azide alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The azide-alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition is a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between an azide and a terminal or internal alkyne to give a 1,2,3-triazole. 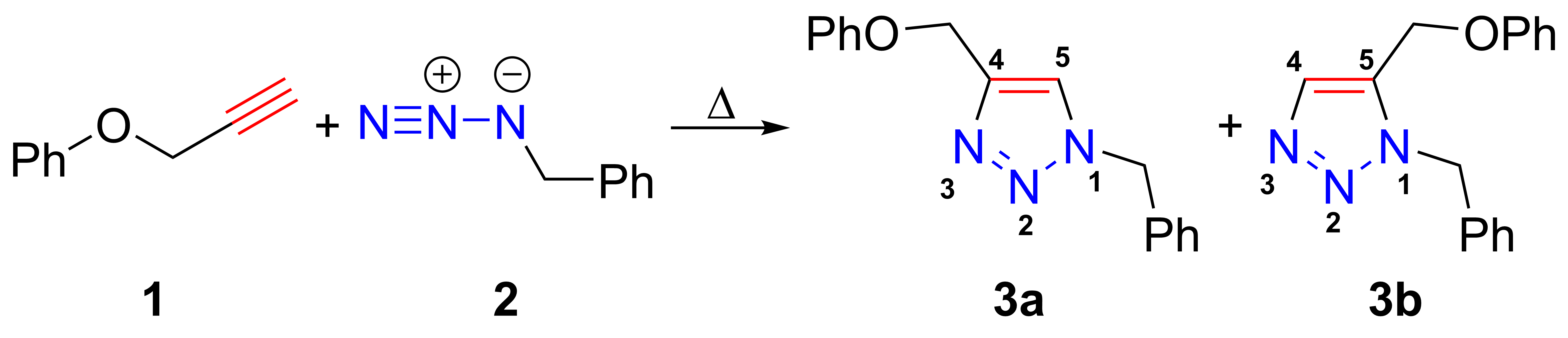 In the reaction above azide 2 reacts neatly with alkyne 1 to afford the product triazole as a mixture of 1,4-adduct (3a) and 1,5-adduct (3b) at 98 °C in 18 hours.
The standard 1,3-cycloaddition between an azide 1,3-dipole and an alkene as dipolarophile has largely been ignored due to lack of reactivity as a result of electron-poor olefins and elimination side reactions. Some success has been found with non-metal-catalyzed cycloadditions, such as the reactions using dipolarophiles that are electron-poor olefins or alkynes.
Although azides are not the most reactive 1,3-dipole available for reaction, they are preferred for their relative lack of side reactions and stability in typical synthetic conditions.
In the reaction above azide 2 reacts neatly with alkyne 1 to afford the product triazole as a mixture of 1,4-adduct (3a) and 1,5-adduct (3b) at 98 °C in 18 hours.
The standard 1,3-cycloaddition between an azide 1,3-dipole and an alkene as dipolarophile has largely been ignored due to lack of reactivity as a result of electron-poor olefins and elimination side reactions. Some success has been found with non-metal-catalyzed cycloadditions, such as the reactions using dipolarophiles that are electron-poor olefins or alkynes.
Although azides are not the most reactive 1,3-dipole available for reaction, they are preferred for their relative lack of side reactions and stability in typical synthetic conditions.
Rolf Huisgen
Rolf Huisgen (; 13 June 1920 – 26 March 2020) was a German chemist. His importance in synthetic organic chemistry extends to the enormous influence he had in post-war chemistry departments in Germany and Austria, due to a large number of his H ...
was the first to understand the scope of this organic reaction. American chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe t ...
Karl Barry Sharpless
Karl Barry Sharpless (born April 28, 1941) is an American chemist and a two-time Nobel laureate in Chemistry known for his work on stereoselective reactions and click chemistry.
Sharpless was awarded half of the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry " ...
has referred to this cycloaddition
In organic chemistry, a cycloaddition is a chemical reaction in which "two or more unsaturated molecules (or parts of the same molecule) combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of the bond multiplicity". T ...
as "the cream of the crop" of click chemistry and "the premier example of a click reaction".
 In the reaction above azide 2 reacts neatly with alkyne 1 to afford the product triazole as a mixture of 1,4-adduct (3a) and 1,5-adduct (3b) at 98 °C in 18 hours.
The standard 1,3-cycloaddition between an azide 1,3-dipole and an alkene as dipolarophile has largely been ignored due to lack of reactivity as a result of electron-poor olefins and elimination side reactions. Some success has been found with non-metal-catalyzed cycloadditions, such as the reactions using dipolarophiles that are electron-poor olefins or alkynes.
Although azides are not the most reactive 1,3-dipole available for reaction, they are preferred for their relative lack of side reactions and stability in typical synthetic conditions.
In the reaction above azide 2 reacts neatly with alkyne 1 to afford the product triazole as a mixture of 1,4-adduct (3a) and 1,5-adduct (3b) at 98 °C in 18 hours.
The standard 1,3-cycloaddition between an azide 1,3-dipole and an alkene as dipolarophile has largely been ignored due to lack of reactivity as a result of electron-poor olefins and elimination side reactions. Some success has been found with non-metal-catalyzed cycloadditions, such as the reactions using dipolarophiles that are electron-poor olefins or alkynes.
Although azides are not the most reactive 1,3-dipole available for reaction, they are preferred for their relative lack of side reactions and stability in typical synthetic conditions.
Copper catalysis
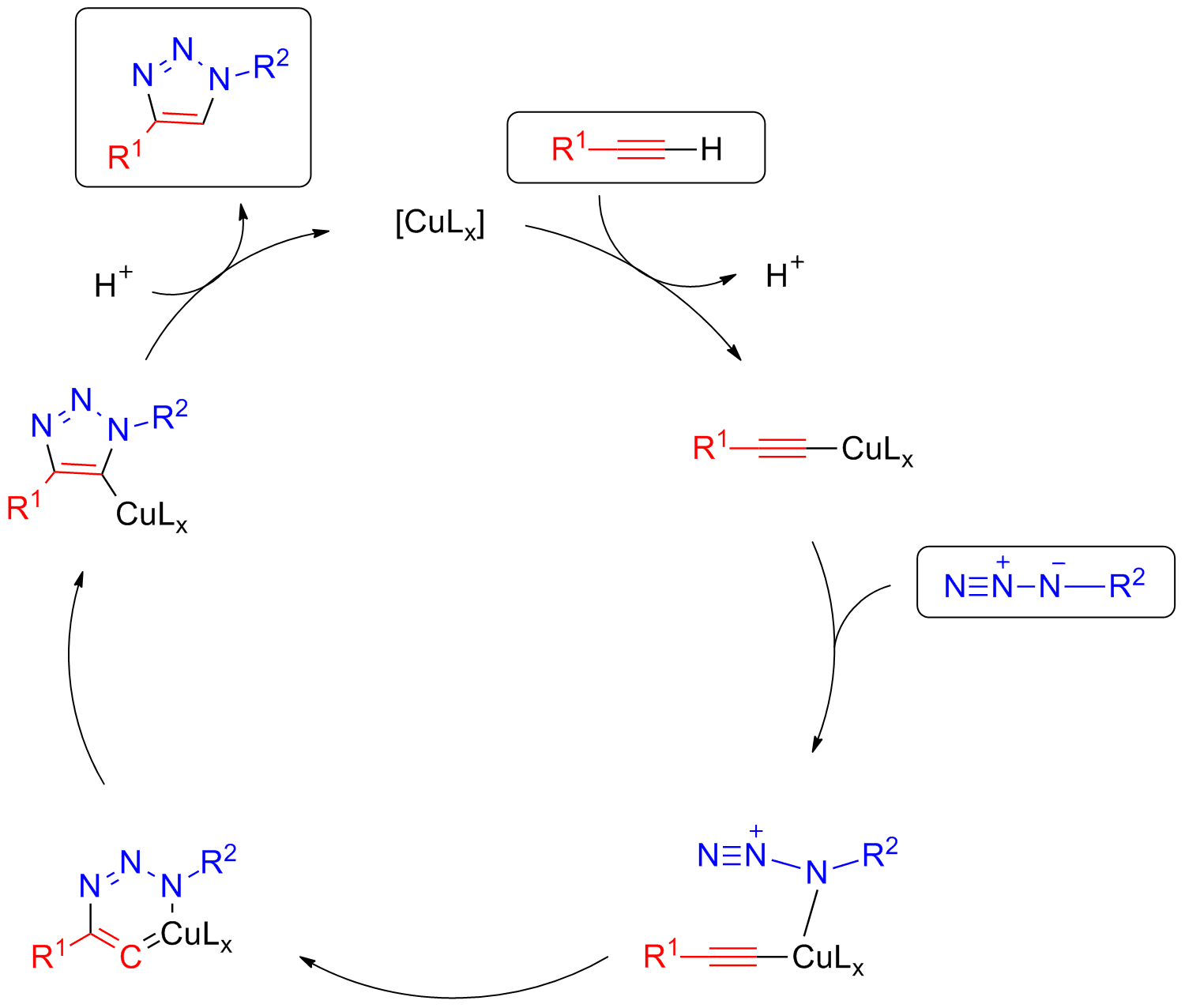
A notable variant of the Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition is the copper(I) catalyzed variant, no longer a true concerted cycloaddition, in which organic azides and terminal alkynes are united to afford 1,4-regioisomers of 1,2,3-triazoles as sole products (substitution at positions 1' and 4' as shown above). The copper(I)-catalyzed variant was first reported in 2002 in independent publications by Morten Meldal at the Carlsberg Laboratory in Denmark and Valery Fokin and K. Barry Sharpless at the Scripps Research Institute. While the copper(I)-catalyzed variant gives rise to a triazole from a terminal alkyne and an azide, formally it is not a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition and thus should not be termed a Huisgen cycloaddition. This reaction is better termed the Copper(I)-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (CuAAC). While the reaction can be performed using commercial sources of copper(I) such as cuprous bromide or iodide, the reaction works much better using a mixture of copper(II) (e.g. copper(II) sulfate) and a reducing agent (e.g. sodium ascorbate) to produce Cu(I) in situ. As Cu(I) is unstable in aqueous solvents, stabilizing ligands are effective for improving the reaction outcome, especially if tris(benzyltriazolylmethyl)amine (TBTA) is used. The reaction can be run in a variety of solvents, and mixtures of water and a variety of (partially) miscible organic solvents including alcohols, DMSO, DMF, ''t''BuOH and acetone. Owing to the powerful coordinating ability of nitriles towards Cu(I), it is best to avoid acetonitrile as the solvent. The starting reagents need not be completely soluble for the reaction to be successful. In many cases, the product can simply be filtered from the solution as the only purification step required. NH-1,2,3-triazoles are also prepared from alkynes in a sequence called the Banert cascade. The utility of the Cu(I)-catalyzed click reaction has also been demonstrated in thepolymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many fo ...
reaction of a bis-azide and a bis-alkyne with copper(I) and TBTA to a conjugated fluorene based polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
. The degree of polymerization
The degree of polymerization, or DP, is the number of monomeric units in a macromolecule or polymer or oligomer molecule.
For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit and the ''number-average'' degree of polymerization is given b ...
easily exceeds 50. With a stopper molecule such as phenyl azide
Phenyl azide is an organic compound with the formula C6H5N3. It is one of the prototypical organic azides. It is a pale yellow oily liquid with a pungent odor. The structure consists of a linear organic azide, azide substituent bound to a phenyl ...
, well-defined phenyl
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6 H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. Phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen ...
end-group
End groups are an important aspect of polymer synthesis and characterization. In polymer chemistry, they are functional groups that are at the very ends of a macromolecule or oligomer (IUPAC). In polymer synthesis, like condensation polymerizati ...
s are obtained.
The copper-mediated azide-alkyne cycloaddition is receiving widespread use in material and surface sciences. Most variations in coupling polymers with other polymers or small molecules have been explored. Current shortcomings are that the terminal alkyne appears to participate in free-radical polymerizations. This requires protection of the terminal alkyne with a trimethyl silyl protecting group and subsequent deprotection after the radical reaction are completed. Similarly the use of organic solvents, copper (I) and inert atmospheres to do the cycloaddition with many polymers makes the "click" label inappropriate for such reactions. An aqueous protocol for performing the cycloaddition with free-radical polymers is highly desirable.
The CuAAC click reaction also effectively couples polystyrene and bovine serum albumin
Bovine serum albumin (BSA or "Fraction V") is a serum albumin protein derived from cows. It is often used as a protein concentration standard in lab experiments.
The nickname "Fraction V" refers to albumin being the fifth fraction of the origin ...
(BSA). The result is an amphiphilic
An amphiphile (from the Greek αμφις amphis, both, and φιλíα philia, love, friendship), or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic (''water-loving'', polar) and lipophilic (''fat-loving'') properties. Such a compo ...
biohybrid. BSA contains a thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl gro ...
group at Cys-34 which is functionalized with an alkyne group. In water the biohybrid micelle
A micelle () or micella () (plural micelles or micellae, respectively) is an aggregate (or supramolecular assembly) of surfactant amphipathic lipid molecules dispersed in a liquid, forming a colloidal suspension (also known as associated coll ...
s with a diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid fo ...
of 30 to 70 nanometer form aggregates.
Copper catalysts
The use of a Cu catalyst in water was an improvement over the same reaction first popularized by Rolf Huisgen in the 1970s, which he ran at elevated temperatures. The traditional reaction is slow and thus requires high temperatures. However, the azides and alkynes are both kinetically stable. As mentioned above, copper-catalysed click reactions work essentially on terminal alkynes. The Cu species undergo metal insertion reaction into the terminal alkynes. The Cu(I) species may either be introduced as preformed complexes, or are otherwise generated in the reaction pot itself by one of the following ways: * A Cu2+ compound is added to the reaction in presence of a reducing agent (e.g. sodium ascorbate) which reduces the Cu from the (+2) to the (+1) oxidation state. The advantage of generating the Cu(I) species in this manner is it eliminates the need of a base in the reaction. Also the presence of reducing agent makes up for any oxygen which may have gotten into the system. Oxygen oxidises the Cu(I) to Cu(II) which impedes the reaction and results in low yields. One of the more commonly used Cu compounds is CuSO4. * Oxidation of Cu(0) metal * Halides of copper may be used where solubility is an issue. However, the iodide and bromide Cu salts require either the presence of amines or higher temperatures. Commonly used solvents are polar aprotic solvents such asTHF
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is ...
, DMSO
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula ( CH3)2. This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds ...
, acetonitrile, DMF as well as in non-polar aprotic solvents such as toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a colorless, water-insoluble liquid with the smell associated with paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, consisting of a methyl group (CH3) a ...
. Neat solvents or a mixture of solvents may be used.
DIPEA (N,N-Diisopropylethylamine) and Et3N (triethylamine
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA ...
) are commonly used bases.
Mechanism
A mechanism for the reaction has been suggested based ondensity functional theory
Density-functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-body ...
calculations. Copper is a 1st row transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that ca ...
. It has the electronic configuration r3d10 4s1. The copper (I) species generated in situ forms a pi complex
The number (; spelled out as "pi") is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. The number appears in many formulas across mathematics and physics. It is an irratio ...
with the triple bond of a terminal alkyne. In the presence of a base, the terminal hydrogen, being the most acidic, is deprotonated first to give a Cu acetylide
In organometallic chemistry, acetylide refers to chemical compounds with the chemical formulas and , where M is a metal. The term is used loosely and can refer to substituted acetylides having the general structure (where R is an organic side c ...
intermediate. Studies have shown that the reaction is second order with respect to Cu. It has been suggested that the transition state involves two copper atoms. One copper atom is bonded to the acetylide while the other Cu atom serves to activate the azide. The metal center coordinates with the electrons on the nitrogen atom. The azide and the acetylide are not coordinated to the same Cu atom in this case. The ligands employed are labile and are weakly coordinating. The azide displaces one ligand to generate a copper-azide-acetylide complex. At this point cyclization
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where ...
takes place. This is followed by protonation
In chemistry, protonation (or hydronation) is the adding of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) to an atom, molecule, or ion, forming a conjugate acid. (The complementary process, when a proton is removed from a Brønsted–Lowry acid ...
; the source of proton being the hydrogen which was pulled off from the terminal acetylene by the base. The product is formed by dissociation and the catalyst ligand complex is regenerated for further reaction cycles.
The reaction is assisted by the copper, which, when coordinated with the acetylide lowers the pKa of the alkyne C-H by up to 9.8 units. Thus under certain conditions, the reaction may be carried out even in the absence of a base.
In the uncatalysed reaction the alkyne remains a poor electrophile. Thus high energy barriers lead to slow reaction rates.

Ligand assistance
Theligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elec ...
s employed are usually labile i.e. they can be displaced easily. Though the ligand plays no direct role in the reaction the presence of a ligand has its advantages.
The ligand protects the Cu ion from interactions leading to degradation and formation of side products and also prevents the oxidation of the Cu(I) species to the Cu(II). Furthermore, the ligand functions as a proton acceptor thus eliminating the need of a base.
Ruthenium catalysis
Theruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element with the symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most other chemical ...
-catalysed 1,3-dipolar azide-alkyne cycloaddition (RuAAC) gives the 1,5-triazole.
Unlike CuAAC in which only terminal alkynes reacted, in RuAAC both terminal and internal alkynes can participate in the reaction. This suggests that ruthenium acetylides are not involved in the catalytic cycle
In chemistry, a catalytic cycle is a multistep reaction mechanism that involves a catalyst. The catalytic cycle is the main method for describing the role of catalysts in biochemistry, organometallic chemistry, bioinorganic chemistry, materials s ...
.
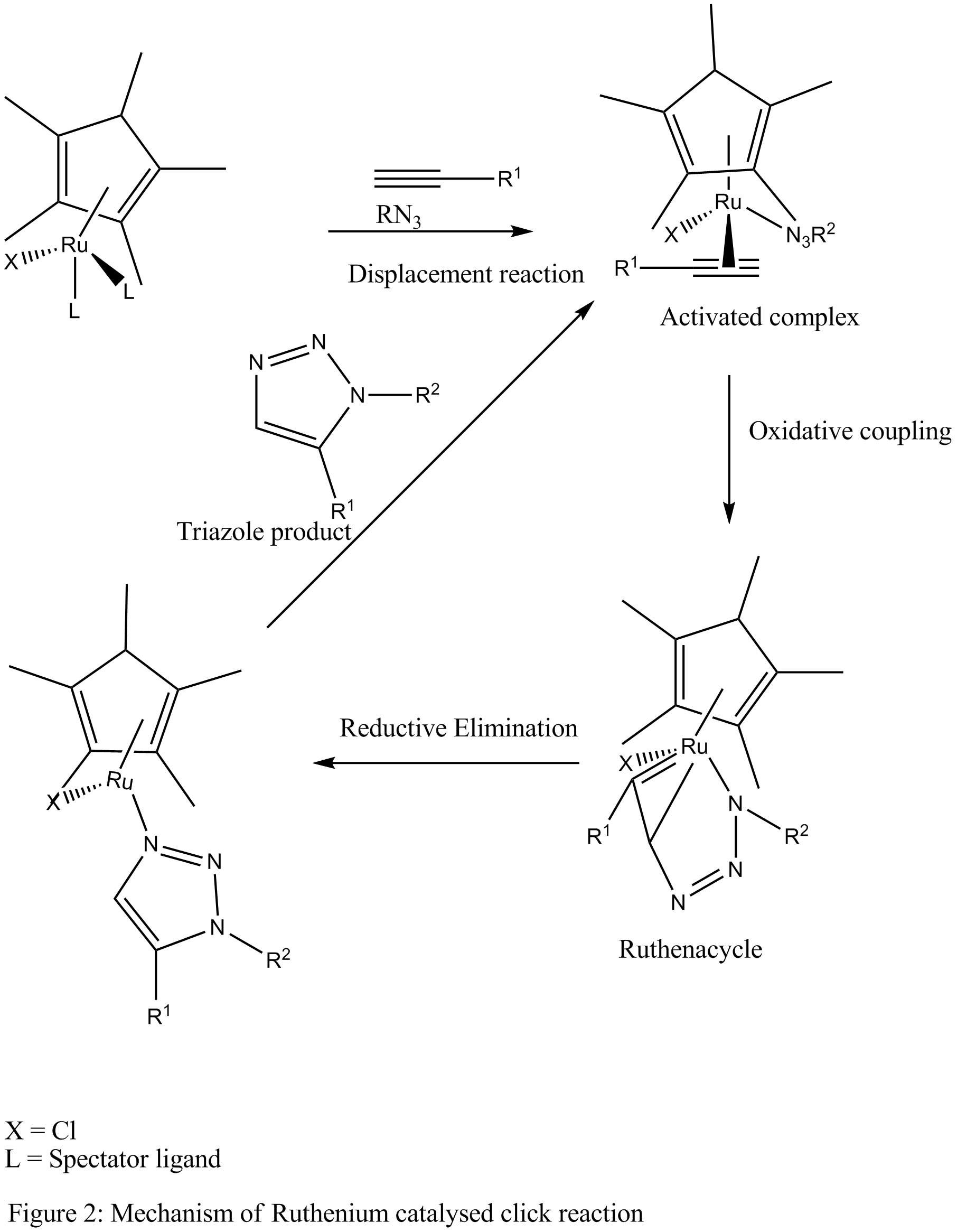
The proposed mechanism suggests that in the first step, the spectator ligand In coordination chemistry, a spectator ligand is a ligand that does not participate in chemical reactions of the complex. Instead, spectator ligands (vs "actor ligands") occupy coordination sites. Spectator ligands tend to be of polydentate, such ...
s undergo displacement reaction to produce an activated complex In chemistry an activated complex is defined by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) as "that assembly of atoms which corresponds to an arbitrary infinitesimally small region at or near the col (saddle point) of a potential ...
which is converted, through oxidative coupling Oxidative coupling in chemistry is a coupling reaction of two molecular entities through an oxidative process. Usually oxidative couplings are catalysed by a transition metal complex like in classical cross-coupling reactions, although the underl ...
of an alkyne and an azide to the ruthenium containing metallacycle (Ruthenacycle). The new C-N bond is formed between the more electronegative and less sterically demanding carbon of the alkyne and the terminal nitrogen of the azide. The metallacycle intermediate then undergoes reductive elimination releasing the aromatic triazole product and regenerating the catalyst or the activated complex for further reaction cycles.
Cp*RuCl(PPh3)2, Cp*Ru(COD) and Cp* uCl4are commonly used ruthenium catalysts. Catalysts containing cyclopentadienyl (Cp) group are also used. However, better results are observed with the pentamethylcyclopentadienyl(Cp*) version. This may be due to the sterically demanding Cp* group which facilitates the displacement of the spectator ligands.

Silver catalysis
Recently, the discovery of a general Ag(I)-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition reaction (Ag-AAC) leading to 1,4-triazoles is reported. Mechanistic features are similar to the generally accepted mechanism of the copper(I)-catalyzed process. Silver(I)-salts alone are not sufficient to promote the cycloaddition. However the ligated Ag(I) source has proven to be exceptional for AgAAC reaction. Curiously, pre-formed silver acetylides do not react with azides; however, silver acetylides do react with azides under catalysis with copper(I).References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Azide Alkyne Huisgen Cycloaddition Cycloadditions Name reactions ms:Tindak balas klik