Cephalopod Limb on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]






 All
All
Cephalopoda Glossary
Tree of Life web project. Barring a few exceptions,









 All
All cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda ( Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...
s possess flexible limbs extending from their heads and surrounding their beaks. These appendages, which function as muscular hydrostats, have been variously termed arms, legs or tentacles.
Description
In the scientific literature, a cephalopod ''arm'' is often treated as distinct from a ''tentacle
In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work main ...
'', though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, often with the latter acting as an umbrella term
In linguistics, semantics, general semantics, and ontologies, hyponymy () is a semantic relation between a hyponym denoting a subtype and a hypernym or hyperonym (sometimes called umbrella term or blanket term) denoting a supertype. In othe ...
for cephalopod limbs. Generally, arms have suckers along most of their length, as opposed to tentacles, which have suckers only near their ends.Young, R.E., M. Vecchione & K.M. Mangold 1999Cephalopoda Glossary
Tree of Life web project. Barring a few exceptions,
octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, ...
es have eight arms and no tentacles, while squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fittin ...
and cuttlefish
Cuttlefish or cuttles are marine molluscs of the order Sepiida. They belong to the class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of ...
have eight arms (or two "legs" and six "arms") and two tentacles.Norman, M. 2000. ''Cephalopods: A World Guide''. ConchBooks, Hackenheim. p. 15. "There is some confusion around the terms ''arms'' versus ''tentacles''. The numerous limbs of nautiluses are called tentacles. The ring of eight limbs around the mouth in cuttlefish, squids and octopuses are called ''arms''. Cuttlefish and squid also have a pair of specialised limbs attached between the bases of the third and fourth arm pairs .. These are known as ''feeding tentacles'' and are used to shoot out and grab prey." The limbs of nautiluses, which number around 90 and lack suckers altogether, are called cirri.
The tentacles of Decapodiformes are thought to be derived from the fourth arm pair of the ancestral coleoid, but the term ''arms IV'' is used to refer to the subsequent, ventral arm pair in modern animals (which is evolutionarily the fifth arm pair).
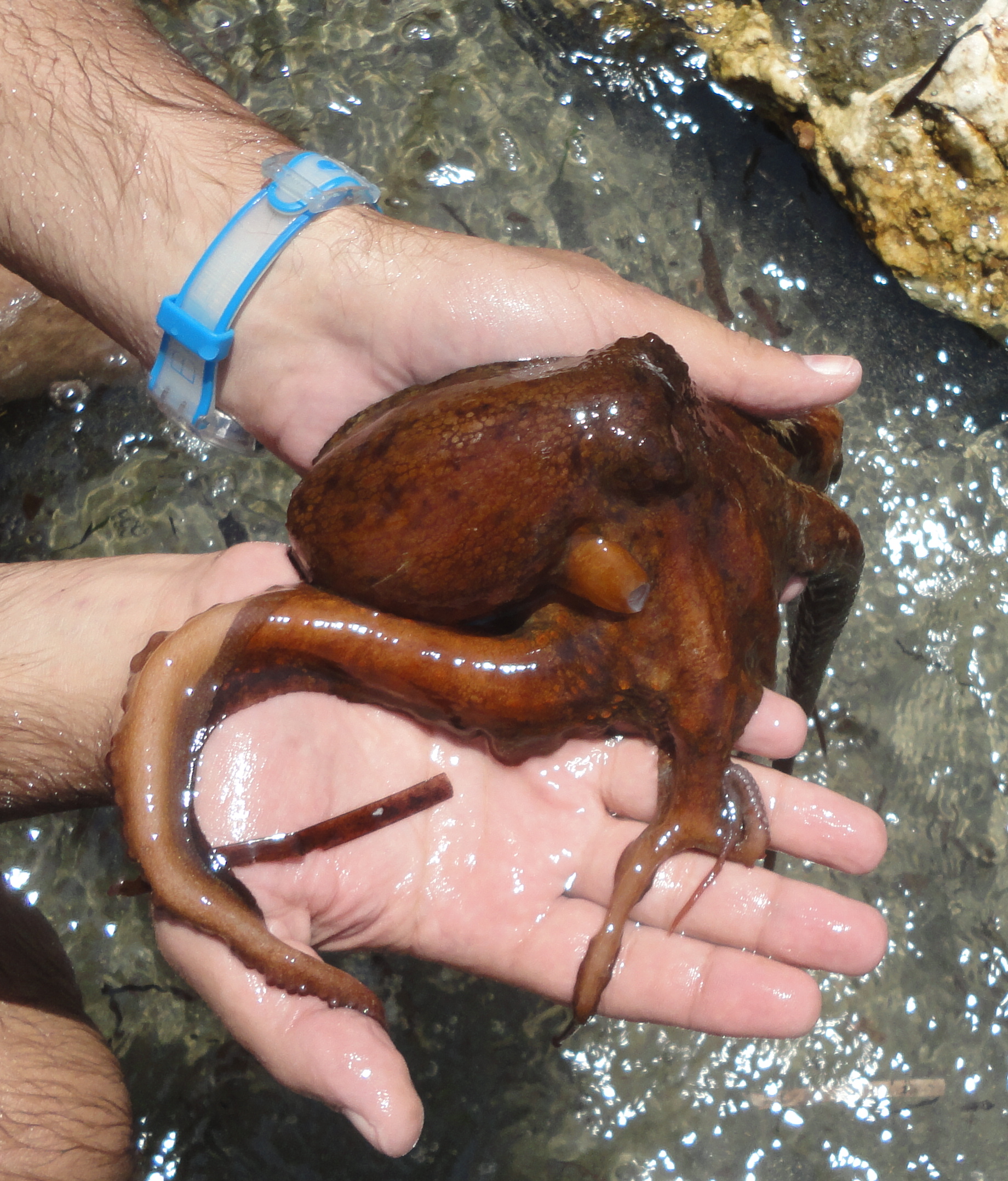
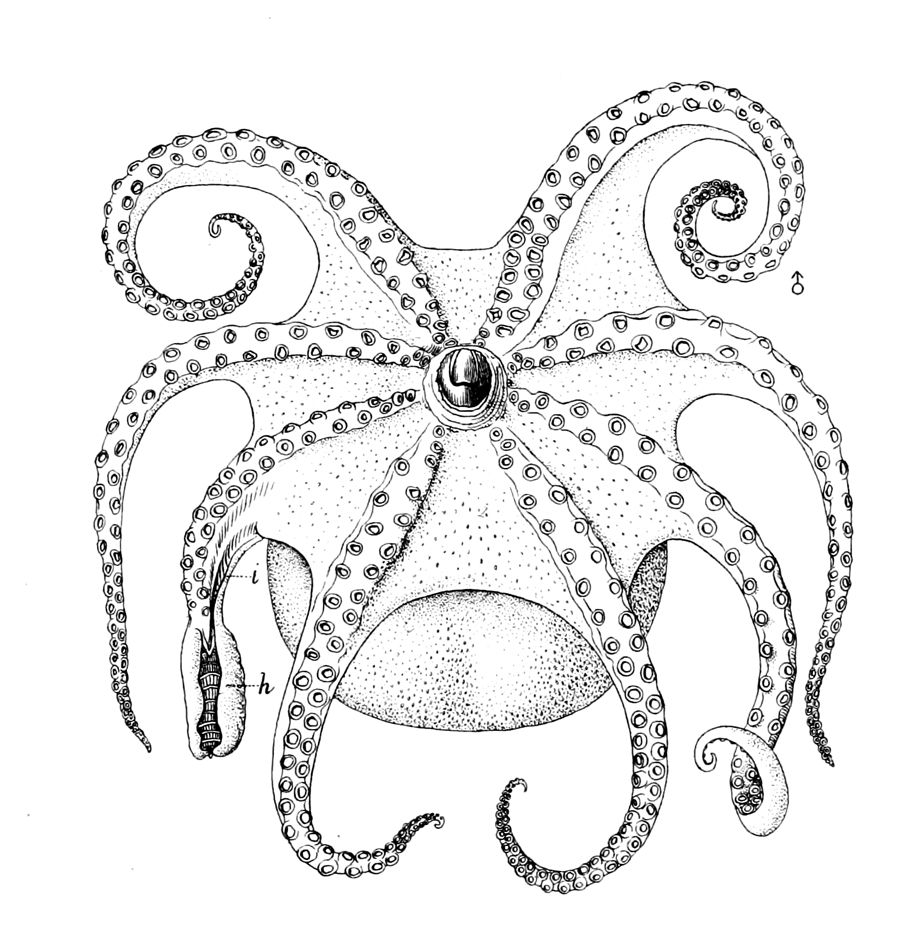
The males of most cephalopods develop a specialised arm for sperm delivery, the hectocotylus.
Anatomically, cephalopod limbs function using a crosshatch of helical collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whol ...
fibres in opposition to internal muscular hydrostatic pressure
Fluid statics or hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies the condition of the equilibrium of a floating body and submerged body " fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and the pressure in a fluid, or exerted by a fluid, on an i ...
.
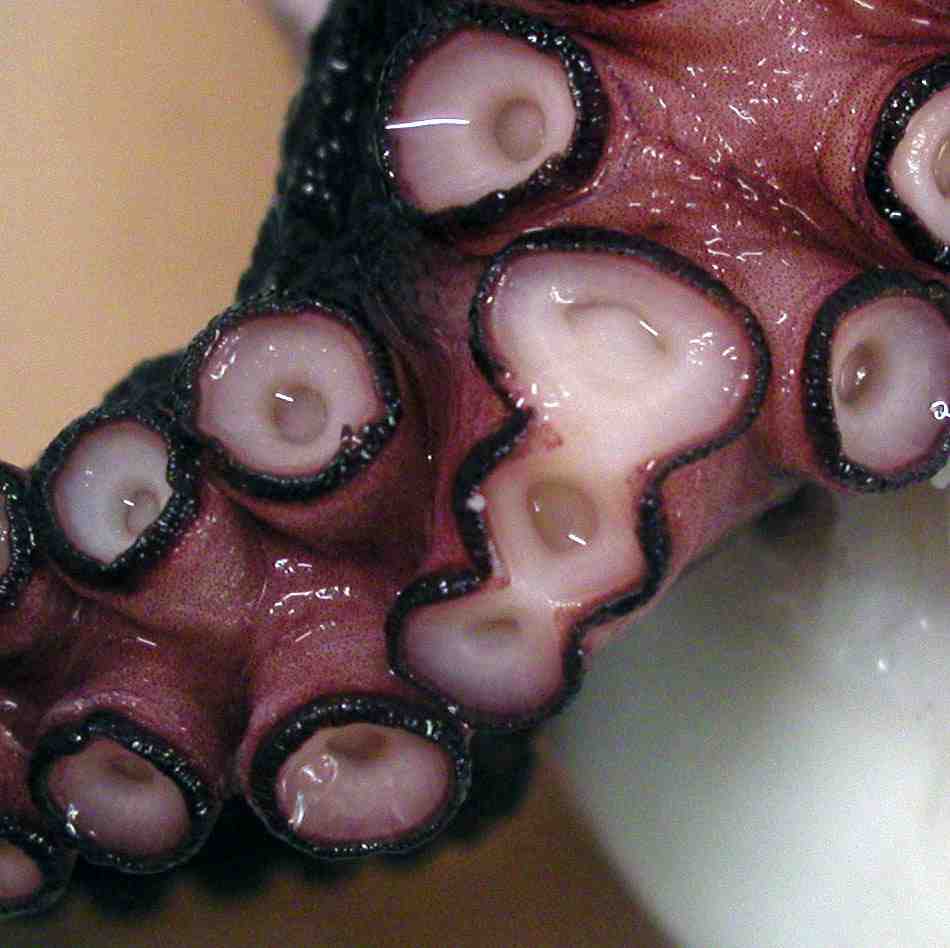
Suckers
Cephalopod limbs bear numerous suckers along their ventral surface as inoctopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, ...
, squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fittin ...
and cuttlefish
Cuttlefish or cuttles are marine molluscs of the order Sepiida. They belong to the class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of ...
arms and in clusters at the ends of the tentacles (if present), as in squid and cuttlefish. Each sucker is usually circular and bowl-like and has two distinct parts: an outer shallow cavity called an ''infundibulum'' and a central hollow cavity called an ''acetabulum''. Both of these structures are thick muscles, and are covered with a chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
ous cuticle to make a protective surface. Suckers are used for grasping substratum, catching prey and for locomotion. When a sucker attaches itself to an object, the infundibulum mainly provides adhesion while the central acetabulum is free. Sequential muscle contraction of the infundibulum and acetabulum causes attachment and detachment.
Abnormalities
Many octopus arm anomalies have been recorded, including a 6-armed octopus (nicknamed Henry the Hexapus), a 7-armed octopus, a 10-armed '' Octopus briareus'', one with a forked arm tip, octopuses with double or bilateral hectocotylization, and specimens with up to 96 arm branches. Branched arms and other limb abnormalities have also been recorded incuttlefish
Cuttlefish or cuttles are marine molluscs of the order Sepiida. They belong to the class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of ...
, squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fittin ...
, and bobtail squid.
Variability
Cephalopod limbs and the suckers they bear are shaped in many distinctive ways, and vary considerably between species. Some examples are shown below.Arms
For hectocotylized arms see hectocotylus variability.Tentacular clubs
Suckers
References
Notes
Citations
{{Cephalopod anatomy Cephalopod zootomy