cartilaginous on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the 
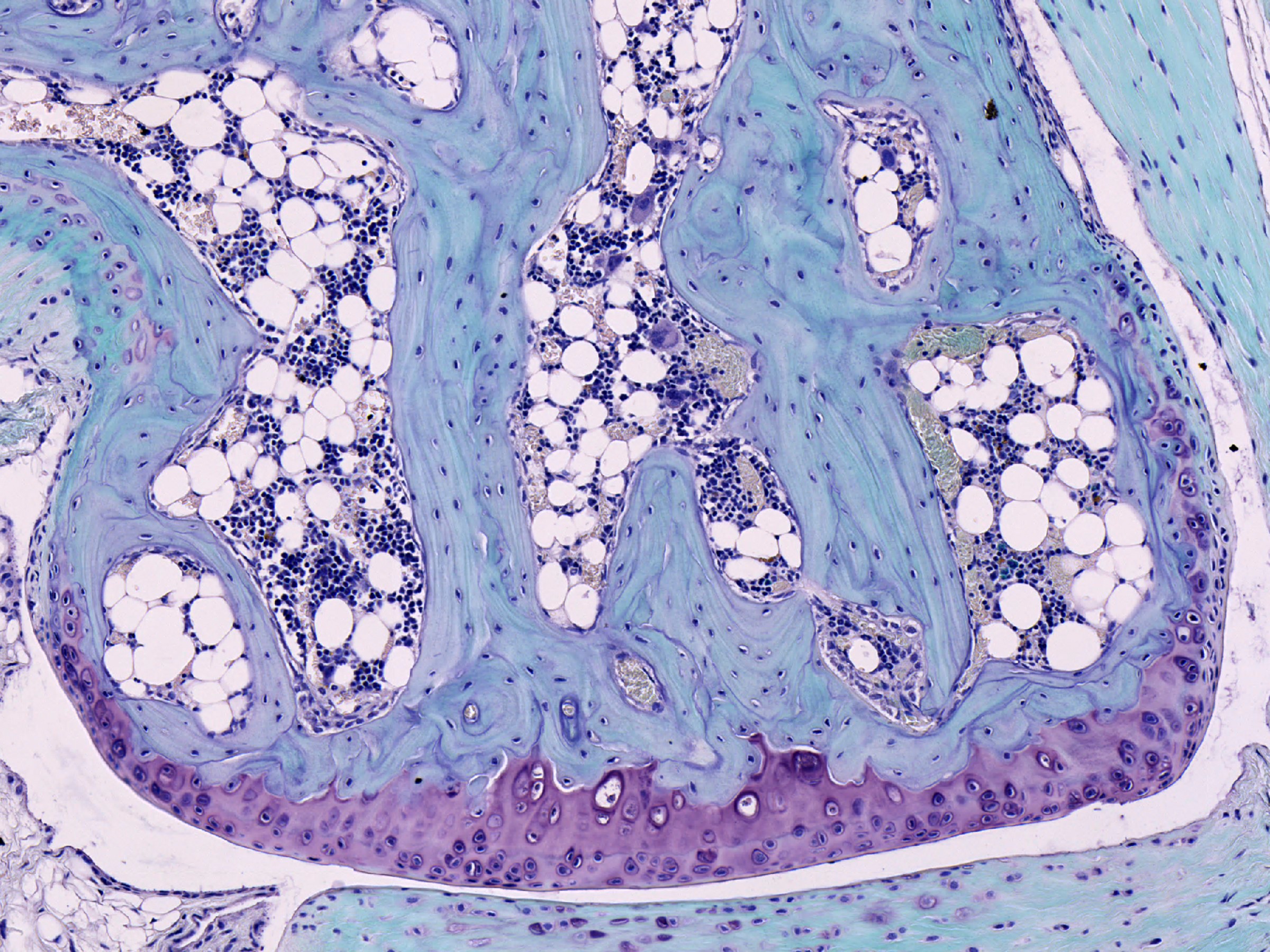 The articular cartilage function is dependent on the molecular composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM consists mainly of
The articular cartilage function is dependent on the molecular composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM consists mainly of


Eflora – Glossary
University of Sydney (2010-06-16). Retrieved on 2015-10-26.
Cartilage.org
International Cartilage Regeneration & Joint Preservation Society
, Cartilage tutorial, University of Kansas Medical Center
text from Gray's anatomy
I've heard 'Ears and nose do not ever stop growing.' Is this false?
CartilageHealth.com
Information on Articular Cartilage Injury Prevention, Repair and Rehabilitation
Osteoarthritis
Cartilage types
Different cartilages
on TheFreeDictionary
Cartilage photomicrographs
{{Authority control Skeletal system Connective tissue
ends
End, END, Ending, or variation, may refer to:
End
*In mathematics:
**End (category theory)
**End (topology)
**End (graph theory)
** End (group theory) (a subcase of the previous)
** End (endomorphism)
*In sports and games
**End (gridiron football ...
of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) and translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-gray in color, with a firm consistency and has ...
, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a se ...
, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. ...
, but also in cyclostomes Cyclostome is a biological term (from the Greek for "round mouth") used in a few different senses:
* for the taxon Cyclostomi, which comprises the extant jawless fishes: the hagfish (Myxini) and the lampreys (Petromyzontidae). This was thought for ...
, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycan
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case ...
s, proteoglycan
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to whi ...
s, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin
Elastin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ELN'' gene. Elastin is a key component of the extracellular matrix in gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates). It is highly elastic and present in connective tissue allowing many tissues in the bo ...
.
Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment sit ...
and carina
Carina may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Carina, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina Heights, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina, Victoria, a locality in Mildura
Serbia
* Carina, Osečina, a village in the Kolubara District
...
.
Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocyte
Chondrocytes (, from Greek χόνδρος, ''chondros'' = cartilage + κύτος, ''kytos'' = cell) are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteo ...
s that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in proteoglycan
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to whi ...
and elastin fibers. Cartilage is classified in three types, ''elastic cartilage
Elastic cartilage, fibroelastic cartilage or yellow fibrocartilage is a type of cartilage present in the pinnae (auricles) of the ear giving it shape, provides shape for the lateral region of the external auditory meatus, medial part of the audit ...
'', '' hyaline cartilage'' and ''fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of ...
'', which differ in relative amounts of collagen and proteoglycan.
Cartilage does not contain blood vessels or nerves. Some fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of ...
such as the meniscus
Meniscus may refer to:
*Meniscus (anatomy), crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structure that partly divides a joint cavity
*Meniscus (liquid), a curve in the upper surface of liquid contained in an object
*Meniscus (optics)
A lens is a tr ...
of the knee does however have blood supply in part. Nutrition is supplied to the chondrocytes by diffusion. The compression of the articular cartilage or flexion of the elastic cartilage generates fluid flow, which assists the diffusion of nutrients to the chondrocytes. Compared to other connective tissues, cartilage has a very slow turnover of its extracellular matrix and is documented to repair at only a very slow rate relative to other tissues.

Structure
Development
In embryogenesis, the skeletal system is derived from the mesoderm germ layer. Chondrification (also known as chondrogenesis) is the process by which cartilage is formed from condensedmesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every ...
tissue, which differentiates into chondroblasts and begins secreting the molecules (aggrecan and collagen type II) that form the extracellular matrix. In all vertebrates, cartilage is the main skeletal tissue in early ontogenetic stages; in osteichthyans, many cartilaginous elements subsequently ossify through endochondral
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the mammalian skeletal system by which bone tissue is produced. Unlike intramembranous ossification, the other process by which bone tissue is produced, ...
and perichondral ossification.
Following the initial chondrification that occurs during embryogenesis, cartilage growth consists mostly of the maturing of immature cartilage to a more mature state. The division of cells within cartilage occurs very slowly, and thus growth in cartilage is usually not based on an increase in size or mass of the cartilage itself. It has been identified that non-coding RNAs (e.g. miRNAs and long non-coding RNAs) as the most important epigenetic modulators can affect the chondrogenesis. This also justifies the non-coding RNAs' contribution in various cartilage-dependent pathological conditions such as arthritis, and so on.
Articular cartilage
 The articular cartilage function is dependent on the molecular composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM consists mainly of
The articular cartilage function is dependent on the molecular composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM consists mainly of proteoglycan
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to whi ...
and collagens. The main proteoglycan in cartilage is aggrecan, which, as its name suggests, forms large aggregates with hyaluronan. These aggregates are negatively charged and hold water in the tissue. The collagen, mostly collagen type II, constrains the proteoglycans. The ECM responds to tensile and compressive forces that are experienced by the cartilage. Cartilage growth thus refers to the matrix deposition, but can also refer to both the growth and remodeling of the extracellular matrix. Due to the great stress on the patellofemoral joint during resisted knee extension, the articular cartilage of the patella is among the thickest in the human body.
Function
Mechanical properties
The mechanical properties of articular cartilage in load-bearing joints such as the knee and hip have been studied extensively at macro, micro, and nano-scales. These mechanical properties include the response of cartilage in frictional, compressive, shear and tensile loading. Cartilage is resilient and displaysviscoelastic
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist shear flow and strain linearly ...
properties.
Frictional properties
Lubricin
Proteoglycan 4 or lubricin is a proteoglycan that in humans is encoded by the ''PRG4'' gene. It acts as a joint/ boundary lubricant.
Function
Lubricin is present in synovial fluid and on the surface (superficial layer) of articular cartilage ...
, a glycoprotein abundant in cartilage and synovial fluid, plays a major role in bio-lubrication and wear protection of cartilage.
Repair
Cartilage has limited repair capabilities: Because chondrocytes are bound in lacunae, they cannot migrate to damaged areas. Therefore,cartilage damage
Cartilage structures and functions can be damaged. Such damage can result from a variety of causes, such as a bad fall or traumatic sport-accident, previous knee injuries or wear and tear over time. Immobilization for long periods can also result i ...
is difficult to heal. Also, because hyaline cartilage does not have a blood supply, the deposition of new matrix is slow. Over the last years, surgeons and scientists have elaborated a series of cartilage repair procedures that help to postpone the need for joint replacement. A tear of the meniscus of the knee cartilage can often be surgically trimmed to reduce problems.
Biological engineering
Biological engineering or
bioengineering is the application of principles of biology and the tools of engineering to create usable, tangible, economically-viable products. Biological engineering employs knowledge and expertise from a number o ...
techniques are being developed to generate new cartilage, using a cellular "scaffolding" material and cultured cells to grow artificial cartilage. Extensive researches have been conducted on freeze-thawed PVA hydrogel
A hydrogel is a crosslinked hydrophilic polymer that does not dissolve in water. They are highly absorbent yet maintain well defined structures. These properties underpin several applications, especially in the biomedical area. Many hydrogels ar ...
s as a base material for such a purpose. These gels have exhibited great promises in terms of biocompatibility, wear resistance, shock absorption, friction coefficient, flexibility, and lubrication, and thus are considered superior to polyethylene-based cartilages. A two-year implantation of the PVA hydrogels as artificial meniscus in rabbits showed that the gels remain intact without degradation, fracture, or loss of properties.
Clinical significance

Disease
Several diseases can affect cartilage. Chondrodystrophies are a group of diseases, characterized by the disturbance of growth and subsequent ossification of cartilage. Some common diseases that affect the cartilage are listed below. * Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is a disease of the whole joint, however, one of the most affected tissues is the articular cartilage. The cartilage covering bones (articular cartilage—a subset of hyaline cartilage) is thinned, eventually completely wearing away, resulting in a "bone against bone" within the joint, leading to reduced motion, and pain. Osteoarthritis affects the joints exposed to high stress and is therefore considered the result of "wear and tear" rather than a true disease. It is treated byarthroplasty
Arthroplasty (literally " e-orming of joint") is an orthopedic surgical procedure where the articular surface of a musculoskeletal joint is replaced, remodeled, or realigned by osteotomy or some other procedure. It is an elective procedure that i ...
, the replacement of the joint by a synthetic joint often made of a stainless steel alloy (cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, pro ...
chromoly) and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE). Chondroitin sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars ( N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroitin chain can have over ...
or glucosamine sulfate supplements, have been claimed to reduce the symptoms of osteoarthritis, but there is little good evidence to support this claim.
* Traumatic rupture or detachment: The cartilage in the knee is frequently damaged but can be partially repaired through knee cartilage replacement therapy
Articular cartilage, most notably that which is found in the knee joint, is generally characterized by very low friction, high wear resistance, and poor regenerative qualities. It is responsible for much of the compressive resistance and load bear ...
. Often when athletes talk of damaged "cartilage" in their knee, they are referring to a damaged meniscus
Meniscus may refer to:
*Meniscus (anatomy), crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structure that partly divides a joint cavity
*Meniscus (liquid), a curve in the upper surface of liquid contained in an object
*Meniscus (optics)
A lens is a tr ...
(a fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of ...
structure) and not the articular cartilage.
* Achondroplasia
Achondroplasia is a genetic disorder with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance whose primary feature is dwarfism. In those with the condition, the arms and legs are short, while the torso is typically of normal length. Those affected ha ...
: Reduced proliferation of chondrocytes in the epiphyseal plate of long bones during infancy and childhood, resulting in dwarfism.
* Costochondritis
Costochondritis, also known as chest wall pain syndrome or costosternal syndrome, is a benign inflammation of the upper costochondral (rib to cartilage) and sternocostal (cartilage to sternum) joints. 90% of patients are affected in multiple rib ...
: Inflammation of cartilage in the ribs, causing chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
.
* Spinal disc herniation : Asymmetrical compression of an intervertebral disc ruptures the sac-like disc, causing a herniation of its soft content. The hernia often compresses the adjacent nerves and causes back pain.
* Relapsing polychondritis
Relapsing polychondritis is a multi-systemic condition characterized by repeated episodes of inflammation and deterioration of cartilage. The often painful disease can cause joint deformity and be life-threatening if the respiratory tract, hear ...
: a destruction, probably autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". ...
, of cartilage, especially of the nose and ears, causing disfiguration. Death occurs by asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that can ...
tion as the larynx loses its rigidity and collapses.
Tumors made up of cartilage tissue, either benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not ...
or malignant, can occur. They usually appear in bone, rarely in pre-existing cartilage. The benign tumors are called chondroma
A chondroma is a benign cartilaginous tumor, which is encapsulated with a lobular growing pattern.
Tumor cells (chondrocytes, cartilaginous cells) resemble normal cells and produce the cartilaginous matrix (amorphous, basophilic material). Prese ...
, the malignant ones chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma is a bone sarcoma, a primary cancer composed of cells derived from transformed cells that produce cartilage. A chondrosarcoma is a member of a category of tumors of bone and soft tissue known as sarcomas. About 30% of bone sarcomas ...
. Tumors arising from other tissues may also produce a cartilage-like matrix, the best-known being pleomorphic adenoma
Pleomorphic adenoma is a common benign salivary gland neoplasm characterised by neoplastic proliferation of epithelial (ductal) cells along with myoepithelial components, having a malignant potentiality. It is the most common type of salivary gla ...
of the salivary glands.
The matrix of cartilage acts as a barrier, preventing the entry of lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adap ...
s or diffusion of immunoglobulins. This property allows for the transplantation of cartilage from one individual to another without fear of tissue rejection.
Imaging
Cartilage does not absorbX-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 ...
s under normal '' in vivo'' conditions, but a dye can be injected into the synovial membrane
The synovial membrane (also known as the synovial stratum, synovium or stratum synoviale) is a specialized connective tissue that lines the inner surface of capsules of synovial joints and tendon sheath. It makes direct contact with the fibro ...
that will cause the x-rays to be absorbed by the dye. The resulting void on the radiographic
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeut ...
film between the bone and meniscus
Meniscus may refer to:
*Meniscus (anatomy), crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structure that partly divides a joint cavity
*Meniscus (liquid), a curve in the upper surface of liquid contained in an object
*Meniscus (optics)
A lens is a tr ...
represents the cartilage. For In vitro x-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 ...
scans, the outer soft tissue is most likely removed, so the cartilage and air boundary are enough to contrast the presence of cartilage due to the refraction of the x-ray.

Other animals
Cartilaginous fish
Cartilaginous fish (chondrichthyes) or sharks,ray
Ray may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), a bony or horny spine on a fin
Science and mathematics
* Ray (geometry), half of a line proceeding from an initial point
* Ray (gr ...
s and chimaera
Chimaeras are cartilaginous fish in the order Chimaeriformes , known informally as ghost sharks, rat fish, spookfish, or rabbit fish; the last three names are not to be confused with rattails, Opisthoproctidae, or Siganidae, respectively.
A ...
s have a skeleton composed entirely of cartilage.
Invertebrate cartilage
Cartilage tissue can also be found among some arthropods such as horseshoe crabs, some mollusks such as marine snails andcephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, a ...
s, and some annelids like sabellid polychaetes.
Arthropods
The most studied cartilage in arthropods is the branchial cartilage of ''Limulus polyphemus
The Atlantic horseshoe crab (''Limulus polyphemus''), also known as the American horseshoe crab, is a species of marine and brackish chelicerate arthropod. Despite their name, horseshoe crabs are more closely related to spiders, ticks, and scorp ...
''. It is a vesicular cell-rich cartilage due to the large, spherical and vacuolated chondrocytes with no homologies in other arthropods. Other type of cartilage found in ''Limulus polyphemus'' is the endosternite cartilage, a fibrous-hyaline cartilage with chondrocytes of typical morphology in a fibrous component, much more fibrous than vertebrate hyaline cartilage, with mucopolysaccharides immunoreactive against chondroitin sulfate antibodies. There are homologous tissues to the endosternite cartilage in other arthropods. The embryos of ''Limulus polyphemus'' express ColA and hyaluronan in the gill cartilage and the endosternite, which indicates that these tissues are fibrillar-collagen-based cartilage. The endosternite cartilage forms close to Hh-expressing ventral nerve cords and expresses ColA and SoxE, a Sox9 analog. This is also seen in gill cartilage tissue.
Mollusks
In cephalopods, the models used for the studies of cartilage are ''Octopus vulgaris
The common octopus (''Octopus vulgaris'') is a mollusc belonging to the class Cephalopoda. ''Octopus vulgaris'' is one of the most studied of all octopus species, and also one of the most intelligent. It ranges from the eastern Atlantic, extends ...
'' and '' Sepia officinalis''. The cephalopod cranial cartilage is the invertebrate cartilage that shows more resemblance to the vertebrate hyaline cartilage. The growth is thought to take place throughout the movement of cells from the periphery to the center. The chondrocytes present different morphologies related to their position in the tissue.
The embryos of ''Sepia officinalis'' express ColAa, ColAb, and hyaluronan in the cranial cartilages and other regions of chondrogenesis. This implies that the cartilage is fibrillar-collagen-based. The ''Sepia officinalis'' embryo expresses hh, whose presence causes ColAa and ColAb expression and is also able to maintain proliferating cells undiferentiated. It has been observed that this species presents the expression SoxD and SoxE, analogs of the vertebrate Sox5/6 and Sox9, in the developing cartilage. The cartilage growth pattern is the same as in vertebrate cartilage.
In gastropods, the interest lies in the odontophore
The odontophore is part of the feeding mechanism in molluscs. It is the cartilage which underlies and supports the radula, a ribbon of teeth. The radula is found in every class of molluscs except for the bivalves.
The feeding apparatus can be exte ...
, a cartilaginous structure that supports the radula. The most studied species regarding this particular tissue is ''Busycotypus canaliculatus
''Busycotypus canaliculatus'', commonly known as the channeled whelk, is a very large predatory sea snail, a marine prosobranch gastropod, a busycon whelk, belonging to the family Busyconidae.Fraussen, K.; Rosenberg, G. (2012). Busycotypus ca ...
''. The odontophore is a vesicular cell rich cartilage, consisting of vacuolated cells containing myoglobin, surrounded by a low amount of extra cellular matrix containing collagen. The odontophore contains muscle cells along with the chondrocytes in the case of ''Lymnaea
''Lymnaea'' is a genus of small to large-sized air-breathing freshwater snails, aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the subfamily Lymnaeinae ( of the family Lymnaeidae, the pond snails.Bouchet, P.; Rosenberg, G. (2013). Lymnaea Lamarck, 179 ...
'' and other mollusks that graze vegetation.
Sabellid polychaetes
The Sabellid polychaetes, or feather duster worms, have cartilage tissue with cellular and matrix specialization supporting their tentacles. They present two distinct extracellular matrix regions. These regions are an acellular fibrous region with a high collagen content, called cartilage-like matrix, and collagen lacking a highly cellularized core, called osteoid-like matrix. The cartilage-like matrix surrounds the osteoid-like matrix. The amount of the acellular fibrous region is variable. The model organisms used in the study of cartilage in sabellid polychaetes are ''Potamilla sp'' and ''Myxicola infundibulum
''Myxicola infundibulum'' is a species of polychaete worm from the family Sabellidae. The body consists of a head, a cylindrical, segmented body and a tail piece. The head consists of a Prostomium (part of the mouth) and a peristomium (area aroun ...
''.
Plants and fungi
Vascular plants, particularly seeds, and the stems of some mushrooms, are sometimes called "cartilaginous", although they contain no cartilage.University of Sydney (2010-06-16). Retrieved on 2015-10-26.
Biomechanics
*Biomechanics
Biomechanics is the study of the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of biological systems, at any level from whole organisms to organs, cells and cell organelles, using the methods of mechanics. Biomechanics is a branch of ...
References
Further reading
*External links
Cartilage.org
International Cartilage Regeneration & Joint Preservation Society
, Cartilage tutorial, University of Kansas Medical Center
text from Gray's anatomy
I've heard 'Ears and nose do not ever stop growing.' Is this false?
CartilageHealth.com
Information on Articular Cartilage Injury Prevention, Repair and Rehabilitation
Osteoarthritis
Cartilage types
Different cartilages
on TheFreeDictionary
Cartilage photomicrographs
{{Authority control Skeletal system Connective tissue