Carbon (fiber) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
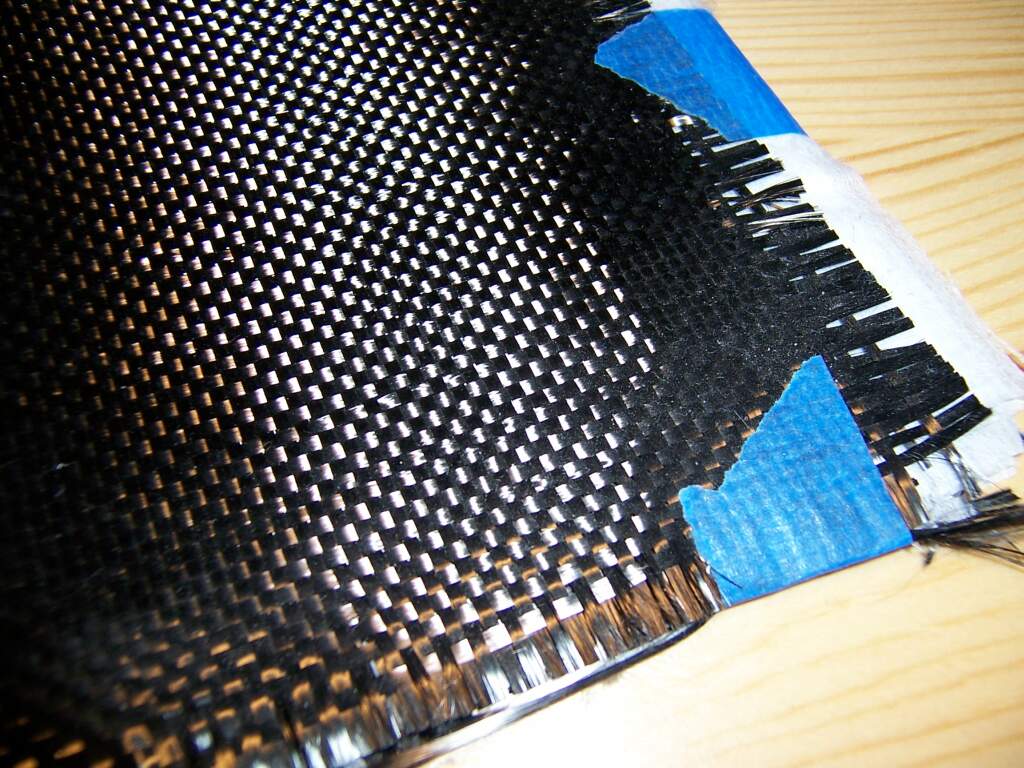 Carbon fibers or carbon fibres (alternatively CF, graphite fiber or graphite fibre) are
Carbon fibers or carbon fibres (alternatively CF, graphite fiber or graphite fibre) are
 During the 1960s, experimental work to find alternative raw materials led to the introduction of carbon fibers made from a petroleum pitch derived from oil processing. These fibers contained about 85% carbon and had excellent flexural strength. Also, during this period, the Japanese Government heavily supported carbon fiber development at home and several Japanese companies such as Toray, Nippon Carbon, Toho Rayon and
During the 1960s, experimental work to find alternative raw materials led to the introduction of carbon fibers made from a petroleum pitch derived from oil processing. These fibers contained about 85% carbon and had excellent flexural strength. Also, during this period, the Japanese Government heavily supported carbon fiber development at home and several Japanese companies such as Toray, Nippon Carbon, Toho Rayon and
 Carbon fiber is frequently supplied in the form of a continuous tow wound onto a reel. The tow is a bundle of thousands of continuous individual carbon filaments held together and protected by an organic coating, or size, such as
Carbon fiber is frequently supplied in the form of a continuous tow wound onto a reel. The tow is a bundle of thousands of continuous individual carbon filaments held together and protected by an organic coating, or size, such as
 In 2012, estimated global demand for carbon fiber market was $1.7 billion with estimated annual growth of 10–12% from 2012 to 2018. The strongest demand for carbon fiber come from aircraft and aerospace, wind energy, as well as the automotive industry with optimized resin systems.
Carbon fiber can have higher cost than other materials which has been one of the limiting factors of adoption. In a comparison between
In 2012, estimated global demand for carbon fiber market was $1.7 billion with estimated annual growth of 10–12% from 2012 to 2018. The strongest demand for carbon fiber come from aircraft and aerospace, wind energy, as well as the automotive industry with optimized resin systems.
Carbon fiber can have higher cost than other materials which has been one of the limiting factors of adoption. In a comparison between

 Precursors for carbon fibers are
Precursors for carbon fibers are
 Despite being known for their electrical conductivity, carbon fibers can carry only very low currents on their own. When woven into larger fabrics, they can be used to reliably provide (infrared) heating in applications requiring flexible electrical heating elements and can easily sustain temperatures past 100 °C. Many examples of this type of application can be seen in
Despite being known for their electrical conductivity, carbon fibers can carry only very low currents on their own. When woven into larger fabrics, they can be used to reliably provide (infrared) heating in applications requiring flexible electrical heating elements and can easily sustain temperatures past 100 °C. Many examples of this type of application can be seen in
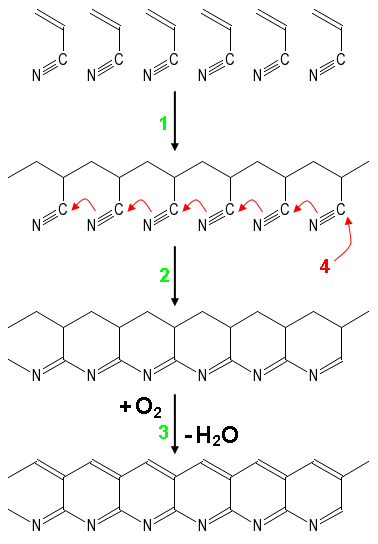 Each carbon filament is produced from a
Each carbon filament is produced from a 
 A common method of manufacture involves heating the spun PAN filaments to approximately 300 °C in air, which breaks many of the hydrogen bonds and oxidizes the material. The
A common method of manufacture involves heating the spun PAN filaments to approximately 300 °C in air, which breaks many of the hydrogen bonds and oxidizes the material. The
Making Carbon Fiber
{{DEFAULTSORT:Carbon Fiber American inventions Allotropes of carbon Synthetic fibers Woven fabrics Nonwoven fabrics Net fabrics
 Carbon fibers or carbon fibres (alternatively CF, graphite fiber or graphite fibre) are
Carbon fibers or carbon fibres (alternatively CF, graphite fiber or graphite fibre) are fiber
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
s about in diameter and composed mostly of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages: high stiffness, high tensile strength, high strength to weight ratio, high chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low thermal expansion. These properties have made carbon fiber very popular in aerospace, civil engineering, military, motorsports, and other competition sports. However, they are relatively expensive compared to similar fibers, such as glass fiber
Glass fiber ( or glass fibre) is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass.
Glassmakers throughout history have experimented with glass fibers, but mass manufacture of glass fiber was only made possible with the inventio ...
, basalt fiber
Basalt fibers are produced from basalt rocks by melting them and converting the melt into fibers.
Basalts are rocks of igneous origin. The main energy consumption for the preparation of basalt raw materials to produce of fibers is made in natural ...
s, or plastic fibers.
To produce a carbon fiber, the carbon atoms are bonded together in crystals that are more or less aligned parallel to the fiber's long axis as the crystal alignment gives the fiber a high strength-to-volume ratio (in other words, it is strong for its size). Several thousand carbon fibers are bundled together to form a tow, which may be used by itself or woven
Woven fabric is any textile formed by weaving. Woven fabrics are often created on a loom, and made of many threads woven on a warp and a weft. Technically, a woven fabric is any fabric made by interlacing two or more threads at right angles to on ...
into a fabric.
Carbon fibers are usually combined with other materials to form a composite
Composite or compositing may refer to:
Materials
* Composite material, a material that is made from several different substances
** Metal matrix composite, composed of metal and other parts
** Cermet, a composite of ceramic and metallic materials ...
. For example, when permeated with a plastic resin and baked
Baking is a method of preparing food that uses dry heat, typically in an oven, but can also be done in hot ashes, or on hot stones. The most common baked item is bread but many other types of foods can be baked. Heat is gradually transferre ...
, it forms carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon compo ...
(often referred to as carbon fiber), which has a very high strength-to-weight ratio
The specific strength is a material's (or muscle's) strength (force per unit area at failure) divided by its density. It is also known as the strength-to-weight ratio or strength/weight ratio or strength-to-mass ratio. In fiber or textile appli ...
and is extremely rigid although somewhat brittle. Carbon fibers are also composited with other materials, such as graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on la ...
, to form reinforced carbon-carbon composites, which have a very high heat tolerance.
History
In 1860,Joseph Swan
Sir Joseph Wilson Swan FRS (31 October 1828 – 27 May 1914) was an English physicist, chemist, and inventor. He is known as an independent early developer of a successful incandescent light bulb, and is the person responsible for develop ...
produced carbon fibers for the first time, for use in light bulbs. In 1879, Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February 11, 1847October 18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventi ...
baked cotton threads or bamboo slivers at high temperatures carbonizing them into an all-carbon fiber filament used in one of the first incandescent light bulbs to be heated by electricity. In 1880, Lewis Latimer developed a reliable carbon wire filament for the incandescent light bulb, heated by electricity.
In 1958, Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through emp ...
created high-performance carbon fibers at the Union Carbide
Union Carbide Corporation is an American chemical corporation wholly owned subsidiary (since February 6, 2001) by Dow Chemical Company. Union Carbide produces chemicals and polymers that undergo one or more further conversions by customers befo ...
Parma Technical Center located outside of Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
. Those fibers were manufactured by heating strands of rayon
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. It is also called viscose. Many types and grades of viscose ...
until they carbonized. This process proved to be inefficient, as the resulting fibers contained only about 20% carbon. In the early 1960s, a process was developed by Dr. Akio Shindo at Agency of Industrial Science and Technology of Japan, using polyacrylonitrile
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN), also known as polyvinyl cyanide and Creslan 61, is a synthetic, semicrystalline organic polymer resin, with the linear formula (C3H3N)n. Though it is thermoplastic, it does not melt under normal conditions. It degrades bef ...
(PAN) as a raw material. This had produced a carbon fiber that contained about 55% carbon. In 1960 Richard Millington of H.I. Thompson Fiberglas Co. developed a process (US Patent No. 3,294,489) for producing a high carbon content (99%) fiber using rayon as a precursor. These carbon fibers had sufficient strength (modulus of elasticity and tensile strength) to be used as a reinforcement for composites having high strength to weight properties and for high temperature resistant applications.
The high potential strength of carbon fiber was realized in 1963 in a process developed by W. Watt, L. N. Phillips, and W. Johnson at the Royal Aircraft Establishment
The Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) was a British research establishment, known by several different names during its history, that eventually came under the aegis of the UK Ministry of Defence (MoD), before finally losing its identity in me ...
at Farnborough, Hampshire
Farnborough is a town in northeast Hampshire, England, part of the borough of Rushmoor and the Farnborough/Aldershot Built-up Area. Farnborough was founded in Saxon times and is mentioned in the Domesday Book of 1086. The name is formed fro ...
. The process was patented by the UK Ministry of Defence
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in state ...
, then licensed by the British National Research Development Corporation to three companies: Rolls-Royce
Rolls-Royce (always hyphenated) may refer to:
* Rolls-Royce Limited, a British manufacturer of cars and later aero engines, founded in 1906, now defunct
Automobiles
* Rolls-Royce Motor Cars, the current car manufacturing company incorporated in ...
, who were already making carbon fiber; Morganite; and Courtaulds
Courtaulds was a United Kingdom-based manufacturer of fabric, clothing, artificial fibres, and chemicals. It was established in 1794 and became the world's leading man-made fibre production company before being broken up in 1990 into Courtaulds ...
. Within a few years, after successful use in 1968 of a ''Hyfil'' carbon-fiber
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon compo ...
fan assembly in the Rolls-Royce Conway
The Rolls-Royce RB.80 Conway was the first turbofan engine to enter service. Development started at Rolls-Royce in the 1940s, but the design was used only briefly, in the late 1950s and early 1960s, before other turbofan designs replaced it. ...
jet engines of the Vickers VC10
The Vickers VC10 is a mid-sized, narrow-body long-range British jet airliner designed and built by Vickers-Armstrongs (Aircraft) Ltd and first flown at Brooklands, Surrey, in 1962. The airliner was designed to operate on long-distance route ...
, Rolls-Royce took advantage of the new material's properties to break into the American market with its RB-211 aero-engine with carbon-fiber compressor blades. Unfortunately, the blades proved vulnerable to damage from bird impact. This problem and others caused Rolls-Royce such setbacks that the company was nationalized in 1971. The carbon-fiber production plant was sold off to form ''Bristol Composite Materials Engineering Ltd'' (Often referred to as Bristol Composites).
In the late 1960s, the Japanese took the lead in manufacturing PAN-based carbon fibers. A 1970 joint technology agreement allowed Union Carbide
Union Carbide Corporation is an American chemical corporation wholly owned subsidiary (since February 6, 2001) by Dow Chemical Company. Union Carbide produces chemicals and polymers that undergo one or more further conversions by customers befo ...
to manufacture Japan's Toray Industries
is a multinational corporation headquartered in Japan that specializes in industrial products centered on technologies in organic synthetic chemistry, polymer chemistry, and biochemistry.
Its founding business areas were fibers and textiles, ...
product. Morganite decided that carbon-fiber production was peripheral to its core business, leaving Courtaulds as the only big UK manufacturer. Courtelle's water-based inorganic process made the product susceptible to impurities that did not affect the organic process used by other carbon-fiber manufacturers, leading Courtaulds ceasing carbon-fiber production in 1991.
 During the 1960s, experimental work to find alternative raw materials led to the introduction of carbon fibers made from a petroleum pitch derived from oil processing. These fibers contained about 85% carbon and had excellent flexural strength. Also, during this period, the Japanese Government heavily supported carbon fiber development at home and several Japanese companies such as Toray, Nippon Carbon, Toho Rayon and
During the 1960s, experimental work to find alternative raw materials led to the introduction of carbon fibers made from a petroleum pitch derived from oil processing. These fibers contained about 85% carbon and had excellent flexural strength. Also, during this period, the Japanese Government heavily supported carbon fiber development at home and several Japanese companies such as Toray, Nippon Carbon, Toho Rayon and Mitsubishi
The is a group of autonomous Japanese multinational companies in a variety of industries.
Founded by Yatarō Iwasaki in 1870, the Mitsubishi Group historically descended from the Mitsubishi zaibatsu, a unified company which existed from 1870 ...
started their own development and production. Since the late 1970s, further types of carbon fiber yarn entered the global market, offering higher tensile strength and higher elastic modulus. For example, T400 from Toray with a tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials ...
of 4,000 MPa and M40, a modulus of 400 GPa. Intermediate carbon fibers, such as IM 600 from Toho Rayon with up to 6,000 MPa were developed. Carbon fibers from Toray, Celanese and Akzo found their way to aerospace application from secondary to primary parts first in military and later in civil aircraft as in McDonnell Douglas, Boeing, Airbus, and United Aircraft Corporation
, former_name = OJSC United Aircraft Corporation (2006–2015)
, type = Public, PJSC
, traded_as =
, industry = Aerospace, defense
, predecessor = Ilyushin, Irkut, Mikoyan, Sukhoi, Tupolev, Yakovlev
, founded =
, founder = Vladimir P ...
planes. In 1988, Dr. Jacob Lahijani invented balanced ultra-high Young's modulus (greater than 100 Mpsi) and high tensile strength pitch carbon fiber (greater than 500 kpsi) used extensively in automotive and aerospace applications. In March 2006, the patent was assigned to the University of Tennessee
The University of Tennessee (officially The University of Tennessee, Knoxville; or UT Knoxville; UTK; or UT) is a public land-grant research university in Knoxville, Tennessee. Founded in 1794, two years before Tennessee became the 16th sta ...
Research Foundation.
Structure and properties
 Carbon fiber is frequently supplied in the form of a continuous tow wound onto a reel. The tow is a bundle of thousands of continuous individual carbon filaments held together and protected by an organic coating, or size, such as
Carbon fiber is frequently supplied in the form of a continuous tow wound onto a reel. The tow is a bundle of thousands of continuous individual carbon filaments held together and protected by an organic coating, or size, such as polyethylene oxide
Polyethylene glycol (PEG; ) is a polyether compound derived from petroleum with many applications, from industrial manufacturing to medicine. PEG is also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or polyoxyethylene (POE), depending on its molecular we ...
(PEO) or polyvinyl alcohol
Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVOH, PVA, or PVAl) is a water- soluble synthetic polymer. It has the idealized formula H2CH(OH)sub>''n''. It is used in papermaking, textile warp sizing, as a thickener and emulsion stabilizer in polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) ...
(PVA). The tow can be conveniently unwound from the reel for use. Each carbon filament in the tow is a continuous cylinder with a diameter of 5–10 micrometer Micrometer can mean:
* Micrometer (device), used for accurate measurements by means of a calibrated screw
* American spelling of micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; ...
s and consists almost exclusively of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
. The earliest generation (e.g. T300, HTA and AS4) had diameters of 16–22 micrometers
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
. Later fibers (e.g. IM6 or IM600) have diameters that are approximately 5 micrometers.
The atomic structure of carbon fiber is similar to that of graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on la ...
, consisting of sheets of carbon atoms
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas ...
arranged in a regular hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A '' regular hexagon'' has ...
al pattern (graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure.
sheets), the difference being in the way these sheets interlock. Graphite is a crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
material in which the sheets are stacked parallel to one another in regular fashion. The intermolecular forces between the sheets are relatively weak Van der Waals force
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and ...
s, giving graphite its soft and brittle characteristics.
Depending upon the precursor to make the fiber, carbon fiber may be turbostratic or graphitic, or have a hybrid structure with both graphitic and turbostratic parts present. In turbostratic carbon fiber the sheets of carbon atoms are haphazardly folded, or crumpled, together. Carbon fibers derived from polyacrylonitrile (PAN) are turbostratic, whereas carbon fibers derived from mesophase pitch are graphitic after heat treatment at temperatures exceeding 2200 °C. Turbostratic carbon fibers tend to have high ultimate tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials ...
, whereas heat-treated mesophase-pitch-derived carbon fibers have high Young's modulus
Young's modulus E, the Young modulus, or the modulus of elasticity in tension or compression (i.e., negative tension), is a mechanical property that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness of a solid material when the force is applied ...
(i.e., high stiffness or resistance to extension under load) and high thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
.
Applications
 In 2012, estimated global demand for carbon fiber market was $1.7 billion with estimated annual growth of 10–12% from 2012 to 2018. The strongest demand for carbon fiber come from aircraft and aerospace, wind energy, as well as the automotive industry with optimized resin systems.
Carbon fiber can have higher cost than other materials which has been one of the limiting factors of adoption. In a comparison between
In 2012, estimated global demand for carbon fiber market was $1.7 billion with estimated annual growth of 10–12% from 2012 to 2018. The strongest demand for carbon fiber come from aircraft and aerospace, wind energy, as well as the automotive industry with optimized resin systems.
Carbon fiber can have higher cost than other materials which has been one of the limiting factors of adoption. In a comparison between steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistan ...
and carbon fiber materials for automotive materials, carbon fiber may be 10-12x more expensive. However, this cost premium has come down over the past decade from estimates of 35x more expensive than steel in the early 2000s.
Composite materials
Carbon fiber is most notably used to reinforcecomposite material
A composite material (also called a composition material or shortened to composite, which is the common name) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or ...
s, particularly the class of materials known as carbon fiber or graphite reinforced polymers. Non-polymer materials can also be used as the matrix for carbon fibers. Due to the formation of metal carbide
In chemistry, a carbide usually describes a compound composed of carbon and a metal. In metallurgy, carbiding or carburizing is the process for producing carbide coatings on a metal piece.
Interstitial / Metallic carbides
The carbides of t ...
s and corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
considerations, carbon has seen limited success in metal matrix composite applications. Reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) consists of carbon fiber-reinforced graphite, and is used structurally in high-temperature applications. The fiber also finds use in filtration
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a ''filter medium'' that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter ...
of high-temperature gases, as an electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials ...
with high surface area and impeccable corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
resistance, and as an anti- static component. Molding a thin layer of carbon fibers significantly improves fire resistance of polymers or thermoset composites because a dense, compact layer of carbon fibers efficiently reflects heat.
The increasing use of carbon fiber composites is displacing aluminum from aerospace applications in favor of other metals because of galvanic corrosion issues.
Carbon fiber can be used as an additive to asphalt to make electrically conductive asphalt concrete. Using this composite material in the transportation infrastructure, especially for airport pavement, decreases some winter maintenance problems that lead to flight cancellation or delay due to the presence of ice and snow. Passing current through the composite material 3D network of carbon fibers dissipates thermal energy that increases the surface temperature of the asphalt, which is able to melt ice and snow above it.
Textiles


 Precursors for carbon fibers are
Precursors for carbon fibers are polyacrylonitrile
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN), also known as polyvinyl cyanide and Creslan 61, is a synthetic, semicrystalline organic polymer resin, with the linear formula (C3H3N)n. Though it is thermoplastic, it does not melt under normal conditions. It degrades bef ...
(PAN), rayon
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. It is also called viscose. Many types and grades of viscose ...
and pitch. Carbon fiber filament yarns are used in several processing techniques: the direct uses are for prepregging, filament winding, pultrusion, weaving, braiding, etc. Carbon fiber yarn is rated by the linear density (weight per unit length; i.e., 1 g/1000 m = 1 tex) or by number of filaments per yarn count, in thousands. For example, 200 tex for 3,000 filaments of carbon fiber is three times as strong as 1,000 carbon filament yarn, but is also three times as heavy. This thread can then be used to weave a carbon fiber filament fabric
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not ...
or cloth
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
. The appearance of this fabric generally depends on the linear density of the yarn and the weave chosen. Some commonly used types of weave are twill
Twill is a type of textile weave with a pattern of diagonal parallel ribs. It is one of three fundamental types of textile weaves along with plain weave and satin. It is made by passing the weft thread over one or more warp threads then ...
, satin
A satin weave is a type of fabric weave that produces a characteristically glossy, smooth or lustrous material, typically with a glossy top surface and a dull back. It is one of three fundamental types of textile weaves alongside plain weave ...
and plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
. Carbon filament yarns can also be knitted or braided
Braided is a musical group consisting of Casey LeBlanc, Ashley Leitão, and Amber Fleury, who all competed on the third season of ''Canadian Idol'' in 2005. They are the third music group to come from an Idol show in the world, after Young Divas ...
.
Microelectrodes
Carbon fibers are used for fabrication of carbon-fibermicroelectrodes
A microelectrode is an electrode used in electrophysiology either for recording neural signals or for the electrical stimulation of nervous tissue (they were first developed by Ida Hyde in 1921). Pulled glass pipettes with tip diameters of 0. ...
. In this application typically a single carbon fiber with diameter of 5–7 μm is sealed in a glass capillary. At the tip the capillary is either sealed with epoxy and polished to make carbon-fiber disk microelectrode or the fiber is cut to a length of 75–150 μm to make carbon-fiber cylinder electrode. Carbon-fiber microelectrodes
A microelectrode is an electrode used in electrophysiology either for recording neural signals or for the electrical stimulation of nervous tissue (they were first developed by Ida Hyde in 1921). Pulled glass pipettes with tip diameters of 0. ...
are used either in amperometry
Amperometry in chemistry is detection of ions in a solution based on electric current or changes in electric current.
Amperometry is used in electrophysiology to study vesicle release events using a carbon fiber electrode. Unlike patch clamp tec ...
or fast-scan cyclic voltammetry
Fast-scan cyclic voltammetry (FSCV) is cyclic voltammetry with a very high scan rate (up to ). Application of high scan rate allows rapid acquisition of a voltammogram within several milliseconds and ensures high temporal resolution of this elect ...
for detection of biochemical signaling.
Flexible heating
 Despite being known for their electrical conductivity, carbon fibers can carry only very low currents on their own. When woven into larger fabrics, they can be used to reliably provide (infrared) heating in applications requiring flexible electrical heating elements and can easily sustain temperatures past 100 °C. Many examples of this type of application can be seen in
Despite being known for their electrical conductivity, carbon fibers can carry only very low currents on their own. When woven into larger fabrics, they can be used to reliably provide (infrared) heating in applications requiring flexible electrical heating elements and can easily sustain temperatures past 100 °C. Many examples of this type of application can be seen in DIY
"Do it yourself" ("DIY") is the method of building, modifying, or repairing things by oneself without the direct aid of professionals or certified experts. Academic research has described DIY as behaviors where "individuals use raw and sem ...
heated articles of clothing and blankets. Due to its chemical inertness, it can be used relatively safely amongst most fabrics and materials; however, shorts caused by the material folding back on itself will lead to increased heat production and can lead to a fire.
Synthesis
polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
such as polyacrylonitrile
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN), also known as polyvinyl cyanide and Creslan 61, is a synthetic, semicrystalline organic polymer resin, with the linear formula (C3H3N)n. Though it is thermoplastic, it does not melt under normal conditions. It degrades bef ...
(PAN), rayon
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. It is also called viscose. Many types and grades of viscose ...
, or petroleum pitch. All these polymers are known as a precursor
Precursor or Precursors may refer to:
* Precursor (religion), a forerunner, predecessor
** The Precursor, John the Baptist
Science and technology
* Precursor (bird), a hypothesized genus of fossil birds that was composed of fossilized parts of u ...
. For synthetic polymers such as PAN or rayon, the precursor is first spun
''Spun'' is a 2002 American black comedy crime drama film directed by Jonas Åkerlund from an original screenplay by William De Los Santos and Creighton Vero, based on three days of De Los Santos's life in the Eugene, Oregon, drug subculture. The ...
into filament yarns, using chemical and mechanical processes to initially align the polymer molecules in a way to enhance the final physical properties of the completed carbon fiber. Precursor compositions and mechanical processes used during spinning filament yarns may vary among manufacturers. After drawing or spinning, the polymer filament yarns are then heated to drive off non-carbon atoms (carbonization
Carbonization is the conversion of organic matters like plants and dead animal remains into carbon through destructive distillation.
Complexity in carbonization
Carbonization is a pyrolytic reaction, therefore, is considered a complex proces ...
), producing the final carbon fiber. The carbon fibers filament yarns may be further treated to improve handling qualities, then wound on to bobbin
A bobbin or spool is a spindle or cylinder, with or without flanges, on which yarn, thread, wire, tape or film is wound. Bobbins are typically found in industrial textile machinery, as well as in sewing machines, fishing reels, tape measu ...
s.
 A common method of manufacture involves heating the spun PAN filaments to approximately 300 °C in air, which breaks many of the hydrogen bonds and oxidizes the material. The
A common method of manufacture involves heating the spun PAN filaments to approximately 300 °C in air, which breaks many of the hydrogen bonds and oxidizes the material. The oxidized
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
PAN is then placed into a furnace having an inert atmosphere of a gas such as argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice a ...
, and heated to approximately 2000 °C, which induces graphitization of the material, changing the molecular bond structure. When heated in the correct conditions, these chains bond side-to-side (ladder polymers), forming narrow graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure.
sheets which eventually merge to form a single, columnar filament. The result is usually 93–95% carbon. Lower-quality fiber can be manufactured using pitch or rayon
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. It is also called viscose. Many types and grades of viscose ...
as the precursor instead of PAN. The carbon can become further enhanced, as high modulus, or high strength carbon, by heat treatment processes. Carbon heated in the range of 1500–2000 °C (carbonization) exhibits the highest tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials ...
(5,650 MPa, or 820,000 psi), while carbon fiber heated from 2500 to 3000 °C (graphitizing) exhibits a higher modulus of elasticity
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity) is the unit of measurement of an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it. The elastic modulus of an object is ...
(531GPa, or 77,000,000psi).
See also
*Basalt fiber
Basalt fibers are produced from basalt rocks by melting them and converting the melt into fibers.
Basalts are rocks of igneous origin. The main energy consumption for the preparation of basalt raw materials to produce of fibers is made in natural ...
* Carbon fiber reinforced polymer
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon compo ...
* Carbon fiber reinforced ceramic material
* Carbon nanotube
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube
Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers.
''Single-wall carbon na ...
* ESD materials
* Graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure.
References
External links
Making Carbon Fiber
{{DEFAULTSORT:Carbon Fiber American inventions Allotropes of carbon Synthetic fibers Woven fabrics Nonwoven fabrics Net fabrics