Boron is a
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their atomic nucleus, nuclei, including the pure Chemical substance, substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements canno ...
with the
symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
B and
atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of ever ...
5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous
metalloid
A metalloid is a type of chemical element which has a preponderance of properties in between, or that are a mixture of, those of metals and nonmetals. There is no standard definition of a metalloid and no complete agreement on which elements are ...
; in its
amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal.
Etymology
The term comes from the Greek language, Gr ...
form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''
boron group
The boron group are the chemical elements in group 13 of the periodic table, comprising boron (B), aluminium (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl), and nihonium (Nh). The elements in the boron group are characterized by having three va ...
'' it has three
valence electron
In chemistry and physics, a valence electron is an electron in the outer shell associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outer shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair form ...
s for forming
covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between ato ...
s, resulting in many compounds such as
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
, the mineral
sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of
boron carbide
Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders,
as well as numerous industrial applications. With a Vickers hard ...
and
boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal ...
.
Boron is synthesized entirely by
cosmic ray spallation
Cosmic ray spallation, also known as the x-process, is a set of naturally occurring nuclear reactions causing nucleosynthesis; it refers to the formation of chemical elements from the impact of cosmic rays on an object. Cosmic rays are highly ener ...
and
supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or whe ...
e and not by
stellar nucleosynthesis
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the creation (nucleosynthesis) of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium and lithium during the Big Bang. A ...
, so it is a low-abundance element in the
Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
and in the
Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the
borate mineral
The borate minerals are minerals which contain a borate anion group. The borate (BO3) units may be polymerised similar to the SiO4 unit of the silicate mineral class. This results in B2O5, B3O6, B2O4 anions as well as more complex structures wh ...
s. These are mined industrially as
evaporite
An evaporite () is a water- soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocean ...
s, such as
borax
Borax is a salt (ionic compound), a hydrated borate of sodium, with chemical formula often written . It is a colorless crystalline solid, that dissolves in water to make a basic solution. It is commonly available in powder or granular form ...
and
kernite. The largest known deposits are in
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
, the largest producer of boron minerals.
Elemental boron is a
metalloid
A metalloid is a type of chemical element which has a preponderance of properties in between, or that are a mixture of, those of metals and nonmetals. There is no standard definition of a metalloid and no complete agreement on which elements are ...
that is found in small amounts in
meteoroid
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as mi ...
s but chemically uncombined boron is not otherwise found naturally on Earth. Industrially, the very pure element is produced with difficulty because of contamination by carbon or other elements that resist removal. Several
allotropes exist:
amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal.
Etymology
The term comes from the Greek language, Gr ...
boron is a brown powder; crystalline boron is silvery to black, extremely hard (about 9.5 on the
Mohs scale
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by ...
), and a poor
electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. Electric current is gene ...
at room temperature. The primary use of the element itself is as
boron filaments with applications similar to
carbon fibers
Carbon fibers or carbon fibres (alternatively CF, graphite fiber or graphite fibre) are fibers about in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages: high stiffness, high tensile strength, high stren ...
in some high-strength materials.
Boron is primarily used in chemical compounds. About half of all production consumed globally is an additive in
fiberglass
Fiberglass ( American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cl ...
for insulation and structural materials. The next leading use is in
polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
s and
ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, ...
s in high-strength, lightweight structural and
heat-resistant materials.
Borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), m ...
is desired for its greater strength and thermal shock resistance than ordinary soda lime glass. As
sodium perborate
Sodium perborate is chemical compound whose chemical formula may be written , , or, more properly, ·. Its name is sometimes abbreviated as PBS (not to be confused with phosphate-buffered saline).
The compound is commonly encountered in anhydr ...
, it is used as a
bleach
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color (whitening) from a fabric or fiber or to clean or to remove stains in a process called bleaching. It often refers specifically, to ...
. A small amount is used as a
dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace of impurity element that is introduced into a chemical material to alter its original electrical or optical properties. The amount of dopant necessary to cause changes is typically very low. Whe ...
in
semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way ...
s, and
reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
intermediates in the
synthesis of organic fine chemicals. A few boron-containing organic pharmaceuticals are used or are in study. Natural boron is composed of two stable isotopes, one of which (
boron-10
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has t ...
) has a number of uses as a neutron-capturing agent.
The intersection of boron with biology is very small. Consensus on it as essential for mammalian life is lacking.
Borate
A borate is any of several boron oxyanions, negative ions consisting of boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate , metaborate , or tetraborate ; or any salt with such anions, such as sodium metaborate, and disodium tetraborate . The name also re ...
s have low toxicity in mammals (similar to
table salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantitie ...
) but are more toxic to
arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s and are occasionally used as
insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed t ...
s. Boron-containing organic antibiotics are known. Although only traces are required, it is an essential
plant nutrient
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth and reproduction, plant metabolism and their external supply. In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle, or that the element i ...
.
History
The word ''boron'' was coined from ''
borax
Borax is a salt (ionic compound), a hydrated borate of sodium, with chemical formula often written . It is a colorless crystalline solid, that dissolves in water to make a basic solution. It is commonly available in powder or granular form ...
'', the mineral from which it was isolated, by analogy with ''carbon'', which boron resembles chemically.

Borax in its mineral form (then known as tincal) first saw use as a glaze, beginning in
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
circa 300 AD. Some crude borax traveled westward, and was apparently mentioned by the alchemist
Jabir ibn Hayyan
Abū Mūsā Jābir ibn Ḥayyān (Arabic: , variously called al-Ṣūfī, al-Azdī, al-Kūfī, or al-Ṭūsī), died 806−816, is the purported author of an enormous number and variety of works in Arabic, often called the Jabirian corpus. The ...
around 700 AD.
Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in '' The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
brought some glazes back to Italy in the 13th century.
Georgius Agricola
Georgius Agricola (; born Georg Pawer or Georg Bauer; 24 March 1494 – 21 November 1555) was a German Humanist scholar, mineralogist and metallurgist. Born in the small town of Glauchau, in the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire ...
, in around 1600 AD, reported the use of borax as a flux in
metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
. In 1777,
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
was recognized in the hot springs (
soffioni) near
Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
, Italy, at which point it became known as ''sal sedativum'', with ostensible medical benefits. The mineral was named
sassolite
Sassolite is a borate mineral, specifically the mineral form of boric acid. It is usually white to gray, and colourless in transmitted light. It can also take on a yellow colour from sulfur impurities, or brown from iron oxides.
History and occ ...
, after
Sasso Pisano in Italy. Sasso was the main source of
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an borax from 1827 to 1872, when
American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
sources replaced it.
Boron compounds were relatively rarely used until the late 1800s when
Francis Marion Smith
Francis Marion Smith (February 2, 1846 – August 27, 1931) (once known nationally and internationally as "Borax Smith" and "The Borax King" ) was an American miner, business magnate and civic builder in the Mojave Desert, the San Francisc ...
's
Pacific Coast Borax Company first popularized and produced them in volume at low cost.
Boron was not recognized as an element until it was isolated by Sir
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for ...
and by
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac (, , ; 6 December 1778 – 9 May 1850) was a French chemist and physicist. He is known mostly for his discovery that water is made of two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen (with Alexander von Humboldt), for two laws ...
and
Louis Jacques Thénard.
In 1808 Davy observed that electric current sent through a solution of borates produced a brown precipitate on one of the electrodes. In his subsequent experiments, he used potassium to
reduce boric acid instead of
electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from n ...
. He produced enough boron to confirm a new element and named it ''boracium''.
Gay-Lussac and Thénard used iron to reduce boric acid at high temperatures. By oxidizing boron with air, they showed that boric acid is its oxidation product.
Jöns Jacob Berzelius
Baron Jöns Jacob Berzelius (; by himself and his contemporaries named only Jacob Berzelius, 20 August 1779 – 7 August 1848) was a Swedish chemist. Berzelius is considered, along with Robert Boyle, John Dalton, and Antoine Lavoisier, to be o ...
identified it as an element in 1824. Pure boron was arguably first produced by the American chemist Ezekiel Weintraub in 1909.
Preparation of elemental boron in the laboratory
The earliest routes to elemental boron involved the reduction of
boric oxide with metals such as
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
or
aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
. However, the product is almost always contaminated with
boride A boride is a compound between boron and a less electronegative element, for example silicon boride (SiB3 and SiB6). The borides are a very large group of compounds that are generally high melting and are covalent more than ionic in nature. Some bo ...
s of those metals. Pure boron can be prepared by reducing volatile boron halides with
hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
at high temperatures. Ultrapure boron for use in the semiconductor industry is produced by the decomposition of
diborane
Diborane(6), generally known as diborane, is the chemical compound with the formula B2H6. It is a toxic, colorless, and pyrophoric gas with a repulsively sweet odor. Diborane is a key boron compound with a variety of applications. It has attracte ...
at high temperatures and then further purified by the
zone melting or
Czochralski processes.
The production of boron compounds does not involve the formation of elemental boron, but exploits the convenient availability of borates.
Characteristics
Allotropes

Boron is similar to
carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
in its capability to form stable
covalently bonded molecular networks. Even nominally disordered (
amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal.
Etymology
The term comes from the Greek language, Gr ...
) boron contains regular boron
icosahedra
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes and . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons".
There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrica ...
which are bonded randomly to each other without
long-range order.
Crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
boron is a very hard, black material with a melting point of above 2000 °C. It forms four major
allotrope
Allotropy or allotropism () is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical State of matter, state, known as allotropes of the elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications o ...
s: α-rhombohedral and β-rhombohedral (α-R and β-R), γ-orthorhombic (γ) and β-tetragonal (β-T). All four phases are stable at
ambient conditions, and β-rhombohedral is the most common and stable. An α-tetragonal phase also exists (α-T), but is very difficult to produce without significant contamination. Most of the phases are based on B
12 icosahedra, but the γ phase can be described as a
rocksalt
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, p ...
-type arrangement of the icosahedra and B
2 atomic pairs.
It can be produced by compressing other boron phases to 12–20 GPa and heating to 1500–1800 °C; it remains stable after releasing the temperature and pressure. The β-T phase is produced at similar pressures, but higher temperatures of 1800–2200 °C. The α-T and β-T phases might coexist at ambient conditions, with the β-T phase being the more stable.
Compressing boron above 160 GPa produces a boron phase with an as yet unknown structure, and this phase is a
superconductor at temperatures below 6–12 K.
Borospherene (
fullerene
A fullerene is an allotrope of carbon whose molecule consists of carbon atoms connected by single and double bonds so as to form a closed or partially closed mesh, with fused rings of five to seven atoms. The molecule may be a hollow sphere, ...
-like B
40 molecules) and
borophene
Borophene is a crystalline atomic monolayer of boron, i.e., it is a two-dimensional allotrope of boron and also known as ''boron sheet''.
First predicted by theory in the mid-1990s,
different borophene structures were experimentally confirmed i ...
(proposed
graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. -like structure) were described in 2014.
Chemistry of the element
Elemental boron is rare and poorly studied because the pure material is extremely difficult to prepare. Most studies of "boron" involve samples that contain small amounts of carbon. The chemical behavior of boron
diagonal relationship, resembles that of
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
more than
aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
. Crystalline boron is chemically inert and resistant to attack by boiling
hydrofluoric or
hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the dige ...
. When finely divided, it is attacked slowly by hot concentrated
hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3 ...
, hot concentrated
nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available ni ...
, hot
sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
or hot mixture of sulfuric and
chromic acid
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixtu ...
s.
The rate of oxidation of boron depends on the crystallinity, particle size, purity and temperature. Boron does not react with air at room temperature, but at higher temperatures it burns to form
boron trioxide
Boron trioxide or diboron trioxide is the oxide of boron with the formula . It is a colorless transparent solid, almost always glassy (amorphous), which can be crystallized only with great difficulty. It is also called boric oxide or boria. It h ...
:
:4 B + 3 O
2 → 2 B
2O
3
Boron undergoes halogenation to give trihalides; for example,
:2 B + 3 Br
2 → 2 BBr
3
The trichloride in practice is usually made from the oxide.
Atomic structure
Boron is the lightest element having an
electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
in a
p-orbital
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any ...
in its ground state. But, unlike most other
p-elements, it rarely obeys the
octet rule
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The rul ...
and usually places only six electrons
(in three
molecular orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of find ...
s) onto its
valence shell
In chemistry and physics, a valence electron is an electron in the outer shell associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outer shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair forms ...
. Boron is the prototype for the
boron group
The boron group are the chemical elements in group 13 of the periodic table, comprising boron (B), aluminium (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl), and nihonium (Nh). The elements in the boron group are characterized by having three va ...
(the
IUPAC group 13), although the other members of this group are metals and more typical p-elements (only aluminium to some extent shares boron's aversion to the octet rule).
Chemical compounds

In the most familiar compounds, boron has the formal oxidation state III. These include oxides, sulfides, nitrides, and halides.
The trihalides adopt a planar trigonal structure. These compounds are
Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
s in that they readily form
adduct
An adduct (from the Latin ''adductus'', "drawn toward" alternatively, a contraction of "addition product") is a product of a direct addition of two or more distinct molecules, resulting in a single reaction product containing all atoms of all co ...
s with electron-pair donors, which are called
Lewis base
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
s. For example, fluoride (F
−) and
boron trifluoride
Boron trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula BF3. This pungent, colourless, and toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds.
Structure and bond ...
(BF
3) combined to give the
tetrafluoroborate
Tetrafluoroborate is the anion . This tetrahedral species is isoelectronic with tetrafluoroberyllate (), tetrafluoromethane (CF4), and tetrafluoroammonium () and is valence isoelectronic with many stable and important species including the perchlo ...
anion, BF
4−. Boron trifluoride is used in the petrochemical industry as a catalyst. The halides react with water to form
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
.
It is found in nature on Earth almost entirely as various oxides of B(III), often associated with other elements. More than one hundred
borate mineral
The borate minerals are minerals which contain a borate anion group. The borate (BO3) units may be polymerised similar to the SiO4 unit of the silicate mineral class. This results in B2O5, B3O6, B2O4 anions as well as more complex structures wh ...
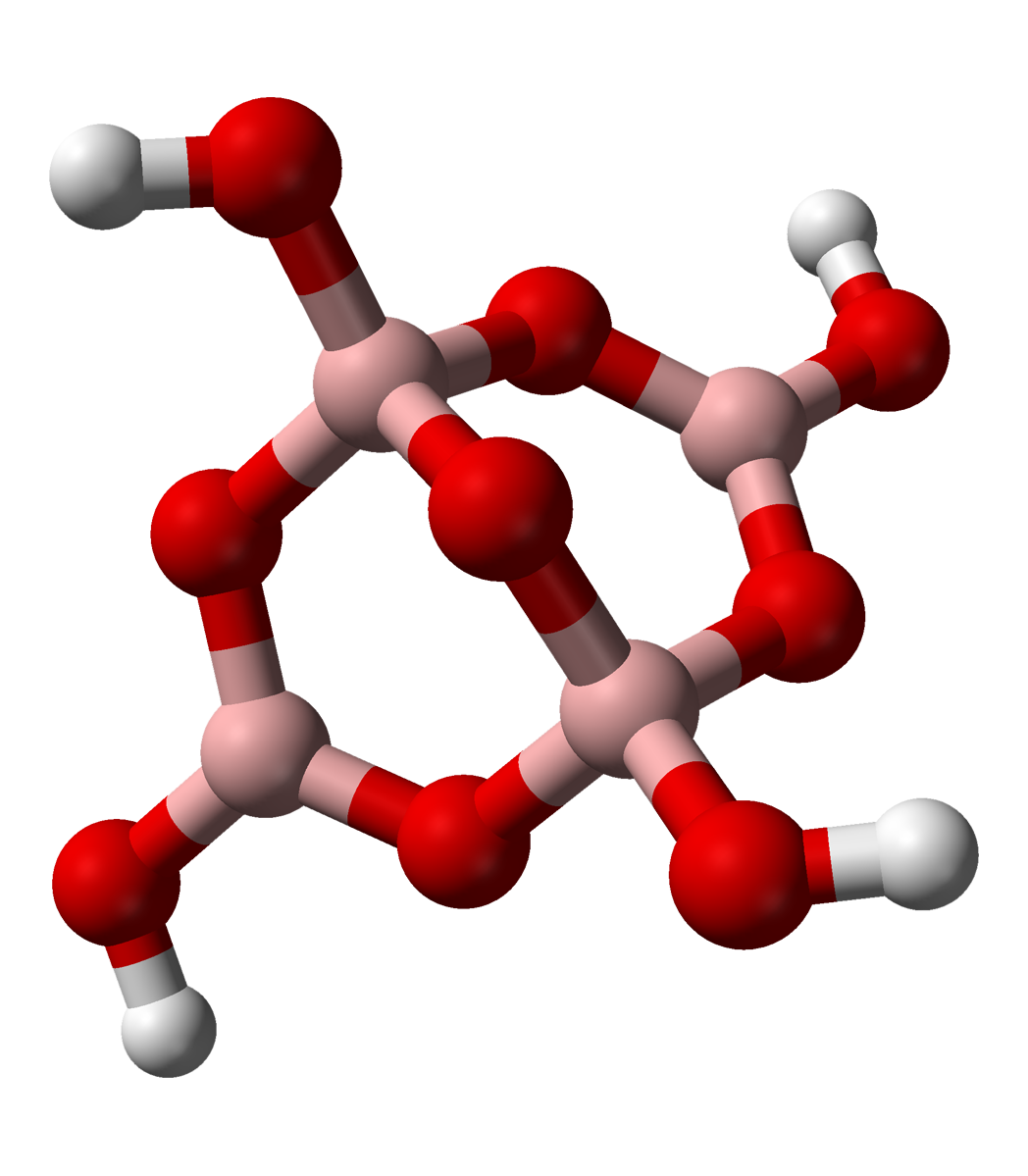
s contain boron in oxidation state +3. These minerals resemble silicates in some respect, although it is often found not only in a tetrahedral coordination with oxygen, but also in a trigonal planar configuration. Unlike silicates, boron minerals never contain it with coordination number greater than four. A typical motif is exemplified by the tetraborate anions of the common mineral
borax
Borax is a salt (ionic compound), a hydrated borate of sodium, with chemical formula often written . It is a colorless crystalline solid, that dissolves in water to make a basic solution. It is commonly available in powder or granular form ...
, shown at left. The formal negative charge of the tetrahedral borate center is balanced by metal cations in the minerals, such as the sodium (Na
+) in borax.
The tourmaline group of borate-silicates is also a very important boron-bearing mineral group, and a number of borosilicates are also known to exist naturally.

Boranes are chemical compounds of boron and hydrogen, with the generic formula of B
xH
y. These compounds do not occur in nature. Many of the boranes readily oxidise on contact with air, some violently. The parent member BH
3 is called borane, but it is known only in the gaseous state, and dimerises to form diborane, B
2H
6. The larger boranes all consist of boron clusters that are polyhedral, some of which exist as isomers. For example, isomers of B
20H
26 are based on the fusion of two 10-atom clusters.
The most important boranes are diborane B
2H
6 and two of its pyrolysis products, pentaborane B
5H
9 and decaborane B
10H
14. A large number of anionic boron hydrides are known, e.g.
12H12sup>2−.
The formal
oxidation number
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. C ...
in boranes is positive, and is based on the assumption that hydrogen is counted as −1 as in active metal hydrides. The mean oxidation number for the borons is then simply the ratio of hydrogen to boron in the molecule. For example, in diborane B
2H
6, the boron oxidation state is +3, but in decaborane B
10H
14, it is
7/
5 or +1.4. In these compounds the oxidation state of boron is often not a whole number.
The
boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal ...
s are notable for the variety of structures that they adopt. They exhibit structures analogous to various
allotropes of carbon
Carbon is capable of forming many allotropes (structurally different forms of the same element) due to its valency. Well-known forms of carbon include diamond and graphite. In recent decades, many more allotropes have been discovered and res ...
, including graphite, diamond, and nanotubes. In the diamond-like structure, called cubic boron nitride (tradename
Borazon
Borazon is a brand name of a cubic form of boron nitride (cBN). Its color ranges from black to brown and gold, depending on the chemical bond. It is one of the hardest known materials, along with various forms of diamond and kinds of boron nitride ...
), boron atoms exist in the tetrahedral structure of carbon atoms in diamond, but one in every four B-N bonds can be viewed as a
coordinate covalent bond
In coordination chemistry, a coordinate covalent bond, also known as a dative bond, dipolar bond, or coordinate bond is a kind of two-center, two-electron covalent bond in which the two electrons derive from the same atom. The bonding of metal i ...
, wherein two electrons are donated by the nitrogen atom which acts as the
Lewis base
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
to a bond to the
Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
ic boron(III) centre. Cubic boron nitride, among other applications, is used as an abrasive, as it has a hardness comparable with diamond (the two substances are able to produce scratches on each other). In the BN compound analogue of graphite, hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), the positively charged boron and negatively charged nitrogen atoms in each plane lie adjacent to the oppositely charged atom in the next plane. Consequently, graphite and h-BN have very different properties, although both are lubricants, as these planes slip past each other easily. However, h-BN is a relatively poor electrical and thermal conductor in the planar directions.
=Organoboron chemistry
=
A large number of organoboron compounds are known and many are useful in
organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
. Many are produced from
hydroboration
In organic chemistry, hydroboration refers to the addition of a hydrogen-boron bond to certain double and triple bonds involving carbon (, , , and ). This chemical reaction is useful in the organic synthesis of organic compounds.
Hydroboration p ...
, which employs
diborane
Diborane(6), generally known as diborane, is the chemical compound with the formula B2H6. It is a toxic, colorless, and pyrophoric gas with a repulsively sweet odor. Diborane is a key boron compound with a variety of applications. It has attracte ...
, B
2H
6, a simple
borane
Trihydridoboron, also known as borane or borine, is an unstable and highly reactive molecule with the chemical formula . The preparation of borane carbonyl, BH3(CO), played an important role in exploring the chemistry of boranes, as it indicated ...
chemical. Organoboron(III) compounds are usually tetrahedral or trigonal planar, for example,
tetraphenylborate
Tetraphenylborate (IUPAC name: Tetraphenylboranuide) is an organoboron anion consisting of a central boron atom with four phenyl groups. Salts of tetraphenylborate uncouple oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation (UK , US ) or e ...
,
(C6H5)4sup>− vs.
triphenylborane, B(C
6H
5)
3. However, multiple boron atoms reacting with each other have a tendency to form novel dodecahedral (12-sided) and icosahedral (20-sided) structures composed completely of boron atoms, or with varying numbers of carbon heteroatoms.
Organoboron chemicals have been employed in uses as diverse as
boron carbide
Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders,
as well as numerous industrial applications. With a Vickers hard ...
(see below), a complex very hard ceramic composed of boron-carbon cluster anions and cations, to
carborane
Carboranes are electron-delocalized (non-classically bonded) clusters composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms.Grimes, R. N., ''Carboranes 3rd Ed.'', Elsevier, Amsterdam and New York (2016), . Like many of the related boron hydrides, these c ...
s, carbon-boron
cluster chemistry
In chemistry, an atom cluster (or simply cluster) is an ensemble of bound atoms or molecules that is intermediate in size between a simple molecule and a nanoparticle; that is, up to a few nanometers (nm) in diameter. The term ''microclus ...
compounds that can be halogenated to form reactive structures including
carborane acid
Carborane acids (X, Y, Z = H, Alk, F, Cl, Br, CF3) are a class of superacids, some of which are estimated to be at least one million times stronger than 100% pure sulfuric acid in terms of their Hammett acidity function values (''H''0 ≤ – ...
, a
superacid
In chemistry, a superacid (according to the classical definition) is an acid with an acidity greater than that of 100% pure sulfuric acid (), which has a Hammett acidity function (''H''0) of −12. According to the modern definition, a superaci ...
. As one example, carboranes form useful molecular moieties that add considerable amounts of boron to other biochemicals in order to synthesize boron-containing compounds for
boron neutron capture therapy
Neutron capture therapy (NCT) is a type of radiotherapy for treating locally invasive malignant tumors such as primary brain tumors, recurrent cancers of the head and neck region, and cutaneous and extracutaneous melanomas. It is a two-step pro ...
for cancer.
=Compounds of B(I) and B(II)
=
As anticipated by its
hydride clusters, boron forms a variety of stable compounds with formal oxidation state less than three.
B2F4 and B
4Cl
4 are well characterized.
Binary metal-boron compounds, the metal borides, contain boron in negative oxidation states. Illustrative is
magnesium diboride
Magnesium diboride is the inorganic compound with the formula MgB2. It is a dark gray, water-insoluble solid. The compound has attracted attention because it becomes superconducting at 39 K (−234 °C). In terms of its composition, Mg ...
(MgB
2). Each boron atom has a formal −1 charge and magnesium is assigned a formal charge of +2. In this material, the boron centers are trigonal planar with an extra double bond for each boron, forming sheets akin to the carbon in
graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on la ...
. However, unlike hexagonal boron nitride, which lacks electrons in the plane of the covalent atoms, the delocalized electrons in magnesium diboride allow it to conduct electricity similar to isoelectronic graphite. In 2001, this material was found to be a high-temperature
superconductor. It is a superconductor under active development. A project at
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Gen ...
to make MgB
2 cables has resulted in superconducting test cables able to carry 20,000 amperes for extremely high current distribution applications, such as the contemplated high luminosity version of the
large hadron collider
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and highest-energy particle collider. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and hundr ...
.
Certain other metal borides find specialized applications as hard materials for cutting tools. Often the boron in borides has fractional oxidation states, such as −1/3 in
calcium hexaboride
Calcium hexaboride (sometimes calcium boride) is a compound of calcium and boron with the chemical formula CaB6. It is an important material due to its high electrical conductivity, hardness, chemical stability, and melting point. It is a black, lu ...
(CaB
6).
From the structural perspective, the most distinctive chemical compounds of boron are the hydrides. Included in this series are the cluster compounds
dodecaborate
The dodecaborate(12) anion, 12H12sup>2−, is a borane with an icosahedral arrangement of 12 boron atoms, with each boron atom being attached to a hydrogen atom. Its symmetry is classified by the molecular point group Ih.
Synthesis and reacti ...
(),
decaborane
Decaborane, also called decaborane(14), is the borane with the chemical formula B10 H14. This white crystalline compound is one of the principal boron hydride clusters, both as a reference structure and as a precursor to other boron hydrides. It ...
(B
10H
14), and the
carborane
Carboranes are electron-delocalized (non-classically bonded) clusters composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms.Grimes, R. N., ''Carboranes 3rd Ed.'', Elsevier, Amsterdam and New York (2016), . Like many of the related boron hydrides, these c ...
s such as C
2B
10H
12. Characteristically such compounds contain boron with coordination numbers greater than four.
Isotopes
Boron has two naturally occurring and stable
isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers ( mass num ...
s,
11B (80.1%) and
10B (19.9%). The mass difference results in a wide range of δ
11B values, which are defined as a fractional difference between the
11B and
10B and traditionally expressed in parts per thousand, in natural waters ranging from −16 to +59. There are 13 known isotopes of boron; the shortest-lived isotope is
7B which decays through
proton emission
Proton emission (also known as proton radioactivity) is a rare type of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a nucleus. Proton emission can occur from high-lying excited states in a nucleus following a beta decay, in which case t ...
and
alpha decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and thereby transforms or 'decays' into a different atomic nucleus, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an at ...
with a
half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ...
of 3.5×10
−22 s. Isotopic fractionation of boron is controlled by the exchange reactions of the boron species B(OH)
3 and
(OH)4sup>−. Boron isotopes are also fractionated during mineral crystallization, during H
2O phase changes in
hydrothermal
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water (Ancient Greek ὕδωρ, ''water'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with th ...
systems, and during
hydrothermal alteration
Metasomatism (from the Greek μετά ''metá'' "change" and σῶμα ''sôma'' "body") is the chemical alteration of a rock by hydrothermal and other fluids. It is the replacement of one rock by another of different mineralogical and chemical co ...
of
rock. The latter effect results in preferential removal of the
sup>10B(OH)4sup>−
ion onto clays. It results in solutions enriched in
11B(OH)
3 and therefore may be responsible for the large
11B enrichment in seawater relative to both
ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wor ...
ic crust and
continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
al crust; this difference may act as an
isotopic signature.
The exotic
17B exhibits a
nuclear halo
In nuclear physics, an atomic nucleus is called a halo nucleus or is said to have a nuclear halo when it has a core nucleus surrounded by a "halo" of orbiting protons or neutrons, which makes the radius of the nucleus appreciably larger than that ...
, i.e. its radius is appreciably larger than that predicted by the
liquid drop model
In nuclear physics, the semi-empirical mass formula (SEMF) (sometimes also called the Weizsäcker formula, Bethe–Weizsäcker formula, or Bethe–Weizsäcker mass formula to distinguish it from the Bethe–Weizsäcker process) is used to approxi ...
.
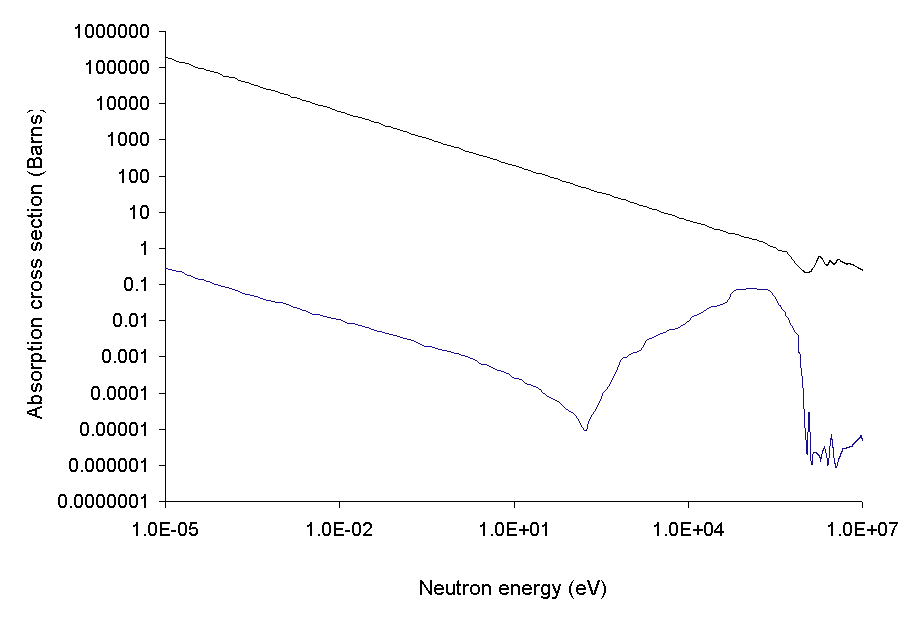
The
10B isotope is useful for capturing
thermal neutron
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium wi ...
s (see
neutron cross section#Typical cross sections). The
nuclear industry
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
enriches natural boron to nearly pure
10B. The less-valuable by-product, depleted boron, is nearly pure
11B.
Commercial isotope enrichment
Because of its high neutron cross-section, boron-10 is often used to control fission in nuclear reactors as a neutron-capturing substance. Several industrial-scale enrichment processes have been developed; however, only the fractionated vacuum distillation of the
dimethyl ether
Dimethyl ether (DME; also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH3OCH3,
(sometimes ambiguously simplified to C2H6O as it is an isomer of ethanol). The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precursor ...
adduct of
boron trifluoride
Boron trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula BF3. This pungent, colourless, and toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds.
Structure and bond ...
(DME-BF
3) and column chromatography of borates are being used.
Enriched boron (boron-10)
Enriched boron or
10B is used in both radiation shielding and is the primary nuclide used in
neutron capture therapy of cancer
Neutron capture therapy (NCT) is a type of radiotherapy for treating locally invasive malignant tumors such as primary brain tumors, recurrent cancers of the head and neck region, and cutaneous and extracutaneous melanomas. It is a two-step pro ...
. In the latter ("boron neutron capture therapy" or BNCT), a compound containing
10B is incorporated into a pharmaceutical which is selectively taken up by a malignant tumor and tissues near it. The patient is then treated with a beam of low energy neutrons at a relatively low neutron radiation dose. The neutrons, however, trigger energetic and short-range secondary
alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be prod ...
and lithium-7 heavy ion radiation that are products of the boron + neutron
nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a transformatio ...
, and this ion radiation additionally bombards the tumor, especially from inside the tumor cells.
In nuclear reactors,
10B is used for reactivity control and in
emergency shutdown systems. It can serve either function in the form of
borosilicate
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), ...
control rods
Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing ...
or as
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
. In
pressurized water reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan and Canada). In a PWR, the primary coolant (water) i ...
s,
10B
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
is added to the reactor coolant when the plant is shut down for refueling. It is then slowly filtered out over many months as
fissile
In nuclear engineering, fissile material is material capable of sustaining a nuclear fission chain reaction. By definition, fissile material can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of thermal energy. The predominant neutron energy may be t ...
material is used up and the fuel becomes less reactive.
In future crewed interplanetary spacecraft,
10B has a theoretical role as structural material (as boron fibers or
BN nanotube material) which would also serve a special role in the radiation shield. One of the difficulties in dealing with
cosmic rays
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our ...
, which are mostly high energy protons, is that some secondary radiation from interaction of cosmic rays and spacecraft materials is high energy
spallation
Spallation is a process in which fragments of material (spall) are ejected from a body due to impact or stress. In the context of impact mechanics it describes ejection of material from a target during impact by a projectile. In planetary p ...
neutrons. Such neutrons can be moderated by materials high in light elements, such as
polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging ( plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including b ...
, but the moderated neutrons continue to be a radiation hazard unless actively absorbed in the shielding. Among light elements that absorb thermal neutrons,
6Li and
10B appear as potential spacecraft structural materials which serve both for mechanical reinforcement and radiation protection.
Depleted boron (boron-11)
= Radiation-hardened semiconductors
=
Cosmic radiation
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our ow ...
will produce secondary neutrons if it hits spacecraft structures. Those neutrons will be captured in
10B, if it is present in the spacecraft's
semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way ...
s, producing a
gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
, an
alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be prod ...
, and a
lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense soli ...
ion. Those resultant decay products may then irradiate nearby semiconductor "chip" structures, causing data loss (bit flipping, or
single event upset
A single-event upset (SEU), also known as a single-event error (SEE), is a change of state caused by one single ionizing particle (ions, electrons, photons...) striking a sensitive node in a live micro-electronic device, such as in a microprocesso ...
). In
radiation-hardened semiconductor designs, one countermeasure is to use ''depleted boron'', which is greatly enriched in
11B and contains almost no
10B. This is useful because
11B is largely immune to radiation damage. Depleted boron is a byproduct of the
nuclear industry
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
(see above).
= Proton-boron fusion
=
11B is also a candidate as a fuel for
aneutronic fusion. When struck by a proton with energy of about 500 k
eV, it produces three alpha particles and 8.7 MeV of energy. Most other fusion reactions involving hydrogen and helium produce penetrating neutron radiation, which weakens reactor structures and induces long-term radioactivity, thereby endangering operating personnel. However, the
alpha particles
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be prod ...
from
11B fusion can be turned directly into electric power, and all radiation stops as soon as the reactor is turned off.
NMR spectroscopy
Both
10B and
11B possess
nuclear spin
In atomic physics, the spin quantum number is a quantum number (designated ) which describes the intrinsic angular momentum (or spin angular momentum, or simply spin) of an electron or other particle. The phrase was originally used to describe ...
. The nuclear spin of
10B is 3 and that of
11B is . These isotopes are, therefore, of use in
nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are perturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a ...
spectroscopy; and spectrometers specially adapted to detecting the boron-11 nuclei are available commercially. The
10B and
11B nuclei also cause splitting in the
resonances
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillat ...
of attached nuclei.
Occurrence


Boron is rare in the Universe and solar system due to trace formation in the
Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
and in stars. It is formed in minor amounts in
cosmic ray spallation
Cosmic ray spallation, also known as the x-process, is a set of naturally occurring nuclear reactions causing nucleosynthesis; it refers to the formation of chemical elements from the impact of cosmic rays on an object. Cosmic rays are highly ener ...
nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons (protons and neutrons) and nuclei. According to current theories, the first nuclei were formed a few minutes after the Big Bang, through nuclear reactions in ...
and may be found uncombined in
cosmic dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are c ...
and
meteoroid
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as mi ...
materials.
In the high oxygen environment of Earth, boron is always found fully oxidized to borate. Boron does not appear on Earth in elemental form. Extremely small traces of elemental boron were detected in Lunar regolith.
Although boron is a relatively rare element in the Earth's crust, representing only 0.001% of the crust mass, it can be highly concentrated by the action of water, in which many borates are soluble.
It is found naturally combined in compounds such as
borax
Borax is a salt (ionic compound), a hydrated borate of sodium, with chemical formula often written . It is a colorless crystalline solid, that dissolves in water to make a basic solution. It is commonly available in powder or granular form ...
and
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
(sometimes found in
volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plat ...
spring waters). About a hundred
borate minerals
The borate minerals are minerals which contain a borate anion group. The borate (BO3) units may be polymerised similar to the SiO4 unit of the silicate mineral class. This results in B2O5, B3O6, B2O4 anions as well as more complex structures whic ...
are known.
On 5 September 2017, scientists reported that the
''Curiosity'' rover detected boron, an essential ingredient for
life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy ...
on
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
, on the planet
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
. Such a finding, along with previous discoveries that water may have been present on ancient Mars, further supports the possible early habitability of
Gale Crater
Gale is a crater, and probable dry lake, at in the northwestern part of the Aeolis quadrangle on Mars. It is in diameter and estimated to be about 3.5–3.8 billion years old. The crater was named after Walter Frederick Gale, an amateur ast ...
on Mars.
Production
Economically important sources of boron are the minerals
colemanite
Colemanite (Ca2B6O11·5H2O) or (CaB3O4(OH)3·H2O) is a borate mineral found in evaporite deposits of alkaline lacustrine environments. Colemanite is a secondary mineral that forms by alteration of borax and ulexite.
It was first described in 18 ...
, rasorite (
kernite),
ulexite
Ulexite (NaCaB5O6(OH)6·5H2O, hydrated sodium calcium borate hydroxide), sometimes known as TV rock or Television stone, is a mineral occurring in silky white rounded crystalline masses or in parallel fibers. The natural fibers of ulexite conduc ...
and
tincal
Borax is a salt (chemistry), salt (ionic compound), a hydration (chemistry), hydrated borate of sodium, with chemical formula often written . It is a colorless crystalline solid, that dissolves in water to make a base (chemistry), basic aqueo ...
. Together these constitute 90% of mined boron-containing ore. The largest global borax deposits known, many still untapped, are in Central and Western
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
, including the provinces of
Eskişehir
Eskişehir ( , ; from "old" and "city") is a city in northwestern Turkey and the capital of the Eskişehir Province. The urban population of the city is 898,369 with a metropolitan population of 797,708. The city is located on the banks of the ...
,
Kütahya
Kütahya () (historically, Cotyaeum or Kotyaion, Greek: Κοτύαιον) is a city in western Turkey which lies on the Porsuk river, at 969 metres above sea level. It is inhabited by some 578,640 people (2022 estimate). The region of Kütahya ha ...
and
Balıkesir. Global proven boron mineral mining reserves exceed one billion metric tonnes, against a yearly production of about four million tonnes.
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
and the United States are the largest producers of boron products. Turkey produces about half of the global yearly demand, through
Eti Mine Works Eti Maden is a Turkish state-owned mining and chemicals company focusing on boron products. It holds a government monopoly on the mining of borate minerals in Turkey, which possesses 72% of the world's known deposits. In 2012, it held a 47% share o ...
( tr, Eti Maden İşletmeleri) a
Turkish state-owned
State ownership, also called government ownership and public ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, or enterprise by the state or a public body representing a community, as opposed to an individual or private party. Public owne ...
mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
and
chemicals
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wit ...
company focusing on boron products. It holds a
government monopoly
In economics, a government monopoly or public monopoly is a form of coercive monopoly in which a government agency or government corporation is the sole provider of a particular good or service and competition is prohibited by law. It is a monopo ...
on the mining of
borate minerals
The borate minerals are minerals which contain a borate anion group. The borate (BO3) units may be polymerised similar to the SiO4 unit of the silicate mineral class. This results in B2O5, B3O6, B2O4 anions as well as more complex structures whic ...
in Turkey, which possesses 72% of the world's known deposits. In 2012, it held a 47%
share of production of global borate minerals, ahead of its main competitor,
Rio Tinto Group
Rio Tinto Group is an Anglo-Australian multinational company that is the world's second-largest metals and mining corporation (behind BHP). The company was founded in 1873 when of a group of investors purchased a mine complex on the Rio Tint ...
.
Almost a quarter (23%) of global boron production comes from the single
Rio Tinto Borax Mine (also known as the U.S. Borax Boron Mine) near
Boron, California.
Market trend
The average cost of crystalline elemental boron is US$5/g. Elemental boron is chiefly used in making boron fibers, where it is deposited by
chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (subst ...
on a
tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
core (see below). Boron fibers are used in lightweight composite applications, such as high strength tapes. This use is a very small fraction of total boron use. Boron is introduced into semiconductors as boron compounds, by ion implantation.
Estimated global consumption of boron (almost entirely as boron compounds) was about 4 million tonnes of B
2O
3 in 2012. As compounds such as borax and kernite its cost was US$377/tonne in 2019. Boron mining and refining capacities are considered to be adequate to meet expected levels of growth through the next decade.
The form in which boron is consumed has changed in recent years. The use of ores like
colemanite
Colemanite (Ca2B6O11·5H2O) or (CaB3O4(OH)3·H2O) is a borate mineral found in evaporite deposits of alkaline lacustrine environments. Colemanite is a secondary mineral that forms by alteration of borax and ulexite.
It was first described in 18 ...
has declined following concerns over
arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, b ...
content. Consumers have moved toward the use of refined borates and boric acid that have a lower pollutant content.
Increasing demand for boric acid has led a number of producers to invest in additional capacity. Turkey's state-owned
Eti Mine Works Eti Maden is a Turkish state-owned mining and chemicals company focusing on boron products. It holds a government monopoly on the mining of borate minerals in Turkey, which possesses 72% of the world's known deposits. In 2012, it held a 47% share o ...
opened a new boric acid plant with the production capacity of 100,000 tonnes per year at
Emet EMET or emet may refer to:
* Emet, a town in Turkey
* Emet (geographic region), a territorial division within the Kalenjin society of pre-colonial Kenya
* EMET Prize, an annual academic and cultural prize in Israel
* Endowment for Middle East T ...
in 2003.
Rio Tinto Group
Rio Tinto Group is an Anglo-Australian multinational company that is the world's second-largest metals and mining corporation (behind BHP). The company was founded in 1873 when of a group of investors purchased a mine complex on the Rio Tint ...
increased the capacity of its boron plant from 260,000 tonnes per year in 2003 to 310,000 tonnes per year by May 2005, with plans to grow this to 366,000 tonnes per year in 2006. Chinese boron producers have been unable to meet rapidly growing demand for high quality borates. This has led to imports of sodium tetraborate (
borax
Borax is a salt (ionic compound), a hydrated borate of sodium, with chemical formula often written . It is a colorless crystalline solid, that dissolves in water to make a basic solution. It is commonly available in powder or granular form ...
) growing by a hundredfold between 2000 and 2005 and boric acid imports increasing by 28% per year over the same period.
The rise in global demand has been driven by high growth rates in
glass fiber
Glass fiber ( or glass fibre) is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass.
Glassmakers throughout history have experimented with glass fibers, but mass manufacture of glass fiber was only made possible with the inventio ...
,
fiberglass
Fiberglass ( American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cl ...
and
borosilicate
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), ...
glassware production. A rapid increase in the manufacture of reinforcement-grade boron-containing fiberglass in Asia, has offset the development of boron-free reinforcement-grade fiberglass in Europe and the US. The recent rises in energy prices may lead to greater use of insulation-grade fiberglass, with consequent growth in the boron consumption. Roskill Consulting Group forecasts that world demand for boron will grow by 3.4% per year to reach 21 million tonnes by 2010. The highest growth in demand is expected to be in Asia where demand could rise by an average 5.7% per year.
Applications
Nearly all boron ore extracted from the Earth is destined for refinement into
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
and
sodium tetraborate pentahydrate. In the United States, 70% of the boron is used for the production of glass and ceramics.
The major global industrial-scale use of boron compounds (about 46% of end-use) is in production of
glass fiber
Glass fiber ( or glass fibre) is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass.
Glassmakers throughout history have experimented with glass fibers, but mass manufacture of glass fiber was only made possible with the inventio ...
for boron-containing insulating and structural
fiberglass
Fiberglass ( American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cl ...
es, especially in Asia. Boron is added to the glass as borax pentahydrate or boron oxide, to influence the strength or fluxing qualities of the glass fibers. Another 10% of global boron production is for
borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), m ...
as used in high strength glassware. About 15% of global boron is used in boron ceramics, including super-hard materials discussed below. Agriculture consumes 11% of global boron production, and bleaches and detergents about 6%.
Elemental boron fiber
Boron fiber
Boron Fiber (also commonly called boron filament) is an amorphous elemental boron product which represents the major industrial use of elemental (free) boron. Boron fiber manifests a combination of high strength and high elastic modulus.
A c ...
s (boron filaments) are high-strength, lightweight materials that are used chiefly for advanced
aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and ast ...
structures as a component of
composite material
A composite material (also called a composition material or shortened to composite, which is the common name) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or ...
s, as well as limited production consumer and sporting goods such as
golf clubs
A golf club is a club used to hit a golf ball in a game of golf. Each club is composed of a shaft with a grip and a club head. Woods are mainly used for long-distance fairway or tee shots; irons, the most versatile class, are used for a variety ...
and
fishing rod
A fishing rod is a long, thin rod used by anglers to catch fish by manipulating a line ending in a hook (formerly known as an ''angle'', hence the term "angling"). At its most basic form, a fishing rod is a straight rigid stick/pole with ...
s. The fibers can be produced by
chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (subst ...
of boron on a
tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
filament.
Boron fibers and sub-millimeter sized crystalline boron springs are produced by
laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The ...
-assisted
chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (subst ...
. Translation of the focused laser beam allows production of even complex helical structures. Such structures show good mechanical properties (
elastic modulus
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity) is the unit of measurement of an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it. The elastic modulus of an object is ...
450 GPa, fracture strain 3.7%, fracture stress 17 GPa) and can be applied as reinforcement of ceramics or in
micromechanical systems.
Boronated fiberglass
Fiberglass is a
fiber reinforced polymer made of
plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adapta ...
reinforced by
glass fiber
Glass fiber ( or glass fibre) is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass.
Glassmakers throughout history have experimented with glass fibers, but mass manufacture of glass fiber was only made possible with the inventio ...
s, commonly woven into a mat. The glass fibers used in the material are made of various types of glass depending upon the fiberglass use. These glasses all contain silica or silicate, with varying amounts of oxides of calcium, magnesium, and sometimes boron. The boron is present as borosilicate, borax, or boron oxide, and is added to increase the strength of the glass, or as a fluxing agent to decrease the melting temperature of
silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
, which is too high to be easily worked in its pure form to make glass fibers.
The highly boronated glasses used in fiberglass are E-glass (named for "Electrical" use, but now the most common fiberglass for general use). E-glass is alumino-borosilicate glass with less than 1% w/w alkali oxides, mainly used for glass-reinforced plastics. Other common high-boron glasses include C-glass, an alkali-lime glass with high boron oxide content, used for glass staple fibers and insulation, and D-glass, a
borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), m ...
, named for its low dielectric constant).
[
]
Not all fiberglasses contain boron, but on a global scale, most of the fiberglass used does contain it. Because the ubiquitous use of fiberglass in construction and insulation, boron-containing fiberglasses consume half the global production of boron, and are the single largest commercial boron market.
Borosilicate glass

Borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), m ...
, which is typically 12–15% B
2O
3, 80% SiO
2, and 2% Al
2O
3, has a low
coefficient of thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.
Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kineti ...
, giving it a good resistance to
thermal shock
Thermal shock is a type of rapidly transient mechanical load.
By definition, it is a mechanical load caused by a rapid change of temperature of a certain point.
It can be also extended to the case of a thermal gradient, which makes different pa ...
.
Schott AG
Schott AG is a German multinational glass company specializing in the manufacture of glass and glass-ceramics. Headquartered in Mainz, Germany, it is owned by the Carl Zeiss Foundation. The company's founder and namesake, Otto Schott, is cre ...
's "Duran" and
Owens-Corning
Owens Corning is an American company that develops and produces insulation, roofing, and fiberglass composites and related materials and products. It is the world's largest manufacturer of fiberglass composites. It was formed in 1935 as a partn ...
's trademarked
Pyrex
Pyrex (trademarked as ''PYREX'' and ''pyrex'') is a brand introduced by Corning Inc. in 1915 for a line of clear, low-thermal-expansion borosilicate glass used for laboratory glassware and kitchenware. It was later expanded to include kitchenwa ...
are two major brand names for this glass, used both in
laboratory glassware
Laboratory glassware refers to a variety of equipment used in scientific work, and traditionally made of glass. Glass can be blown, bent, cut, molded, and formed into many sizes and shapes, and is therefore common in chemistry, biology, and anal ...
and in consumer
cookware and bakeware
Cookware and bakeware is food preparation equipment, such as cooking pots, pans, baking sheets etc. used in kitchens. Cookware is used on a stove or range cooktop, while bakeware is used in an oven. Some utensils are considered both cookwar ...
, chiefly for this resistance.
Boron carbide ceramic

Several boron compounds are known for their extreme hardness and toughness.
Boron carbide
Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders,
as well as numerous industrial applications. With a Vickers hard ...
is a ceramic material which is obtained by decomposing B
2O
3 with carbon in an electric furnace:
:2 B
2O
3 + 7 C → B
4C + 6 CO
Boron carbide's structure is only approximately B
4C, and it shows a clear depletion of carbon from this suggested stoichiometric ratio. This is due to its very complex structure. The substance can be seen with
empirical formula
In chemistry, the empirical formula of a chemical compound is the simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound. A simple example of this concept is that the empirical formula of sulfur monoxide, or SO, would simply be SO, as is the ...
B
12C
3 (i.e., with B
12 dodecahedra being a motif), but with less carbon, as the suggested C
3 units are replaced with C-B-C chains, and some smaller (B
6) octahedra are present as well (see the boron carbide article for structural analysis). The repeating polymer plus semi-crystalline structure of boron carbide gives it great structural strength per weight. It is used in
tank armor,
bulletproof vest
A bulletproof vest, also known as a ballistic vest or a bullet-resistant vest, is an item of body armor that helps absorb the impact and reduce or stop penetration to the torso from firearm-fired projectiles and fragmentation from explosions. Th ...
s, and numerous other structural applications.
Boron carbide's ability to absorb neutrons without forming long-lived
radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transfer ...
s (especially when doped with extra boron-10) makes the material attractive as an
absorbent for neutron radiation arising in nuclear power plants. Nuclear applications of boron carbide include shielding, control rods and shut-down pellets. Within control rods, boron carbide is often powdered, to increase its surface area.
High-hardness and abrasive compounds
Boron carbide and cubic boron nitride powders are widely used as abrasives.
Boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal ...
is a material isoelectronic to
carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
. Similar to carbon, it has both hexagonal (soft graphite-like h-BN) and cubic (hard, diamond-like c-BN) forms. h-BN is used as a high temperature component and lubricant. c-BN, also known under commercial name
borazon
Borazon is a brand name of a cubic form of boron nitride (cBN). Its color ranges from black to brown and gold, depending on the chemical bond. It is one of the hardest known materials, along with various forms of diamond and kinds of boron nitride ...
, is a superior abrasive. Its hardness is only slightly smaller than, but its chemical stability is superior, to that of diamond.
Heterodiamond Heterodiamond is a superhard material containing boron, carbon, and nitrogen (BCN). It is formed at high temperatures and high pressures, e.g., by application of an explosive shock wave to a mixture of diamond and cubic boron nitride (c-BN). The he ...
(also called BCN) is another diamond-like boron compound.
Metallurgy
Boron is added to
boron steels at the level of a few parts per million to increase hardenability. Higher percentages are added to steels used in the
nuclear industry
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
due to boron's neutron absorption ability.
Boron can also increase the surface hardness of steels and alloys through
boriding
Boriding, also called boronizing, is the process by which boron is added to a metal or alloy. It is a type of surface hardening. In this process boron atoms are diffused into the surface of a metal component. The resulting surface contains metal ...
. Additionally metal
boride A boride is a compound between boron and a less electronegative element, for example silicon boride (SiB3 and SiB6). The borides are a very large group of compounds that are generally high melting and are covalent more than ionic in nature. Some bo ...
s are used for coating tools through
chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (subst ...
or
physical vapor deposition
Physical vapor deposition (PVD), sometimes called physical vapor transport (PVT), describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods which can be used to produce thin films and coatings on substrates including metals, ceramics, glass, and polym ...
. Implantation of boron ions into metals and alloys, through
ion implantation
Ion implantation is a low-temperature process by which ions of one element are accelerated into a solid target, thereby changing the physical, chemical, or electrical properties of the target. Ion implantation is used in semiconductor device fa ...
or
ion beam deposition
Ion beam deposition (IBD) is a process of applying materials to a target through the application of an ion beam.
Ion beam deposition setup with mass separator
An ion beam deposition apparatus typically consists of an ion source, ion optics, and ...
, results in a spectacular increase in surface resistance and microhardness. Laser alloying has also been successfully used for the same purpose. These borides are an alternative to diamond coated tools, and their (treated) surfaces have similar properties to those of the bulk boride.
For example,
rhenium diboride
Rhenium diboride (ReB2) is a synthetic superhard material. It was first synthesized in 1962 and re-emerged recently due to hopes of achieving high hardness comparable to that of diamond. The reported ultrahigh hardness has been questioned, alth ...
can be produced at ambient pressures, but is rather expensive because of rhenium. The hardness of ReB
2 exhibits considerable
anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the property of a material which allows it to change or assume different properties in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. It can be defined as a difference, when measured along different axes, in a material's physic ...
because of its hexagonal layered structure. Its value is comparable to that of
tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: WC) is a chemical compound (specifically, a carbide) containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into ...
,
silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal s ...
,
titanium diboride
Titanium diboride (TiB2) is an extremely hard ceramic which has excellent heat conductivity, oxidation stability and wear resistance. TiB2 is also a reasonable electrical conductor,J. Schmidt et al. "Preparation of titanium diboride TiB2 by spark ...
or
zirconium diboride
Zirconium diboride (ZrB2) is a highly covalent refractory ceramic material with a hexagonal crystal structure. ZrB2 is an ultra high temperature ceramic (UHTC) with a melting point of 3246 °C. This along with its relatively low density of ...
.
Similarly, AlMgB
14 + TiB
2 composites possess high hardness and wear resistance and are used in either bulk form or as coatings for components exposed to high temperatures and wear loads.
Detergent formulations and bleaching agents
Borax is used in various household laundry and cleaning products, including the "
20 Mule Team Borax" laundry booster and "
Boraxo" powdered hand soap. It is also present in some
tooth bleaching
Tooth whitening or tooth bleaching is the process of lightening the color of human teeth. Whitening is often desirable when teeth become yellowed over time for a number of reasons, and can be achieved by changing the intrinsic or extrinsic color o ...
formulas.
Sodium perborate
Sodium perborate is chemical compound whose chemical formula may be written , , or, more properly, ·. Its name is sometimes abbreviated as PBS (not to be confused with phosphate-buffered saline).
The compound is commonly encountered in anhydr ...
serves as a source of
active oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well a ...
in many
detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are m ...
s,
laundry detergent
Laundry detergent is a type of detergent (cleaning agent) used for cleaning dirty laundry (clothes). Laundry detergent is manufactured in powder (washing powder) and liquid form.
While powdered and liquid detergents hold roughly equal share o ...
s,
cleaning product
Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances (usually liquids, powders, sprays, or granules) used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, bad smells, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removing ...
s, and laundry
bleaches. However, despite its name, "Borateem" laundry bleach no longer contains any boron compounds, using
sodium percarbonate instead as a bleaching agent.
Insecticides
Boric acid is used as an insecticide, notably against ants, fleas, and cockroaches.
Semiconductors
Boron is a useful
dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace of impurity element that is introduced into a chemical material to alter its original electrical or optical properties. The amount of dopant necessary to cause changes is typically very low. Whe ...
for such semiconductors as
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
,
germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors ...
, and
silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal s ...
. Having one fewer valence electron than the host atom, it donates a
hole resulting in
p-type conductivity. Traditional method of introducing boron into semiconductors is via its
atomic diffusion
Atomic may refer to:
* Of or relating to the atom, the smallest particle of a chemical element that retains its chemical properties
* Atomic physics, the study of the atom
* Atomic Age, also known as the "Atomic Era"
* Atomic scale, distances com ...
at high temperatures. This process uses either solid (B
2O
3), liquid (BBr
3), or gaseous boron sources (B
2H
6 or BF
3). However, after the 1970s, it was mostly replaced by
ion implantation
Ion implantation is a low-temperature process by which ions of one element are accelerated into a solid target, thereby changing the physical, chemical, or electrical properties of the target. Ion implantation is used in semiconductor device fa ...
, which relies mostly on BF
3 as a boron source. Boron trichloride gas is also an important chemical in semiconductor industry, however, not for doping but rather for
plasma etching
Plasma etching is a form of plasma processing used to fabricate integrated circuits. It involves a high-speed stream of glow discharge ( plasma) of an appropriate gas mixture being shot (in pulses) at a sample. The plasma source, known as etch spec ...
of metals and their oxides.
Triethylborane
Triethylborane (TEB), also called triethylboron, is an organoborane (a compound with a B–C bond). It is a colorless pyrophoric liquid. Its chemical formula is or , abbreviated . It is soluble in organic solvents tetrahydrofuran and hexane.
Pr ...
is also injected into
vapor deposition reactors as a boron source. Examples are the plasma deposition of boron-containing hard carbon films, silicon nitride–boron nitride films, and for
doping of
diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, b ...
film with boron.
Magnets
Boron is a component of
neodymium magnet
A hard_disk_drive.html"_;"title="Nickel-plated_neodymium_magnet_on_a_bracket_from_a_hard_disk_drive">Nickel-plated_neodymium_magnet_on_a_bracket_from_a_hard_disk_drive_
file:Nd-magnet.jpg.html" ;"title="hard_disk_drive_.html" ;"title="hard_disk_d ...
s (Nd
2Fe
14B), which are among the strongest type of permanent magnet. These magnets are found in a variety of electromechanical and electronic devices, such as
magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) medical imaging systems, in compact and relatively small motors and
actuator
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover".
An actuator requires a control device (controlled by control signal) a ...
s. As examples, computer HDDs (hard disk drives), CD (compact disk) and DVD (digital versatile disk) players rely on neodymium magnet motors to deliver intense rotary power in a remarkably compact package. In mobile phones 'Neo' magnets provide the magnetic field which allows tiny speakers to deliver appreciable audio power.
Shielding and neutron absorber in nuclear reactors
Boron shielding is used as a control for
nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat fr ...
s, taking advantage of its high
cross-section
Cross section may refer to:
* Cross section (geometry)
** Cross-sectional views in architecture & engineering 3D
*Cross section (geology)
* Cross section (electronics)
* Radar cross section, measure of detectability
* Cross section (physics)
**Abs ...
for neutron capture.
In
pressurized water reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan and Canada). In a PWR, the primary coolant (water) i ...
s a variable concentration of boronic acid in the cooling water is used as a
neutron poison
In applications such as nuclear reactors, a neutron poison (also called a neutron absorber or a nuclear poison) is a substance with a large neutron absorption cross-section. In such applications, absorbing neutrons is normally an undesirable eff ...
to compensate the variable reactivity of the fuel. When new rods are inserted the concentration of boronic acid is maximal, and is reduced during the lifetime.
Other nonmedical uses
* Because of its distinctive green flame, amorphous boron is used in
pyrotechnic flares.
* In the 1950s, there were several studies of the use of
boranes
Boranes is the name given to compounds with the formula BxHy and related anions. Many such boranes are known. Most common are those with 1 to 12 boron atoms. Although they have few practical applications, the boranes exhibit structures and bond ...
as energy-increasing "
Zip fuel" additives for jet fuel.
*
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human die ...
and
casein
Casein ( , from Latin ''caseus'' "cheese") is a family of related phosphoproteins ( αS1, aS2, β, κ) that are commonly found in mammalian milk, comprising about 80% of the proteins in cow's milk and between 20% and 60% of the proteins in hum ...
-based adhesives contain sodium tetraborate decahydrate (Na
2B
4O
7·10 H
2O)
* Some anti-corrosion systems contain borax.
* Sodium borates are used as a
flux
Flux describes any effect that appears to pass or travel (whether it actually moves or not) through a surface or substance. Flux is a concept in applied mathematics and vector calculus which has many applications to physics. For transport ...
for soldering silver and gold and with
ammonium chloride for welding ferrous metals. They are also fire retarding additives to plastics and rubber articles.
*
Boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
(also known as orthoboric acid) H
3BO
3 is used in the production of textile fiberglass and
flat panel display
A flat-panel display (FPD) is an electronic display used to display visual content such as text or images. It is present in consumer, medical, transportation, and industrial equipment.
Flat-panel displays are thin, lightweight, provide better l ...
s
and in many
PVAc- and
PVOH
Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVOH, PVA, or PVAl) is a water-soluble synthetic polymer. It has the idealized formula H2CH(OH)sub>''n''. It is used in papermaking, textile warp sizing, as a thickener and emulsion stabilizer in polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) a ...
-based adhesives.
*
Triethylborane
Triethylborane (TEB), also called triethylboron, is an organoborane (a compound with a B–C bond). It is a colorless pyrophoric liquid. Its chemical formula is or , abbreviated . It is soluble in organic solvents tetrahydrofuran and hexane.
Pr ...
is a substance which ignites the
JP-7
Turbine Fuel Low Volatility JP-7, commonly known as JP-7 (referred to as Jet Propellant 7 prior to MIL-DTL-38219) is a specialized type of jet fuel developed in 1955 for the United States Air Force (USAF) for use in its supersonic military aircr ...
fuel of the
Pratt & Whitney J58 turbojet
The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, a ...
/
ramjet
A ramjet, or athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the forward motion of the engine to produce thrust. Since it produces no thrust when stationary (no ram air) ramjet-powered vehicles require an ass ...
engines powering the
Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird
The Lockheed SR-71 "Blackbird" is a long-range, high-altitude, Mach 3+ strategic reconnaissance aircraft developed and manufactured by the American aerospace company Lockheed Corporation. It was operated by the United States Air Force ...
. It was also used to ignite the
F-1 Engines on the
Saturn V
Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, with multistage rocket, three stages, and powered with liquid-propellant r ...
Rocket utilized by
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
's
Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
and
Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations ...
programs from 1967 until 1973. Today
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal o ...
uses it to ignite the engines on their
Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a partially reusable medium lift launch vehicle that can carry cargo and crew into Earth orbit, produced by American aerospace company SpaceX.
The rocket has two stages. The first (booster) stage carries the second stage and pay ...
rocket.
[Mission Status Center, June 2, 2010, 1905 GMT](_blank)
, '' SpaceflightNow'', accessed 2010-06-02, Quotation: "The flanges will link the rocket with ground storage tanks containing liquid oxygen, kerosene fuel, helium, gaseous nitrogen and the first stage ignitor source called triethylaluminum-triethylborane, better known as TEA-TEB." Triethylborane is suitable for this because of its
pyrophoric
A substance is pyrophoric (from grc-gre, πυροφόρος, , 'fire-bearing') if it ignites spontaneously in air at or below (for gases) or within 5 minutes after coming into contact with air (for liquids and solids). Examples are organolith ...
properties, especially the fact that it burns with a very high temperature. Triethylborane is an industrial
initiator
An initiator can refer to:
* A person who instigates something.
* Modulated neutron initiator, a neutron source used in some nuclear weapons
** Initiator, an Explosive booster
** Initiator, the first Nuclear chain reaction
* Pyrotechnic initiator, ...
in
radical
Radical may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
* Radical politics, the political intent of fundamental societal change
*Radicalism (historical), the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe an ...
reactions, where it is effective even at low temperatures.
* Borates are used as environmentally benign
wood preservative
Wood easily degrades without sufficient preservation. Apart from structural wood preservation measures, there are a number of different chemical preservatives and processes (also known as "timber treatment", "lumber treatment" or "pressure treat ...
s.
Pharmaceutical and biological applications
Boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
has antiseptic, antifungal, and antiviral properties and for these reasons is applied as a water clarifier in swimming pool water treatment.
Mild solutions of boric acid have been used as eye antiseptics.
Bortezomib
Bortezomib, sold under the brand name Velcade among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma. This includes multiple myeloma in those who have and have not previously received treatment. It is ...
(marketed as Velcade and Cytomib). Boron appears as an active element in the organic pharmaceutical bortezomib, a new class of drug called the proteasome inhibitor, for the treatment of myeloma and one form of lymphoma (it is in currently in experimental trials against other types of lymphoma). The boron atom in bortezomib binds the catalytic site of the
26S proteasome with high affinity and specificity.
* A number of potential boronated pharmaceuticals using
boron-10
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has t ...
, have been prepared for use in
boron neutron capture therapy
Neutron capture therapy (NCT) is a type of radiotherapy for treating locally invasive malignant tumors such as primary brain tumors, recurrent cancers of the head and neck region, and cutaneous and extracutaneous melanomas. It is a two-step pro ...
(BNCT).
* Some boron compounds show promise in treating
arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In som ...
, though none have as yet been generally approved for the purpose.
Tavaborole (marketed as Kerydin) is an
Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its pre ...
inhibitor which is used to treat toenail fungus. It gained FDA approval in July 2014.
Dioxaborolane chemistry enables radioactive
fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts ty ...
(
18F) labeling of
antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
or
red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hol ...
s, which allows for
positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, ...
(PET) imaging of
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
and
hemorrhages
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
, respectively. A
Human-
Derived,
Genetic,
Positron-emitting and
Fluorescent (HD-GPF) reporter system uses a human protein,
PSMA and non-immunogenic, and a small molecule that is positron-emitting (boron bound
18 F) and fluorescence for dual modality PET and fluorescent imaging of genome modified cells, e.g.
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
,
CRISPR/Cas9
Cas9 (CRISPR associated protein 9, formerly called Cas5, Csn1, or Csx12) is a 160 kilodalton protein which plays a vital role in the immunological defense of certain bacteria against DNA viruses and plasmids, and is heavily utilized in genetic ...
, or
CAR T-cells, in an entire mouse. The dual-modality small molecule targeting
PSMA was tested in humans and found the location of primary and
metastatic
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
, fluorescence-guided removal of cancer, and detects single cancer cells in tissue margins.
Research areas
Magnesium diboride
Magnesium diboride is the inorganic compound with the formula MgB2. It is a dark gray, water-insoluble solid. The compound has attracted attention because it becomes superconducting at 39 K (−234 °C). In terms of its composition, Mg ...
is an important
superconducting material with the transition temperature of 39 K. MgB
2 wires are produced with the
powder-in-tube process and applied in superconducting magnets.
Amorphous boron is used as a melting point depressant in nickel-chromium braze alloys.
Hexagonal
boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal ...
forms atomically thin layers, which have been used to enhance the
electron mobility
In solid-state physics, the electron mobility characterises how quickly an electron can move through a metal or semiconductor when pulled by an electric field. There is an analogous quantity for holes, called hole mobility. The term carrier mobil ...
in
graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. devices. It also forms nanotubular structures (
boron nitride#Boron nitride nanotubes, BNNTs), which have high strength, high chemical stability, and high
thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
, among its list of desirable properties.
Biological role
Boron is an essential plant
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excre ...
, required primarily for maintaining the integrity of cell walls. However, high soil concentrations of greater than 1.0
ppm lead to marginal and tip necrosis in leaves as well as poor overall growth performance. Levels as low as 0.8 ppm produce these same symptoms in plants that are particularly sensitive to boron in the soil. Nearly all plants, even those somewhat tolerant of soil boron, will show at least some symptoms of boron toxicity when soil boron content is greater than 1.8 ppm. When this content exceeds 2.0 ppm, few plants will perform well and some may not survive.
It is thought that boron plays several essential roles in animals, including humans, but the exact physiological role is poorly understood.
A small human trial published in 1987 reported on postmenopausal women first made boron deficient and then repleted with 3 mg/day. Boron supplementation markedly reduced urinary calcium excretion and elevated the serum concentrations of 17 beta-estradiol and testosterone.
The U.S. Institute of Medicine has not confirmed that boron is an essential nutrient for humans, so neither a
Recommended Dietary Allowance
The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) is a system of nutrition recommendations from the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) of the National Academies (United States). It was introduced in 1997 in order to broaden the existing guidelines known as Rec ...
(RDA) nor an Adequate Intake have been established. Adult dietary intake is estimated at 0.9 to 1.4 mg/day, with about 90% absorbed. What is absorbed is mostly excreted in urine. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level for adults is 20 mg/day.
In 2013, a hypothesis suggested it was possible that boron and molybdenum catalyzed the production of
RNA on
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
with life being transported to Earth via a meteorite around 3 billion years ago.
There exist several known boron-containing natural
antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s. The first one found was
boromycin
Boromycin is a bacteriocidal polyether- macrolide antibiotic. It was initially isolated from the '' Streptomyces antibioticus'', and is notable for being the first natural product found to contain the element boron. It is effective against most ...
, isolated from
streptomyces
''Streptomyces'' is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positiv ...
.
Congenital endothelial dystrophy type 2, a rare form of
corneal dystrophy
Corneal dystrophy is a group of rare hereditary disorders characterised by bilateral abnormal deposition of substances in the transparent front part of the eye called the cornea.
Signs and symptoms
Corneal dystrophy may not significantly affect v ...
, is linked to mutations in
SLC4A11
Sodium bicarbonate transporter-like protein 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC4A11'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." m ...
gene that encodes a transporter reportedly regulating the intracellular concentration of boron.
Analytical quantification
For determination of boron content in food or materials, the
colorimetric
Colorimetry is "the science and technology used to quantify and describe physically the human color perception".
It is similar to spectrophotometry, but is distinguished by its interest in reducing spectra to the physical correlates of color ...
''curcumin method'' is used. Boron is converted to boric acid or
borate
A borate is any of several boron oxyanions, negative ions consisting of boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate , metaborate , or tetraborate ; or any salt with such anions, such as sodium metaborate, and disodium tetraborate . The name also re ...
s and on reaction with
curcumin
Curcumin is a bright yellow chemical produced by plants of the ''Curcuma longa'' species. It is the principal curcuminoid of turmeric (''Curcuma longa''), a member of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is sold as a herbal supplement, cosmet ...
in acidic solution, a red colored boron-
chelate
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are ...
complex,
rosocyanine
Rosocyanine and rubrocurcumin are two red colored materials, which are formed by the reaction between curcumin and borates.
Application
The color reaction between borates and curcumin is used within the spectrophotometrical determination and qu ...
, is formed.
Health issues and toxicity
Elemental boron,
boron oxide Boron oxide may refer to one of several oxides of boron:
*Boron trioxide
Boron trioxide or diboron trioxide is the oxide of boron with the formula . It is a colorless transparent solid, almost always glassy (amorphous), which can be crystallized ...
,
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
, borates, and many
organoboron compounds
Organoborane or organoboron compounds are chemical compounds of boron and carbon that are organic derivatives of BH3, for example trialkyl boranes. Organoboron chemistry or organoborane chemistry is the chemistry of these compounds.
Organoboron ...
are relatively nontoxic to humans and animals (with toxicity similar to that of table salt). The
LD50 (dose at which there is 50% mortality) for animals is about 6 g per kg of body weight. Substances with LD
50 above 2 g/kg are considered nontoxic. An intake of 4 g/day of boric acid was reported without incident, but more than this is considered toxic in more than a few doses. Intakes of more than 0.5 grams per day for 50 days cause minor digestive and other problems suggestive of toxicity. Dietary supplementation of boron may be helpful for bone growth, wound healing, and antioxidant activity, and insufficient amount of boron in diet may result in
boron deficiency.
Single medical doses of 20 g of
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
for
neutron capture therapy
Neutron capture therapy (NCT) is a type of radiotherapy for treating locally invasive malignant tumors such as primary brain tumors, recurrent cancers of the head and neck region, and cutaneous and extracutaneous melanomas. It is a two-step pr ...
have been used without undue toxicity.
Boric acid is more toxic to insects than to mammals, and is routinely used as an insecticide.
The
boranes
Boranes is the name given to compounds with the formula BxHy and related anions. Many such boranes are known. Most common are those with 1 to 12 boron atoms. Although they have few practical applications, the boranes exhibit structures and bond ...
(boron hydrogen compounds) and similar gaseous compounds are quite poisonous. As usual, boron is not an element that is intrinsically poisonous, but the toxicity of these compounds depends on structure (for another example of this phenomenon, see
phosphine
Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting ...
).
The boranes are also highly flammable and require special care when handling, some combinations of boranes and other compounds are highly explosive. Sodium borohydride presents a fire hazard owing to its reducing nature and the liberation of hydrogen on contact with acid. Boron halides are corrosive.

Boron is necessary for plant growth, but an excess of boron is toxic to plants, and occurs particularly in acidic soil.
It presents as a yellowing from the tip inwards of the oldest leaves and black spots in barley leaves, but it can be confused with other stresses such as magnesium deficiency in other plants.
See also
*
Allotropes of boron
Boron can be prepared in several crystalline and amorphous forms. Well known crystalline forms are α-rhombohedral (α-R), β-rhombohedral (β-R), and β-tetragonal (β-T). In special circumstances, boron can also be synthesized in the form of ...
*
Boron deficiency
*
Boron oxide Boron oxide may refer to one of several oxides of boron:
*Boron trioxide
Boron trioxide or diboron trioxide is the oxide of boron with the formula . It is a colorless transparent solid, almost always glassy (amorphous), which can be crystallized ...
*
Boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal ...
*
Boron neutron capture therapy
Neutron capture therapy (NCT) is a type of radiotherapy for treating locally invasive malignant tumors such as primary brain tumors, recurrent cancers of the head and neck region, and cutaneous and extracutaneous melanomas. It is a two-step pro ...
*
Boronic acid
A boronic acid is an organic compound related to boric acid () in which one of the three hydroxyl groups () is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (represented by R in the general formula ). As a compound containing a carbon–boron bond, membe ...
*
Hydroboration-oxidation reaction
*
Suzuki coupling
The Suzuki reaction is an organic reaction, classified as a cross-coupling reaction, where the coupling partners are a boronic acid and an organohalide and the catalyst is a palladium(0) complex. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, ...
References
External links
Boronat
The Periodic Table of Videos
''Periodic Videos'' (also known as ''The Periodic Table of Videos'') is a video project and YouTube channel on chemistry. It consists of a series of videos about chemical elements and the periodic table, with additional videos on other topics i ...
(University of Nottingham)
* J. B. Calvert
Boron 2004, private website
{{Authority control
Chemical elements
Metalloids
Neutron poisons
Pyrotechnic fuels
Rocket fuels
Nuclear fusion fuels
Dietary minerals
Reducing agents
Articles containing video clips
Chemical elements with rhombohedral structure
 Borax in its mineral form (then known as tincal) first saw use as a glaze, beginning in
Borax in its mineral form (then known as tincal) first saw use as a glaze, beginning in  Boron is similar to
Boron is similar to  Boron undergoes halogenation to give trihalides; for example,
:2 B + 3 Br2 → 2 BBr3
The trichloride in practice is usually made from the oxide.
Boron undergoes halogenation to give trihalides; for example,
:2 B + 3 Br2 → 2 BBr3
The trichloride in practice is usually made from the oxide.
 In the most familiar compounds, boron has the formal oxidation state III. These include oxides, sulfides, nitrides, and halides.
The trihalides adopt a planar trigonal structure. These compounds are
In the most familiar compounds, boron has the formal oxidation state III. These include oxides, sulfides, nitrides, and halides.
The trihalides adopt a planar trigonal structure. These compounds are  Boranes are chemical compounds of boron and hydrogen, with the generic formula of BxHy. These compounds do not occur in nature. Many of the boranes readily oxidise on contact with air, some violently. The parent member BH3 is called borane, but it is known only in the gaseous state, and dimerises to form diborane, B2H6. The larger boranes all consist of boron clusters that are polyhedral, some of which exist as isomers. For example, isomers of B20H26 are based on the fusion of two 10-atom clusters.
The most important boranes are diborane B2H6 and two of its pyrolysis products, pentaborane B5H9 and decaborane B10H14. A large number of anionic boron hydrides are known, e.g. 12H12sup>2−.
The formal
Boranes are chemical compounds of boron and hydrogen, with the generic formula of BxHy. These compounds do not occur in nature. Many of the boranes readily oxidise on contact with air, some violently. The parent member BH3 is called borane, but it is known only in the gaseous state, and dimerises to form diborane, B2H6. The larger boranes all consist of boron clusters that are polyhedral, some of which exist as isomers. For example, isomers of B20H26 are based on the fusion of two 10-atom clusters.
The most important boranes are diborane B2H6 and two of its pyrolysis products, pentaborane B5H9 and decaborane B10H14. A large number of anionic boron hydrides are known, e.g. 12H12sup>2−.
The formal  Binary metal-boron compounds, the metal borides, contain boron in negative oxidation states. Illustrative is
Binary metal-boron compounds, the metal borides, contain boron in negative oxidation states. Illustrative is  Enriched boron or 10B is used in both radiation shielding and is the primary nuclide used in
Enriched boron or 10B is used in both radiation shielding and is the primary nuclide used in 
 Boron is rare in the Universe and solar system due to trace formation in the
Boron is rare in the Universe and solar system due to trace formation in the 
 Several boron compounds are known for their extreme hardness and toughness.
Several boron compounds are known for their extreme hardness and toughness.
 Boron is necessary for plant growth, but an excess of boron is toxic to plants, and occurs particularly in acidic soil. It presents as a yellowing from the tip inwards of the oldest leaves and black spots in barley leaves, but it can be confused with other stresses such as magnesium deficiency in other plants.
Boron is necessary for plant growth, but an excess of boron is toxic to plants, and occurs particularly in acidic soil. It presents as a yellowing from the tip inwards of the oldest leaves and black spots in barley leaves, but it can be confused with other stresses such as magnesium deficiency in other plants.