business chess on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Business chess is a variant of chess played in teams. It was invented in 1992 by Dr. Grachya Ovakimyan of
Business chess is a variant of chess played in teams. It was invented in 1992 by Dr. Grachya Ovakimyan of
 The board, pieces, their positions and rules of movement are the same as for standard
The board, pieces, their positions and rules of movement are the same as for standard

 To carry out a Branching the team on its move copies the position from board 1 to a free demonstration board, apply differing continuations (for example, on a demonstration board 1 move e4, and on a board 2 ŌĆō g3). In this case, the rating of the original (maternal) branch is distributed between the child branches according to the decision made by the team making the branch. As a result of the subsequent branching there will appear branches 3, 4, and 5.
If in the course of a game one of the teams gets a branch with a lost position (e.g. branch 1 in
To carry out a Branching the team on its move copies the position from board 1 to a free demonstration board, apply differing continuations (for example, on a demonstration board 1 move e4, and on a board 2 ŌĆō g3). In this case, the rating of the original (maternal) branch is distributed between the child branches according to the decision made by the team making the branch. As a result of the subsequent branching there will appear branches 3, 4, and 5.
If in the course of a game one of the teams gets a branch with a lost position (e.g. branch 1 in  As a result of such a redistribution, the rating of the lost branch is added to the rating of the remaining one and the opponent gets points equal to the lost branch rating (in the given case, three points).
A Business chess
As a result of such a redistribution, the rating of the lost branch is added to the rating of the remaining one and the opponent gets points equal to the lost branch rating (in the given case, three points).
A Business chess  On Figure 4 the increasing number of branches is shown (after move 7, there are already two branches, after move 11, three, after the move 12, four, and after move 18, five branches). Then, as a result of the selection and drawing (on moves 24, 25, 29 and 37, respectively) the number of branches gradually decreases. After move 37 and until the end of the game there remains only one branch, with a rating of eight.
A very important tactical element of the business chess scenario is chess Passing. Such a pass enables one to transfer, in a single move, one unit of rating from one branch to another without loss of points. It is a way of adjusting branch ratings as the team reassesses their positions. The game tree with Passing has a more complicated form (see Figure 5).
On Figure 4 the increasing number of branches is shown (after move 7, there are already two branches, after move 11, three, after the move 12, four, and after move 18, five branches). Then, as a result of the selection and drawing (on moves 24, 25, 29 and 37, respectively) the number of branches gradually decreases. After move 37 and until the end of the game there remains only one branch, with a rating of eight.
A very important tactical element of the business chess scenario is chess Passing. Such a pass enables one to transfer, in a single move, one unit of rating from one branch to another without loss of points. It is a way of adjusting branch ratings as the team reassesses their positions. The game tree with Passing has a more complicated form (see Figure 5).
 Only one member of the team may move pieces and ratings on the demonstration board after the team decides collectively. This stops players crowding in front of the demonstration boards. For this purpose the zone before the rows of demonstration boards is separated from the zone of team location by red lines which only one team member may cross.
Only one member of the team may move pieces and ratings on the demonstration board after the team decides collectively. This stops players crowding in front of the demonstration boards. For this purpose the zone before the rows of demonstration boards is separated from the zone of team location by red lines which only one team member may cross.
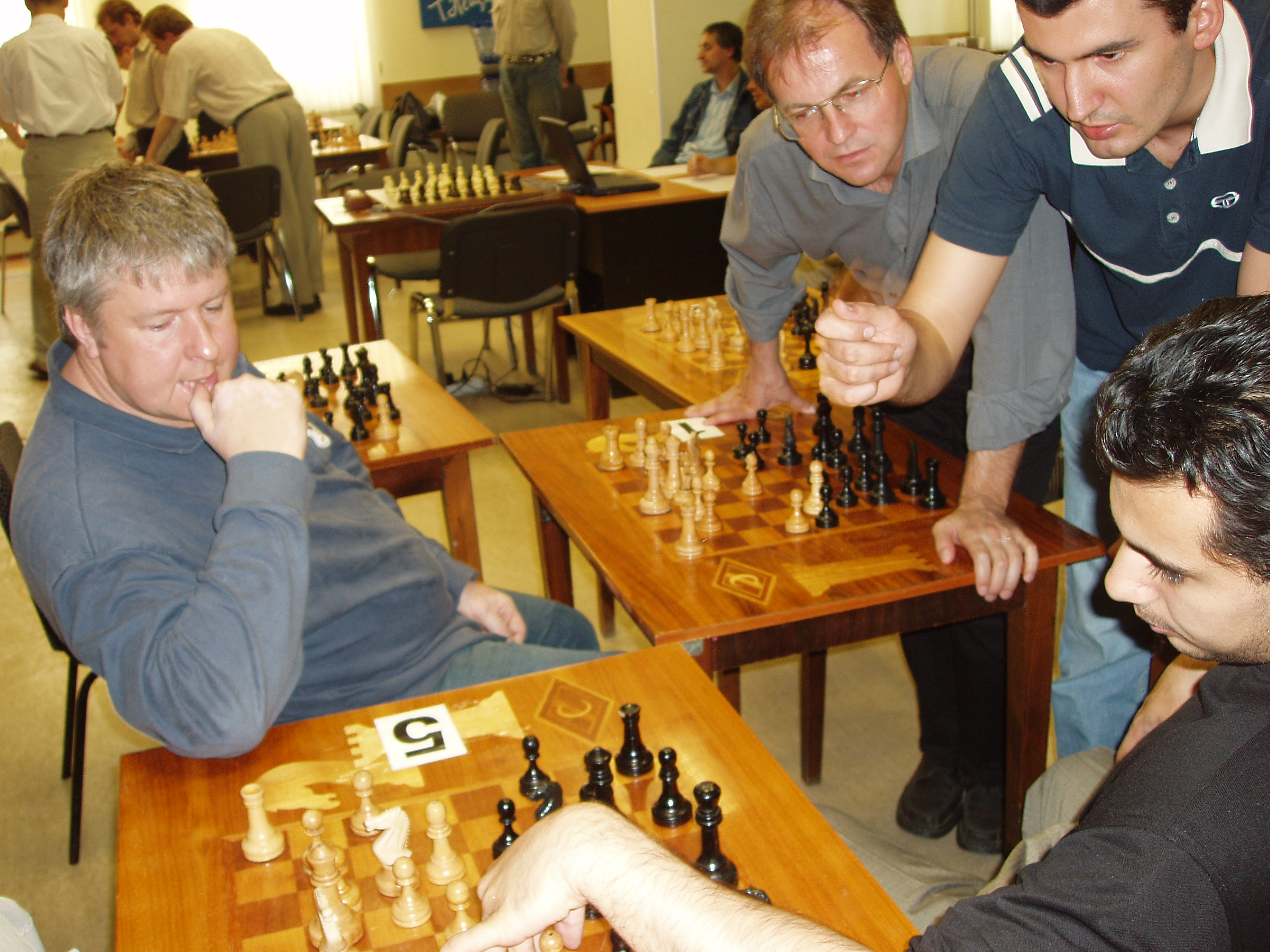 Each team is provided five ordinary chess boards to freely discuss positions and calculate variants (
Each team is provided five ordinary chess boards to freely discuss positions and calculate variants (
Business chess site
Business Chess on the site of Moscow chess federation - Chessmoscow.ru
Business Chess on the Chess-News.ru
Chess academy of Armenia
{{Chess variants Board games introduced in 1992 Chess variants Chess in Russia Chess in Armenia Business simulation games Russian inventions
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, ą£ąŠčüą║ą▓ą░, r=Moskva, p=m╔Ésk╦łva, a=ą£ąŠčüą║ą▓ą░.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
with the aim of making chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to dist ...
more entertaining and spectacular.
In the opinion of the inventor, free and open discussion between team members and collective decision-making process may make the game spectacular by increasing its dynamism and presenting the various stages of chess players' thinking, evaluation of positions, calculation of variants, choice of alternatives, and so on. In turn, in order to ensure active team discussion and effective decision-making process the ''Interactive Cognitive Scenario'' was developed.
Ovakimyan describes this version of chess as a sports
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, ...
business game
Business game (also called business simulation game) refers to simulation games that are used as an educational tool for teaching business. Business games may be carried out for various business training such as: general management, finance, organ ...
.
Key ideas
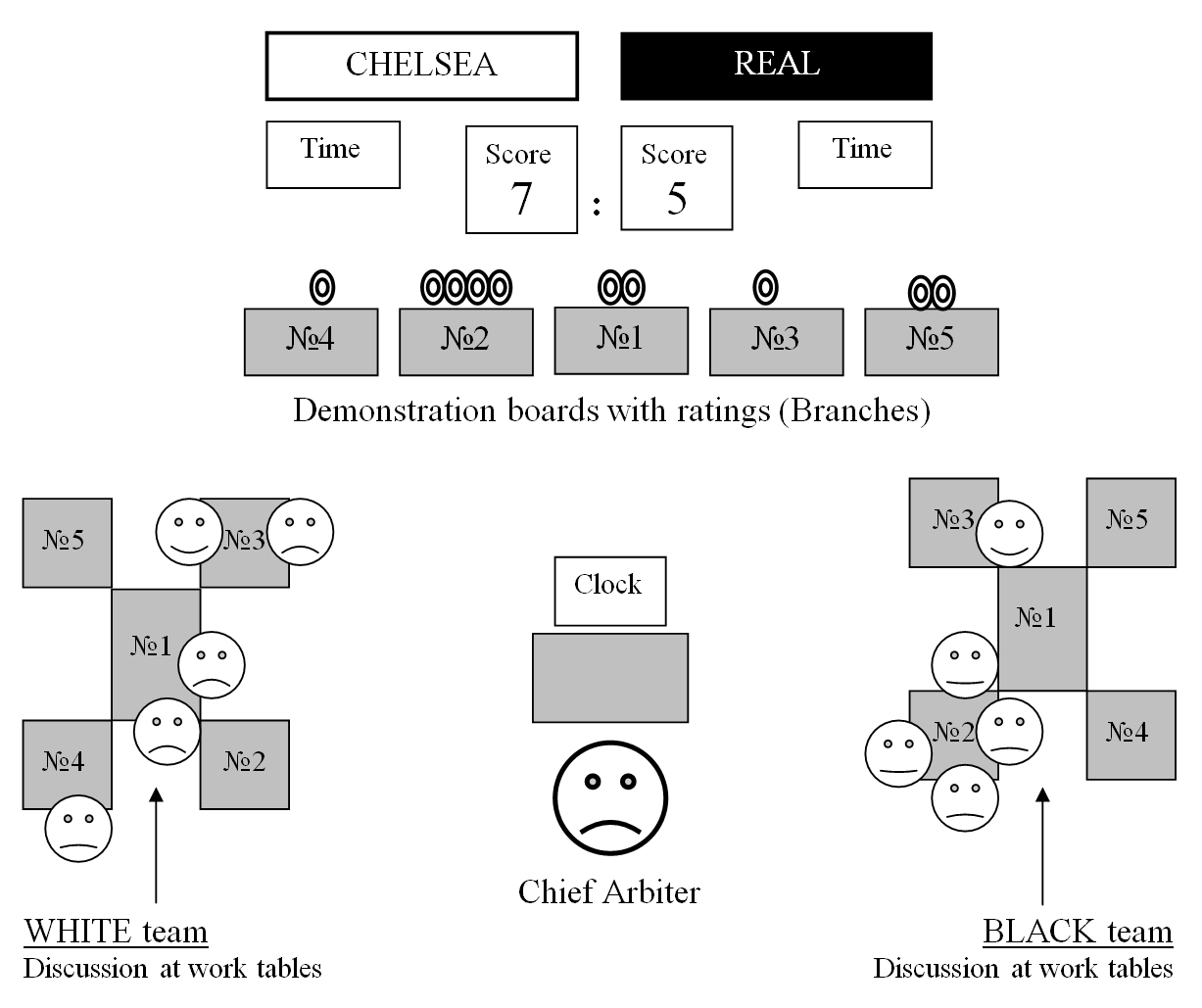
* Branch ŌĆō version of a chess game having own rating, that is played on one demonstration chessboard ( Photo 2). * Branch rating ŌĆō a number indicating how important the branch, which is a marks (colored chips), located in the upper part of the demonstration chessboard ( Photo 2). The score of each branch is equal to its chess result, multiplied by the rating of the given branch. * Branching ŌĆō splitting a branch of a single move by splitting one of the existing branches (the "parent
A parent is a caregiver of the offspring in their own species. In humans, a parent is the caretaker of a child (where "child" refers to offspring, not necessarily age). A ''biological parent'' is a person whose gamete resulted in a child, a male t ...
") into two and distributing the ratings between the two " child" branches. Different moves will subsequently be made in each branch. This can only be done if there is a free demonstration chessboard.
* Selection ŌĆō removing a branch in a single move in recognition of defeat from a position on that branch, and redistribution of its branch rating between those of its remaining siblings. The opponent team gets points equal to the lost branch rating.
* Passing ŌĆō transferring one unit (colored chip) in a single move from one branch rating to a sibling, with no gain nor loss of points.
Description
 The board, pieces, their positions and rules of movement are the same as for standard
The board, pieces, their positions and rules of movement are the same as for standard chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to dist ...
. But several parallel branches (versions of the same game) can be played at the same time on the several boards, with the help of rating (importance) indicators of a certain branch (red marks on top of the board, see Photo 2). The game is for two teams, recommended each to have five members. During the game members of one team may discuss it, as well as actively move, and then form the alternative (parallel) branches. They also can change the rating of each branch by transferring its marks. With the possibility of changing the number of simultaneously played branches and their ratings, qualitatively new, tactical and strategic methods of competition appear which are inherent only in this version of chess.
In the Interactive Cognitive Scenario the following mechanisms are envisaged: ( Photo 1 and Figure 1
Figure 1 is a Toronto, Ontario-based online social networking service for healthcare professionals to post and comment on medical images.
Figure 1 was founded in Toronto by Dr. Joshua Landy, Richard Penner and Gregory Levey. The platform launched ...
):
# Official moves in business chess are made on demonstration chessboards. Up to five such boards may be displayed side-by-side each with a branch arising during one game. Each demonstration board involved in a game has its rating ( Photo 2). The basic mechanisms of the scenario ŌĆō ''Branching'', ''Selection'' and ''Passing'' of chess positions ŌĆō are shown on the demonstration boards. These mechanisms affect the current and final score in a game and require members of both teams to coordinate their actions and carry out their decisions.
# To discuss positions and calculate variants, each of the teams is provided with five ordinary chessboards with full sets of pieces.
# To limit the time of a game there is only one chess clock
A chess clock consists of two adjacent clocks with buttons to stop one clock while starting the other, so that the two clocks never run simultaneously. Chess clocks are used in chess and other two-player games where the players move in turn, and ...
, however many branches are played in parallel. It is started after the team makes a move in all branches. The time of each team is limited to one hour. If one branch remains in the endgame
Endgame, Endgames, End Game, End Games, or similar variations may refer to:
Film
* ''The End of the Game'' (1919 film)
* ''The End of the Game'' (1975 film), short documentary U.S. film
* ''Endgame'' (1983 film), 1983 Italian post-apocalyptic f ...
, an additional five minutes is given.
Interactive Cognitive Scenario
Demonstration boards
Parallel variants of a game (branches) can be played on five nearby demonstration boards, numbered 1 to 5, each of which has its own rating (See Photo 2). Teams can decide to change the number of branches and their ratings. The score of each branch (on a particular board) is equal to its chess result, multiplied by the rating of the given branch. The final score of the game is equal to the sum of results of all branches. The game begins on one demonstration board only, representing branch 1 (seeFigure 1
Figure 1 is a Toronto, Ontario-based online social networking service for healthcare professionals to post and comment on medical images.
Figure 1 was founded in Toronto by Dr. Joshua Landy, Richard Penner and Gregory Levey. The platform launched ...
) with rating 10. Branching is used (see Figure 2
Figure may refer to:
General
*A shape, drawing, depiction, or geometric configuration
*Figure (wood), wood appearance
*Figure (music), distinguished from musical motif
*Noise figure, in telecommunication
*Dance figure, an elementary dance patte ...
) to increase the number of branches.
 To carry out a Branching the team on its move copies the position from board 1 to a free demonstration board, apply differing continuations (for example, on a demonstration board 1 move e4, and on a board 2 ŌĆō g3). In this case, the rating of the original (maternal) branch is distributed between the child branches according to the decision made by the team making the branch. As a result of the subsequent branching there will appear branches 3, 4, and 5.
If in the course of a game one of the teams gets a branch with a lost position (e.g. branch 1 in
To carry out a Branching the team on its move copies the position from board 1 to a free demonstration board, apply differing continuations (for example, on a demonstration board 1 move e4, and on a board 2 ŌĆō g3). In this case, the rating of the original (maternal) branch is distributed between the child branches according to the decision made by the team making the branch. As a result of the subsequent branching there will appear branches 3, 4, and 5.
If in the course of a game one of the teams gets a branch with a lost position (e.g. branch 1 in Figure 3
Figure may refer to:
General
*A shape, drawing, depiction, or geometric configuration
* Figure (wood), wood appearance
*Figure (music), distinguished from musical motif
*Noise figure, in telecommunication
* Dance figure, an elementary dance patte ...
), then the team may resign the game in that branch and transfer all the chips of its rating to the demonstration board of another (parallel) branch, where the team has an undefeated position (e.g. branch 2). This represents the so-called Selection, which offers a team a possibility of winning back what has been lost.
 As a result of such a redistribution, the rating of the lost branch is added to the rating of the remaining one and the opponent gets points equal to the lost branch rating (in the given case, three points).
A Business chess
As a result of such a redistribution, the rating of the lost branch is added to the rating of the remaining one and the opponent gets points equal to the lost branch rating (in the given case, three points).
A Business chess game tree
In the context of Combinatorial game theory, which typically studies sequential games with perfect information, a game tree is a graph representing all possible game states within such a game. Such games include well-known ones such as chess, ch ...
structure resulting from operations of Branching and Selection is shown in Figure 4.
 On Figure 4 the increasing number of branches is shown (after move 7, there are already two branches, after move 11, three, after the move 12, four, and after move 18, five branches). Then, as a result of the selection and drawing (on moves 24, 25, 29 and 37, respectively) the number of branches gradually decreases. After move 37 and until the end of the game there remains only one branch, with a rating of eight.
A very important tactical element of the business chess scenario is chess Passing. Such a pass enables one to transfer, in a single move, one unit of rating from one branch to another without loss of points. It is a way of adjusting branch ratings as the team reassesses their positions. The game tree with Passing has a more complicated form (see Figure 5).
On Figure 4 the increasing number of branches is shown (after move 7, there are already two branches, after move 11, three, after the move 12, four, and after move 18, five branches). Then, as a result of the selection and drawing (on moves 24, 25, 29 and 37, respectively) the number of branches gradually decreases. After move 37 and until the end of the game there remains only one branch, with a rating of eight.
A very important tactical element of the business chess scenario is chess Passing. Such a pass enables one to transfer, in a single move, one unit of rating from one branch to another without loss of points. It is a way of adjusting branch ratings as the team reassesses their positions. The game tree with Passing has a more complicated form (see Figure 5).
 Only one member of the team may move pieces and ratings on the demonstration board after the team decides collectively. This stops players crowding in front of the demonstration boards. For this purpose the zone before the rows of demonstration boards is separated from the zone of team location by red lines which only one team member may cross.
Only one member of the team may move pieces and ratings on the demonstration board after the team decides collectively. This stops players crowding in front of the demonstration boards. For this purpose the zone before the rows of demonstration boards is separated from the zone of team location by red lines which only one team member may cross.
Discussion
Figure 1
Figure 1 is a Toronto, Ontario-based online social networking service for healthcare professionals to post and comment on medical images.
Figure 1 was founded in Toronto by Dr. Joshua Landy, Richard Penner and Gregory Levey. The platform launched ...
). At each board the team (or part of it) discusses the position arising in one of the branches of a game ( Photo 3 and Video). The team itself determines how it organizes discussions and makes decisions. Interactive Cognitive Scenario only suggests the possibility of alternative actions of each team member (using branching) in combination with the possibility of subsequent rejection from them when it becomes clear for team that these actions were erroneous (using selection).
Game parameters
There is a huge number of possible ways the Interactive Cognitive Scenario can be realized. Therefore, before a game is played some parameters should be agreed: * Initial game rating * The number of demonstration boards (the maximum allowed number of branches) * The number of players in each team and the rules for their replacement during the game * The rules of branching, selection, distribution, redistribution and passing * The time allowed for thinking over the moves and the form of time control.Spectators
Focus on chess
During the game, spectators are able to hear and see team discussions: what information and in what scope the players analyze, how much and what options are offered for continuation, at what depth they are calculated, how the evaluations of positions changes during the passing and what final decisions are taken as a result. For the first time this becomes available for spectators' assessment directly, rather than via expert analysis. The demonstration boards show several competing versions of the game (branches). Their number and ratings change throughout the game and directly affect the current and final score of the game.Focus on people
Business chess creates a team spirit and socio-psychological atmosphere that is not specific to chess. It may be of interest even for spectators who do not care much for chess. Playing business chess brings out familiar social problems for the teams such asleadership
Leadership, both as a research area and as a practical skill, encompasses the ability of an individual, group or organization to "lead", influence or guide other individuals, teams, or entire organizations. The word "leadership" often gets vi ...
and psychological compatibility, a division of labor and specialization, choosing effective ways of management
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a Government agency, government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includ ...
(authoritarian, democratic, etc.) and problem solving, generating new ideas, their discussion, implementation and development in a competitive environment, and so on.
Spectators can also watch almost all varieties of situations typical in group competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indiv ...
, and their continuous change, depending on the availability or shortage of advantages, time, alternative ways of development, and so on.
Tournaments
Tournaments have been held regularly since 1997. Running commentary of one of them was broadcast onArmenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
n national television.
In Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, ą£ąŠčüą║ą▓ą░, r=Moskva, p=m╔Ésk╦łva, a=ą£ąŠčüą║ą▓ą░.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
Russian leading grandmasters participated in two representative tournaments. The first was held in the Central House of Chess by M. M. Botvinnik in 2004, the proceedings of which were broadcast by the ''Sports'' channel of Russian TV. The second was held in the Moscow Chess Club by T. V. Petrosian in 2005.
Wider aspects
Apart from being a sport, Business Chess can also be used forscientific modelling
Scientific modelling is a scientific activity, the aim of which is to make a particular part or feature of the world easier to understand, define, quantify, visualize, or simulate by referencing it to existing and usually commonly accepted ...
of mental activity, the processes of problem solving and a choice of strategy, as a general education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty ...
al business game
Business game (also called business simulation game) refers to simulation games that are used as an educational tool for teaching business. Business games may be carried out for various business training such as: general management, finance, organ ...
, method of psychological evaluation
Psychological evaluation is a method to assess an individual's behavior, personality, cognitive abilities, and several other domains. A common reason for a psychological evaluation is to identify psychological factors that may be inhibiting a pers ...
, psychological training
Training is teaching, or developing in oneself or others, any skills and knowledge or fitness that relate to specific useful competencies. Training has specific goals of improving one's capability, capacity, productivity and performance. I ...
and play therapy
Play therapy refers to a range of methods of capitalising on children's natural urge to explore and harnessing it to meet and respond to the developmental and later also their mental health needs. It is also used for forensic or psychological as ...
. Such opportunity is conditioned by team active discussion and a multistage process of group decision-making based on sociocultural evolution
Sociocultural evolution, sociocultural evolutionism or social evolution are theories of sociobiology and cultural evolution that describe how societies and culture change over time. Whereas sociocultural development traces processes that tend t ...
depending on changing conditions ( game). It can be seen that the main mechanisms of Interactive Cognitive Scenario (branching and selection) resemble biological mechanisms of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
(genetic mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
and natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
).
Scientific model
Business chess as a scientific model can be effectively used for researches in following areas: game theory,bifurcation theory
Bifurcation theory is the mathematical study of changes in the qualitative or topological structure of a given family of curves, such as the integral curves of a family of vector fields, and the solutions of a family of differential equations. ...
, information theory, control theory
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a ...
and decision theory
Decision theory (or the theory of choice; not to be confused with choice theory) is a branch of applied probability theory concerned with the theory of making decisions based on assigning probabilities to various factors and assigning numerical ...
, the theory of innovation diffusion, management science
Management science (or managerial science) is a wide and interdisciplinary study of solving complex problems and making strategic decisions as it pertains to institutions, corporations, governments and other types of organizational entities. It is ...
, sociocultural evolution
Sociocultural evolution, sociocultural evolutionism or social evolution are theories of sociobiology and cultural evolution that describe how societies and culture change over time. Whereas sociocultural development traces processes that tend t ...
, cognitive psychology and social psychology
Social psychology is the scientific study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the real or imagined presence of other people or by social norms. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the ...
, research into natural intelligence and artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligenceŌĆöperceiving, synthesizing, and inferring informationŌĆödemonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech r ...
, and so on. Thus as an expert system the application of existing chess computer programs is possible.
In school
Experts in the field of child psychology agree that the system of national school education must first socialize pupils, that is, accustom and adapt them for the life insocial structure
In the social sciences, social structure is the aggregate of patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of individuals. Likewise, society is believed to be grouped into structurally rel ...
s. With this purpose it is reasonable to use Business Chess as a general educational business game. The primary goal of similar lessons is to carry out intellectual and socially-psychological trainings for the pupils to make them skilled in constructive communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inqui ...
, communicative competence The concept of communicative competence, as developed in linguistics, originated in response to perceived inadequacy of the notion of linguistic competence. That is, communicative competence encompasses a language user's grammatical knowledge of sy ...
, efficient management
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a Government agency, government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includ ...
, social self-organization
Self-organization, also called spontaneous order in the social sciences, is a process where some form of overall order arises from local interactions between parts of an initially disordered system. The process can be spontaneous when suff ...
, psychological strength and adaptation in group. It is supposed, that it promotes effective socialization and harmonious development of cogitative ( cognitive), behavioral ( interactive) and emotional ( motivational) components of pupils' person
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of prope ...
ality studying at comprehensive schools.
It is also reasonable to use Business Chess for carrying out psychological evaluation
Psychological evaluation is a method to assess an individual's behavior, personality, cognitive abilities, and several other domains. A common reason for a psychological evaluation is to identify psychological factors that may be inhibiting a pers ...
at schools. The opportunity to register a lot of individual and group psychological parameters at the same time so as to observe their changes in dynamics, allows a complex estimation of intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be des ...
, aptitude
An aptitude is a component of a competence to do a certain kind of work at a certain level. Outstanding aptitude can be considered "talent". Aptitude is inborn potential to perform certain kinds of activities, whether physical or mental, and ...
, level of achievement, personal situational correlations and mental development. Available expert systems
In artificial intelligence, an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert.
Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning through bodies of knowledge, represented mainly as ifŌĆ ...
in the form of modern chess computer programs enhance reliability of such researches.
A section of the "Business Chess" book is devoted to this subject, and also a lot of popular articles are included in the collection entitled "Sports business games: Business Chess, Go, Renju and others", 2007.
References
External links
Business chess site
Business Chess on the site of Moscow chess federation - Chessmoscow.ru
Business Chess on the Chess-News.ru
Chess academy of Armenia
{{Chess variants Board games introduced in 1992 Chess variants Chess in Russia Chess in Armenia Business simulation games Russian inventions