Approach Behavior on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation),
 Ventral tegmental area
*The
Ventral tegmental area
*The
Figure 3: Neural circuits underlying motivated 'wanting' and hedonic 'liking'.
/ref> The hotspot within the nucleus accumbens shell is located in the rostrodorsal quadrant of the medial shell, while the hedonic coldspot is located in a more posterior region. The posterior ventral pallidum also contains a hedonic hotspot, while the anterior ventral pallidum contains a hedonic coldspot. In rats, microinjections of opioids,
 Incentive salience is the "wanting" or "desire" attribute, which includes a motivational component, that is assigned to a rewarding stimulus by the nucleus accumbens shell (NAcc shell). The degree of dopamine neurotransmission into the NAcc shell from the
Incentive salience is the "wanting" or "desire" attribute, which includes a motivational component, that is assigned to a rewarding stimulus by the nucleus accumbens shell (NAcc shell). The degree of dopamine neurotransmission into the NAcc shell from the
Table 1: Summary of plasticity observed following exposure to drug or natural reinforcers
Certain epigenetic modifications of
Figure 4: Epigenetic basis of drug regulation of gene expression
/ref> Addictive drugs and behaviors are rewarding and
 The first clue to the presence of a reward system in the brain came with an accident discovery by James Olds and Peter Milner in 1954. They discovered that rats would perform behaviors such as pressing a bar, to administer a brief burst of electrical stimulation to specific sites in their brains. This phenomenon is called intracranial self-stimulation or
The first clue to the presence of a reward system in the brain came with an accident discovery by James Olds and Peter Milner in 1954. They discovered that rats would perform behaviors such as pressing a bar, to administer a brief burst of electrical stimulation to specific sites in their brains. This phenomenon is called intracranial self-stimulation or
Scholarpedia Reward
Scholarpedia Reward signals
{{Portal bar, Psychology, Biology Cognitive neuroscience Behavioral neuroscience Behaviorism Behavior modification Addiction Neuroanatomy Neuropsychology Dopamine
associative learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of l ...
(primarily positive reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher fr ...
and classical conditioning
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent stimulus (e.g. food) is paired with a previously neutral stimulus (e.g. a triangle). It also refers to the learni ...
), and positively-valenced emotion
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or suffering, displeasure. There is currently no scientific ...
s, particularly ones involving pleasure as a core component (e.g., joy
The word joy refers to the emotion evoked by well-being, success, or good fortune, and is typically associated with feelings of intense, long lasting happiness.
Dictionary definitions
Dictionary definitions of joy typically include a sense of ...
, euphoria and ecstasy). Reward is the attractive and motivational property of a stimulus that induces appetitive behavior, also known as approach behavior, and consummatory behavior. A rewarding stimulus has been described as "any stimulus, object, event, activity, or situation that has the potential to make us approach and consume it is by definition a reward". In operant conditioning, rewarding stimuli function as positive reinforcer
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher fre ...
s; however, the converse statement also holds true: positive reinforcers are rewarding.
The reward system motivates animals to approach stimuli or engage in behaviour that increases fitness (sex, energy-dense foods, etc.). Survival for most animal species depends upon maximizing contact with beneficial stimuli and minimizing contact with harmful stimuli. Reward cognition serves to increase the likelihood of survival and reproduction by causing associative learning, eliciting approach and consummatory behavior, and triggering positively-valenced emotions. Thus, reward is a mechanism that evolved to help increase the adaptive fitness of animals. In drug addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use o ...
, certain substances over-activate the reward circuit, leading to compulsive substance-seeking behavior resulting from synaptic plasticity in the circuit.
Primary rewards are a class of rewarding stimuli which facilitate the survival of one's self and offspring, and they include homeostatic (e.g., palatable food) and reproductive (e.g., sexual contact and parental investment) rewards. Intrinsic rewards are unconditioned rewards that are attractive and motivate behavior because they are inherently pleasurable. Extrinsic rewards (e.g., money or seeing one's favorite sports team winning a game) are conditioned rewards that are attractive and motivate behavior but are not inherently pleasurable. Extrinsic rewards derive their motivational value as a result of a learned association (i.e., conditioning) with intrinsic rewards. Extrinsic rewards may also elicit pleasure (e.g., euphoria from winning a lot of money in a lottery) after being classically conditioned with intrinsic rewards.
Definition
In neuroscience, the reward system is a collection of brain structures and neural pathways that are responsible for reward-related cognition, includingassociative learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of l ...
(primarily classical conditioning
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent stimulus (e.g. food) is paired with a previously neutral stimulus (e.g. a triangle). It also refers to the learni ...
and operant reinforcement), incentive salience (i.e., motivation and "wanting", desire, or craving for a reward), and positively-valenced emotion
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or suffering, displeasure. There is currently no scientific ...
s, particularly emotions that involve pleasure (i.e., hedonic "liking").
Terms that are commonly used to describe behavior related to the "wanting" or desire component of reward include appetitive behavior, approach behavior, preparatory behavior, instrumental behavior, anticipatory behavior, and seeking. Terms that are commonly used to describe behavior related to the "liking" or pleasure component of reward include consummatory behavior and taking behavior.
The three primary functions of rewards are their capacity to:
#produce associative learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of l ...
(i.e., classical conditioning
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent stimulus (e.g. food) is paired with a previously neutral stimulus (e.g. a triangle). It also refers to the learni ...
and operant reinforcement);
#affect decision-making and induce approach behavior (via the assignment of motivational salience to rewarding stimuli);
#elicit positively-valenced emotions, particularly pleasure.
Neuroanatomy
Overview
The brain structures that compose the reward system are located primarily within thecortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop
The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop (CBGTC loop) is a system of neural circuits in the brain. The loop involves connections between the cortex, the basal ganglia, the thalamus, and back to the cortex. It is of particular relevance t ...
; the basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an exter ...
portion of the loop drives activity within the reward system. Most of the pathways that connect structures within the reward system are glutamatergic
Glutamatergic means "related to glutamate". A glutamatergic agent (or drug) is a chemical that directly modulates the excitatory amino acid (glutamate/aspartate) system in the body or brain. Examples include excitatory amino acid receptor agonis ...
interneurons, GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSNs), and dopaminergic projection neurons, although other types of projection neurons contribute (e.g., orexinergic projection neurons). The reward system includes the ventral tegmental area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is th ...
, ventral striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutam ...
(i.e., the nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for " nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypot ...
and olfactory tubercle), dorsal striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutama ...
(i.e., the caudate nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. While the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes due to its role in Parkinson's d ...
and putamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a round structure located at the base of the forebrain (telencephalon). The putamen and caudate nucleus together form the dorsal striatum. It is also one of the structures that compose the basal ...
), substantia nigra (i.e., the pars compacta
The pars compacta (SNpc) is a portion of the ''substantia nigra'', located in the midbrain. It is formed by dopaminergic neurons and located medial to the pars reticulata. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the death of dopaminergic neuron ...
and pars reticulata
The pars reticulata (SNpr) is a portion of the substantia nigra and is located lateral to the pars compacta. Most of the neurons that project out of the pars reticulata are inhibitory GABAergic neurons (i.e., these neurons release GABA, which is ...
), prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46 ...
, anterior cingulate cortex
In the human brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It c ...
, insular cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes) within each hemisphere of the mammalian b ...
, hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , ' seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, ...
, hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamu ...
(particularly, the orexinergic nucleus in the lateral hypothalamus
The lateral hypothalamus (LH), also called the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), contains the primary orexinergic nucleus within the hypothalamus that widely projects throughout the nervous system; this system of neurons mediates an array of cognit ...
), thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, ...
(multiple nuclei), subthalamic nucleus, globus pallidus (both external
External may refer to:
* External (mathematics), a concept in abstract algebra
* Externality
In economics, an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party' ...
and internal
Internal may refer to:
*Internality as a concept in behavioural economics
*Neijia, internal styles of Chinese martial arts
*Neigong or "internal skills", a type of exercise in meditation associated with Daoism
*''Internal (album)'' by Safia, 2016
...
), ventral pallidum
The ventral pallidum (VP) is a structure within the basal ganglia of the brain. It is an output nucleus whose fibres project to thalamic nuclei, such as the ventral anterior nucleus, the ventral lateral nucleus, and the medial dorsal nucleus.
The ...
, parabrachial nucleus, amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex verte ...
, and the remainder of the extended amygdala The extended amygdala is a macrostructure in the brain that is involved in reward cognition and defined by connectivity and neurochemical staining. It includes the central medial amygdala, sublenticular substantia innominata, and the bed nucleus o ...
. The dorsal raphe nucleus
The dorsal raphe nucleus is located on the midline of the brainstem and is one of the raphe nuclei. It has rostral and caudal subdivisions.
* The rostral aspect of the ''dorsal'' raphe is further divided into interfascicular, ventral, ventrolatera ...
and cerebellum appear to modulate some forms of reward-related cognition (i.e., associative learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of l ...
, motivational salience, and positive emotions) and behaviors as well. The laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LTD), pedunculopontine nucleus (PPTg), and lateral habenula (LHb) (both directly and indirectly via the rostromedial tegmental nucleus) are also capable of inducing aversive salience and incentive salience through their projections to the ventral tegmental area (VTA). The LDT and PPTg both send glutaminergic projections to the VTA that synapse on dopaminergic neurons, both of which can produce incentive salience. The LHb sends glutaminergic projections, the majority of which synapse on GABAergic RMTg neurons that in turn drive inhibition of dopaminergic VTA neurons, although some LHb projections terminate on VTA interneurons. These LHb projections are activated both by aversive stimuli and by the absence of an expected reward, and excitation of the LHb can induce aversion.
Most of the dopamine pathways (i.e., neurons that use the neurotransmitter dopamine to communicate with other neurons) that project out of the ventral tegmental area are part of the reward system; in these pathways, dopamine acts on D1-like receptor
The D1-like receptors are a subfamily of dopamine receptors that bind the endogenous neurotransmitter dopamine. The D1-like subfamily consists of two G protein–coupled receptors that are coupled to Gs and mediate excitatory neurotransmission
...
s or D2-like receptor
The D2-like receptors are a subfamily of dopamine receptors that bind the endogenous neurotransmitter dopamine. The D2-like subfamily consists of three G-protein coupled receptors that are coupled to Gi/Go and mediate inhibitory neurotransmission ...
s to either stimulate (D1-like) or inhibit (D2-like) the production of cAMP. The GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the striatum are components of the reward system as well. The glutamatergic projection nuclei in the subthalamic nucleus, prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, thalamus, and amygdala connect to other parts of the reward system via glutamate pathways. The medial forebrain bundle
The medial forebrain bundle (MFB), is a neural pathway containing fibers from the basal olfactory regions, the periamygdaloid region and the septal nuclei, as well as fibers from brainstem regions, including the ventral tegmental area and ni ...
, which is a set of many neural pathways that mediate brain stimulation reward
Brain stimulation reward (BSR) is a pleasurable phenomenon elicited via direct stimulation of specific brain regions, originally discovered by James Olds and Peter Milner. BSR can serve as a robust operant reinforcer. Targeted stimulation activat ...
(i.e., reward derived from direct electrochemical stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus
The lateral hypothalamus (LH), also called the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), contains the primary orexinergic nucleus within the hypothalamus that widely projects throughout the nervous system; this system of neurons mediates an array of cognit ...
), is also a component of the reward system.
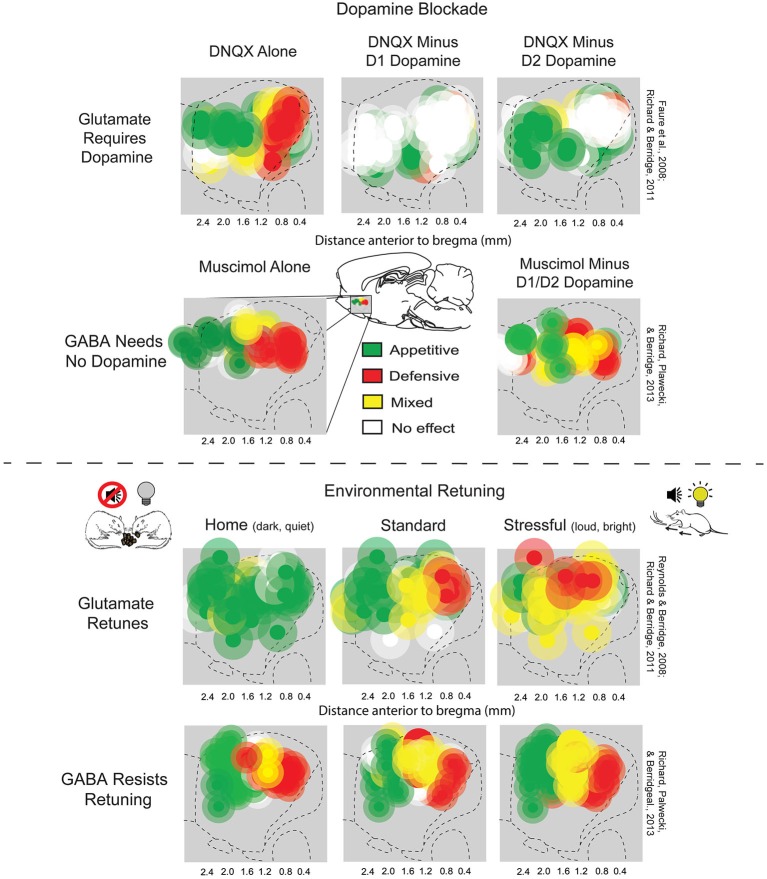
Two theories exist with regard to the activity of the nucleus accumbens and the generation liking and wanting. The inhibition (or hyperpolarization) hypothesis proposes that the nucleus accumbens exerts tonic inhibitory effects on downstream structures such as the ventral pallidum, hypothalamus or ventral tegmental area, and that in inhibiting in the nucleus accumbens (NAcc), these structures are excited, "releasing" reward related behavior. While GABA receptor agonists are capable of eliciting both "liking" and "wanting" reactions in the nucleus accumbens, glutaminergic inputs from the basolateral amygdala, ventral hippocampus, and medial prefrontal cortex can drive incentive salience. Furthermore, while most studies find that NAcc neurons reduce firing in response to reward, a number of studies find the opposite response. This had led to the proposal of the disinhibition (or depolarization) hypothesis, that proposes that excitation or NAcc neurons, or at least certain subsets, drives reward related behavior.
After nearly 50 years of research on brain-stimulation reward, experts have certified that dozens of sites in the brain will maintain intracranial self-stimulation. Regions include the lateral hypothalamus and medial forebrain bundles, which are especially effective. Stimulation there activates fibers that form the ascending pathways; the ascending pathways include the mesolimbic dopamine pathway, which projects from the ventral tegmental area to the nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for " nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypot ...
. There are several explanations as to why the mesolimbic dopamine pathway is central to circuits mediating reward. First, there is a marked increase in dopamine release from the mesolimbic pathway when animals engage in intracranial self-stimulation. Second, experiments consistently indicate that brain-stimulation reward stimulates the reinforcement of pathways that are normally activated by natural rewards, and drug reward or intracranial self-stimulation can exert more powerful activation of central reward mechanisms because they activate the reward center directly rather than through the peripheral nerves
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain an ...
. Third, when animals are administered addictive drugs or engage in naturally rewarding behaviors, such as feeding or sexual activity, there is a marked release of dopamine within the nucleus accumbens. However, dopamine is not the only reward compound in the brain.
Key pathway
 Ventral tegmental area
*The
Ventral tegmental area
*The ventral tegmental area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is th ...
(VTA) is important in responding to stimuli and cues that indicate a reward is present. Rewarding stimuli (and all addictive drugs) act on the circuit by triggering the VTA to release dopamine signals to the nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for " nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypot ...
, either directly or indirectly. The VTA has two important pathways: The mesolimbic pathway
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmentum, ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the for ...
projecting to limbic (striatal) regions and underpinning the motivational behaviors and processes, and the ''mesocortical pathway'' projecting to the prefrontal cortex, underpinning cognitive functions, such as learning external cues, etc.Kokane, S. S., & Perrotti, L. I. (2020). Sex Differences and the Role of Estradiol in Mesolimbic Reward Circuits and Vulnerability to Cocaine and Opiate Addiction. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 14.
*Dopaminergic neurons in this region converts the amino acid tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the G ...
into DOPA using the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase
Tyrosine hydroxylase or tyrosine 3-monooxygenase is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of the amino acid L-tyrosine to L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA). It does so using molecular oxygen (O2), as well as iron (Fe2+) and t ...
, which is then converted to dopamine using the enzyme dopa-decarboxylase.
Striatum (Nucleus Accumbens)
*The striatum is broadly involved in acquiring and eliciting learned behaviors in response to a rewarding cue. The VTA projects to the striatum, and activates the GABA-ergic Medium Spiny Neurons via D1 and D2 receptors within the ventral (Nucleus Accumbens) and dorsal striatum.
*The ''Ventral Striatum'' (the Nucleus Accumbens) is broadly involved in acquiring behavior when fed into by the VTA, and eliciting behavior when fed into by the PFC. The NAc shell projects to the pallidum and the VTA, regulating limbic and autonomic functions. This modulates the reinforcing properties of stimuli, and short term aspects of reward. The NAc Core projects to the substantia nigra and is involved in the development of reward-seeking behaviors and its expression. It is involved in spatial learning, conditional response, and impulsive choice; the long term elements of reward.
*The Dorsal Striatum is involved in learning, the ''Dorsal Medial Striatum'' in goal directed learning, and the ''Dorsal Lateral Striatum'' in stimulus-response learning foundational to Pavlovian response. On repeated activation by a stimuli, the Nucleus Accumbens can activate the Dorsal Striatum via an intrastriatal loop. The transition of signals from the NAc to the DS allows reward associated cues to activate the DS without the reward itself being present. This can activate cravings and reward-seeking behaviors (and is responsible for triggering relapse during abstinence in addiction).Koob, G. F., & Volkow, N. D. (2016). Neurobiology of addiction: a neurocircuitry analysis. The Lancet Psychiatry, 3(8), 760-773.
Prefrontal Cortex
*The VTA dopaminergic neurons project to the PFC, activating glutaminergic neurons that project to multiple other regions, including the Dorsal Striatum and NAc, ultimately allowing the PFC to mediate salience and conditional behaviors in response to stimuli.
*Notably, abstinence from addicting drugs activates the PFC, glutamatergic projection to the NAc, which leads to strong cravings, and modulates reinstatement of addiction behaviors resulting from abstinence. The PFC also interacts with the VTA through the mesocortical pathway, and helps associate environmental cues with the reward.
Hippocampus
*The Hippocampus has multiple functions, including in the creation and storage of memories . In the reward circuit, it serves to contextual memories and associated cues. It ultimately underpins the reinstatement of reward-seeking behaviors via cues, and contextual triggers.
Amygdala
*The AMY receives input from the VTA, and outputs to the NAc. The amygdala is important in creating powerful emotional flashbulb memories, and likely underpins the creation of strong cue-associated memories. It also is important in mediating the anxiety effects of withdrawal, and increased drug intake in addiction.
Pleasure centers
Pleasure is a component of reward, but not all rewards are pleasurable (e.g., money does not elicit pleasure unless this response is conditioned). Stimuli that are naturally pleasurable, and therefore attractive, are known as ''intrinsic rewards'', whereas stimuli that are attractive and motivate approach behavior, but are not inherently pleasurable, are termed ''extrinsic rewards''. Extrinsic rewards (e.g., money) are rewarding as a result of a learned association with an intrinsic reward. In other words, extrinsic rewards function as motivational magnets that elicit "wanting", but not "liking" reactions once they have been acquired. The reward system contains – i.e., brain structures that mediate pleasure or "liking" reactions from intrinsic rewards. hedonic hotspots have been identified in subcompartments within the nucleus accumbens shell,ventral pallidum
The ventral pallidum (VP) is a structure within the basal ganglia of the brain. It is an output nucleus whose fibres project to thalamic nuclei, such as the ventral anterior nucleus, the ventral lateral nucleus, and the medial dorsal nucleus.
The ...
, parabrachial nucleus, orbitofrontal cortex
The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes of the brain which is involved in the cognitive process of decision-making. In non-human primates it consists of the association cortex areas Brodmann area 11, 1 ...
(OFC), and insular cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes) within each hemisphere of the mammalian b ...
.Figure 3: Neural circuits underlying motivated 'wanting' and hedonic 'liking'.
/ref> The hotspot within the nucleus accumbens shell is located in the rostrodorsal quadrant of the medial shell, while the hedonic coldspot is located in a more posterior region. The posterior ventral pallidum also contains a hedonic hotspot, while the anterior ventral pallidum contains a hedonic coldspot. In rats, microinjections of opioids,
endocannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tet ...
, and orexin
Orexin (), also known as hypocretin, is a neuropeptide that regulates arousal, wakefulness, and appetite. The most common form of narcolepsy, type 1, in which the individual experiences brief losses of muscle tone ("drop attacks" or cataplexy) ...
are capable of enhancing liking reactions in these hotspots. The hedonic hotspots located in the anterior OFC and posterior insula have been demonstrated to respond to orexin and opioids in rats, as has the overlapping hedonic coldspot in the anterior insula and posterior OFC. On the other hand, the parabrachial nucleus hotspot has only been demonstrated to respond to benzodiazepine receptor agonists.
Hedonic hotspots are functionally linked, in that activation of one hotspot results in the recruitment of the others, as indexed by the induced expression of c-Fos, an immediate early gene
Immediate early genes (IEGs) are genes which are activated transiently and rapidly in response to a wide variety of cellular stimuli. They represent a standing response mechanism that is activated at the transcription level in the first round of ...
. Furthermore, inhibition of one hotspot results in the blunting of the effects of activating another hotspot. Therefore, the simultaneous activation of every hedonic hotspot within the reward system is believed to be necessary for generating the sensation of an intense euphoria.
Wanting and liking
 Incentive salience is the "wanting" or "desire" attribute, which includes a motivational component, that is assigned to a rewarding stimulus by the nucleus accumbens shell (NAcc shell). The degree of dopamine neurotransmission into the NAcc shell from the
Incentive salience is the "wanting" or "desire" attribute, which includes a motivational component, that is assigned to a rewarding stimulus by the nucleus accumbens shell (NAcc shell). The degree of dopamine neurotransmission into the NAcc shell from the mesolimbic pathway
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmentum, ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the for ...
is highly correlated with the magnitude of incentive salience for rewarding stimuli.
Activation of the dorsorostral region of the nucleus accumbens correlates with increases in wanting without concurrent increases in liking. However, dopaminergic neurotransmission into the nucleus accumbens shell is responsible not only for appetitive motivational salience (i.e., incentive salience) towards rewarding stimuli, but also for aversive motivational salience, which directs behavior away from undesirable stimuli. In the dorsal striatum, activation of D1 expressing MSNs produces appetitive incentive salience, while activation of D2 expressing MSNs produces aversion. In the NAcc, such a dichotomy is not as clear cut, and activation of both D1 and D2 MSNs is sufficient to enhance motivation, likely via disinhibiting the VTA through inhibiting the ventral pallidum.
Robinson and Berridge's 1993 incentive-sensitization theory proposed that ''reward'' contains separable psychological components: wanting (incentive) and liking (pleasure). To explain increasing contact with a certain stimulus such as chocolate, there are two independent factors at work – our desire to have the chocolate (wanting) and the pleasure effect of the chocolate (liking). According to Robinson and Berridge, wanting and liking are two aspects of the same process, so rewards are usually wanted and liked to the same degree. However, wanting and liking also change independently under certain circumstances. For example, rats that do not eat after receiving dopamine (experiencing a loss of desire for food) act as though they still like food. In another example, activated self-stimulation electrodes in the lateral hypothalamus of rats increase appetite, but also cause more adverse reactions to tastes such as sugar and salt; apparently, the stimulation increases wanting but not liking. Such results demonstrate that the reward system of rats includes independent processes of wanting and liking. The wanting component is thought to be controlled by dopaminergic pathways
Dopaminergic pathways (dopamine pathways, dopaminergic projections) in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including movement, cognition, executive functions, reward, motivation, and neuroendocrine control. ...
, whereas the liking component is thought to be controlled by opiate-benzodiazepine systems.
Anti-reward system
Koobs & Le Moal proposed that there exists a separate circuit responsible for the attenuation of reward-pursuing behavior, which they termed the anti-reward circuit. This component acts as brakes on the reward circuit, thus preventing the over pursuit of food, sex, etc. This circuit involves multiple parts of the amygdala (the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, the central nucleus), the Nucleus Accumbens, and signal molecules including norepinephrine, corticotropin-releasing factor, and dynorphin. This circuit is also hypothesized to mediate the unpleasant components of stress, and is thus thought to be involved in addiction and withdrawal. While the reward circuit mediates the initial positive reinforcement involved in the development of addiction, it is the anti-reward circuit that later dominates via negative reinforcement that motivates the pursuit of the rewarding stimuli.Learning
Rewarding stimuli can drive learning in both the form of classical conditioning (Pavlovian conditioning) and operant conditioning (instrumental conditioning). In classical conditioning, a reward can act as an unconditioned stimulus that, when associated with the conditioned stimulus, causes the conditioned stimulus to elicit both musculoskeletal (in the form of simple approach and avoidance behaviors) and vegetative responses. In operant conditioning, a reward may act as a reinforcer in that it increases or supports actions that lead to itself. Learned behaviors may or may not be sensitive to the value of the outcomes they lead to; behaviors that are sensitive to the contingency of an outcome on the performance of an action as well as the outcome value are goal-directed, while elicited actions that are insensitive to contingency or value are calledhabit
A habit (or wont as a humorous and formal term) is a routine of behavior that is repeated regularly and tends to occur subconsciously.
s. This distinction is thought to reflect two forms of learning, model free and model based. Model free learning involves the simple caching and updating of values. In contrast, model based learning involves the storage and construction of an internal model of events that allows inference and flexible prediction. Although pavlovian conditioning is generally assumed to be model-free, the incentive salience assigned to a conditioned stimulus is flexible with regard to changes in internal motivational states.
Distinct neural systems are responsible for learning associations between stimuli and outcomes, actions and outcomes, and stimuli and responses. Although classical conditioning is not limited to the reward system, the enhancement of instrumental performance by stimuli (i.e., Pavlovian-instrumental transfer
Pavlovian-instrumental transfer (PIT) is a psychological phenomenon that occurs when a conditioned stimulus (CS, also known as a "cue") that has been associated with rewarding or aversive stimuli via classical conditioning alters motivational sal ...
) requires the nucleus accumbens. Habitual and goal directed instrumental learning are dependent upon the lateral striatum and the medial striatum, respectively.
During instrumental learning, opposing changes in the ratio of AMPA
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid, better known as AMPA, is a compound that is a specific agonist for the AMPA receptor, where it mimics the effects of the neurotransmitter glutamate.
There are several types of glutamatergic ...
to NMDA
''N''-methyl--aspartic acid or ''N''-methyl--aspartate (NMDA) is an amino acid derivative that acts as a specific agonist at the NMDA receptor mimicking the action of glutamate, the neurotransmitter which normally acts at that receptor. Unlike ...
receptors and phosphorylated ERK occurs in the D1-type and D2-type MSNs that constitute the direct and indirect pathways, respectively. These changes in synaptic plasticity and the accompanying learning is dependent upon activation of striatal D1 and NMDA receptors. The intracellular cascade activated by D1 receptors involves the recruitment of protein kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulatio ...
, and through resulting phosphorylation of DARPP-32, the inhibition of phosphatases that deactivate ERK. NMDA receptors activate ERK through a different but interrelated Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway. Alone NMDA mediated activation of ERK is self-limited, as NMDA activation also inhibits PKA mediated inhibition of ERK deactivating phosphatases. However, when D1 and NMDA cascades are co-activated, they work synergistically, and the resultant activation of ERK regulates synaptic plasticity in the form of spine restructuring, transport of AMPA receptors, regulation of CREB
CREB-TF (CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein) is a cellular transcription factor. It binds to certain DNA sequences called cAMP response elements (CRE), thereby increasing or decreasing the transcription of the genes. CREB was first de ...
, and increasing cellular excitability via inhibiting Kv4.2
Disorders
Addiction
ΔFosB
Protein fosB, also known as FosB and G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 3 (G0S3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (''FOSB'') gene.
The FOS gene family consists of four members: FOS, F ...
(DeltaFosB) – a gene transcription factor – overexpression in the D1-type medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for " nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypot ...
is the ''crucial'' common factor among virtually all forms of addiction (i.e., behavioral addiction
Behavioral addiction is a form of addiction that involves a compulsion to engage in a rewarding non- substance-related behavior – sometimes called a natural reward – despite any negative consequences to the person's physical, mental, social ...
s and drug addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use oft ...
s) that induces addiction-related behavior and neural plasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity, or brain plasticity, is the ability of neural networks in the brain to change through growth and reorganization. It is when the brain is rewired to function in some way that differs from how it p ...
. In particular, ΔFosB promotes self-administration, reward sensitization
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use oft ...
, and reward cross-sensitization effects among specific addictive drugs and behaviors.Table 1: Summary of plasticity observed following exposure to drug or natural reinforcers
Certain epigenetic modifications of
histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn a ...
protein tails (i.e., histone modifications) in specific regions of the brain are also known to play a crucial role in the molecular basis of addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use o ...
s.Figure 4: Epigenetic basis of drug regulation of gene expression
/ref> Addictive drugs and behaviors are rewarding and
reinforcing
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher freq ...
(i.e., are ''addictive'') due to their effects on the dopamine reward pathway.
The lateral hypothalamus
The lateral hypothalamus (LH), also called the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), contains the primary orexinergic nucleus within the hypothalamus that widely projects throughout the nervous system; this system of neurons mediates an array of cognit ...
and medial forebrain bundle
The medial forebrain bundle (MFB), is a neural pathway containing fibers from the basal olfactory regions, the periamygdaloid region and the septal nuclei, as well as fibers from brainstem regions, including the ventral tegmental area and ni ...
has been the most-frequently-studied brain-stimulation reward site, particularly in studies of the effects of drugs on brain stimulation reward.Roy A. Wise, Drug-activation of brain reward pathways, ''Drug and Alcohol Dependence'' 1998; 51 13–22. The neurotransmitter system that has been most-clearly identified with the habit-forming actions of drugs-of-abuse is the mesolimbic dopamine system, with its efferent targets in the nucleus accumbens and its local GABAergic afferents. The reward-relevant actions of amphetamine and cocaine are in the dopaminergic synapses of the nucleus accumbens and perhaps the medial prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA4 ...
. Rats also learn to lever-press for cocaine injections into the medial prefrontal cortex, which works by increasing dopamine turnover in the nucleus accumbens. Nicotine infused directly into the nucleus accumbens also enhances local dopamine release, presumably by a presynaptic action on the dopaminergic terminals of this region. Nicotinic receptors localize to dopaminergic cell bodies and local nicotine injections increase dopaminergic cell firing that is critical for nicotinic reward. Some additional habit-forming drugs are also likely to decrease the output of medium spiny neurons as a consequence, despite activating dopaminergic projections. For opiates, the lowest-threshold site for reward effects involves actions on GABAergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is th ...
, a secondary site of opiate-rewarding actions on medium spiny output neurons of the nucleus accumbens. Thus the following form the core of currently characterised drug-reward circuitry; GABAergic afferents to the mesolimbic dopamine neurons (primary substrate of opiate reward), the mesolimbic dopamine neurons themselves (primary substrate of psychomotor stimulant reward), and GABAergic efferents to the mesolimbic dopamine neurons (a secondary site of opiate reward).
Motivation
Dysfunctional motivational salience appears in a number of psychiatric symptoms and disorders.Anhedonia
Anhedonia is a diverse array of deficits in hedonic function, including reduced motivation or ability to experience pleasure. While earlier definitions emphasized the inability to experience pleasure, anhedonia is currently used by researchers t ...
, traditionally defined as a reduced capacity to feel pleasure, has been re-examined as reflecting blunted incentive salience, as most anhedonic populations exhibit intact “liking”. On the other end of the spectrum, heightened incentive salience that is narrowed for specific stimuli is characteristic of behavioral and drug addictions. In the case of fear or paranoia, dysfunction may lie in elevated aversive salience.
Neuroimaging studies across diagnoses associated with anhedonia have reported reduced activity in the OFC and ventral striatum. One meta analysis reported anhedonia was associated with reduced neural response to reward anticipation in the caudate nucleus, putamen, nucleus accumbens and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC).
Mood disorders
Certain types of depression are associated with reduced motivation, as assessed by willingness to expend effort for reward. These abnormalities have been tentatively linked to reduced activity in areas of the striatum, and while dopaminergic abnormalities are hypothesized to play a role, most studies probing dopamine function in depression have reported inconsistent results. Although postmortem and neuroimaging studies have found abnormalities in numerous regions of the reward system, few findings are consistently replicated. Some studies have reported reduced NAcc, hippocampus, medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), and orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) activity, as well as elevated basolateral amygdala and subgenual cingulate cortex (sgACC) activity during tasks related to reward or positive stimuli. These neuroimaging abnormalities are complemented by little post mortem research, but what little research has been done suggests reduced excitatory synapses in the mPFC. Reduced activity in the mPFC during reward related tasks appears to be localized to more dorsal regions(i.e. the pregenual cingulate cortex), while the more ventral sgACC is hyperactive in depression. Attempts to investigate underlying neural circuitry in animal models has also yielded conflicting results. Two paradigms are commonly used to simulate depression, chronic social defeat (CSDS), and chronic mild stress (CMS), although many exist. CSDS produces reduced preference for sucrose, reduced social interactions, and increased immobility in the forced swim test. CMS similarly reduces sucrose preference, and behavioral despair as assessed by tail suspension and forced swim tests. Animals susceptible to CSDS exhibit increased phasic VTA firing, and inhibition of VTA-NAcc projections attenuates behavioral deficits induced by CSDS. However, inhibition of VTA- projections exacerbates social withdrawal. On the other hand, CMS associated reductions in sucrose preference and immobility were attenuated and exacerbated by VTA excitation and inhibition, respectively. Although these differences may be attributable to different stimulation protocols or poor translational paradigms, variable results may also lie in the heterogenous functionality of reward related regions. Optogenetic stimulation of the mPFC as a whole produces antidepressant effects. This effect appears localized to the rodent homologue of the pgACC (the prelimbic cortex), as stimulation of the rodent homologue of the sgACC (the infralimbic cortex) produces no behavioral effects. Furthermore, deep brain stimulation in the infralimbic cortex, which is thought to have an inhibitory effect, also produces an antidepressant effect. This finding is congruent with the observation that pharmacological inhibition of the infralimbic cortex attenuates depressive behaviors.Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social wit ...
is associated with deficits in motivation, commonly grouped under other negative symptoms such as reduced spontaneous speech. The experience of “liking” is frequently reported to be intact, both behaviorally and neurally, although results may be specific to certain stimuli, such as monetary rewards. Furthermore, implicit learning and simple reward-related tasks are also intact in schizophrenia. Rather, deficits in the reward system are apparent during reward-related tasks that are cognitively complex. These deficits are associated with both abnormal striatal and OFC activity, as well as abnormalities in regions associated with cognitive functions such as the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC).
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
In those with ADHD, core aspects of the reward system are underactive, making it challenging to derive reward from regular activities. Those with the disorder experience a boost of motivation after a high-stimulation behaviour triggers a release of dopamine. In the aftermath of that boost and reward, the return to baseline levels results in an immediate drop in motivation. Impairments of dopaminergic andserotonergic
Serotonergic () or serotoninergic () means "pertaining to or affecting serotonin". Serotonin is a neurotransmitter. A synapse is serotonergic if it uses serotonin as its neurotransmitter. A serotonergic neuron ''produces'' serotonin. A substance is ...
function are said to be key factors in ADHD. These impairments can lead to executive dysfunction
In psychology and neuroscience, executive dysfunction, or executive function deficit, is a disruption to the efficacy of the executive functions, which is a group of cognitive processes that regulate, control, and manage other cognitive processes ...
such as dysregulation of reward processing and motivational dysfunction, including anhedonia.
History
brain stimulation reward
Brain stimulation reward (BSR) is a pleasurable phenomenon elicited via direct stimulation of specific brain regions, originally discovered by James Olds and Peter Milner. BSR can serve as a robust operant reinforcer. Targeted stimulation activat ...
. Typically, rats will press a lever hundreds or thousands of times per hour to obtain this brain stimulation, stopping only when they are exhausted. While trying to teach rats how to solve problems and run mazes, stimulation of certain regions of the brain where the stimulation was found seemed to give pleasure to the animals. They tried the same thing with humans and the results were similar. The explanation to why animals engage in a behavior that has no value to the survival of either themselves or their species is that the brain stimulation is activating the system underlying reward.
In a fundamental discovery made in 1954, researchers James Olds and Peter Milner found that low-voltage electrical stimulation of certain regions of the brain of the rat acted as a reward in teaching the animals to run mazes and solve problems. It seemed that stimulation of those parts of the brain gave the animals pleasure, and in later work humans reported pleasurable sensations from such stimulation. When rats were tested in Skinner box
An operant conditioning chamber (also known as a Skinner box) is a laboratory apparatus used to study animal behavior. The operant conditioning chamber was created by B. F. Skinner while he was a graduate student at Harvard University. The cha ...
es where they could stimulate the reward system by pressing a lever, the rats pressed for hours. Research in the next two decades established that dopamine is one of the main chemicals aiding neural signaling in these regions, and dopamine was suggested to be the brain's "pleasure chemical".
Ivan Pavlov
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov ( rus, Ива́н Петро́вич Па́влов, , p=ɪˈvan pʲɪˈtrovʲɪtɕ ˈpavləf, a=Ru-Ivan_Petrovich_Pavlov.ogg; 27 February 1936), was a Russian and Soviet experimental neurologist, psychologist and physio ...
was a psychologist who used the reward system to study classical conditioning
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent stimulus (e.g. food) is paired with a previously neutral stimulus (e.g. a triangle). It also refers to the learni ...
. Pavlov used the reward system by rewarding dogs with food after they had heard a bell or another stimulus. Pavlov was rewarding the dogs so that the dogs associated food, the reward, with the bell, the stimulus.
Edward L. Thorndike used the reward system to study operant conditioning. He began by putting cats in a puzzle box and placing food outside of the box so that the cat wanted to escape. The cats worked to get out of the puzzle box to get to the food. Although the cats ate the food after they escaped the box, Thorndike learned that the cats attempted to escape the box without the reward of food. Thorndike used the rewards of food and freedom to stimulate the reward system of the cats. Thorndike used this to see how the cats learned to escape the box.Fridlund, Alan and James Kalat. Mind and Brain, the Science of Psychology. California: Cengage Learning, 2014. Print.
Other species
Animals quickly learn to press a bar to obtain an injection of opiates directly into the midbrain tegmentum or thenucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for " nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypot ...
. The same animals do not work to obtain the opiates if the dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmentum, ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the for ...
are inactivated. In this perspective, animals, like humans, engage in behaviors that increase dopamine release.
Kent Berridge, a researcher in affective neuroscience
Affective neuroscience is the study of how the brain processes emotions. This field combines neuroscience with the psychological study of personality, emotion, and mood. The basis of emotions and what emotions are remains an issue of debate withi ...
, found that sweet (''liked'' ) and bitter (''disliked'' ) tastes produced distinct orofacial expressions, and these expressions were similarly displayed by human newborns, orangutans, and rats. This was evidence that pleasure (specifically, ''liking'') has objective features and was essentially the same across various animal species. Most neuroscience studies have shown that the more dopamine released by the reward, the more effective the reward is. This is called the hedonic impact, which can be changed by the effort for the reward and the reward itself. Berridge discovered that blocking dopamine systems did not seem to change the positive reaction to something sweet (as measured by facial expression). In other words, the hedonic impact did not change based on the amount of sugar. This discounted the conventional assumption that dopamine mediates pleasure. Even with more-intense dopamine alterations, the data seemed to remain constant. However, a clinical study from January 2019 that assessed the effect of a dopamine precursor ( levodopa), antagonist (risperidone
Risperidone, sold under the brand name Risperdal among others, is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It is taken either by mouth or by injection (subcutaneous or intramuscular). The injectable versions ...
), and a placebo on reward responses to music – including the degree of pleasure experienced during musical chills, as measured by changes in electrodermal activity
Electrodermal activity (EDA) is the property of the human body that causes continuous variation in the electrical characteristics of the skin. Historically, EDA has also been known as skin conductance, galvanic skin response (GSR), electrodermal ...
as well as subjective ratings – found that the manipulation of dopamine neurotransmission bidirectionally regulates pleasure cognition (specifically, the hedonic impact of music) in human subjects. This research demonstrated that increased dopamine neurotransmission acts as a ''sine qua non
''Sine qua non'' (, ) or ''condicio sine qua non'' (plural: ''condiciones sine quibus non'') is an indispensable and essential action, condition, or ingredient. It was originally a Latin legal term for " conditionwithout which it could not be" ...
'' condition for pleasurable hedonic reactions to music in humans.
Berridge developed the incentive salience hypothesis to address the ''wanting'' aspect of rewards. It explains the compulsive use of drugs by drug addicts even when the drug no longer produces euphoria, and the cravings experienced even after the individual has finished going through withdrawal. Some addicts respond to certain stimuli involving neural changes caused by drugs. This sensitization in the brain is similar to the effect of dopamine because ''wanting'' and ''liking'' reactions occur. Human and animal brains and behaviors experience similar changes regarding reward systems because these systems are so prominent.
See also
References
*External links
Scholarpedia Reward
Scholarpedia Reward signals
{{Portal bar, Psychology, Biology Cognitive neuroscience Behavioral neuroscience Behaviorism Behavior modification Addiction Neuroanatomy Neuropsychology Dopamine