Casemate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which guns are fired, in a
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which guns are fired, in a
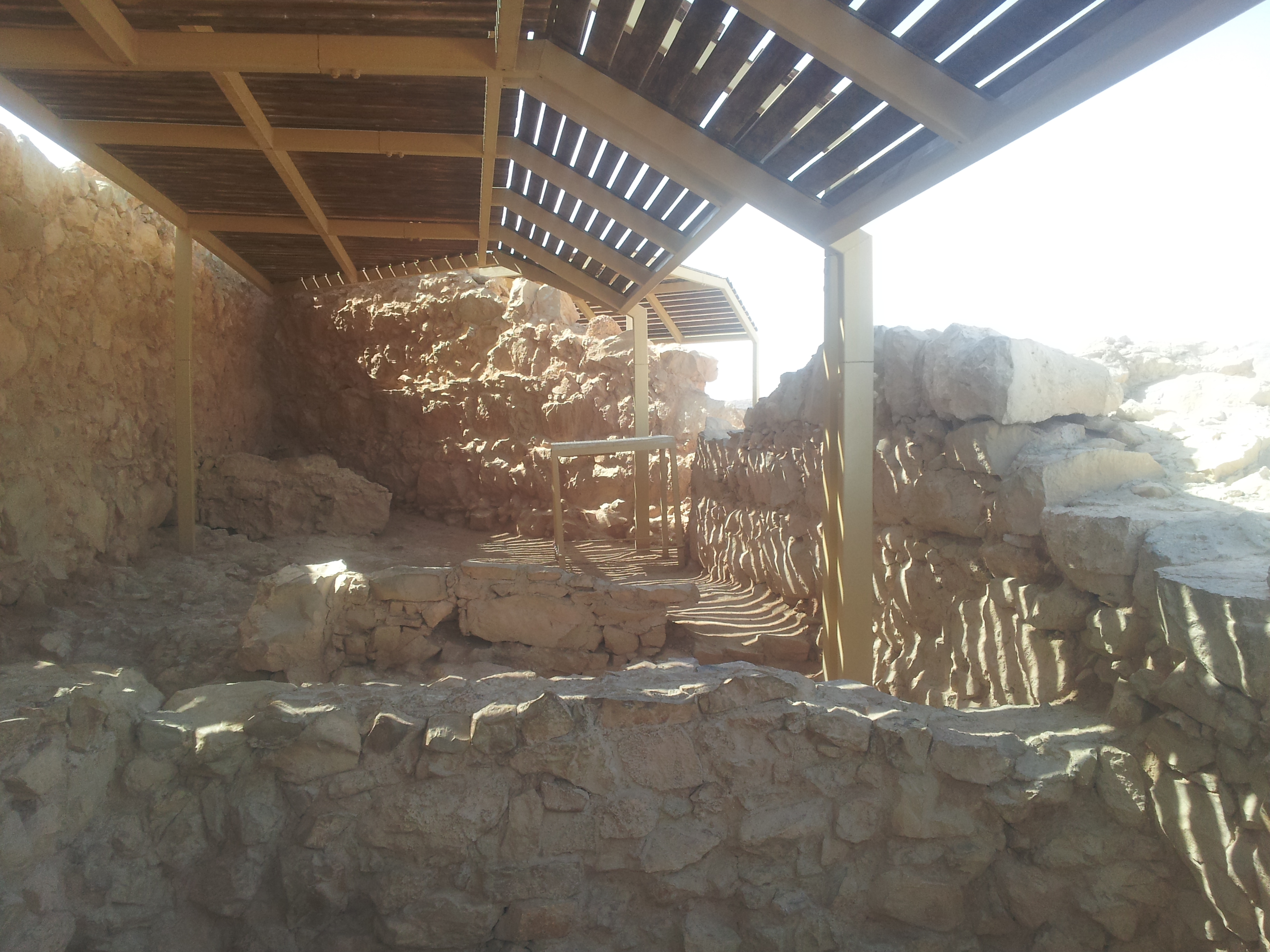 The term ''casemate wall'' is used in the archaeology of Israel/Palestine and the wider Near East, having the meaning of a double wall protecting a city or fortress, with transverse walls separating the space between the walls into chambers. These could be used as such, for storage or residential purposes, or could be filled with soil and rocks during siege in order to raise the resistance of the outer wall against battering rams. Originally thought to have been introduced to the region by the
The term ''casemate wall'' is used in the archaeology of Israel/Palestine and the wider Near East, having the meaning of a double wall protecting a city or fortress, with transverse walls separating the space between the walls into chambers. These could be used as such, for storage or residential purposes, or could be filled with soil and rocks during siege in order to raise the resistance of the outer wall against battering rams. Originally thought to have been introduced to the region by the
 In fortifications designed to resist artillery, a casemate was originally a vaulted chamber usually constructed underneath the
In fortifications designed to resist artillery, a casemate was originally a vaulted chamber usually constructed underneath the
 In the early 19th century, French military engineer Baron Haxo designed a free-standing casemate that could be built on the top of the rampart, to protect guns and gunners from the high-angle fire of mortars and howitzers.
In the early 19th century, French military engineer Baron Haxo designed a free-standing casemate that could be built on the top of the rampart, to protect guns and gunners from the high-angle fire of mortars and howitzers.
 The advantages of casemated artillery were proved in the
The advantages of casemated artillery were proved in the  Towards the end of the century,
Towards the end of the century,

 Following experience gained in the
Following experience gained in the
 In warship design the term "casemate" has been used in a number of ways, but it generally refers to a protected space for guns within a ship's hull or superstructure.
The first ironclad warship, the (1858), was a wooden steamship whose hull was covered with armored plating, tested to withstand the largest smoothbore guns available at the time. The response by the British
In warship design the term "casemate" has been used in a number of ways, but it generally refers to a protected space for guns within a ship's hull or superstructure.
The first ironclad warship, the (1858), was a wooden steamship whose hull was covered with armored plating, tested to withstand the largest smoothbore guns available at the time. The response by the British 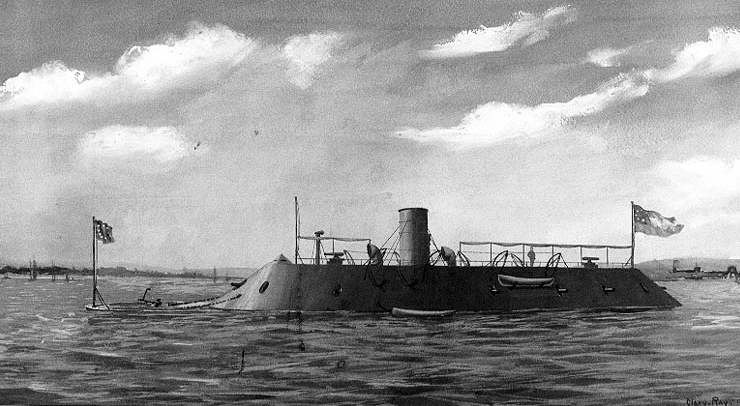 The
The
 A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which guns are fired, in a
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which guns are fired, in a fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere ...
, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
, the term "casemate wall" means a double city wall with the space between the walls separated into chambers, which could be filled up to better withstand battering rams in case of siege (see Antiquity: casemate wall).
In its original early modern meaning, the term referred to a vaulted chamber in a fort, which may have been used for storage, accommodation, or artillery which could fire through an opening or embrasure. Although the outward faces of brick or masonry casemates proved vulnerable to advances in artillery performance, the invention of reinforced concrete allowed newer designs to be produced well into the 20th century. With the introduction of ironclad warships, the definition was widened to include a protected space for guns in a ship, either within the hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
or in the lower part of the superstructure. Although the main armament of ships quickly began to be mounted in revolving gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanis ...
s, secondary batteries continued to be mounted in casemates; however several disadvantages eventually also led to their replacement by turrets. In tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful ...
s that do not have a turret for the main gun, the structure that accommodates the gun is also called a casemate.
Etymology
First recorded in French in the mid-16th century, from the Italian ''casamatta'' or Spanish ''casamata'', perhaps meaning a slaughterhouse, although it could derive from ''casa'' (in the sense of " hut"), and ''matta'' (Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
), "done with reeds and wickers", thus a low-roof hut without windows or other openings set in marshy place. It could also come from ''casa matta'' with in the sense of "false". However, it may have been ultimately derived from the Greek ''chásmata'' ( ''χάσματα''), a gap or aperture.
Antiquity: casemate wall
 The term ''casemate wall'' is used in the archaeology of Israel/Palestine and the wider Near East, having the meaning of a double wall protecting a city or fortress, with transverse walls separating the space between the walls into chambers. These could be used as such, for storage or residential purposes, or could be filled with soil and rocks during siege in order to raise the resistance of the outer wall against battering rams. Originally thought to have been introduced to the region by the
The term ''casemate wall'' is used in the archaeology of Israel/Palestine and the wider Near East, having the meaning of a double wall protecting a city or fortress, with transverse walls separating the space between the walls into chambers. These could be used as such, for storage or residential purposes, or could be filled with soil and rocks during siege in order to raise the resistance of the outer wall against battering rams. Originally thought to have been introduced to the region by the Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-cent ...
, this has been disproved by the discovery of examples predating their arrival, the earliest being at Ti'inik (Taanach) where such a wall has been dated to the 16th century BC. Casemate walls became a common type of fortification in the Southern Levant between the Middle Bronze Age (MB) and Iron Age II, being more numerous during the Iron Age and peaking in Iron Age II (10th-6th century BC). However, the construction of casemate walls had begun to be replaced by sturdier solid walls by the 9th century BC, probably due the development of more effective battering rams by the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew ...
. Casemate walls could surround an entire settlement, but most only protected part of it. The three different types included freestanding casemate walls, then integrated ones where the inner wall was part of the outer buildings of the settlement, and finally filled casemate walls, where the rooms between the walls were filled with soil right away, allowing for a quick, but nevertheless stable construction of particularly high walls.
Modern period
Land fortification
Early modern period
 In fortifications designed to resist artillery, a casemate was originally a vaulted chamber usually constructed underneath the
In fortifications designed to resist artillery, a casemate was originally a vaulted chamber usually constructed underneath the rampart
Rampart may refer to:
* Rampart (fortification), a defensive wall or bank around a castle, fort or settlement
Rampart may also refer to:
* "O'er the Ramparts We Watched" is a key line from " The Star-Spangled Banner", the national anthem of the ...
. It was intended to be impenetrable and could be used for sheltering troops or stores. With the addition of an embrasure through the scarp
Scarp may refer to:
Landforms and geology
* Cliff, a significant vertical, or near vertical, rock exposure
* Escarpment, a steep slope or long rock that occurs from erosion or faulting and separates two relatively level areas of differing elevatio ...
face of the rampart, it could be used as a protected gun position. In bastion forts, artillery casemates were sometimes built into the flanks of bastions, but in action they quickly filled with smoke making them inoperable and for that reason, had fallen out of favor during the 17th century.
18th and 19th centuries
Three tiers of artillery casemates at the mid-19th century Fort Point, San Francisco In the late 18th century,Marc René, marquis de Montalembert
Marc René, marquis de Montalembert (16 July 1714 – 29 March 1800) was a French military engineer and writer, known for his work on fortifications.
Life
He was born at Angoulême, and entered the French Army in 1732. He fought in the War of t ...
(1714–1800) experimented with improved casemates for artillery, with ventilation systems that overcame the problem of smoke dispersal found in earlier works. For coastal fortifications, he advocated multi-tiered batteries of guns in masonry casemates, that could bring concentrated fire to bear on passing warships. In 1778, he was commissioned to build a fort on the Île-d'Aix, defending the port of Rochefort, Charente-Maritime
Rochefort ( oc, Ròchafòrt), unofficially Rochefort-sur-Mer (; oc, Ròchafòrt de Mar, link=no) for disambiguation, is a city and commune in Southwestern France, a port on the Charente estuary. It is a subprefecture of the Charente-Maritime ...
. The outbreak of the Anglo-French War forced him to hastily to build his casemated fort from wood but he was able to prove that his well-designed casemates were capable of operating without choking the gunners with smoke. The defenses of the new naval base at Cherbourg
Cherbourg (; , , ), nrf, Chèrbourg, ) is a former commune and subprefecture located at the northern end of the Cotentin peninsula in the northwestern French department of Manche. It was merged into the commune of Cherbourg-Octeville on 28 Febr ...
were later constructed according to his system. After seeing Montalembert's coastal forts, American engineer Jonathan Williams acquired a translation of his book and took it to the United States, where it inspired the Second and Third Systems of coastal fortification; the first fully developed example being Castle Williams
Castle Williams is a circular fortification of red sandstone on the northwest point of Governors Island, part of a system of forts designed and constructed in the early 19th century to protect New York City from naval attack. It is a prominent ...
in New York Harbor which was started in 1807.
 In the early 19th century, French military engineer Baron Haxo designed a free-standing casemate that could be built on the top of the rampart, to protect guns and gunners from the high-angle fire of mortars and howitzers.
In the early 19th century, French military engineer Baron Haxo designed a free-standing casemate that could be built on the top of the rampart, to protect guns and gunners from the high-angle fire of mortars and howitzers.
 The advantages of casemated artillery were proved in the
The advantages of casemated artillery were proved in the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
of 1853-1856, when attempts by the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
to subdue the casemated Russian forts at Kronstadt were unsuccessful, while a casemated gun tower at Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
, the Malakoff Tower
Malakoff Tower ( pt, Torre Malakoff) is a tower located in Recife Antigo, Recife. This monument was built between 1835 and 1855 to be used as an observatory and as the main entrance and gateway for ''Arsenal da Marinha'' (Navy Arsenals) square. ...
, could only be captured by a surprise French infantry attack while the garrison was being changed. In the early 1860s, the British, apprehensive about a possible French invasion, fortified the naval dockyards of southern England with curved batteries of large guns in casemates, fitted with laminated iron shields tested to withstand the latest projectiles.
However, in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
(1861-1865), the exposed masonry of casemate batteries was found to be vulnerable to modern rifled artillery; Fort Pulaski
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
was quickly breached in a few hours by only ten of these guns. In contrast, hastily constructed earthworks proved much more resilient. This led to casemates for artillery again falling out of favor. In continental Europe, they were often replaced by rotating gun turrets, but elsewhere large coastal guns were mounted in less expensive concrete gun pits or barbette
Barbettes are several types of gun emplacement in terrestrial fortifications or on naval ships.
In recent naval usage, a barbette is a protective circular armour support for a heavy gun turret. This evolved from earlier forms of gun protectio ...
s, sometimes using disappearing carriages to conceal the gun except at the moment of firing. Casemates for secure barrack accommodation and storage continued to be built; the 1880s French forts of the Séré de Rivières system for example, had a central structure consisting of two stories of casemates, buried under layers of earth, concrete and sand to a depth of , intended to defeat the new high explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An ...
shells.
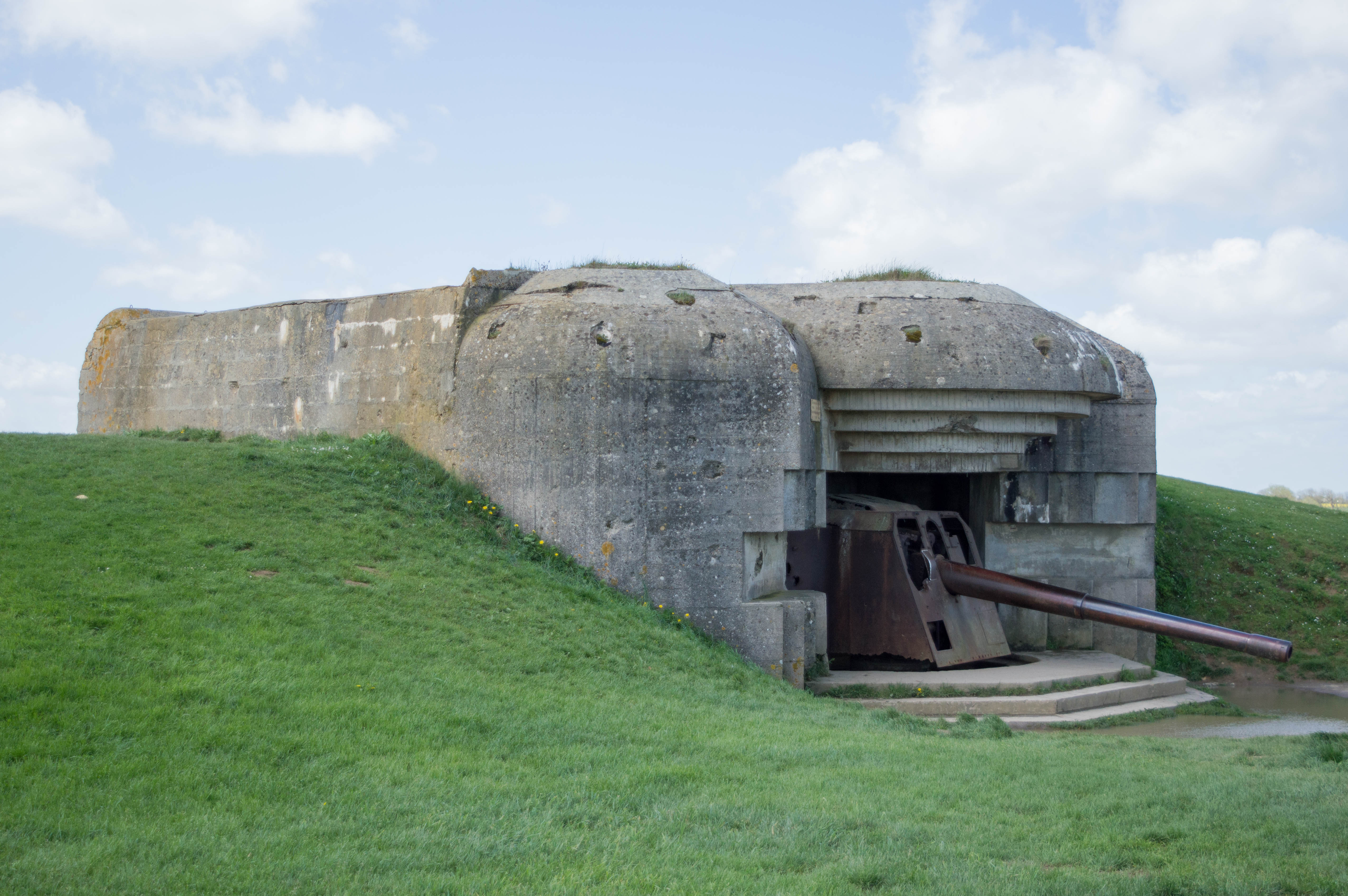
 Towards the end of the century,
Towards the end of the century, Imperial Germany
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
had developed a new form of fortification called a ''feste'' ( German article: ''Festung#Feste''), in which the various elements of each fort were more widely dispersed in the landscape. These works, the first of which was Fort de Mutzig near Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
, had separate artillery blocks, infantry positions and underground barracks, all built of reinforced concrete and connected by tunnels or entrenchments. Although the main armament of these forts was still mounted in armored turrets, local defense was provided by separate protected positions for field guns; these concrete structures were copied by the French who called them ''casemates de Bourges'' ( French article: ''Casemate de Bourges'') after the proving ground where they had been tested.
20th century

 Following experience gained in the
Following experience gained in the World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, French engineers began to design a new scheme of fortifications to protect their eastern border, which became known as the Maginot Line. The main element of this line were large underground forts based on the ''feste'' principle, whose main armament was in turrets, however the countryside between them was defended by smaller self-sufficient works based on the earlier ''casemates de bourges'', housing either light field guns or anti-tank guns. As the World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
approached, similar casemate designs were adopted by other European nations as they offered protection from attacking aircraft. The German Organisation Todt undertook the development of casemates for thé large coastal guns of the Atlantic Wall
The Atlantic Wall (german: link=no, Atlantikwall) was an extensive system of coastal defences and fortifications built by Nazi Germany between 1942 and 1944 along the coast of continental Europe and Scandinavia as a defence against an anticip ...
. Built of concrete up to thick, they were thought to be able to withstand any form of attack. Work by the Western Allies to develop countermeasures that could defeat casemates and other types of bunker resulted in weapons such as tank-mounted spigot mortars, rocket-assisted projectiles, recoilless rifles, various types of demolition charge and earthquake bombs.
Naval
 In warship design the term "casemate" has been used in a number of ways, but it generally refers to a protected space for guns within a ship's hull or superstructure.
The first ironclad warship, the (1858), was a wooden steamship whose hull was covered with armored plating, tested to withstand the largest smoothbore guns available at the time. The response by the British
In warship design the term "casemate" has been used in a number of ways, but it generally refers to a protected space for guns within a ship's hull or superstructure.
The first ironclad warship, the (1858), was a wooden steamship whose hull was covered with armored plating, tested to withstand the largest smoothbore guns available at the time. The response by the British Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
to this perceived threat was to build an iron-hulled frigate, . However, it was realised that to armor all of the hull to fully withstand the latest rifled artillery would make it unfeasibly heavy, so it was decided to create an armored box or casemate around the main gun deck, leaving the bow and stern unarmored.
 The
The American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
saw the use of casemate ironclads: armored steamboats with a very low freeboard and their guns on the main deck ('Casemate deck') protected by a sloped armoured casemate, which sat atop the hull. Although both sides of the Civil War used casemate ironclads, the ship is mostly associated with the southern Confederacy, as the north also employed turreted monitors
Monitor or monitor may refer to:
Places
* Monitor, Alberta
* Monitor, Indiana, town in the United States
* Monitor, Kentucky
* Monitor, Oregon, unincorporated community in the United States
* Monitor, Washington
* Monitor, Logan County, West ...
, which the south was unable to produce. The most famous naval battle of the war was the duel at Hampton Roads between the Union turreted ironclad and the Confederate casemate ironclad (built from the scuttled remains of ).
"Casemate ship" was an alternative term for " central battery ship" (UK) or "center battery ship" (US).Hovgaard, William, ''Modern History of Warships'', pp. 14–15. The casemate (or central battery) was an armored box that extended the full width of the ship protecting many guns. The armored sides of the box were the sides of hull of the ship. There was an armored bulkhead at the front and rear of the casemate, and a thick deck protecting the top. The lower edge of the casemate sat on top of ship's belt armour. Some ships, such as (laid down 1873), had a two-story casemate.Hovgaard, William, ''Modern History of Warships'', p. 18.
A "casemate" was an armored room in the side of a warship, from which a gun would fire. A typical casemate held a 6-inch gun, and had a front plate (forming part of the side of the ship), with thinner armor plates on the sides and rear, with a protected top and floor,Hovgaard, William, ''Modern History of Warships'', pp. 78–79. and weighed about 20 tons (not including the gun and mounting).Brown, David K, ''Warrior to Dreadnought'', p. 129. Casemates were similar in size to turrets; ships carrying them had them in pairs, one on each side of the ship.
left, Casemate-mounted 5"/50 caliber gun on
The first battleships to carry them were the British laid down in 1889. They were adopted as a result of live-firing trials against in 1888.Brown, David K, ''Warrior to Dreadnought'', pp. 101–02, 129. Casemates were adopted because it was thought that the fixed armor plate at the front would provide better protection than a turret, and because a turret mounting would require external power and could therefore be put out of action if power were lost – unlike a casemate gun, which could be worked by hand. The use of casemates enabled the 6-inch guns to be dispersed, so that a single hit would not knock out all of them. Casemates were also used in protected and armored cruisers, starting with the 1889 .Brown, David K, ''Warrior to Dreadnought'', pp. 134–35. and retrofitted to the 1888 during construction.
In the pre-dreadnought generation of warships, casemates were placed initially on the main deck, and later on the upper deck as well. Casemates on the main deck were very close to the waterline. In the ''Edgar''-class cruisers, the guns in the casemates were only above the waterline.Brown, David K, ''Warrior to Dreadnought'', p. 136. Casemates that were too close to the waterline or too close to the bow (such as in the 1912 ''Iron Duke''-class dreadnoughts) were prone to flooding, making the guns ineffective.Brown, David K, ''The Grand Fleet, Warship Design and Developments 1906–1922'', p. 42.
Casemates on the , showing their vulnerability to flooding
Shipboard casemate guns were partially rendered obsolete by the arrival of "all-big gun" battleship, pioneered by in 1906, but were reintroduced as the increasing torpedo threat from destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed ...
s forced an increase in secondary armament calibre. Many battleships had their casemates plated over during modernization in the 1930s (or after the Attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii ...
, in the case of US vessels) but some, like carried them to the end of World War II. The last ships built with casemates as new construction were the American s of the early 1920s and the 1933 Swedish aircraft cruiser . In both cases the casemates were built into the forward angles of the forward superstructure (and the aft superstructure as well, in the Omahas).
Armoured vehicles
A Jagdtiger, an example of a casemate armoured vehicle The Swedish Strv 103 was used until the 1990s In regards to armored fighting vehicles, casemate design refers to vehicles that have their main gun mounted directly within the hull and lack the rotatingturret
Turret may refer to:
* Turret (architecture), a small tower that projects above the wall of a building
* Gun turret, a mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon
* Objective turret, an indexable holder of multiple lenses in an optical microscope
* M ...
commonly associated with tanks. Such a design generally makes the vehicle mechanically simpler in design, less costly in construction, lighter in weight and lower in profile. The saved weight can be used to mount a heavier, more powerful gun or alternatively increase the vehicle's armor protection in comparison to regular, turreted tanks. However, in combat the crew has to rotate the entire vehicle if an enemy target presents itself outside of the vehicle's limited gun traverse arc. This can prove very disadvantageous in combat situations.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, casemate-type armored fighting vehicles were heavily used by both the combined German Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
forces, and the Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
. They were mainly employed as tank destroyers and assault guns. Tank destroyers, intended to operate mostly from defensive ambush operations, did not need a rotating turret as much as offensively used tanks, while assault guns were mainly used against fortified infantry positions and could afford a longer reaction time if a target presented itself outside the vehicle's gun traverse arc. Thus, the weight and complexity of a turret was thought to be unnecessary, and could be saved in favor of more capable guns and armor. In many cases, casemate vehicles would be used as both tank destroyers or assault guns, depending on the tactical situation. The Wehrmacht employed several casemate tank destroyers, initially with the still-''Panzerjäger
''Panzerjäger'' (German "armour-hunters" or "tank-hunters", abbreviated to ''Pz.Jg.'' in German) was a branch of service of the German Wehrmacht during the Second World War. It was an anti-tank arm-of-service that operated self-propelled a ...
'' designation '' Elefant'' with an added, fully enclosed five-sided (including its armored roof) casemate atop the hull, with later casemate-style tank destroyers bearing the '' Jagdpanzer'' (literally 'hunting tank') designation, with much more integration of the casemate's armour with the tank hull itself. Examples are the Jagdpanzer IV, the Jagdtiger
The ''Jagdtiger'' ("Hunting Tiger"; officially designated ''Panzerjäger Tiger Ausf. B'') is a German casemate-type heavy tank destroyer ('' Jagdpanzer'') of World War II. It was built upon the slightly lengthened chassis of a Tiger II. Its o ...
and the Jagdpanther.These translate as 'Hunting Tiger' and 'Hunting Panther', respectively Assault guns were designated as 'Sturmgeschütz', like the Sturmgeschütz III and Sturmgeschütz IV. In the Red Army, casemate tank destroyers and self-propelled guns bore an "SU-" or "ISU-" prefix, with the "SU-" prefix an abbreviation for Samokhodnaya Ustanovka, or "self-propelled gun". Examples are the SU-100 or the ISU-152. Both Germany and the Soviet Union mainly built casemate AFVs by using the chassis of already existing turreted tanks, instead of designing them from scratch.
While casemate AFVs played a very important role in World War II (the ''Sturmgeschütz'' III for example was the most numerous armored fighting vehicle of the German Army during the entire war), they became much less common in the post-war period. Heavy casemate tank destroyer designs such as the US T28 and the British Tortoise never went beyond prototype status, while casemate vehicles of a more regular weight, such as the Soviet SU-122-54, saw only very limited service. The general decline of casemate vehicles can be seen in the technological progress which resulted in the rise of universal main battle tanks, which unified in them the capability to take up the roles and tasks which in the past had to be diverted between several different classes of vehicles. However, vehicles such as the German Kanonenjagdpanzer of the 1960s still let the casemate concept live on, while the Swedish Army went as far as employing a casemate tank design, the Stridsvagn 103
The Stridsvagn 103 (Strv 103), also known as the Alternative S and S-tank, is a Swedish post- World War II main battle tank, designed and manufactured in Sweden. "Strv" is the Swedish military abbreviation of ''stridsvagn'', Swedish for chariot ...
, or "S-Tank", as their main armored fighting vehicle from the 1960s until the 1990s, favoring it over contemporary turreted designs. Other casemate design ideas, such as the projected German Versuchsträger 1–2 with two main guns, were developed even later.
See also
* Bunker *Fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere ...
* Gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanis ...
* Pillbox (military)
References
External links
* {{Authority control Fortification (architectural elements) Weapon fixtures