Basal Ganglia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the
 The striatum is a subcortical structure generally divided into the dorsal striatum and ventral striatum, although a medial lateral classification has been suggested to be more relevant behaviorally and is being more widely used.
The striatum is composed mostly of medium spiny neurons. These GABAergic neurons project to the external (lateral) globus pallidus and internal (medial) globus pallidus as well as the substantia nigra
The striatum is a subcortical structure generally divided into the dorsal striatum and ventral striatum, although a medial lateral classification has been suggested to be more relevant behaviorally and is being more widely used.
The striatum is composed mostly of medium spiny neurons. These GABAergic neurons project to the external (lateral) globus pallidus and internal (medial) globus pallidus as well as the substantia nigra
 The substantia nigra is a midbrain gray matter portion of the basal ganglia that has two parts – the
The substantia nigra is a midbrain gray matter portion of the basal ganglia that has two parts – the
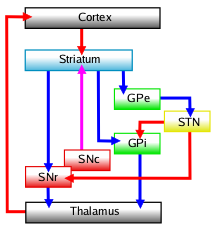
 Multiple models of basal ganglia circuits and function have been proposed, however there have been questions raised about the strict divisions of the direct and
Multiple models of basal ganglia circuits and function have been proposed, however there have been questions raised about the strict divisions of the direct and 
Basal ganglia
Scholarpedia
, 2(6):1825. In
File:Basal ganglia coronal sections.gif, Basal ganglia highlighted in green on coronal T1 MRI images
File:Basal ganglia sagittal sections.gif, Basal ganglia highlighted in green on sagittal T1 MRI images
File:Basal ganglia transversal sections.gif, Basal ganglia highlighted in green on transversal T1 MRI images
Imaging of Basal Ganglia
at USUHS *
The International Basal Ganglia Society
Basal ganglia
– Official journal of LIMPE (Lega Italiana per la Lotta Contro la Malattia di Parkinson, le Sindromi Extrapiramidali e le Demenze, Italy), the German Parkinson Society (DPG, Deutsche Parkinson Gesellschaft), and the Japanese Basal Ganglia Society (JBAGS Japan Basal Ganglia Society) {{DEFAULTSORT:Basal Ganglia Motor system Biology of obsessive–compulsive disorder
brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
s of vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
s. In human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s, and some primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
s, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an external and internal region, and in the division of the striatum. The basal ganglia are situated at the base of the forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three primary ...
and top of the midbrain. Basal ganglia are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consistin ...
, thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, ...
, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit learning, conditional learning, eye movement
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms (e.g. primates, rodents, flies, birds, fish, cats, crabs, octopus) to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of interest ...
s, cognition, and emotion
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or suffering, displeasure. There is currently no scientific ...
.
The main components of the basal ganglia – as defined functionally – are the striatum, consisting of both the dorsal striatum ( caudate nucleus and putamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a round structure located at the base of the forebrain (telencephalon). The putamen and caudate nucleus together form the dorsal striatum. It is also one of the structures that compose the basal ...
) and the ventral striatum ( nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), the globus pallidus, the ventral pallidum
The ventral pallidum (VP) is a structure within the basal ganglia of the brain. It is an output nucleus whose fibres project to thalamic nuclei, such as the ventral anterior nucleus, the ventral lateral nucleus, and the medial dorsal nucleus.
The ...
, the substantia nigra, and the subthalamic nucleus. Each of these components has a complex internal anatomical and neurochemical organization. The largest component, the striatum (dorsal and ventral), receives input from many brain areas beyond the basal ganglia, but only sends output to other components of the basal ganglia. The globus pallidus receives input from the striatum, and sends inhibitory output to a number of motor-related areas. The substantia nigra is the source of the striatal input of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which plays an important role in basal ganglia function. The subthalamic nucleus receives input mainly from the striatum and cerebral cortex and projects to the globus pallidus.
Popular theories implicate the basal ganglia primarily in action selection – in helping to decide which of several possible behaviors to execute at any given time. In more specific terms, the basal ganglia's primary function is likely to control and regulate activities of the motor and premotor cortical areas so that voluntary movements can be performed smoothly. Experimental studies show that the basal ganglia exert an inhibitory influence on a number of motor systems, and that a release of this inhibition permits a motor system to become active. The "behavior switching" that takes place within the basal ganglia is influenced by signals from many parts of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46 ...
, which plays a key role in executive functions. It has also been hypothesized that the basal ganglia are not only responsible for motor action selection, but also for the selection of more cognitive actions. Computational models of action selection in the basal ganglia incorporate this.
The basal ganglia are of major importance for normal brain function and behaviour. Their dysfunction results in a wide range of neurological conditions including disorders of behaviour control and movement, as well as cognitive deficits that are similar to those that result from damage to the prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46 ...
. Those of behaviour include Tourette syndrome
Tourette syndrome or Tourette's syndrome (abbreviated as TS or Tourette's) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood or adolescence. It is characterized by multiple movement (motor) tics and at least one vocal (phonic) ...
, obsessive–compulsive disorder
Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental and behavioral disorder in which an individual has intrusive thoughts and/or feels the need to perform certain routines repeatedly to the extent where it induces distress or impairs general ...
, and addiction. Movement disorders
Movement disorder refers to any clinical syndrome with either an excess of movement or a paucity of voluntary and involuntary movements, unrelated to weakness or spasticity. Movement disorders are synonymous with basal ganglia or extrapyramidal d ...
include, most notably Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
, which involves degeneration of the dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra; Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease (HD), also known as Huntington's chorea, is a neurodegenerative disease that is mostly inherited. The earliest symptoms are often subtle problems with mood or mental abilities. A general lack of coordination and an uns ...
, which primarily involves damage to the striatum; dystonia; and more rarely hemiballismus
Hemiballismus or hemiballism is a basal ganglia syndrome resulting from damage to the subthalamic nucleus in the basal ganglia. Hemiballismus is a rare hyperkinetic movement disorder, that is characterized by violent involuntary limb movements, ...
. The basal ganglia have a limbic
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ''Ps ...
sector whose components are assigned distinct names: the nucleus accumbens, ventral pallidum
The ventral pallidum (VP) is a structure within the basal ganglia of the brain. It is an output nucleus whose fibres project to thalamic nuclei, such as the ventral anterior nucleus, the ventral lateral nucleus, and the medial dorsal nucleus.
The ...
, and ventral tegmental area (VTA). There is considerable evidence that this limbic part plays a central role in reward learning as well as cognition and frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
functioning, via the mesolimbic pathway
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmentum, ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the for ...
from the VTA to the nucleus accumbens that uses the neurotransmitter dopamine, and the mesocortical pathway
The mesocortical pathway is a dopaminergic pathway that connects the ventral tegmentum to the prefrontal cortex. It is one of the four major dopamine pathways in the brain. It is essential to the normal cognitive function of the dorsolateral pref ...
. A number of highly addictive drugs, including cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Ameri ...
, amphetamine, and nicotine
Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As ...
, are thought to work by increasing the efficacy of this dopamine signal. There is also evidence implicating overactivity of the VTA dopaminergic projection in schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social wit ...
.
Structure
In terms of development, the humancentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
is often classified based on the original three primitive vesicles from which it develops: These primary vesicles form in the normal development of the neural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural fold become elevated, ...
of the embryo and initially include the prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon
The hindbrain or rhombencephalon or lower brain is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes. Metencephal ...
, in rostral to caudal (from head to tail) orientation. Later in development of the nervous system each section itself turns into smaller components. During development, the cells that migrate tangentially to form the basal ganglia are directed by the lateral and medial ganglionic eminence
The ganglionic eminence (GE) is a transitory structure in the development of the nervous system that guides cell and axon migration. It is present in the embryonic and fetal stages of neural development found between the thalamus and caudate nucl ...
s. The following table demonstrates this developmental classification and traces it to the anatomic structures found in the basal ganglia. The structures relevant to the basal ganglia are shown in bold.
The basal ganglia form a fundamental component of the cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb ...
. In contrast to the cortical layer that lines the surface of the forebrain, the basal ganglia are a collection of distinct masses of gray matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Grey matter is distingui ...
lying deep in the brain not far from the junction of the thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, ...
. They lie to the side of and surround the thalamus. Like most parts of the brain, the basal ganglia consist of left and right sides that are virtual mirror images of each other.
In terms of anatomy, the basal ganglia are divided into four distinct structures, depending on how superior or rostral they are (in other words depending on how close to the top of the head they are): Two of them, the striatum and the pallidum
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rod ...
, are relatively large; the other two, the substantia nigra and the subthalamic nucleus, are smaller. In the illustration to the right, two coronal sections of the human brain show the location of the basal ganglia components. Of note, and not seen in this section, the subthalamic nucleus and substantia nigra lie farther back (posteriorly
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
) in the brain than the striatum and pallidum.
Striatum
 The striatum is a subcortical structure generally divided into the dorsal striatum and ventral striatum, although a medial lateral classification has been suggested to be more relevant behaviorally and is being more widely used.
The striatum is composed mostly of medium spiny neurons. These GABAergic neurons project to the external (lateral) globus pallidus and internal (medial) globus pallidus as well as the substantia nigra
The striatum is a subcortical structure generally divided into the dorsal striatum and ventral striatum, although a medial lateral classification has been suggested to be more relevant behaviorally and is being more widely used.
The striatum is composed mostly of medium spiny neurons. These GABAergic neurons project to the external (lateral) globus pallidus and internal (medial) globus pallidus as well as the substantia nigra pars reticulata
The pars reticulata (SNpr) is a portion of the substantia nigra and is located lateral to the pars compacta. Most of the neurons that project out of the pars reticulata are inhibitory GABAergic neurons (i.e., these neurons release GABA, which is ...
. The projections into the globus pallidus and substantia nigra are primarily dopaminergic, although enkephalin, dynorphin
Dynorphins (Dyn) are a class of opioid peptides that arise from the precursor protein prodynorphin. When prodynorphin is cleaved during processing by proprotein convertase 2 (PC2), multiple active peptides are released: dynorphin A, dynorphin ...
and substance P
Substance P (SP) is an undecapeptide (a peptide composed of a chain of 11 amino acid residues) and a member of the tachykinin neuropeptide family. It is a neuropeptide, acting as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. Substance P and its clo ...
are expressed. The striatum also contains interneurons that are classified into nitrergic neurons (due to use of nitric oxide as a neurotransmitter), tonically active (i.e. constantly releasing neurotransmitter unless inhibited) cholinergic interneurons, parvalbumin
Parvalbumin (PV) is a calcium-binding protein with low molecular weight (typically 9-11 kDa). In humans, it is encoded by the ''PVALB'' gene. It is not a member of the albumin family; it is named for its size (''parv-'', from Latin ''parvus'' smal ...
-expressing neurons and calretinin
Calretinin, also known as calbindin 2 (formerly 29 kDa calbindin), is a calcium-binding protein involved in calcium signaling. In humans, the calretinin protein is encoded by the ''CALB2'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes an intracellular ...
-expressing neurons. The dorsal striatum receives significant glutamatergic
Glutamatergic means "related to glutamate". A glutamatergic agent (or drug) is a chemical that directly modulates the excitatory amino acid (glutamate/aspartate) system in the body or brain. Examples include excitatory amino acid receptor agonis ...
inputs from the cortex, as well as dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta. The dorsal striatum is generally considered to be involved in sensorimotor activities. The ventral striatum receives glutamatergic inputs from the limbic areas as well as dopaminergic inputs from the VTA, via the mesolimbic pathway
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmentum, ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the for ...
. The ventral striatum is believed to play a role in reward and other limbic functions. The dorsal striatum is divided into the caudate and putamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a round structure located at the base of the forebrain (telencephalon). The putamen and caudate nucleus together form the dorsal striatum. It is also one of the structures that compose the basal ...
by the internal capsule
The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the ...
while the ventral striatum is composed of the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. The caudate has three primary regions of connectivity, with the head of the caudate demonstrating connectivity to the prefrontal cortex, cingulate cortex and amygdala. The body and tail show differentiation between the dorsolateral rim and ventral caudate, projecting to the sensorimotor and limbic regions of the striatum respectively. Striatopallidal fibres connect the striatum to the pallidus.
Pallidum
The ''pallidum'' consists of a large structure called the globus pallidus ("pale globe") together with a smaller ventral extension called theventral pallidum
The ventral pallidum (VP) is a structure within the basal ganglia of the brain. It is an output nucleus whose fibres project to thalamic nuclei, such as the ventral anterior nucleus, the ventral lateral nucleus, and the medial dorsal nucleus.
The ...
. The globus pallidus appears as a single neural mass, but can be divided into two functionally distinct parts, called the internal (or medial) and external (lateral) segments, abbreviated GPi and GPe. Both segments contain primarily GABAergic neurons, which therefore have inhibitory effects on their targets. The two segments participate in distinct neural circuits. The GPe receives input mainly from the striatum, and projects to the subthalamic nucleus. The GPi receives signals from the striatum via the "direct" and "indirect" pathways. Pallidal neurons operate using a disinhibition principle. These neurons fire at steady high rates in the absence of input, and signals from the striatum cause them to pause or reduce their rate of firing. Because pallidal neurons themselves have inhibitory effects on their targets, the net effect of striatal input to the pallidum is a reduction of the tonic inhibition exerted by pallidal cells on their targets (disinhibition) with an increased rate of firing in the targets.
Substantia nigra
 The substantia nigra is a midbrain gray matter portion of the basal ganglia that has two parts – the
The substantia nigra is a midbrain gray matter portion of the basal ganglia that has two parts – the pars compacta
The pars compacta (SNpc) is a portion of the ''substantia nigra'', located in the midbrain. It is formed by dopaminergic neurons and located medial to the pars reticulata. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the death of dopaminergic neuron ...
(SNc) and the pars reticulata
The pars reticulata (SNpr) is a portion of the substantia nigra and is located lateral to the pars compacta. Most of the neurons that project out of the pars reticulata are inhibitory GABAergic neurons (i.e., these neurons release GABA, which is ...
(SNr). SNr often works in unison with GPi, and the SNr-GPi complex inhibits the thalamus. Substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) however, produces the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is very significant in maintaining balance in the striatal pathway. The circuit portion below explains the role and circuit connections of each of the components of the basal ganglia.
Subthalamic nucleus
The subthalamic nucleus is a diencephalic gray matter portion of the basal ganglia, and the only portion of the ganglia that produces an excitatory neurotransmitter, glutamate. The role of the subthalamic nucleus is to stimulate the SNr-GPi complex and it is part of theindirect pathway
The indirect pathway, sometimes known as the indirect pathway of movement, is a neuronal circuit through the basal ganglia and several associated nuclei within the central nervous system (CNS) which helps to prevent unwanted muscle contractions f ...
. The subthalamic nucleus receives inhibitory input from the external part of the globus pallidus and sends excitatory input to the GPi.
Circuit connections

 Multiple models of basal ganglia circuits and function have been proposed, however there have been questions raised about the strict divisions of the direct and
Multiple models of basal ganglia circuits and function have been proposed, however there have been questions raised about the strict divisions of the direct and indirect pathway
The indirect pathway, sometimes known as the indirect pathway of movement, is a neuronal circuit through the basal ganglia and several associated nuclei within the central nervous system (CNS) which helps to prevent unwanted muscle contractions f ...
s, their possible overlap and regulation. The circuitry model has evolved since the first proposed model in the 1990s by DeLong in the parallel ''processing model'', in which the cortex and substantia nigra pars compacta project into the dorsal striatum giving rise to an inhibitory indirect and excitatory direct pathway.
*The inhibitory indirect pathway involved the inhibition of the globus pallidus externus, allowing for the disinhibition of the globus pallidus internus
The internal globus pallidus (GPi or medial globus pallidus; in rodents its homologue is known as the entopeduncular nucleus) and the external globus pallidus (GPe) make up the globus pallidus. The GPi is one of the output nuclei of the basal gang ...
(through STN) allowing it to inhibit the thalamus.
*The direct or excitatory pathway involved the disinhibition of the thalamus through the inhibition of the GPi/SNr. However the speed of the direct pathway would not be concordant with the indirect pathway in this model leading to problems with it. To get over this, a hyperdirect pathway where the cortex sends glutamatergic projections through the subthalamic nucleus exciting the inhibitory GPe under the ''center surround model'', as well as a shorter indirect pathway have been proposed.
Generally, the basal ganglia circuitry is divided into five pathways: one limbic, two associative (prefrontal), one oculomotor, and one motor pathway. (The motor and oculomotor pathways are sometimes grouped into one motor pathway.) The five general pathways are organized as follows:
*The motor loop involving projections from the supplementary motor area
The supplementary motor area (SMA) is a part of the motor cortex of primates that contributes to the control of movement. It is located on the midline surface of the hemisphere just in front of (anterior to) the primary motor cortex leg representa ...
, arcuate premotor area, motor cortex and somatosensory cortex into the putamen, which projects into the ventrolateral GPi and caudolateral SNr which projects into the cortex through the ventralis lateralis pars medialis and ventralis lateralis pars oralis.
*The oculomotor loop involved projections from the frontal eye fields, the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), and the posterior parietal cortex into the caudate, into the caudal dorsomedial GPi and ventrolateral SNr, finally looping back into the cortex through the lateral ventralis anterior pars magnocellularis(VAmc).
*The first cognitive/associative pathway proposes a pathway from the DLPFC, into the dorsolateral caudate, followed by a projection into the lateral dorsomedial GPi, and rostral SNr before projecting into the lateral VAmc and medial pars magnocellularis.
*The second cognitive/associative pathway proposed is a circuit projecting from the lateral orbitofrontal cortex
The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes of the brain which is involved in the cognitive process of decision-making. In non-human primates it consists of the association cortex areas Brodmann area 11, 1 ...
, the temporal gyrus, and anterior cingulate cortex into the ventromedial caudate, followed by a projection into the lateromedial GPi, and rostrolateral SNr before looping into the cortex via the medial VAmc and medial magnocellularis.
*The limbic circuit involving the projections from the ACC, hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , ' seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, ...
, entorhinal cortex, and insula into the ventral striatum, then into the rostrodorsal GPi, ventral pallidum
The ventral pallidum (VP) is a structure within the basal ganglia of the brain. It is an output nucleus whose fibres project to thalamic nuclei, such as the ventral anterior nucleus, the ventral lateral nucleus, and the medial dorsal nucleus.
The ...
and rostrodorsal SNr, followed by a loop back into the cortex through the posteromedial part of the medial dorsal nucleus. However, more subdivisions of loops have been proposed, up to 20,000.
The direct pathway, originating in the dorsal striatum inhibits the GPi and SNr, resulting in a net disinhibition or excitation of the thalamus. This pathway consists of medium spiny neurons (MSNs) that express dopamine receptor D1
Dopamine receptor D1, also known as DRD1. It is one of the two types of D1-like receptor family - receptors D1 and D5. It is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD1 gene.
Tissue distribution
D1 receptors are the most abundant kind of d ...
, muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4
The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 4 (CHRM4), is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''CHRM4'' gene.
Function
M4 muscarinic receptors are coupled to Gi/o heterotrimeric protei ...
, and adenosine receptor A1. The direct pathway has been proposed to facilitate motor actions, timing of motor actions, gating of working memory, and motor responses to specific stimuli.
The (long) indirect pathway originates in the dorsal striatum and inhibits the GPe, resulting in disinhibition of the GPi which is then free to inhibit the thalamus. This pathway consists of MSNs that express dopamine receptor D2
Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''DRD2'' gene. After work from Paul Greengard's lab had suggested that dopamine receptors were the site of action of antipsychotic drugs, several groups, i ...
, muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1, and adenosine receptor A2a
The adenosine A2A receptor, also known as ADORA2A, is an adenosine receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.
Structure
This protein is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family which possess seven transmembrane alph ...
. This pathway has been proposed to result in global motor inhibition(inhibition of all motor activity), and termination of responses. Another shorter indirect pathway has been proposed, which involves cortical excitation of the subthalamic nucleus resulting in direct excitation of the GPe, and inhibition of the thalamus. This pathway is proposed to result in inhibition of specific motor programs based on associative learning.
A combination of these indirect pathways resulting in a hyperdirect pathway that results in inhibition of basal ganglia inputs besides one specific focus has been proposed as part of the ''center surround theory''. This hyperdirect pathway is proposed to inhibit premature responses, or globally inhibit the basal ganglia to allow for more specific top down control by the cortex.
The interactions of these pathways are currently under debate. Some say that all pathways directly antagonize each other in a "push pull" fashion, while others support the ''center surround theory'', in which one focused input into the cortex is protected by inhibition of competing inputs by the rest of the indirect pathways.
Neurotransmitters
The basal ganglia contains many afferentglutamatergic
Glutamatergic means "related to glutamate". A glutamatergic agent (or drug) is a chemical that directly modulates the excitatory amino acid (glutamate/aspartate) system in the body or brain. Examples include excitatory amino acid receptor agonis ...
inputs, with predominantly GABAergic efferent fibers, modulatory cholinergic
Cholinergic agents are compounds which mimic the action of acetylcholine and/or butyrylcholine. In general, the word " choline" describes the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the ''N'',''N'',''N''-trimethylethanolammonium cati ...
pathways, significant dopamine in the pathways originating in the ventral tegmental area and substantia nigra, as well as various neuropeptides. Neuropeptides found in the basal ganglia include substance P
Substance P (SP) is an undecapeptide (a peptide composed of a chain of 11 amino acid residues) and a member of the tachykinin neuropeptide family. It is a neuropeptide, acting as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. Substance P and its clo ...
, neurokinin A, cholecystokinin
Cholecystokinin (CCK or CCK-PZ; from Greek ''chole'', "bile"; ''cysto'', "sac"; ''kinin'', "move"; hence, ''move the bile-sac (gallbladder)'') is a peptide hormone of the gastrointestinal system responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat an ...
, neurotensin
Neurotensin is a 13 amino acid neuropeptide that is implicated in the regulation of luteinizing hormone and prolactin release and has significant interaction with the dopaminergic system. Neurotensin was first isolated from extracts of bovine ...
, neurokinin B
Neurokinin B (NKB) belongs in the family of tachykinin peptides. Neurokinin B is implicated in a variety of human functions and pathways such as the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone.
Additionally, NKB is associated with pregnancy in fem ...
, neuropeptide Y, somatostatin, dynorphin
Dynorphins (Dyn) are a class of opioid peptides that arise from the precursor protein prodynorphin. When prodynorphin is cleaved during processing by proprotein convertase 2 (PC2), multiple active peptides are released: dynorphin A, dynorphin ...
, enkephaline. Other neuromodulators found in the basal ganglia include nitric oxide, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
, and phenylethylamine.
Functional connectivity
The functional connectivity, measured by regional co-activation during functional neuroimaging studies, is broadly consistent with the parallel processing models of basal ganglia function. The putamen was generally coactivated with motor areas such as thesupplementary motor area
The supplementary motor area (SMA) is a part of the motor cortex of primates that contributes to the control of movement. It is located on the midline surface of the hemisphere just in front of (anterior to) the primary motor cortex leg representa ...
, caudal anterior cingulate cortex and primary motor cortex, while the caudate and rostral putamen were more frequently coactivated with the rostral ACC and DLPFC. The ventral striatum was significantly associated with the amygdala and hippocampus, which although was not included in the first formulations of basal ganglia models, has been an addition to more recent models.
Function
Eye movements
One intensively studied function of the basal ganglia is its role in controllingeye movement
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms (e.g. primates, rodents, flies, birds, fish, cats, crabs, octopus) to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of interest ...
s. Eye movement is influenced by an extensive network of brain regions that converges on a midbrain area called the superior colliculus (SC). The SC is a layered structure whose layers form two-dimensional retinotopic maps of visual space. A "bump" of neural activity in the deep layers of the SC drives an eye movement directed toward the corresponding point in space.
The SC receives a strong inhibitory projection from the basal ganglia, originating in the substantia nigra pars reticulata
The pars reticulata (SNpr) is a portion of the substantia nigra and is located lateral to the pars compacta. Most of the neurons that project out of the pars reticulata are inhibitory GABAergic neurons (i.e., these neurons release GABA, which is ...
(SNr). Neurons in the SNr usually fire continuously at high rates, but at the onset of an eye movement they "pause", thereby releasing the SC from inhibition. Eye movements of all types are associated with "pausing" in the SNr; however, individual SNr neurons may be more strongly associated with some types of movements than others. Neurons in some parts of the caudate nucleus also show activity related to eye movements. Since the great majority of caudate cells fire at very low rates, this activity almost always shows up as an increase in firing rate. Thus, eye movements begin with activation in the caudate nucleus, which inhibits the SNr via the direct GABAergic projections, which in turn disinhibits the SC.
Role in motivation
Extracellular dopamine in the basal ganglia has been linked to motivational states in rodents, with high levels being linked to satiated state, medium levels with seeking, and low with aversion. The limbic basal ganglia circuits are influenced heavily by extracellular dopamine. Increased dopamine results in inhibition of theVentral pallidum
The ventral pallidum (VP) is a structure within the basal ganglia of the brain. It is an output nucleus whose fibres project to thalamic nuclei, such as the ventral anterior nucleus, the ventral lateral nucleus, and the medial dorsal nucleus.
The ...
, entopeduncular nucleus, and substantia nigra pars reticulata
The pars reticulata (SNpr) is a portion of the substantia nigra and is located lateral to the pars compacta. Most of the neurons that project out of the pars reticulata are inhibitory GABAergic neurons (i.e., these neurons release GABA, which is ...
, resulting in disinhibition of the thalamus. This model of direct D1, and indirect D2 pathways explain why selective agonists of each receptor are not rewarding, as activity at both pathways is required for disinhibition. The disinhibition of the thalamus leads to activation of the prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46 ...
and ventral striatum, selective for increased D1 activity leading to reward. There is also evidence from non-human primate and human electrophysiology studies that other basal ganglia structures including the globus pallidus internus and subthalamic nucleus are involved in reward processing.
Decision making
Two models have been proposed for the basal ganglia, one being that actions are generated by a "critic" in the ventral striatum and estimates value, and the actions are carried out by an "actor" in the dorsal striatum. Another model proposes the basal ganglia acts as a selection mechanism, where actions are generated in the cortex and are selected based on context by the basal ganglia. The CBGTC loop is also involved in reward discounting, with firing increasing with an unexpected or greater than expected reward. One review supported the idea that the cortex was involved in learning actions regardless of their outcome, while the basal ganglia was involved in selecting appropriate actions based on associative reward based trial and error learning.Working memory
The basal ganglia has been proposed to gate what enters and what doesn't enter working memory. One hypothesis proposes that the direct pathway (Go, or excitatory) allows information into the PFC, where it stays independent of the pathway, however another theory proposes that in order for information to stay in the PFC the direct pathway needs to continue reverberating. The short indirect pathway has been proposed to, in a direct push pull antagonism with the direct pathway, close the gate to the PFC. Together these mechanisms regulate working memory focus.Clinical significance
Basal ganglia disease
Basal ganglia disease is a group of physical problems that occur when the group of nuclei in the brain known as the basal ganglia fail to properly suppress unwanted movements or to properly prime upper motor neuron circuits to initiate motor funct ...
is a group of movement disorder
Movement disorder refers to any clinical syndrome with either an excess of movement or a paucity of voluntary and involuntary movements, unrelated to weakness or spasticity. Movement disorders are synonymous with basal ganglia or extrapyramidal ...
s that result from either excessive output from the basal ganglia to the thalamus – hypokinetic disorders, or from insufficient output – hyperkinetic disorders. Hypokinetic disorders arise from an excessive output from the basal ganglia, which inhibits the output from the thalamus to the cortex, and thus limits voluntary movement. Hyperkinetic disorders result from a low output from the basal ganglia to the thalamus which gives not enough inhibition to the thalamic projections to the cortex and thus gives uncontrolled/involuntary movements. Dysfunction of the basal ganglia circuitry can also lead to other disorders.
The following is a list of disorders that have been linked to the basal ganglia:
History
The acceptance that the basal ganglia system constitutes one major cerebral system took time to arise. The first anatomical identification of distinct subcortical structures was published by Thomas Willis in 1664. For many years, the term corpus striatum was used to describe a large group of subcortical elements, some of which were later discovered to be functionally unrelated. For many years, theputamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a round structure located at the base of the forebrain (telencephalon). The putamen and caudate nucleus together form the dorsal striatum. It is also one of the structures that compose the basal ...
and the caudate nucleus were not associated with each other. Instead, the putamen was associated with the pallidum
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rod ...
in what was called the nucleus lenticularis or nucleus lentiformis.
A thorough reconsideration by Cécile and Oskar Vogt (1941) simplified the description of the basal ganglia by proposing the term striatum to describe the group of structures consisting of the caudate nucleus, the putamen, and the mass linking them ventrally
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
, the nucleus accumbens. The striatum was named on the basis of the striated (striped) appearance created by radiating dense bundles of striato-pallido-nigral axons, described by anatomist Samuel Alexander Kinnier Wilson (1912) as "pencil-like".
The anatomical link of the striatum with its primary targets, the pallidum
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rod ...
and the substantia nigra, was discovered later. The name '' globus pallidus'' was attributed by Déjerine to Burdach (1822). For this, the Vogts proposed the simpler "pallidum
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rod ...
". The term "locus niger" was introduced by Félix Vicq-d'Azyr
Félix Vicq d'Azyr (; 23 April 1748 – 20 June 1794) was a French physician and anatomist, the originator of comparative anatomy and discoverer of the theory of homology in biology.
Biography
Vicq d'Azyr was born in Valognes, Normandy, the son ...
as ''tache noire'' in (1786), though that structure has since become known as the substantia nigra, due to contributions by Von Sömmering in 1788. The structural similarity between the substantia nigra and globus pallidus was noted by Mirto in 1896. Together, the two are known as the pallidonigral ensemble, which represents the core of the basal ganglia. Altogether, the main structures of the basal ganglia are linked to each other by the striato-pallido-nigral bundle, which passes through the pallidum
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rod ...
, crosses the internal capsule
The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the ...
as the "comb bundle of Edinger", and finally reaches the substantia nigra.
Additional structures that later became associated with the basal ganglia are the "body of Luys" (1865) (nucleus of Luys on the figure) or subthalamic nucleus, whose lesion was known to produce movement disorders. More recently, other areas such as the centromedian nucleus
In the anatomy of the brain, the centromedian nucleus, also known as the centrum medianum, (CM or Cm-Pf) is a part of the intralaminar thalamic nuclei (ITN) in the thalamus. There are two centromedian nuclei arranged bilaterally.
In humans, it c ...
and the pedunculopontine complex have been thought to be regulators of the basal ganglia.
Near the beginning of the 20th century, the basal ganglia system was first associated with motor functions, as lesions of these areas would often result in disordered movement in humans (chorea
Chorea (or choreia, occasionally) is an abnormal involuntary movement disorder, one of a group of neurological disorders called dyskinesias. The term ''chorea'' is derived from the grc, χορεία ("dance"; see choreia), as the quick movem ...
, athetosis
Athetosis is a symptom characterized by slow, involuntary, convoluted, writhing movements of the fingers, hands, toes, and feet and in some cases, arms, legs, neck and tongue. Movements typical of athetosis are sometimes called ''athetoid'' moveme ...
, Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
).
Terminology
The nomenclature of the basal ganglia system and its components has always been problematic. Early anatomists, seeing the macroscopic anatomical structure but knowing nothing of the cellular architecture or neurochemistry, grouped together components that are now believed to have distinct functions (such as the internal and external segments of the globus pallidus), and gave distinct names to components that are now thought to be functionally parts of a single structure (such as the caudate nucleus and putamen). The term "basal" comes from the fact that most of its elements are located in the basal part of the forebrain. The term ganglia is a misnomer: In modern usage, neural clusters are called "ganglia" only in theperipheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain ...
; in the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
they are called "nuclei". For this reason, the basal ganglia are also occasionally known as the "basal nuclei". Terminologia anatomica (1998), the international authority for anatomical naming, retained "nuclei basales", but this is not commonly used.
The International Basal Ganglia Society (IBAGS) informally considers the basal ganglia to be made up of the striatum, the pallidum (with two nuclei), the substantia nigra (with its two distinct parts), and the subthalamic nucleus, whereas Terminologia anatomica excludes the last two. Some neurologists have included the centromedian nucleus
In the anatomy of the brain, the centromedian nucleus, also known as the centrum medianum, (CM or Cm-Pf) is a part of the intralaminar thalamic nuclei (ITN) in the thalamus. There are two centromedian nuclei arranged bilaterally.
In humans, it c ...
of the thalamus as part of the basal ganglia, and some have also included the pedunculopontine nucleus.
Other animals
The basal ganglia form one of the basic components of theforebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three primary ...
, and can be recognized in all species of vertebrates. Even in the lamprey (generally considered one of the most primitive of vertebrates), striatal, pallidal, and nigral elements can be identified on the basis of anatomy and histochemistry.
The names given to the various nuclei of the basal ganglia are different in different species. In cat
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members of ...
s and rodents the internal globus pallidus is known as the ''entopeduncular nucleus''.Peter Redgrave (2007Basal ganglia
Scholarpedia
, 2(6):1825. In
bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s the striatum is called the ''paleostriatum augmentatum'' and the external globus pallidus is called the ''paleostriatum primitivum''.
A clear emergent issue in comparative anatomy of the basal ganglia is the development of this system through phylogeny as a convergent cortically re-entrant loop in conjunction with the development and expansion of the cortical mantle. There is controversy, however, regarding the extent to which convergent selective processing occurs versus segregated parallel processing within re-entrant closed loops of the basal ganglia. Regardless, the transformation of the basal ganglia into a cortically re-entrant system in mammalian evolution occurs through a re-direction of pallidal (or "paleostriatum primitivum") output from midbrain targets such as the superior colliculus, as occurs in sauropsid brain, to specific regions of the ventral thalamus and from there back to specified regions of the cerebral cortex that form a subset of those cortical regions projecting into the striatum. The abrupt rostral re-direction of the pathway from the internal segment of the globus pallidus into the ventral thalamus—via the path of the ansa lenticularis—could be viewed as a footprint of this evolutionary transformation of basal ganglia outflow and targeted influence.
See also
*Alexander Cools
Alexander ("Lex") Rudolf Cools (1941 in The Hague – 7 September 2013 in Nijmegen) was a Dutch behavioral pharmacologist.
He obtained his Ph.D. under the supervision of Jacques van Rossum and Jo Vossen in 1973 at the Radboud University Nijmeg ...
* Nathaniel A. Buchwald
Additional images
References
External links
Imaging of Basal Ganglia
at USUHS *
The International Basal Ganglia Society
Basal ganglia
– Official journal of LIMPE (Lega Italiana per la Lotta Contro la Malattia di Parkinson, le Sindromi Extrapiramidali e le Demenze, Italy), the German Parkinson Society (DPG, Deutsche Parkinson Gesellschaft), and the Japanese Basal Ganglia Society (JBAGS Japan Basal Ganglia Society) {{DEFAULTSORT:Basal Ganglia Motor system Biology of obsessive–compulsive disorder