berkelium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Berkelium is a transuranic
 Berkelium is a soft, silvery-white, radioactive
Berkelium is a soft, silvery-white, radioactive

 Although very small amounts of berkelium were possibly produced in previous nuclear experiments, it was first intentionally synthesized, isolated and identified in December 1949 by
Although very small amounts of berkelium were possibly produced in previous nuclear experiments, it was first intentionally synthesized, isolated and identified in December 1949 by
/ref> The name choice for element 97 followed the previous tradition of the Californian group to draw an analogy between the newly discovered Further separation was carried out in the presence of a
Further separation was carried out in the presence of a
^_U -> ce^_U -> beta^-23.5 \ \ce] ^_Np -> beta^-2.3565 \ \ce] ^_Pu (the times are ^_Cm ->[][64.15 \ \ce] ^_Bk -> beta^-330 \ \ce] ^_Cf
The thus-produced 249Bk has a long half-life of 330 days and thus can capture another neutron. However, the product, 250Bk, again has a relatively short half-life of 3.212 hours and thus does not yield any heavier berkelium isotopes. It instead decays to the californium isotope 250Cf:
:^_Bk -> ce^_Bk -> beta^-3.212 \ \ce] ^_Cf
Although 247Bk is the most stable isotope of berkelium, its production in nuclear reactors is very difficult because its potential progenitor 247Cm has never been observed to undergo beta decay. Thus, 249Bk is the most accessible isotope of berkelium, which still is available only in small quantities (only 0.66 grams have been produced in the US over the period 1967–1983) at a high price of the order 185 United States dollar, USD per microgram.Hammond C. R. "The elements" in It is the only berkelium isotope available in bulk quantities, and thus the only berkelium isotope whose properties can be extensively studied.
The isotope 248Bk was first obtained in 1956 by bombarding a mixture of curium isotopes with 25 MeV α-particles. Although its direct detection was hindered by strong signal interference with 245Bk, the existence of a new isotope was proven by the growth of the decay product 248Cf which had been previously characterized. The half-life of 248Bk was estimated as hours, though later 1965 work gave a half-life in excess of 300 years (which may be due to an isomeric state). Berkelium-247 was produced during the same year by irradiating 244Cm with alpha-particles:
:
Berkelium-242 was synthesized in 1979 by bombarding 235U with 11B, 238U with 10B, 232Th with 14N or 232Th with 15N. It converts by electron capture to 242Cm with a half-life of minutes. A search for an initially suspected isotope 241Bk was then unsuccessful; 241Bk has since been synthesized.
:
 There is currently no use for any isotope of berkelium outside basic scientific research. Berkelium-249 is a common target nuclide to prepare still heavier transuranium elements and superheavy elements,Stwertka, Albert. ''A Guide to the Elements'', Oxford University Press, 1996, p. 211. such as
There is currently no use for any isotope of berkelium outside basic scientific research. Berkelium-249 is a common target nuclide to prepare still heavier transuranium elements and superheavy elements,Stwertka, Albert. ''A Guide to the Elements'', Oxford University Press, 1996, p. 211. such as
"Evaluation of nuclear criticality safety. data and limits for actinides in transport"
, p. 16 Berkelium-247 can maintain chain reaction both in a thermal-neutron and in a fast-neutron reactor, however, its production is rather complex and thus the availability is much lower than its critical mass, which is about 75.7 kg for a bare sphere, 41.2 kg with a water reflector and 35.2 kg with a steel reflector (30 cm thickness).
Berkelium
at ''
radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
with the symbol Bk and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
97. It is a member of the actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The info ...
and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California
Berkeley ( ) is a city on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay in northern Alameda County, California, United States. It is named after the 18th-century Irish bishop and philosopher George Berkeley. It borders the cities of Oakland and Emery ...
, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (then the University of California Radiation Laboratory) where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it bein ...
, plutonium, curium
Curium is a transuranic, radioactive chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first inte ...
and americium
Americium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a transuranic member of the actinide series, in the periodic table located under the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named ...
.
The major isotope of berkelium, 249Bk, is synthesized in minute quantities in dedicated high-flux nuclear reactors, mainly at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee, United States, and at the Research Institute of Atomic Reactors
The Research Institute of Atomic Reactors (; RIAR) is an institute for nuclear reactor research in Dimitrovgrad in Ulyanovsk Oblast, Russia. The institute houses eight nuclear research reactors: SM, Arbus (ACT-1), MIR.M1, RBT-6, RBT-10 / 1, RB ...
in Dimitrovgrad, Russia
Dimitrovgrad (russian: Димитровград; ), formerly Melekess () until 1972, is a city in Ulyanovsk Oblast, Russia. It is the administrative center of Melekessky District, although it is not within the district and is an independent ci ...
. The production of the second-most important isotope, 247Bk, involves the irradiation of the rare isotope 244Cm with high-energy alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produce ...
s.
Just over one gram of berkelium has been produced in the United States since 1967. There is no practical application of berkelium outside scientific research which is mostly directed at the synthesis of heavier transuranium elements and superheavy elements. A 22-milligram batch of berkelium-249 was prepared during a 250-day irradiation period and then purified for a further 90 days at Oak Ridge in 2009. This sample was used to synthesize the new element tennessine
Tennessine is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Ts and atomic number 117. It is the second-heaviest known element and the penultimate element of the 7th period of the periodic table.
The discovery of tennessine was officially ann ...
for the first time in 2009 at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eight ...
, after it was bombarded with calcium-48
Calcium-48 is a scarce isotope of calcium containing 20 protons and 28 neutrons. It makes up 0.187% of natural calcium by mole fraction. Although it is unusually neutron-rich for such a light nucleus, its beta decay is extremely hindered, and so ...
ions for 150 days. This was the culmination of the Russia–US collaboration on the synthesis of the heaviest elements on the periodic table.
Berkelium is a soft, silvery-white, radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
metal. The berkelium-249 isotope emits low-energy electrons and thus is relatively safe to handle. It decays with a half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
of 330 days to californium-249, which is a strong emitter of ionizing alpha particles. This gradual transformation is an important consideration when studying the properties of elemental berkelium and its chemical compounds, since the formation of californium brings not only chemical contamination, but also free-radical effects and self-heating from the emitted alpha particles.
Characteristics
Physical
 Berkelium is a soft, silvery-white, radioactive
Berkelium is a soft, silvery-white, radioactive actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The info ...
metal. In the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of ch ...
, it is located to the right of the actinide curium
Curium is a transuranic, radioactive chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first inte ...
, to the left of the actinide californium and below the lanthanide terbium
Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white, rare earth metal that is malleable, and ductile. The ninth member of the lanthanide series, terbium is a fairly electropositive metal that reacts with wa ...
with which it shares many similarities in physical and chemical properties. Its density of 14.78 g/cm3 lies between those of curium (13.52 g/cm3) and californium (15.1 g/cm3), as does its melting point of 986 °C, below that of curium (1340 °C) but higher than that of californium (900 °C). Berkelium is relatively soft and has one of the lowest bulk moduli among the actinides, at about 20 GPa
Grading in education is the process of applying standardized measurements for varying levels of achievements in a course. Grades can be assigned as letters (usually A through F), as a range (for example, 1 to 6), as a percentage, or as a numbe ...
(2 Pa).
ions shows two sharp fluorescence peaks at 652 nanometers (red light) and 742 nanometers (deep red – near-infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from arou ...
) due to internal transitions at the f-electron shell. The relative intensity of these peaks depends on the excitation power and temperature of the sample. This emission can be observed, for example, after dispersing berkelium ions in a silicate glass, by melting the glass in presence of berkelium oxide or halide.
Between 70 K and room temperature, berkelium behaves as a Curie–Weiss paramagnetic material with an effective magnetic moment of 9.69 Bohr magneton
In atomic physics, the Bohr magneton (symbol ) is a physical constant and the natural unit for expressing the magnetic moment of an electron caused by its orbital or spin angular momentum.
The Bohr magneton, in SI units is defined as
\mu_\mathrm ...
s (µB) and a Curie temperature
In physics and materials science, the Curie temperature (''T''C), or Curie point, is the temperature above which certain materials lose their magnet, permanent magnetic properties, which can (in most cases) be replaced by magnetization, induce ...
of 101 K. This magnetic moment is almost equal to the theoretical value of 9.72 µB calculated within the simple atomic L-S coupling model. Upon cooling to about 34 K, berkelium undergoes a transition to an antiferromagnetic
In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins (on different sublattices) pointing in opposite directions. ...
state. Enthalpy of dissolution
In thermochemistry, the enthalpy of solution ( heat of solution or enthalpy of solvation) is the enthalpy change associated with the dissolution of a substance in a solvent at constant pressure resulting in infinite dilution.
The enthalpy of so ...
in hydrochloric acid at standard conditions is −600 kJ/mol, from which the standard enthalpy of formation
In chemistry and thermodynamics, the standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of the substance from its constituent elements in their reference state, wi ...
(Δf''H''°) of aqueous ions is obtained as −601 kJ/mol. The standard electrode potential
In electrochemistry, standard electrode potential E^\ominus, or E^\ominus_, is a measure of the reducing power of any element or compound. The IUPAC "Gold Book" defines it as: ''"the value of the standard emf (electromotive force) of a cell in wh ...
/Bk is −2.01 V. The ionization potential of a neutral berkelium atom is 6.23 eV.
Allotropes
At ambient conditions, berkelium assumes its most stable α form which has a hexagonal symmetry,space group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of an object in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of an object that leave it unch ...
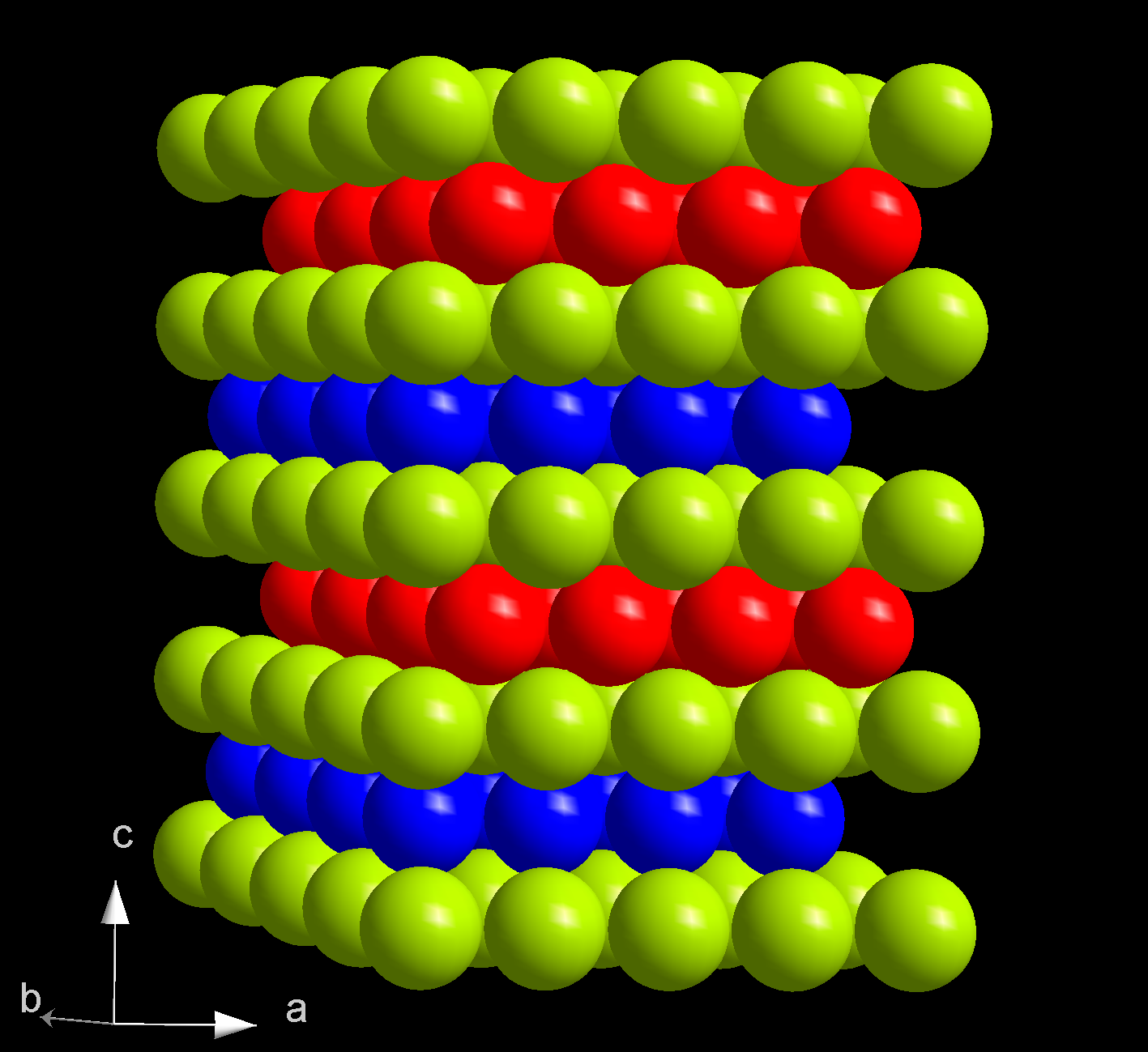
''P63/mmc'', lattice parameters of 341 pm and 1107 pm. The crystal has a double- hexagonal close packing structure with the layer sequence ABAC and so is isotypic (having a similar structure) with α-lanthanum and α-forms of actinides beyond curium. This crystal structure changes with pressure and temperature. When compressed at room temperature to 7 GPa, α-berkelium transforms to the β modification, which has a face-centered cubic (''fcc'') symmetry and space group ''Fmm''. This transition occurs without change in volume, but the enthalpy increases by 3.66 kJ/mol. Upon further compression to 25 GPa, berkelium transforms to an orthorhombic γ-berkelium structure similar to that of α-uranium. This transition is accompanied by a 12% volume decrease and delocalization of the electrons at the 5f electron shell. No further phase transitions are observed up to 57 GPa.
Upon heating, α-berkelium transforms into another phase with an ''fcc'' lattice (but slightly different from β-berkelium), space group ''Fmm'' and the lattice constant of 500 pm; this ''fcc'' structure is equivalent to the closest packing with the sequence ABC. This phase is metastable and will gradually revert to the original α-berkelium phase at room temperature. The temperature of the phase transition is believed to be quite close to the melting point.
Chemical
Like allactinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The info ...
s, berkelium dissolves in various aqueous inorganic acids, liberating gaseous hydrogen and converting into the state. This trivalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.
Description
The combining capacity, or affinity of an ...
oxidation state (+3) is the most stable, especially in aqueous solutions, but tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.
Description
The combining capacity, or affinity of ...
(+4), pentavalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.
Description
The combining capacity, or affinity of an ...
(+5), and possibly divalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.
Description
The combining capacity, or affinity of an ...
(+2) berkelium compounds are also known. The existence of divalent berkelium salts is uncertain and has only been reported in mixed lanthanum(III) chloride-strontium chloride
Strontium chloride (SrCl2) is a salt of strontium and chlorine.
It is a 'typical' salt, forming neutral aqueous solutions. As with all compounds of strontium, this salt emits a bright red colour in flame, and is commonly used in fireworks to that ...
melts. A similar behavior is observed for the lanthanide analogue of berkelium, terbium
Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white, rare earth metal that is malleable, and ductile. The ninth member of the lanthanide series, terbium is a fairly electropositive metal that reacts with wa ...
. Aqueous solutions of ions are green in most acids. The color of ions is yellow in hydrochloric acid and orange-yellow in sulfuric acid. Berkelium does not react rapidly with oxygen at room temperature, possibly due to the formation of a protective oxide layer surface. However, it reacts with molten metals, hydrogen, halogens, chalcogen
The chalcogens (ore forming) ( ) are the chemical elements in group 16 of the periodic table. This group is also known as the oxygen family. Group 16 consists of the elements oxygen (O), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), tellurium (Te), and the radioact ...
s and pnictogens to form various binary compounds.
Isotopes
About twenty isotopes and six nuclear isomers (excited states of an isotope) of berkelium have been characterized with the mass numbers ranging from 233 to 253 (except 235, 237, and 239). All of them are radioactive. The longesthalf-lives
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
are observed for 247Bk (1,380 years), 248Bk (over 300 years), and 249Bk (330 days); the half-lives of the other isotopes range from microseconds to several days. The isotope which is the easiest to synthesize is berkelium-249. This emits mostly soft β-particles which are inconvenient for detection. Its alpha radiation
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and thereby transforms or 'decays' into a different atomic nucleus, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an atomi ...
is rather weak (1.45%) with respect to the β-radiation, but is sometimes used to detect this isotope. The second important berkelium isotope, berkelium-247, is an alpha-emitter, as are most actinide isotopes.
Occurrence
All berkelium isotopes have a half-life far too short to beprimordial
Primordial may refer to:
* Primordial era, an era after the Big Bang. See Chronology of the universe
* Primordial sea (a.k.a. primordial ocean, ooze or soup). See Abiogenesis
* Primordial nuclide, nuclides, a few radioactive, that formed before t ...
. Therefore, any primordial berkelium − that is, berkelium present on the Earth during its formation − has decayed by now.
On Earth, berkelium is mostly concentrated in certain areas, which were used for the atmospheric nuclear weapons tests
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected b ...
between 1945 and 1980, as well as at the sites of nuclear incidents, such as the Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nucl ...
, Three Mile Island accident and 1968 Thule Air Base B-52 crash
On 21 January 1968, an aircraft accident, sometimes known as the Thule affair or Thule accident (; da, Thuleulykken), involving a United States Air Force (USAF) B-52 bomber occurred near Thule Air Base in the Danish territory of Greenland. Th ...
. Analysis of the debris at the testing site of the first United States' first thermonuclear weapon, Ivy Mike, (1 November 1952, Enewetak Atoll), revealed high concentrations of various actinides, including berkelium. For reasons of military secrecy, this result was not published until 1956.
Nuclear reactors produce mostly, among the berkelium isotopes, berkelium-249. During the storage and before the fuel disposal, most of it beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For e ...
s to californium-249. The latter has a half-life of 351 years, which is relatively long when compared to the other isotopes produced in the reactor, and is therefore undesirable in the disposal products.
The transuranium elements from americium
Americium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a transuranic member of the actinide series, in the periodic table located under the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named ...
to fermium, including berkelium, occurred naturally in the natural nuclear fission reactor at Oklo, but no longer do so.
Berkelium is also one of the elements that have been detected in Przybylski's Star.
History

 Although very small amounts of berkelium were possibly produced in previous nuclear experiments, it was first intentionally synthesized, isolated and identified in December 1949 by
Although very small amounts of berkelium were possibly produced in previous nuclear experiments, it was first intentionally synthesized, isolated and identified in December 1949 by Glenn T. Seaborg
Glenn Theodore Seaborg (; April 19, 1912February 25, 1999) was an American chemist whose involvement in the synthesis, discovery and investigation of ten transuranium elements earned him a share of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. His work in ...
, Albert Ghiorso
Albert Ghiorso (July 15, 1915 – December 26, 2010) was an American nuclear scientist and co-discoverer of a record 12 chemical elements on the periodic table. His research career spanned six decades, from the early 1940s to the late 1990s.
Biog ...
, Stanley Gerald Thompson, and Kenneth Street Jr. They used the 60-inch cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: Jan ...
at the University of California, Berkeley. Similar to the nearly simultaneous discovery of americium
Americium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a transuranic member of the actinide series, in the periodic table located under the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named ...
(element 95) and curium
Curium is a transuranic, radioactive chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first inte ...
(element 96) in 1944, the new elements berkelium and californium (element 98) were both produced in 1949–1950.Abstract/ref> The name choice for element 97 followed the previous tradition of the Californian group to draw an analogy between the newly discovered
actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The info ...
and the lanthanide element positioned above it in the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of ch ...
. Previously, americium was named after a continent as its analogue europium, and curium honored scientists Marie
Marie may refer to:
People Name
* Marie (given name)
* Marie (Japanese given name)
* Marie (murder victim), girl who was killed in Florida after being pushed in front of a moving vehicle in 1973
* Marie (died 1759), an enslaved Cree person in ...
and Pierre Curie
Pierre Curie ( , ; 15 May 1859 – 19 April 1906) was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity, and radioactivity. In 1903, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics with his wife, Marie Curie, and Henri Becquer ...
as the lanthanide above it, gadolinium, was named after the explorer of the rare-earth elements Johan Gadolin. Thus the discovery report by the Berkeley group reads: "It is suggested that element 97 be given the name berkelium (symbol Bk) after the city of Berkeley in a manner similar to that used in naming its chemical homologue terbium
Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white, rare earth metal that is malleable, and ductile. The ninth member of the lanthanide series, terbium is a fairly electropositive metal that reacts with wa ...
(atomic number 65) whose name was derived from the town of Ytterby, Sweden, where the rare earth minerals were first found." This tradition ended with berkelium, though, as the naming of the next discovered actinide, californium, was not related to its lanthanide analogue dysprosium, but after the discovery place.
The most difficult steps in the synthesis of berkelium were its separation from the final products and the production of sufficient quantities of americium for the target material. First, americium ( 241Am) nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insolubl ...
solution was coated on a platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Platin ...
foil, the solution was evaporated and the residue converted by annealing to americium dioxide
Americium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a transuranic member of the actinide series, in the periodic table located under the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named ...
(). This target was irradiated with 35 MeV alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produce ...
s for 6 hours in the 60-inch cyclotron at the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley. The (α,2n) reaction induced by the irradiation yielded the 243Bk isotope and two free neutrons:
: + → + 2
After the irradiation, the coating was dissolved with nitric acid and then precipitated as the hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It ...
using concentrated aqueous ammonia solution
Ammonia solution, also known as ammonia water, ammonium hydroxide, ammoniacal liquor, ammonia liquor, aqua ammonia, aqueous ammonia, or (inaccurately) ammonia, is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH3(aq). Although ...
. The product was centrifugated and re-dissolved in nitric acid. To separate berkelium from the unreacted americium, this solution was added to a mixture of ammonium and ammonium sulfate
Ammonium sulfate (American English and international scientific usage; ammonium sulphate in British English); (NH4)2SO4, is an inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses. The most common use is as a soil fertilizer. It contains 21% nitrogen a ...
and heated to convert all the dissolved americium into the oxidation state +6. Unoxidized residual americium was precipitated by the addition of hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include the commonly used pharmaceutical antidepress ...
as americium(III) fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts ty ...
(). This step yielded a mixture of the accompanying product curium and the expected element 97 in form of trifluorides. The mixture was converted to the corresponding hydroxides by treating it with potassium hydroxide, and after centrifugation, was dissolved in perchloric acid
Perchloric acid is a mineral acid with the formula H Cl O4. Usually found as an aqueous solution, this colorless compound is a stronger acid than sulfuric acid, nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It is a powerful oxidizer when hot, but aqueous so ...
.
 Further separation was carried out in the presence of a
Further separation was carried out in the presence of a citric acid
Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in t ...
/ ammonium buffer solution
A buffer solution (more precisely, pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer) is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is ...
in a weakly acidic medium ( pH≈3.5), using ion exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, ...
at elevated temperature. The chromatographic
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a ...
separation behavior was unknown for the element 97 at the time, but was anticipated by analogy with terbium. The first results were disappointing because no alpha-particle emission signature could be detected from the elution product. With further analysis, searching for characteristic X-rays and conversion electron signals, a berkelium isotope was eventually detected. Its mass number was uncertain between 243 and 244 in the initial report, but was later established as 243.
Synthesis and extraction
Preparation of isotopes
Berkelium is produced by bombarding lighter actinides uranium (238U) or plutonium (239Pu) with neutrons in a nuclear reactor. In a more common case of uranium fuel, plutonium is produced first by neutron capture (the so-called (n,γ) reaction or neutron fusion) followed by beta-decay: :half-lives
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
)
Plutonium-239 is further irradiated by a source that has a high neutron flux, several times higher than a conventional nuclear reactor, such as the 85-megawatt High Flux Isotope Reactor (HFIR) at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee, USA. The higher flux promotes fusion reactions involving not one but several neutrons, converting 239Pu to 244Cm and then to 249Cm:
:
Curium-249 has a short half-life of 64 minutes, and thus its further conversion to 250Cm has a low probability. Instead, it transforms by beta-decay into 249Bk:
:Separation
The fact that berkelium readily assumes oxidation state +4 in solids, and is relatively stable in this state in liquids greatly assists separation of berkelium away from many other actinides. These are inevitably produced in relatively large amounts during the nuclear synthesis and often favor the +3 state. This fact was not yet known in the initial experiments, which used a more complex separation procedure. Various inorganic oxidation agents can be applied to the solutions to convert it to the +4 state, such asbromate
The bromate anion, BrO, is a bromine-based oxoanion. A bromate is a chemical compound that contains this ion. Examples of bromates include sodium bromate, (), and potassium bromate, ().
Bromates are formed many different ways in municipal drinki ...
s (), bismuthate Bismuthate is an ion. Its chemical formula is BiO3−. It has bismuth in its +5 oxidation state.
It is a very strong oxidizing agent. It reacts with hot water to make bismuth(III) oxide and oxygen. It also reacts with acids. Sodium bismuthate is th ...
s (), chromate Chromate or chromat, and their derived terms, may refer to:
Chemistry
* Chromate and dichromate, ions
* Monochromate, an ion
* Trichromate, an ion
* Tetrachromate, an ion
* Chromate conversion coating, a method for passivating metals
Biology ...
s ( and ), silver(I) thiolate (), lead(IV) oxide (), ozone (), or photochemical oxidation procedures. More recently, it has been discovered that some organic and bio-inspired molecules, such as the chelator called 3,4,3-LI(1,2-HOPO), can also oxidize Bk(III) and stabilize Bk(IV) under mild conditions. is then extracted with ion exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, ...
, extraction chromatography or liquid-liquid extraction using HDEHP (bis-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid), amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent suc ...
s, tributyl phosphate
Tributyl phosphate, known commonly as TBP, is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula (CH3CH2CH2CH2O)3PO. This colourless, odorless liquid finds some applications as an extractant and a plasticizer. It is an ester of phosphoric ac ...
or various other reagents. These procedures separate berkelium from most trivalent actinides and lanthanides, except for the lanthanide cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. Cerium is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the +3 ...
(lanthanides are absent in the irradiation target but are created in various nuclear fission decay chains).
A more detailed procedure adopted at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory was as follows: the initial mixture of actinides is processed with ion exchange using lithium chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula Li Cl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorid ...
reagent, then precipitated as hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It ...
s, filtered and dissolved in nitric acid. It is then treated with high-pressure elution
In analytical and organic chemistry, elution is the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent; as in washing of loaded ion-exchange resins to remove captured ions.
In a liquid chromatography experiment, for exa ...
from cation exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, ...
resins, and the berkelium phase is oxidized and extracted using one of the procedures described above. Reduction of the thus-obtained to the +3 oxidation state yields a solution, which is nearly free from other actinides (but contains cerium). Berkelium and cerium are then separated with another round of ion-exchange treatment.
Bulk metal preparation
In order to characterize chemical and physical properties of solid berkelium and its compounds, a program was initiated in 1952 at the Material Testing Reactor,Arco, Idaho
Arco is a city in Butte County, Idaho, United States. The population was 879 as of the 2020 United States census, down from 995 at the 2010 census. Arco is the county seat and largest city in Butte County.
History
Originally known as Root Ho ...
, US. It resulted in preparation of an eight-gram plutonium-239 target and in the first production of macroscopic quantities (0.6 micrograms) of berkelium by Burris B. Cunningham and Stanley Gerald Thompson in 1958, after a continuous reactor irradiation of this target for six years. This irradiation method was and still is the only way of producing weighable amounts of the element, and most solid-state studies of berkelium have been conducted on microgram or submicrogram-sized samples.
The world's major irradiation sources are the 85-megawatt High Flux Isotope Reactor at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee, USA, and the SM-2 loop reactor at the Research Institute of Atomic Reactors
The Research Institute of Atomic Reactors (; RIAR) is an institute for nuclear reactor research in Dimitrovgrad in Ulyanovsk Oblast, Russia. The institute houses eight nuclear research reactors: SM, Arbus (ACT-1), MIR.M1, RBT-6, RBT-10 / 1, RB ...
(NIIAR) in Dimitrovgrad, Russia
Dimitrovgrad (russian: Димитровград; ), formerly Melekess () until 1972, is a city in Ulyanovsk Oblast, Russia. It is the administrative center of Melekessky District, although it is not within the district and is an independent ci ...
, which are both dedicated to the production of transcurium elements (atomic number greater than 96). These facilities have similar power and flux levels, and are expected to have comparable production capacities for transcurium elements, although the quantities produced at NIIAR are not publicly reported. In a "typical processing campaign" at Oak Ridge, tens of grams of curium
Curium is a transuranic, radioactive chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first inte ...
are irradiated to produce decigram
To help compare different Order of magnitude, orders of magnitude, the following lists describe various mass levels between 10−59 kilogram, kg and 1052 kg. The least massive thing listed here is a graviton, and the most massive thing ...
quantities of californium, milligram quantities of berkelium-249 and einsteinium
Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. Einsteinium is a member of the actinide series and it is the seventh transuranium element. It was named in honor of Albert Einstein.
Einsteinium was discovered as a comp ...
, and picogram
To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following lists describe various mass levels between 10−59 kg and 1052 kg. The least massive thing listed here is a graviton, and the most massive thing is the observable univer ...
quantities of fermium. In total, just over one gram of berkelium-249 has been produced at Oak Ridge since 1967.
The first berkelium metal sample weighing 1.7 micrograms was prepared in 1971 by the reduction of fluoride with lithium vapor at 1000 °C; the fluoride was suspended on a tungsten wire above a tantalum crucible containing molten lithium. Later, metal samples weighing up to 0.5 milligrams were obtained with this method.
:
Similar results are obtained with fluoride. Berkelium metal can also be produced by the reduction of oxide with thorium or lanthanum.
Compounds
Oxides
Two oxides of berkelium are known, with the berkelium oxidation state of +3 () and +4 ( ). oxide is a brown solid, while oxide is a yellow-green solid with a melting point of 1920 °C and is formed from BkO2 by reduction with molecular hydrogen: : Upon heating to 1200 °C, the oxide undergoes a phase change; it undergoes another phase change at 1750 °C. Such three-phase behavior is typical for the actinide sesquioxides. oxide, BkO, has been reported as a brittle gray solid but its exact chemical composition remains uncertain.Halides
Inhalide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluor ...
s, berkelium assumes the oxidation states +3 and +4. The +3 state is the most stable, especially in solutions, while the tetravalent halides and are only known in the solid phase. The coordination of berkelium atom in its trivalent fluoride and chloride is tricapped trigonal prismatic, with the coordination number of 9. In trivalent bromide, it is bicapped trigonal prismatic (coordination 8) or octahedral
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
(coordination 6), and in the iodide it is octahedral.
fluoride () is a yellow-green ionic solid and is isotypic with uranium tetrafluoride
Uranium tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula UF4. It is a green solid with an insignificant vapor pressure and low solubility in water. Uranium in its tetravalent ( uranous) state is important in various technological process ...
or zirconium tetrafluoride
Zirconium(IV) fluoride ( Zr F4) is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass. It is insoluble in water. It is the main component of fluorozirconate glasses.
Three crystalline phases of ZrF4 have been reported, � ...
. fluoride () is also a yellow-green solid, but it has two crystalline structures. The most stable phase at low temperatures is isotypic with yttrium(III) fluoride
Yttrium(III) fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula Y F3. It is not known naturally in 'pure' form. The fluoride minerals containing essential yttrium include tveitite-(Y) (Y,Na)6Ca6Ca6F42 and gagarinite-(Y) NaCaY( ...
, while upon heating to between 350 and 600 °C, it transforms to the structure found in lanthanum trifluoride
Lanthanum trifluoride is a refractory ionic compound of lanthanum and fluorine.
The LaF3 structure
Bonding is ionic with lanthanum highly coordinated. The cation sits at the center of a trigonal prism. Nine fluorine atoms are close: three at ...
.
Visible amounts of chloride () were first isolated and characterized in 1962, and weighed only 3 billionths of a gram
The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one one thousandth of a kilogram.
Originally defined as of 1795 as "the absolute weight of a volume of pure water equal to th ...
. It can be prepared by introducing hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride g ...
vapors into an evacuated quartz tube containing berkelium oxide at a temperature about 500 °C. This green solid has a melting point of 600 °C, and is isotypic with uranium(III) chloride
Uranium(III) chloride, UCl3, is a water soluble salt of uranium. UCl3 is used mostly to reprocess spent nuclear fuel. Uranium(III) chloride is synthesized in various ways from uranium(IV) chloride; however, UCl3 is less stable than UCl4.
Prepar ...
. Upon heating to nearly melting point, converts into an orthorhombic phase.
Two forms of bromide are known: one with berkelium having coordination 6, and one with coordination 8. The latter is less stable and transforms to the former phase upon heating to about 350 °C. An important phenomenon for radioactive solids has been studied on these two crystal forms: the structure of fresh and aged 249BkBr3 samples was probed by X-ray diffraction over a period longer than 3 years, so that various fractions of berkelium-249 had beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For e ...
ed to californium-249. No change in structure was observed upon the 249BkBr3—249CfBr3 transformation. However, other differences were noted for 249BkBr3 and 249CfBr3. For example, the latter could be reduced with hydrogen to 249CfBr2, but the former could not – this result was reproduced on individual 249BkBr3 and 249CfBr3 samples, as well on the samples containing both bromides. The intergrowth of californium in berkelium occurs at a rate of 0.22% per day and is an intrinsic obstacle in studying berkelium properties. Beside a chemical contamination, 249Cf, being an alpha emitter, brings undesirable self-damage of the crystal lattice and the resulting self-heating. The chemical effect however can be avoided by performing measurements as a function of time and extrapolating the obtained results.
Other inorganic compounds
The pnictides of berkelium-249 of the type BkX are known for the elements nitrogen, phosphorus,arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but ...
and antimony. They crystallize in the rock-salt structure
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, p ...
and are prepared by the reaction of either hydride () or metallic berkelium with these elements at elevated temperature (about 600 °C) under high vacuum.
sulfide, , is prepared by either treating berkelium oxide with a mixture of hydrogen sulfide and carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is a neurotoxic, colorless, volatile liquid with the formula and structure . The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non ...
vapors at 1130 °C, or by directly reacting metallic berkelium with elemental sulfur. These procedures yield brownish-black crystals.
and hydroxides are both stable in 1 molar solutions of sodium hydroxide. phosphate () has been prepared as a solid, which shows strong fluorescence under excitation with a green light. Berkelium hydrides are produced by reacting metal with hydrogen gas at temperatures about 250 °C. They are non-stoichiometric with the nominal formula (0 < ''x'' < 1). Several other salts of berkelium are known, including an oxysulfide (), and hydrated nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insolubl ...
(), chloride (), sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
() and oxalate (). Thermal decomposition at about 600 °C in an argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
atmosphere (to avoid oxidation to ) of yields the crystals of oxysulfate (). This compound is thermally stable to at least 1000 °C in inert atmosphere.
Organoberkelium compounds
Berkelium forms a trigonal (η5–C5H5)3Bkmetallocene
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (, abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene de ...
complex with three cyclopentadienyl Cyclopentadienyl can refer to
* Cyclopentadienyl anion, or cyclopentadienide,
** Cyclopentadienyl ligand
* Cyclopentadienyl radical, •
* Cyclopentadienyl cation,
See also
*Pentadienyl
In organic chemistry, pentadienyl refers to the organic ...
rings, which can be synthesized by reacting chloride with the molten beryllocene () at about 70 °C. It has an amber color and a density of 2.47 g/cm3. The complex is stable to heating to at least 250 °C, and sublimates without melting at about 350 °C. The high radioactivity of berkelium gradually destroys the compound (within a period of weeks). One cyclopentadienyl ring in (η5–C5H5)3Bk can be substituted by chlorine to yield . The optical absorption spectra of this compound are very similar to those of (η5–C5H5)3Bk.
Applications
 There is currently no use for any isotope of berkelium outside basic scientific research. Berkelium-249 is a common target nuclide to prepare still heavier transuranium elements and superheavy elements,Stwertka, Albert. ''A Guide to the Elements'', Oxford University Press, 1996, p. 211. such as
There is currently no use for any isotope of berkelium outside basic scientific research. Berkelium-249 is a common target nuclide to prepare still heavier transuranium elements and superheavy elements,Stwertka, Albert. ''A Guide to the Elements'', Oxford University Press, 1996, p. 211. such as lawrencium
Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named in honor of Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radi ...
, rutherfordium and bohrium
Bohrium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Bh and atomic number 107. It is named after Danish physicist Niels Bohr. As a synthetic element, it can be created in a laboratory but is not found in nature. All known isotopes of bohrium ...
. It is also useful as a source of the isotope californium-249, which is used for studies on the chemistry of californium in preference to the more radioactive californium-252 that is produced in neutron bombardment facilities such as the HFIR.
A 22 milligram batch of berkelium-249 was prepared in a 250-day irradiation and then purified for 90 days at Oak Ridge in 2009. This target yielded the first 6 atoms of tennessine
Tennessine is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Ts and atomic number 117. It is the second-heaviest known element and the penultimate element of the 7th period of the periodic table.
The discovery of tennessine was officially ann ...
at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR), Dubna
Dubna ( rus, Дубна́, p=dʊbˈna) is a town in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It has a status of ''naukograd'' (i.e. town of science), being home to the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, an international nuclear physics research center and one o ...
, Russia, after bombarding it with calcium ions in the U400 cyclotron for 150 days. This synthesis was a culmination of the Russia-US collaboration between JINR and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory on the synthesis of elements 113 to 118 which was initiated in 1989.
Nuclear fuel cycle
The nuclear fission properties of berkelium are different from those of the neighboring actinides curium and californium, and they suggest berkelium to perform poorly as a fuel in a nuclear reactor. Specifically, berkelium-249 has a moderately large neutron capturecross section
Cross section may refer to:
* Cross section (geometry)
** Cross-sectional views in architecture & engineering 3D
*Cross section (geology)
* Cross section (electronics)
* Radar cross section, measure of detectability
* Cross section (physics)
**Abs ...
of 710 barns
A barn is an agricultural building usually on farms and used for various purposes. In North America, a barn refers to structures that house livestock, including cattle and horses, as well as equipment and fodder, and often grain.Allen G ...
for thermal neutrons
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium wi ...
, 1200 barns resonance integral
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, ...
, but very low fission cross section for thermal neutrons. In a thermal reactor, much of it will therefore be converted to berkelium-250 which quickly decays to californium-250. In principle, berkelium-249 can sustain a nuclear chain reaction in a fast breeder reactor. Its critical mass
In nuclear engineering, a critical mass is the smallest amount of fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties (specifically, its nuclear fiss ...
is relatively high at 192 kg; it can be reduced with a water or steel reflector but would still exceed the world production of this isotope.Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire"Evaluation of nuclear criticality safety. data and limits for actinides in transport"
, p. 16 Berkelium-247 can maintain chain reaction both in a thermal-neutron and in a fast-neutron reactor, however, its production is rather complex and thus the availability is much lower than its critical mass, which is about 75.7 kg for a bare sphere, 41.2 kg with a water reflector and 35.2 kg with a steel reflector (30 cm thickness).
Health issues
Little is known about the effects of berkelium on human body, and analogies with other elements may not be drawn because of different radiation products ( electrons for berkelium andalpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produce ...
s, neutrons, or both for most other actinides). The low energy of electrons emitted from berkelium-249 (less than 126 keV) hinders its detection, due to signal interference with other decay processes, but also makes this isotope relatively harmless to humans as compared to other actinides. However, berkelium-249 transforms with a half-life of only 330 days to the strong alpha-emitter californium-249, which is rather dangerous and has to be handled in a glovebox in a dedicated laboratory.
Most available berkelium toxicity data originate from research on animals. Upon ingestion by rats, only about 0.01% of berkelium ends in the blood stream. From there, about 65% goes to the bones, where it remains for about 50 years, 25% to the lungs (biological half-life about 20 years), 0.035% to the testicles or 0.01% to the ovaries where berkelium stays indefinitely. The balance of about 10% is excreted. In all these organs berkelium might promote cancer, and in the skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
, its radiation can damage red blood cells. The maximum permissible amount of berkelium-249 in the human skeleton is 0.4 nanogram
To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following lists describe various mass levels between 10−59 kg and 1052 kg. The least massive thing listed here is a graviton, and the most massive thing is the observable universe. ...
s.Pradyot Patnaik. ''Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals'' McGraw-Hill, 2002,
References
Bibliography
* * *External links
Berkelium
at ''
The Periodic Table of Videos
''Periodic Videos'' (also known as ''The Periodic Table of Videos'') is a video project and YouTube channel on chemistry. It consists of a series of videos about chemical elements and the periodic table, with additional videos on other topics i ...
'' (University of Nottingham)
{{good article
Chemical elements
Chemical elements with double hexagonal close-packed structure
Actinides
Synthetic elements