Bubonic plague on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bubonic plague is one of three types of
 Bubonic plague is an infection of the lymphatic system, usually resulting from the bite of an infected flea, ''Xenopsylla cheopis'' (the Oriental rat flea). Several flea species carried the bubonic plague, such as ''Pulex irritans'' (the human flea), ''Xenopsylla cheopis'', and ''
Bubonic plague is an infection of the lymphatic system, usually resulting from the bite of an infected flea, ''Xenopsylla cheopis'' (the Oriental rat flea). Several flea species carried the bubonic plague, such as ''Pulex irritans'' (the human flea), ''Xenopsylla cheopis'', and ''
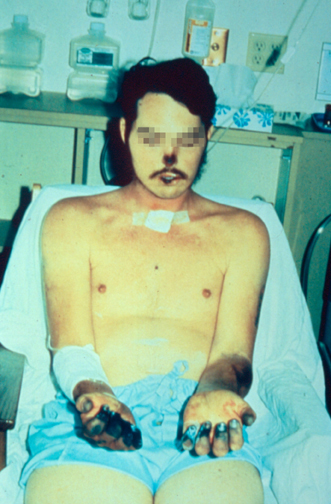 After being transmitted via the bite of an infected flea, the ''Y. pestis'' bacteria become localized in an inflamed lymph node, where they begin to colonize and reproduce. Infected lymph nodes develop hemorrhages, which result in the death of tissue.'' Y. pestis'' bacilli can resist phagocytosis and even reproduce inside phagocytes and kill them. As the disease progresses, the lymph nodes can
After being transmitted via the bite of an infected flea, the ''Y. pestis'' bacteria become localized in an inflamed lymph node, where they begin to colonize and reproduce. Infected lymph nodes develop hemorrhages, which result in the death of tissue.'' Y. pestis'' bacilli can resist phagocytosis and even reproduce inside phagocytes and kill them. As the disease progresses, the lymph nodes can
 Samples taken for testing include:
* Buboes: Swollen lymph nodes (buboes) characteristic of bubonic plague, a fluid sample can be taken from them with a needle.
* Blood
* Lungs
Samples taken for testing include:
* Buboes: Swollen lymph nodes (buboes) characteristic of bubonic plague, a fluid sample can be taken from them with a needle.
* Blood
* Lungs
 Globally between 2010 and 2015, there were 3,248 documented cases, which resulted in 584 deaths. The countries with the greatest number of cases are the
Globally between 2010 and 2015, there were 3,248 documented cases, which resulted in 584 deaths. The countries with the greatest number of cases are the  In July 2020, in
In July 2020, in
 In the
In the
 The scale of death and social upheaval associated with plague outbreaks has made the topic prominent in many historical and fictional accounts since the disease was first recognized. The Black Death in particular is described and referenced in numerous contemporary sources, some of which, including works by
The scale of death and social upheaval associated with plague outbreaks has made the topic prominent in many historical and fictional accounts since the disease was first recognized. The Black Death in particular is described and referenced in numerous contemporary sources, some of which, including works by
plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
caused by the plague bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
('' Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, headaches, and vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenter ...
, as well as swollen and painful lymph nodes occurring in the area closest to where the bacteria entered the skin. Acral necrosis, the dark discoloration of skin, is another symptom. Occasionally, swollen lymph nodes, known as " buboes," may break open.
The three types of plague are the result of the route of infection: bubonic plague, septicemic plague, and pneumonic plague. Bubonic plague is mainly spread by infected flea
Flea, the common name for the order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult fleas grow to about long, ...
s from small animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage ...
s. It may also result from exposure to the body fluids from a dead plague-infected animal. Mammals such as rabbits, hares, and some cat species are susceptible to bubonic plague, and typically die upon contraction. In the bubonic form of plague, the bacteria enter through the skin through a flea bite and travel via the lymphatic vessels to a lymph node, causing it to swell. Diagnosis is made by finding the bacteria in the blood, sputum, or fluid from lymph nodes.
Prevention is through public health measures such as not handling dead animals in areas where plague is common. While vaccines against the plague have been developed, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
recommends that only high-risk groups, such as certain laboratory personnel and health care workers, get inoculated. Several antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s are effective for treatment, including streptomycin, gentamicin, and doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus ...
.
Without treatment, plague results in the death of 30% to 90% of those infected. Death, if it occurs, is typically within 10 days. With treatment, the risk of death is around 10%. Globally between 2010 and 2015 there were 3,248 documented cases, which resulted in 584 deaths. The countries with the greatest number of cases are the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
, and Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
.
The plague is considered the likely cause of the Black Death that swept through Asia, Europe, and Africa in the 14th century and killed an estimated 50 million people, including about 25% to 60% of the European population. Because the plague killed so many of the working population, wages rose due to the demand for labor. Some historians see this as a turning point in European economic development. The disease is also considered to have been responsible for the Plague of Justinian, originating in the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantino ...
in the 6th century CE, as well as the third epidemic, affecting China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
, and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, originating in the Yunnan Province
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the ...
in 1855. The term ''bubonic'' is derived from the Greek word βουβών, meaning "groin".
Cause
 Bubonic plague is an infection of the lymphatic system, usually resulting from the bite of an infected flea, ''Xenopsylla cheopis'' (the Oriental rat flea). Several flea species carried the bubonic plague, such as ''Pulex irritans'' (the human flea), ''Xenopsylla cheopis'', and ''
Bubonic plague is an infection of the lymphatic system, usually resulting from the bite of an infected flea, ''Xenopsylla cheopis'' (the Oriental rat flea). Several flea species carried the bubonic plague, such as ''Pulex irritans'' (the human flea), ''Xenopsylla cheopis'', and ''Ceratophyllus fasciatus
''Ceratophyllus'' is a widespread genus of fleas found in temperate climates. Some of its members include the chicken flea, '' Ceratophyllus gallinae'', and the poultry flea, '' Ceratophyllus niger''.
Species
* '' Ceratophyllus adustus'' Jord ...
''. ''Xenopsylla cheopis'' was the most effective flea species for transmittal. In very rare circumstances, as in septicemic plague, the disease can be transmitted by direct contact with infected tissue or exposure to the cough of another human. The flea is parasitic on house and field rats and seeks out other prey when its rodent hosts die. Rats were an amplifying factor to bubonic plague due to their common association with humans as well as the nature of their blood. The rat's blood allowed the rat to withstand a major concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', ''number concentration'', ...
of the plague. The bacteria form aggregates in the gut of infected fleas and this results in the flea regurgitating ingested blood, which is now infected, into the bite site of a rodent or human host. Once established, bacteria rapidly spread to the lymph nodes and multiply. The fleas that transmit the disease only directly infect humans when the rat population in the area is wiped out from a mass infection. Furthermore, in areas of a large population of rats, the animals can harbor low levels of the plague infection without causing human outbreaks. With no new rat inputs being added to the population from other areas, the infection would only spread to humans in very rare cases of overcrowding.
Signs and symptoms
 After being transmitted via the bite of an infected flea, the ''Y. pestis'' bacteria become localized in an inflamed lymph node, where they begin to colonize and reproduce. Infected lymph nodes develop hemorrhages, which result in the death of tissue.'' Y. pestis'' bacilli can resist phagocytosis and even reproduce inside phagocytes and kill them. As the disease progresses, the lymph nodes can
After being transmitted via the bite of an infected flea, the ''Y. pestis'' bacteria become localized in an inflamed lymph node, where they begin to colonize and reproduce. Infected lymph nodes develop hemorrhages, which result in the death of tissue.'' Y. pestis'' bacilli can resist phagocytosis and even reproduce inside phagocytes and kill them. As the disease progresses, the lymph nodes can hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, v ...
and become swollen and necrotic. Bubonic plague can progress to lethal septicemic plague in some cases. The plague is also known to spread to the lungs and become the disease known as the pneumonic plague. Symptoms appear 2–7 days after getting bitten and they include:Sebbane, Florent et al. "Kinetics of disease progression and host response in a rat model of bubonic plague." ''The American journal of pathology'' vol. 166,5 (2005)
* Chills
* General ill feeling ( malaise)
* High fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
>
* Muscle cramps
* Seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with lo ...
* Smooth, painful lymph gland swelling called a bubo, commonly found in the groin, but may occur in the armpits or neck, most often near the site of the initial infection (bite or scratch)
* Pain may occur in the area before the swelling appears
* Gangrene of the extremities such as toes, fingers, lips, and tip of the nose.
The best-known symptom of bubonic plague is one or more infected, enlarged, and painful lymph nodes, known as buboes. Buboes associated with the bubonic plague are commonly found in the armpits, upper femoral, groin, and neck region. Symptoms include heavy breathing, continuous vomiting of blood ( hematemesis), aching limbs, coughing, and extreme pain caused by the decay or decomposition of the skin while the person is still alive. Additional symptoms include extreme fatigue, gastrointestinal problems, spleen inflammation, lenticulae (black dots scattered throughout the body), delirium, coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
, organ failure, and death. Organ failure is a result of the bacteria infecting organs through the bloodstream. Other forms of the disease include septicemic plague and pneumonic plague in which the bacterium reproduces in the person's blood and lungs respectively.
Diagnosis
Laboratory testing is required in order todiagnose
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine "cause and effect". In systems enginee ...
and confirm plague. Ideally, confirmation is through the identification of ''Y. pestis'' culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
from a patient sample. Confirmation of infection can be done by examining serum
Serum may refer to:
* Serum (blood), plasma from which the clotting proteins have been removed
**Antiserum, blood serum with specific antibodies for passive immunity
* Serous fluid, any clear bodily fluid
*Truth serum, a drug that is likely to mak ...
taken during the early and late stages of infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
. To quickly screen for the ''Y. pestis'' antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
in patients, rapid dipstick
A dipstick is one of several measurement devices.
Some dipsticks are dipped into a liquid to perform a chemical test or to provide a measure of quantity of the liquid.
Since the late 20th century, a flatness/levelness measuring device trademarke ...
tests have been developed for field use. Samples taken for testing include:
* Buboes: Swollen lymph nodes (buboes) characteristic of bubonic plague, a fluid sample can be taken from them with a needle.
* Blood
* Lungs
Samples taken for testing include:
* Buboes: Swollen lymph nodes (buboes) characteristic of bubonic plague, a fluid sample can be taken from them with a needle.
* Blood
* Lungs
Prevention
Bubonic plague outbreaks are controlled by pest control and modern sanitation techniques. This disease uses fleas commonly found on rats as a vector to jump from animals to humans. The mortality rate hits its peak during the hot and humid months of June, July, and August. Furthermore, the plague most affected those of poor upbringing due to greater exposure, poor sanitation techniques and lack of a healthy immune system due to a poor diet. The successful control of rat populations in dense urban areas is essential to outbreak prevention. One example is the use of a machine called the Sulfurozador, used to deliver sulphur dioxide to eradicate the pest that spread the bubonic plague, in Buenos Aires, Argentina during the early 18th century. Targeted chemoprophylaxis,sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation syste ...
, and vector control also played a role in controlling the 2003 Oran outbreak of the bubonic plague. Another means of prevention in large European cities was a city-wide quarantine to not only limit interaction with people who were infected, but also to limit the interaction with the infected rats.
Treatment
Several classes ofantibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and preventio ...
are effective in treating bubonic plague. These include aminoglycosides such as streptomycin and gentamicin, tetracyclines (especially doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus ...
), and the fluoroquinolone ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin i ...
. Mortality associated with treated cases of bubonic plague is about 1–15%, compared to a mortality of 40–60% in untreated cases.
People potentially infected with the plague need immediate treatment and should be given antibiotics within 24 hours of the first symptoms to prevent death. Other treatments include oxygen, intravenous fluids, and respiratory support. People who have had contact with anyone infected by pneumonic plague are given prophylactic antibiotics. Using the broad-based antibiotic streptomycin has proven to be dramatically successful against the bubonic plague within 12 hours of infection.Echenberg, Myron (2002). Pestis Redux: The Initial Years of the Third Bubonic Plague Pandemic, 1894–1901. Journal of World History, vol 13,2
Epidemiology
Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
, and Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
.
For over a decade since 2001, Zambia, India, Malawi, Algeria, China, Peru, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo had the most plague cases with over 1,100 cases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo alone. From 1,000 to 2,000 cases are conservatively reported per year to the WHO. From 2012 to 2017, reflecting political unrest and poor hygienic conditions, Madagascar began to host regular epidemics.
Between 1900 and 2015, the United States had 1,036 human plague cases with an average of 9 cases per year. In 2015, 16 people in the Western United States developed plague, including 2 cases in Yosemite National Park
Yosemite National Park ( ) is an American national park in California, surrounded on the southeast by Sierra National Forest and on the northwest by Stanislaus National Forest. The park is managed by the National Park Service and covers an ...
. These US cases usually occur in rural northern New Mexico, northern Arizona, southern Colorado, California, southern Oregon, and far western Nevada.
In November 2017, the Madagascar Ministry of Health reported an outbreak to the WHO (World Health Organization) with more cases and deaths than any recent outbreak in the country. Unusually, most of the cases were pneumonic rather than bubonic.
In June 2018, a child was confirmed to be the first person in Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Monta ...
to be infected by bubonic plague in nearly 30 years.
A couple died in May 2019, in Mongolia, while hunting marmots. Another two people in the province of Inner Mongolia, China were treated in November 2019 for the disease.
Bayannur
Bayannur or Bayannao'er (; mn, ''Bayannaɣur qota'', Mongolian Cyrillic Баяннуур хот) is a prefecture-level city in western Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. Until 1 December 2003, the area was called Bayannur League.
...
, Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
of China, a human case of bubonic plague was reported. Officials responded by activating a city-wide plague-prevention system for the remainder of the year. Also in July 2020, in Mongolia, a teenager died from bubonic plague after consuming infected marmot meat.
History
''Yersinia pestis'' has been discovered in archaeological finds from the Late Bronze Age (~3800 BP). The bacteria is identified by ancient DNA in human teeth from Asia and Europe dating from 2,800 to 5,000 years ago. Some authors have suggested that the plague was responsible for the Neolithic decline.First pandemic
The first recorded epidemic affected the Sasanian Empire and their arch-rivals, the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) and was named the Plague of Justinian after emperorJustinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized '' renov ...
, who was infected but survived through extensive treatment. The pandemic resulted in the deaths of an estimated 25 million (6th century outbreak) to 50 million people (two centuries of recurrence). The historian Procopius wrote, in Volume II of ''History of the Wars'', of his personal encounter with the plague and the effect it had on the rising empire. In the spring of 542, the plague arrived in Constantinople, working its way from port city to port city and spreading around the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
, later migrating inland eastward into Asia Minor and west into Greece and Italy. The Plague of Justinian is said to have been "completed" in the middle of the 8th century. Because the infectious disease spread inland by the transferring of merchandise through Justinian's efforts in acquiring luxurious goods of the time and exporting supplies, his capital became the leading exporter of the bubonic plague. Procopius, in his work ''Secret History'', declared that Justinian was a demon of an emperor who either created the plague himself or was being punished for his sinfulness.
Second pandemic
 In the
In the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
Europe experienced the deadliest disease outbreak in history when the Black Death, the infamous pandemic of bubonic plague, hit in 1347, killing one-third of the European human population. Some historians believe that society subsequently became more violent as the mass mortality rate cheapened life and thus increased warfare, crime, popular revolt, waves of flagellants, and persecution. The Black Death originated in Central Asia and spread from Italy and then throughout other European countries. Arab historians Ibn Al-Wardni and Almaqrizi believed the Black Death originated in Mongolia. Chinese records also showed a huge outbreak in Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
in the early 1330s.
In 2022, researchers presented evidence that the plague originated near Lake Issyk-Kul in Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
. The Mongols had cut the trade route (the Silk Road) between China and Europe, which halted the spread of the Black Death from eastern Russia to Western Europe. The European epidemic began with an attack that Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
s launched on the Italian merchants' last trading station in the region, Caffa
uk, Феодосія, Теодосія crh, Kefe
, official_name = ()
, settlement_type=
, image_skyline = THEODOSIA 01.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, image_caption = Genoese fortress of Caffa
, image_shield = Fe ...
in the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
.
In late 1346, plague broke out among the besiegers and from them penetrated the town. The Mongol forces catapulted plague-infested corpses into Caffa as a form of attack, one of the first known instances of biological warfare. When spring arrived, the Italian merchants fled on their ships, unknowingly carrying the Black Death. Carried by the fleas on rats, the plague initially spread to humans near the Black Sea and then outwards to the rest of Europe as a result of people fleeing from one area to another. Rats migrated with humans, traveling among grain bags, clothing, ships, wagons, and grain husks. Continued research indicates that black rats, those that primarily transmitted the disease, prefer grain as a primary meal. Due to this, the major bulk grain fleets that transported major city's food shipments from Africa and Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
to heavily populated areas, and were then unloaded by hand, played a role in increasing the transmission effectiveness of the plague.
Third pandemic
The plague resurfaced for a third time in the mid-19th century; this is also known as "the modern pandemic". Like the two previous outbreaks, this one also originated inEastern Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
, most likely in Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the ...
, a province of China, where there are several natural plague foci. The initial outbreaks occurred in the second half of the 18th century. The disease remained localized in Southwest China for several years before spreading. In the city of Canton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ente ...
, beginning in January 1894, the disease had killed 80,000 people by June. Daily water-traffic with the nearby city of Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a List of cities in China, city and Special administrative regions of China, special ...
rapidly spread the plague there, killing over 2,400 within two months during the 1894 Hong Kong plague
The 1894 Hong Kong plague, part of the third plague pandemic, was a major outbreak of the bubonic plague in Hong Kong. While the plague was harshest in 1894, it returned annually between 1895 and 1929, and killed over 20,000 in total, with a fa ...
.
The third pandemic spread the disease to port cities throughout the world in the second half of the 19th century and the early 20th century via shipping routes. The plague infected people in Chinatown in San Francisco from 1900 to 1904, and in the nearby locales of Oakland and the East Bay again from 1907 to 1909. During the former outbreak, in 1902, authorities made permanent the Chinese Exclusion Act
The Chinese Exclusion Act was a United States federal law signed by President Chester A. Arthur on May 6, 1882, prohibiting all immigration of Chinese laborers for 10 years. The law excluded merchants, teachers, students, travelers, and diplo ...
, a law originally signed into existence by President Chester A. Arthur in 1882. The Act was supposed to last for 10 years, but was renewed in 1892 with the Geary Act, then followed by the 1902 decision. The last major outbreak in the United States occurred in Los Angeles in 1924, though the disease is still present in wild rodents and can be passed to humans that come in contact with them. According to the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
, the pandemic was considered active until 1959, when worldwide casualties dropped to 200 per year. In 1994, a plague outbreak in five Indian states caused an estimated 700 infections (including 52 deaths) and triggered a large migration of Indians within India as they tried to avoid the disease.
It was during the 1894 Hong Kong plague outbreak that Alexandre Yersin
Alexandre Emile Jean Yersin (22 September 1863 – 1 March 1943) was a Swiss-French physician and bacteriologist. He is remembered as the co-discoverer of the bacillus responsible for the bubonic plague or pest, which was later named in his ...
isolated the bacterium responsible ('' Yersinia pestis''), a few days after Japanese bacteriologist Kitasato Shibasaburō
Baron was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist. He is remembered as the co-discoverer of the infectious agent of bubonic plague in Hong Kong during an outbreak in 1894, almost simultaneously with Alexandre Yersin.
Kitasato was nominat ...
had isolated it. However, the latter's description was imprecise and also expressed doubts of its relation to the disease, and thus the bacterium is today only named after Yersin.
Society and culture
 The scale of death and social upheaval associated with plague outbreaks has made the topic prominent in many historical and fictional accounts since the disease was first recognized. The Black Death in particular is described and referenced in numerous contemporary sources, some of which, including works by
The scale of death and social upheaval associated with plague outbreaks has made the topic prominent in many historical and fictional accounts since the disease was first recognized. The Black Death in particular is described and referenced in numerous contemporary sources, some of which, including works by Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer (; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for '' The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He w ...
, Boccaccio, and Petrarch
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credited ...
, are considered part of the Western canon. '' The Decameron'', by Boccaccio, is notable for its use of a frame story involving individuals who have fled Florence for a secluded villa to escape the Black Death. First-person, sometimes sensationalized or fictionalized, accounts of living through plague years have also been popular across centuries and cultures. For example, Samuel Pepys's diary makes several references to his first-hand experiences of the Great Plague of London in 1665–6.
Later works, such as Albert Camus
Albert Camus ( , ; ; 7 November 1913 – 4 January 1960) was a French philosopher, author, dramatist, and journalist. He was awarded the 1957 Nobel Prize in Literature at the age of 44, the second-youngest recipient in history. His work ...
's novel ''The Plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
'' or Ingmar Bergman
Ernst Ingmar Bergman (14 July 1918 – 30 July 2007) was a Swedish film director, screenwriter, producer and playwright. Widely considered one of the greatest and most influential filmmakers of all time, his films are known as "profoun ...
's film '' The Seventh Seal'' have used bubonic plague in settings, such as quarantined cities in either medieval or modern times, as a backdrop to explore a variety of concepts. Common themes include the breakdown of society, institutions, and individuals during the plague, the cultural and psychological existential confrontation with mortality, and the allegorical use of the plague about contemporary moral or spiritual questions.
Biological warfare
Some of the earliest instances of biological warfare were said to have been products of the plague, as armies of the 14th century were recorded catapulting diseased corpses over the walls of towns and villages to spread the pestilence. This was done by Jani Beg when he attacked the city of Kaffa in 1343. Later, plague was used during theSecond Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific T ...
as a bacteriological weapon by the Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emper ...
. These weapons were provided by Shirō Ishii's units and used in experiments on humans before being used in the field. For example, in 1940, the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service bombed Ningbo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sate ...
with fleas carrying the bubonic plague. During the Khabarovsk War Crime Trials, the accused, such as Major General Kiyoshi Kawashima, testified that, in 1941, 40 members of Unit 731 air-dropped plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
-contaminated fleas on Changde. These operations caused epidemic plague outbreaks.
Continued research
Substantial research has been done regarding the origin of the plague and how it traveled through the continent. Mitochondrial DNA of modern rats in Western Europe indicated that these rats came from two different areas, one being Africa and the other being unclear of a specific origin. The research regarding this pandemic has greatly increased with technology. Through archaeo-molecular investigation, researchers have discovered the DNA of plague bacillus in the dental core of those that fell ill to the plague. Analysis of teeth of the deceased allows researchers to further understand both the demographics and mortuary patterns of the disease. For example, in 2013 in England, archeologists uncovered a burial mound to reveal 17 bodies, mainly children, who had died of the Bubonic plague. They analyzed these burial remains using radiocarbon dating to determine they were from the 1530s, and dental core analysis revealed the presence of Yersinia pestis. Other evidence for rats that are currently still being researched consists of gnaw marks on bones, predator pellets and rat remains that were preserved in situ. This research allows individuals to trace early rat remains to track the path traveled and in turn connect the impact of the Bubonic Plague to specific breeds of rats. Burial sites, known as plague pits, offer archaeologists an opportunity to study the remains of people who died from the plague. Another research study indicates that these separate pandemics were all interconnected. A current computer model indicates that the disease did not go away in between these pandemics. It rather lurked within the rat population for years without causing human epidemics.See also
* List of cutaneous conditions * List of epidemics * Miasma theory *Plague (disease)
Plague is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium '' Yersinia pestis''. Symptoms include fever, weakness and headache. Usually this begins one to seven days after exposure. There are three forms of plague, each affecting a different pa ...
* Plague doctor
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bubonic Plague History of medieval medicine Plague (disease) Rodent-carried diseases Zoonotic bacterial diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate