed chocolates in England by 1868. Manufacturing their first Easter egg
Easter eggs, also called Paschal eggs, are eggs that are decorated for the Christian feast of Easter, which celebrates the resurrection of Jesus. As such, Easter eggs are common during the season of Eastertide (Easter season). The oldest tr ...
in 1875, Cadbury created the modern chocolate Easter egg after developing a pure cocoa butter that could easily be molded into smooth shapes. In 1893, Milton S. Hershey
Milton Snavely Hershey (September 13, 1857 – October 13, 1945) was an American chocolatier, businessman, and philanthropist.
Trained in the confectionery business, Hershey pioneered the manufacture of caramel, using fresh milk. He launched t ...
purchased chocolate processing equipment at the World's Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition (also known as the Chicago World's Fair) was a world's fair held in Chicago in 1893 to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492. The centerpiece of the Fair, hel ...
in Chicago, and soon began the career of Hershey's chocolates with chocolate-coated caramels.
Introduction to the United States
The Baker Chocolate Company, which makesBaker's Chocolate
Baker's Chocolate is a brand name for the line of baking chocolates owned by Kraft Heinz. Products include a variety of bulk chocolates, including white and unsweetened, and sweetened coconut flakes. It is one of the largest national brands of ch ...
, is the oldest producer of chocolate in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
. In 1765 Dr. James Baker and John Hannon founded the company in Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
. Using cocoa beans
The cocoa bean (technically cocoa seed) or simply cocoa (), also called the cacao bean (technically cacao seed) or cacao (), is the dried and fully fermented seed of ''Theobroma cacao'', from which cocoa solids (a mixture of nonfat substances ...
from the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
, the pair built their chocolate business, which is still in operation.
White chocolate
White chocolate is a confectionery typically made of sugar, milk, and cocoa butter. It is pale ivory colored, and lacks many of the compounds found in milk and dark chocolates. It is solid at room temperature because the melting point of cocoa ...
was first introduced to the U.S. in 1946 by Frederick E. Hebert of Hebert Candies in Shrewsbury, Massachusetts
Shrewsbury (/ˈʃruzberi/ ''SHROOZ-bury'') is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. Shrewsbury, unlike the surrounding towns of Grafton, Millbury, Westborough, Northborough, Boylston, and West Boylston did not become a ...
, near Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, after he had tasted "white coat" candies while traveling in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
.
Etymology
 Cocoa, pronounced by the Olmecs as ''kakawa'', dates to 1000 BC or earlier. The word "chocolate" entered the English language from Spanish in about 1600. The word entered Spanish from the word ''chocolātl'' in
Cocoa, pronounced by the Olmecs as ''kakawa'', dates to 1000 BC or earlier. The word "chocolate" entered the English language from Spanish in about 1600. The word entered Spanish from the word ''chocolātl'' in Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have small ...
, the language of the Aztecs. The origin of the Nahuatl word is uncertain, as it does not appear in any early Nahuatl source, where the word for chocolate drink is ''cacahuatl'', "cocoa water". It is possible that the Spaniards coined the word (perhaps in order to avoid ''caca'', a vulgar Spanish word for "faeces") by combining the Yucatec Mayan word ''chocol'', "hot", with the Nahuatl word ''atl'', "water". A widely cited proposal is that the derives from unattested ''xocolatl'' meaning "bitter drink" is unsupported; the change from ''x-'' to ''ch-'' is unexplained, as is the ''-l-''. Another proposed etymology derives it from the word ''chicolatl'', meaning "beaten drink", which may derive from the word for the frothing stick, ''chicoli''. Other scholars reject all these proposals, considering the origin of first element of the name to be unknown. The term "chocolatier
A chocolatier is a person or company who makes confectionery from chocolate. Chocolatiers are distinct from chocolate makers, who create chocolate from cacao beans and other ingredients.
Education and training
Traditionally, chocolatiers, ...
", for a chocolate confection maker, is attested from 1888.
Types
 Several types of chocolate can be distinguished. Pure, unsweetened chocolate, often called "baking chocolate", contains primarily
Several types of chocolate can be distinguished. Pure, unsweetened chocolate, often called "baking chocolate", contains primarily cocoa solids
Dry cocoa solids are the components of cocoa beans remaining after cocoa butter, the fatty component of the bean, is extracted from chocolate liquor, roasted cocoa beans that have been ground into a liquid state. Cocoa butter is 46% to 57% of t ...
and cocoa butter in varying proportions. Much of the chocolate consumed today is in the form of sweet chocolate, which combines chocolate with sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or do ...
.
By cocoa content
Raw chocolate
Raw chocolate is chocolate produced primarily from unroastedcocoa bean
The cocoa bean (technically cocoa seed) or simply cocoa (), also called the cacao bean (technically cacao seed) or cacao (), is the dried and fully Fermentation, fermented seed of ''Theobroma cacao'', from which cocoa solids (a mixture of non ...
s.
Dark
Dark chocolate is produced by adding fat and sugar to the cocoa mixture. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration calls this "sweet chocolate", and requires a 15% concentration of chocolate liquor. European rules specify a minimum of 35% cocoa solids. A higher amount of cocoa solids indicates more bitterness. Semisweet chocolate is dark chocolate with low sugar content. Bittersweet chocolate is chocolate liquor to which some sugar (typically a third), more cocoa butter and vanilla are added. It has less sugar and more liquor than semisweet chocolate, but the two are interchangeable in baking. It is also known to last for two years if stored properly. , there is no high-quality evidence that dark chocolate affects blood pressure significantly or provides other health benefits.Milk
Milk chocolate is sweet chocolate that also contains milk powder or condensed milk. In the UK and Ireland, milk chocolate must contain a minimum of 20% total dry cocoa solids; in the rest of the European Union, the minimum is 25%.White
 White chocolate, although similar in texture to that of milk and dark chocolate, does not contain any cocoa solids that impart a dark color. In 2002, the US
White chocolate, although similar in texture to that of milk and dark chocolate, does not contain any cocoa solids that impart a dark color. In 2002, the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
established a standard for white chocolate as the "common or usual name of products made from cocoa fat (i.e., cocoa butter), milk solids, nutritive carbohydrate sweeteners, and other safe and suitable ingredients, but containing no nonfat cocoa solids".
By application
Baking chocolate
 Baking chocolate, or cooking chocolate, is chocolate intended to be used for baking and in sweet foods that may or may not be sweetened. Dark chocolate,
Baking chocolate, or cooking chocolate, is chocolate intended to be used for baking and in sweet foods that may or may not be sweetened. Dark chocolate, milk chocolate
Milk chocolate is a solid chocolate confectionery containing cocoa, sugar and milk. Chocolate was originally sold and consumed as a beverage in pre-Columbian times, and upon its introduction to Western Europe. Major milk chocolate producers incl ...
, and white chocolate
White chocolate is a confectionery typically made of sugar, milk, and cocoa butter. It is pale ivory colored, and lacks many of the compounds found in milk and dark chocolates. It is solid at room temperature because the melting point of cocoa ...
, are produced and marketed as baking chocolate. However, lower quality baking chocolate may not be as flavorful compared to higher-quality chocolate, and may have a different mouthfeel
Mouthfeel refers to the physical sensations in the mouth caused by food or drink, making it distinct from taste. It is a fundamental sensory attribute which, along with taste and smell, determines the overall flavor of a food item. Mouthfeel ...
.
Poorly tempered or untempered chocolate may have whitish spots on the dark chocolate part, called chocolate bloom
Chocolate bloom is either of two types of whitish coating that can appear on the surface of chocolate: fat bloom, caused by changes in the fat crystals in the chocolate; and sugar bloom, due to crystals formed by the action of moisture on the s ...
; it is an indication that sugar or fat has separated due to poor storage. It is not toxic and can be safely consumed.
Modeling chocolate
Modeling chocolate is a chocolate paste made by melting chocolate and combining it withcorn syrup
Corn syrup is a food syrup which is made from the starch of corn (called maize in many countries) and contains varying amounts of sugars: glucose, maltose and higher oligosaccharides, depending on the grade. Corn syrup is used in foods to soft ...
, glucose syrup
Glucose syrup, also known as confectioner's glucose, is a syrup made from the hydrolysis of starch. Glucose is a sugar. Maize (corn) is commonly used as the source of the starch in the US, in which case the syrup is called "corn syrup", but ...
, or golden syrup.
Production
Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre i ...
is the largest producer of cocoa in the world. The two main jobs associated with creating chocolate candy are chocolate makers and chocolatiers. Chocolate makers use harvested cocoa beans and other ingredients to produce couverture chocolate
Couverture chocolate is a chocolate that contains a higher percentage of cocoa butter (32–39%) than baking or eating chocolate. This additional cocoa butter, combined with proper tempering, gives the chocolate more sheen, a firmer "snap" when ...
(covering). Chocolatiers use the finished couverture to make chocolate candies ( bars, truffles
A truffle is the fruiting body of a subterranean ascomycete fungus, predominantly one of the many species of the genus ''Tuber''. In addition to ''Tuber'', many other genera of fungi are classified as truffles including '' Geopora'', '' Pe ...
, etc.).
Production costs can be decreased by reducing cocoa solids content or by substituting cocoa butter with another fat. Cocoa growers object to allowing the resulting food to be called "chocolate", due to the risk of lower demand for their crops.
Genome
The sequencing in 2010 of the genome of the cacao tree may allow yields to be improved. Due to concerns aboutglobal warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
effects on lowland climate in the narrow band of latitudes where cocoa is grown (20 degrees north and south of the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also ...
), the commercial company Mars, Incorporated
Mars, Incorporated is an American multinational manufacturer of confectionery, pet food, and other food products and a provider of animal care services, with US$40 billion in annual sales in 2021.
Mars was ranked as the fourth-largest pri ...
and the University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant un ...
, are conducting genomic research in 2017–18 to improve the survivability of cacao plants in hot climates.
Cacao varieties
cocoa bean
The cocoa bean (technically cocoa seed) or simply cocoa (), also called the cacao bean (technically cacao seed) or cacao (), is the dried and fully Fermentation, fermented seed of ''Theobroma cacao'', from which cocoa solids (a mixture of non ...
s, the dried and fermented seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao
''Theobroma cacao'', also called the cacao tree and the cocoa tree, is a small ( tall) evergreen tree in the family Malvaceae. Its seeds, cocoa beans, are used to make chocolate liquor, cocoa solids, cocoa butter and chocolate. The largest pr ...
''), a small, 4–8 m tall (15–26 ft tall) evergreen
In botany, an evergreen is a plant which has foliage that remains green and functional through more than one growing season. This also pertains to plants that retain their foliage only in warm climates, and contrasts with deciduous plants, whic ...
tree native to the deep tropical region of the Americas. Recent genetic studies suggest the most common genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
of the plant originated in the Amazon basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Boli ...
and was gradually transported by humans throughout South and Central America. Early forms of another genotype have also been found in what is now Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
. The scientific name, '' Theobroma'', means "food of the gods
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater ...
". The fruit, called a cocoa pod, is ovoid, long and wide, ripening yellow to orange, and weighing about when ripe.
Cacao tree
''Theobroma cacao'', also called the cacao tree and the cocoa tree, is a small ( tall) evergreen tree in the family Malvaceae. Its seeds, cocoa beans, are used to make chocolate liquor, cocoa solids, cocoa butter and chocolate. The largest p ...
s are small, understory trees that need rich, well-drained soils. They naturally grow within 20° of either side of the equator because they need about 2000 mm of rainfall a year, and temperatures in the range of . Cacao trees cannot tolerate a temperature lower than .
The three main varieties of cocoa bean
The cocoa bean (technically cocoa seed) or simply cocoa (), also called the cacao bean (technically cacao seed) or cacao (), is the dried and fully Fermentation, fermented seed of ''Theobroma cacao'', from which cocoa solids (a mixture of non ...
s used in chocolate are criollo
Criollo or criolla (Spanish for creole) may refer to:
People
* Criollo people, a social class in the Spanish race-based colonial caste system (the European descendants)
Animals
* Criollo duck, a species of duck native to Central and South Ameri ...
, forastero, and trinitario.
Processing
Cocoa pods are harvested by cutting them from the tree using amachete
Older machete from Latin America
Gerber machete/saw combo
Agustín Cruz Tinoco of San Agustín de las Juntas, Oaxaca">San_Agustín_de_las_Juntas.html" ;"title="Agustín Cruz Tinoco of San Agustín de las Juntas">Agustín Cruz Tinoco of San ...
, or by knocking them off the tree using a stick. It is important to harvest the pods when they are fully ripe, because if the pod is unripe, the beans will have a low cocoa butter content, or low sugar content, reducing the ultimate flavor.
Microbial fermentation
The beans (which aresterile
Sterile or sterility may refer to:
*Asepsis
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and parasites). There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgi ...
within their pods) and their surrounding pulp are removed from the pods and placed in piles or bins to ferment. Micro-organisms, present naturally in the environment, ferment the pectin
Pectin ( grc, πηκτικός ': "congealed" and "curdled") is a heteropolysaccharide, a structural acid contained in the primary lamella, in the middle lamella, and in the cell walls of terrestrial plants. The principal, chemical component o ...
-containing material. Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constit ...
s produce ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
, lactic acid bacteria
Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped ( bacilli) or spherical ( cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bact ...
produce lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula . It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as nat ...
, and acetic acid bacteria
Acetic acid bacteria (AAB) are a group of Gram-negative bacteria which oxidize sugars or ethanol and produce acetic acid during fermentation. The acetic acid bacteria consist of 10 genera in the family Acetobacteraceae. Several species of acetic ...
produce acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main componen ...
. In some cocoa-producing regions an association between filamentous fungi
A mold () or mould () is one of the structures certain fungi can form. The dust-like, colored appearance of molds is due to the formation of spores containing fungal secondary metabolites. The spores are the dispersal units of the fungi. Not ...
and bacteria (called "cocobiota") acts to produce metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, ...
s beneficial to human health when consumed. The fermentation process, which takes up to seven days, also produces several flavor precursors, that eventually provide the chocolate taste.
After fermentation, the beans must be dried to prevent mold growth. Climate and weather permitting, this is done by spreading the beans out in the sun from five to seven days. In some growing regions (for example, Tobago
Tobago () is an island and ward within the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trinidad and about off the northeastern coast of Venezuela. It also lies to the southeast of Grenada. The offic ...
), the dried beans are then polished for sale by "dancing the cocoa": spreading the beans onto a floor, adding oil or water, and shuffling the beans against each other using bare feet.
The dried beans are then transported to a chocolate manufacturing facility. The beans are cleaned (removing twigs, stones, and other debris), roasted, and graded. Next, the shell of each bean is removed to extract the nib. The nibs are ground and liquefied, resulting in pure chocolate liquor
Chocolate liquor (cocoa liquor) is pure cocoa mass (cocoa paste) in solid or semi-solid form. Like the cocoa beans (nibs) from which it is produced, it contains both cocoa solids and cocoa butter in roughly equal proportion.
It is produced fr ...
. The liquor can be further processed into cocoa solids and cocoa butter.
Moist incubation
The beans are dried without fermentation. The nibs are removed and hydrated in an acidic solution. Then they are heated for 72 hours and dried again.Gas chromatography
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substanc ...
/mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is u ...
showed that the incubated chocolate had higher levels of Strecker aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl gro ...
s, and lower levels of pyrazine
Pyrazine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C4H4N2. It is a symmetrical molecule with point group D2h. Pyrazine is less basic than pyridine, pyridazine and pyrimidine. It is a ''"deliquescent crystal or wax-li ...
s.
Blending
Chocolate liquor is blended with the cocoa butter in varying quantities to make different types of chocolate or couverture. The basic blends of ingredients for the various types of chocolate (in order of highest quantity of cocoa liquor first), are: * Dark chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, cocoa liquor, and (sometimes) vanilla
* Milk chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, cocoa liquor, milk or milk powder, and vanilla
* White chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, milk or milk powder, and vanilla
Usually, an
* Dark chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, cocoa liquor, and (sometimes) vanilla
* Milk chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, cocoa liquor, milk or milk powder, and vanilla
* White chocolate: sugar, cocoa butter, milk or milk powder, and vanilla
Usually, an emulsifying agent
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although ...
, such as soy lecithin
Lecithin (, from the Greek ''lekithos'' "yolk") is a generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues which are amphiphilic – they attract both water and fatty substances (and so ar ...
, is added, though a few manufacturers prefer to exclude this ingredient for purity reasons and to remain GMO
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. The exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies, with ...
-free, sometimes at the cost of a perfectly smooth texture. Some manufacturers are now using PGPR, an artificial emulsifier derived from castor oil that allows them to reduce the amount of cocoa butter while maintaining the same mouthfeel
Mouthfeel refers to the physical sensations in the mouth caused by food or drink, making it distinct from taste. It is a fundamental sensory attribute which, along with taste and smell, determines the overall flavor of a food item. Mouthfeel ...
.
The texture is also heavily influenced by processing, specifically conching (see below). The more expensive chocolate tends to be processed longer and thus has a smoother texture and mouthfeel, regardless of whether emulsifying agents are added.
Different manufacturers develop their own "signature" blends based on the above formulas, but varying proportions of the different constituents are used. The finest, plain dark chocolate couverture contains at least 70% cocoa (both solids and butter), whereas milk chocolate usually contains up to 50%. High-quality white chocolate couverture contains only about 35% cocoa butter.
Producers of high-quality, small-batch chocolate argue that mass production produces bad-quality chocolate. Some mass-produced chocolate contains much less cocoa (as low as 7% in many cases), and fats other than cocoa butter. Vegetable oils and artificial
Artificiality (the state of being artificial or manmade) is the state of being the product of intentional human manufacture, rather than occurring naturally through processes not involving or requiring human activity.
Connotations
Artificiality ...
vanilla flavor are often used in cheaper chocolate to mask poorly fermented and/or roasted beans.
In 2007, the Chocolate Manufacturers Association in the United States, whose members include Hershey, Nestlé
Nestlé S.A. (; ; ) is a Switzerland, Swiss multinational food and drink processing conglomerate corporation headquartered in Vevey, Vaud, Switzerland. It is the largest publicly held food company in the world, measured by revenue and other me ...
, and Archer Daniels Midland
The Archer-Daniels-Midland Company, commonly known as ADM, is an American multinational food processing and commodities trading corporation founded in 1902 and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. The company operates more than 270 plants and 4 ...
, lobbied
In politics, lobbying, persuasion or interest representation is the act of lawfully attempting to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of government officials, most often legislators or members of regulatory agencies. Lobbying, which ...
the Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
(FDA) to change the legal definition of chocolate to let them substitute partially hydrogenated vegetable oils
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple es ...
for cocoa butter, in addition to using artificial sweeteners and milk substitutes. Currently, the FDA does not allow a product to be referred to as "chocolate" if the product contains any of these ingredients.
In the EU a product can be sold as chocolate if it contains up to 5% vegetable oil, and must be labeled as "family milk chocolate" rather than "milk chocolate" if it contains 20% milk.
According to Canadian Food and Drug Regulations, a "chocolate product" is a food product that is sourced from at least one "cocoa product" and contains at least one of the following: "chocolate, bittersweet chocolate, semi-sweet chocolate, dark chocolate, sweet chocolate, milk chocolate, or white chocolate". A "cocoa product" is defined as a food product that is sourced from cocoa beans and contains "cocoa nibs, cocoa liquor, cocoa mass, unsweetened chocolate, bitter chocolate, chocolate liquor, cocoa, low-fat cocoa, cocoa powder, or low-fat cocoa powder".
Conching
 The penultimate process is called conching. A conche is a container filled with metal beads, which act as grinders. The refined and blended chocolate mass is kept in a liquid state by frictional heat. Chocolate before conching has an uneven and gritty texture. The conching process produces cocoa and sugar particles smaller than the tongue can detect (typically around 20
The penultimate process is called conching. A conche is a container filled with metal beads, which act as grinders. The refined and blended chocolate mass is kept in a liquid state by frictional heat. Chocolate before conching has an uneven and gritty texture. The conching process produces cocoa and sugar particles smaller than the tongue can detect (typically around 20 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Uni ...
) and reduces rough edges, hence the smooth feel in the mouth. The length of the conching process determines the final smoothness and quality of the chocolate. High-quality chocolate is conched for about 72 hours, and lesser grades about four to six hours. After the process is complete, the chocolate mass is stored in tanks heated to about until final processing.
Tempering
The final process is called tempering. Uncontrolledcrystallization
Crystallization is the process by which solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposi ...
of cocoa butter typically results in crystals of varying size, some or all large enough to be seen with the naked eye. This causes the surface of the chocolate to appear mottled and matte, and causes the chocolate to crumble rather than snap when broken. The uniform sheen and crisp bite of properly processed chocolate are the results of consistently small cocoa butter crystals produced by the tempering process.
The fats in cocoa butter can crystallize in six different forms ( polymorphous crystallization). The primary purpose of tempering is to assure that only the best form is present. The six different crystal forms have different properties.
 As a solid piece of chocolate, the cocoa butter fat particles are in a crystalline rigid structure that gives the chocolate its solid appearance. Once heated, the crystals of the polymorphic cocoa butter can break apart from the rigid structure and allow the chocolate to obtain a more fluid consistency as the temperature increases – the melting process. When the heat is removed, the cocoa butter crystals become rigid again and come closer together, allowing the chocolate to solidify.
The temperature in which the crystals obtain enough energy to break apart from their rigid conformation would depend on the milk fat content in the chocolate and the shape of the fat molecules, as well as the form of the cocoa butterfat. Chocolate with a higher fat content will melt at a lower temperature.
Making chocolate considered "good" is about forming as many type V crystals as possible. This provides the best appearance and texture and creates the most stable crystals, so the texture and appearance will not degrade over time. To accomplish this, the temperature is carefully manipulated during the crystallization.
As a solid piece of chocolate, the cocoa butter fat particles are in a crystalline rigid structure that gives the chocolate its solid appearance. Once heated, the crystals of the polymorphic cocoa butter can break apart from the rigid structure and allow the chocolate to obtain a more fluid consistency as the temperature increases – the melting process. When the heat is removed, the cocoa butter crystals become rigid again and come closer together, allowing the chocolate to solidify.
The temperature in which the crystals obtain enough energy to break apart from their rigid conformation would depend on the milk fat content in the chocolate and the shape of the fat molecules, as well as the form of the cocoa butterfat. Chocolate with a higher fat content will melt at a lower temperature.
Making chocolate considered "good" is about forming as many type V crystals as possible. This provides the best appearance and texture and creates the most stable crystals, so the texture and appearance will not degrade over time. To accomplish this, the temperature is carefully manipulated during the crystallization.
 Generally, the chocolate is first heated to to melt all six forms of crystals. Next, the chocolate is cooled to about , which will allow crystal types IV and V to form. At this temperature, the chocolate is agitated to create many small crystal "seeds" which will serve as nuclei to create small crystals in the chocolate. The chocolate is then heated to about to eliminate any type IV crystals, leaving just type V. After this point, any excessive heating of the chocolate will destroy the temper and this process will have to be repeated. Other methods of chocolate tempering are used as well. The most common variant is introducing already tempered, solid "seed" chocolate. The temper of chocolate can be measured with a chocolate temper meter to ensure accuracy and consistency. A sample cup is filled with the chocolate and placed in the unit which then displays or prints the results.
Two classic ways of manually tempering chocolate are:
* Working the molten chocolate on a heat-absorbing surface, such as a stone slab, until thickening indicates the presence of sufficient crystal "seeds"; the chocolate is then gently warmed to working temperature.
* Stirring solid chocolate into molten chocolate to "inoculate" the liquid chocolate with crystals (this method uses the already formed crystals of the solid chocolate to "seed" the molten chocolate).
Chocolate tempering machines (or temperers) with computer controls can be used for producing consistently tempered chocolate. In particular,
Generally, the chocolate is first heated to to melt all six forms of crystals. Next, the chocolate is cooled to about , which will allow crystal types IV and V to form. At this temperature, the chocolate is agitated to create many small crystal "seeds" which will serve as nuclei to create small crystals in the chocolate. The chocolate is then heated to about to eliminate any type IV crystals, leaving just type V. After this point, any excessive heating of the chocolate will destroy the temper and this process will have to be repeated. Other methods of chocolate tempering are used as well. The most common variant is introducing already tempered, solid "seed" chocolate. The temper of chocolate can be measured with a chocolate temper meter to ensure accuracy and consistency. A sample cup is filled with the chocolate and placed in the unit which then displays or prints the results.
Two classic ways of manually tempering chocolate are:
* Working the molten chocolate on a heat-absorbing surface, such as a stone slab, until thickening indicates the presence of sufficient crystal "seeds"; the chocolate is then gently warmed to working temperature.
* Stirring solid chocolate into molten chocolate to "inoculate" the liquid chocolate with crystals (this method uses the already formed crystals of the solid chocolate to "seed" the molten chocolate).
Chocolate tempering machines (or temperers) with computer controls can be used for producing consistently tempered chocolate. In particular, continuous
Continuity or continuous may refer to:
Mathematics
* Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include
** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics
** Continuous g ...
tempering machines are used in large volume applications. Various methods and apparatuses for continuous flow tempering. In general, molten chocolate coming in at 40–50 °C is cooled in heat exchangers to crystallization temperates of about 26–30 °C, passed through a tempering column consisting of spinning plates to induce shear, then warmed slightly to re-melt undesirable crystal formations.
Shaping
Chocolate is molded in different shapes for different uses: *Chocolate bar
A chocolate bar (Commonwealth English) or candy bar (some dialects of American English) is a confection containing chocolate, which may also contain layerings or mixtures that include nuts, fruit, caramel, nougat, and wafers. A flat, easily brea ...
s (tablets) are rectangular blocks of chocolate meant to be broken down to cubes (or other predefined shapes), which can then be used for consumption, cooking and baking. The term is also used for combination bars, which are a type of candy bar
A candy bar is a type of candy that is in the shape of a bar. The most common type of candy bar is the chocolate bar, including both bars made of solid chocolate and combination candy bars, which are candy bars that combine chocolate with othe ...
s
* Chocolate chip
Chocolate chips or chocolate morsels are small chunks of sweetened chocolate, used as an ingredient in a number of desserts (notably chocolate chip cookies and muffins), in trail mix and less commonly in some breakfast foods such as pancakes. ...
s are small pieces of chocolate, usually drop-like, which are meant for decoration and baking
* ''Pistoles'', ''callets'' and ''fèves'' are small, coin-like or bean-like pieces of chocolate meant for baking and patisserie applications (also see Pistole (coin) and Fève (trinket))
* Chocolate blocks are large, cuboid
In geometry, a cuboid is a hexahedron, a six-faced solid. Its faces are quadrilaterals. Cuboid means "like a cube", in the sense that by adjusting the length of the edges or the angles between edges and faces a cuboid can be transformed into a c ...
chunks of chocolate meant for professional use and further processing
* Other, more specialized shapes for chocolate include sticks, curls and hollow semi-spheres
Storage
 Chocolate is very sensitive to temperature and humidity. Ideal storage temperatures are between , with a relative humidity of less than 50%. If refrigerated or frozen without containment, chocolate can absorb enough moisture to cause a whitish discoloration, the result of fat or sugar crystals rising to the surface. Various types of "blooming" effects can occur if chocolate is stored or served improperly.
Chocolate is very sensitive to temperature and humidity. Ideal storage temperatures are between , with a relative humidity of less than 50%. If refrigerated or frozen without containment, chocolate can absorb enough moisture to cause a whitish discoloration, the result of fat or sugar crystals rising to the surface. Various types of "blooming" effects can occur if chocolate is stored or served improperly.
Chocolate bloom
Chocolate bloom is either of two types of whitish coating that can appear on the surface of chocolate: fat bloom, caused by changes in the fat crystals in the chocolate; and sugar bloom, due to crystals formed by the action of moisture on the s ...
is caused by storage temperature fluctuating or exceeding , while sugar bloom is caused by temperature below or excess humidity. To distinguish between different types of bloom, one can rub the surface of the chocolate lightly, and if the bloom disappears, it is fat bloom. Moving chocolate between temperature extremes, can result in an oily texture. Although visually unappealing, chocolate suffering from bloom is safe for consumption and taste unaffected. Bloom can be reversed by retempering the chocolate or using it for any use that requires melting the chocolate.
Chocolate is generally stored away from other foods, as it can absorb different aromas. Ideally, chocolates are packed or wrapped, and placed in proper storage with the correct humidity and temperature. Additionally, chocolate is frequently stored in a dark place or protected from light by wrapping paper. The glossy shine, snap, aroma, texture, and taste of the chocolate can show the quality and if it was stored well.
Composition
Nutrition
One hundred grams of milk chocolate supplies 540calories
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of ...
. It is 59% carbohydrates
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or m ...
(52% as sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or do ...
and 3% as dietary fiber
Dietary fiber (in British English fibre) or roughage is the portion of plant-derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Dietary fibers are diverse in chemical composition, and can be grouped generally by t ...
), 30% fat and 8% protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
(table). Approximately 65% of the fat in milk chocolate is saturated, mainly palmitic acid
Palmitic acid (hexadecanoic acid in IUPAC nomenclature) is a fatty acid with a 16-carbon chain. It is the most common saturated fatty acid found in animals, plants and microorganisms.Gunstone, F. D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra. The ...
and stearic acid
Stearic acid ( , ) is a saturated fatty acid with an 18-carbon chain. The IUPAC name is octadecanoic acid. It is a waxy solid and its chemical formula is C17H35CO2H. Its name comes from the Greek word στέαρ "''stéar''", which means ta ...
, while the predominant unsaturated fat
An unsaturated fat is a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain. A fatty acid chain is monounsaturated if it contains one double bond, and polyunsaturated if it contains more than one double bond ...
is oleic acid
Oleic acid is a fatty acid that occurs naturally in various animal and vegetable fats and oils. It is an odorless, colorless oil, although commercial samples may be yellowish. In chemical terms, oleic acid is classified as a monounsaturated o ...
(table).
100-grams of milk chocolate is an ''excellent source'' (over 19% of the Daily Value
The Reference Daily Intake (RDI) used in nutrition labeling on food and dietary supplement products in the U.S. and Canada is the daily intake level of a nutrient that is considered to be sufficient to meet the requirements of 97–98% of healthy ...
, DV) of riboflavin
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is a vitamin found in food and sold as a dietary supplement. It is essential to the formation of two major coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide. These coenzymes are involved i ...
, vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. ...
and the dietary minerals
In the context of nutrition, a mineral is a chemical element required as an essential nutrient by organisms to perform functions necessary for life. However, the four major structural elements in the human body by weight (oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of ...
, phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
. Chocolate is a ''good source'' (10–19% DV) of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
.
Effects on health
Chocolate may be a factor forheartburn
Heartburn, also known as pyrosis, cardialgia or acid indigestion, is a burning sensation in the central chest or upper central abdomen. Heartburn is usually due to regurgitation of gastric acid (gastric reflux) into the esophagus. It is the ...
in some people because one of its constituents, theobromine
Theobromine, also known as xantheose, is the principal alkaloid of '' Theobroma cacao'' (cacao plant). Theobromine is slightly water- soluble (330 mg/L) with a bitter taste. In industry, theobromine is used as an additive and precursor to ...
, may affect the esophageal sphincter
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
muscle in a way that permits stomach acids to enter the esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to t ...
. Theobromine poisoning is an overdosage reaction to the bitter alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of simila ...
, which happens more frequently in domestic animals
This page gives a list of domesticated animals, also including a list of animals which are or may be currently undergoing the process of domestication and animals that have an extensive relationship with humans beyond simple predation. This includ ...
than humans. However, daily intake of 50–100 g cocoa (0.8–1.5 g theobromine) by humans has been associated with sweating, trembling and severe headache. Chocolate contains alkaloids such as theobromine and phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace am ...
, which have physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemica ...
effects in humans, but the presence of theobromine renders it toxic to some animals, including dogs and cats.
According to a 2005 study, the average lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
concentration of cocoa beans is ≤ 0.5 ng/g, which is one of the lowest reported values for a natural food. However, during cultivation and production, chocolate may absorb lead from the environment (such as in atmospheric emissions of leaded gasoline, which is still being used in Nigeria). Reports from 2014 indicate that "chocolate might be a significant source" of lead ingestion for children if consumption is high (with dark chocolate containing higher amounts), and "one 10 g cube of dark chocolate may contain as much as 20% of the daily lead oral limit."
Chocolate and cocoa contain moderate to high amounts of oxalate
Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate) is an anion with the formula C2O42−. This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4), and several esters such as dimethyl ...
, which may increase the risk of kidney stone
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine s ...
s.
A few studies have documented allergic reactions
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic derm ...
from chocolate in children. Other research has shown that dark chocolate can aggravate acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and ...
in men who are prone to it. Research has also shown that consuming dark chocolate does not substantially affect blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure ...
. Chocolate and cocoa are under preliminary research to determine if consumption affects the risk of certain cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
or cognitive abilities.
One tablespoonful (5 grams) of dry unsweetened cocoa powder
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* '' Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter an ...
has 12.1 mg of caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class. It is mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally as a Nootropic, cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional perfor ...
and a 25-g single serving of dark chocolate has 22.4 mg of caffeine. Although a single 7 oz. serving of coffee may contain 80–175 mg, studies have shown psychoactive effects in caffeine doses as low as 9 mg, and a dose as low as 12.5 mg was shown to have effects on cognitive performance.
Phytochemicals
No particular compound within chocolate has been associated with any specific health outcome; it is more likely that its observed, overall beneficial effect in humans "may owe something more to the whole than to any given part.". However, thepolyphenol
Polyphenols () are a large family of naturally occurring organic compounds characterized by multiples of phenol units. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some ...
epicatechin is regarded as potentially significant. Cocoa solids are a source of flavonoids
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.
Chemically, flavonoids ...
and alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of simila ...
s, such as theobromine
Theobromine, also known as xantheose, is the principal alkaloid of '' Theobroma cacao'' (cacao plant). Theobromine is slightly water- soluble (330 mg/L) with a bitter taste. In industry, theobromine is used as an additive and precursor to ...
, phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace am ...
, and caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class. It is mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally as a Nootropic, cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional perfor ...
.
Labeling
Some manufacturers provide the percentage of chocolate in a finished chocolate confection as a label quoting percentage of "cocoa" or "cacao". This refers to the combined percentage of both cocoa solids and cocoa butter in the bar, not just the percentage of cocoa solids. The BelgianAMBAO AMBAO is a certification mark for chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consum ...
certification mark indicates that no non-cocoa vegetable fats have been used in making the chocolate. A long-standing dispute between Britain on the one hand and Belgium and France over British use of vegetable fats in chocolate ended in 2000 with the adoption of new standards which permitted the use of up to five percent vegetable fats in clearly labelled products. This British style of chocolate has sometimes been pejoratively referred to as "vegelate".
Chocolates that are organic
Organic may refer to:
* Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity
* Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ
Chemistry
* Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product ...
or fair trade certified carry labels accordingly.
In the United States, some large chocolate manufacturers lobbied the federal government to permit confections containing cheaper hydrogenated vegetable oil in place of cocoa butter to be sold as "chocolate". In June 2007, in response to consumer concern about the proposal, the FDA reiterated "Cacao fat, as one of the signature characteristics of the product, will remain a principal component of standardized chocolate."
Industry
Chocolate, prevalent throughout the world, is a steadily growing, US$50 billion-a-year worldwide business. Europe accounts for 45% of the world's chocolate revenue, and the US spent $20 billion in 2013.Big Chocolate
"Big Chocolate" is a business term assigned to multi-national chocolate food producers, akin to the terms "Big Oil," " Big Pharma," and "Big Tobacco".
Definition
According to self-described fair trade proponents including Ghanaian cooperative ...
is the grouping of major international chocolate companies in Europe and the U.S. U.S. companies Mars and Hershey's alone generated $13 billion a year in chocolate sales and account for two-thirds of U.S. production in 2004. Despite the expanding reach of the chocolate industry internationally, cocoa farmers and labourers in the Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre i ...
are unaware of the uses of the beans; the high cost of chocolate products in the Ivory Coast make it inaccessible to the majority of the population, who do not know what it tastes like.
Manufacturers
 Chocolate manufacturers produce a range of products from chocolate bars to
Chocolate manufacturers produce a range of products from chocolate bars to fudge
Fudge is a type of confection that is made by mixing sugar, butter and milk, heating it to the soft-ball stage at , and then beating the mixture while it cools so that it acquires a smooth, creamy consistency. In texture, this crystalline can ...
. Large manufacturers of chocolate products include Cadbury
Cadbury, formerly Cadbury's and Cadbury Schweppes, is a British multinational confectionery company fully owned by Mondelez International (originally Kraft Foods) since 2010. It is the second largest confectionery brand in the world after Mar ...
(the world's largest confectionery manufacturer), Ferrero, Guylian, The Hershey Company
The Hershey Company, commonly known as Hershey's, is an American multinational company and one of the largest chocolate manufacturers in the world. It also manufactures baked products, such as cookies and cakes, and sells beverages like milksh ...
, Lindt & Sprüngli
Chocoladefabriken Lindt & Sprüngli AG, doing business as Lindt, is a Swiss chocolatier and confectionery company founded in 1845 and known for its chocolate truffles and chocolate bars, among other sweets. It is based in Kilchberg, where its ...
, Mars, Incorporated
Mars, Incorporated is an American multinational manufacturer of confectionery, pet food, and other food products and a provider of animal care services, with US$40 billion in annual sales in 2021.
Mars was ranked as the fourth-largest pri ...
, Milka
Milka is a brand of chocolate confectionery, originally made in Switzerland in 1901 by Suchard. It has then been produced in Lörrach, Germany for the past 100 years. Since 2012 it has been owned by US-based company Mondelez International, when ...
, Neuhaus and Suchard.
Guylian is best known for its chocolate sea shells; Cadbury for its Dairy Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulatin ...
and Creme Egg. The Hershey Company, the largest chocolate manufacturer in North America, produces the Hershey Bar
The Hershey's Milk Chocolate Bar (commonly called the Hershey's Bar, or more simply the Hershey Bar) is a flagship chocolate bar manufactured by The Hershey Company. Hershey refers to it as "The Great American Chocolate Bar". The Hershey Milk Cho ...
and Hershey's Kisses
Hershey's Kisses is a brand of chocolate first produced by the Hershey Company in 1907. The bite-sized pieces of chocolate have a distinctive conical shape, sometimes described as flat-bottomed teardrops. Hershey's Kisses chocolates are wrapped i ...
. Mars Incorporated, a large privately owned U.S. corporation, produces Mars Bar
Mars, commonly known as Mars bar, is the name of two varieties of chocolate bar produced by Mars, Incorporated. It was first manufactured in 1932 in Slough, England by Forrest Mars, Sr. The bar consists of caramel and nougat coated with milk c ...
, Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
, M&M's
M&M's (stylized as m&m's) are multi-colored button-shaped chocolates, each of which has the letter "m" printed in lower case in white on one side, consisting of a candy shell surrounding a filling which varies depending upon the variety of M&M ...
, Twix, and Snickers
Snickers is a chocolate bar made by the American company Mars, Incorporated, consisting of nougat topped with caramel and peanuts that is encased in milk chocolate. The annual global sales of Snickers was over $3 billion .
In the United ...
. Lindt
Chocoladefabriken Lindt & Sprüngli AG, doing business as Lindt, is a Swiss chocolatier and confectionery company founded in 1845 and known for its chocolate truffles and chocolate bars, among other sweets. It is based in Kilchberg, where its ...
is known for its truffle balls and gold foil-wrapped Easter bunnies.
Food conglomerates Nestlé
Nestlé S.A. (; ; ) is a Switzerland, Swiss multinational food and drink processing conglomerate corporation headquartered in Vevey, Vaud, Switzerland. It is the largest publicly held food company in the world, measured by revenue and other me ...
SA and Kraft Foods
The second incarnation of Kraft Foods is an American food manufacturing and processing conglomerate, split from Kraft Foods Inc. in 2012 and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. It became part of Kraft Heinz in 2015.
A merger with Heinz, arran ...
both have chocolate brands. Nestlé acquired Rowntree's
Rowntree's is a British confectionery brand and former business based in York, England. Rowntree developed the Kit Kat (introduced in 1935), Aero (introduced in 1935), Fruit Pastilles (introduced in 1881), Smarties (introduced in 1937) brands ...
in 1988 and now markets chocolates under their brand, including Smarties
Smarties are colour-varied sugar-coated chocolate confectionery. They have been manufactured since 1937, originally by H.I. Rowntree & Company in the United Kingdom, and now by Nestlé.
Smarties are oblate spheroids with a minor axis of abou ...
(a chocolate candy) and Kit Kat
Kit Kat (stylised as KitKat in various countries) is a chocolate-covered wafer bar confection created by Rowntree's of York, United Kingdom, and is now produced globally by Nestlé (which acquired Rowntree's in 1988), except in the United Sta ...
(a chocolate bar); Kraft Foods through its 1990 acquisition of Jacobs Suchard, now owns Milka and Suchard. In February 2010, Kraft also acquired British-based Cadbury; Fry's, Trebor Basset and the fair trade
Fair trade is an arrangement designed to help producers in developing countries achieve sustainable and equitable trade relationships. The fair trade movement combines the payment of higher prices to exporters with improved social and envir ...
brand Green & Black's
Green & Black's is a British chocolate company founded in 1991. The company produces a range of organic food products, including: chocolate bars, ice cream, biscuits and hot chocolate.
Green & Black's was bought by Cadbury in 2005, and later b ...
also belongs to the group.
Child labor in cocoa harvesting
The widespread use of children in cocoa production is controversial, not only for the concerns aboutchild labor
Child labour refers to the exploitation of children through any form of work that deprives children of their childhood, interferes with their ability to attend regular school, and is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such e ...
and exploitation, but also because up to 12,000 of the 200,000 children working in the Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre i ...
, the world's biggest producer of cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter an ...
, may be victims of trafficking
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations.
There are various ...
or slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. Most attention on this subject has focused on West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali ...
, which collectively supplies 69 percent of the world's cocoa, and the Ivory Coast in particular, which supplies 35 percent of the world's cocoa. Thirty percent of children under age 15 in sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
are child laborers, mostly in agricultural activities including cocoa farming. Major chocolate producers, such as Nestlé
Nestlé S.A. (; ; ) is a Switzerland, Swiss multinational food and drink processing conglomerate corporation headquartered in Vevey, Vaud, Switzerland. It is the largest publicly held food company in the world, measured by revenue and other me ...
, buy cocoa at commodities exchange
A commodities exchange is an exchange, or market, where various commodities are traded. Most commodity markets around the world trade in agricultural products and other raw materials (like wheat, barley, sugar, maize, cotton, cocoa, coffee, m ...
s where Ivorian cocoa is mixed with other cocoa.
In 2009, Salvation Army International Development (SAID) UK stated that 12,000 children have been trafficked on cocoa farms in the Ivory Coast of Africa, where half of the world's chocolate is made. SAID UK states that it is these child slaves who are likely to be working in "harsh and abusive" Salvation Army International Development (SAID) UK (2009).Human Trafficking – Promises
." conditions for the production of chocolate, and an increasing number of health-food and anti-slavery organisations are highlighting and campaigning against the use of trafficking in the chocolate industry. As of 2017, approximately 2.1 million children in Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire were involved in farming cocoa, carrying heavy loads, clearing forests, and being exposed to pesticides. According to Sona Ebai, the former secretary-general of the Alliance of Cocoa Producing Countries: "I think child labor cannot be just the responsibility of industry to solve. I think it's the proverbial all-hands-on-deck: government, civil society, the private sector. And there, you need leadership." Reported in 2018, a 3-year
pilot program
A pilot study, pilot project, pilot test, or pilot experiment is a small-scale preliminary study conducted to evaluate feasibility, duration, cost, adverse events, and improve upon the study design prior to performance of a full-scale research pr ...
– conducted by Nestlé with 26,000 farmers mostly located in Côte d'Ivoire – observed a 51% decrease in the number of children doing hazardous jobs in cocoa farming. The US Department of Labor
The United States Department of Labor (DOL) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is responsible for the administration of federal laws governing occupational safety and health, wage and hour standards, unemploy ...
formed the Child Labor Cocoa Coordinating Group as a public-private partnership with the governments of Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire to address child labor practices in the cocoa industry. The International Cocoa Initiative involving major cocoa manufacturers established the Child Labor Monitoring and Remediation System intended to monitor thousands of farms in Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire for child labor conditions, but the program reached less than 20% of the child laborers. Despite these efforts, goals to reduce child labor in West Africa by 70% before 2020 are frustrated by persistent poverty, absence of schools, expansion of cocoa farmland, and increased demand for cocoa.
In April 2018, the Cocoa Barometer report stated: "Not a single company or government is anywhere near reaching the sector-wide objective of the elimination of child labor, and not even near their commitments of a 70% reduction of child labor by 2020".
Fair trade
In the 2000s, some chocolate producers began to engage infair trade
Fair trade is an arrangement designed to help producers in developing countries achieve sustainable and equitable trade relationships. The fair trade movement combines the payment of higher prices to exporters with improved social and envir ...
initiatives, to address concerns about the marginalization of cocoa laborers in developing countries. Traditionally, Africa and other developing countries received low prices for their exported commodities such as cocoa, which caused poverty to abound. Fairtrade seeks to establish a system of direct trade from developing countries to counteract this unfair system. One solution for fair labor practices is for farmers to become part of an Agricultural cooperative
An agricultural cooperative, also known as a farmers' co-op, is a cooperative in which farmers pool their resources in certain areas of activity.
A broad typology of agricultural cooperatives distinguishes between agricultural service cooperati ...
. Cooperatives pay farmers a fair price for their cocoa so farmers have enough money for food, clothes, and school fees. One of the main tenets of fair trade is that farmers receive a fair price, but this does not mean that the larger amount of money paid for fair trade cocoa goes directly to the farmers. The effectiveness of fair trade has been questioned. In a 2014 article, ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Eco ...
'' stated that workers on fair trade farms have a lower standard of living than on similar farms outside the fair trade system.
Usage and consumption
Bars
 Chocolate is sold in
Chocolate is sold in chocolate bar
A chocolate bar (Commonwealth English) or candy bar (some dialects of American English) is a confection containing chocolate, which may also contain layerings or mixtures that include nuts, fruit, caramel, nougat, and wafers. A flat, easily brea ...
s, which come in dark chocolate, milk chocolate
Milk chocolate is a solid chocolate confectionery containing cocoa, sugar and milk. Chocolate was originally sold and consumed as a beverage in pre-Columbian times, and upon its introduction to Western Europe. Major milk chocolate producers incl ...
and white chocolate
White chocolate is a confectionery typically made of sugar, milk, and cocoa butter. It is pale ivory colored, and lacks many of the compounds found in milk and dark chocolates. It is solid at room temperature because the melting point of cocoa ...
varieties. Some bars that are mostly chocolate have other ingredients blended into the chocolate, such as nuts, raisins, or crisped rice. Chocolate is used as an ingredient in a huge variety of bars, which typically contain various confectionary ingredients (e.g., nougat
Nougat ( , ; ; az, nuqa; fa, نوقا) is a family of confections made with sugar or honey, roasted nuts (almonds, walnuts, pistachios, hazelnuts, and macadamia nuts are common), whipped egg whites, and sometimes chopped candied fruit. ...
, wafer
A wafer is a crisp, often sweet, very thin, flat, light and dry biscuit, often used to decorate ice cream, and also used as a garnish on some sweet dishes. Wafers can also be made into cookies with cream flavoring sandwiched between them. They ...
s, caramel
Caramel ( or ) is an orange-brown confectionery product made by heating a range of sugars. It can be used as a flavoring in puddings and desserts, as a filling in bonbons, or as a topping for ice cream and custard.
The process of carameli ...
, nuts, etc.) which are coated in chocolate.
Coating and filling
 Chocolate is used as a flavouring product in many
Chocolate is used as a flavouring product in many dessert
Dessert is a course that concludes a meal. The course consists of sweet foods, such as confections, and possibly a beverage such as dessert wine and liqueur. In some parts of the world, such as much of Greece and West Africa, and most parts o ...
s, such as chocolate cake
Chocolate cake or chocolate gâteau (from ) is a cake flavored with melted chocolate, cocoa powder, or both.
History
Chocolate cake is made with chocolate. It can also include other ingredients. These include fudge, vanilla creme, and other ...
s, chocolate brownie
A chocolate brownie or simply a brownie is a chocolate baked confection. Brownies come in a variety of forms and may be either fudgy or cakey, depending on their density. Brownies often, but not always, have a glossy "skin" on their upper crust ...
s, chocolate mousse
A mousse (; ; "foam") is a soft prepared food that incorporates air bubbles to give it a light and airy texture. Depending on preparation techniques, it can range from light and fluffy to creamy and thick. A mousse may be sweet or savory. as e ...
and chocolate chip cookies. Numerous types of candy
Candy, also called sweets (British English) or lollies (Australian English, New Zealand English), is a confection that features sugar as a principal ingredient. The category, called ''sugar confectionery'', encompasses any sweet confection, i ...
and snack
A snack is a small portion of food generally eaten between meals. Snacks come in a variety of forms including packaged snack foods and other processed foods, as well as items made from fresh ingredients at home.
Traditionally, snacks are ...
s contain chocolate, either as a filling (e.g., M&M's
M&M's (stylized as m&m's) are multi-colored button-shaped chocolates, each of which has the letter "m" printed in lower case in white on one side, consisting of a candy shell surrounding a filling which varies depending upon the variety of M&M ...
) or as a coating (e.g., chocolate-coated raisins or chocolate-coated peanuts).
Beverages
Some non-alcoholic beverages contain chocolate, such aschocolate milk
Chocolate milk is a type of flavoured milk made by mixing cocoa solids with milk (either dairy or plant-based). It is a food pairing in which the milk's mouthfeel masks the dietary fibres of the cocoa solids.
Types
The liquid carbohy ...
, hot chocolate
Hot chocolate, also known as hot cocoa or drinking chocolate, is a heated drink consisting of shaved chocolate, melted chocolate or cocoa powder, heated milk or water, and usually a sweetener like whipped cream or marshmallows. Hot chocolate ...
, chocolate milkshakes and tejate. Some alcoholic liqueurs are flavoured with chocolate, such as chocolate liqueur
Chocolate liqueur is a chocolate flavored liqueur made from a base liquor of whisky or vodka. Unlike chocolate liquor, chocolate liqueur does contain alcohol and is often used as a sweetening ingredient in mixology, baking, and cooking.
His ...
and creme de cacao
Chocolate liqueur is a chocolate flavored liqueur made from a base liquor of whisky or vodka. Unlike chocolate liquor, chocolate liqueur does contain alcohol and is often used as a sweetening ingredient in mixology, baking, and cooking.
His ...
. Chocolate is a popular flavour of ice cream
Ice cream is a sweetened frozen food typically eaten as a snack or dessert. It may be made from milk or cream and is flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit such as ...
and pudding
Pudding is a type of food. It can be either a dessert or a savoury (salty or spicy) dish served as part of the main meal.
In the United States, ''pudding'' means a sweet, milk-based dessert similar in consistency to egg-based custards, inst ...
, and chocolate sauce
Chocolate syrup is a sweet, chocolate-flavored condiment. It is often used as a topping or dessert sauce for various desserts, such as ice cream, or mixed with milk to make chocolate milk or blended with milk and ice cream to make a chocolate m ...
is a commonly added as a topping on ice cream sundae
A sundae () is an ice cream dessert of American origin that typically consists of one or more scoops of ice cream topped with sauce or syrup and in some cases other toppings such as: sprinkles, whipped cream, marshmallows, peanuts, maraschi ...
s. The caffè mocha
A mocha ( or ), also called mocaccino (), is a chocolate-flavoured warm beverage that is a variant of a caffè latte (), commonly served in a glass rather than a mug. Other commonly used spellings are mochaccino and also mochachino. The name ...
is an espresso
Espresso (, ) is a coffee-brewing method of Italian origin, in which a small amount of nearly boiling water (about ) is forced under of pressure through finely-ground coffee beans. Espresso can be made with a wide variety of coffee beans a ...
beverage containing chocolate.
Popular culture
Religious and cultural links
 Chocolate is associated with festivals such as
Chocolate is associated with festivals such as Easter
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the '' Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samue ...
, when moulded chocolate rabbits and eggs are traditionally given in Christian communities, and Hanukkah
or English translation: 'Establishing' or 'Dedication' (of the Temple in Jerusalem)
, nickname =
, observedby = Jews
, begins = 25 Kislev
, ends = 2 Tevet or 3 Tevet
, celebrations = Lighting candles each nig ...
, when chocolate coins are given in Jewish communities. Chocolate hearts and chocolate in heart-shaped boxes are popular on Valentine's Day
Valentine's Day, also called Saint Valentine's Day or the Feast of Saint Valentine, is celebrated annually on February 14. It originated as a Christian feast day honoring one or two early Christian martyrs named Saint Valentine and, thr ...
and are often presented along with flowers and a greeting card
A greeting card is a piece of card stock, usually with an illustration or photo, made of high quality paper featuring an expression of friendship or other sentiment. Although greeting cards are usually given on special occasions such as birthdays ...
. In 1868, Cadbury
Cadbury, formerly Cadbury's and Cadbury Schweppes, is a British multinational confectionery company fully owned by Mondelez International (originally Kraft Foods) since 2010. It is the second largest confectionery brand in the world after Mar ...
created a decorated box of chocolates in the shape of a heart for Valentine's Day. Boxes of filled chocolates quickly became associated with the holiday. Chocolate is an acceptable gift on other holidays and on occasions such as birthdays.
Many confectioners make holiday-specific chocolate candies. Chocolate Easter eggs or rabbits and Santa Claus
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnigh ...
figures are two examples. Such confections can be solid, hollow, or filled with sweets or fondant.
Books and film
Chocolate has been the center of several successful book and film adaptations. In 1964,Roald Dahl
Roald Dahl (13 September 1916 – 23 November 1990) was a British novelist, short-story writer, poet, screenwriter, and wartime fighter ace of Norwegian descent. His books have sold more than 250 million copies worldwide. Dahl has be ...
published a children's novel titled ''Charlie and the Chocolate Factory
''Charlie and the Chocolate Factory'' is a 1964 children's novel by British author Roald Dahl. The story features the adventures of young Charlie Bucket inside the chocolate factory of eccentric chocolatier Willy Wonka.
The story was originall ...
''. The novel centers on a poor boy named Charlie Bucket who takes a tour through the greatest chocolate factory in the world, owned by the eccentric Willy Wonka
Willy Wonka is a fictional character appearing in British author Roald Dahl's 1964 children's novel ''Charlie and the Chocolate Factory'' and its 1972 sequel '' Charlie and the Great Glass Elevator''. He is the eccentric founder and proprieto ...
. Two film adaptations of the novel were produced: ''Willy Wonka & the Chocolate Factory
''Willy Wonka & the Chocolate Factory'' is a 1971 American musical fantasy film directed by Mel Stuart and starring Gene Wilder as Willy Wonka. It is an adaptation of the 1964 novel '' Charlie and the Chocolate Factory'' by Roald Dahl. The fi ...
'' (1971) and ''Charlie and the Chocolate Factory
''Charlie and the Chocolate Factory'' is a 1964 children's novel by British author Roald Dahl. The story features the adventures of young Charlie Bucket inside the chocolate factory of eccentric chocolatier Willy Wonka.
The story was originall ...
'' (2005). A third adaptation, an origin prequel film titled '' Wonka'', is scheduled for release in 2023.
'' Like Water for Chocolate'' a 1989 love story by novelist Laura Esquivel
Laura Beatriz Esquivel Valdés (born September 30, 1950) is a Mexican novelist, screenwriter and politician, serving in the LXIII Legislature of the Mexican Congress in the Chamber of Deputies for the Morena Party from 2015 to 2018. Her first ...
, was adapted to film in 1992. '' Chocolat'', a 1999 novel by Joanne Harris
Joanne Michèle Sylvie Harris (born 3 July 1964) is an English-French author, best known for her novel '' Chocolat'' (1999), which was adapted the following year for the film '' Chocolat''.
Early life
Harris was born in Barnsley, Yorkshire, t ...
, was adapted for film in '' Chocolat'' which was released a year later.
See also
* ''Candida krusei
''Candida krusei'' is a budding yeast (a species of fungus) involved in chocolate production. ''Candida krusei'' is an emerging fungal nosocomial pathogen primarily found in the immunocompromised and those with hematological malignancies. It ha ...
''
* Candy making
Candy making or candymaking is the preparation and cookery of candies and sugar confections. Candy making includes the preparation of many various candies, such as hard candies, jelly beans, gumdrops, taffy, liquorice, cotton candy, choco ...
* Children in cocoa production
* Chocolataire
* Chocolate almonds
Chocolate-covered almonds are a confection created by covering almonds with chocolate.
History
In 1742, William Parks printed a copy of Eliza Smith's cookbook, ''The Compleat Housewife''. "Chocolate almonds" was the only chocolate recipe it contai ...
* Chocolate chip
Chocolate chips or chocolate morsels are small chunks of sweetened chocolate, used as an ingredient in a number of desserts (notably chocolate chip cookies and muffins), in trail mix and less commonly in some breakfast foods such as pancakes. ...
* Chocoholic
A chocoholic is a person who craves or compulsively consumes chocolate. The word "chocoholic" was first used in 1968, according to Merriam-Webster. It is a portmanteau of "chocolate" and "alcoholic". The term is used loosely or humorously to des ...
* '' Cuestión moral: si el chocolate quebranta el ayuno eclesiástico''
* List of chocolate-covered foods
This is a list of chocolate-covered foods. Chocolate is a typically sweet, usually brown, food preparation of ''Theobroma cacao'' seeds, roasted and ground, often flavored, as with vanilla. It is made in the form of a liquid, paste or in a block ...
* List of chocolate beverages
This is a list of notable chocolate drinks. Chocolate is a processed, typically sweetened food produced from the seed of the tropical ''Theobroma cacao'' tree. Its earliest documented use is by the Olmecs of south central Mexico around 1100 BC. ...
* List of chocolate companies
* ''Theobroma cacao
''Theobroma cacao'', also called the cacao tree and the cocoa tree, is a small ( tall) evergreen tree in the family Malvaceae. Its seeds, cocoa beans, are used to make chocolate liquor, cocoa solids, cocoa butter and chocolate. The largest pr ...
'', the cocoa/chocolate plant
* United States military chocolate
Military chocolate has been a part of the standard United States military ration since the original Ration D or D ration bar of 1937. Today, military chocolate is issued to troops as part of basic field rations and sundry packs. Chocolate rati ...
* Types of chocolate
Chocolate is a food product made from roasted and ground cocoa pods mixed with fat (e.g. cocoa butter) and powdered sugar to produce a solid confectionery. There are several types of chocolate, classified primarily according to the proportion ...
References
Further reading
* * * Norton, Marcy. ''Sacred Gifts, Profane Pleasures: A History of Tobacco and Chocolate in the Atlantic World'' (Cornell UP, 2008) * * Rosenblum, Mort (2006). ''Chocolate: A Bittersweet Saga of Dark and Light''. North Point Press. * Ryan, Órla (2011). ''Chocolate Nations: Living and Dying for Cocoa in West Africa''. Zed Books. * * Young, Allen M. (2007). ''The Chocolate Tree: A Natural History of Cacao'' (Rev. and expanded ed.). University Press of Florida. * *External links
* * * * * *Chocolate Tempering
"Chocolate and Tea"
American Enterprise Exhibition, National Museum of American History (exhibit on 18th century American trade) {{Authority control Aphrodisiac foods Articles containing video clips Baking Candy Cooking Desserts Mesoamerican cuisine Snack foods