Brain Size on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The size of the brain is a frequent topic of study within the fields of

 From early primates to hominids and finally to ''Homo sapiens'', the brain is progressively larger, with exception of extinct Neanderthals whose brain size exceeded modern Homo sapiens. The volume of the human brain has increased as humans have evolved (see Homininae), starting from about 600 cm3 in ''
From early primates to hominids and finally to ''Homo sapiens'', the brain is progressively larger, with exception of extinct Neanderthals whose brain size exceeded modern Homo sapiens. The volume of the human brain has increased as humans have evolved (see Homininae), starting from about 600 cm3 in ''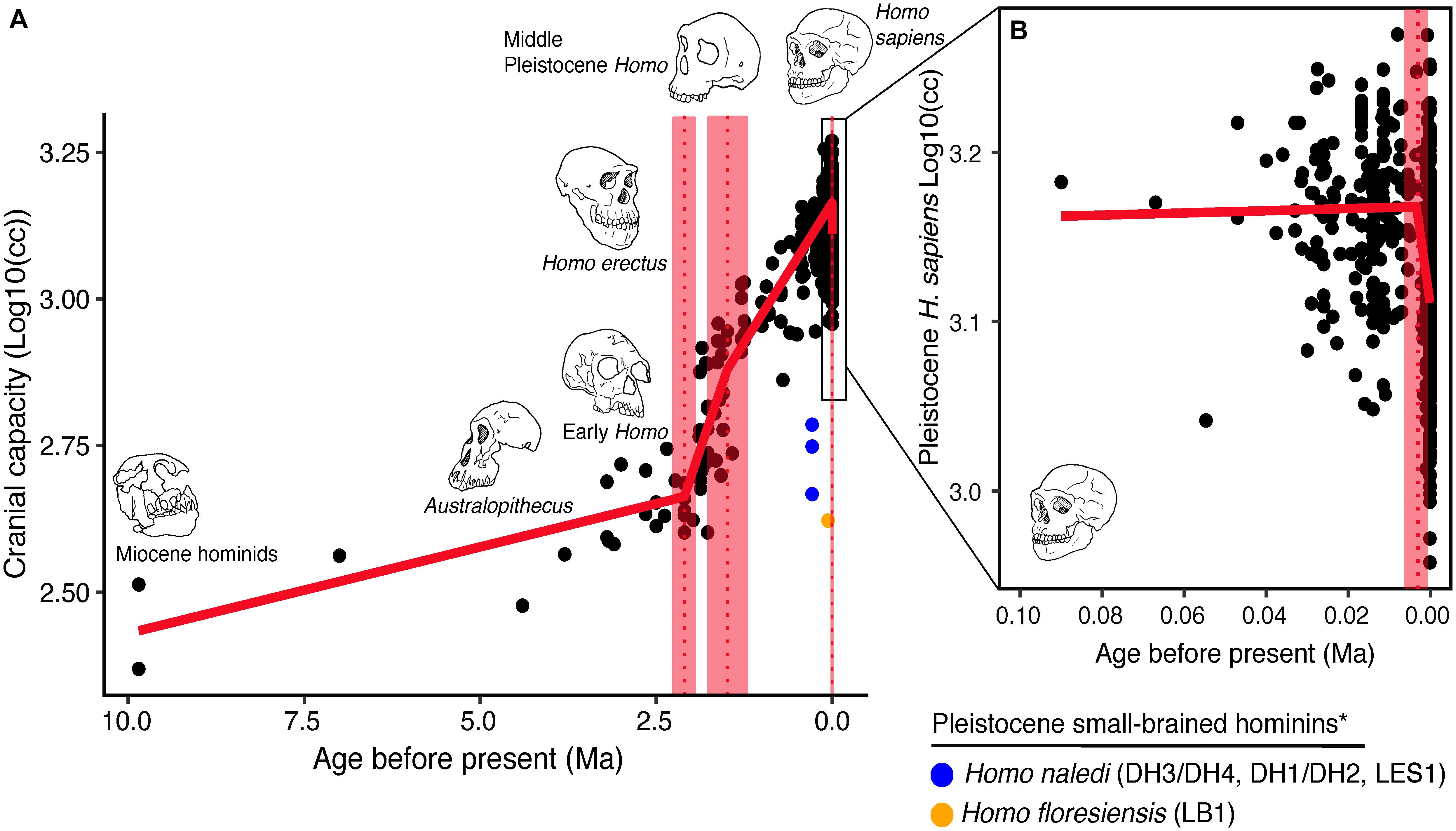

 A human baby's brain at birth averages 369 cm3 and increases, during the first year of life, to about 961 cm3, after which the growth rate declines. Brain volume peaks at the teenage years, and after the age of 40 it begins declining at 5% per decade, speeding up around 70. Average adult male brain weight is , while an adult female has an average brain weight of . (This does not take into account neuron density nor brain-to-body mass ratio; men on average also have larger bodies than women.) Males have been found to have on average greater cerebral, cerebellar and cerebral cortical lobar volumes, except possibly left parietal. The gender differences in size vary by more specific brain regions. Studies have tended to indicate that men have a relatively larger
A human baby's brain at birth averages 369 cm3 and increases, during the first year of life, to about 961 cm3, after which the growth rate declines. Brain volume peaks at the teenage years, and after the age of 40 it begins declining at 5% per decade, speeding up around 70. Average adult male brain weight is , while an adult female has an average brain weight of . (This does not take into account neuron density nor brain-to-body mass ratio; men on average also have larger bodies than women.) Males have been found to have on average greater cerebral, cerebellar and cerebral cortical lobar volumes, except possibly left parietal. The gender differences in size vary by more specific brain regions. Studies have tended to indicate that men have a relatively larger
anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having i ...
, biological anthropology, animal science and evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
. Brain size is sometimes measured by weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity.
Some standard textbooks define weight as a vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weight as a scalar qua ...
and sometimes by volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). ...
(via MRI scans or by skull volume). Neuroimaging intelligence testing
Neuroimaging intelligence testing concerns the use of neuroimaging techniques to evaluate human intelligence. Neuroimaging technology has advanced such that scientists hope to use neuroimaging increasingly for investigations of brain function relat ...
can be used to study the volumetric measurements of the brain. Regarding "intelligence testing", a question that has been frequently investigated is the relation of brain size to intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can ...
. This question is quite controversial and will be addressed further in the section on intelligence. The measure of brain size and cranial capacity is not just important to humans, but to all mammals.
Humans
In humans, the rightcerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum ( brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemisphere ...
is typically larger than the left, whereas the cerebellar hemispheres are typically closer in size. The adult human brain weighs on average about . In men the average weight is about 1370 g and in women about 1200 g. The volume is around 1260 cm3 in men and 1130 cm3 in women, although there is substantial individual variation. Yet another study argued that adult human brain weight is 1,300-1,400g for adult humans and 350-400g for newborn humans. There is a range of volume and weights, and not just one number that one can definitively rely on, as with body mass. It is also important to note that variation between individuals is not as important as variation within species, as overall the differences are much smaller. The mechanisms of interspecific and intraspecific variation also differ.
Variation and evolution

 From early primates to hominids and finally to ''Homo sapiens'', the brain is progressively larger, with exception of extinct Neanderthals whose brain size exceeded modern Homo sapiens. The volume of the human brain has increased as humans have evolved (see Homininae), starting from about 600 cm3 in ''
From early primates to hominids and finally to ''Homo sapiens'', the brain is progressively larger, with exception of extinct Neanderthals whose brain size exceeded modern Homo sapiens. The volume of the human brain has increased as humans have evolved (see Homininae), starting from about 600 cm3 in ''Homo habilis
''Homo habilis'' ("handy man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.31 million years ago to 1.65 million years ago (mya). Upon species description in 1964, ''H. habilis'' was highly ...
'' up to 1680 cm3 in Homo neanderthalensis, which was the hominid with the biggest brain size. The increase in brain size stopped with neanderthals. Since then, the average brain size has been shrinking over the past 28,000 years. One study suggests that this decrease in brain size "was surprisingly recent, occurring in the last 3,000 years", not the past 28,000 years. The cranial capacity has decreased from around 1,550 cm3 to around 1,440 cm3 in males while the female cranial capacity has shrunk from around 1,500 cm3 to around 1,240 cm3. Other sources with bigger sample sizes of modern Homo sapiens find approximately the same cranial capacity for males but a higher cranial capacity of around 1330 cm3 in females. However, a study that reanalyzed data used in the study that suggested a decrease in brain size in the last 3,000 years, indicates that brain size did not decrease over this timespan and neither within 300 ka as suggested by other studies. It concluded that "the samples need to be specific enough to test the hypothesis across different times and populations".


''H. floresiensis small brain
'' Homo floresiensis'' is ahominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The ...
from the island of Flores
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Including the Komodo Islands off its west coast (but excluding the Solor Archipelago to the east of Flores), the land area is 15,530.58 km2, and t ...
in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
with fossils dating from 60,000-100,000 years ago. Despite its relatively derived position in the hominin phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological s ...
, CT imaging of its skull reveals that its brain volume was only 417 cm3, less than that of even ''Homo habilis
''Homo habilis'' ("handy man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.31 million years ago to 1.65 million years ago (mya). Upon species description in 1964, ''H. habilis'' was highly ...
'', which is believed to have gone extinct far earlier (around 1.65 million years ago.). The reason for this regression in brain size is believed to be '' island syndrome'' in which the brains of insular species become smaller due to reduced predation risk. This is beneficial as it reduces the basal metabolic rate
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. It is reported in energy units per unit time ranging from watt (joule/second) to ml O2/min or joule per hour per kg body mass J/(h·kg). P ...
without significant increases in predation risk.
Genetic causes of recent decrease
In recent years, experiments have been conducted drawing conclusions to brain size in association to the gene mutation that causesmicrocephaly
Microcephaly (from New Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it ...
, a neural developmental disorder that affects cerebral cortical volume.
Sociocultural causes of suggested recent decrease
A 2021 study proposed that the recent decrease in brain size in the last 3,000 years has resulted from externalization of knowledge andgroup decision-making Group decision-making (also known as collaborative decision-making or collective decision-making) is a situation faced when individuals collectively make a choice from the alternatives before them. The decision is then no longer attributable to any ...
, partly via the advent of social system
In sociology, a social system is the patterned network of relationships constituting a coherent whole that exist between individuals, groups, and institutions. It is the formal structure of role and status that can form in a small, stable group. A ...
s of distributed cognition, social organization, division of labor and sharing of information. A 2022 study, that reanalyzed data used in the study, refutes their conclusion that the brain size did decrease at all during the last 3,000 years.
Hydrocephalus
Exceptional cases ofhydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary i ...
, such as what was reported by John Lorber in 1980 and by a study with rats, suggest that relatively high levels of intelligence and relatively normal functioning are possible even with very small brains. It is unclear what conclusions could be drawn from such reports – such as about brain capacities, redundancies, mechanics and size requirements.
Biogeographic variation
Efforts to find racial or ethnic variation in brain size are generally considered to be a pseudoscientific endeavor and have traditionally been tied to scientific racism and attempts to demonstrate a racial intellectual hierarchy.Gould, S. J. (1981). ''The Mismeasure of Man''. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. The majority of efforts to demonstrate this have relied on indirect data that assessed skull measurements as opposed to direct brain observations. These are considered scientifically discredited. A large-scale 1984 survey of global variation in skulls has concluded that variation in skull and head sizes is unrelated to race, but rather climatic heat preservation, stating "We find little support for the use of brain size in taxonomic assessment (other than with paleontological extremes over time). Racial taxonomies which include cranial capacity, head shape, or any other trait influenced by climate confound ecotypic and phyletic causes. For Pleistocene hominids, we doubt that the volume of the braincase is any more taxonomically 'valuable' than any other trait."Sex
 A human baby's brain at birth averages 369 cm3 and increases, during the first year of life, to about 961 cm3, after which the growth rate declines. Brain volume peaks at the teenage years, and after the age of 40 it begins declining at 5% per decade, speeding up around 70. Average adult male brain weight is , while an adult female has an average brain weight of . (This does not take into account neuron density nor brain-to-body mass ratio; men on average also have larger bodies than women.) Males have been found to have on average greater cerebral, cerebellar and cerebral cortical lobar volumes, except possibly left parietal. The gender differences in size vary by more specific brain regions. Studies have tended to indicate that men have a relatively larger
A human baby's brain at birth averages 369 cm3 and increases, during the first year of life, to about 961 cm3, after which the growth rate declines. Brain volume peaks at the teenage years, and after the age of 40 it begins declining at 5% per decade, speeding up around 70. Average adult male brain weight is , while an adult female has an average brain weight of . (This does not take into account neuron density nor brain-to-body mass ratio; men on average also have larger bodies than women.) Males have been found to have on average greater cerebral, cerebellar and cerebral cortical lobar volumes, except possibly left parietal. The gender differences in size vary by more specific brain regions. Studies have tended to indicate that men have a relatively larger amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex ver ...
and hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus ...
, while women have a relatively larger caudate and hippocampi. When covaried for intracranial volume, height, and weight, Kelly (2007) indicates women have a higher percentage of gray matter, whereas men have a higher percentage of white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribu ...
and cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the ...
. There is high variability between individuals in these studies, however.
However, Yaki (2011) found no statistically significant
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the p ...
gender differences in the gray matter ratio for most ages (grouped by decade), except in the 3rd and 6th decades of life in the sample of 758 women and 702 men aged 20–69. The average male in their third decade (ages 20–29) had a significantly higher gray matter ratio than the average female of the same age group. In contrast, among subjects in their sixth decade, the average woman had a significantly larger gray matter ratio, though no meaningful difference was found among those in their 7th decade of life.
Total cerebral and gray matter volumes peak during the ages from 10–20 years (earlier in girls than boys), whereas white matter and ventricular volumes increase. There is a general pattern in neural development of childhood peaks followed by adolescent declines (e.g. synaptic pruning). Consistent with adult findings, average cerebral volume is approximately 10% larger in boys than girls. However, such differences should not be interpreted as imparting any sort of functional advantage or disadvantage; gross structural measures may not reflect functionally relevant factors such as neuronal connectivity and receptor density, and of note is the high variability of brain size even in narrowly defined groups, for example children at the same age may have as much as a 50% differences in total brain volume. Young girls have on average relative larger hippocampal volume, whereas the amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex ver ...
e are larger in boys. However, multiple studies have found a higher synaptic density in males: a 2008 study reported that men had a significantly higher average synaptic density of 12.9 × 108 per cubic millimeter, whereas in women it was 8.6 × 108 per cubic millimeter, a 33% difference. Other studies have found an average of 4 billion more neurons in the male brain, corroborating this difference, as each neuron has on average 7,000 synaptic connections to other neurons.
Significant dynamic changes in brain structure take place through adulthood and aging, with substantial variation between individuals. In later decades, men show greater volume loss in whole brain volume and in the frontal lobes
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove betwe ...
, and temporal lobes
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pro ...
, whereas in women there is increased volume loss in the hippocampi and parietal lobes. Men show a steeper decline in global gray matter volume, although in both sexes it varies by region with some areas exhibiting little or no age effect. Overall white matter volume does not appear to decline with age, although there is variation between brain regions.
Genetic contribution
Adult twin studies have indicated highheritability
Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of ''variation'' in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. The concept of her ...
estimates for overall brain size in adulthood (between 66% and 97%). The effect varies regionally within the brain, however, with high heritabilities of frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
volumes (90-95%), moderate estimates in the hippocampi (40-69%), and environmental factors influencing several medial brain areas. In addition, lateral ventricle
The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right ventricle, respectively.
Each lateral ventricle resemble ...
volume appears to be mainly explained by environmental factors, suggesting such factors also play a role in the surrounding brain tissue. Genes may cause the association between brain structure and cognitive functions, or the latter may influence the former during life. A number of candidate genes have been identified or suggested, but they await replication.
Intelligence
Studies demonstrate a correlation between brain size and intelligence, larger brains predicting higher intelligence. It is however not clear if the correlation is causal. The majority of MRI studies report moderate correlations around 0.3 to 0.4 between brain volume and intelligence. The most consistent associations are observed within the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes, the hippocampus, and the cerebellum, but only account for a relatively small amount of variance in IQ, which suggests that while brain size may be related to human intelligence, other factors also play a role. In addition, brain volumes do not correlate strongly with other and more specific cognitive measures. In men, IQ correlates more with gray matter volume in thefrontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
and parietal lobe, which is roughly involved in sensory integration and attention, whereas in women it correlates with gray matter volume in the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
and Broca's area
Broca's area, or the Broca area (, also , ), is a region in the frontal lobe of the dominant hemisphere, usually the left, of the brain with functions linked to speech production.
Language processing has been linked to Broca's area since Pier ...
, which is involved in language.
Research measuring brain volume, P300 auditory evoked potentials, and intelligence shows a dissociation, such that both brain volume and speed of P300 correlate with measured aspects of intelligence, but not with each other. Evidence conflicts on the question of whether brain size variation also predicts intelligence between siblings, as some studies find moderate correlations and others find none. A recent review by Nesbitt, Flynn et al. (2012) point out that crude brain size is unlikely to be a good measure of IQ, for example brain size also differs between men and women, but without well documented differences in IQ.
A discovery in recent years is that the structure of the adult human brain changes when a new cognitive or motor skill, including vocabulary, is learned. Structural neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity, or brain plasticity, is the ability of neural networks in the brain to change through growth and reorganization. It is when the brain is rewired to function in some way that differs from how it p ...
(increased gray matter volume) has been demonstrated in adults after three months of training in a visual-motor skill, as the qualitative change (i.e. learning of a new task) appear more critical for the brain to change its structure than continued training of an already-learned task. Such changes (e.g. revising for medical exams) have been shown to last for at least 3 months without further practicing; other examples include learning novel speech sounds, musical ability, navigation skills and learning to read mirror-reflected words.
Other animals
The largest brains are those ofsperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the sperm whale famil ...
s, weighing about . An elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantida ...
's brain weighs just over , a bottlenose dolphin
Bottlenose dolphins are aquatic mammals in the genus ''Tursiops.'' They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus definitively contains two species: the comm ...
's , whereas a human brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of ...
is around . Brain size tends to vary according to body size. The relationship is not proportional, though: the brain-to-body mass ratio varies. The largest ratio found is in the shrew
Shrews (family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to differ ...
. Averaging brain weight across all orders of mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
, it follows a power law
In statistics, a power law is a functional relationship between two quantities, where a relative change in one quantity results in a proportional relative change in the other quantity, independent of the initial size of those quantities: one q ...
, with an exponent
Exponentiation is a mathematical operation, written as , involving two numbers, the '' base'' and the ''exponent'' or ''power'' , and pronounced as " (raised) to the (power of) ". When is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to r ...
of about 0.75. There are good reasons to expect a power law: for example, the body-size to body-length relationship follows a power law with an exponent of 0.33, and the body-size to surface-area relationship follows a power law with an exponent of 0.67. The explanation for an exponent of 0.75 is not obvious; however, it is worth noting that several physiological variables appear to be related to body size by approximately the same exponent—for example, the basal metabolic rate
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. It is reported in energy units per unit time ranging from watt (joule/second) to ml O2/min or joule per hour per kg body mass J/(h·kg). P ...
.
This power law formula applies to the "average" brain of mammals taken as a whole, but each family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
(cats, rodents, primates, etc.) departs from it to some degree, in a way that generally reflects the overall "sophistication" of behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as we ...
. Primates
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
, for a given body size, have brains 5 to 10 times as large as the formula predicts. Predators tend to have relatively larger brains than the animals they prey on; placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguishe ...
mammals (the great majority) have relatively larger brains than marsupials
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a po ...
such as the opossum. A standard measure for assessing an animal's brain size compared to what would be expected from its body size is known as the encephalization quotient
Encephalization quotient (EQ), encephalization level (EL), or just encephalization is a relative brain size measure that is defined as the ratio between observed to predicted brain mass for an animal of a given size, based on nonlinear regress ...
. The encephalization quotient for humans is between 7.4-7.8.
When the mammalian brain increases in size, not all parts increase at the same rate. In particular, the larger the brain of a species, the greater the fraction taken up by the cortex. Thus, in the species with the largest brains, most of their volume is filled with cortex: this applies not only to humans, but also to animals such as dolphins, whales or elephants. The evolution of ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture ...
'' over the past two million years has been marked by a steady increase in brain size, but much of it can be accounted for by corresponding increases in body size. There are, however, many departures from the trend that are difficult to explain in a systematic way: in particular, the appearance of modern man about 100,000 years ago was marked by a decrease in body size at the same time as an increase in brain size. Even so, it is noteworthy that Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an Extinction, extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ag ...
s, which became extinct about 40,000 years ago, had larger brains than modern ''Homo sapiens''.
Not all investigators are happy with the amount of attention that has been paid to brain size. Roth and Dicke, for example, have argued that factors other than size are more highly correlated with intelligence, such as the number of cortical neurons and the speed of their connections. Moreover, they point out that intelligence depends not just on the amount of brain tissue, but on the details of how it is structured. It is also well known that crow
A crow is a bird of the genus '' Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifica ...
s, raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus '' Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between " crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigne ...
s, and grey parrots are quite intelligent even though they have small brains.
While humans have the largest encephalization quotient of extant animals, it is not out of line for a primate. Some other anatomical trends are correlated in the human evolutionary path with brain size: the basicranium
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria.
Structure
Structures found at the base of the skull are for ...
becomes more flexed with increasing brain size relative to basicranial length.
Cranial capacity
Cranial capacity is a measure of the volume of the interior of theskull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
of those vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
who have a brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
. The most commonly used unit of measure is the cubic centimetre (cm3). The volume of the cranium is used as a rough indicator of the size of the brain, and this in turn is used as a rough indicator of the potential intelligence of the organism. Cranial capacity is often tested by filling the cranial cavity with glass beads and measuring their volume, or by CT scan imaging. A more accurate way of measuring cranial capacity, is to make an endocranial cast and measure the amount of water the cast displaces. In the past there have been dozens of studies done to estimate cranial capacity on skulls. Most of these studies have been done on dry skull using linear dimensions, packing methods or occasionally radiological methods.
Knowledge of the volume of the cranial cavity can be important information for the study of different populations with various differences like geographical, racial, or ethnic origin. Other things can also affect cranial capacity such as nutrition. It is also used to study correlating between cranial capacity with other cranial measurements and in comparing skulls from different beings. It is commonly used to study abnormalities of cranial size and shape or aspects of growth and development of the volume of the brain. Cranial capacity is an indirect approach to test the size of the brain. A few studies on cranial capacity have been done on living beings through linear dimensions.
However, larger cranial capacity is not always indicative of a more intelligent organism, since larger capacities are required for controlling a larger body, or in many cases are an adaptive feature for life in a colder environment. For instance, among modern ''Homo sapiens'', northern populations have a 20% larger visual cortex than those in the southern latitude populations, and this potentially explains the population differences in human brain size (and roughly cranial capacity). Neurological functions are determined more by the organization of the brain rather than the volume. Individual variability is also important when considering cranial capacity, for example the average Neanderthal cranial capacity for females was 1300 cm3 and 1600 cm3 for males. Neanderthals had larger eyes and bodies relative to their height, thus a disproportionately large area of their brain was dedicated to somatic and visual processing, functions not normally associated with intelligence. When these areas were adjusted to match anatomically modern human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
proportions it was found Neanderthals had brains 15-22% smaller than in anatomically-modern humans. When the neanderthal version of the NOVA1 gene is inserted into stem cells it creates neurons with fewer synapses than stem cells containing the human version.
Parts of a cranium found in China in the 1970s show that the young man had a cranial capacity of around 1700cm at least 160,000 years ago. This is greater than the average of modern humans.
In an attempt to use cranial capacity as an objective indicator of brain size, the encephalization quotient
Encephalization quotient (EQ), encephalization level (EL), or just encephalization is a relative brain size measure that is defined as the ratio between observed to predicted brain mass for an animal of a given size, based on nonlinear regress ...
(EQ) was developed in 1973 by Harry Jerison. It compares the size of the brain of the specimen to the expected brain size of animals with roughly the same weight. This way a more objective judgement can be made on the cranial capacity of an individual animal. A large scientific collection of brain endocasts and measurements of cranial capacity has been compiled by Holloway.
Examples of cranial capacity
Apes
* Orangutan
Orangutans are great apes native to the rainforests of Indonesia and Malaysia. They are now found only in parts of Borneo and Sumatra, but during the Pleistocene they ranged throughout Southeast Asia and South China. Classified in the genu ...
s:
* Chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative t ...
s:
* Gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four ...
s:
Hominids
* Anatomically-modern human: average 1473cm
* Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an Extinction, extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ag ...
s: 1500-, 1740cm
* Xujiayao 6 (160 to 200 ka ago): ca. 1700cm
* ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor ...
''; 850 – 1100 cm3
* ''Australopithecus anamensis
''Australopithecus anamensis'' is a hominin species that lived approximately between 4.2 and 3.8 million years ago and is the oldest known ''Australopithecus'' species, living during the Plio-Pleistocene era.
Nearly one hundred fossil specimens ...
''; 365–370 cm3
* ''Australopithecus afarensis
''Australopithecus afarensis'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would no ...
''; 438 cm3
* ''Australopithecus africanus
''Australopithecus africanus'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived between about 3.3 and 2.1 million years ago in the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene of South Africa. The species has been recovered from Taung, Sterkfontei ...
'' 452 cm3
* ''Paranthropus boisei
''Paranthropus boisei'' is a species of australopithecine from the Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2.5 to 1.15 million years ago. The holotype specimen, OH 5, was discovered by palaeoanthropologist Mary Leakey in 1959, and described by ...
'' 521 cm3
* ''Paranthropus robustus
''Paranthropus robustus'' is a species of robust australopithecine from the Early and possibly Middle Pleistocene of the Cradle of Humankind, South Africa, about 2.27 to 0.87 (or, more conservatively, 2 to 1) million years ago. It has been iden ...
'' 530 cm3
See also
* Brain-to-body mass ratio *Encephalization quotient
Encephalization quotient (EQ), encephalization level (EL), or just encephalization is a relative brain size measure that is defined as the ratio between observed to predicted brain mass for an animal of a given size, based on nonlinear regress ...
* List of animals by number of neurons
*Craniometry
Craniometry is measurement of the cranium (the main part of the skull), usually the human cranium. It is a subset of cephalometry, measurement of the head, which in humans is a subset of anthropometry, measurement of the human body. It is dis ...
— includes historical discussion
* Neuroscience and intelligence
*Human brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of ...
References
Further reading
* {{animal cognition Neuroscience