atrial on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the
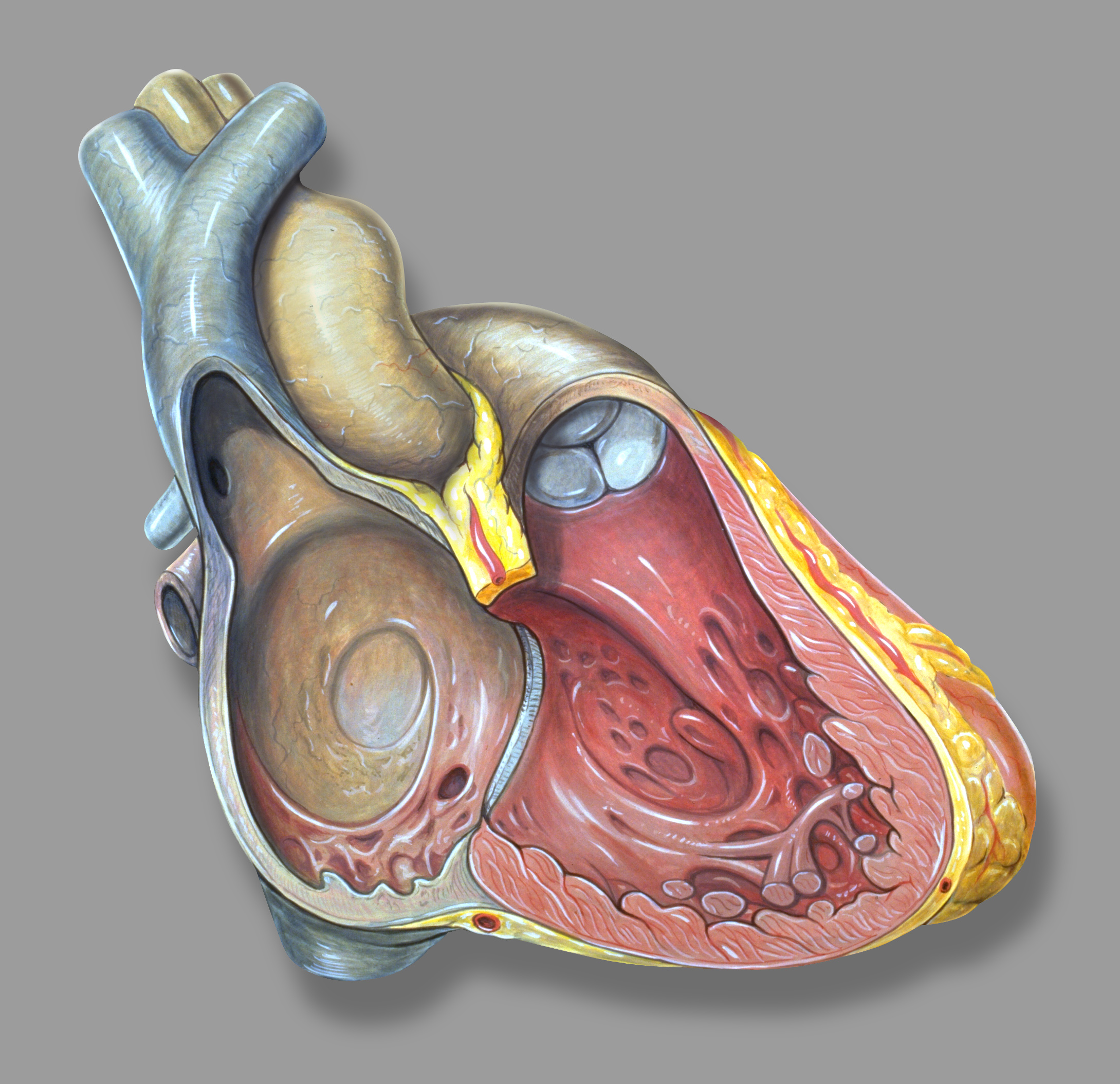
 High in the upper part of the left atrium is a muscular ear-shaped pouch – the left atrial appendage. This appears to "function as a decompression chamber during left ventricular systole and during other periods when left atrial pressure is high".
The left atrial appendage can be seen on a standard posteroanterior X-ray, where the lower level of the left hilum becomes concave. The left atrial appendage can serve as an approach for mitral valve surgery.
The body of the left atrial appendage is anterior to the left atrium and parallel to the left
High in the upper part of the left atrium is a muscular ear-shaped pouch – the left atrial appendage. This appears to "function as a decompression chamber during left ventricular systole and during other periods when left atrial pressure is high".
The left atrial appendage can be seen on a standard posteroanterior X-ray, where the lower level of the left hilum becomes concave. The left atrial appendage can serve as an approach for mitral valve surgery.
The body of the left atrial appendage is anterior to the left atrium and parallel to the left
 In patients with atrial fibrillation, mitral valve disease, and other conditions,
In patients with atrial fibrillation, mitral valve disease, and other conditions,
heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to ...
that receives blood from the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valve
A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart v ...
s.
There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lungs. ...
, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae
In anatomy, the venae cavae (; singular: vena cava ; ) are two large veins (great vessels) that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the ...
of the systemic circulation
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
. During the cardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following ...
the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventri ...
, then contract in systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''su ...
to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
have at least one atrium.
The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is est ...
''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do.
Structure

Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
s have a four-chambered heart consisting of the right and left atrium, and the right and left ventricle. The atria are the two upper chambers. The right atrium receives and holds deoxygenated blood from the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein ...
, inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
, anterior cardiac veins, smallest cardiac veins and the coronary sinus
In anatomy, the coronary sinus () is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle (myocardium). It delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium, as do the superior and inferior ven ...
, which it then sends down to the right ventricle (through the tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ve ...
), which in turn sends it to the pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
for pulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lungs. ...
. The left atrium receives the oxygenated blood from the left and right pulmonary veins
The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four ''main pulmonary veins'', two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary vein ...
, which it pumps to the left ventricle (through the mitral valve
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all on ...
(left atrioventricular valve) for pumping out through the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
for systemic circulation
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
.
The right atrium and ventricle are often referred to together as the right heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxid ...
, and the left atrium and ventricle as the left heart. As the atria do not have valves at their inlets a venous pulsation is normal, and can be detected in the jugular vein
The jugular veins are veins that take deoxygenated blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid mus ...
as the jugular venous pressure.
Internally, there are the rough pectinate muscles
The pectinate muscles (musculi pectinati) are parallel muscular ridges in the walls of the atria of the heart.
Structure
Behind the crest (crista terminalis) of the right atrium the internal surface is smooth. Pectinate muscles make up the par ...
and crista terminalis
The crista terminalis or terminal crest represents the junction between the sinus venosus and the heart in the developing embryo. In the development of the human heart, the right horn and transverse portion of the sinus venosus ultimately become in ...
of His
His or HIS may refer to:
Computing
* Hightech Information System, a Hong Kong graphics card company
* Honeywell Information Systems
* Hybrid intelligent system
* Microsoft Host Integration Server
Education
* Hangzhou International School, ...
, which act as a boundary inside the atrium and the smooth-walled part of the right atrium, the ''sinus venarum'', which are derived from the sinus venosus
The sinus venosus is a large quadrangular cavity which precedes the atrium on the venous side of the chordate heart. In mammals, it exists distinctly only in the embryonic heart, where it is found between the two venae cavae. However, the sinus v ...
. The sinus venarum is the adult remnant of the sinus venosus and it surrounds the openings of the venae cavae
In anatomy, the venae cavae (; singular: vena cava ; ) are two large veins (great vessels) that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the ...
and the coronary sinus.
Attached to each atrium is an atrial appendage.
Right atrial appendage
The right atrial appendage is located at the front upper surface of the right atrium. Looking from the front, the right atrial appendage appears wedge-shaped or triangular. Its base surrounds thesuperior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein ...
.> The right atrial appendage is a pouch-like extension of the right atrium and is covered by a trabecula network of pectinate muscles
The pectinate muscles (musculi pectinati) are parallel muscular ridges in the walls of the atria of the heart.
Structure
Behind the crest (crista terminalis) of the right atrium the internal surface is smooth. Pectinate muscles make up the par ...
. The interatrial septum
The interatrial septum is the wall of tissue that separates the right and left atria of the heart.
Structure
The interatrial septum is a that lies between the left atrium and right atrium of the human heart. The interatrial septum lies at an ...
separates the right atrium from the left atrium; this is marked by a depression in the right atrium – the fossa ovalis. The atria are depolarised by calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
.
Left atrial appendage
 High in the upper part of the left atrium is a muscular ear-shaped pouch – the left atrial appendage. This appears to "function as a decompression chamber during left ventricular systole and during other periods when left atrial pressure is high".
The left atrial appendage can be seen on a standard posteroanterior X-ray, where the lower level of the left hilum becomes concave. The left atrial appendage can serve as an approach for mitral valve surgery.
The body of the left atrial appendage is anterior to the left atrium and parallel to the left
High in the upper part of the left atrium is a muscular ear-shaped pouch – the left atrial appendage. This appears to "function as a decompression chamber during left ventricular systole and during other periods when left atrial pressure is high".
The left atrial appendage can be seen on a standard posteroanterior X-ray, where the lower level of the left hilum becomes concave. The left atrial appendage can serve as an approach for mitral valve surgery.
The body of the left atrial appendage is anterior to the left atrium and parallel to the left pulmonary vein
The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four ''main pulmonary veins'', two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary vei ...
s. The left pulmonary artery passes posterosuperiorly and is separated from the atrial appendage by the transverse sinus
The transverse sinuses (left and right lateral sinuses), within the human head, are two areas beneath the brain which allow blood to drain from the back of the head. They run laterally in a groove along the interior surface of the occipital bone. ...
. With certain conditions, the left atrial appendage may be associated with risks of stroke from blood clot
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of ...
formation, because of which surgeons may choose to close it during open-heart surgery.
Conduction system
The sinoatrial (SA) node is located in the posterior aspect of the right atrium, next to the superior vena cava. This is a group of pacemaker cells which spontaneously depolarize to create an action potential. Thecardiac action potential
The cardiac action potential is a brief change in voltage (membrane potential) across the cell membrane of heart cells. This is caused by the movement of charged atoms (called ions) between the inside and outside of the cell, through proteins cal ...
then spreads across both atria causing them to contract, forcing the blood they hold into their corresponding ventricles.
The atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node or AV node electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the lower back section of t ...
(AV node) is another node in the cardiac electrical conduction system. This is located between the atria and the ventricles.
Blood supply
The left atrium is supplied mainly by the left circumflex coronary artery, and its small branches. The oblique vein of the left atrium is partly responsible for venous drainage; it derives from the embryonic left superior vena cava.Development
Duringembryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
at about two weeks, a primitive atrium begins to be formed. It begins as one chamber, which over the following two weeks becomes divided by the septum primum
During heart development of a human embryo, the single primitive atrium becomes divided into right and left by a , the septum primum. The septum primum () grows downward into the single atrium.
Development
The gap below it is known as the osti ...
into the left atrium and the right atrium. The interatrial septum
The interatrial septum is the wall of tissue that separates the right and left atria of the heart.
Structure
The interatrial septum is a that lies between the left atrium and right atrium of the human heart. The interatrial septum lies at an ...
has an opening in the right atrium, the foramen ovale, which provides access to the left atrium; this connects the two chambers, which is essential for fetal blood circulation. At birth, when the first breath is taken fetal blood flow is reversed to travel through the lungs. The foramen ovale is no longer needed and it closes to leave a depression (the fossa ovalis) in the atrial wall.
In some cases, the foramen ovale fails to close. This abnormality is present in approximately 25% of the general population. This is known as a ''patent foramen ovale'', an atrial septal defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this d ...
. It is mostly unproblematic, although it can be associated with paradoxical embolization
Embolization refers to the passage and lodging of an embolus within the bloodstream. It may be of natural origin (pathological), in which sense it is also called embolism, for example a pulmonary embolism; or it may be artificially induced ...
and stroke.
Within the fetal right atrium, blood from the inferior vena cava and the superior vena cava flow in separate streams to different locations in the heart; this has been reported to occur through the Coandă effect
The Coandă effect ( or ) is the tendency of a fluid jet to stay attached to a convex surface. ''Merriam-Webster'' describes it as "the tendency of a jet of fluid emerging from an orifice to follow an adjacent flat or curved surface and to en ...
.
Function
In human physiology, the atria facilitate circulation primarily by allowing uninterrupted venous flow to the heart duringventricular systole
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following ...
. By being partially empty and distensible, atria prevent the interruption of venous flow to the heart that would occur during ventricular systole if the veins ended at the inlet valves of the heart. In normal physiologic states, the output of the heart is pulsatile, and the venous inflow to the heart is continuous and non-pulsatile. But without functioning atria, venous flow becomes pulsatile, and the overall circulation rate decreases significantly.
Atria have four essential characteristics that cause them to promote continuous venous flow. (1) There are no atrial inlet valves to interrupt blood flow during atrial systole. (2) The atrial systole contractions are incomplete and thus do not contract to the extent that would block flow from the veins through the atria into the ventricles. During atrial systole, blood not only empties from the atria to the ventricles, but blood continues to flow uninterrupted from the vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated ...
s right through the atria into the ventricles. (3) The atrial contractions must be gentle enough so that the force of contraction does not exert significant back pressure that would impede venous flow. (4) The "let go" of the atria must be timed so that they relax before the start of ventricular contraction, to be able to accept venous flow without interruption.
By preventing the inertia of interrupted venous flow that would otherwise occur at each ventricular systole, atria allow approximately 75% more cardiac output than would otherwise occur. The fact that atrial contraction is 15% of the amount of the succeeding ventricular ejection has led to a misplaced emphasis on their role in pumping up the ventricles (the so-called "atrial kick"), whereas the key benefit of atria is in preventing circulatory inertia and allowing uninterrupted venous flow to the heart.
Also of importance in maintaining the blood flow are the presence of atrial volume receptors. These are low-pressure baroreceptor
Baroreceptors (or archaically, pressoreceptors) are sensors located in the carotid sinus (at the bifurcation of external and internal carotids) and in the aortic arch. They sense the blood pressure and relay the information to the brain, so that ...
s in the atria, which send signals to the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus i ...
when a drop in atrial pressure (which indicates a drop in blood volume) is detected. This triggers a release of vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travel ...
.
Disorders
Atrial septal defect
In an adult, anatrial septal defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this d ...
results in the flow of blood in the reverse direction – from the left atrium to the right – which reduces cardiac output, potentially causing cardiac failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, an ...
, and in severe or untreated cases cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and poss ...
and sudden death.
Left atrial appendage thrombosis
 In patients with atrial fibrillation, mitral valve disease, and other conditions,
In patients with atrial fibrillation, mitral valve disease, and other conditions, blood clots
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of c ...
have a tendency to form in the left atrial appendage. The clots may dislodge (forming emboli
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule (fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas (gas embolism), amniotic fluid (amnioti ...
), which may lead to ischemic
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi ...
damage to the brain, kidneys, or other organs supplied by the systemic circulation.
In those with uncontrollable atrial fibrillation, left atrial appendage excision may be performed at the time of any open heart surgery to prevent future clot formation within the appendage.
Functional abnormalities
* Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome *Atrial flutter
Atrial flutter (AFL) is a common abnormal heart rhythm that starts in the atrial chambers of the heart. When it first occurs, it is usually associated with a fast heart rate and is classified as a type of supraventricular tachycardia. Atrial ...
* Atrial tachycardia
Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm problem in which the heart's electrical impulse comes from an ectopic pacemaker (that is, an abnormally located cardiac pacemaker) in the upper chambers ( atria) of the heart, rather than from the sin ...
* Sinus tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is an elevated sinus rhythm characterized by an increase in the rate of electrical impulses arising from the sinoatrial node. In adults, sinus tachycardia is defined as a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute (bpm). The ...
* Multifocal atrial tachycardia – several types
* Premature atrial contraction
Premature atrial contraction (PAC), also known as atrial premature complexes (APC) or atrial premature beats (APB), are a common cardiac dysrhythmia characterized by premature heartbeats originating in the atria. While the sinoatrial node typi ...
Other animals
Many other animals, including mammals, also have four-chambered hearts, which have a similar function. Some animals (amphibians and reptiles) have a three-chambered heart, in which the blood from each atrium is mixed in the single ventricle before being pumped to the aorta. In these animals, the left atrium still serves the purpose of collecting blood from the pulmonary veins. In some fish, the circulatory system is very simple: a two-chambered heart including one atrium and one ventricle. Among sharks, the heart consists of four chambers arranged serially (and therefore called a serial heart): blood flows into the most posterior chamber, the sinus venosus, and then to the atrium which moves it to the third chamber, the ventricle, before it reaches the conus anteriosus, which itself is connected to the ventral aorta. This is considered a primitive arrangement, and many vertebrates have condensed the atrium with the sinus venosus and the ventricle with the conus anteriosus. With the advent of lungs came a partitioning of the atrium into two parts divided by a septum. Among frogs, the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is mixed in the ventricle before being pumped out to the body's organs; in turtles, the ventricle is almost entirely divided by a septum, but retains an opening through which some mixing of blood occurs. In birds, mammals, and some other reptiles (alligators in particular) the partitioning of both chambers is complete.See also
*Syncytium
A syncytium (; plural syncytia; from Greek: σύν ''syn'' "together" and κύτος ''kytos'' "box, i.e. cell") or symplasm is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells (i.e., cells with a single nucl ...
* Left atrial volume
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Atrium (Heart) Cardiac anatomy de:Herz#Räume und Gefäße